Abstract
Corazonin (Crz) is widely found in insects and crustaceans. In insects, Crz participates in the regulation of various physiological activities, including heartbeat, body color change, molting, and reproduction. However, the physiological effects of Crz in crustaceans remain largely unclear. In this study, the cDNAs encoding Crz and its putative receptor were isolated from the mud crab Scylla paramamosain. Tissue distribution analysis revealed that Sp-Crz was predominantly expressed in neural tissues, while its receptor (Sp-CrzR) was widely expressed in S. paramamosain, with a high expression level in the Y-organ. During ovarian development, Sp-Crz expression in the eyestalk ganglion was upregulated at the early and late vitellogenic stages, whereas its expression level in the cerebral ganglion displayed an initial downregulation at the early stage, followed by a remarkable upregulation at the late vitellogenic stage. The expression level of Sp-CrzR mRNA in the ovary increased significantly at the late vitellogenic stage. However, an opposite expression pattern was observed in the hepatopancreas and Y-organ. The immunohistochemistry result showed that Sp-Crz was distributed in the cells of the lamina ganglionaris, the medulla interna, and the X-organ of the eyestalk ganglion. It was revealed that the level of Sp-Vg in the hepatopancreas was not affected by the addition of Sp-Crz in vitro. However, the expression of Sp-VgR in ovarian explants was significantly induced by 6 h treatment with Sp-Crz at a concentration of 1 nM. In addition, the level of Sp-VgR in the ovary was significantly upregulated by 12 h injection of Sp-Crz. After long-term administration of Sp-Crz, the expression of Sp-VgR in the ovary, the E2 content in hemolymph, the oocyte diameter, and the gonadosomatic index of S. paramamosain were significantly increased. In summary, these findings collectively indicate that the Sp-Crz signaling system participates in regulating the ovarian development of the mud crab. This study provides a new insight into the biological function of Crz during the ovarian development of the mud crab, which is of great significance for the sustainable development and utilization of mud crab resources.
Key Contribution:
This study identified Crz and its receptor genes for the first time in Scylla paramamosain, suggesting that the Sp-Crz signaling system plays a stimulatory role in ovarian development.
1. Introduction
Neuropeptides are important regulators in arthropods and are involved in many biological events, including metamorphosis, metabolism, sexual behavior and reproduction [1,2,3,4]. Corazonin (Crz) was initially isolated from the American cockroach Periplaneta americana, exerting a cardiac-stimulating peptide [5]. Subsequently, the presence of Crz has been found in many other species, such as the silkworm Bombyx mori, cricket Gryllus bimaculatus and ant Harpegnathos saltator [6,7,8,9,10]. The Crz precursor contains a signal peptide, a mature peptide with 11 amino acids, and a precursor-related peptide [11]. In insects, there are six different Crz mature peptide isoforms, differing from each other only by one amino acid [12,13]. Among them, [Arg7]-Crz is the only isoform found in crustaceans, and its mature peptide sequence is pQTFQYSRGWTNamide [11,14]. To date, Crz has been extensively identified in crustaceans, including the green shore crab Carcinus maenas [15], the red claw crayfish Cherax quadricarinatus [16], and the swimming crab Portunus trituberculatus [11].
Although Crz was originally described as a cardiac-stimulating peptide [5], it not only performs this function but also has other distinct physiological roles. For example, Crz was involved in body color darkening events in the locust Locusta migratoria during the transition to the gregarious stage [7,17]. However, in the hawkmoth Manduca sexta, Crz was reported to regulate molting behavior by stimulating the secretion of ecdysis-triggering hormone and pre-ecdysis-triggering hormone [8]. In addition, Crz was shown to inhibit silk spitting efficiency in the silkworm B. mori [18] and control caste identity in the ant Harpegnathos saltator [10]. In the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster, Crz was associated with stress responses and reproductive processes [19,20,21]. It has been revealed that silencing Crz in the fruit fly brain significantly enhanced the expression of vitellogenin and the deposition of eggs [22,23]. Additionally, Crz can influence sperm transfer and mating duration by regulating trehalose levels in the oriental fruit fly Bactrocera dorsalis [24]. Compared to the extensive research in insects, the function of Crz in crustaceans is poorly understood. Recently, it was revealed that Crz has the ability to induce molting behavior in C. quadricarinatus [16,20] and is involved in the regulation of vitellogenesis and molting hormone synthesis in P. trituberculatus [11].
Generally, G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) is a key element for neuropeptides to exert their biological effects [25]. GPCRs are classified into at least five subfamilies: glutamate, rhodopsin, adhesion, frizzled/taste2, and secretin [26]. As a member of the rhodopsin-like receptor family, corazonin receptor (CrzR) is characterized by a DRF motif and an NSxxNPxxY motif, which couples to cAMP and/or Ca2+ to regulate physiological activities [15,27,28]. The first Crz receptor was reported in the fruit fly D. melanogaster [28], and its homologs were subsequently identified in the hawkmoth M. sexta [8], the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae [9], the silkworm B. mori [29], the house fly Musca domestica [30], the blood-gorging bug Rhodnius prolixus [31], and the mosquito Aedes aegypti [32]. In addition, a sequence encoding CrzR has also been isolated in crustaceans, including the lobster Sagmariasus verreauxi [33], the green shore crab C. maenas [15], the land crab Gecarcinus lateralis [34], and the swimming crab P. trituberculatus [11]. The specific presence of CrzR in Inka cells supports the finding that Crz controls the release of ecdysis-triggering hormone, therefore regulating ecdysis behavior [8,24]. In D. melanogaster, knockdown of CrzR affects feeding behavior and modulates stress responses and metabolism [35,36,37]. In B. dorsalis, silencing of CrzR inhibits pupariation and cuticular melanization by disrupting dopamine synthesis [24].
The mud crab Scylla paramamosain is an economically important marine culture crab species, which is popular in China and Southeast Asia regions. In this study, we identified the cDNA sequences of Crz and its putative receptor in the mud crab by transcriptome sequencing and molecular cloning, and explored their expression profiles in female mud crab by reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR), quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR), and immunohistochemistry. Finally, the potential regulatory role of Crz in ovarian development was systematically examined through both in vitro and in vivo investigations in S. paramamosain.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
Based on ovarian color, gonadosomatic index (GSI), and ovary histological features, the ovarian development cycle of S. paramamosain is divided into three stages: pre-vitellogenic, early vitellogenic, and late vitellogenic stages [38]. Mud crabs at these three stages were collected from a commercial fishery in Xiamen, Fujian province, China, for the experiments. Prior to the experimental procedures, crabs were acclimatized for a week under a standardized condition (temperature: 25 ± 0.5 °C; salinity: 28 ± 0.5 ppt). During this period, animals were fed fresh Manila clams Ruditapes philippinarum, and the seawater containing sufficient oxygen was renewed daily to maintain the optimal dissolved oxygen level. For tissue distribution analysis, 11 tissues were sampled from females at the early vitellogenic stage, including the eyestalk ganglion, cerebral ganglion, thoracic ganglion, ovary, hepatopancreas, Y-organ, heart, muscle, stomach, middle gut, and gill. In addition, samples of the eyestalk ganglion, cerebral ganglion, ovary, hepatopancreas, and Y-organ were collected from crabs (n = 4) for qPCR analysis of Sp-Crz and Sp-CrzR gene expression. Samples were flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C until RNA isolation.
2.2. RNA Isolation and Molecular Cloning
Total RNA isolation was performed by utilizing a Trizol reagent kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). Total RNA concentration was quantified by using a Nanodrop instrument (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), while RNA integrity was assessed through 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis. After removal of potential genomic DNA contamination with DNase I (Invitrogen), the first-strand cDNA was synthesized by employing a RevertAidTM First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Thermo Scientific). The cDNA sequences encoding Sp-Crz and its cognate receptor were found through bioinformatic analysis from the S. paramamosain transcriptome database (SRR3086590). Subsequently, specific primers were designed using Primer 5.0 software. The cDNA sequences of Sp-Crz and its receptor were verified by PCR with the first-strand cDNA (diluted 10-fold) as a template. The PCR products were separated by 2% agarose gel electrophoresis, and then purified by an Agarose Gel Purification and Extraction Kit (Aidlab, Beijing, China). Finally, DNA fragments were cloned into the pMD19-T vector (Takara, Ohtsu, Japan) for sequencing (Sangon Biotech., Ltd., Shanghai, China). The primer sequences employed in this study are detailed in Table A1.
The open reading frame (ORF) and deduced amino acid sequences of Sp-Crz and Sp-CrzR were identified using the ORF finder tool (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/orffinder/, accessed on 16 April 2024). Transmembrane domain prediction for Sp-CrzR was conducted with TMHMM Server (https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM-2.0/, accessed on 18 August 2024). Multiple sequence alignment and subsequent phylogenetic reconstruction were performed using ClustalW 2.0 and MEGA 6.0, respectively. The phylogenetic tree was constructed based on the neighbor-joining (NJ) algorithm with bootstrap sampling repeated 1000 times and outgroup rooting by software MEGA 6.0.
2.3. Expression Profiles of Sp-Crz and Sp-CrzR in the Female Mud Crab
The expression profiles of Sp-Crz and Sp-CrzR in various tissues of female mud crab S. paramamosain were analyzed by RT-PCR. Total RNA extracted from 11 distinct tissues was reverse-transcribed to cDNA for amplification. PCR reactions were conducted with Ex-Taq® DNA polymerase (Takara) under the following conditions: 95 °C for 3 min; 32 cycles of 95 °C for 30 s, 58 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 30 s; a final extension at 72 °C for 10 min. The negative control was amplification of deionized water, while amplification of β-actin served as the reference gene. Amplified products were subjected to 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis and visualized under a UV gel imager (Thermo Scientific).
The expression profiles of Sp-Crz and Sp-CrzR in the eyestalk ganglion, cerebral ganglion, ovary, hepatopancreas, and Y-organ of female mud crabs during vitellogenesis were analyzed by qPCR (n = 4). The qPCR assay was performed using a QuantStudio 5 real-time PCR machine (Applied Biosystems, Carlsbad, CA, USA) with a 20 μL reaction mixture, which contained 10 μL SYBR R© Select Master Mix, 2 μL diluted cDNA (10×), 1 μL of each primer, and 6 μL deionized water. The thermal cycling protocol included an initial denaturation at 95 °C for 3 min, 40 cycles of 95 °C for 10 s, 58 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 30 s, followed by melting curve analysis (60–95 °C). All samples were tested in three replicates, with β-actin amplification serving as the reference gene for data normalization. Primer sequences are provided in Table A1.
2.4. Localization of Sp-Crz in the Eyestalk Ganglion by Immunohistochemistry
To determine localization of Sp-Crz in the eyestalk ganglion, a polyclonal mouse antibody against the mature Crz peptide (pQTFQYSRGWTN-amide) conjugated to keyhole limpet hemocyanin via an N-terminal cysteine was generated by GL Biochem Ltd. (Shanghai, China). The serum containing antibodies was collected after two months of immunization, followed by purification through affinity chromatography.
Samples of eyestalk ganglion were fixed in a 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) solution prepared in 0.1 M PBS (pH 7.2) for 12 h at 4 °C, which were transferred to 70% ethanol and then dehydrated through an ethanol series. Tissues were embedded in paraffin and sectioned to 7 µm thickness, followed by being blocked by 5% bovine serum (BSA) prepared in PBS for 1 h at room temperature. Sections were then incubated in primary antibody (mouse anti-Crz) diluted to a final working concentration of 1:1000 or pre-immune serum (negative control) for 12 h at 4 °C. Subsequently, the tissue sections were rinsed with PBS three times with 5 min intervals, followed by incubation in anti-mouse IgG conjugated to horseradish Peroxidase (1:1000 dilution; Thermo Scientific) for 2 h at room temperature, and then rinsed with PBS thrice at 5 min intervals. Finally, the sections were stained by using a Metal enhanced DAB substrate Kit (Solarbio, Beijing, China), and imaged using an Olympus CKX53 system (Tokyo, Japan).
2.5. In Vitro Effect of Sp-Crz on Sp-Vg and Sp-VgR Expression
In this study, the possible role of Sp-Crz in the ovarian development of S. paramamosain was explored by in vitro experiments. Female crabs at the early vitellogenic stage were anesthetized on ice for 10 min to immobilize them and minimize stress, then sterilized with 75% ethanol for 10 min to eliminate surface contaminants and reduce the risk of microbial contamination. Subsequently, ovarian and hepatopancreatic tissues were dissected and washed five times using crab saline containing antibiotics (300 IU/mL penicillin G and 300 IU/mL streptomycin). Tissues were cut into sizes of approximately 50 mg and then placed in 24-well culture plates. After 1 h pre-incubation in L15 medium containing penicillin G (300 IU/mL) and streptomycin (300 IU/mL) at 25 °C, tissues were treated with Sp-Crz dissolved in L15 medium at concentrations of 1, 10, and 100 nM, while the control was treated without any peptide, and each treatment included four repeats (n = 4). Finally, samples were collected at the 2nd, 4th, and 6th h following Sp-Crz treatment for analysis of Sp-Vg (FJ812090.1) and Sp-VgR (KF860893.1) expression levels by qPCR.
2.6. In Vivo Effect of Sp-Crz on the Ovarian Development of the Mud Crab
Based on the results of in vitro experiments, the potential effect of Sp-Crz on the ovarian development of mud crab was proposed here. Therefore, in vivo experiments were further performed to explore its precise role. Crabs at the early vitellogenic stage were randomly assigned to two groups (n = 7): one group of crabs received Sp-Crz (10 ng/g body weight) prepared in 100 μL crab saline, while the other group was injected with 100 μL crab saline alone. The injection was administered to the joint membrane at the fifth leg using a microinjector (Hamilton, Bonaduz, Switzerland). After 12 h, crabs were anesthetized on ice, and 1 mL of hemolymph was collected for the estradiol (E2) assay, while hepatopancreas and ovarian tissues were sampled for analysis of gene expression.
In the long-term experiment, crabs were randomly divided into three groups, with each group containing 10 crabs (n = 10). The pre-injection control group was sampled before injection. Afterwards, the experimental group was injected with 100 μL crab saline containing Sp-Crz (10 ng/g body weight), while the blank control group was injected with 100 μL crab saline. The injection was performed three times at 5-day intervals, and crabs were sampled approximately 24 h after the third injection. An amount of 1 mL of hemolymph was collected from each crab for the E2 assay. Subsequently, hepatopancreas and ovary samples were collected for analysis of gene expression. The gonadosomatic index was calculated, and ovary samples were subjected to histological analysis by hematoxylin and eosin staining.
2.7. Determination of Estradiol (E2) Concentration in Hemolymph
The concentration of E2 in hemolymph was detected using a DetectX® ELISA Kit (Arbor Assays, Ann Arbor, MI, USA) as described in our previous study [39]. Briefly, E2 was extracted from 1 mL of hemolymph with 5 mL of ether, and samples were analyzed according to the manufacturer’s protocol in duplicate. Afterwards, E2 concentration was calculated by using the Arbor Assays online calculation tool (www.myassays.com/arbor-assays-estradiol-serum-eia-kit.assay, accessed on 15 August 2024).
2.8. Statistical Analysis
In this study, the 2−ΔΔCt method was used to calculate the target gene expression. Data were tested for homogeneity with Levene’s test, and statistical significance was determined by Student’s t-test or one-way ANOVA with Duncan’s post hoc test (SPSS 20.0). The data are shown as mean ± SEM (standard error of the mean).
3. Results
3.1. Cloning and Sequence Analysis of Sp-Crz and Its Receptor
In this study, we obtained the cDNA sequences encoding Crz and its cognate receptor from the S. paramamosain cerebral ganglion through transcriptome sequencing and PCR amplification. The ORF of Sp-Crz (GenBank: PQ880023) comprises 354 bp, encoding a 117 aa precursor. The precursor contains a 19 aa signal peptide, an RKR proteolytic cleavage site, which allows the formation of a mature Crz peptide, and a related peptide. There is an amidated site at the C-terminal of the mature Crz (Figure 1). The mature Crz sequence is highly conserved among arthropods (Figure 2).
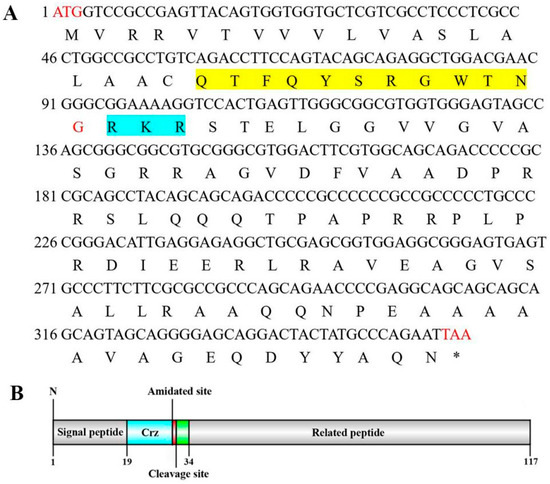
Figure 1.
(A) Sequence of Sp-Crz and its encoded protein in the mud crab S. paramamosain. Mature peptide and proteolytic cleavage site are highlighted in yellow and blue, respectively. Start codon, stop codon, and amidation site are marked in red. (B) Structural diagram illustrating the domains of Sp-Crz.

Figure 2.
Multiple sequence alignment of Sp-Crz and its homologous proteins. P. trituberculatus (XP_045123222.1), C. maenas (AVA26882.1), Eriocheir sinensis (XP_050736175.1), Penaeus vannamei (XP_069978095.1), Penaeus japonicus (XP_042891384.1), Macrobrachium rosenbergii (ALA65535.1), Amyelois transitella (XP_060806943.1), Cyphomyrmex costatus (XP_018392400.1), Nasonia vitripennis (XP_001600665.1). Sp-Crz was highlighted by the red dot.
In addition, the Sp-CrzR ORF (GenBank: PQ880024) spans 1899 bp, encoding a 663 aa putative receptor protein. This protein contains seven transmembrane structural domains (TMs), suggesting it belongs to a G protein-coupled receptor. Sequence analysis revealed that Sp-CrzR showed high identity to CrzRs in P. trituberculatus (93.99%) and C. maenas (83.02%), and exhibited high sequence similarity to the deorphanized arthropod CrzRs in the TMs (Figure 3). In addition, phylogenetic analysis showed that CrzRs were grouped into a monophyletic cluster, which is clearly distinguished from both adipokinetic hormone receptors (AKHRs) and adipokinetic hormone/corazonin-related peptide receptors (ACPRs). AKHRs and red pigment concentrating hormone receptors (RPCHRs) were clustered into the same clade, while ACPRs formed a sister group to the AKH/PRCH receptor clade. Sp-CrzR clustered closely with CrzRs from C. maenas, P. trituberculatus, Apis mellifera, Pyrrhocoris apterus, A. aegypti, D. melanogaster and Magallana gigas (Figure 4).

Figure 3.
Sequence alignment of Sp-CrzR and the deorphanized receptors in arthropods. P. trituberculatus (OL694706.1), C. maenas (AVA26879.1), M. gigas (AKA95277.1), A. mellifera (NP_001137393.1), A. aegypti (AVI09462.1), D. melanogaster (AAM21341.1). Sp-CrzR was highlighted by the red dot. The conserved residues are shown with black shading, and conserved changes are indicated with gray shading. The transmembrane domains are marked with black boxes. The DRF motif and NSxxNPxxY motif are highlighted with red boxes.
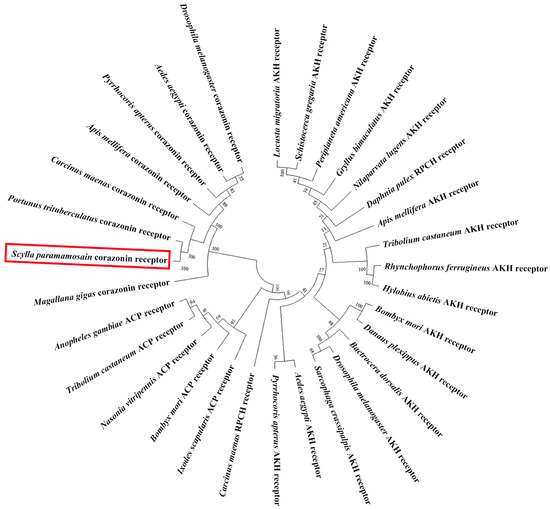
Figure 4.
Phylogenetic relationship of CrzR, AKHR, ACPR, and RPCHR in arthropods. CrzR: P. trituberculatus (UZH25339.1), Crassostrea gigas (AKA95277.1), C. maenas (AVA26879.1), A. mellifera (NP_001137393.1), A. aegypti (AVI09462.1), D. melanogaster (AAM21341.1), P. apterus (ARV86500.1). Adipokinetic hormone/corazonin-related peptide receptor (ACPR): Tribolium castaneum (NP_001280549.1), Ixodes scapularis (AHB51764.1), A. gambiae (ABX52399.1), B. mori (ACT79362.1), N. vitripennis (NP_001164571.1). Red pigment concentrating hormone receptor (RPCHR): Daphnia pulex (ARD09217.1), C. maenas (AVA26880.1). Adipokinetic hormone receptor (AKHR): L. migratoria (ANW09575.1), D. melanogaster (AAS64647.1), G. bimaculatus (ADZ17179.1), B. dorsalis (AQX83416.1), P. americana (ABB20590.1), A. aegypti (CAY77164.1), Schistocerca gregaria (AVG47955.1), T. castaneum (NP_001076809.1), A. mellifera (NP_001035354.1), B. mori (NP_001037049.1), Danaus plexippus (OWR46881.1), Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (QGA72493.1), Nilaparvata lugens (AZP54622.1), P. apterus (ARV86499.1), Hylobius abietis (AVI00624.1), Sarcophaga crassipalpis (AOC38019.1). Sp-CrzR is highlighted with a red box.
3.2. Expression Profiles of Sp-Crz and Sp-CrzR in Female S. paramamosain
The expression of Sp-Crz and its receptor in different tissues of female S. paramamosain at the early stage was examined by RT-PCR. It showed that, among the 11 tissues tested, Sp-Crz was expressed in the eyestalk ganglion, and a weak expression was detected in the cerebral ganglion, ovary and Y-organ. In addition, Sp-CrzR was extensively expressed in the eyestalk and cerebral ganglia, the Y-organ, and the ovary and hepatopancreas of S. paramamosain (Figure 5A).
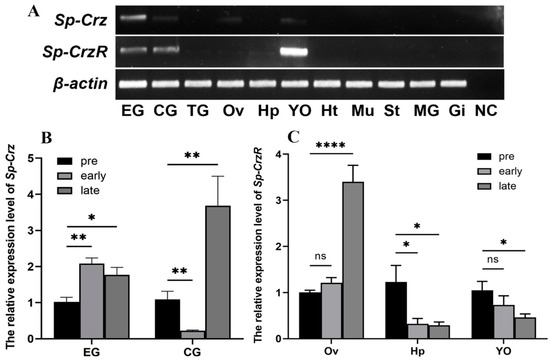
Figure 5.
Expression patterns of Sp-Crz and its receptor in female mud crab S. paramamosain. (A) Expression pattern of Sp-Crz and Sp-CrzR in different tissues of S. paramamosain. EG: eyestalk ganglion; CG: cerebral ganglion; TG: thoracic ganglion; Ov: ovary; Hp: hepatopancreas; YO: Y-organ; Ht: heart; Mu: muscle; St: stomach; MG: middle gut; Gi: gill; NC: the amplification of deionized water was set as the negative control. (B,C) Sp-Crz and Sp-CrzR expression profile during ovarian development of S. paramamosain. pre: pre-vitellogenic stage; early: early vitellogenic stage; late: late vitellogenic stage. Data represent mean ± SEM (n = 4). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001 indicate significant differences when compared to the pre-vitellogenic stage.
To elucidate the possible involvement of the Sp-Crz signaling system in vitellogenesis of female S. paramamosain, qPCR was utilized to examine the expression profiles of Sp-Crz and Sp-CrzR at different vitellogenic stages. The results suggested that the expression level of Sp-Crz in the eyestalk ganglion was significantly increased at the early and late vitellogenic stages (p < 0.05), while in the cerebral ganglion, its expression was significantly downregulated (p < 0.01) at the early vitellogenic stage and subsequently upregulated (p < 0.01) at the late vitellogenic stage (Figure 5B). In addition, the level of Sp-CrzR expression in the ovary was significantly increased at the late vitellogenic stage (p < 0.001) during ovarian development. In the hepatopancreas and Y-organ, the expression pattern of Sp-CrzR was opposite to that in the ovary (Figure 5C).
3.3. Localization of Sp-Crz in the Eyestalk Ganglion of S. paramamosain
The distribution of Sp-Crz-expressing cells in the eyestalk ganglion was examined by immunohistochemistry. The eyestalk ganglion of S. paramamosain consists of four parts (from inner to outer), namely the lamina ganglionaris (LG), medulla externa (ME), medulla interna (MI) and medulla terminalis (MT). The X-organ is situated laterally at the base of MT and consists of clusters of endocrine cells. The immunohistochemical results showed that a positive signal of Sp-Crz was located in the cells of LG (Figure 6B), MI (Figure 6C), and the X-organ in MT (Figure 6D).
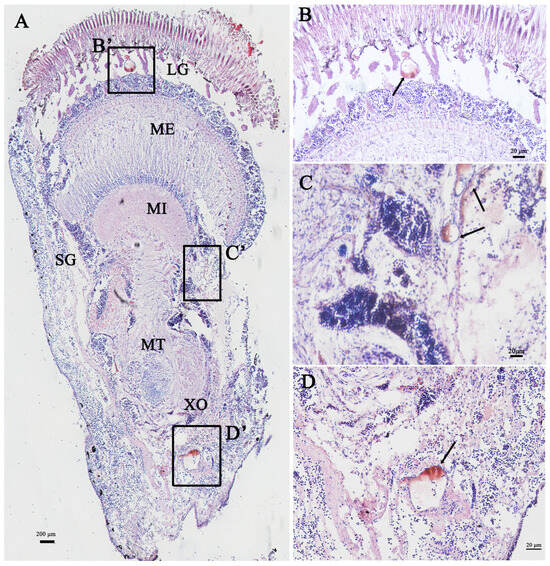
Figure 6.
Localization of Crz in the eyestalk ganglion of S. paramamosain at the early vitellogenic stage. (A) Immunoreactive cells of Sp-Crz in the eyestalk ganglion. Scale bar: 200 µm. (B–D) Enlargement of the boxed regions (B’, C’ and D’) in A, showing Sp-Crz-expressing cell distribution in LG (B), MI (C) and the X-organ in MT (D). Scale bar: 20 µm. XO: X-organ; SG: sinus gland; LG: lamina ganglionaris; ME: medulla externa; MI: medulla interna; MT: medulla terminalis.
3.4. Effects of Sp-Crz on Vitellogenesis of S. paramamosain
To explore the possible effect of Sp-Crz on vitellogenesis, synthetic peptide was applied to ovarian and hepatopancreatic explants at the early vitellogenic stage. This revealed that the level of Sp-Vg transcript in the hepatopancreas did not significantly change in response to 2, 4, and 6 h treatment of Sp-Crz at any concentration (Figure 7A–C). The level of Sp-VgR expression in the ovary was not affected by 2 and 4 h incubation of Sp-Crz at any concentration (Figure 7D,E); however, it was significantly increased by 6 h treatment of 1 nM Sp-Crz (p < 0.05, Figure 7F).
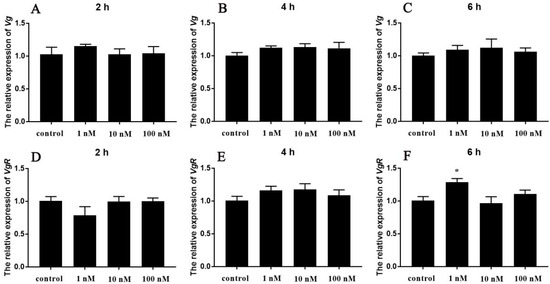
Figure 7.
In vitro effects of synthetic Sp-Crz on Sp-Vg and Sp-VgR expression of S. paramamosain. (A–C) The level of Sp-Vg expression in the hepatopancreas after 2, 4, and 6 h treatment of Sp-Crz; (D–F) the level of Sp-VgR expression in the ovary after 2, 4, and 6 h treatment of Sp-Crz. Data represent mean ± SEM (n = 4). Asterisk (* p < 0.05) indicates statistically significant differences when compared to control.
3.5. In Vivo Effects of Sp-Crz on S. paramamosain Ovarian Development
The potential role of Sp-Crz in the ovarian development of S. paramamosain was further investigated by in vivo experiments. It was found that the level of Vg transcript in the hepatopancreas was not significantly changed after 12 h injection of Sp-Crz (Figure 8A); however, the expression of VgR transcript in the ovary was remarkably induced by 12 h injection of Sp-Crz (Figure 8B). In addition, the results showed that the E2 content in hemolymph of S. paramamosain was not significantly altered by 12 h Sp-Crz injection (Figure 8C).
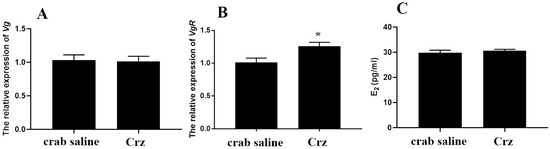
Figure 8.
(A) The level of Vg transcript in the hepatopancreas after 12 h injection of Sp-Crz; (B) the level of VgR transcript in the ovary after 12 h injection of Sp-Crz; (C) E2 titer in hemolymph after 12 h injection of Sp-Crz. Data represent mean ± SEM (n = 7). Asterisk (* p < 0.05) indicates statistically significant differences when compared to crab saline control.
In the long-term injection experiment, it was revealed that prolonged injection of Sp-Crz had no effect on Vg expression in the hepatopancreas (Figure 9A) but significantly induced ovarian VgR gene expression (Figure 9B). In addition, the GSI and E2 content in hemolymph of S. paramamosain were significantly increased after long-term injection of Sp-Crz (Figure 9C,D). Histological results demonstrated that oocyte diameter and yolk granule number were significantly increased by long-term injection of Sp-Crz (Figure 10).
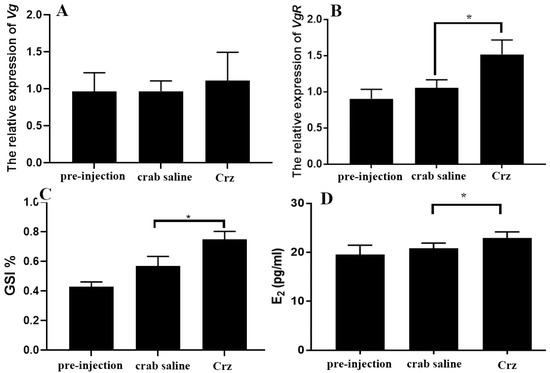
Figure 9.
Effect of long-term injection of Sp-Crz on ovarian development. (A) The level of Vg transcript in the hepatopancreas after long-term injection of Sp-Crz; (B) the level of VgR transcript in the ovary after long-term injection of Sp-Crz; (C) effect of long-term injection of Sp-Crz on GSI of the mud crab; (D) E2 titer in hemolymph after long-term injection of Sp-Crz. Data represent mean ± SEM (n = 10). Asterisk (* p < 0.05) indicates statistically significant differences when compared to crab saline control.
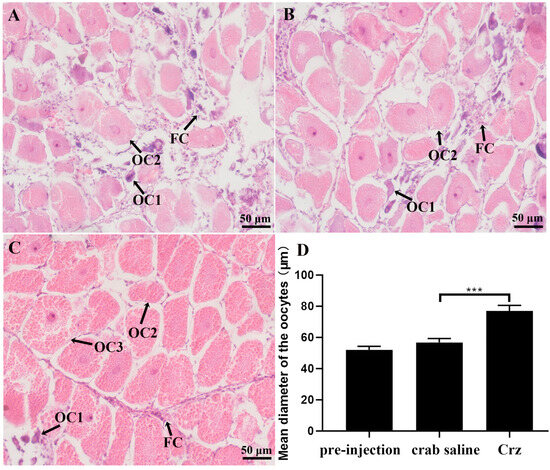
Figure 10.
Histological changes in S. paramamosain ovary after long-term injection of Sp-Crz. (A) Pre-injection control; (B) blank control injected with crab saline; (C) experimental group injected with Sp-Crz. OC1: pre-vitellogenic oocyte; OC2: early vitellogenic oocyte; OC3: late vitellogenic oocyte; FC: follicular cell. Scale bars: 50 μm. (D) Mean diameter of oocytes. “***” indicates significant difference from the crab saline control (p < 0.001).
4. Discussion
Crz was originally identified in P. americana, where it exists as a cardiac-stimulating peptide [5]. To date, the function of Crz has been well studied in insects, where it works as a pleiotropic neuropeptide to regulate a range of physiological activities, including heartbeat, molt, reproduction and body color change [8,10,40,41]. However, its function in crustaceans is poorly understood. In this current study, we isolated the sequences encoding Crz and its cognate receptor from S. paramamosain, and assigned its stimulatory role in the ovarian development of this species.
The identified Sp-Crz precursor from the mud crab S. paramamosain shares similar structural features to the reported Crz precursors [12,42], which include a signal peptide, a mature hormone, a dibasic cleavage site (KR) and a related peptide (Figure 1A). The C-terminal of the mature peptide contains an amidated signal, indicating the active hormone is an amidated peptide. The sequence of Sp-Crz is pQTFQYSRGWTN-amide, which further consolidates the fact that [Arg7]-Crz is the only isoform in crustaceans [11]. Sequence alignments suggested that the sequence of mature Crz is highly conserved among crustaceans and insects (Figure 2), indicating its possibly conserved function in arthropods. CrzR belongs to the rhodopsin-like receptor family of GPCRs, which is the largest subfamily of GPCRs [31,43]. Characteristic features include a DRF motif at the cytoplasmic edge of the third transmembrane domain and an NSxxNPxxY motif in the seventh transmembrane domain [27]. These motifs are considered crucial for G protein activation and protein stabilization [44]. We isolated the Sp-CrzR sequence, which meets the above characteristics. Multiple sequence alignments revealed a high similarity in the seven transmembrane domains between crustacean and insect CrzRs (Figure 3). Phylogenetic analysis confirmed that the isolated Sp-CrzR is a homolog of other deorphanized CrzRs, which forms three distinct clades with AKH and ACP receptors (Figure 4). AKH, ACP, RPCH and Crz are the core regulatory factors of the neuroendocrine system in arthropods, which evolved from a common ancestral gene through replication and differentiation [14,15], exhibiting close correlations in their molecules and receptors in terms of evolutionary origin and structural characteristics. The receptors of these neuropeptides all belong to the GPCR superfamily and have conserved transmembrane domains [45]. However, the differences in their tissue-specific expression patterns and downstream signaling pathways enable them to mediate diverse physiological functions.
In the present study, tissue expression analysis revealed that Sp-Crz was mainly expressed in the eyestalk and cerebral ganglia. Such a result is consistent with the dominance of Crz expression in the central nervous system (CNS) in insects and crustaceans. It was suggested that Bd-Crz is highly expressed in the CNS in the oriental fruit fly B. dorsalis. A similar expression pattern was also reported in the swimming crab P. trituberculatus, where Pt-Crz was expressed in the eyestalk and cerebral ganglia [11,24]. Neuropeptides generally function through interactions with their cognate receptors; therefore, the expression pattern of the Crz receptor in S. paramamosain may provide a cue to explore the function of Crz in this species. Our results showed that Sp-CrzR was highly expressed in the Y-organ, which is the main gland for ecdysteroid synthesis and secretion [46]. This suggests that Sp-Crz might regulate ecdysteroid biosynthesis in the mud crab, which is consistent with recent findings in the swimming crab P. trituberculatus [47] and the red claw crayfish C. quadricarinatus [16]. In addition, the detection of Sp-CrzR in the ovary indicated that Crz might be involved in the ovarian development of S. paramamosain. The presence of Sp-CrzR in the hepatopancreas, an important organ for vitellogenin synthesis in crustaceans [48], further supports the idea that Crz might play a role in the regulation of vitellogenesis in S. paramamosain.
We investigated the mRNA expression profiles of Sp-Crz and Sp-CrzR at three different stages of ovarian development in S. paramamosain. It was revealed that the level of Sp-Crz expression in the eyestalk and cerebral ganglia exhibited significant changes at different stages during ovarian development. In addition, the level of Sp-CrzR expression in the ovary showed a significant increase at the late vitellogenic stage. Such results suggest a potential role of Sp-Crz in the process of vitellogenesis. However, the level of Sp-CrzR expression in the hepatopancreas and Y-organ was significantly decreased during ovarian development. In the swimming crab P. trituberculatus, the Crz/CrzR signaling pathway is involved in the regulation of vitellogenesis and ecdysteroid biosynthesis [11,44]. These findings suggest that the expression profiles of Sp-Crz and Sp-CrzR are closely related to the stage of vitellogenesis and may play an important role in regulating this physiological process.
Eyestalk ganglia play an important role in the neurosecretory system of crustaceans, which is involved in regulating diverse physiological processes, including molting behavior, metamorphosis and gonadal development. The main functional part of the eyestalk is the X-organ sinus gland (XO-SG) complex, whose structure and function are similar to those of the hypothalamus–pituitary system in vertebrates [49,50]. In the present study, Sp-Crz was distributed in the X-organ located in the medulla terminalis, suggesting that Sp-Crz probably originates from the X-organ.
To further explore the precise role of Sp-Crz in regulating the ovarian development of S. paramamosain, we conducted in vivo and in vitro experiments. In this study, the gene Vg and its receptor VgR, which are closely related to ovarian development, were selected to observe their transcriptional responses to Sp-Crz. Vg provides nutrient supplies such as proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids to the oocyte, while VgR can integrate exogenous Vg into the oocyte through mediated endocytosis, which is essential for the development of the oocyte [51]. In in vitro experiments, Sp-Crz did not significantly affect the level of Vg expression in the hepatopancreas but induced the expression of VgR at 6 h by 1 nM (Figure 7F). However, Sp-Crz injection significantly increased the expression of VgR in the ovary in both short-term and long-term in vitro experiments, which is consistent with previous findings in P. trituberculatus [11]. In addition, long-term injection of Sp-Crz resulted in a significant increase in the GSI of S. paramamosain, which consolidated the conclusion that Sp-Crz has a stimulatory effect on ovarian development in the mud crab. In our previous study, SIFa and ACP were also reported to have similar effects during ovarian development [39,43]. E2 is an important sex steroid hormone in vertebrates, which plays a crucial role in vitellogenesis, oocyte growth and ovary maturation [52]. Studies have revealed that estrogen is also widely present in crustaceans and may be involved in reproductive regulation [53]. Recently, it was demonstrated that two genes (StAR3 and 17βHSD8) are involved in the synthesis of estrogen in crustaceans [53]. Through in vivo experiments, our study observed that long-term injection of Sp-Crz for 16 days resulted in a significant increase in E2 levels in hemolymph, suggesting that Sp-Crz may regulate ovarian development through E2. In addition, it showed that the prostaglandin E synthase (PGES) gene is upregulated during ovarian maturation, with a significant increase in the central nervous system [54]. PGES is a key enzyme for the synthesis of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), and PGE2 has been proven to promote ovarian maturation [55]. Therefore, whether the prostanoid pathway is involved in Sp-Crz-regulated ovarian development in the mud crab warrants further study, which will provide a more comprehensive understanding of its reproductive regulatory mechanisms.
In this study, we successfully isolated the coding sequences of Crz and its receptor (Sp-CrzR) from S. paramamosain. The findings revealed that Sp-Crz might play an important role in regulating ovarian development in S. paramamosain. These findings provide new insights into the understanding of the physiological role of Crz in crustaceans, which can contribute to the development of artificial breeding technology in the mud crab aquaculture industry.
Author Contributions
S.Y.: Writing—Original Draft, Formal Analysis, Software, Investigation, Data Curation. L.L.: Writing—Review and Editing. Y.T.: Software, Investigation. A.L.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing—Original Draft, Writing—Review and Editing, Funding Acquisition. H.Y.: Conceptualization, Resources, Writing—Review and Editing, Supervision, Funding Acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers: 32102787 and 32273113).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of the Fisheries College of Jimei University (Approval Code: 2021-04; Approval Date: 22 January 2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Summary of primers used in this study.
Table A1.
Summary of primers used in this study.
| Primer | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Sp-Crz-OF | ATGGTGGCGGGGATCTCGTCTACCG | ORF validation |
| Sp-Crz-OR | TCACAGCTGTGTGTCCAACTCGCGG | ORF validation |
| Sp-Crz-F | AAAGTGTTCCGCAGTGAGC | RT-PCR |
| Sp-Crz-R | GTAGGGAGTCCAGCAGATGA | RT-PCR |
| Sp-CrzR-F | TCATCTGCTGGACTCCCTAC | RT-PCR |
| Sp-CrzR-R | TTCGTGCGACCTTCTGGT | RT-PCR |
| RV-M | GAGCGCATAACAATTTCACACA | RT-PCR |
| M13-47 | CGCCAGGGTTTTCCCAGTCACG | RT-PCR |
| Sp-Crz-qF | GTGAGTGCCCTTCTTCGC | qPCR |
| Sp-Crz-qR | GCAGTTTGGATGTTGTTTCG | qPCR |
| Sp-CrzR-qF | GGCAGCGTCCACCAGAA | qPCR |
| Sp-CrzR-qR | GCCCAAGCAAGCCAGAG | qPCR |
| Sp-Vg-qF | CGCAACCGCCACTGAAGAT | qPCR |
| Sp-Vg-qR | CCACCATGCTGCTCACGACT | qPCR |
| Sp-VgR-qF | TTCTATACCAGGCCACTACC | qPCR |
| Sp-VgR-qR | TTTTCACTCCAAGCACACTC | qPCR |
| β-actin-qF | GAGCGAGAAATCGTTCGTGAC | qPCR |
| β-actin-qR | GGAAGGAAGGCTGGAAGAGAG | qPCR |
References
- Hauser, F.; Cazzamali, G.; Williamson, M.; Blenau, W.; Grimmelikhuijzen, C.J.P. A review of neurohormone GPCRs present in the fruitfly Drosophila melanogaster and the honey bee. Apis mellifera. Prog. Neurobiol. 2006, 80, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, E.C. Post-genomic approaches to resolve neuropeptide signaling in Drosophila. In Invertebrate Neuropeptides and Hormones: Basic Knowledge and Recent Advances; Transworld Research Network: Trivandrum, India, 2006; pp. 179–224. [Google Scholar]
- Nässel, D.R. Neuropeptides in the nervous system of Drosophila and other insects: Multiple roles as neuromodulators and neurohormones. Prog. Neurobiol. 2002, 68, 1–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghert, P.H.; Veenstra, J.A. Drosophila neuropeptide signaling. Adv. Genet. 2003, 49, 1–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veenstra, J.A. Isolation and structure of corazonin, a cardioactive peptide from the American cockroach. FEBS Lett. 1989, 250, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.-J.; Ishibashi, J.; Saito, H.; Tawfik, A.I.; Sakakibara, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Derua, R.; Waelkens, E.; Baggerman, G.; De Loof, A.; et al. Identification of [Arg7] corazonin in the silkworm, Bombyx mori and the cricket, Gryllus bimaculatus, as a factor inducing dark color in an albino strain of the locust, Locusta migratoria. J. Insect Physiol. 2000, 46, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Pener, M.P. A neuropeptide controlling the dark pigmentation in color polymorphism of the migratory locust, Locusta migratoria. J. Insect Physiol. 1994, 40, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Spalovská-Valachová, I.; Cho, K.-H.; Zitnanova, I.; Park, Y.; Adams, M.E.; Žitňan, D. Corazonin receptor signaling in ecdysis initiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6704–6709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmont, M.; Cazzamali, G.; Williamson, M.; Hauser, F.; Grimmelikhuijzen, C.J.P. Identification of four evolutionarily related G protein-coupled receptors from the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 344, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gospocic, J.; Shields, E.J.; Glastad, K.M.; Lin, Y.; Penick, C.A.; Yan, H.; Mikheyev, A.S.; Linksvayer, T.A.; Garcia, B.A.; Berger, S.L.; et al. The neuropeptide corazonin controls social behavior and caste identity in ants. Cell 2017, 170, 748–759.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, S.; Ge, F.; Han, Y.; Wang, M.; Xie, X.; Zhu, D. Putative role of corazonin in the ovarian development of the swimming crab Portunus trituberculatus. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 976754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verleyen, P.; Baggerman, G.; Mertens, I.; Vandersmissen, T.; Huybrechts, J.; Lommel, A.V.; Loof, A.D.; Schoofs, L. Cloning and characterization of a third isoform of corazonin in the honey bee Apis mellifera. Peptides 2006, 27, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Predel, R.; Neupert, S.; Russell, W.K.; Scheibner, O.; Nachman, R.J. Corazonin in insects. Peptides 2007, 28, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, K.K.; Stafflinger, E.; Schneider, M.; Hauser, F.; Cazzamali, G.; Williamson, M.; Kollmann, M.; Schachtner, J.; Grimmelikhuijzen, C.J.P. Discovery of a novel insect neuropeptide signaling system closely related to the insect adipokinetic hormone and corazonin hormonal systems. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 10736–10747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, J.L.; Oliphant, A.; Wilcockson, D.C.; Audsley, N.; Down, R.E.; Lafont, R.; Webster, S.G. Functional characterization and signaling systems of corazonin and red pigment concentrating hormone in the green shore crab, Carcinus maenas. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh Nhut, T.; Mykles, D.L.; Elizur, A.; Ventura, T. Ecdysis triggering hormone modulates molt behaviour in the redclaw crayfish Cherax quadricarinatus, providing a mechanistic evidence for conserved function in molt regulation across Pancrustacea. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2020, 298, 113556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, A.I.; Tanaka, S.; De Loof, A.; Schoofs, L.; Baggerman, G.; Waelkens, E.; Derua, R.; Milner, Y.; Yerushalmi, Y.; Pener, M.P. Identification of the gregarization-associated dark-pigmentotropin in locusts through an albino mutant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 7083–7087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Hua, Y.J.; Roller, L.; Tanaka, S. Corazonin reduces the spinning rate in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J. Insect Physiol. 2002, 48, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapan, N.; Lushchak, O.V.; Luo, J.; Nässel, D.R. Identified peptidergic neurons in the Drosophila brain regulate insulin-producing cells, stress responses and metabolism by coexpressed short neuropeptide F and corazonin. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 69, 4051–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayler, T.D.; Pacheco, D.A.; Hergarden, A.C.; Murthy, M.; Anderson, D.J. A neuropeptide circuit that coordinates sperm transfer and copulation duration in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 20697–20702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, K. Functional Analysis of Corazonin and Its Receptor in Drosophila melanogaster. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Oyeyinka, A.; Kansal, M.; O’Sullivan, S.M.; Gualtieri, C.; Smith, Z.M.; Vonhoff, F.J. Corazonin neurons contribute to dimorphic ethanol sedation sensitivity in Drosophila melanogaster. Front. Neural Circuits 2022, 16, 702901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Kim, K.M.; Kikuno, K.; Wang, Z.; Choi, Y.J.; Park, J.H. Developmental regulation and functions of the expression of the neuropeptide corazonin in Drosophila melanogaster. Cell Tissue Res. 2008, 331, 659–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Q.L.; Jiang, H.B.; Gui, S.H.; Chen, E.H.; Wei, D.D.; Li, H.M.; Wang, J.J.; Smagghe, G. A Role of corazonin receptor in larval-pupal transition and pupariation in the oriental fruit fly Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) (Diptera: Tephritidae). Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Gu, G.X.; Teng, Z.W.; Wu, S.F.; Huang, J.; Song, Q.S.; Ye, G.Y.; Fang, Q. Identification and expression profiles of neuropeptides and their G protein-coupled receptors in the rice stem borer Chilo suppressalis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredriksson, R.; Lagerström, M.C.; Lundin, L.-G.; Schiöth, H.B. The G-protein-coupled receptors in the human genome form five main families. Phylogenetic analysis, paralogon groups, and fingerprints. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003, 63, 1256–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldham, W.M.; Hamm, H.E. Heterotrimeric G protein activation by G-protein-coupled receptors. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzamali, G.; Saxild, N.P.E.; Grimmelikhuijzen, C.J.P. Molecular cloning and functional expression of a Drosophila corazonin receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 298, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, H.; Yang, H.; He, X.; Jiang, X.; Shi, Y.; Alatangaole, D.; Shi, L.; Zhou, N. Specific activation of the G protein-coupled receptor BNGR-A21 by the neuropeptide corazonin from the silkworm, Bombyx mori, Dually Couples to the Gq and Gs Signaling Cascades. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 11662–11675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, K.; Conner, W.C.; Choi, D.Y.; Park, J.H. Characterization, expression, and evolutionary aspects of corazonin neuropeptide and its receptor from the house fly, Musca domestica (Diptera: Muscidae). Gene 2012, 497, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamoudi, Z.; Lange, A.B.; Orchard, I. Identification and characterization of the corazonin receptor and possible physiological roles of the corazonin-signaling pathway in Rhodnius prolixus. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oryan, A.; Wahedi, A.; Paluzzi, J.-P.V. Functional characterization and quantitative expression analysis of two GnRH-related peptide receptors in the mosquito, Aedes aegypti. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 497, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, S.J.; Fitzgibbon, Q.P.; Smith, G.G.; Ventura, T. In silico prediction of the G-protein coupled receptors expressed during the metamorphic molt of Sagmariasus verreauxi (Crustacea: Decapoda) by mining transcriptomic data: RNA-seq to repertoire. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2016, 228, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, N.M.; Mykles, D.L.; Elizur, A.; Ventura, T. Characterization of G-protein coupled receptors from the blackback land crab Gecarcinus lateralis Y organ transcriptome over the molt cycle. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boerjan, B.; Verleyen, P.; Huybrechts, J.; Schoofs, L.; De Loof, A. In search for a common denominator for the diverse functions of arthropod corazonin: A role in the physiology of stress? Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2010, 166, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubrak, O.I.; Lushchak, O.V.; Zandawala, M.; Nässel, D.R. Systemic corazonin signalling modulates stress responses and metabolism in Drosophila. Open Biol. 2016, 6, 160152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, K.; Choi, S.H.; Im, J.; Lee, G.G.; Loeffler, F.; Park, J.H. Regulation of ethanol-related behavior and ethanol metabolism by the corazonin neurons and corazonin receptor in Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ye, H.; Huang, H.; Yang, Y.; Gong, J. An insulin-like androgenic gland hormone gene in the mud crab, Scylla paramamosain, extensively expressed and involved in the processes of growth and female reproduction. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2014, 204, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Tang, Y.; Liu, F.; Lu, L.; Liu, A.; Ye, H. Evaluation of the effect of adipokinetic hormone/corazonin-related peptide (ACP) on ovarian development in the mud crab, Scylla paramamosain. Animals 2024, 14, 3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sláma, K.; Sakai, T.; Takeda, M. Effect of corazonin and crustacean cardioactive peptide on heartbeat in the adult American cockroach (Periplaneta americana). Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2006, 62, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roller, L.; Tanaka, Y.; Tanaka, S. Corazonin and corazonin-like substances in the central nervous system of the Pterygote and Apterygote insects. Cell Tissue Res. 2003, 312, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggerman, G.; Cerstiaens, A.; De Loof, A.; Schoofs, L. Peptidomics of the larval Drosophila melanogaster central nervous system. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 40368–40374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Tang, Y.; Lu, L.; Gong, S.; Liu, A.; Ye, H. SIFa and its receptors play a possibly stimulatory role during ovarian development of the mud crab Scylla paramamosain. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1494264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, J.A.; Shi, L.; Javitch, J.A. Structural mimicry in G protein-coupled receptors: Implications of the high-resolution structure of rhodopsin for structure-function analysis of rhodopsin-like receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 60, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zandawala, M.; Haddad, A.S.; Hamoudi, Z.; Orchard, I. Identification and characterization of the adipokinetic hormone/corazonin-related peptide signaling system in Rhodnius prolixus. FEBS J. 2015, 282, 3603–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, L.A.R.; Normann, R.S.; Chung, J.S.; Vinagre, A.S. A brief and updated introduction to the neuroendocrine system of crustaceans. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2024, 590, 112265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Zhang, J.; Tu, S.; Zhou, Q.; Zhu, D. Corazonin stimulates ecdysteroid synthesis during the molting process of the swimming crab, Portunus trituberculatus. Biology 2024, 13, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zmora, N.; Trant, J.; Chan, S.M.; Chung, J.S. Vitellogenin and its messenger RNA during ovarian development in the female blue crab, callinectes sapidus: Gene expression, synthesis, transport, and Cleavage1. Biol. Reprod. 2007, 77, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H.; Ye, H. Neuropeptides in the cerebral ganglia of the mud crab, Scylla paramamosain: Transcriptomic analysis and expression profiles during vitellogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaraj, H.; Natarajan, A. Molecular mechanisms regulating molting in a crustacean. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Chen, Y.; Zou, Z.; Lin, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Characterization and expression profile of vitellogenin gene from Scylla paramamosain. Gene 2013, 520, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Wang, T.; Liu, A.; Ye, H. A single-cell atlas of crab ovary provides new insights into oogenesis in crustaceans. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, 2409688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; He, K.; Blaney, L.; Chung, J.S. 17β-Estradiol (E2) may be involved in the mode of crustacean female sex hormone (CFSH) action in the blue crab, Callinectes sapidus. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 962576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duangprom, S.; Saetan, J.; Phanaksri, T.; Songkoomkrong, S.; Surinlert, P.; Tamtin, M.; Sobhon, P.; Kornthong, N. Acceleration of ovarian maturation in the female mud crab with RNA interference of the vitellogenesis-inhibiting hormone (VIH). Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 880235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumpownon, C.; Engsusophon, A.; Siangcham, T.; Sugiyama, E.; Soonklang, N.; Meeratana, P.; Wanichanon, C.; Hanna, P.J.; Setou, M.; Sobhon, P. Variation of prostaglandin E2 concentrations in ovaries and its effects on ovarian maturation and oocyte proliferation in the giant fresh water prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2015, 223, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).