Metolachlor Exposure Impaired Neurogenesis During Embryonic Development of Zebrafish (Danio rerio)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Zebrafish Husbandry
2.2. Metolachlor Treatment
2.3. RNA Purification and Reverse Transcription
2.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.5. Synthesis of Riboprobes for ngn1
2.6. Whole-Mount In Situ Hybridization
2.7. TUNEL Assay
2.8. Fiji Software Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
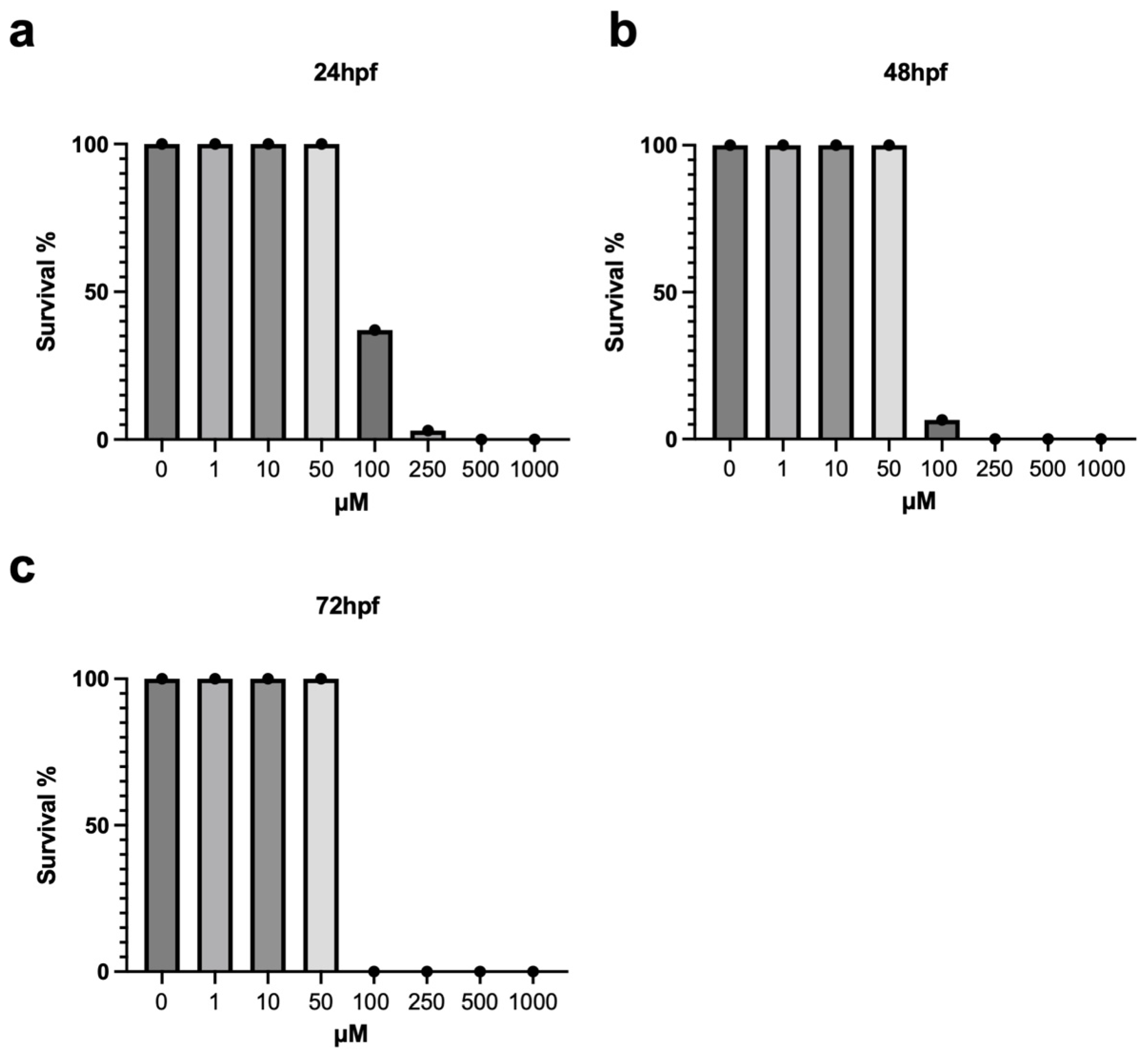
3.1. Survival Rate and Morphological Analysis of Zebrafish Embryos Exposed to Metolachlor
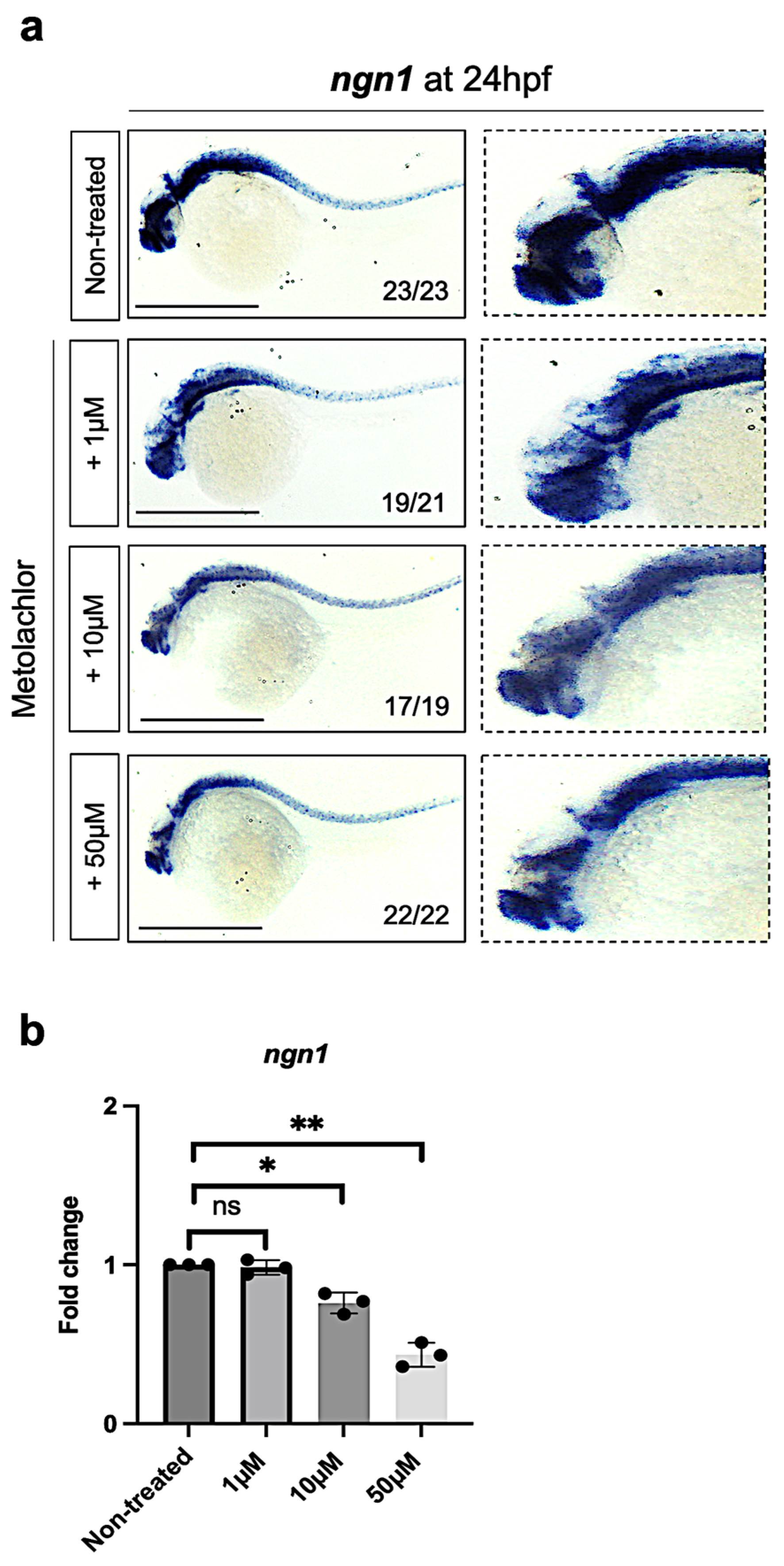
3.2. Metolachlor Exposure Affects the Expression of Neurogenin-1 (ngn1), a Proneural bHLH Transcription Factor in Zebrafish Embryos
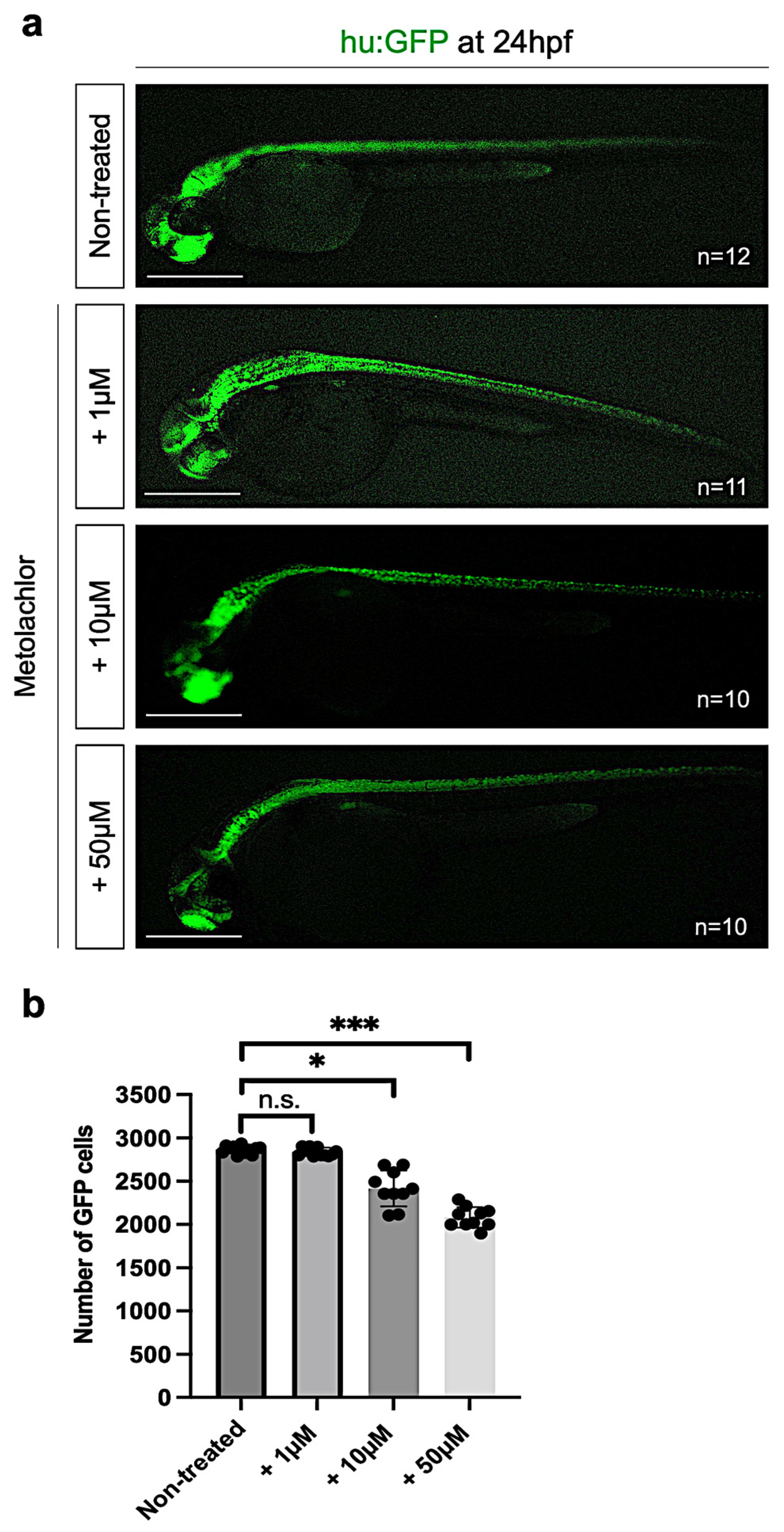
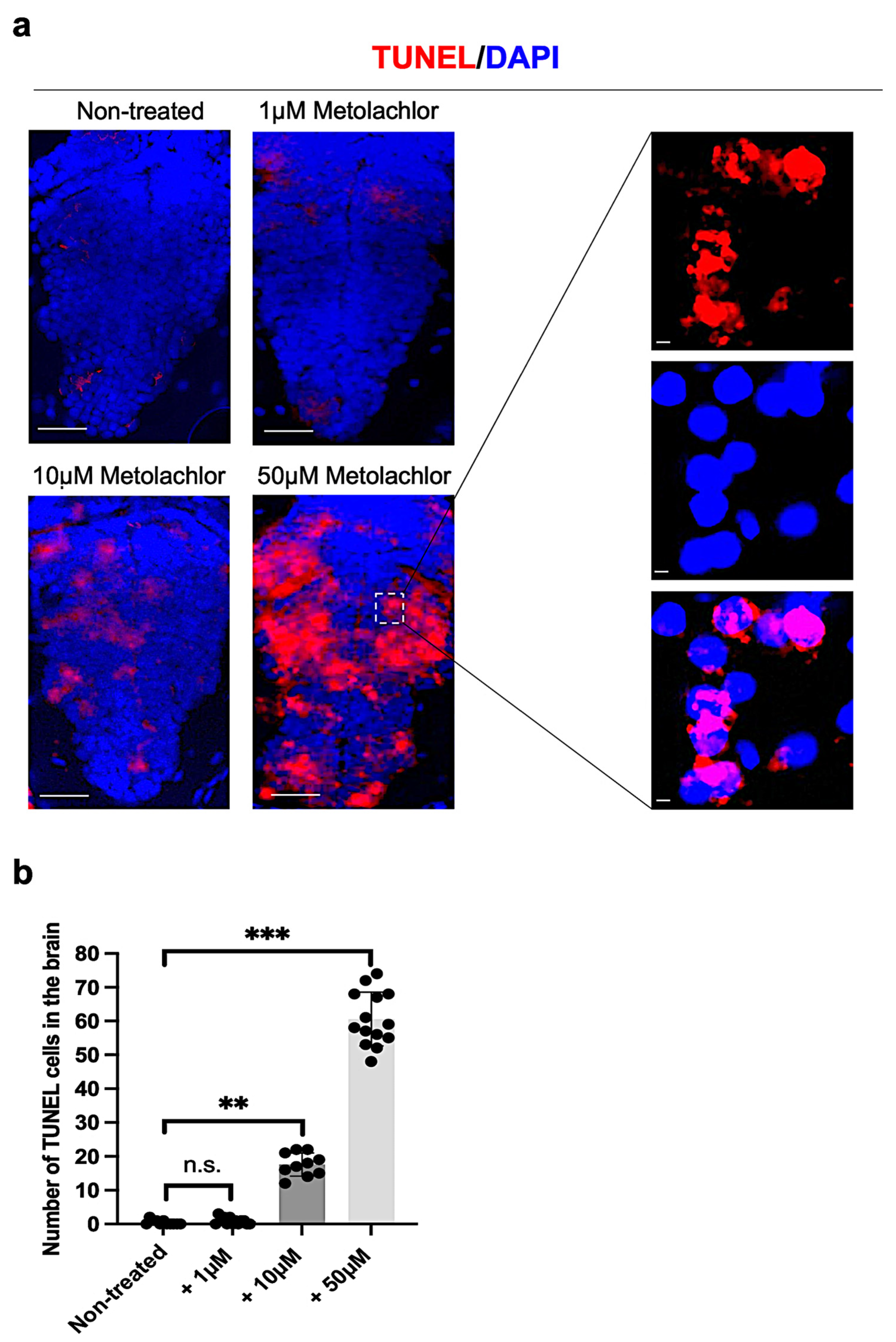
3.3. Metolachlor Exposure Induces Apoptotic Cell Death and Affects Neuronal Development
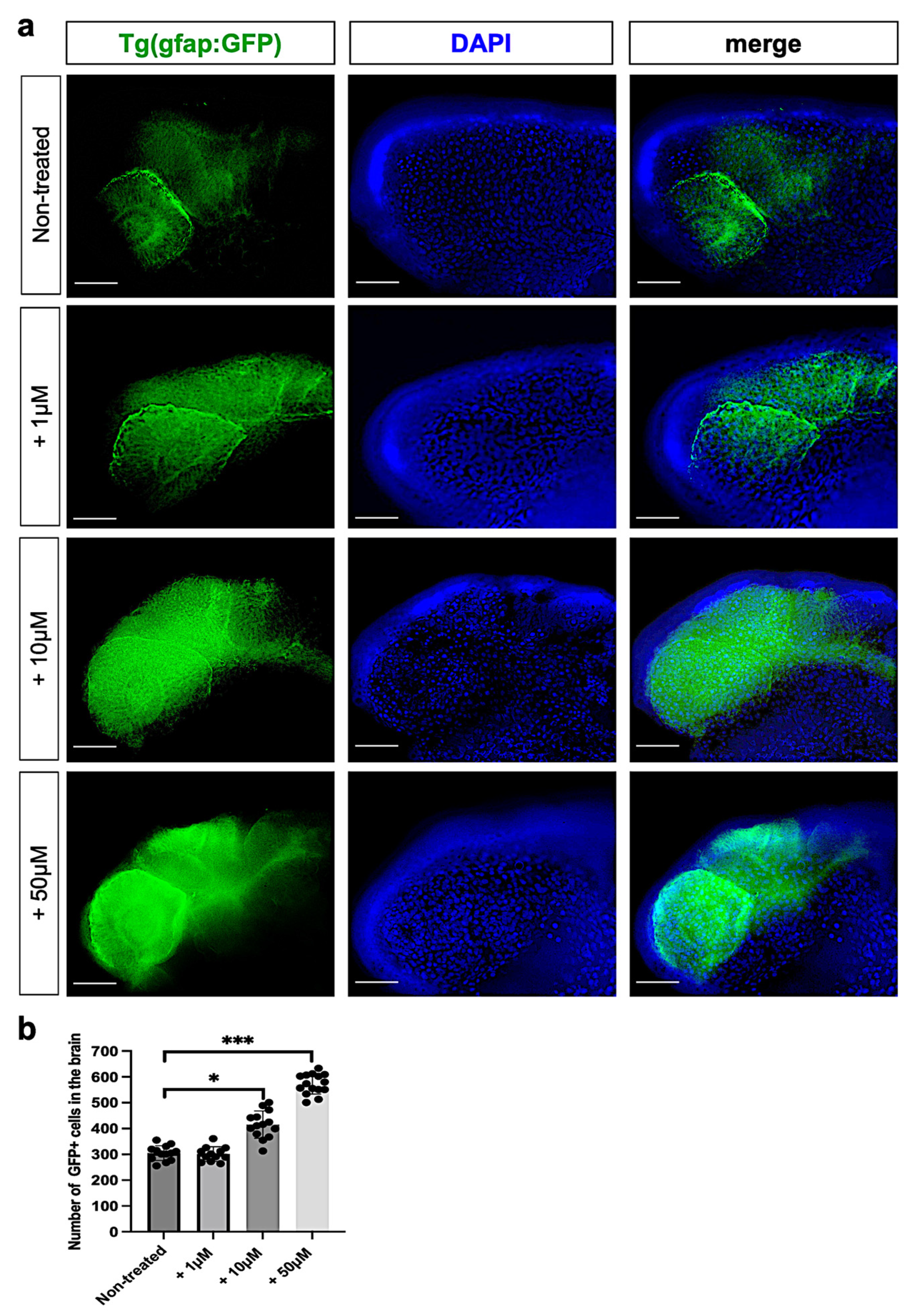
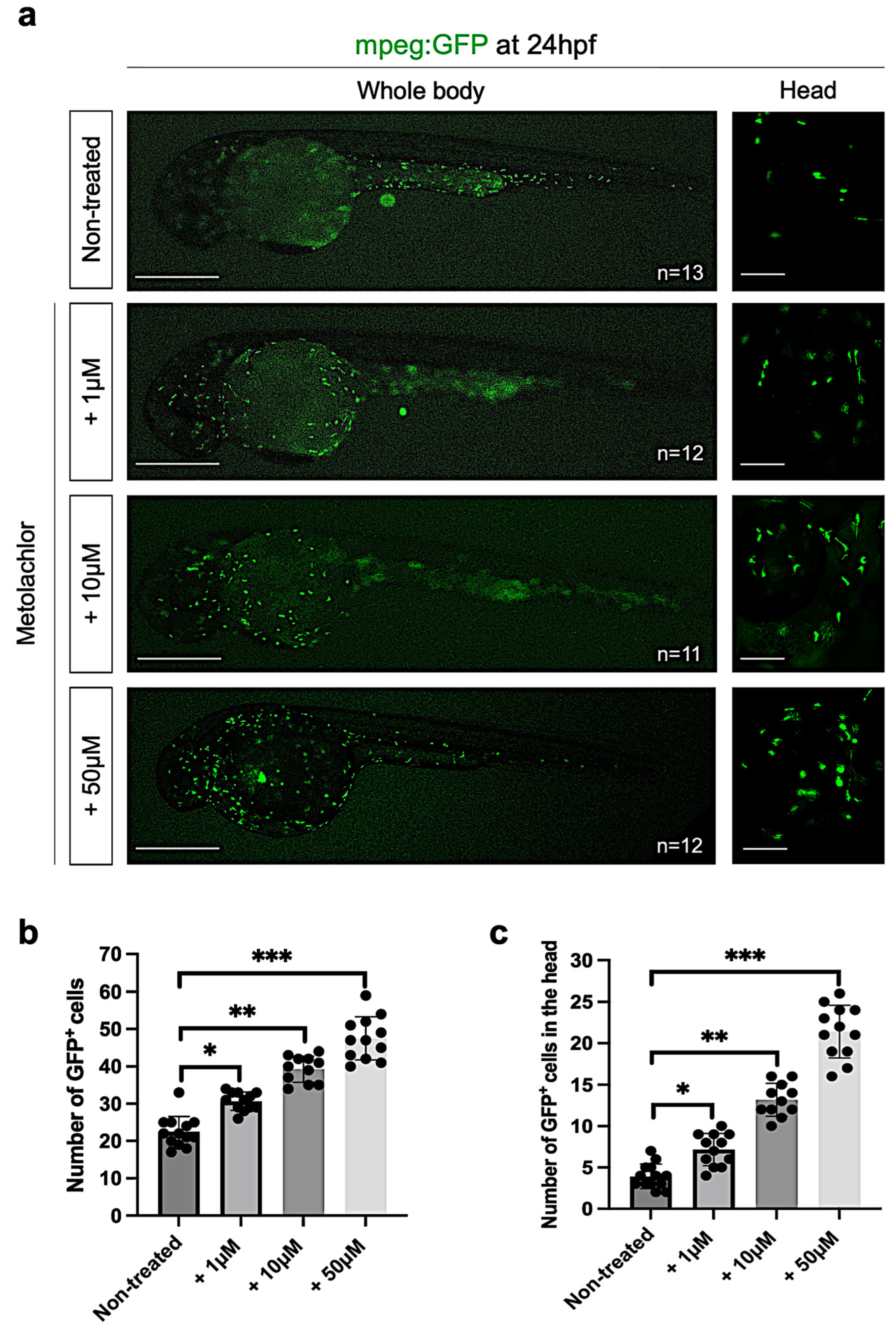
3.4. Metolachlor Exposure Increases Astrogliosis and Inflammation in Zebrafish Embryos
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sule, R.O.; Condon, L.; Gomes, A.V. A Common Feature of Pesticides: Oxidative Stress—The Role of Oxidative Stress in Pesticide-Induced Toxicity. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 5563759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damalas, C.A.; Eleftherohorinos, I.G. Pesticide exposure, safety issues, and risk assessment indicators. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 1402–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.; Li, W.; Li, Q.; Zhang, D.; Fang, W.; Yan, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Jin, X.; Cao, A. Metolachlor metal-organic framework nanoparticles for reducing leaching, ecotoxicity and improving bioactivity. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 5366–5378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza, R.M.; Seibert, D.; Quesada, H.B.; de Jesus Bassetti, F.; Fagundes-Klen, M.R.; Bergamasco, R. Occurrence, impacts and general aspects of pesticides in surface water: A review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 135, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinou, I.K.; Hela, D.G.; Albanis, T.A. The status of pesticide pollution in surface waters (rivers and lakes) of Greece. Part I. Review on occurrence and levels. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 141, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, D.M.; Greiner, D.; Fretheim, M.; Ubben, M.; Dhanwada, K.R. Mechanism of metolachlor action due to alterations in cell cycle progression. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2013, 29, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, P.; Oliva-Teles, L.; Guimarães, L.; Carvalho, A.P. Occurrence of Pharmaceutical and Pesticide Transformation Products in Freshwater: Update on Environmental Levels, Toxicological Information and Future Challenges. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 260, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, P.; Davis, D.E.; Truelove, B. Effects of Metolachlor on Germination, Growth, Leucine Uptake, and Protein Synthesis. Weed Sci. 1979, 27, 634–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercurio, P.; Mueller, J.F.; Eaglesham, G.; O’Brien, J.; Flores, F.; Negri, A.P. Degradation of Herbicides in the Tropical Marine Environment: Influence of Light and Sediment. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozmánková, E.; Pípal, M.; Bláhová, L.; Njattuvetty Chandran, N.; Morin, B.; Gonzalez, P.; Bláha, L. Environmentally relevant mixture of S-metolachlor and its two metabolites affects thyroid metabolism in zebrafish embryos. Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 221, 105444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rašković, B.; Poleksić, V.; Vuković, G.; Špirović Trifunović, B.; Božić, G.; Ćupić Miladinović, D.; Marković, Z.; Brkić, D. Acute and Subchronic Exposure of the Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) to Herbicide S-Metolachlor. Water 2023, 15, 4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goutte, A.; Martin, N.; Alliot, F.; Angelier, F.; Blanchouin, A.; Costantini, D.; Lesimple, M.; Ribout, C.; Traoré, S.; Villalta, R.; et al. From cells to recapture rates: Responses and recovery of a wild fish after an experimental exposure to a widely used herbicide. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2024, 44, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velisek, J.; Stara, A.; Zuskova, E.; Kubec, J.; Buric, M.; Kouba, A. Effects of s-metolachlor on early life stages of marbled crayfish. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 153, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.P.; Fernandes, M.A.; Martins, J.D.; Santos, M.S.; Moreno, A.J.; Vicente, J.A.; Videira, R.A.; Jurado, A.S. Toxicity assessment of the herbicide metolachlor comparative effects on bacterial and mitochondrial model systems. Toxicol. Vitr. 2009, 23, 1585–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacialli, P.; Ricci, S.; Servetto, G.P.; Franceschini, V.; Ruiz-Zepeda, F.; Vigliaturo, R. Altered Morpho-Functional Features of Neurogenesis in Zebrafish Embryos Exposed to Non-Combustion-Derived Magnetite. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacialli, P.; Ricci, S.; Frabetti, F.; Ferrando, S.; Franceschini, V. Exposure of Zebrafish Embryos to Urea Affects NOS1 Gene Expression in Neuronal Cells. Environments 2024, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ivantsova, E.; Souders, C.L.; Martyniuk, C.J. The agrochemical S-metolachlor disrupts molecular mediators and morphology of the swim bladder: Implications for locomotor activity in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintaneiro, C.; Patrício, D.; Novais, S.C.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Monteiro, M.S. Endocrine and physiological effects of linuron and S-metolachlor in zebrafish developing embryos. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou-Yang, K.; Feng, T.; Han, Y.; Li, G.; Li, J.; Ma, H. Bioaccumulation, metabolism and endocrine-reproductive effects of metolachlor and its S-enantiomer in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 802, 149826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.C.; Hong, S.K.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.H.; Yoon, E.J.; Kim, C.H.; Miki, N.; Huh, T.L. Structural comparison of zebrafish Elav/Hu and their differential expressions during neurogenesis. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 279, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellett, F.; Pase, L.; Hayman, J.W.; Andrianopoulos, A.; Lieschke, G.J. mpeg1 promoter transgenes direct macrophage-lineage expression in zebrafish. Blood 2011, 117, e49–e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardos, R.L.; Raymond, P.A. GFAP transgenic zebrafish. Gene Expr. Patterns 2006, 6, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahony, C.B.; Cacialli, P.; Pasche, C.; Monteiro, R.; Savvides, S.N.; Bertrand, J.Y. Hapln1b, a central organizer of the ECM, modulates kit signaling to control developmental hematopoiesis in zebrafish. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 4935–4948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.Y.; Cowden, J.; Simmons, S.O.; Padilla, S.; Ramabhadran, R. Gene expression changes in developing zebrafish as potential markers for rapid developmental neurotoxicity screening. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2010, 32, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacialli, P.; Lucini, C. Analysis of the Expression of Neurotrophins and Their Receptors in Adult Zebrafish Kidney. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacialli, P. Expression of Nerve Growth Factor and Its Receptor TrkA in the Reproductive System of Adult Zebrafish. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, S.; Lazzari, M.; Maurizii, M.; Franceschini, V.; Milani, L.; Cacialli, P. Analysis of clasp2 Transcription Pattern in Male Germ Cells during Spermatogenesis: A Comparative Study in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) and Guppy (Poecilia reticulata). Animals 2023, 13, 3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.Y.; Einhorn, Z.; Mercurio, S.; Lee, S.; Lau, B.; Mione, M.; Wilson, S.W.; Guo, S. Neurogenin1 is a determinant of zebrafish basal forebrain dopaminergic neurons and is regulated by the conserved zinc finger protein Tof/Fezl. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 5143–5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Chen, Z.; del Barco Barrantes, I.; de la Pompa, J.L.; Anderson, D.J. neurogenin1 is essential for the determination of neuronal precursors for proximal cranial sensory ganglia. Neuron 1998, 20, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Nadal-Vicens, M.; Misono, S.; Lin, M.Z.; Zubiaga, A.; Hua, X.; Fan, G.; Greenberg, M.E. Neurogenin promotes neurogenesis and inhibits glial differentiation by independent mechanisms. Cell 2001, 104, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Hu, X.; Qian, L.; O’Callaghan, J.P.; Hong, J.S. Astrogliosis in CNS pathologies: Is there a role for microglia? Mol. Neurobiol. 2010, 41, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andermann, P.; Ungos, J.; Raible, D.W. Neurogenin1 defines zebrafish cranial sensory ganglia precursors. Dev. Biol. 2002, 251, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGraw, H.F.; Nechiporuk, A.; Raible, D.W. Zebrafish dorsal root ganglia neural precursor cells adopt a glial fate in the absence of neurogenin1. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 12558–12569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blader, P.; Fischer, N.; Gradwohl, G.; Guillemot, F.; Strähle, U. The activity of neurogenin1 is controlled by local cues in the zebrafish embryo. Development 1997, 124, 4557–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzh, V.; Sleptsova, I.; Liao, J.; He, J.; Gong, Z. Expression of zebrafish bHLH genes ngn1 and nrd defines distinct stages of neural differentiation. Dev. Dyn. 1998, 213, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyimah, E.; Xu, H.; Dong, X.; Qiu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Bu, Y.; Akoto, O. Developmental neurotoxicity of low concentrations of bisphenol A and S exposure in zebrafish. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, V.; Chauhan, S.S.; Ansari, M.I.; Jagdale, P.; Ayanur, A.; Parthasarathi, R.; Anbumani, S. 4-Methylbenzylidene camphor induced neurobehavioral toxicity in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Environ. Res. 2024, 242, 117746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Meng, Z.; Zhou, L.; Cao, Z.; Liao, X.; Ye, R.; Lu, H. Effects of acetochlor on neurogenesis and behaviour in zebrafish at early developmental stages. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 954–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, S.; Altun, S.; Özkaraca, M.; Ghosi, A.; Toraman, E.; Arslan, H. Cypermethrin, chlorpyrifos, deltamethrin, and imidacloprid exposure up-regulates the mRNA and protein levels of bdnf and c-fos in the brain of adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 2018, 203, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, M. Apoptosis in zebrafish development. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 136, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, K.; Li, Y.; Long, L.; Li, D.; Jia, Q.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Q.; Tang, Y.; Wen, L.; Kung, H.F.; et al. Knockdown of FoxO3a induces increased neuronal apoptosis during embryonic development in zebrafish. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 484, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blahová, J.; Plhalová, L.; Hostovský, M.; Divišová, L.; Dobšíková, R.; Mikulíková, I.; Stěpánová, S.; Svobodová, Z. Oxidative stress responses in zebrafish Danio rerio after subchronic exposure to atrazine. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 61, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel, N.A.; Sachett, A.; Schneider, S.E.; Garbinato, C.; Decui, L.; Eichwald, T.; Conterato, G.M.M.; Latini, A.; Piato, A.; Siebel, A.M. Exposure to the herbicide 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid impairs mitochondrial function, oxidative status, and behavior in adult zebrafish. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 45874–45882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, K.K. Glial fibrillary acidic protein: From intermediate filament assembly and gliosis to neurobiomarker. Trends Neurosci. 2015, 38, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iribarne, M.; Hyde, D.R. Different inflammation responses modulate Müller glia proliferation in the acute or chronically damaged zebrafish retina. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 892271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewett, S.J.; Jackman, N.A.; Claycomb, R.J. Interleukin-1β in Central Nervous System Injury and Repair. Eur. J. Neurodegener. Dis. 2012, 1, 195–211. [Google Scholar]
- Ogryzko, N.V.; Hoggett, E.E.; Solaymani-Kohal, S.; Tazzyman, S.; Chico, T.J.; Renshaw, S.A.; Wilson, H.L. Zebrafish tissue injury causes upregulation of interleukin-1 and caspase-dependent amplification of the inflammatory response. Dis. Model. Mech. 2014, 7, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Balazs, R.; Soiampornkul, R.; Thangnipon, W.; Cotman, C.W. Interleukin-1 beta impairs brain derived neurotrophic factor-induced signal transduction. Neurobiol. Aging 2008, 29, 1380–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argaw, A.T.; Zhang, Y.; Snyder, B.J.; Zhao, M.L.; Kopp, N.; Lee, S.C.; Raine, C.S.; Brosnan, C.F.; John, G.R. IL-1beta regulates blood-brain barrier permeability via reactivation of the hypoxia-angiogenesis program. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 5574–5584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, T.; Wu, Y.; Jin, W.; Wen, Z. Microglia Colonization of Developing Zebrafish Midbrain Is Promoted by Apoptotic Neuron and Lysophosphatidylcholine. Dev. Cell 2016, 38, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| il1b | F: 5′-ATGGCGAACGTCATCCAAGA-3′ | R: 5′-GAGACCCGCTGATCTCCTTG-3′ |
| ef1a | F: 5′-CCTGGGAGTGAAACAGCTG-3′ | R: 5′-GCCTCCAGCATGTTGTCAC-3′ |
| ngn1 | F: 5′-TGCACAACCTTAACGACGCATTGG-3′ | R: 5′-TGCCCAGATGTAGTTGTGAGCGAA-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fazzina, M.; Insidioso, S.; Cacialli, P. Metolachlor Exposure Impaired Neurogenesis During Embryonic Development of Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fishes 2025, 10, 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10060292
Fazzina M, Insidioso S, Cacialli P. Metolachlor Exposure Impaired Neurogenesis During Embryonic Development of Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fishes. 2025; 10(6):292. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10060292
Chicago/Turabian StyleFazzina, Martina, Stefano Insidioso, and Pietro Cacialli. 2025. "Metolachlor Exposure Impaired Neurogenesis During Embryonic Development of Zebrafish (Danio rerio)" Fishes 10, no. 6: 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10060292
APA StyleFazzina, M., Insidioso, S., & Cacialli, P. (2025). Metolachlor Exposure Impaired Neurogenesis During Embryonic Development of Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fishes, 10(6), 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10060292








