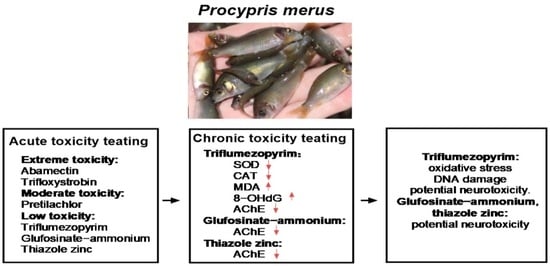
Toxicity and Safety Assessment of Key Pesticides Used in Rice Fields on Rice Flower Carp (Procypris merus)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Organisms, Materials, and Reagents
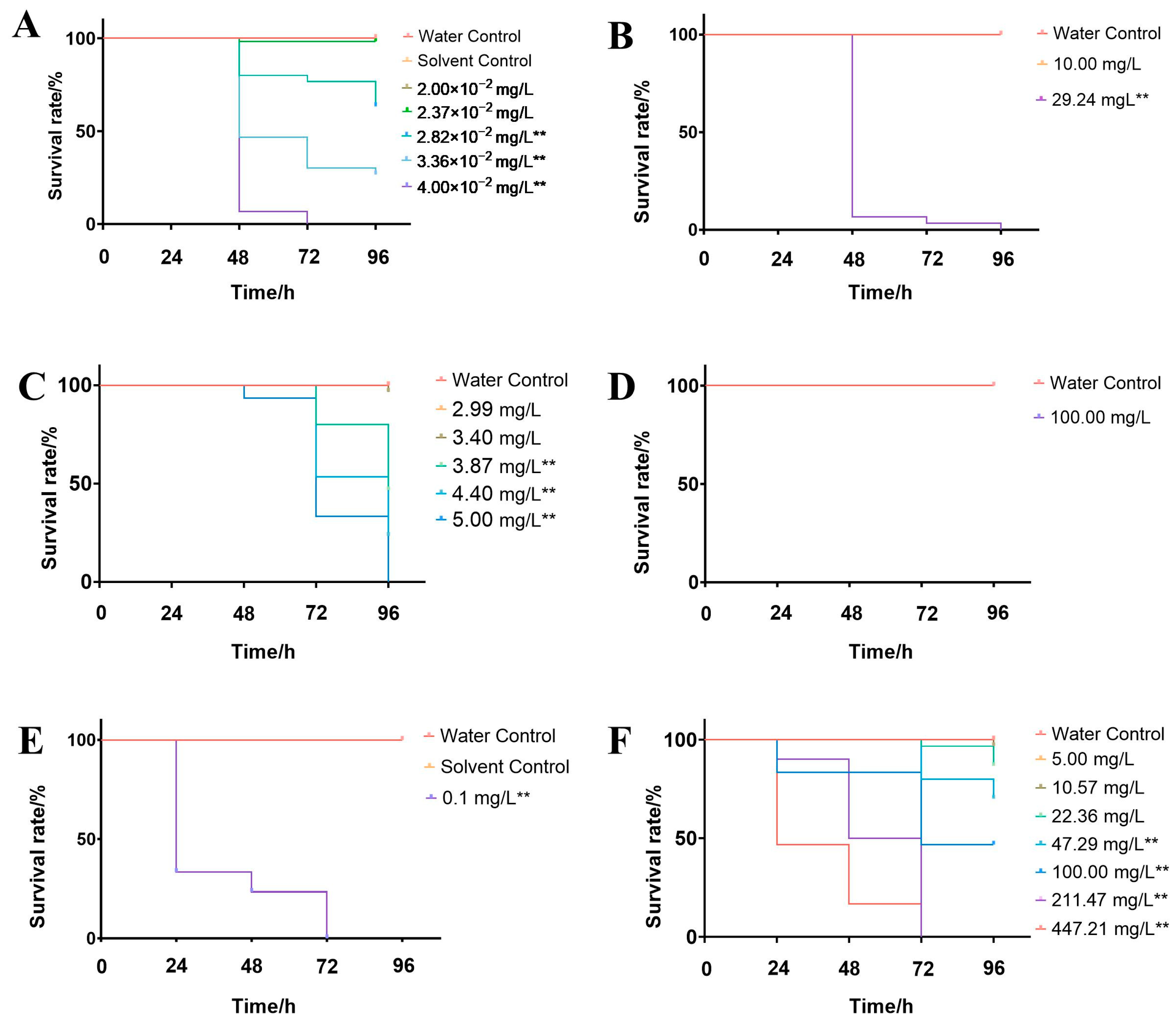
2.2. Acute Toxicity Testing
2.3. Chronic Toxicity Testing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Acute Toxicity of Rice Field Pesticides to P. merus
3.2. Effects of Rice-Field Chemical Pesticides on the Growth of P. merus
- Hepatosomatic index (HSI) and condition factor (CF):
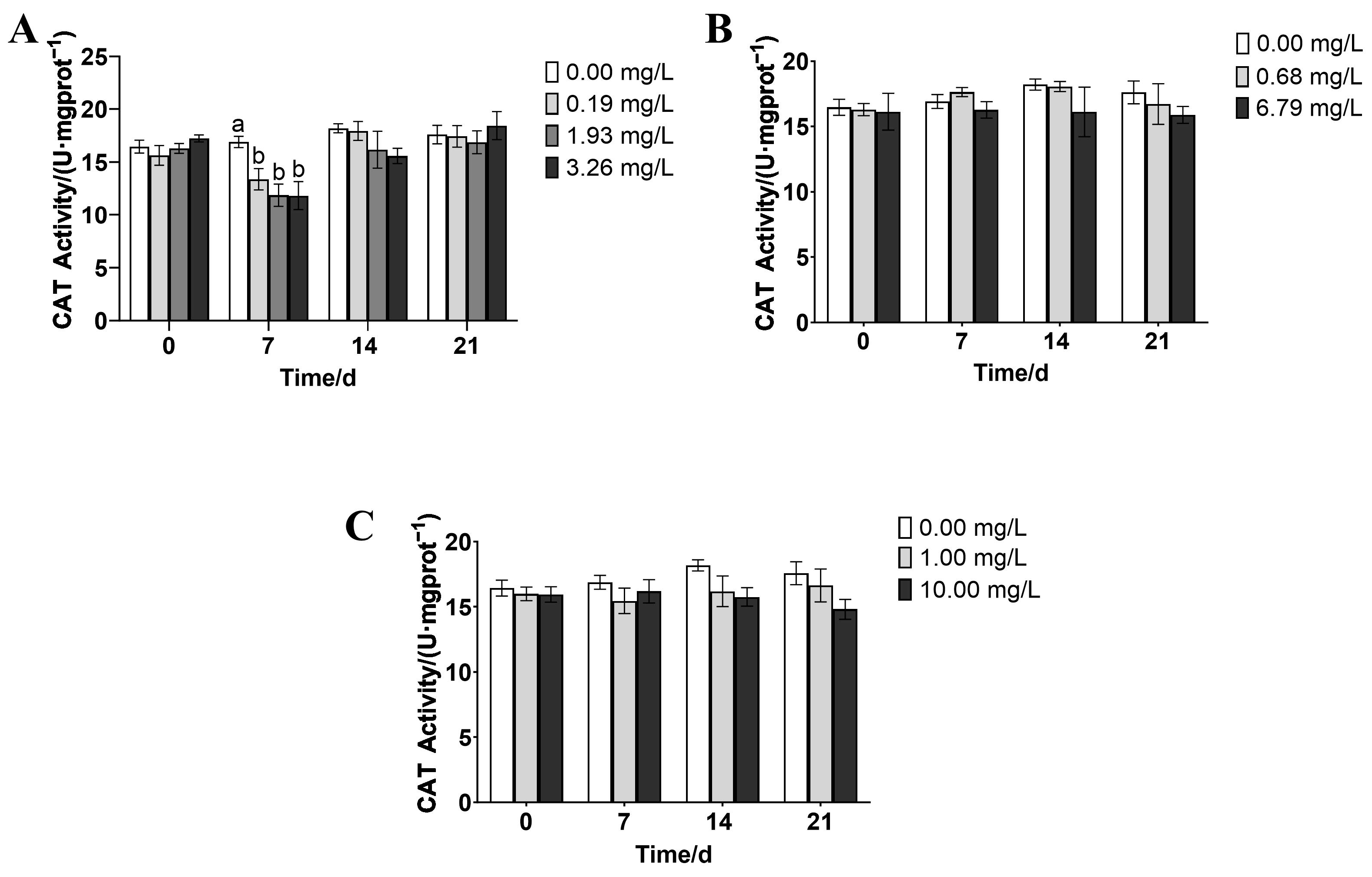
3.3. Effects of Rice-Field Pesticides on the Antioxidant Enzyme Activity of P. merus
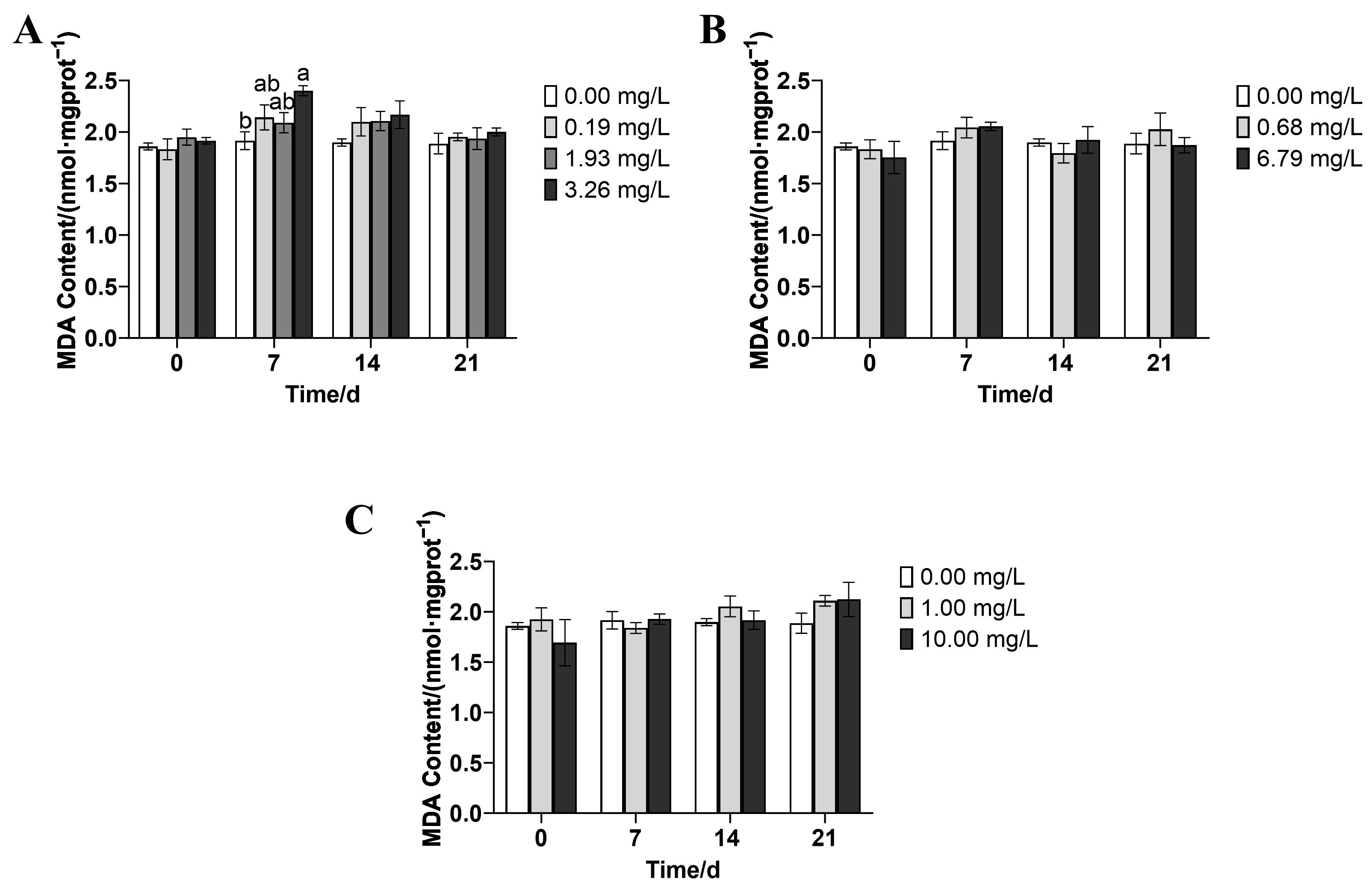
3.4. Effects of Rice-Field Pesticides on Malondialdehyde (MDA) Content in P. merus
3.5. Effects of Paddy-Field Pesticides on Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) Activity in P. merus
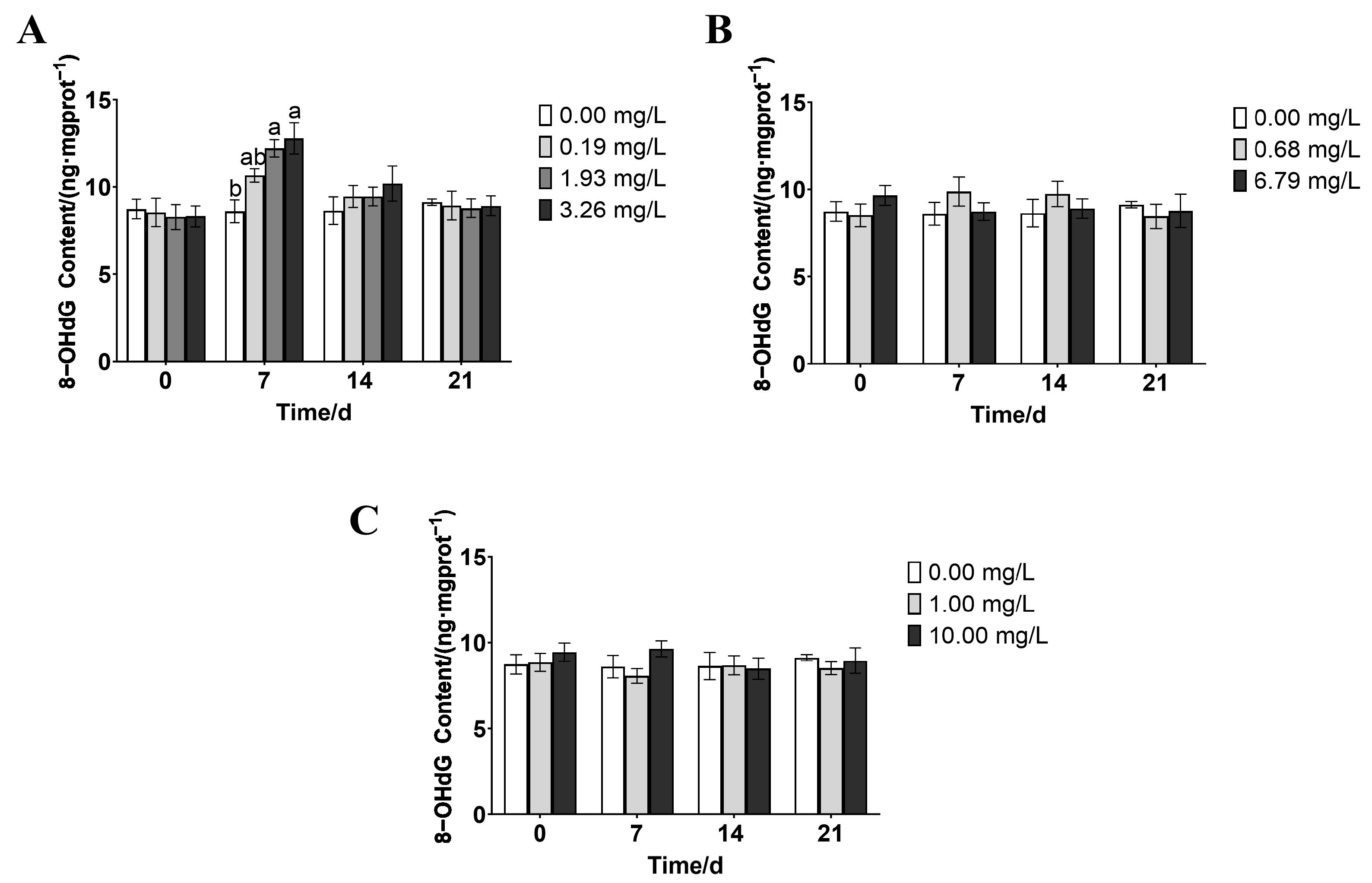
3.6. Effects of Paddy Field Pesticides on 8-Hydroxy-2′-Deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) Content in P. merus
4. Discussion
4.1. Toxicity Analysis of Paddy-Field Pesticides on P. merus
4.2. Effects of Paddy Field Pesticides on the Antioxidant System of P. merus
4.3. Effects of Rice-Field Pesticides on DNA Oxidative Damage in P. merus
4.4. Effects of Rice-Field Pesticides on Neural Transmission in P. merus
4.5. Effects of Paddy-Field Pesticides on the Growth of P. merus
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan, T.; Xie, Y.Y.; Zhou, B.; Kuang, X.; Li, Q.Z.; Zhao, F.Q.; Li, Q.D.; He, B. Rice-fish farming improved antioxidant defences, glucose metabolism, and muscle nutrient of Carassius auratus in Sichuan province. Metabolites 2024, 14, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumon, K.A.; Rico, A.; Ter Horst, M.M.S.; Van den Brink, P.J.; Haque, M.M.; Rashid, H. Risk assessment of pesticides used in rice-prawn concurrent systems in Bangladesh. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.B.; Liu, K.; Shi, W.; Xuan, F.J.; Wang, W.D. Scientific paradigm of integrated farming of rice and fish. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 5451–5464. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C.; Tian, W.; Wu, Y.; Wei, J.; Yang, L.; Wei, Y.; Jiang, J. Microplastics have additive effects on cadmium accumulation and toxicity in Rice flower carp (Procypris merus). Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 930, 172679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Du, X.; Wen, L.; Li, Y.; Qin, J.; Chen, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wu, X.; Luo, H.; Lin, Y.; et al. Transcriptome analysis reveals the involvement of ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in the regulation of muscle growth of rice flower carp. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2022, 41, 100948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, M.; Li, X.; Ping, K.; Ji, X.; Yang, H.; Dong, J. Hepatotoxicity of the pesticide avermectin exposure to freshwater-farmed carp: Evidence from in vivo and in vitro research. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 20654–20670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, K.; Ferreira Silva, I.; Mano-Sousa, B.J.; Duarte-Almeida, J.M.; Castro, W.V.; Azambuja Ribeiro, R.I.M.; Santos, H.B.; Thomé, R.G. Abamectin promotes behavior changes and liver injury in zebrafish. Chemosphere 2023, 311, 136941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fırat, Ö.; Tutus, R. Comparative acute toxicity assessment of organophosphate and avermectin insecticides on a freshwater Fish Oreochromis niloticus. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 105, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Dong, Z.; Liu, F.; Pan, E.; He, N.; Ma, F.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Dong, J. Avermectin induces carp neurotoxicity by mediating blood-brain barrier dysfunction, oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis through PI3K/Akt and NF-κB pathways. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 243, 113961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Gu, F.; Du, Y.; Li, X.; Gong, C.; Pu, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, X. Risk assessment and resistance inheritance of triflumezopyrim resistance in Laodelphax striatellus. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 2851–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Silipunyo, T.; Huang, H.; Yin, Q.; Han, B.; Wang, M. Risk assessment of triflumezopyrim and Imidacloprid in rice through an evaluation of residual data. Molecules 2022, 27, 5685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, S.; Das, S.; Kumar, R.; Das, I.I.; Mohanty, A.K.; Sahoo, L.; Gokulakrishnan, M.; Sundaray, J.K. Biochemical and histopathological alterations in freshwater fish, Labeo rohita (Hamilton, 1822) upon chronic exposure to a commonly used hopper insecticide, triflumezopyrim. Chemosphere 2023, 337, 139128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanda, V.; Kumar, R.; Yadav, N.; Sangwan, S.; Duhan, A. Ultimate fate, transformation, and toxicological consequences of herbicide pretilachlor to biotic components and associated environment: An overview. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2024, 44, 41–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, T.; Srivastava, R.; Yadav, S.; Singh, N.; Prajapati, R.; Singh, P.K.; Yadav, S.; Atri, N. Pretilachlor-induced physiological, biochemical and morphological changes in Indian paddy field agroecosystem inhabited Anabaena doliolum. Environ. Res. 2023, 238, 117201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, R.; Verma, S.K. Acute toxicity and behavioural responses in Clarias batrachus (Linnaeus) exposed to herbicide pretilachlor. Heliyon 2018, 4, e01090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Chen, Y.; Yu, R.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Q.; Cai, L. Pretilachlor has the potential to induce endocrine disruption, oxidative stress, apoptosis and immunotoxicity during zebrafish embryo development. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 42, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Pan, B.; Lin, Y. Teratogenic effects of embryonic exposure to pretilachlor on the larvae of zebrafish. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2017, 36, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Mou, L.; Ou, G.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, D. Comparative analysis of toxicity and metabolomic profiling of rac-glufosinate and L-glufosinate in zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2023, 261, 106618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, H.K.; Beffa, R.; Preston, C.; Westra, P.; Dayan, F.E. A novel insight into the mode of action of glufosinate: How reactive oxygen species are formed. Photosynth. Res. 2020, 144, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, H.K.; Dayan, F.E. Glufosinate-ammonium: A review of the current state of knowledge. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 3911–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.Q.; He, D.Y.; Liang, Q.Y.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Z.S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.H.; Zhao, P.X.; et al. Loss of OsARF18 function confers glufosinate resistance in rice. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1355–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Feng, T.; Chen, L.; Wang, H.; Sun, N.; Zhao, S.; Yang, T.; Jiao, W.; Feng, G.; et al. Glufosinate-ammonium causes liver injury in zebrafish by blocking the Nrf2 pathway. Environ. Toxicol. 2024, 39, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Chen, X.; Yang, D.H.; Yang, J.F.; Kang, G.Y.; Zhao, B.Q.; Li, X.M.; Pu, Y.Z.; Zheng, N.; Dong, W. Toxic effects of glufosinate-ammonium on zebrafish embryos and larvae. Chin. J. Pestic. Sci. 2016, 18, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.L. Application and development progress of trifloxystrobin. Mod. Agrochem. 2019, 18, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Fang, N.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, J. Trifloxystrobin induced developmental toxicity by disturbing the ABC transporters, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in adult zebrafish. Chemosphere 2024, 349, 140747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wu, S.; Lv, L.; Liu, X.; Chen, L.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Q. Mitochondrial dysfunction, apoptosis and transcriptomic alterations induced by four strobilurins in zebrafish (Danio rerio) early life stages. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Liu, G.L.; Liu, L.; Ling, F.; Wang, G.X. Assessment of trifloxystrobin uptake kinetics, developmental toxicity and mRNA expression in rare minnow embryos. Chemosphere 2015, 120, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cao, F.; Zhao, F.; Yang, Y.; Teng, M.; Wang, C.; Qiu, L. Developmental toxicity, oxidative stress and immunotoxicity induced by three strobilurins (pyraclostrobin, trifloxystrobin and picoxystrobin) in zebrafish embryos. Chemosphere 2018, 207, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, L.; Laborda, P.; Zhao, Y.; Li, K.; Liu, F. First method for dissolving zinc thiazole and re-evaluation of its antibacterial properties against rice bacterial blight disease. Phytopathol. Res. 2019, 1, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.Y.; Reziya, M.M.T.; Cai, C.; Lv, T.Y.; Sheng, Q.; Luo, M. Determination sensitivity of fire blight pathogen Erwinia amylovora to zinc thiazole and several other bactericides. Plant Prot. 2022, 48, 118–126. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, L.L.; Tao, F.Y.; Sun, Y.Q.; Wu, H.M. Acute and chronic toxicities of zinc thiazole to Daphnia magna. Chin. J. Pestic. Sci. 2020, 22, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 31270.12-2014; Test Guidelines on Environmental Safety Assessment for Chemical Pesticides—Part 12: Fish Acute Toxicity Test. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Fan, B.; Fan, M.; Liu, Z.T.; Li, J.; Dyer, S.; Wang, X.N.; Huang, Y. Species sensitivity and application in ecotoxicology and water quality criterion for Gobiocypris rarus. Res. Environ. Sci. 2019, 32, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, H.; Deng, D.; Zhu, F.; Chen, S.; Geng, J.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, K.; Jiang, J.; Yin, S.; Zhang, C. Acute exposure to glufosinate-ammonium induces hepatopancreas toxicity in juvenile Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 488, 137487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataoka, H.; Ryu, S.; Sakiyama, N.; Makita, M. Simple and rapid determination of the herbicides glyphosate and glufosinate in river water, soil and carrot samples by gas chromatography with flame photometric detection. J. Chromatogr. A 1996, 726, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordova, D.; Benner, E.A.; Schroeder, M.E.; Holyoke, C.W., Jr.; Zhang, W.; Pahutski, T.F.; Leighty, R.M.; Vincent, D.R.; Hamm, J.C. Mode of action of triflumezopyrim: A novel mesoionic insecticide which inhibits the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 74, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil, A.T.; Abdelbasset, W.K.; Shichiyakh, R.A.; Widjaja, G.; Altimari, U.S.; Aravindhan, S.; Thijail, H.A.; Mustafa, Y.F.; Naserabad, S.S. Protective effects of summer savory (Satureja hortensis) oil on growth, biochemical, and immune system performance of common carp exposed to pretilachlor herbicide. Vet. Res. Commun. 2022, 46, 1063–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soni, R.; Verma, S.K. Impact of herbicide pretilachlor on reproductive physiology of walking catfish, Clarias batrachus (Linnaeus). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 46, 2065–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saber Batiha, G.; Alqahtani, A.; Ilesanmi, O.B.; Saati, A.A.; El-Mleeh, A.; Hetta, H.F.; Magdy Beshbishy, A. Avermectin derivatives, pharmacokinetics, therapeutic and toxic dosages, mechanism of action, and their biological effects. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.Z.; Chen, Z.X.; Bai, S.Y.; Wang, H.T.; Hao, Q.R.; Wu, S.; Du, N.N.; Mou, Z.B. Acute toxicity of five drugs in aquaculture on rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss juveniles. Chin. J. Fish. 2015, 28, 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Sanches, A.L.M.; Vieira, B.H.; Reghini, M.V.; Moreira, R.A.; Freitas, E.C.; Espíndola, E.L.G.; Daam, M.A. Single and mixture toxicity of abamectin and difenoconazole to adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 2017, 188, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villares, M.; Lourenço, N.; Berthelet, J.; Lamotte, S.; Regad, L.; Medjkane, S.; Prina, E.; Rodrigues-Lima, F.; Späth, G.F.; Weitzman, J.B. Trifloxystrobin blocks the growth of Theileria parasites and is a promising drug to treat buparvaquone resistance. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Jiang, C.; Wu, Z.Q.; Gong, Y.X.; Wang, G.X. Toxic effects of three strobilurins (trifloxystrobin, azoxystrobin and kresoxim-methyl) on mRNA expression and antioxidant enzymes in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) juveniles. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 98, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maharajan, K.; Muthulakshmi, S.; Nataraj, B.; Ramesh, M.; Kadirvelu, K. Toxicity assessment of pyriproxyfen in vertebrate model zebrafish embryos (Danio rerio): A multi biomarker study. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 196, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, M.S.; Domingues de Melo, G.; Sandrini-Neto, L.; Di Domenico, M.; Prodocimo, M.M. A meta-analytic review of fish antioxidant defense and biotransformation systems following pesticide exposure. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, R.; Ghaffar, A.; Abbas, G.; Jabeen, G.; Khan, I.; Abbas, R.Z.; Noreen, S.; Iqbal, Z.; Chaudhary, I.R.; Ishaq, H.M.; et al. Thiamethoxam at sublethal concentrations induces histopathological, serum biochemical alterations and DNA damage in fish (Labeo rohita). Toxin Rev. 2020, 41, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Zhou, K.; Luo, X.; Long, W.; Yin, Z.; Huang, Z.; Hong, Y. Effects of glyphosate on neurotoxicity, oxidative stress and immune suppression in red swamp crayfish, Procambarus clarkii. Aquat. Toxicol. 2024, 275, 107050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alak, G.; Yeltekin, A.; Tas, I.H.; Ucar, A.; Parlak, V.; Topal, A.; Kocaman, E.M.; Atamanalp, M. Investigation of 8-OHdG, CYP1A, HSP70 and transcriptional analyses of antioxidant defence system in liver tissues of rainbow trout exposed to eprinomectin. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 65, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, L.; Du, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Li, B.; Yang, Y. Fluoxastrobin-induced effects on acute toxicity, development toxicity, oxidative stress, and DNA damage in Danio rerio embryos. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 137069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Huang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Xu, D.; Huang, Q.; Huang, Z. Cytotoxicity induced by abamectin in hepatopancreas cells of Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis: An in vitro assay. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 262, 115198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakkannan, G.; Mohanty, A.K.; Das, I.I.; Nayak, S.; Sahoo, L.; Kumar, R.; Rasal, A.; Rather, M.A.; Ahmad, I.; Sundaray, J.K. Triflumezopyrim induced oxidative stress, DNA damage and apoptosis on Labeo rohita: Insights from bioinformatics, histopathological and molecular approaches. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 304, 140911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, H.; Ren, Z.; Cui, Z. The toxic effects of deltamethrin on Danio rerio: The correlation among behavior response, physiological damage and AChE. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 109826–109833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, R.A.; Araújo, C.V.M.; Junio da Silva Pinto, T.; Menezes da Silva, L.C.; Goulart, B.V.; Viana, N.P.; Montagner, C.C.; Fernandes, M.N.; Gaeta Espindola, E.L. Fipronil and 2,4-D effects on tropical fish: Could avoidance response be explained by changes in swimming behavior and neurotransmission impairments? Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capkin, E.; Boran, H.; Altinok, I. Response of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) in the erythrocyte and liver of rainbow trout exposed to carbosulfan Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 14, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Guan, X.; Pu, L.; Shen, L.; Hua, H. Acute toxicity, biochemical and transcriptomic analysis of Procambarus clarkii exposed to avermectin. Pest Manag. Sci. 2023, 79, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, M.; Xu, P.; Wen, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, Q.; He, J.; He, C.; Kong, C.; Song, C.; Li, H. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor signaling-mediated 13-s-hydroxyoctadecenoic acid is involved in lipid metabolic disorder and oxidative stress in the liver of freshwater drum, Aplodinotus grunniens. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, D.; Deveci, H.A.; Nur, G. Manifestations of oxidative stress and liver injury in clothianidin exposed Oncorhynchus mykiss. Toxicol. Res. 2021, 10, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Aweya, J.J.; Yao, D.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y. Taurine metabolism is modulated in Vibrio-infected Penaeus vannamei to shape shrimp antibacterial response and survival. Microbiome 2022, 10, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
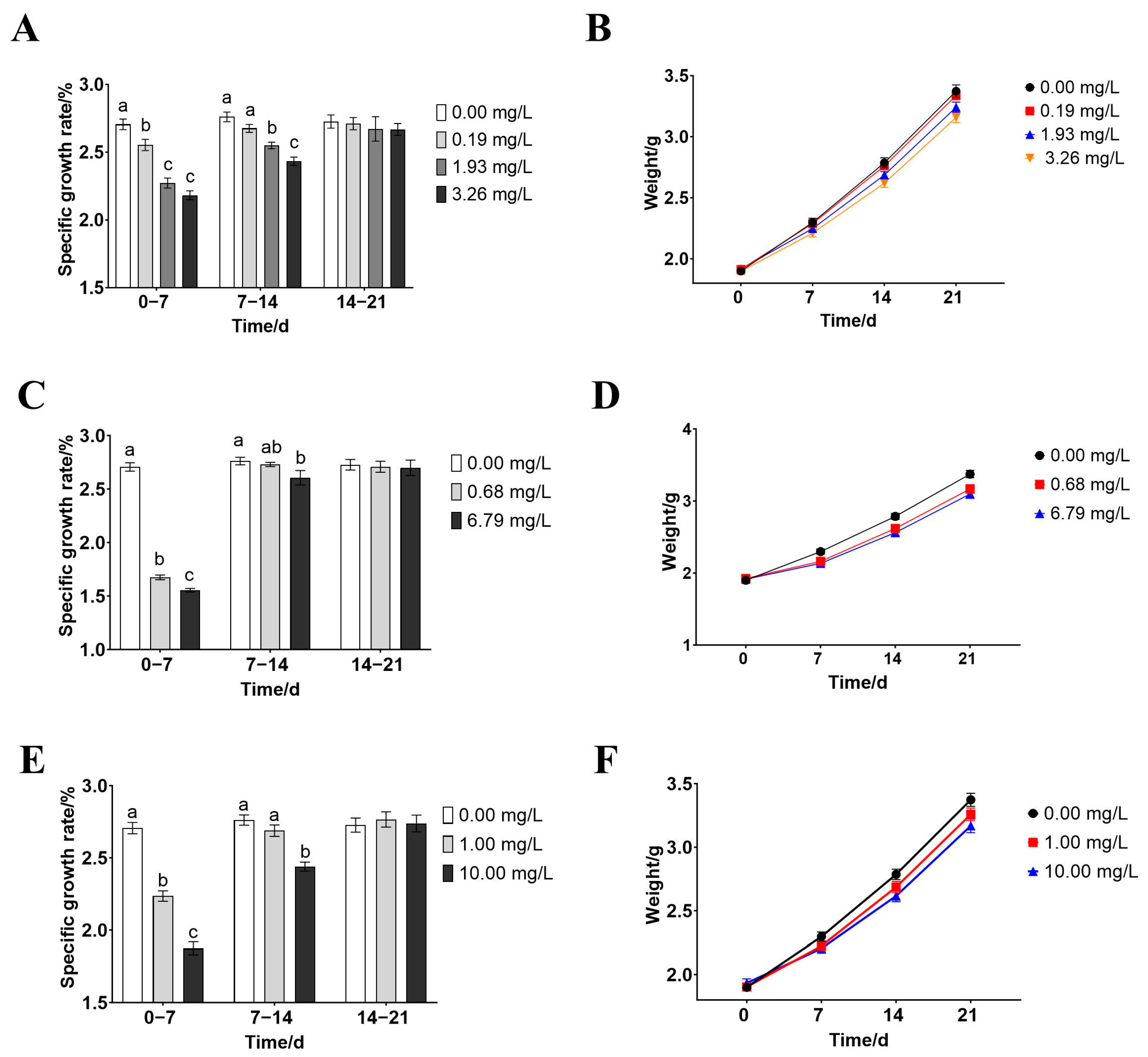
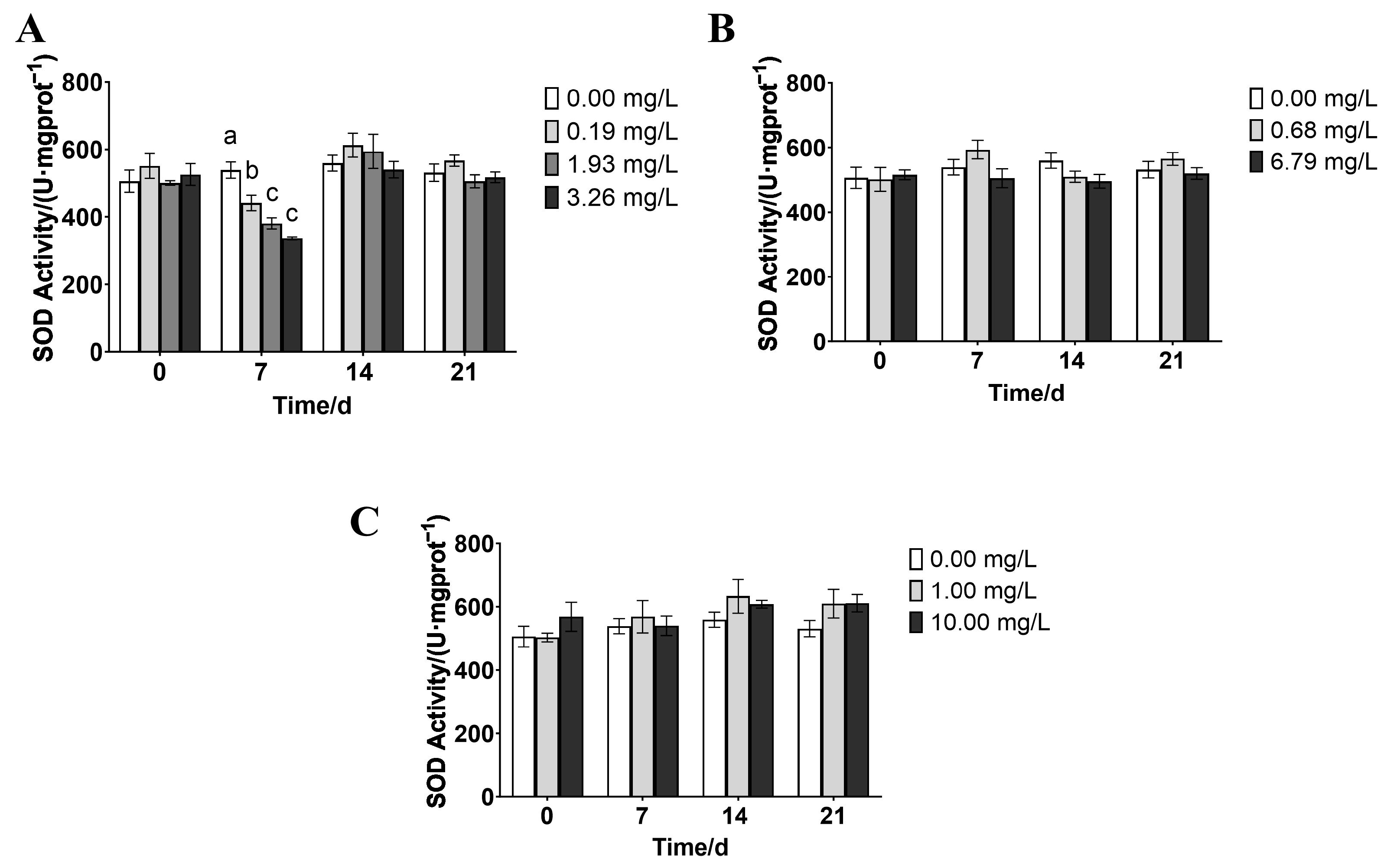

| Pesticide | Field Relevant | 1/10 LC50 | 1/100 LC50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trflumezopyrim | 3.26 | 1.93 | 0.19 |
| Glufosinate-Ammonium | 7.50 | 10.00 | 1.00 |
| Zinc Thiazole | 8.36 | 6.79 | 0.68 |
| Type | Pesticides | Treatment (h) | Regression Equation | Correlation R2 | LC50 (mg/L) | 95% Confidence Interval | Toxicity Grade |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insecticide | Avermectin | ||||||
| 24 | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 48 | y = 14.14x + 21.08 | 0.98 ** | 0.32 × 10−1 | 0.30 × 10−1–0.36 × 10−1 | Extreme Toxicity | ||
| 72 | y = 17.55x + 26.54 | 0.98 ** | 0.31 × 10−1 | 0.28 × 10−1–0.33 × 10−1 | Extreme Toxicity | ||
| 96 | y = 17.07x + 25.97 | 0.99 ** | 0.30 × 10−1 | 0.28 × 10−1–0.33 × 10−1 | Extreme Toxicity | ||
| Trflumezopyrim | |||||||
| 24 | - | - | 10.00 < LC50 < 29.24 | - | Low Toxicity | ||
| 48 | - | - | 10.00 < LC50 < 29.24 | - | Low Toxicity | ||
| 72 | - | - | 10.00 < LC50 < 29.24 | - | Low Toxicity | ||
| 96 | - | - | 10.00 < LC50 < 29.24 | - | Low Toxicity | ||
| Herbicide | Pretilachlor | ||||||
| 24 | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 48 | y = 12.16x − 10.31 | 0.75 | 7.04 | - | Moderate Toxicity | ||
| 72 | y = 14.59x − 9.61 | 0.98 ** | 4.56 | 4.23–4.15 | Moderate Toxicity | ||
| 96 | y = 16.01x − 9.29 | 0.99 ** | 3.80 | 3.54–4.08 | Moderate Toxicity | ||
| Glufosinate-ammonium | |||||||
| 24 | - | - | LC50 > 100.00 | - | Low Toxicity | ||
| 48 | - | - | LC50 > 100.00 | - | Low Toxicity | ||
| 72 | - | - | LC50 > 100.00 | - | Low Toxicity | ||
| 96 | - | - | LC50 > 100.00 | - | Low Toxicity | ||
| Fungicide | Trifloxystrobin | ||||||
| 24 | - | - | LC50 < 0.10 | - | Extreme Toxicity | ||
| 48 | - | - | LC50 < 0.10 | - | Extreme Toxicity | ||
| 72 | - | - | LC50 < 0.10 | - | Extreme Toxicity | ||
| 96 | - | - | LC50 < 0.10 | - | Extreme Toxicity | ||
| Zinc Thiazole | |||||||
| 24 | y = 1.65x − 4.29 | 0.98 * | 390.89 | - | Low Toxicity | ||
| 48 | y = 3.27x − 7.64 | 0.99 ** | 215.69 | 148.52–339.08 | Low Toxicity | ||
| 72 | y = 3.88x − 7.40 | 1.00 ** | 80.36 | 57.24–117.33 | Low Toxicity | ||
| 96 | y = 2.67x − 4.88 | 0.99 ** | 67.89 | 45.66–109.18 | Low Toxicity |
| Pesticide | Treatment | Concentration (mg/L) | Condition Factor (g/cm) | Hepatosomatic Index (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trflumezopyrim | 0 d | 0.00 | 40.39 ± 0.78 | 3.54 ± 0.16 |
| 0.19 | 40.60 ± 1.03 | 3.56 ± 0.24 | ||
| 1.93 | 38.62 ± 0.72 | 3.59 ± 0.20 | ||
| 3.26 | 39.06 ± 0.70 | 3.58 ± 0.22 | ||
| 7 d | 0.00 | 42.31 ± 0.39 | 3.56 ± 0.04 a | |
| 0.19 | 42.49 ± 0.33 | 3.52 ± 0.04 a | ||
| 1.93 | 41.48 ± 0.43 | 3.45 ± 0.05 ab | ||
| 3.26 | 41.43 ± 0.30 | 3.38 ± 0.04 b | ||
| 14 d | 0.00 | 48.12 ± 0.25 | 3.55 ± 0.05 | |
| 0.19 | 47.97 ± 0.23 | 3.56 ± 0.03 | ||
| 1.93 | 47.47 ± 0.25 | 3.54 ± 0.03 | ||
| 3.26 | 47.90 ± 0.25 | 3.55 ± 0.04 | ||
| 21 d | 0.00 | 55.78 ± 0.37 | 3.61 ± 0.02 | |
| 0.19 | 55.78 ± 0.40 | 3.57 ± 0.03 | ||
| 1.93 | 54.83 ± 0.37 | 3.58 ± 0.03 | ||
| 3.26 | 55.39 ± 0.34 | 3.57 ± 0.04 | ||
| Glufosinate-Ammonium | 0 d | 0.00 | 40.39 ± 0.78 | 3.54 ± 0.16 |
| 1.00 | 39.12 ± 0.68 | 3.53 ± 0.15 | ||
| 10.00 | 38.83 ± 1.07 | 3.54 ± 0.24 | ||
| 7 d | 0.00 | 42.31 ± 0.39 | 3.56 ± 0.04 a | |
| 1.00 | 41.62 ± 0.39 | 3.32 ± 0.04 b | ||
| 10.00 | 41.47 ± 0.17 | 3.07 ± 0.11 c | ||
| 14 d | 0.00 | 47.59 ± 0.39 | 3.55 ± 0.05 a | |
| 1.00 | 47.22 ± 0.27 | 3.43 ± 0.07 ab | ||
| 10.00 | 46.85 ± 0.41 | 3.31 ± 0.06 b | ||
| 21 d | 0.00 | 55.78 ± 0.37 | 3.61 ± 0.02 | |
| 1.00 | 54.91 ± 0.46 | 3.59 ± 0.04 | ||
| 10.00 | 53.72 ± 0.31 | 3.52 ± 0.04 | ||
| Zinc Thiazole | 0 d | 0.00 | 40.39 ± 0.78 | 3.54 ± 0.16 |
| 0.68 | 41.33 ± 1.14 | 3.46 ± 0.18 | ||
| 6.79 | 39.78 ± 1.23 | 3.53 ± 0.26 | ||
| 7 d | 0.00 | 42.31 ± 0.39 | 3.56 ± 0.04 a | |
| 0.68 | 42.12 ± 0.28 | 3.38 ± 0.09 a | ||
| 6.79 | 41.51 ± 0.22 | 2.99 ± 0.10 b | ||
| 14 d | 0.00 | 47.59 ± 0.39 | 3.55 ± 0.05 | |
| 0.68 | 47.12 ± 0.28 | 3.54 ± 0.03 | ||
| 6.79 | 46.66 ± 0.29 | 3.56 ± 0.03 | ||
| 21 d | 0.00 | 55.78 ± 0.37 | 3.61 ± 0.02 | |
| 0.68 | 55.03 ± 0.29 | 3.58 ± 0.03 | ||
| 6.79 | 55.10 ± 0.24 | 3.59 ± 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, Q.; Ruan, Y.; Liang, R.; Jin, R.; Jin, Z.; Xie, L.; Chi, Y.; Xia, J.; Zhu, P. Toxicity and Safety Assessment of Key Pesticides Used in Rice Fields on Rice Flower Carp (Procypris merus). Fishes 2025, 10, 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10060248
Shao Q, Ruan Y, Liang R, Jin R, Jin Z, Xie L, Chi Y, Xia J, Zhu P. Toxicity and Safety Assessment of Key Pesticides Used in Rice Fields on Rice Flower Carp (Procypris merus). Fishes. 2025; 10(6):248. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10060248
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Qianxue, Yongming Ruan, Ru Liang, Ruixin Jin, Zhixi Jin, Lin Xie, Yongqing Chi, Jiaojiao Xia, and Pingyang Zhu. 2025. "Toxicity and Safety Assessment of Key Pesticides Used in Rice Fields on Rice Flower Carp (Procypris merus)" Fishes 10, no. 6: 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10060248
APA StyleShao, Q., Ruan, Y., Liang, R., Jin, R., Jin, Z., Xie, L., Chi, Y., Xia, J., & Zhu, P. (2025). Toxicity and Safety Assessment of Key Pesticides Used in Rice Fields on Rice Flower Carp (Procypris merus). Fishes, 10(6), 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10060248