Abstract
Understanding the feeding ecology and habitat use of vulnerable shark species is crucial for effective conservation. This study focuses on two large filter-feeding sharks, the megamouth shark (Megachasma pelagios) and whale shark (Rhincodon typus), in Northwestern Pacific waters. Stable isotope analysis (δ13C and δ15N) was conducted on white muscle samples (n = 91) of M. pelagios and fin clips (n = 90) of R. typus, collected via large-mesh drift nets and set nets in Taiwanese waters. In this study, we investigated feeding strategies, ontogenetic dietary shifts, habitat use, and isotopic niche variation in both species. For R. typus, the observed positive correlation between δ13C and δ15N supports the previously proposed active suction filter feeding, as well as implying both a diet with an increasing proportion of higher trophic level prey and an ontogenetic shift. In contrast, M. pelagios displayed a negative correlation, consistent with a previous study associating such patterns with primary or secondary consumers, further aligning with its reported planktonic prey dominance. Both species had increasing δ13C with growth, signifying a shift to nutrient-rich habitats. Only R. typus exhibited ontogenetic diet changes (δ15N). SIBER (Stable Isotope Bayesian Ellipses in R) analysis revealed distinct feeding strategies and habitat use between the two species, potential sexual segregation, and wider isotopic niche widths for males in both species. The findings underscore the importance of considering species-specific behaviors and sex-based differences in conservation strategies.
Key Contribution:
This study provides the first comparative stable isotope analysis of megamouth and whale sharks in the northwestern Pacific. Distinct feeding strategies and ontogenetic habitat shifts were identified, including sex-based isotopic niche differences. These findings highlight the need for species- and sex-specific considerations in shark conservation planning.
1. Introduction
Elasmobranchs, comprising approximately 1200 extant species, exhibit diverse trophic niches and play fundamental roles in marine ecosystems by regulating organisms across various trophic levels [1,2,3]. Among elasmobranchs, large shark species are usually known as K-selected animals, and they exhibit late maturity, small litter size, and slow growth rate, making their population more vulnerable [4,5]. The global population of sharks has decreased due to the high fishing pressure over the past few decades [6,7]. Acquiring detailed biological information on large shark species is necessary for sustainable management decision-making. Feeding ecology is one of the research projects that helps elucidate the role of animals across and within sub-regions of the ecosystems and provides more information for management strategy [8,9].
There are several methods to study feeding ecology, such as feeding behavior observation, stomach content analysis (SCA), and stable isotope analysis (SIA). Historically, stomach composition research was the typical method, which provides detailed insights into recent feeding events and short-term dietary patterns [10]. However, the SCA method was usually lethal and limited by sample size, high rates of empty stomachs or prey digestive level, especially on large shark species [11,12,13]. To complement the limitation of SAC and the broader understanding of long-term dietary trends, the stable isotope is employed as a reliable tool for feeding ecology research, and it has been used broadly for marine animals, such as mammals, teleost, and elasmobranchs [14,15,16,17].
Stable isotopes are non-radioactive forms of elements that do not decay over time; by examining the ratio of heavy to light isotopes of elements of animals, researchers can infer long-term dietary sources, trophic relationships, and/or habitat use, offering a more comprehensive picture of feeding ecology [18]. Various isotope values provide different information, e.g., the δ13C and δ15N from individuals reflect the inhabited environment and assimilated food habits over time, respectively [18,19,20]. Typically, the gradient δ13C could be found from nearshore to offshore, or benthic to pelagic food webs; therefore, δ13C is commonly used to study dietary sources or productivity of the environment [21,22]. δ15N is often used to determine the relative trophic position of animals in a food web; higher δ15N are positively correlated with higher trophic levels, likewise, animals from lower trophic positions usually exhibit lower δ15N.
Additionally, the potential ontogenetic shifts and sexual segregation of many vulnerable shark species have been described by using stable isotope research. For example, the male white sharks (Carcharodon carcharias) prefer to forage either further offshore or closer to western coastal waters as they grow in South Africa [23]. Significant differences in δ13C and δ15N values were detected among neonate, juvenile, and adult silky sharks (Carcharhinus falciformis), indicating an ontogenetic shift in trophic ecology in the Eastern Tropical Pacific Ocean [24]. The majority of previous SIA research focused on predators in the ecosystem, such as scalloped hammerhead shark (Sphyrna lewini), blue shark (Prionace glauca), bull shark (Carcharhinus leucas), tiger shark (Galeocerdo cuvier), etc. [25,26,27]. However, the filter feeders also received attention from several fronts because they are more vulnerable to environmental threats such as pollution, fishing pressure, or coastal human activities [28,29,30]. Among the marine filter-feeding sharks, there were two well-known species in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean, the whale shark (Rhincodon typus) and the megamouth shark (Megachasma pelagios).
Whale sharks are the world’s largest fish, reaching a maximum total length (TL) of approximately 20 m [31,32,33,34]. This filer-feeding species feeds on various plankton and small bony fishes, but the prey items change in different spatiotemporal waters [35,36,37,38]. Whitehead et al. indicated that different food webs lead to various stable isotopic values for whale sharks, the La Paz Bay (eastern Pacific) group occupied a wider isotopic niche than in the Yucatan Peninsula (western Atlantic) [14]. Stable isotopes have been widely used in whale shark research, with numerous studies reporting increases in trophic levels with body size in various regions, such as La Paz Bay, Ningaloo, Veraval, and the Gulf of Goubet, most of which are located in the Indian Ocean [37,38,39,40]. One study using stable isotope analysis on whale sharks from the western Pacific Ocean suggested that the turnover time of different tissues (plasma and fin cartilage) was approximately 9 months to 3 years based on feeding experiments of three captive individuals [41]. However, the stable isotope information of the field population from the western Pacific Ocean is still limited [41].
Megamouth sharks are seldom recorded globally, with fewer than 300 individuals being reported in the last 40 years [42,43]. Researchers described this species as viviparous with oophagy, which can reach ~700 cm TL, the size at maturity was ~400 cm TL for males but ~500 cm TL for females [44,45]. The specific vertical movement behavior during dawn and dusk has been verified for megamouth shark according to the tracking and capture records [43,46,47]. The megamouth shark may attract prey by reflecting external light sources, such as the light produced by bioluminescent prey, on the white band (a highly reflective structure on the upper jaw) during feeding [48]. Zooplanktonic prey, mainly Euphausia pacifica was found in the diet of megamouth shark, but Nematoscelis difficilis has also been identified in the stomach [49,50]. Only one previous study suggested the preference for the pelagic habitat and the zooplanktonic prey-feeding behavior of the megamouth based on stable isotope analysis (δ13C = −22.5‰; δ15N = 10.4‰) from only one stranded individual in Brazil [51]. Nevertheless, detailed research on megamouth shark ecology is still missing, leaving a knowledge gap on habitat use, and feeding habitats between male and female life history stages.
Therefore, this study aims to address this general knowledge gap by evaluating the stable isotope of the whale shark and megamouth shark in the western North Pacific Ocean. We hypothesized that the isotopic composition would differ between R. typus and M. pelagios, and that the value would be influenced by size and sex. Overall, this study aims to provide useful information on the feeding and habitat use of R. typus and M. pelagios in different sex and life history stages.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
The tissue samples were collected from R. typus, caught as bycatch in set nets in coastal waters off Taiwan from 2008 to 2018 (Figure 1). In Taiwan R. typus was consumed greatly before the 1990s, after which its population dramatically declined; therefore, the total allowable catch (TAC) system of R. typus was established in 2002, completely banned fishing in 2008, and listed as a conservation species in 2020 [52]. According to the project requirement of the Taiwan Fisheries Agency, the individual photos, body length (cm TL), and sex information were recorded during the tagging processes. A small piece of fin clip (skin with muscle tissue) was collected from the caudal fin of R. typus before release, the samples were preserved in 95% ethanol immediately for analysis later.
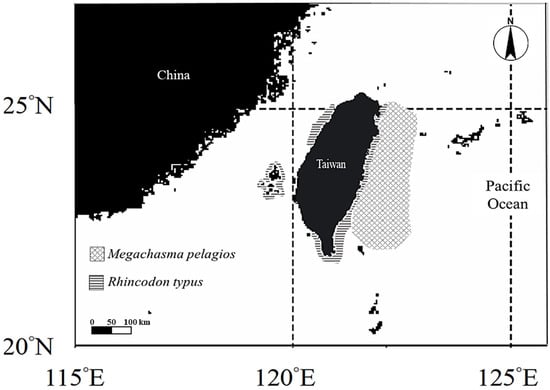
Figure 1.
Fishing ground of M. pelagios, in the eastern Taiwan waters (the operation area of large-mesh drift net fishery) and fishing ground of R. typus, around Taiwan waters (the operation area of set net fishery).
On the other hand, M. pelagios was categorized as of least concerned species on the IUCN red list because of limited research and population information [53]. Nevertheless, in order to preserve the highly biologically diverse waters surrounding Taiwan, the Taiwan Fisheries Agency implemented a mandatory catch report system for this species in 2013 and banned its fishing in 2020 [43]. The white muscle samples of M. pelagios were collected during 2013 and 2019 from bycatch. All M. pelagios were the bycatch of large-mesh (mesh size 90 cm) drift net vessels, which operated in the eastern waters of Taiwan (Figure 1). After the shark landing in the port or fish market, the TL (cm), weight (kg), and sex were recorded. The white muscle specimens and some prey items from stomach were collected right after the sharks were dissected and preserved in 95% ethanol for further analysis.
Previous study had suggested that the different preservation methods, such as salt and formalin-ethanol could have effects on stable isotopic signatures, but the magnitude of the difference was found to be small and directionally consistent, suggesting the method may be suitable for stable isotope analysis [54].
2.2. Life History Stages
Ontogenetic shifts and sexual segregation are commonly gradually found in large shark species in different life history stages due to various purposes, for instance, nutrition, refuge, mating, and reproductive requirements. Therefore, the life history stages were identified into three stages (groups) in this study; the reproductive organs’ development was observed for M. pelagios (C. J. Yu, personal observation): group I (immature): males and females have undeveloped gonads; group II (maturing): developing reproductive organs, such as slightly rotated clasper from males and inflating ovaries or uteri from females; group III (mature): developed claspers with semen from males or inflated ovaries and uteri with mating scars from females. Additionally, R. typus were separated into three groups based on sampling size range due to almost no mature individual in this study. The individuals ≤ 400 cm TL were in group I, from 401 to 600 cm TL were in group II, and >600 cm TL were in group III, respectively.
2.3. Pretreatment of SIA
The SIA samples of M. pelagios and R. typus were dried for 2–4 days at 60 °C and grinded into homogeneous powder. The tissue powder samples were weighed ~3 mg, transferred into tin cups, and sent to the Société Générale de Surveillance (SGS), Switzerland Taiwan Ltd. for further δ13C and δ15N analysis. The steps for analysis were as follow: powder samples were wrapped in a tin cup, placed into the elemental analyzer (EA), and burned at 1000–1050 °C. After the carbon and nitrogen from the sample were converted to CO2 and N2 under the high temperature and were separated by the chromatography column. The gas was sent into the Finnigan DELTAplus XP stable isotope ratio mass spectrometer through the ConFlo IV or ConFlo III for analysis.
2.4. Stable Isotope and Trophic Position Analysis
2.4.1. Stable Isotope
The results were expressed in delta (δ) notation, and the specimens were analyzed through continuous flow isotope-ratio mass spectrometer [18]. These values are calculated as:
where X is 13C or 15N, and R is the isotope ratio 13C/12C or 15N/14N, respectively. The value is related to Peedee Belemnite (PDB) and atmospheric N2 for 13C and δ15N. This δ13C and δ15N study also calculated the sample C:N ratio, indicating satisfactory lipid removal efficiency.
2.4.2. Trophic Position
The relative trophic position (TP) values of M. pelagios and R. typus were estimated from 15N [55]. The equation is as below:
where λ is the trophic position of reference organism, δ15Nsecondary consumer is the stable isotope of consumer, δ15Nbase is the stable isotope of reference organism, and Δn is the trophic enrichment factor represents a best estimate of isotopic enrichment between consumer and its prey [55]. According to previous study, the species used for estimating δ15Nbase should come from the same habitat as the consumer [55]. Therefore, δ15N of euphotic POM (1.1‰) from the North-Eastern Taiwan water was chosen to be the baseline for R. typus, in this case λ is 1 [56]. On the other hand, δ15N of identifiable stomach composition (δ15NEuphausiacea = 6.95‰) of M. pelagios was used for calculating trophic position in this study, as Euphausiacea is the primary consumer, it was assigned a trophic position of 2. The trophic enrichment factor (TEF) was assumed as 3.4‰ per trophic level, based on the empirical observation that δ15N values typically increase by this amount with each trophic level [55,57].
2.5. Data Analysis
The Shapiro–Wilk (S–W) normality test was used to test normality of isotope value for M. pelagios and R. typus, respectively. When normal distribution was found, Student’s t-test was used to test the differences between sexes, otherwise Kruskal–Wallis (K–W) test was used in non-normal conditions. The analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to test the difference between sex and size groups. M. pelagios and R. typus specimens used in this study were both separated into three size groups (I, II, and III) for discussing the shift in trophic position. Statistically, significant level (α) was 0.05. Stable Isotope Bayesian Ellipses in R (SIBER) was used to calculate the small sample size corrected SIBER ellipse area (SEAc) for the niche breadth and niche overlap [58]. Moreover, the overlap percentage (Overlap%) of both shark between sexes and different size groups were calculated. The Overlap% value was identified as low (≤35%), medium (36–70%), and high (>70%), respectively [58]. Simple linear regression analyses were carried out between δ15N and δ13C values across species and sexes within species.
3. Results
3.1. SIA for M. pelagios and R. typus: Interspecific Comparison
In total, 91 M. pelagios (37 males and 54 females) and 90 R. typus (58 males and 32 females) tissue samples were used in SIA (Table 1). The body size of M. pelagios ranged from 290 to 710 cm TL, and that of R. typus from 284 to 1190 cm TL. The values of δ13C and δ15N in M. pelagios were −18.14 to −14.99‰ (mean ± SD: −17.2 ± 0.69‰, n = 91) and 6.83 to 11.67‰ (9.04 ± 0.9‰, n = 91), respectively (Table 1). The values of δ13C and δ15N in R. typus were −18.89 to −13.68‰ (−15.67 ± 0.78‰, n = 90) and 5.17 to 13.01‰ (9.02 ± 1.79‰, n = 90), respectively (Table 1). The C:N ratio of both sharks was <3.5, indicating that the samples were free from the effects of lipid extraction on the stable isotope composition, as lipids are suggested to be removed from samples when their C:N ratios exceed 3.5 (presumed to be lipid-rich) [55,59].

Table 1.
δ13C, δ15N, and trophic position (TP) value of M. pelagios and R. typus in different sex and size groups from Taiwan waters.
The S–W normality test for the δ13C values were asymmetrical for both M. pelagios (Shapiro–Wilk normality test, W = 0.96, p < 0.05) and R. typus (Shapiro–Wilk normality test, W = 0.89, p < 0.05), but δ15N values were symmetrical for both M. pelagios (Shapiro–Wilk normality test, W = 0.99, p = 0.98) and R. typus (Shapiro–Wilk normality test, W = 0.99, p = 0.75). No significant difference was observed between male and female individuals in δ13C for M. pelagios (Kruskal–Wallis test, H = 0.54, p = 0.46), R. typus (Kruskal–Wallis test, H = 0.23, p = 0.63), and in δ15N for R. typus (Student’s t-test, t = 1.23, p = 0.11); however, δ15N was significantly different between female and male M. pelagios (Student’s t-test, t = 1.83, p < 0.05). No significant difference was observed between body size and sex for both M. pelagios in terms of δ13C (ANOVA, F = 1.45, p = 0.24) and δ15N (ANOVA, F = 2.53, p = 0.09), as well as for R. typus in terms of δ13C (ANOVA, F = 0.65, p = 0.52) and δ15N (ANOVA, F = 0.96, p = 0.39).
Figure 2 presents the result of SIBER analysis for two species and sexes; the niche width of R. typus was broader than that of M. pelagios. Their isotopic niches were separated into two groups (overlap% = 0), but medium to high overlap was found between male and female individuals for both species (Figure 2). The δ13C of M. pelagios (−17.20 ± 0.69) was lower than that of R. typus (−15.67 ± 0.78), indicating different habitats (Table 1). Although δ15N was comparable between the two species, the TP of R. typus (3.33 ± 0.53) was higher than that of M. pelagios (2.62 ± 0.27), implying that R. typus was distributed around Taiwan waters (Table 1). Furthermore, the isotopic niche width of males was larger than that of females for both species (Table 2).
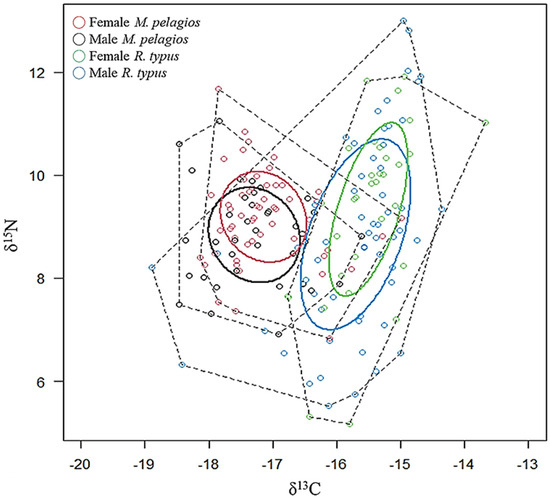
Figure 2.
Individual stable isotope value (δ13C and δ15N) bio-plot, SEAc (small sample size corrected SIBER ellipse area), and TA (convex hull area) of M. pelagios and R. typus. (Solid line: SEAc, dash line: TA).

Table 2.
The convex hull area (TA), standard ellipse area (SEA), and small sample size corrected SIBER ellipse area (SEAc) of M. pelagios and R. typus in different sex and size groups (♀: female; ♂: male).
3.2. SIA for M. pelagios and R. typus: Intraspecific Comparison
3.2.1. M. pelagios
For M. pelagios, the stable isotopic niche width was similar across different sizes and maturity stages for both sexes (SEAc: 1.63, 2.19, and 1.94 for Groups I, II, and III in males; 3.17, 1.30, and 2.00 for Groups I, II, and III in females, respectively) (Table 2). The niche of female and male sharks displayed medium to high overlap in Groups I and II but only medium overlap in Group III, indicating potential sexual segregation (Figure 3). The δ13C value increased slightly, but the δ15N value decreased slightly with the increase in the body size of M. pelagios (Figure 4).
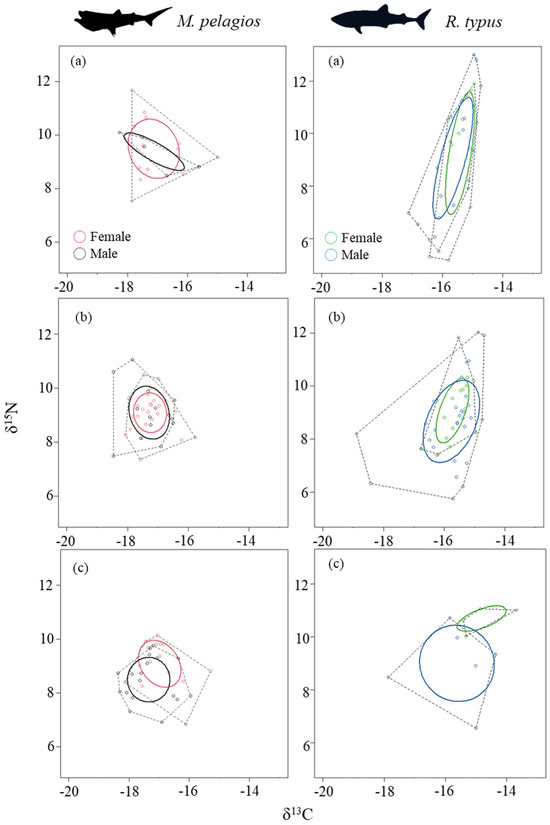
Figure 3.
The SEAc (small sample size corrected SIBER ellipse area) and TA (convex hull area) difference between (a) group I; (b) group II; and (c) group III of female and male M. pelagios and R. typus. (Solid line: SEAc, dash line: TA).
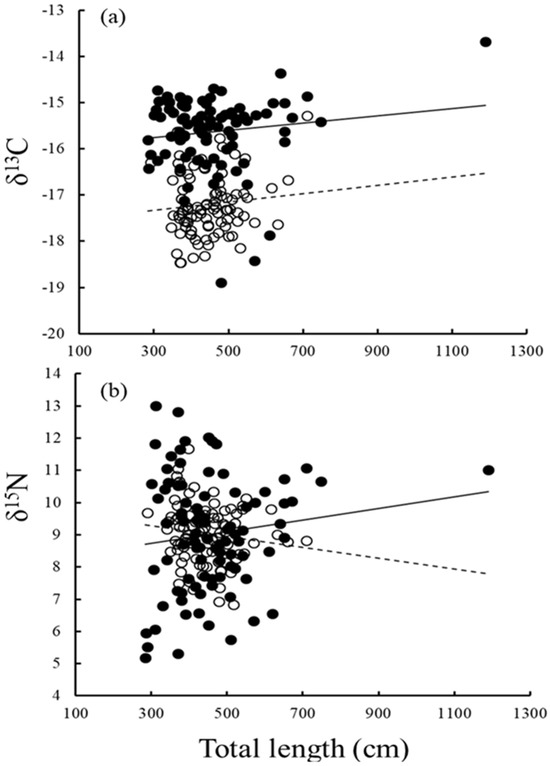
Figure 4.
Relationship between (a) δ13C and (b) δ15N value and total length of M. pelagios (○, ---) and R. typus (●, —).
3.2.2. R. typus
The stable isotopic niche width shifted between different size groups of R. typus. The niche width increased with an increase in the body size of male individuals (SEAc: 3.25, 4.27, and 6.91, respectively), but not in female individuals (SEAc: 3.01, 1.80, and 1.41, respectively), suggesting sexual segregation (Table 2). The niche overlap between male and female R. typus was medium or high in Groups I and II and low in Group III (Figure 3). Both δ13C and δ15N values increased slightly with body size in R. typus, indicating ontogenetic changes (Figure 4).
4. Discussion
Sample collection of large shark species, especially filter-feeding sharks, is challenging due to their body size and unpredictable migration/movement. This study obtained tissue specimens through cooperation with fishers and observers participating in the catch reporting system of the Taiwan Fisheries Agency. We also attempted to collect stomach content samples from M. pelagios. Euphausiacea and Medusozoa (jellyfish) were the most commonly observed prey; however, most planktonic prey items were too fragile to be reliably identified. In most cases, the stomach contents were digested into small pieces, which prevented us from determining the number of prey, which is consistent with the observation of a previous study [50]. Additionally, there was only one mature R. typus individual (>10 m TL) in this study and over 90% of the individuals were immature or juveniles, the bias towards immature individuals is not unusual in other studies [40,60,61]. Furthermore, juveniles, immature, and mature M. pelagios individuals were included in this study, with 36% of the specimens being mature, providing a relatively complete size spectrum.
In this study, ethanol storage was chosen as a reasonable method for preservation because the tissue samples were originally collected for molecular research. Before the fishery ban, M. pelagios were sold in the market, and only small pieces of tissue such as skin or white muscle were available for scientific use. Alongside this, fin clips were the only sample we took from R. typus because of the Animal Conservation Act. Differences in the species, tissue type, sample storage method, and experimental treatment lead to differences in the metabolic rate estimated and can affect the SIA results [62,63]. However, a study has demonstrated that the relatively high lipid content in the muscles and livers of certain large-bodied terrestrial omnivores does not significantly affect stable isotope estimates and that ethanol preservation offers a viable alternative for storing tissues when freezing or drying is impractical [64]. Arrington and Winemiller also indicated that different preservation methods such as formalin-ethanol had minimal and consistent directional effects on stable isotopic signatures for fish, implying that ethanol is acceptable for use in stable isotope analysis [54].
According to the previous study, tissue turnover rates in large, long-lived fishes like elasmobranchs are primarily influenced by catabolism, with younger animals experiencing more pronounced effects [65]. Also, fin clips were suggested as composed of several structural components such as cartilage, skin, and small amounts of muscle, providing a mixed representation of the feeding and environment of the study animal [65]. Previous study indicated the turnover rate of plasma for R. typus is approximately 70–200 days, but the fin cartilage appeared to have longer turnover rates (230–851 days) [41]. In addition, different methods for preservation and preparation of R. typus tissue were examined for isotopic analysis. Hussey et al. compared the δ13C and δ15N values between non-lipid extracted (BULK) and lipid extracted (LE) frozen white muscle samples of R. typus (without rinsed), indicating that both δ13C and δ15N increased (+3.3‰; +0.4–0.6‰) after LE process [66]. Nevertheless, Marcus et al. revealed that the δ13C and δ15N values of R. typus dermal tissue changed through LE (+1.7‰; +0.9‰), deionized water rinsed (DIW) (−1.1‰; +1.7‰), and LE + DIW (+1.3‰; +1.3‰) [63]. Additionally, numerous studies have mentioned that urea may affect SIA results; however, after conducting experiments on 14 elasmobranch species, Carlisle et al. ultimately concluded that while urea generally has a direct influence on δ15N values, the effects of urea and lipids on δ13C and δ15N vary depending on the relative concentration of these compounds between species [67]. Different treatment experiments were not taken in this study, all the tissue samples were originally collected and preserved in ethanol for analysis. The previous studies have shown various results on different tissue types or treatments but are unable to find an explicit method for SIA data correction for our results [63,66]. However, the outcomes of this study are still likely to reflect dietary and habitat use tendencies integrated over long-term scales from several months to years of M. pelagios and R. typus. Future research is suggested to validate the results of SIA by conducting different species, tissue samples, and treatments.
SIA revealed differences in the feeding strategies and trophic niches between M. pelagios and R. typus (Figure 2). Abrantes and Sheaves observed a linear negative relationship between δ15N and δ13C, suggesting this is the feature of primary producers, primary consumers, or secondary consumers; this finding not only aligns with our SIA results for M. pelagios but also agrees with our observation that M. pelagios feeds mainly on zooplanktonic preys [68]. However, there is a significant difference in δ15N between male and female M. pelagios, which may be caused by sexual segregation, different foraging grounds, or metabolic rates; further evidence from SCA is required to clarify this observation. SIA demonstrated a positive relationship between δ15N and δ13C for R. typus, revealing that for R. typus has a more complex diet than filter feeding. Studies have implied that R. typus can feed on a broad spectrum of prey, which is consistent with our finding of a wide trophic niche of R. typus. Nakaya et al. stated that M. pelagios is an engulfment feeder and has special morphological characteristics, such as a large mouth, long jaw cartilages, and flexible skin around the pharynx, which are similar to those of engulfment-feeding whale species, such as humpback whale (Megaptera novaeangliae) [69]. This foraging strategy seems beneficial for slow-swimming species, such as M. pelagios, which has a swim speed of 1.5 km h−1 [46]. By contrast, R. typus displays a more active suction-filtering behavior, allowing more opportunities to prey on small fishes and squids, which have better swimming ability [35,37]. There was even some evidence showing the rapid mouth-gulping behavior of R. typus to consume prey close to the seabed in shallow water if the prey densities are large enough [70,71]. This study indicates that as the filtering feeders inhabiting the western North Pacific Ocean, M. pelagios and R. typus have distinct feeding strategies.
The lack of trophic niche overlaps between M. pelagios and R. typus suggests different habitat use (Figure 2). Thums et al. remarked that R. typus usually spends time gaining energy from the sun at the sea surface to regulate body temperature [72]. Moreover, it aggregates and forages at or near the sea surface, implying that it mainly inhabits shallow waters [73,74,75,76]. By contrast, M. pelagios are distributed in deeper waters, usually around 100 m, and rarely appear near the surface, making their discovery challenging [43,46,77]. The two filter feeders were also found to be distributed in different parts of Taiwan waters: R. typus was collected from coastal set-net fishery around Taiwan waters, whereas M. pelagios was mainly caught in large-mesh driftnet fishery from the eastern waters of Taiwan (Figure 1).
The trophic niche of male sharks was larger, implying a wider distribution, for both M. pelagios and R. typus (SEAc: 2.11 and 4.49, respectively; Table 2). In many cases, male sharks have been reported to display more active movement than females. Kock et al. described that female great white sharks (Carcharodon carcharias) were frequently found offshore areas, whereas males were rarely discovered in False Bay [78]. Female bull sharks (Carcharhinus leucas) were caught and monitored more frequently in coastal waters; however, male sharks were only found in isolated waters far from the coast in New Caledonia [79]. A significant difference was also found in δ15N between male and female M. pelagios in this study, which may be caused by sexual segregation, metabolic rate, or prey items from different habitats during their life history. Yu et al. reported a widespread distribution of male M. pelagios in different waters, including the western and eastern Pacific Ocean, but female sharks were spotted mainly in the western North Pacific Ocean [43]. Male sharks are likely to move in a wide area to increase their chances of meeting females and mating, whereas females tend to focus on coastal areas, which have abundant food, and may stay at a particular place to give birth [80,81].
Trophic position (TP) estimation is helpful for ecosystem-based fisheries management strategies; however, there is a wide spectrum of opinions on the estimation methods, especially the empirically determined trophic enrichment. Minagawa and Wada provided critical evidence for the stable isotope enrichment of δ15N along food chains, demonstrating a consistent TEF of approximately 3.4‰ (ranging from 1.3 to 5.3‰) by measuring the animals from the East China Sea, The Bering Sea, Lake Ashinoko and Usujiri intertidal zone [57]. This was followed by a previous study, which suggested the simplest model for estimating the trophic position of secondary consumers, with the mean trophic fractionation of d15N is 3.4‰ (1 SD = 1‰), which was widely applicable [55]. Additionally, the compound-specific isotope analysis of amino acids (AA-CSIA) was proposed as an unbiased approach to evaluating trophic dynamics in food webs by distinguishing between “source” and “trophic” amino acids (the difference between δ15Nglutamic acid and δ15Nphenylalanine). Some research demonstrated that isotopic fractionation from processes like deamination and transamination results in a δ15N enrichment with a TEF of 7.6‰ between glutamic acid and phenylalanine, while dietary protein quality further influences TEFs, with herbivores showing a TEF of ~7.6‰ and epibenthic carnivores (sand tiger shark, Carcharias taurus; lemon shark, Negaprion brevirostris; and leopard shark, Triakis semifasciata) exhibiting a lower TEF (<7.6‰) [82,83]. However, several studies have highlighted considerable variation in TEFs (even from AA-CSIA calculation) due to factors such as species, tissue type, environment, etc. [84,85,86]. As options vary, this study follows the widely adopted TP calculation method and TEF proposed by Post to provide insights into M. pelagios and R. typus [55]. Thus, it is recommended that future experimental research focus on examining TEFs in indicator species, such as filter-feeding elasmobranchs.
Based on the mean TP values, both M. pelagios and R. typus were inferred to be lower trophic level consumers, but SIA provided different information on their life history and feeding habits. Both M. pelagios and R. typus exhibited sexual segregation and ontogenetic changes, and the niche overlap between male and female sharks in Group III was medium for M. pelagios but low for R. typus (Figure 3c, Table 2). Sexual segregation may result from various factors, such as forced mating behavior from male sharks, reduced resource competition, and finding an appropriate area for offspring [87]. Ontogenetic shifts are common in elasmobranchs throughout their different life stages, different diet preferences between juveniles and adults have been suggested for R. typus [88]. Greenland sharks (Somniosus microcephalus) exhibited an ontogenetic dietary shift from low-trophic-level prey, such as squids, to high-trophic-level prey, such as seals and benthic fishes, implying that the larger sharks can prey on fast-swimming species [89]. The δ13C and δ15N values of blue shark (Prionace glauca) indicated ontogenetic changes in prey consumption and habitats between life stages, with small and large individuals preferring coastal waters, whereas large juveniles preferred oceans [90].
We observed a slight positive correlation between δ13C and body length for both M. pelagios and R. typus, indicating that they move to a more productive or inshore environment as they grow, with R. typus preferring a more productive environment (sea surface) than M. pelagios. R. typus caught in set nets around Taiwan were all from coastal waters no deeper than 50 m, which were enrich producers, whereas M. pelagios mainly inhabits deeper waters, usually approximately 100 m, according to the operation depth of a gillnet and tracking study [46]. Together, data from previous studies indicate that M. pelagios may be born in warm tropical waters, which is a lower productive environment, and these sharks may then move toward the zooplankton-rich current as they grow [45,50,51]. Furthermore, the findings of Borrell et al. on δ13C and body length for R. typus were similar to those in our study [37]. Together, these results imply that whale sharks are born in open or deeper waters, where they grow for a period, and then move toward productive coastal waters to feed on planktonic prey [91,92,93]. In other words, a large dietary component of juvenile and submature R. typusi is derived from benthic and coastal habitats [38]. These sharks give birth in low-productive waters, likely to protect their young from other predators [93].
The relationship between δ15N and body length differed between M. pelagios and R. typus: as the body size increased, the δ15N values of M. pelagios decreased slightly, whereas those of R. typus increased, although we lack large and mature R. typus individuals (Figure 4, Table 1). Our data indicated that M. pelagios is a secondary consumer, engaging in engulfment feeding of mainly small zooplanktonic prey, such as Euphausiacea and Medusozoa, in all life stages. However, how changes in the metabolic rate with growth affect δ15N remains unclear. The δ15N data of R. typus in this study suggested that it feeds on higher-trophic-level prey. A study implied that R. typus may change their habitat and prey preferences as they grow; juveniles may cruise various waters for feeding and growth, which is consistent with the wide range of their δ15N values, whereas larger individuals tend to feed on the higher-trophic-level prey because of better swimming ability and well-developed filtering structures on the gills [14,37,94,95,96].
5. Conclusions
In summary, our analysis of M. pelagios and R. typus around Taiwan waters revealed distinct feeding strategies and habitat use despite both species inhabiting the western North Pacific. M. pelagios is an engulfment feeder targeting small zooplankton across all life stages, with sexual segregation suggesting different habitat use by mature males and females. In contrast, R. typus shows ontogenetic shifts in diet and habitat, with larger individuals capable of active suction feeding. Due to limited stomach content samples, further SCA and SIA across regions, sexes, and sizes are needed. This study provides key biological insights to inform regional fisheries management and support species-specific conservation strategies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.-J.Y., S.-J.J., and H.-H.H.; methodology, C.-J.Y. and K.-M.L.; validation formal analysis, C.-J.Y. and K.-M.L.; data curation, C.-J.Y. and H.-H.H.; writing—original draft preparation, C.-J.Y.; writing—review and editing, C.-J.Y., S.-J.J., H.-H.H., K.-M.L., and A.Y.; visualization, C.-J.Y. and H.-H.H.; supervision, S.-J.J., K.-M.L., and A.Y.; project administration, S.-J.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Fisheries Agency, Council of Agriculture, Taiwan, R. O. C. (grant numbers FA104-11.1.4-F1-2), the funding was to S.S.J. and H.H.H. for sample collection. We also express our gratitude to the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan, R. O. C. (grant numbers MOST 104-2313-B-019-002, MOST 107-2611-M-019-013), and Ocean Conservation Administration, Ocean Affairs Council, Taiwan, R. O. C. (grant numbers 108-C-43, 109-C-24) for the projects and funding to S.S.J. and C.J.Y. for stable isotope analysis. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted under the approved animal use protocols #112014 and #113015, issued by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC), College of Life Science, National Taiwan Ocean University (NTOU), Taiwan. These approvals serve as evidence of ethical compliance with the institution’s guidelines for animal research.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data and materials used in this research are not publicly available due to confidentiality but can be made available by the authors upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the observers from Taiwan Fisheries Sustainable Development Association and Taiwan Ocean Conservation and Fisheries Sustainability Foundation, and all the crew from Nanfangao, Hualien, and Chenggong fish market, for making contact with a research institution and collecting the sample. We would like to thank Lisa Hoopes for the comments that further improve our manuscript. Finally, we would like to extend particular thanks to Y. H. Lin and members from the National Taiwan Ocean University and George Chen Shark Research Center, who assisted with the field trip, sample collecting and experiment.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Vaudo, J.J.; Heithaus, M.R. Dietary niche overlap in a nearshore elasmobranch mesopredator community. Mar. Ecol. Prog. 2011, 425, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barría, C.; Coll, M.; Navarro, J. Unravelling the ecological role and trophic relationships of uncommon and threatened elasmobranchs in the western Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. 2015, 539, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipley, O.N.; Murchie, K.J.; Frisk, M.G.; O’Shea, O.R.; Winchester, M.M.; Brooks, E.J.; Pearson, J.; Power, M. Trophic niche dynamics of three nearshore benthic predators in The Bahamas. Hydrobiologia 2018, 813, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, M.J. Elasmobranchs. In Fish Population Dynamics; Gulland, J.A., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd: New York, NY, USA, 1977; pp. 187–215. [Google Scholar]
- King, J.R.; McFarlane, G.A. Marine fish life history strategies: Applications to fishery management. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2003, 10, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, L.N.; Krawchuk, M.A.; Dulvy, N.K. Why have global shark and ray landings declined: Improved management or overfishing? Fish Fish. 2016, 17, 438–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacoureau, N.; Rigby, C.L.; Kyne, P.M.; Sherley, R.B.; Winker, H.; Carlson, J.K.; Fordham, S.V.; Barreto, R.; Fernando, D.; Francis, M.P.; et al. Half a century of global decline in oceanic sharks and rays. Nature 2021, 589, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowder, L.; Norse, E. Essential ecological insights for marine ecosystem-based management and marine spatial planning. Mar. Policy 2008, 32, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, K.L.; Leslie, H.M. Ecosystem Based Management for the Oceans; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; 392p. [Google Scholar]
- Hyslop, E.J. Stomach contents analysis—A review of methods and their application. J. Fish Biol. 1980, 17, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessa, R.P.; Almeida, Z. Feeding habits of the bonnethead shark, Sphyrna tiburo, from northern Brazil. Cybium 1998, 22, 383–394. [Google Scholar]
- Joyce, W.N.; Campana, S.E.; Natanson, L.J.; Kohler, N.E.; Pratt, H.L., Jr.; Jensen, C.F. Analysis of stomach contents of the porbeagle shark (Lamna nasus Bonnaterre) in the northwest Atlantic. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2002, 59, 1263–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braccini, J.M. Feeding ecology of two high-order predators from south-eastern Australia: The coastal broadnose and the deepwater sharpnose sevengill sharks. Mar. Ecol. Prog. 2008, 371, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, D.A.; Murillo-Cisneros, D.; Elorriaga-Verplancken, F.R.; Hacohen-Domené, A.; De La Parra, R.; Gonzalez-Armas, R.; Galvan-Magaña, F. Stable isotope assessment of whale sharks across two ocean basins: Gulf of California and the Mexican Caribbean. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2020, 527, 151359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feddern, M.L.; Holtgrieve, G.W.; Ward, E.J. Stable isotope signatures in historic harbor seal bone link food web-assimilated carbon and nitrogen resources to a century of environmental change. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 2328–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedden, A.V.; Rogers, T.L. Stable isotope oscillations in whale baleen are linked to climate cycles, which may reflect changes in feeding for humpback and Southern right whales in the Southern Hemisphere. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 832075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.B.; Bustamante, P.; Guillou, G.; Arkhipkin, A.I. Using stable isotope chronologies within squid gladii (Doryteuthis gahi) to evaluate dietary differences by fishing region and season. Mar. Ecol. Prog. 2023, 703, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, B.J.; Fry, B. Stable isotopes in ecosystem studies. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1987, 18, 293–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeNiro, M.J.; Epstein, S. Carbon isotopic evidence for different feeding patterns in two hyrax species occupying the same habitat. Science 1978, 201, 906–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeNiro, M.J.; Epstein, S. Influence of diet on the distribution of nitrogen isotopes in animals. Geochim Cosmochim Acta. 1981, 45, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- France, R.L. Carbon-13 enrichment in benthic compared to planktonic algae—Foodweb implications. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1995, 124, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.J.; Cahoon, L.B. Stable isotope analyses differentiate between different trophic pathways supporting rocky-reef fishes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1993, 95, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, G.C.A.; Rizzuto, S.; Stürup, M.; Inger, R.; Barker, S.; van Wyk, J.H.; Towner, A.V.; Hughes, W.H.O. Sex, size and isotopes: Cryptic trophic ecology of an apex predator, the white shark Carcharodon carcharias. Mar. Biol. 2018, 165, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galindo-Rosado, M.A.; Galván-Magaña, F.; Torres-Rojas, Y.E.; Delgado-Huertas, A.; Aguiñiga-García, S. Use of δ15N and δ13C in reconstructing the ontogenetic feeding habits of silky shark (Carcharhinus falciformis): Reassessing their trophic role in the Eastern Tropical Pacific Ocean. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2023, 106, 657–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matich, P.; Heithaus, M.R.; Layman, C.A. Size-based variation in intertissue comparisons of stable carbon and nitrogen isotopic signatures of bull sharks (Carcharhinus leucas) and tiger sharks (Galeocerdo cuvier). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2010, 67, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Aguilar, S.B.; Escobar-Sánchez, O.; Galván-Magaña, F.; Abitia-Cárdenas, L.A. Trophic ecology of the blue shark (Prionace glauca) based on stable isotopes (δ13C and δ15N) and stomach content. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2016, 96, 1403–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estupiñán-Montaño, C.; Tamburin, E.; Delgado-Huertas, A. Stable isotope evidence for movements of hammerhead sharks Sphyrna lewini, connecting two natural protected areas in the Colombian Pacific. Mar. Biodivers. 2021, 51, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossi, M.C.; Coppola, D.; Baini, M.; Giannetti, M.; Guerranti, C.; Marsili, L.; Panti, C.; de Sabata, E.; Clò, S. Large filter feeding marine organisms as indicators of microplastic in the pelagic environment: The case studies of the Mediterranean basking shark (Cetorhinus maximus) and fin whale (Balaenoptera physalus). Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 100, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croll, D.A.; Dewar, H.; Dulvy, N.K.; Fernando, D.; Francis, M.P.; Galván-Magaña, F.; Hall, M.; Heinrichs, S.; Marshall, A.; Mccauley, D.; et al. Vulnerabilities and fisheries impacts: The uncertain future of manta and devil rays. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. 2016, 26, 562–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germanov, E.S.; Marshall, A.D.; Hendrawan, I.G.; Admiraal, R.; Rohner, C.A.; Argeswara, J.; Wulandari, R.; Himawan, M.R.; Loneragan, N.R. Microplastics on the menu: Plastics pollute Indonesian manta ray and whale shark feeding grounds. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 487857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compagno, L.J.V. Sharks of the World: An Annotated and Illustrated Catalogue of Shark Species Know to Date; FAO Species Catalogue for Fishery Purposes; No. 1, Vol. 2. Bullhead, Mackerel and Carpet Sharks (Heterodontiformes, Lamniformes and Orectolobiformes); FAO: Rome, Italy, 2001; 269p. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.T.; Liu, K.M.; Joung, S.J. Preliminary report on Taiwan’s whale shark fishery. In Elasmobranch Biodiversity, Conservation and Management: Proceedings of the International Seminar and Workshop, Sabah, Malaysia, July 1997 IUCN SSC.; Fowler, S.L., Reed, T.M., Dipper, F.A., Eds.; Shark Specialist Group, IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2002; pp. 162–167. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, H.H.; Joung, S.J.; Hueter, R.E.; Liu, K.M. Age and growth of the whale shark (Rhincodon typus) in the north-western Pacific. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2014, 65, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, J.J.; Meekan, M.G.; Hsu, H.H.; Fanning, L.P.; Campana, S.E. Annual bands in vertebrae validated by bomb radiocarbon assays provide estimates of age and growth of whale sharks. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, E.; Nelson, D.R. Young whale sharks, Rhincodon typus, feeding on a copepod bloom near La Paz, Mexico. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1997, 50, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.D.; Eckert, S.A. Foraging ecology of whale sharks (Rhincodon typus) within Bahía de Los Angeles, Baja California Norte, México. Fish. Res. 2007, 84, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrell, A.; Aguilar, A.; Gazo, M.; Kumarran, R.P.; Cardona, L. Stable isotope profiles in whale shark (Rhincodon typus) suggest segregation and dissimilarities in the diet depending on sex and size. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2011, 92, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, L.; Virtue, P.; Nichols, P.D.; Ferreira, L.C.; Pethybridge, H.; Meekan, M. Stable isotope analysis of dermal tissue reveals foraging behavior of whale sharks at Ningaloo Reef, Western Australia. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prebble, C.; Mary, E. Residency and Trophic Ecology of Juvenile Whale Sharks (Rhincodon typus) in the Western Indian Ocean. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK, 2018; 170p. [Google Scholar]
- Boldrocchi, G.; Omar, M.; Azzola, A.; Bettinetti, R. The ecology of the whale shark in Djibouti. Aquat. Ecol. 2020, 54, 535–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, A.S.; Matsumoto, R.; Chikaraishi, Y.; Miyairi, Y.; Yokoyama, Y.; Sato, K.; Ohkouchi, N.; Nagata, T. Enhancing insights into foraging specialization in the world’s largest fish using a multi-tissue, multi-isotope approach. Ecol. Monogr. 2019, 89, e01339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, L.R.; Compagno, L.J.V.; Struhsaker, P.J. Megamouth—A new species, genus, and family of lamnoid shark (Megachasma pelagios, family Megachasmidae) from the Hawaiian Islands. Proc. Calif. Acad. Sci. 1983, 43, 87–110. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.J.; Joung, S.J.; Hsu, H.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Hsieh, T.C.; Liu, K.M.; Yamaguchi, A. Spatial–temporal distribution of megamouth shark, Megachasma pelagios, inferred from over 250 individuals recorded in the three oceans. Animals 2021, 11, 2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, J.I.; Clark, E.; Yano, K.; Nakaya, K. The Gross anatomy of the female reproductive tract and associated organs of the Fukuoka megamouth shark (Megachasma pelagios). In Biology of the Magamouth Shark; Yano, K., Morrissey, J.F., Yabumoto, Y., Nakaya, K., Eds.; Tokai University Press: Tokyo, Japan, 1997; pp. 115–119. [Google Scholar]
- Nakaya, K. Biology of the megamouth shark, Megachasma pelagios (Lamniformes: Megachasmidae). In Proceedings of an International Symposium, into the Unknown, Researching Mysterious Deep-Sea Animals; Okinawa Churaumi Aquarium: Okinawa, Japan, 2010; pp. 69–83. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.R.; McKibben, J.N.; Strong, W.R.; Lowe, C.G.; Sisneros, J.A.; Schroeder, D.M.; Lavenberg, R.J. An acoustic tracking of a megamouth shark, Megachasma pelagios: A crepuscular vertical migrator. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1997, 49, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerkin, P.J.; Arostegui, M.C.; Chiang, W.C.; Lin, S.J.; Miller, C.D.; Braun, C.D. First telemetry insights into the movements and vertical habitat use of megamouth shark (Megachasma pelagios) in the northwest Pacific. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2024, 212, 104385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchatelet, L.; Moris, V.C.; Tomita, T.; Mahillon, J.; Sato, K.; Behets, C.; Mallefet, J. The megamouth shark, Megachasma pelagios, is not a luminous species. PLoS ONE. 2020, 15, e0242196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, K.; Toda, M.; Uchida, S.; Yasuzumi, F. Gross anatomy of the viscera and stomach contents of a megamouth shark, Megachasma pelagios, from Hakata Bay, Japan, with a comparison of the intestinal structure of other planktivorous elasmobranchs. In Biology of the Magamouth Shark; Yano, K., Morrissey, J.F., Yabumoto, Y., Nakaya, K., Eds.; Tokai University Press: Tokyo, Japan, 1997; pp. 105–113. [Google Scholar]
- Sawamoto, S.; Matsumoto, R. Stomach contents of a megamouth shark Megachasma pelagios from the Kuroshio Extension: Evidence for feeding on a euphausiid swarm. Plankton Benthos Res. 2012, 7, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- de Moura, J.F.; Merico, A.; Montone, R.C.; Silva, J.; Seixas, T.G.; de Oliveira Godoy, J.M.; Pierre, T.D.; Hauser-Davis, R.A.; Di Beneditto, A.P.M.; Reis, E.C.; et al. Assessment of trace elements, POPs, 210Po and stable isotopes (15N and 13C) in a rare filter-feeding shark: The megamouth. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 95, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.H.; Joung, S.J.; Liu, K.M. Fisheries, management and conservation of the whale shark Rhincodon typus in Taiwan. J. Fish. Boil. 2012, 80, 1595–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyne, P.M.; Liu, K.M.; Simpfendorfer, C. Megachasma pelagios. In the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species; IUCN Press: Gland, Switzerland, 2019; p. e.T39338A124402302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrington, D.A.; Winemiller, K.O. Preservation effects on stable isotope analysis of fish muscle. Trans. Am. 2002, 131, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, D.M. Using stable isotopes to estimate trophic position: Models, methods, and assumptions. Ecology 2002, 83, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, P.C.; Okuda, N.; Yeh, C.F.; Wang, P.L.; Gong, G.C.; Hsieh, C.H. Carbon and nitrogen isoscape of particulate organic matter in the East China Sea. Prog. Oceanogr. 2021, 197, 102667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minagawa, M.; Wada, E. Stepwise enrichment of 15N along food chains: Further evidence and the relation between δ15N and animal age. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 1984, 48, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.L.; Inger, R.; Parnell, A.C.; Bearhop, S. Comparing isotopic niche widths among and within communities: SIBER–Stable Isotope Bayesian Ellipses in R. J. Anim. Ecol. 2011, 80, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, D.M.; Layman, C.A.; Arrington, D.A.; Takimoto, G.; Quattrochi, J.; Montana, C.G. Getting to the fat of the matter: Models, methods and assumptions for dealing with lipids in stable isotope analyses. Oecologia 2007, 152, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowat, D.; Brooks, K.; March, A.; McCarten, C.; Jouannet, D.; Riley, L.; Jeffreys, G.; Perri, M.; Vely, M.; Pardigon, B. Long-term membership of whale sharks (Rhincodon typus) in coastal aggregations in Seychelles and Djibouti. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 62, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohner, C.A.; Richardson, A.J.; Prebble, C.E.; Marshall, A.D.; Bennett, M.B.; Weeks, S.J.; Cliff, G.; Wintner, S.P.; Pierce, S.J. Laser photogrammetry improves size and demographic estimates for whale sharks. PeerJ 2015, 3, e886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacNeil, M.A.; Skomal, G.B.; Fisk, A.T. Stable isotopes from multiple tissues reveal diet switching in sharks. Mar. Ecol. Prog. 2005, 302, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, L.; Virtue, P.; Nichols, P.D.; Meekan, M.G.; Pethybridge, H. Effects of sample treatment on the analysis of stable isotopes of carbon and nitrogen in zooplankton, micronekton and a filter-feeding shark. Mar. Biol. 2017, 164, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javornik, J.; Hopkins, I.I.I.J.B.; Zavadlav, S.; Levanič, T.; Lojen, S.; Polak, T.; Jerina, K. Effects of ethanol storage and lipids on stable isotope values in a large mammalian omnivore. J. Mammal. 2019, 100, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussey, N.E.; MacNeil, M.A.; Olin, J.A.; McMeans, B.C.; Kinney, M.J.; Chapman, D.D.; Fisk, A.T. Stable isotopes and elasmobranchs: Tissue types, methods, applications and assumptions. J. Fish Biol. 2012, 80, 1449–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussey, N.E.; Olin, J.A.; Kinney, M.J.; McMeans, B.C.; Fisk, A.T. Lipid extraction effects on stable isotope values (δ13C and δ15N) of elasmobranch muscle tissue. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2012, 434, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlisle, A.B.; Litvin, S.Y.; Madigan, D.J.; Lyons, K.; Bigman, J.S.; Ibarra, M.; Bizzarro, J.J. Interactive effects of urea and lipid content confound stable isotope analysis in elasmobranch fishes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 74, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrantes, K.; Sheaves, M. Use of a δ13C–δ15N relationship to determine animal trophic positions in a tropical Australian estuarine wetland. Austral. Ecol. 2010, 35, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaya, K.; Matsumoto, R.; Suda, K. Feeding strategy of the megamouth shark Megachasma pelagios (Lamniformes: Megachasmidae). J. Fish. Biol. 2008, 73, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohner, C.A.; Armstrong, A.J.; Pierce, S.J.; Prebble, C.E.; Cagua, E.F.; Cochran, J.E.; Berumen, M.L.; Richardson, A.J. Whale sharks target dense prey patches of sergestid shrimp off Tanzania. J. Plankton Res. 2015, 37, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Antonio, B.; Barry, C.; Beck, A. Whale shark (Rhincodon typus) observed gulping on the seafloor at Ningaloo reef aggregation site. Mar. Freshw. Behav. Physiol. 2024, 57, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thums, M.; Meekan, M.; Stevens, J.; Wilson, S.; Polovina, J. Evidence for behavioural thermoregulation by the world’s largest fish. J. R. Soc. 2013, 10, 20120477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyman, W.D.; Graham, R.T.; Kjerfve, B.; Johannes, R.E. Whale sharks Rhincodon typus aggregate to feed on fish spawn in Belize. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 215, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, P.J.; Maslanka, M.; Hueter, R.E.; Davis, R.L.; De la Parra, R.; Mulvany, S.L.; Habegger, M.L.; Strother, J.A.; Mara, K.R.; Gardiner, J.M.; et al. Feeding anatomy, filter-feeding rate, and diet of whale sharks Rhincodon typus during surface ram filter feeding off the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico. Zoology 2010, 113, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequeira, A.M.; Mellin, C.; Fordham, D.A.; Meekan, M.G.; Bradshaw, C.J. Predicting current and future global distributions of whale sharks. Glob. Change Biol. 2014, 20, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cade, D.E.; Levenson, J.J.; Cooper, R.; de la Parra, R.; Webb, D.H.; Dove, A.D. Whale sharks increase swimming effort while filter feeding, but appear to maintain high foraging efficiencies. J. Exp. Biol. 2020, 223, jeb224402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, D.A.; Dando, M.; Fowler, S. Sharks of the World: A Complete Guide; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2021; p. 607. [Google Scholar]
- Kock, A.; O’Riain, M.J.; Mauff, K.; Meÿer, M.; Kotze, D.; Griffiths, C. Residency, habitat use and sexual segregation of white sharks, Carcharodon carcharias in False Bay, South Africa. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werry, J.M.; Clua, E. Sex-based spatial segregation of adult bull sharks, Carcharhinus leucas, in the New Caledonian great lagoon. Aquat. Living Resour. 2013, 26, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeney, D.B.; Heupel, M.R.; Hueter, R.E.; Heist, E.J. Microsatellite and mitochondrial DNA analyses of the genetic structure of blacktip shark (Carcharhinus limbatus) nurseries in the northwestern Atlantic, Gulf of Mexico, and Caribbean Sea. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 1911–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knip, D.M.; Heupel, M.R.; Simpfendorfer, C.A. Habitat use and spatial segregation of adult spottail sharks Carcharhinus sorrah in tropical nearshore waters. J. Fish Biol. 2012, 80, 767–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chikaraishi, Y.; Ogawa, N.O.; Kashiyama, Y.; Takano, Y.; Suga, H.; Tomitani, A.; Miyashita, H.; Kitazato, H.; Ohkouchi, N. Determination of aquatic food-web structure based on compound-specific nitrogen isotopic composition of amino acids. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2009, 7, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoen, D.K.; Kim, S.L.; Hussey, N.E.; Wallsgrove, N.J.; Drazen, J.C.; Popp, B.N. Amino acid 15N trophic enrichment factors of four large carnivorous fishes. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2014, 453, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinnegar, J.K.; Polunin, N.V.C. Differential fractionation of δ13C and δ15N among fish tissues: Implications for the study of trophic interactions. Funct. Ecol. 1999, 13, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderklift, M.A.; Ponsard, S. Sources of variation in consumer-diet δ 15 N enrichment: A meta-analysis. Oecologia 2003, 136, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, J.J.; Wallsgrove, N.J.; Popp, B.N.; Holland, K.N. Nursery habitat use and foraging ecology of the brown stingray Dasyatis lata determined from stomach contents, bulk and amino acid stable isotopes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. 2011, 433, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucientes, G.R.; Queiroz, N.; Sousa, L.L.; Tarroso, P.; Sims, D.W. Sexual segregation of pelagic sharks and the potential threat from fisheries. Biol. Lett. 2009, 5, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketchum, J.T.; Galván-Magaña, F.; Klimley, A.P. Segregation and foraging ecology of whale sharks, Rhincodon typus, in the southwestern Gulf of California. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2013, 96, 779–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.; Christiansen, J.S.; Grønkjær, P.; Bushnell, P.; Steffensen, J.F.; Kiilerich, H.O.; Præbel, K.; Hedeholm, R. Greenland shark (Somniosus microcephalus) stomach contents and stable isotope values reveal an ontogenetic dietary shift. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estupiñán-Montaño, C.; Galván-Magaña, F.; Sánchez-González, A.; Elorriaga-Verplancken, F.R.; Delgado-Huertas, A.; Páez-Rosas, D. Dietary ontogeny of the blue shark, Prionace glauca, based on the analysis of δ13C and δ15N in vertebrae. Mar. Biol. 2019, 166, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfson, F.H. Records of seven juveniles of the whale shark Rhiniodon typus. J. Fish. Biol. 1983, 22, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukuyev, E.I. The new finds in recently born individuals of the whale shark Rhiniodon typus (Rhiniodontidae) in the Atlantic Ocean. J. Ichthyol. 1995, 36, 203–205. [Google Scholar]
- Rowat, D.; Gore, M.A.; Baloch, B.B.; Islam, Z.; Ahmed, E.; Ali, Q.M.; Culloch, R.M.; Hameed, S.; Hasnain, S.A.; Hussain, B.; et al. New records of neonatal whale shark (Rhincodon typus) from the Northern Indian Ocean. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2008, 82, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrick, J.A.F. Additional information on the morphology of an embryo whale shark. Proc. US Natl. Mus. 1964, 115, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Taylor, J.G. Seasonal occurrence, distribution and movements of the whale shark, Rhincodon typus, at Ningaloo reef, Western Australia. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1996, 47, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, C.A.J. Distribution, seasonality, lengths, and feeding behaviour of whale sharks (Rhincodon typus) observed in New Zealand waters. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2002, 36, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).