Abstract
In aquaculture, pre-slaughter fasting reduces stress and improves muscle quality. Fasting periods of 55–58 degree days (°C d) enhance muscle structure and post-mortem biochemistry in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss), although optimal durations vary with temperature. This study investigated the effects of fasting from none to extended durations on 495 rainbow trout under summer (22 °C) and winter (8 °C) conditions. In summer, elevated temperatures increased muscle glycogen, leading to lower pH and delayed rigor mortis (RM), especially in fasted groups, where RM peaked at 24 h post-mortem. In winter, RM occurred earlier. Prolonged fasting increased acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity, with high baseline levels in non-fasted summer fish. Muscle lightness at 0 h post-mortem was highest in non-fasted winter fish but declined to summer levels in fasted groups. Antioxidant enzyme activity (glutathione-S-transferase, glutathione peroxidase) increased with fasting in winter, while summer heat masked responses. The expression of genes for mineralocorticoid receptors and heat shock proteins remained stable in warm conditions. Summer delayed metabolic decline due to higher glycogen-triggered excessive AChE activity from heat stress. Winter supported faster metabolic adjustment and more regulated enzyme activity. These findings highlight the need to adjust fasting strategies seasonally to optimize muscle traits, especially under thermal variations.
Key Contribution:
This study reveals that seasonal temperatures strongly modulate the post-mortem muscle response in rainbow trout, where summer heat delays rigor mortis and pH decline due to high glycogen, while fasting amplifies AChE activity under chronic heat stress and enhances antioxidant responses in winter. These findings underscore the need to adjust fasting strategies to environmental conditions to safeguard muscle traits under thermal variations.
1. Introduction
In aquaculture, pre-slaughter fasting is a common practice, particularly during specific operations such as transport and harvest. This strategy offers several practical benefits, including improved water quality—by reducing ammonia and carbon dioxide excretion—and a lower risk of carcass contamination during evisceration due to gastrointestinal emptying [,,]. Additionally, fasting has been shown to moderately improve certain flesh quality traits, such as color [], firmness [], and flavor []. However, it also influences post-mortem muscle physiology, including glycogen levels, pH decline, and the progression of rigor mortis (RM) [,]. In rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss), extended fasting has not been associated with negative effects on behavior, stress responses, or muscle integrity [,]. Nevertheless, identifying an optimal fasting duration that supports both animal welfare and meat quality remains a key challenge in fish production systems, as prolonged feed deprivation may potentially affect both animal welfare and muscle characteristics.
Fish muscle condition is influenced by numerous factors, including species, age, nutritional status, fat content and distribution, as well as the stress response triggered during the pre-slaughter period [,]. In this context, fasting has been strategically applied to modify muscle composition, potentially reducing lipid accumulation in certain species. However, the evidence supporting consistent fat reduction remains inconclusive [,]. Similarly, the effects of prolonged fasting on muscle quality are not yet fully understood. Current studies indicate that the ideal fasting duration to preserve muscle integrity and minimize adverse effects is relatively short—typically between one and three days for rainbow trout [,] and no more than seven days in gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) [].
Establishing a precise maximum fasting duration based solely on elapsed time is complex, as the effects on animal welfare and muscle quality are strongly influenced by environmental factors—particularly water temperature []. This complexity stems from the poikilothermic nature of fish, which lack internal temperature regulation. As a result, their metabolic rate, feed intake, and oxygen demand fluctuate with ambient temperature []. To address this variability, the concept of degree days (°C d), the cumulative product of time and temperature, is used to better estimate optimal fasting periods. Research suggests that fasting durations between 12 and 55 °C d do not significantly affect metabolic or stress indicators in rainbow trout when compared to non-fasted controls. These findings are supported by multiple studies focused on identifying fasting intervals that ensure adequate gut emptying while maintaining animal welfare and preserving muscle condition [,,,,].
Because °C represents the cumulative sum of daily average water temperatures over time, comparing fasting durations in days across varying thermal conditions can be misleading. The actual number of fasting days required to reach a specific °C d threshold depends on the ambient temperature, which fluctuates seasonally and is increasingly affected by climate change. For instance, 55–58 °C d of fasting in summer may equate to a much shorter time span than in winter due to higher water temperatures. Warmer conditions accelerate metabolic processes, potentially reducing the necessary fasting period, whereas colder temperatures may demand extended durations. While optimal °C d intervals have been proposed, their consistent impact on muscle physiology across diverse thermal environments remains unclear. Several studies have investigated fasting under different °C d regimes in rainbow trout reared in cold-water environments. Reported ranges include 55 to 200 °C d at an average of 10.2 ± 1.1 °C [], 17.2 to 55.3 °C d at 6.15 ± 0.6 °C [], and 11.5 to 34.1 °C d at 11.36 ± 0.16 °C []. Additional trials examined withholding feed for 3 to 14 days at 3.8–4.2 °C []. Collectively, these findings suggest minimal impact on stress, health, and muscle parameters within certain °C d thresholds. However, studies at higher temperatures (19.5 to 58.0 °C d, average 19.33 ± 0.56 °C) show that fasting up to three days is tolerated without adverse welfare effects. Still, effects on muscle quality beyond this limit remain uncertain. Given the sensitivity of rainbow trout, a cold-water species with an optimal range of 12–18 °C and a thermal limit of 23–25 °C [,], further seasonal studies are warranted, particularly under the growing pressure of climate-induced thermal stress.
Given the limited research directly comparing ideal degree-day conditions across different thermal conditions, this study aims to assess post-mortem biochemical and physiological muscle parameters in rainbow trout exposed to different pre-slaughter fasting durations under two different average temperature conditions, with an emphasis on extended fasting periods. By examining how temperature-dependent metabolic variation influences muscle responses to fasting, the research contributes to a deeper understanding of thermal biology in poikilothermic aquaculture species.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup
The research was conducted at the aquaculture facilities of the School of Forestry Engineering at the Polytechnic University of Madrid (UPM), located in Madrid, Spain. It was carried out independently under two distinct seasonal conditions: summer (May 2022) and winter (December 2022), with average water temperatures of 22.0 ± 0.06 °C and 8.80 ± 1.79 °C, respectively, and different batches of fish were used for each season. These temperatures represent the typical seasonal fluctuations in the region, providing realistic environmental conditions for the study. The fish were exposed to these temperature variations, which naturally occur in aquaculture systems. Water was sourced from an underground well and distributed across several tanks, passing through a biofilter before being recirculated back to the well, as part of a recirculating aquaculture system (RAS). Weekly monitoring of water quality parameters revealed no significant differences between tanks. The average (mean ± SEM) values for the physicochemical properties were as follows: dissolved oxygen 8.0 ± 0.3 mg O2/L, alkalinity 40.7 ± 14.2 mg/L, pH 7.0 ± 0.2, un-ionized ammonia (NH3) 0.05 ± 0.01 mg/L, nitrite (NO2−) 0.25 ± 0.05 mg/L, and nitrate (NO3−) 34.3 ± 2.51 mg/L. The fish were kept under natural lighting conditions, with a photoperiod of 10 h of light and 14 h of darkness (10L:14D) during summer, and 9 h of light with 15 h of darkness (9L:15D) during winter.
For each seasonal trial, a total of 495 rainbow trout were used, sourced from a commercial facility in Cifuentes, Guadalajara, Spain. Upon arrival, the fish underwent a standardized two-week acclimation period. To ensure consistent body weight distribution, fish were weighed individually at the start of each trial (initial average body weight: 200–400 g; 10–11 months old) and were divided into 9 tanks (1 m × 1 m × 0.85 m, holding 0.85 m3 of water), with a consistent stocking density of 17.05 ± 0.051 kg/m3 (55 fish per tank) in both trials. During this acclimation phase, the fish were fed daily at 1.5% of their body weight using EFICO YS 887F 3 (BioMar), a commercial growth feed. The feed’s formulation, as per the product’s specification sheet, contained 42% crude protein, 23% fat, 4.1% ash, 2.0% crude fiber, and 30 ppm astaxanthin, meeting the standard nutritional needs for rainbow trout.
Following the feeding period, the fish underwent fasting treatments, which were adjusted based on thermal conditions to ensure comparable degree-day conditions across the seasonal trials. Each fasting treatment (“0D”, “50D”, and “100D”) was randomly assigned to three replicate tanks (N = 3).
Summer treatments:
- ○
- 0D: no fasting
- ○
- 50D: 3-day fasting (65.5 ± 0.22 °C d)
- ○
- 100D: 6-day fasting (131.3 ± 0.07 °C d)
Winter treatments:
- ○
- 0D: no fasting
- ○
- 50D: 6-day fasting (58.7 ± 2.21 °C d)
- ○
- 100D: 13-day fasting (114.5 ± 1.86 °C d)
While the fasting durations were intended to target 0, 50, and 100 degree-days, there were slight variations in the actual degree-day conditions (e.g., 65.5 °C d for the 50D summer treatment and 114.5 °C d for the 100D winter treatment). These variations were considered to reflect realistic environmental conditions while still aiming for comparable metabolic impacts across seasons.
2.2. Sampling Procedures
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Technical University of Madrid for the project WELLSTUN with the reference MDPDSDLPDC-FTB-ANIMALES-20221021. At the end of the fasting treatments, 15 fish from each tank were selected using nets for sampling. The fish were humanely slaughtered using the Ike Jime method, which aims to minimize stress and preserve meat quality. This technique involves puncturing the brain with a sharp instrument, followed by severing the head []. To minimize handling stress and ensure precise sampling, individual fish were carefully removed from the tanks before slaughter. After slaughter, 10 fish from each tank were dissected to obtain samples of dorsal muscle (adjacent to the dorsal fin). Each muscle sample was placed into separate Eppendorf tubes for various analyses: muscle glycogen quantification, acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity assays, RNA extraction, and muscle color analysis. The remaining 5 fish were used exclusively for assessing RM progression. All analyses were carried out under standardized conditions to ensure consistency.
2.3. Assay Methods
2.3.1. Muscle Glycogen and AChE Activity
Muscle glycogen content was quantified by homogenizing 0.5 g muscle tissue in perchloric acid, following the procedure described by Dreiling et al. []. For AChE activity, in muscle samples we analyzed in 0.1 M phosphate buffer (pH 8) using acetylthiocholine iodide (0.075 M) and dithiobisnitrobenzoic acid (DTNB, 0.01 M) as substrates, as outlined by Ellman et al. []. Absorbance was measured at 412 nm every 36 s for 3 min.
2.3.2. Muscle Color Analysis
Muscle color was analyzed using a Minolta CM-2500c Spectrophotometer (Minolta, Osaka, Japan). Measurements were taken from the dorsal muscle (right side, posterior to the dorsal fin) at 0 and 24 h post-mortem. Color parameters (a* and b*) were recorded using the CIE Lab* scale []. Hue (h*) and chroma (C*) values were calculated as follows: h* = arctan(b*/a*) × 57.29 and C* = √(a*^2 + b*^2)), providing information on perceived color (hue) and color intensity (chroma).
2.3.3. Rigor Mortis and pH
The progression of RM was evaluated following Cuttinger’s method [] at 0 and 24 h post-mortem. During the 24 h period, the carcasses were stored on trays with ice inside a standard refrigerator at approximately 4 °C. Each trout was placed laterally on a flat surface, with the section from the dorsal fin to the tail left unsupported over the edge (Figure 1). The RM angle was determined using the formula α = tan−1(X/Y). In this equation, X corresponds to the horizontal length (cm) of a right triangle’s leg, while Y refers to the vertical leg length (cm). Muscle pH was recorded at the anterior section of the dorsal muscle, after it was detached from the head, at both 0 and 24 h post-mortem using a temperature-compensated pH meter (HANNA, Salaj, Romania, model HI9125).
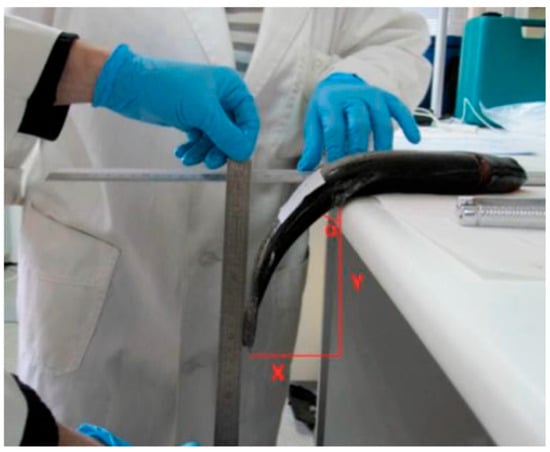

Figure 1.
Rigor mortis measurement.
2.3.4. Gene Expression Analysis
RNA was extracted from muscle tissue using the Maxwell RSC Simply RNA Tissue kit (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The quality and concentration of the isolated RNA were assessed using a Nanodrop 2000 ND-2000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) by measuring A260/A280 ratios. For complementary DNA (cDNA) synthesis, 2 μg of total RNA were reverse transcribed using the iScript cDNA Synthesis Kit (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). Gene expression was evaluated using RT-qPCR on a CFX Touch™ Real-Time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad, USA) in accordance with MIQE guidelines []. The analysis focused on stress-related genes (gr1, hsp70, hsp90, mr), oxidative stress indicators (cat, sod, gpx, gst), and metabolic genes (eno, hif1), with elf1, 18S, and rps16 used as reference genes. Primer pairs were validated specifically for rainbow trout [,,], and details, including sequences, accession numbers, and efficiencies are presented in Table 1. Before running the analysis, dilution curves were created using pooled samples to determine the optimal cDNA dilution for each target gene. This step also ensured the absence of primer-dimers and confirmed reaction specificity, as indicated by single peaks in the melting curve analysis for each primer pair. All reactions were performed in triplicate on 384-well plates with a final volume of 5 μL, consisting of 2.5 μL iTaq™ Universal SYBR® Green Supermix (Bio-Rad, USA), 0.25 μM of each forward and reverse primer, and 1 μL of diluted cDNA per sample. The qPCR protocol included an initial denaturation at 95 °C for 3 min, followed by 40 amplification cycles of 95 °C for 10 s and 60 °C for 30 s. The data were processed using Bio-Rad CFX Maestro 2.3 software, with reference gene stability evaluated using the geNorm algorithm in Excel. Relative mRNA expression levels were calculated using the 2−ΔΔCT method, with the 0D winter group serving as the normalization reference (set to a value of 1).

Table 1.
Primer sequences utilized for gene expression analysis along with their corresponding accession numbers.
2.4. Data Analysis
The data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism version 9.0.0.121 (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). Prior to analysis, the normality of the data was assessed using the Shapiro–Wilk test, and homogeneity of variances was confirmed with Bartlett’s test. A two-way ANOVA was conducted to evaluate the effects of fasting duration (0, 50, or 100 °C d) and season (summer or winter), with both factors treated as fixed variables. Tukey’s post-hoc test was used for pairwise comparisons, and statistical significance was set at p < 0.05. Pearson’s correlation coefficients (r) were calculated for muscle parameters (excluding RM), and the results were represented using a double-gradient color map to enhance clarity and visualization.
3. Results
3.1. Muscle Glycogen, pH, and Rigor Mortis
Muscle glycogen concentration was significantly higher in the summer (11.30 ± 5.31 mg/g) compared to winter (2.53 ± 1.28 mg/g), regardless of fasting status (Table 2). A notable interaction between season and pre-slaughter fasting was observed for RM at 0 h post-mortem, with lower values recorded in summer; specifically, the 0D group had higher values than the 50D and 100D groups. Conversely, winter showed consistently higher RM values across all groups. At 24 h post-mortem, however, no significant differences were found. Muscle pH showed no significant interaction between fasting and season at either 0 or 24 h post-mortem. Nonetheless, winter consistently exhibited higher pH values than summer at both time points (0 h: winter 6.97 ± 0.15 vs. summer 6.66 ± 0.10; 24 h: winter 6.59 ± 0.06 vs. summer 6.50 ± 0.10). Additionally, at 24 h post-mortem, summer samples at 0D had higher pH values compared to those at 50D and 100D.

Table 2.
Muscle glycogen concentration, pH, and rigor mortis angle (RM) in rainbow trout subjected to different pre-slaughter fasting periods and seasons at 0 and 24 h post-mortem.
3.2. Acetylcholinesterase Activity
The activity of AChE in muscle tissue showed a significant interaction between pre-slaughter fasting and season (Figure 2). Non-fasted fish in winter exhibited the lowest AChE muscle activity compared to other groups. For 0D, winter groups showed lower activity than those in summer (0.14 ± 0.18 vs. 0.79 ± 0.30 mU/mg). However, in fasted fish, no significant differences were observed between the seasons. In summer, 100D fish had higher AChE activity than both 0D and 50D fish (100D: 1.03 ± 0.36 vs. 50D: 0.73 ± 0.29 vs. 0D: 0.79 ± 0.30 mU/mg), while in winter, 0D fish displayed lower activity than 100D fish (0.14 ± 0.18 vs. 1.11 ± 0.30 mU/mg).
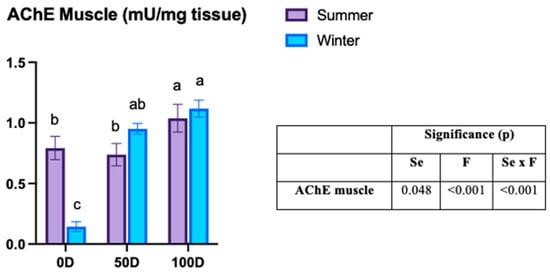
Figure 2.
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity in rainbow trout subjected to varying pre-slaughter fasting durations across seasons. Results are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 30). 0D: no fasting; 50D: 65.5 ± 0.22 °C d of fasting in summer (3 days) and 58.7 ± 2.21 °C d in winter (6 days); 100D: 131.3 ± 0.07 °C d of fasting in summer (6 days) and 114.5 ± 1.86 °C d in winter (13 days). Se: season; F: fasting duration. A two-way ANOVA was conducted to evaluate the effects of fasting duration (0, 50, or 100 °C d) and season (summer or winter), with both factors treated as fixed variables. Tukey’s post-hoc test was used for pairwise comparisons, and statistically significant differences between groups are marked with distinct letters (a, b, c) (p < 0.05).
3.3. Fillet Color
Regarding fillet color parameters, at 0 h post-mortem, the b* and h* values were significantly affected by the season, with both parameters being higher in summer (b*: 9.18 ± 2.39 vs. 7.92 ± 2.65; h*: 68.27 ± 6.24 vs. 59.51 ± 11.56). The remaining color parameters (L*, a*, and C*) exhibited a significant interaction between pre-slaughter fasting and season. In non-fasted individuals, L* values were higher in winter, while a* values were greater in summer, a pattern also observed for C* in the 100D group.
At 24 h post-mortem, a*, b*, and C* did not show a significant interaction between fasting and season, though a* values were higher in summer (6.10 ± 1.74 vs. 3.58 ± 1.99) and b* values were higher in winter (8.85 ± 3.5 vs. 7.50 ± 2.69). The other parameters, L* and h*, displayed significant interactions, with differences between summer and winter observed across all fasted and non-fasted groups. Specifically, L* was higher in all groups during summer, while h* was greater in winter (see Table 3).

Table 3.
Fillet color parameters of rainbow trout with different pre-slaughter fasting periods and seasons at 0 and 24 h post-mortem.
3.4. Muscle Gene Expression
Figure 3 illustrates gene expression of muscle tissue. The gene expression in muscle tissue, particularly involving gst and mr genes, displayed a significant interaction between pre-slaughter fasting and season. For gst, a marked difference was observed in winter between fasted and non-fasted individuals, with increased expression in both 50D and 100D. Conversely, mr gene expression in winter was lower in 100D compared to 50D. During the summer, gene expression did not exhibit notable variation across treatments. However, the influence of seasons was evident with higher expression of gpx, hif1, hsp70, hsp90, and enolase during the winter season (gpx: 0.83 ± 0.090 vs. 0.59 ± 0.023; hif1: 0.89 ± 0.094 vs. 0.52 ± 0.034; hsp70: 1.11 ± 0.085 vs. 0.12 ± 0.023; hsp90: 1.11 ± 0.085 vs. 0.029 ± 0.005; enolase: 0.94 ± 0.104 vs. 0.61 ± 0.045).
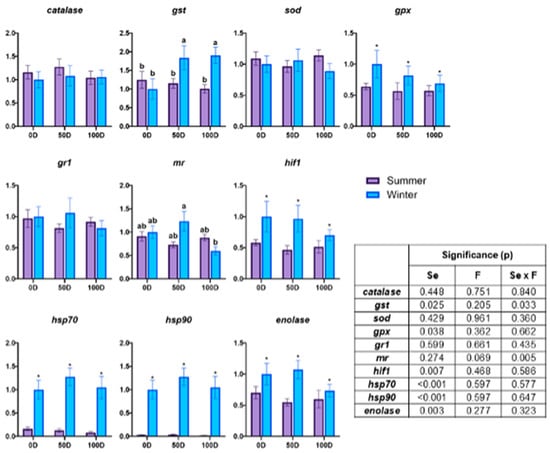
Figure 3.
Gene expression in the muscle tissue of rainbow trout subjected to different pre-slaughter fasting durations and seasons. The data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 30). 0D: no fasting; 50D: 65.5 ± 0.22 °C d of fasting in summer (3 days) and 58.7 ± 2.21 °C d of fasting in winter (6 days); 100D: 131.3 ± 0.07 °C d of fasting in summer (6 days) and 114.5 ± 1.86 °C d of fasting in winter (13 days); gst: glutathione S-transferase; sod: superoxide dismutase; gpx: glutathione peroxidase; gr1: glucocorticoid receptor 1; mr: mineralocorticoid receptor; hif1: hypoxia-inducible factor 1; hsp70: heat shock protein 70; hsp90: heat shock protein 90; Se: season; F: pre-slaughter fasting. A two-way ANOVA was conducted to evaluate the effects of fasting duration (0, 50, or 100 °C d) and season (summer or winter), with both factors treated as fixed variables. Tukey’s post-hoc test was used for pairwise comparisons. Significant seasonal differences are marked with an asterisk (*) (p < 0.05), and distinct letters (a, b) indicate significant differences between groups (p < 0.05).
3.5. Correlation Analysis
The data revealed several significant correlations among muscle parameters (Figure 4). Muscle glycogen showed a negative correlation with pH0-24, L*0, h*24, gst, hsp70, and hsp90, while also correlating positively with L*24, b*0, h*0, and a*24. Conversely, pH0 was positively correlated with L*0, a*0, b*24, h*24, hif1, hsp70, hsp90, and enolase but negatively correlated with h*0, L*24, and a*24. pH24 had positive correlations with L*0, h*24, hif1, hsp70, hsp90, and enolase, whereas negative correlations were noted with b*0, h*0, and L*24. AChE activity was positively correlated with h*0 and L*24 but negatively correlated with L*0 and a*0. L*0 and h*0 had positive and negative correlations with gpx, hif1, hsp70, hsp90, and enolase, respectively. Additionally, b*0 and L*24 were negatively correlated with hif1, hsp70, and hsp90. H*0 showed negative correlations with gpx, hif1, hsp70, hsp90, and enolase, while a*24 was negatively correlated with the heat shock proteins hsp70 and hsp90. In contrast, b*24 exhibited a positive correlation with mr and h*24 was positively correlated with gst, hif1, hsp70, hsp90, and enolase.
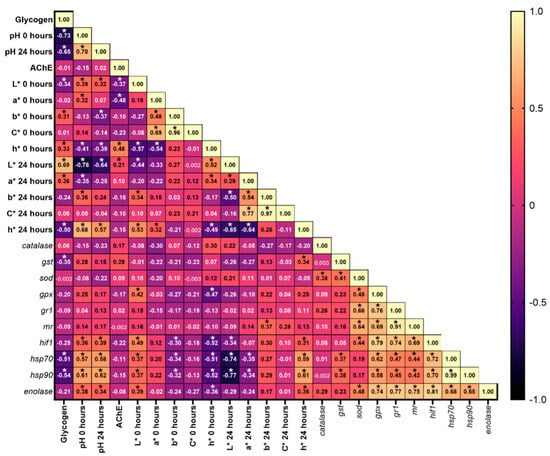
Figure 4.
Heatmap displaying Pearson’s correlation coefficients among muscle parameters (glycogen, pH, AChE activity, color metrics, and gene expression). The values inside each box represent the r value for the correlations. * p < 0.05. L*: lightness; a*: redness; b*: yellowness; C*: chroma = √(a2 + b2); h*: Hue = arctan(b*/a*) × 57.29; gst: glutathione S-transferase; sod: superoxide dismutase; gpx: glutathione peroxidase; gr1: glucocorticoid receptor 1; mr: mineralocorticoid receptor; hif1: hypoxia-inducible factor 1; hsp70: heat shock protein 70; hsp90: heat shock protein 90.
4. Discussion
4.1. Muscle Glycogen, pH, and Rigor Mortis
Muscle glycogen serves as a crucial energy source during physical activity [] and, to a lesser extent, during fasting. Depending on the species and environmental conditions, some fish primarily rely on liver glycogen when food is scarce [], while others use muscle glycogen [,] or utilize both reserves simultaneously []. In line with previous studies, our results indicate that muscle glycogen levels were largely unaffected by varying fasting durations. For example, Black and Love [] observed that muscle glycogen levels in Atlantic cod remained stable during extended fasting periods. The higher muscle glycogen concentrations in summer compared to winter may be attributed to reduced swimming activity in warmer water, as suggested by Yin et al. []. Given that the optimal temperature for rainbow trout is 12–18 °C [], it is plausible that the need for glycogen mobilization is lower in warmer water temperatures, contributing to higher glycogen levels in summer.
Muscle glycogen levels directly influence post-mortem pH, as evidenced by the significant negative correlation between glycogen and pH at both 0 and 24 h post-mortem (r = −0.73 and r = −0.65, respectively). Both muscle glycogen and pH are crucial in determining the onset and progression of RM, which, in turn, impacts the flesh quality of fish []. After death, glycogen undergoes anaerobic breakdown, producing lactic acid that leads to a decline in muscle pH. Typically, this pH drop ranges from 7.5 to 6.5 in fish []. The rate and extent of this decline are influenced by the glycogen content prior to death. In our study, higher glycogen levels in summer were associated with a lower initial pH value at 0 h post-mortem and a less pronounced pH decline from 0 to 24 h post-mortem compared to winter. After 24 h post-mortem, however, winter also experienced a pH decline, although it was more marked. Similarly, López-Luna et al. [] reported a decline in muscle pH post-mortem, where fasting reduced glycogen reserves in rainbow trout, limiting lactic acid production through aerobic glycogenolysis [] and leading to higher pH levels. The higher pH in fasted groups during winter compared to summer likely reflects increased physical activity, which may have promoted anaerobic glycogenolysis by depleting glycogen stores prior to slaughter, raising pH at both 0 and 24 h post-mortem, particularly in the fasted fish. This finding is consistent with Bermejo-Poza et al. [], who observed higher pH levels 24 h post-mortem in fish slaughtered after 9 days of fasting, a result attributed to reduced lactic acid production and lower glycogen reserves.
RM in rainbow trout typically begins between 2 and 9 h post-mortem, reaching full stiffness at approximately 24 h []. Our results indicate that RM increased between 0 and 24 h post-mortem during summer, with the values at 24 h likely representing the point of maximum rigor, as also observed by Bermejo-Poza et al. []. Additionally, Love et al. [] found that RM development is closely linked to pH, with maximum rigor occurring at the lowest pH values, which corresponds with our summer data. However, in winter, we observed a decrease in RM between 0 and 24 h post-mortem, suggesting that maximum rigor had been reached just before 24 h and was already in decline, which is consistent with the higher initial rigor values at 0 h compared to the summer. Typically, higher temperatures accelerate the onset and intensity of RM due to the faster pH drop, which speeds up biochemical reactions and protein denaturation []. However, in our study, trout in summer showed lower RM at 0 h post-mortem, possibly linked to the higher muscle glycogen reserves observed in summer fish. Since ATP production after death relies primarily on anaerobic glycolysis, greater glycogen availability could sustain ATP levels for longer, delaying the depletion of ATP and, consequently, the onset of rigor mortis. ATP is essential for keeping calcium pumps active and preventing sustained muscle contraction. Once ATP is exhausted, these pumps fail, leading to calcium accumulation in the sarcoplasm and the irreversible muscle contraction characteristic of rigor mortis []. Therefore, interpreting RM progression not only in terms of pH and lactic acid generation but also considering glycogen depletion and ATP availability provides a more complete understanding of our findings. Moreover, the storage of carcasses at 4 °C likely slowed glycolytic activity and ATP consumption post-mortem, especially in summer fish, further delaying the onset of rigor compared to winter fish, which may have reached peak rigor before the 24 h mark.
Regarding the effect of fasting, Bermejo-Poza et al. [] found that fish fasted for 9 days exhibited a higher rigor angle at 24 h post-mortem compared to those fasted for only 2 days. In contrast, our study only detected differences in RM between fasted and non-fasted fish at 0 h post-mortem, with fasted fish displaying lower rigor values at that point. This discrepancy could be attributed to the contrasting baseline glycogen levels observed across seasons. In summer, glycogen concentrations were particularly high, which may have rendered the fasting period insufficient to meaningfully reduce energy reserves and thus influence RM development. On the other hand, winter fish exhibited generally low glycogen levels across all groups, possibly falling below the threshold necessary to delay or alter the rigor process, regardless of fasting. These seasonal differences in metabolic status might have masked or diminished the effects of fasting on rigor mortis progression in our experimental conditions.
4.2. Acetylcholinesterase Activity
AChE plays a vital role in hydrolyzing acetylcholine (ACh) at nerve synapses and neuromuscular junctions []. Strategically positioned at these sites, AChE efficiently terminates neurotransmission after ACh release, allowing the cell to return to its resting state and prepare for the next signal. This action is crucial for behaviors such as predator evasion, foraging, and prey detection. However, an increase in AChE activity may indicate a physiological stress response. To counteract cholinergic overstimulation, the body elevates AChE activity, which helps restore balance in the cholinergic system and prevents its overload, allowing the organism to better cope with stressors such as fasting or elevated temperatures. While AChE itself is not a direct marker of muscle condition, it serves as an indicator of muscle stress, reflecting a variety of physiological processes [].
The relationship between AChE activity and fasting duration is particularly evident in winter, where a significant increase in AChE activity occurs as fasting duration extends. In contrast, during summer, AChE activity was higher at baseline in the 0D group and remained elevated throughout the 50D period, with a further increase observed in the 100D fasting group. These findings align with those of Bermejo-Poza et al. [], who reported increased AChE activity after 10 days of fasting (107 °C d), likely linked to the proteolytic function of the enzyme. During prolonged fasting, AChE levels rise in tissues undergoing catabolism, contributing to tissue degradation in both mice [] and fish [].
Beyond its metabolic role [], elevated AChE activity observed during fasting could also be indicative of heightened food-seeking behavior. A notable observation in our study was the higher baseline AChE activity in unfasted fish during summer compared to winter, suggesting that muscle AChE may be more sensitive to environmental stressors, such as temperature. This increased sensitivity could negatively affect flesh properties through its impact on anaerobic muscle activity and the subsequent increase in lactic acid production, as previously noted by Daskalova []. A similar study on rainbow trout found higher muscle AChE activity in fish exposed to natural conditions with slightly warmer temperatures compared to those kept in a controlled laboratory environment []. The researchers attributed this difference to temperature effects and increased physical activity in wild trout. Factors such as body size [,] and acclimation temperature [] are known to influence AChE activity in fish, highlighting the complex interplay of environmental factors in modulating this enzyme’s function.
4.3. Flesh Color
The flesh color of salmonids is a key quality attribute for consumers, with vibrant red and orange hues often associated with higher freshness, superior quality, and premium pricing []. These colors are characterized by lower L* and h* values, alongside higher a*, b*, and C* values []. In commercially farmed rainbow trout, carotenoids are uniformly distributed throughout the fillet, typically yielding color values of L* = 42.81, a* = 4.15, and b* = 7.73 for fish weighing approximately 250 g []. However, research on the impact of stress on fish meat color remains somewhat controversial. Our study found several significant correlations between muscle color parameters and gene expression associated with stress responses. Lightness (L*), representing the amount of light reflected from a surface [], is frequently used as an indicator of stress response in fish fillets []. Previous studies have shown that rapid and intense pH declines, often linked to acute stress, result in paler flesh []. Gatica et al. [] observed lighter flesh color in crowded Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) on days 0 and 1 post-mortem, and Bosworth et al. [] reported similar findings in stressed channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) over several days post-processing. Likewise, Wu et al. [] found that stressed rainbow trout fillets exhibited lighter colors. Although the summer season showed a greater pH decline compared to winter in the 0D group, with temperature being the main stressor, our results align more closely with Erikson and Misimi [], who observed darker flesh color in Atlantic salmon due to perimortem stress. This may explain the lower L* values at 0 h post-mortem for the summer 0D group compared to the winter group. Furthermore, in the winter, a decrease in L* values was seen in the fasted groups (50D and 100D) at 0 h post-mortem, bringing them to levels similar to those observed in the summer, where no significant differences between groups were found. The overall increase in lightness at 24 h post-mortem across all summer groups is likely a result from the normal discoloration process that occurs over time []. The color parameters a* (redness) and b* (yellowness) are associated with fat content in salmonids [] and contribute to the appealing salmon-pink hue that consumers often associate with higher quality [,]. The most vibrant colors are typically observed in salmonids with higher lipid content, which correlates with increased a* and b* values. Higher fat content enhances the digestibility, deposition, and retention of carotenoids, responsible for the salmon-pink hue []. Therefore, higher muscle fat content is usually linked to more vibrant fillet color and improved sensory attributes, including moisture and flavor, though it may slightly reduce texture firmness [,,]. These relationships between fat content and muscle color have been documented in rainbow trout [], brown trout (Salmo trutta) [], and Atlantic salmon [,]. Generally, a positive correlation exists between muscle fat content and fillet lightness, particularly when comparing fish with different levels of diet-induced adiposity [,,]. Lipid accumulation occurs in the intramuscular adipose tissue, a non-pigmented, opaque white tissue, which leads to a lighter muscle appearance. This effect was evident in non-fasted individuals during summer, where a higher fat content corresponded with lighter flesh color. However, while higher fat content can enhance color, it is less important for consumers in rainbow trout due to the species’ naturally low lipid levels, as its meat is predominantly composed of polyunsaturated fats, making it the leanest of oily fish []. At 24 h post-mortem, a* values increased across all summer groups without significant differences, while winter groups showed a decrease in a*. In contrast, b* values exhibited an opposite trend, increasing in winter, consistent with Erikson and Misimi [], who reported intensified yellow coloration during ice storage. However, b* values in summer decreased, which aligns with findings from López-Luna et al. []. Teimouri et al. [] suggested that enhanced coloration could improve product quality, while Welker et al. [] indicated that yellow pigmentation in rainbow trout fillets might be perceived as unusual, potentially leading to economic losses. While Teimouri et al. [] noted that increased yellow pigmentation might positively influence consumer preferences, no study has yet quantified the impact of coloration on consumer perceptions and preferences. Similar reductions in both red and yellow tones have been reported in other species, such as gilthead sea bream, after seven days of storage []. The acidification resulting from anaerobic glycolysis during storage, which is more pronounced in summer, may influence flesh color, particularly the b* index. Studies on fish, such as halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus), have shown that decreased muscle pH leads to greater muscle insolubility and protein denaturation [], altering light reflection and affecting color perception []. In winter, a significant decrease in muscle color saturation (C*) was observed as fasting duration increased, with the lowest values seen in the 100D group at 0 h post-mortem, lower than those in summer. A similar trend was seen for hue (h*), where all winter groups exhibited lower h* values compared to summer. However, by 24 h post-mortem, h* values increased in winter, surpassing those in summer. In summer, h* values decreased as redness increased, a pattern documented by Nickell and Bromage [], particularly in the 100D group at 24 h post-mortem, which displayed a lower hue and a stronger tendency toward redness compared to the 50D and 0D groups. This decrease in h* may be linked to a stress response induced by warmer temperatures, which increases metabolic activity and leads to a lower h* value [].
4.4. Muscle Gene Expression
Fish muscle characteristics are shaped by a variety of physiological and biochemical factors, including physicochemical properties and metabolic processes []. During fasting periods, fish adapt by altering lipid metabolism through oxidative pathways, which become crucial energy sources for skeletal muscles [,,]. However, these oxidative pathways can also produce lipoperoxides, acting as precursors for reactive oxygen species (ROS). If ROS are not effectively neutralized, they can lead to oxidative stress, negatively impacting flesh quality [,,,]. Fortunately, fish have evolved robust antioxidant defense systems to combat oxidative stress [,]. These include superoxide dismutase (SOD), which detoxifies superoxide anions; catalase (CAT), which reduces hydrogen peroxide (H2O2); glutathione peroxidase (GPx), which decreases H2O2 and organic peroxides via glutathione-dependent reactions; and glutathione transferase (GST), which helps eliminate toxic compounds through conjugation [,,,,]. Consequently, increased antioxidant activity can protect muscle integrity by minimizing oxidative damage and reducing spoilage []. Our study observed an upregulation of antioxidant defenses in the fasted groups (50D and 100D) during winter, a finding consistent with studies in other species, such as the common dentex (Dentex dentex) [] and the Yangtze sturgeon (Acipenser dabryanus) []. While we did not directly measure muscle texture, the increased expression of gpx and gst in the winter-fasted groups may suggest potential improvements in muscle characteristics, similar to observations in other species [,]. However, further research is needed to confirm these effects in rainbow trout.
Interestingly, despite the need for antioxidant mobilization during fasting, no significant differences in gst and gpx levels were observed in summer compared to the control group, as noted by Florescu et al. [] and Sánchez-Moya et al. []. This stabilization of enzymatic activity may be due to metabolic adjustments aimed at conserving energy during thermal stress, allowing the fish to prioritize essential survival functions [,]. Elevated temperatures, as indicated by Villalba et al. [], may also independently affect antioxidant responses, potentially compromising flesh quality. The reduced expression of gst and gpx in summer could indicate a shift toward lipid utilization for energy, although less efficiently than at optimal temperatures of 12 to 18 °C for rainbow trout [], as observed by Balbuena-Pecino et al. [] in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). This shift might be related to a decreased capacity for metabolic oxidation or incomplete activation of the antioxidant system [].
Although we found no significant seasonal differences in mineralocorticoid receptor (mr) expression among the fasting groups, it is noteworthy that the higher average temperature did not show substantial variation across treatments. This was unexpected, as glucocorticoid receptors are crucial for maintaining energy homeostasis during adaptive stress responses, such as food deprivation []. Given the optimal water temperature for rainbow trout, the variation in mr expression during winter may reflect a more pronounced adaptive response in the fasting groups, whereas in summer, individuals may prioritize essential physiological functions, as noted by Villalba et al. [] in liver tissue from the same subjects. In muscle tissue, mr primarily facilitates nutrient storage and limits energy substrate mobilization under certain conditions. Its activation is essential for the muscle’s ability to switch between fuel sources and plays a key role in regulating glucose metabolism during both basal and stress conditions []. This may explain why the 50D group in winter showed greater nutrient mobilization than the 100D group, which may have adapted to prolonged withholding of feed by altering its metabolic needs. Furthermore, in mammals, mineralocorticoids regulate water retention. While their role in fish osmoregulation is minor, any potential effects on muscle water content could impact other flesh attributes, such as texture [].
During the winter treatments, hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (hif1), a crucial regulator of metabolism in response to oxygen availability and energy balance [,], was observed at higher levels. Although elevated water temperatures are generally associated with lower dissolved oxygen levels, which can activate hif1 [,], hif1 levels were not higher in summer than in winter. Seasonal shifts from summer to winter, including changes in day length, food availability, and other environmental factors, may drive increased hif1 expression in winter as part of the fish’s broader seasonal adaptation strategy. As noted by Villalba et al. [], in certain liver samples, expression of heat shock proteins (HSPs) such as hsp70 and hsp90 was consistently high during the winter period, while in the summer fish, expression was undetectable. This strong and consistent seasonal difference was the most pronounced among all the gene targets analyzed. Under typical conditions, HSPs are upregulated in response to various stressors, including heat, hypoxia, and handling stress, as part of the cellular protective machinery [,]. Therefore, the near absence of HSP expression in summer is unexpected, given the elevated temperatures and the presumed chronic thermal stress.
One possible explanation is the suppressive effect of chronic stress-induced cortisol on HSP expression. Elevated cortisol levels, which were measured during the summer period, have been reported to downregulate or inhibit the transcription of HSP genes, particularly during prolonged or repeated stress exposure []. This hormonal feedback may have blunted the expected heat-induced HSP upregulation. In the Kaluga (Huso dauricus), high expression levels of hsp70 and hsp90 were found in liver, gill, and muscle tissues during low temperatures, suggesting that these proteins play a critical role in survival during harsh winter conditions []. Conversely, other studies in Iberian fishes report increased hsp70 expression during gradual warming, highlighting species-specific and context-dependent responses to thermal stimuli []. In our study, the winter upregulation of HSPs may reflect an anticipatory or protective response to cold-related metabolic or oxidative stress, while in summer, the combined effects of chronic heat exposure and elevated cortisol might have suppressed hsp gene activation as part of a dysregulated or maladaptive stress response.
Similarly to the hif1 findings, enolase gene expression was higher during winter, suggesting an increase in energy production via upregulation of glycolysis-related genes. This enhancement may support energy reserve mobilization through glycolysis under challenging conditions, such as reduced food availability [,].
5. Conclusions
Rainbow trout is a crucial species in aquaculture, and its muscle characteristics are shaped by pre-slaughter practices and environmental conditions. Our study highlights how these properties are significantly affected by various pre-slaughter practices and environmental factors, including thermal conditions and fasting durations.
In summer, higher water temperatures lead to increased muscle glycogen levels due to reduced swimming activity caused by heat stress, resulting in a lower pH and delayed RM onset. However, overactivation of AChE was observed, likely due to cumulative heat stress. In contrast, winter conditions promoted faster metabolic adjustments, with more regulated enzyme activity, especially in fasting groups. Maximum rigor in winter occurred just before 24 h post-mortem, with a more pronounced pH drop compared to summer. Notable differences in AChE activity, L* values, and gene expression markers were found when comparing fasting and seasonal temperatures. Summer showed higher baseline AChE activity and lower L* values, indicating that heat stress exacerbates the effects of fasting. Winter resulted in significant changes in the 50D and 100D groups. Summer temperatures were associated with stable gene expression of markers, such as gst, mr, hsp70, and hsp90, suggesting possible adaptation to fasting in elevated temperatures. However, this is contradicted by evidence that elevated temperatures contribute to cumulative stress, negatively affecting flesh properties.
These findings underscore the importance of adjusting fasting durations according to thermal conditions to optimize post-mortem muscle characteristics and metabolic processes. For standard aquaculture practices with rainbow trout, we recommend limiting short-term fasting to 50 °C d during summer. In winter, fish demonstrated effective metabolic adaptation to longer fasting durations (50 and 100 °C d), highlighting their resilience and flexibility. This adaptability to colder conditions emphasizes the metabolic flexibility of rainbow trout, offering potential strategies to balance animal welfare and production goals.
However, it is essential to acknowledge the limitations of this study. We focused on specific physiological and molecular parameters known to influence post-mortem muscle characteristics. While these parameters provide valuable insights into metabolic responses under different fasting durations and seasonal conditions, other factors, such as texture, lipid oxidation, or sensory attributes, were not considered. Future research incorporating a broader range of indicators will further enhance our understanding of how pre-slaughter handling affects the final product.
In conclusion, the balance between thermal conditions, fasting duration, and metabolic adaptation is crucial for ensuring optimal outcomes in both fish welfare and product quality. As global warming continues to raise water temperatures, understanding how heat stress interacts with fasting strategies becomes more critical. Therefore, developing adaptive management protocols that anticipate these environmental shifts will be essential for maintaining sustainable and resilient aquaculture systems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.D.l.F., M.T.D., M.F.-M., M.V. and R.B.-P.; methodology, A.M.V., Á.D.l.L.-P., E.G.d.C., A.C. and R.G.-G.; validation, R.B.-P., J.D.l.F. and M.V.; investigation, A.M.V.; data curation, A.M.V. and R.B.-P.; writing—original draft preparation, A.M.V.; writing—review and editing, Á.D.l.L.-P., J.D.l.F., E.G.d.C., M.T.D., M.F.-M., A.C., R.G.-G., M.V. and R.B.-P.; supervision, J.D.l.F. and R.B.-P.; funding acquisition, J.D.l.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación (MAPA), through the WELLSTUN project PNAC/21.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Technical University of Madrid for the project WELLSTUN with the reference MDPDSDLPDC-FTB-ANIMALES-20221021.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
At this time, the research data associated with this study is not available for public deposit as it is being integrated into the final stages of the author’s doctoral thesis publication process. Once this process is completed, the data will be deposited in a suitable public repository and will be available for access. The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| a* | Redness |
| ACh | Acetylcholine |
| AChE | Acetylcholinesterase |
| b* | Yellowness |
| CAT | Catalase |
| C* | Chroma |
| °C d | Degree days |
| CIE | Commission Internationale de l’Eclairage |
| cDNA | Complementary DNA |
| DTNB | Dithiobisnitrobenzoic acid |
| EFSA | European Food Safety Authority |
| elf1 | Elongation factor 1 |
| ENO | Enolase |
| FW | Forward primer |
| GPx | Glutathione peroxidase |
| GST | Glutathione-S-transferase |
| GR1 | Glucocorticoid receptor 1 |
| h* | Hue |
| HIF1 | Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 |
| HSP70 | Heat shock protein 70 |
| HSP90 | Heat shock protein 90 |
| L* | Lightness |
| MIQE | Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experiments |
| mr | Mineralocorticoid receptor gene |
| NH3 | Ammonia |
| NO2− | Nitrite |
| NO3− | Nitrate |
| O2 | Oxygen |
| RAS | Recirculating Aquaculture System |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| RM | Rigor mortis |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RV | Reverse primer |
| rps16 | Ribosomal protein S16 |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| SEM | Standard Error of the Mean |
| sod | Superoxide dismutase |
| UPM | Polytechnic University of Madrid |
References
- Bermejo-Poza, R.; De La Fuente, J.; Pérez, C.; González De Chavarri, E.; Diaz, M.T.; Torrent, F.; Villarroel, M. Determination of optimal degree days of fasting before slaughter in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2017, 473, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lines, J.A.; Spence, J. Safeguarding the welfare of farmed fish at harvest. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 38, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robb, D.H.F.; Kestin, S.C.; Warriss, P.D. Muscle activity at slaughter: I. Changes in flesh colour and gaping in rainbow trout. Aquaculture 2000, 182, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regost, C.; Arzel, J.; Cardinal, M.; Laroche, M.; Kaushik, S.J. Fat deposition and flesh quality in seawater reared, triploid brown trout (Salmo trutta) as affected by dietary fat levels and starvation. Aquaculture 2001, 193, 325–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, A.; García García, B.; Garrido, M.D.; Hernández, M.D. The influence of starvation time prior to slaughter on the quality of commercial-sized gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) during ice storage. Aquaculture 2008, 284, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmeri, G.; Turchini, G.M.; Marriott, P.J.; Morrison, P.; De Silva, S.S. Biometric, nutritional and sensory characteristic modifications in farmed Murray cod (Maccullochella peelii peelii) during the purging process. Aquaculture 2009, 287, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mørkøre, T.; Mazo, T.; Tahirovic, V.; Einen, O. Impact of starvation and handling stress on rigor development and quality of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquaculture 2008, 277, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jentoft, S.; Aastveit, A.H.; Torjesen, P.A.; Andersen, Ø. Effects of stress on growth, cortisol and glucose levels in non-domesticated Eurasian perch (Perca fluviatilis) and domesticated rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2005, 141, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pottinger, T.G.; Rand-Weaver, M.; Sumpter, J.P. Overwinter fasting and re-feeding in rainbow trout: Plasma growth hormone and cortisol levels in relation to energy mobilisation. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 136, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, B.M.; Parisi, G.; Scappini, F.; Zampacavallo, G. Fish welfare and quality as affected by pre-slaughter and slaughter management. Aquac. Int. 2005, 13, 29–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, M.D.; García-Gallego, M.; Trenzado, C.E.; Guil-Guerrero, J.L.; Furné, M.; Domezain, A.; Alba, I.; Sanz, A. Influence of dietary lipids and culture density on rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) flesh composition and quality parameter. Aquac. Eng. 2014, 63, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einen, O.; Waagan, B.; Thomassen, M.S. Effects on weight loss, body shape, slaughter- and fillet-yield, proximate and fatty acid composition. Aquaculture 1998, 167, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Grigorakis, K.; Alexis, M.N. Effects of fasting on the meat quality and fat deposition of commercial-size farmed gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata, L.) fed different dietary regimes. Aquac. Nutr. 2005, 11, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Luna, J.; Torrent, F.; Villarroel, M. Fasting up to 34 °C days in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, has little effect on flesh quality. Aquaculture 2014, 420–421, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, T.; Cai, L.; Zhu, Y. Influence of fasting on muscle composition and antioxidant defenses of market-size Sparus macrocephalus. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2007, 8, 906–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority). Available online: www.efsa.europa.eu/ (accessed on 3 January 2025).
- Noble, C.; Gismervik, K.; Iversen, M.H.; Kolarevic, J.; Nilsson, J.; Stien, L.H.; Turnbull, J.F. Welfare Indicators for Farmed Rainbow Trout: Tools for Assessing Fish Welfare, p. 310. Available online: https://nofima.no/fishwell/trout/ (accessed on 23 April 2025).
- Bermejo-Poza, R.; De La Fuente, J.; Pérez, C.; Lauzurica, S.; De Chávarri, E.G.; Diaz, M.; Villarroel, M. Reducing the effect of pre-slaughter fasting on the stress response of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Anim. Welf. 2016, 25, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bermejo-Poza, R.; Fernández-Muela, M.; De La Fuente, J.; Pérez, C.; De Chavarri, E.G.; Díaz, M.T.; Torrent, F.; Villarroel, M. Physio-metabolic response of rainbow trout during prolonged food deprivation before slaughter. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 45, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Muela, M.; Bermejo-Poza, R.; Cabezas, A.; Pérez, C.; González De Chavarri, E.; Díaz, M.T.; Torrent, F.; Villarroel, M.; De La Fuente, J. Effects of Fasting on Intermediary Metabolism Enzymes in the Liver and Muscle of Rainbow Trout. Fishes 2023, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Luna, J.; Vásquez, L.; Torrent, F.; Villarroel, M. Short-term fasting and welfare prior to slaughter in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquaculture 2013, 400–401, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Luna, J.; Bermejo-Poza, R.; Torrent Bravo, F.; Villarroel, M. Effect of degree-days of fasting stress on rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquaculture 2016, 462, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waagbø, R.; Jørgensen, S.M.; Timmerhaus, G.; Breck, O.; Olsvik, P.A. Short-term starvation at low temperature prior to harvest does not impact the health and acute stress response of adult Atlantic salmon. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Kang, Y.; Wang, J. Transcriptomic responses to heat stress in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss head kidney. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2018, 82, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, A.P.; Gamperl, A.K.; Hicks, J.M.T.; Shiels, H.A.; Jain, K.E. Maximum cardiac performance of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) at temperatures approaching their upper lethal limit. J. Exp. Biol. 1996, 199, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar-Duque, D.; Holguín, J.P.; Estrella, I.A.; Lomas Martínez, G. Mejoramiento de la calidad en la carne de la trucha arcoíris mediante la técnica de sacrificio Ikejime: Caso Ecuador. Cienc. Ergo Sum 2019, 26, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreiling, C.E.; Brown, D.E.; Casale, L.; Kelly, L. Muscle glycogen: Comparison of iodine binding and enzyme digestion assays and application to meat samples. Meat Sci. 1987, 20, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, D.; Andres, V.J.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Internationale de l’Eclairage (CIE). Recommendations on Uniform Colour Spaces Colour Difference Equations, Psychometric Colour Terms; Vol. Supplement No 2 to CIE Publication No 15. Colourimetry; Bureau Central de la CIE: Paris, France, 1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, R.W.; Lanier, T.C.; Giesbrecht, F. An evaluation of simple methods for following rigor development in fish. J. Food Sci. 1990, 55, 346–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The MIQE Guidelines: Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Meilán, I.; Tort, L.; Khansari, A.R. Rainbow trout integrated response after recovery from short-term acute hypoxia. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 1021927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holen, E.; Austgulen, M.H.; Espe, M. RNA from baker’s yeast cultured with and without lipopolysaccharide (LPS) modulates gene transcription in an intestinal epithelial cell model, RTgutGC from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2021, 119, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teles, M.; Tridico, R.; Callol, A.; Fierro-Castro, C.; Tort, L. Differential expression of the corticosteroid receptors GR1, GR2 and MR in rainbow trout organs with slow release cortisol implants. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2013, 164, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marandel, L.; Seiliez, I.; Véron, V.; Skiba-Cassy, S.; Panserat, S. New insights into the nutritional regulation of gluconeogenesis in carnivorous rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): A gene duplication trail. Physiol. Genom. 2015, 47, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ings, J.S.; Servos, M.R.; Vijayan, M.M. Hepatic transcriptomics and protein expression in rainbow trout exposed to municipal wastewater effluent. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 2368–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, T.G.; Brauner, C.J.; Hochachka, P.W. Muscle glucose utilization during sustained swimming in the carp (Cyprinus carpio). Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1994, 267, R1226–R1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barcellos, L.J.G.; Marqueze, A.; Trapp, M.; Quevedo, R.M.; Ferreira, D. The effects of fasting on cortisol, blood glucose and liver and muscle glycogen in adult jundiá Rhamdia quelen. Aquaculture 2010, 300, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, A.L.L.; Ip, Y.K. Effect of fasting on glycogen metabolism and activities of glycolytic and gluconeogenic enzymes in the mudskipper Boleophthalmus boddaerti. J. Fish Biol. 1989, 34, 349–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, I.; Gutiérrez, J.; Planas, J. Changes in plasma glucagon, insulin and tissue metabolites associated with prolonged fasting in brown trout (Salmo trutta fario) during two different seasons of the year. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Physiol. 1992, 102, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehner, T.; Wieser, W. Energetics and metabolic correlates of starvation in juvenile perch (Perca fluviatilis). J. Fish Biol. 1994, 45, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, D.; Love, R.M. The sequential mobilisation and restoration of energy reserves in tissues of Atlantic cod during starvation and refeeding. J. Comp. Physiol. B 1986, 156, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, M.; Li, H.; Yu, X. An acute increase in water temperature can decrease the swimming performance and energy utilization efficiency in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 47, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warriss, P.D. Meat Science: An Introductory Text, 2nd ed.; Cabi Publication: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bermejo-Poza, R.; De La Fuente, J.; Pérez, C.; Lauzurica, S.; González, E.; Diaz, M.T.; Villarroel, M. The effect of intermittent feeding on the pre-slaughter fasting response in rainbow trout. Aquaculture 2015, 443, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, K.G.; Gill, C.O. The microbiology of DFD fresh meats: A review. Meat Sci. 1981, 5, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, R.M.; Robertson, I.; Smith, G.L.; Whittle, K.J. The texture of cod muscle. J. Texture Stud. 1974, 5, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalle Zotte, A.; Concollato, A.; Secci, G.; Cullere, M.; Parisi, G. Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) farmed at two different temperatures: Post rigor mortis changes in function of the stunning method. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 65, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, N.G. Animal Welfare and Meat Science; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Park, I. Effect of prolonged starvation on the activities of malic enzyme and acetylcholinesterase in tissues of Japanese quail. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1995, 27, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daskalova, A. Farmed fish welfare: Stress, post-mortem muscle metabolism, and stress-related meat quality changes. Int. Aquat. Res. 2019, 11, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchiang, K.; Sharma, R. Dietary restriction regulates brain acetylcholinesterase in female mice as a function of age. Biogerontology 2011, 12, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, D.; Crestani, M.; Rosa Shettinger, M.; Maria Morsch, V.; Baldisserotto, B.; Angel Tierno, M.; Moraes, G.; Vieira, V.L.P. Effects of the herbicides clomazone, quinclorac, and metsulfuron methyl on acetylcholinesterase activity in the silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen) (Heptapteridae). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2005, 61, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturm, A.; Radau, T.S.; Hahn, T.; Schulz, R. Inhibition of rainbow trout acetylcholinesterase by aqueous and suspended particle-associated organophosphorous insecticides. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauvais, S.L.; Cole, K.J.; Atchinson, G.J.; Coffey, M. Factors affecting brain cholinesterase activity in bluegill (Lepomis macrochirus). Water Air Soil Poll. 2002, 135, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, A.; Wogram, J.; Hansen, P.D.; Liess, M. Potential use of cholinesterase in monitoring low levels of organophosphates in small streams: Natural variability in three-spined stickleback (Gasterosteus aculeatus) and relation to pollution. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1999, 18, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baslow, M.H.; Nigrelli, R.F. The effect of thermal acclimation on brain cholinesterase activity of the killifish, Fundulus heteroclitus. Zoologica 1964, 49, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S. Salmon color and the consumer. In Microbehavior and Macroresults: Proceedings of the Tenth Biennial Conference of the International Institute of Fisheries Economics and Trade; Johnston, R.S., Shriver, A.L., Eds.; International Institute of Fisheries Economics and Trade: Corvallis, OR, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Nickell, D.; Bromage, N. Problems of Pigmentation: Lipids and Maturation; Institute of Aquaculture, University of Stirling: Stirling, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Prieto, C. Características De Calidad de la Carne De Trucha Arco Iris Oncorhynchus mykiss De Tres Granjas Piscícolas Del Estado De Chihuahua; Universidad Autónoma de Chihuahua: Chihuahua, Mexico, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Gilchrist, A.L. Lightness and brightness. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, R267–R269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; You, X.; Sun, W.; Xiong, G.; Shi, L.; Qiao, Y.; Wu, W.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Ding, A.; et al. Insight into acute heat stress on meat qualities of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) during short-time transportation. Aquaculture 2021, 543, 737013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatica, M.C.; Monti, G.E.; Knowles, T.G.; Gallo, C.B. Effects of crowding on blood constituents and flesh quality variables in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Arch. Med. Vet. 2010, 42, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosworth, B.G.; Small, B.C.; Gregory, D.; Kim, J.; Black, S.; Jerrett, A. Effects of rested-harvest using the anesthetic AQUI-STM on channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus, physiology and fillet quality. Aquaculture 2007, 262, 302–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erikson, U.; Misimi, E. Atlantic salmon skin and fillet color changes effected by perimortem handling stress, rigor mortis, and ice storage. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, C50–C59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefèvre, F.; Bugeon, J.; Aupérin, B.; Aubin, J. Rearing oxygen level and slaughter stress effects on rainbow trout flesh quality. Aquaculture 2008, 284, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marty-Mahé, P.; Loisel, P.; Fauconneau, B.; Haffray, P.; Brossard, D.; Davenel, A. Quality traits of brown trouts (Salmo trutta) cutlets described by automated color image analysis. Aquaculture 2004, 232, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einen, O.; Skrede, A. Quality characteristics in raw and smoked fillets of Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar, fed high-energy diets. Aquac. Nutr. 1998, 4, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einen, O.; Mørkøre, T.; Rørå, A.M.B.; Thomassen, M.S. Feed ration prior to slaughter a potential tool for managing product quality of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Aquaculture 1999, 178, 149–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginés, R.; Palicio, M.; Zamorano, M.; Argüello, A.; López, J.; Afonso, J. Starvation before slaughtering as a tool to keep freshness attributes in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Aquacult. Int. 2002, 10, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teimouri, M.; Amirkolaie, A.K.; Yeganeh, S. The effects of dietary supplement of Spirulina platensis on blood carotenoid concentration and fillet color stability in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2013, 414, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welker, C.; de Negro, P.; Sarti, M. Green algal carotenoids and yellow pigmentation of rainbow trout. Aquac. Int. 2001, 9, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, N.; Geiger, S.E.; Dollinger, E. Chalkiness in halibut in relation to muscle pH and protein denaturation. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1965, 22, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warris, P.D. Instrumental measurement of colour. In Meat Quality and Meat Packaging; ECCEAMST: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 1996; p. 221. [Google Scholar]
- Merkin, G.V.; Roth, B.; Gjerstad, C.; Dahl-Paulsen, E.; Nortvedt, R. Effect of pre-slaughter procedures on stress responses and some quality parameters in sea-farmed rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2010, 309, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, A.; Fernández-Segovia, I.; Serra, J.A.; Barat, J.M. Comparison of wild and cultured sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) quality. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 1514–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbuena-Pecino, S.; Riera-Heredia, N.; Vélez, E.J.; Gutiérrez, J.; Navarro, I.; Riera-Codina, M.; Capilla, E. Temperature affects musculoskeletal development and muscle lipid metabolism of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, A.E.; Pérez-Jiménez, A.; Hidalgo, M.C.; Abellan, E.; Cardenete, G. Oxidative stress and antioxidant defenses after prolonged starvation in Dentex dentex liver. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2004, 139, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Yan, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yin, L.; Feng, L.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Wu, P.; Wang, Y.; et al. Dietary isoleucine improved flesh quality, muscle antioxidant capacity, and muscle growth associated with AKT/TOR/S6K1 and AKT/FOXO3a signaling in hybrid bagrid catfish (Pelteobagrus vachelli♀ × Leiocassis longirostris♂). J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 12, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vranković, J.; Stanković, M.; Marković, Z. Levels of antioxidant enzyme activities in cultured rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fed with different diet compositions. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 2021, 41, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; He, K.; Yan, T.; Wu, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Gong, Q. Effect of starvation and refeeding on oxidative stress and antioxidant defenses in Yangtze sturgeon (Acipenser dabryanus). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 45, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensminger, D.C.; Salvador-Pascual, A.; Arango, B.G.; Allen, K.N.; Vázquez-Medina, J.P. Fasting ameliorates oxidative stress: A review of physiological strategies across life history events in wild vertebrates. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2021, 256, 110929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, T.; Xu, L.; Zhu, X.; Cheng, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Bao, L.; Chu, W. Influence of short-term fasting on oxidative stress, antioxidant-related signaling molecules and autophagy in the intestine of adult Siniperca chuatsi. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 21, 100933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Shi, X.; Huang, X.; Zhuang, P. Oxidative stress and antioxidant defenses after long-term fasting in blood of Chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis). Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 8, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatas, T.; Onalan, S.; Yildirim, S. Effects of prolonged fasting on levels of metabolites, oxidative stress, immune-related gene expression, histopathology, and DNA damage in the liver and muscle tissues of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 47, 1119–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florescu, I.E.; Georgescu, S.E.; Dudu, A.; Balaș, M.; Voicu, S.; Grecu, I.; Dediu, L.; Dinischiotu, A.; Costache, M. Oxidative stress and antioxidant defense mechanisms in response to starvation and refeeding in the intestine of stellate sturgeon (Acipenser stellatus) juveniles from aquaculture. Animals 2021, 11, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Moya, A.; Perelló-Amorós, M.; Vélez, E.J.; Viñuales, J.; García-Pérez, I.; Blasco, J.; Gutiérrez, J.; Fernández-Borràs, J. Interaction between the effects of sustained swimming activity and dietary macronutrient proportions on the redox status of gilthead sea bream juveniles (Sparus aurata). Antioxidants 2022, 11, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalba, A.M.; De La Llave-Propín, Á.; De La Fuente, J.; Ruiz, N.; Pérez, C.; De Chavarri, E.G.; Díaz, M.T.; Cabezas, A.; González-Garoz, R.; Villarroel, M.; et al. Seasonal comparison of uniform pre-slaughter fasting practices on stress response in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2025, 596, 741750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, M.A.K.; Kikusato, M.; Maekawa, T.; Shirakawa, H.; Toyomizu, M. Metabolic characteristics and oxidative damage to skeletal muscle in broiler chickens exposed to chronic heat stress. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2010, 155, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faught, E.; Vijayan, M.M. The Mineralocorticoid Receptor Functions as a Key Glucose Regulator in the Skeletal Muscle of Zebrafish. Endocrinology 2022, 163, bqac149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Yoshiki, M.; Takahashi, H.; Yoshida, M.; Ogino, Y.; Ikeuchi, T.; Nakamachi, T.; Konno, N.; Matsuda, K.; Sakamoto, H. Principal function of mineralocorticoid signaling suggested by constitutive knockout of the mineralocorticoid receptor in medaka fish. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, J.M.; Velloso, L.A. Hypoxia inducible factor as a central regulator of metabolism–implications for the development of obesity. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soñanez-Organis, J.G.; Vázquez-Medina, J.P.; Crocker, D.E.; Ortiz, R.M. Prolonged fasting activates hypoxia inducible factors-1α, -2α, and -3α in a tissue-specific manner in northern elephant seal pups. Gene 2013, 526, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soimato, A.J.; Raberg, C.M.I.; Gassmann, M.; Sistonen, L.; Nikinmaa, M. Characterization of a hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1a) from rainbow trout. J. Biochem. Chem. 2001, 276, 19699–19705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Pu, D.; Zheng, J.; Li, P.; Lü, H.; Wei, X.; Li, M.; Li, D.; Gao, L. Hypoxia-induced physiological responses in fish: From organism to tissue to molecular levels. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 267, 115609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beg, M.U.; Al-Subiai, S.; Beg, K.R.; Butt, S.A.; Al-Jandal, N.; Al-Hasan, E.; Al-Hussaini, M. Seasonal effect on heat shock proteins in fish from Kuwait bay. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 84, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, I.; Viant, M.R.; Rosenblum, E.S.; Gantner, A.S.; Tjeerdema, R.S.; Johnson, M.L. Cellular responses to temperature stress in steelhead trout (Onchorynchus mykiss) parr with different rearing histories. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2006, 32, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Zhao, W.; Shi, Z.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Wei, J.; Gao, F. Cloning HSP70 and HSP90 genes of kaluga (Huso dauricus) and the effects of temperature and salinity stress on their gene expression. Cell Stress Chaperones 2016, 21, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesus, T.F.; Inácio, Â.; Coelho, M.M. Different levels of hsp70 and hsc70 mRNA expression in Iberian fish exposed to distinct river conditions. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2013, 36, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, S. Effects of short-term fasting on spontaneous activity and excess post-exercise oxygen consumption in four juvenile fish species with different foraging strategies. Biol. Open 2020, 9, bio051755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ntantali, O.; Malandrakis, E.E.; Abbink, W.; Bastiaansen, J.; Chatzoglou, E.; Karapanagiotidis, I.T.; Golomazou, E.; Panagiotaki, P. Effects of short-term intermittent fasting on growth performance, fatty acids profile, glycolysis and cholesterol synthesis gene expression in European seabass Dicentrarchus labrax. Fishes 2023, 8, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).