The Effect of Ontogenetic Dietary Shifts on the Trophic Structure of Fish Communities Based on the Trophic Spectrum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
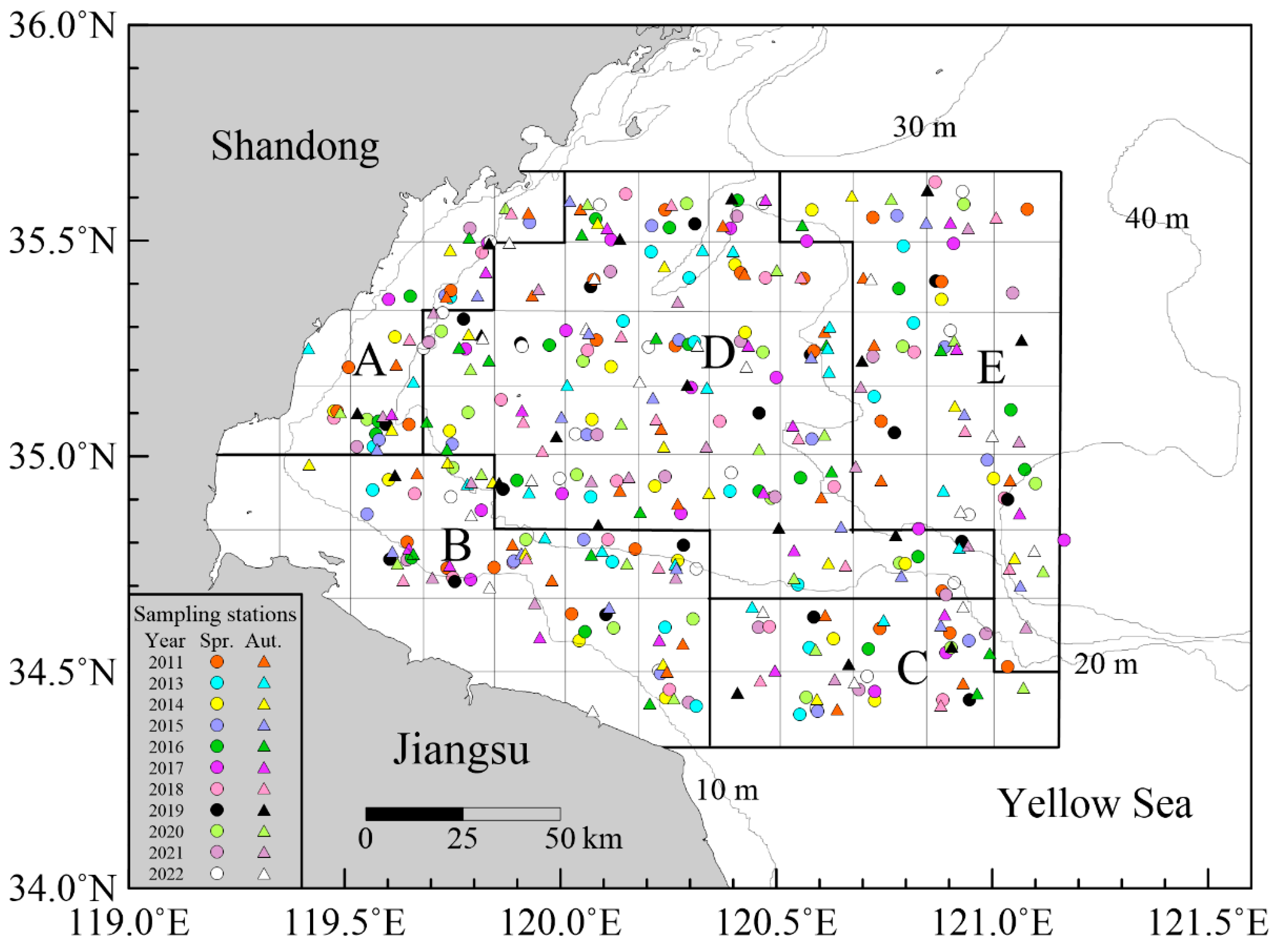
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Functional Group Classification
2.3. Stable Isotope Analysis and Trophic Level
2.4. Trophic Spectrum
2.5. Trophic Indicators
3. Results
3.1. Relative Biomass and Trophic Levels of Fish Species
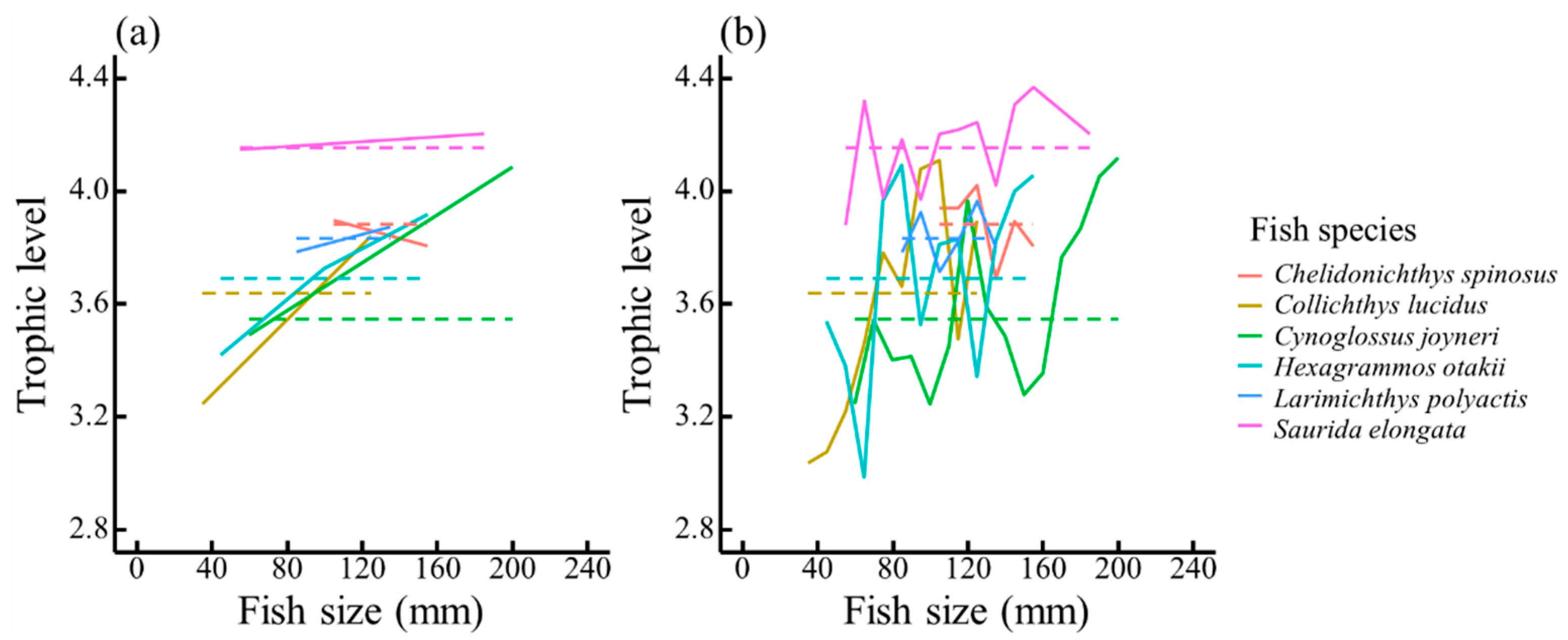
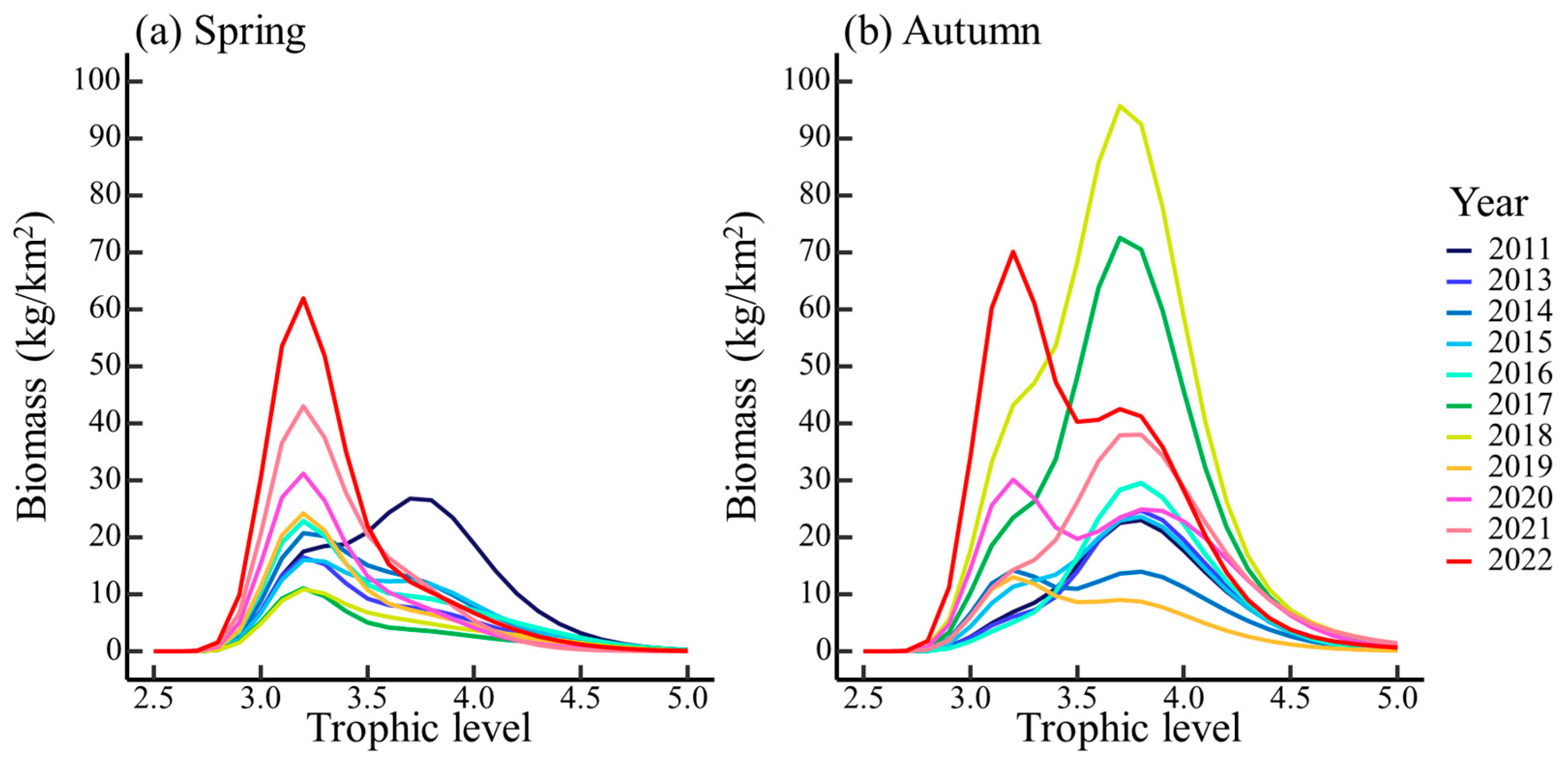
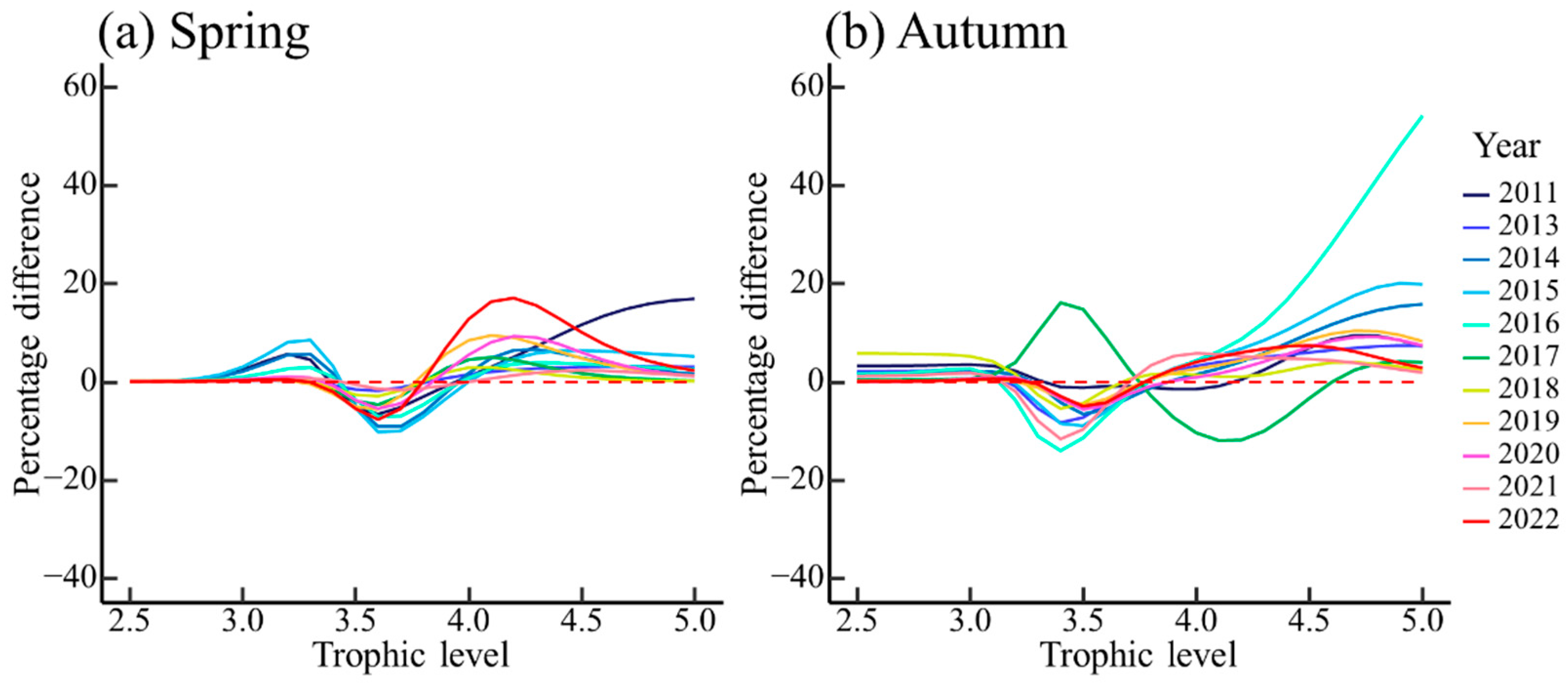
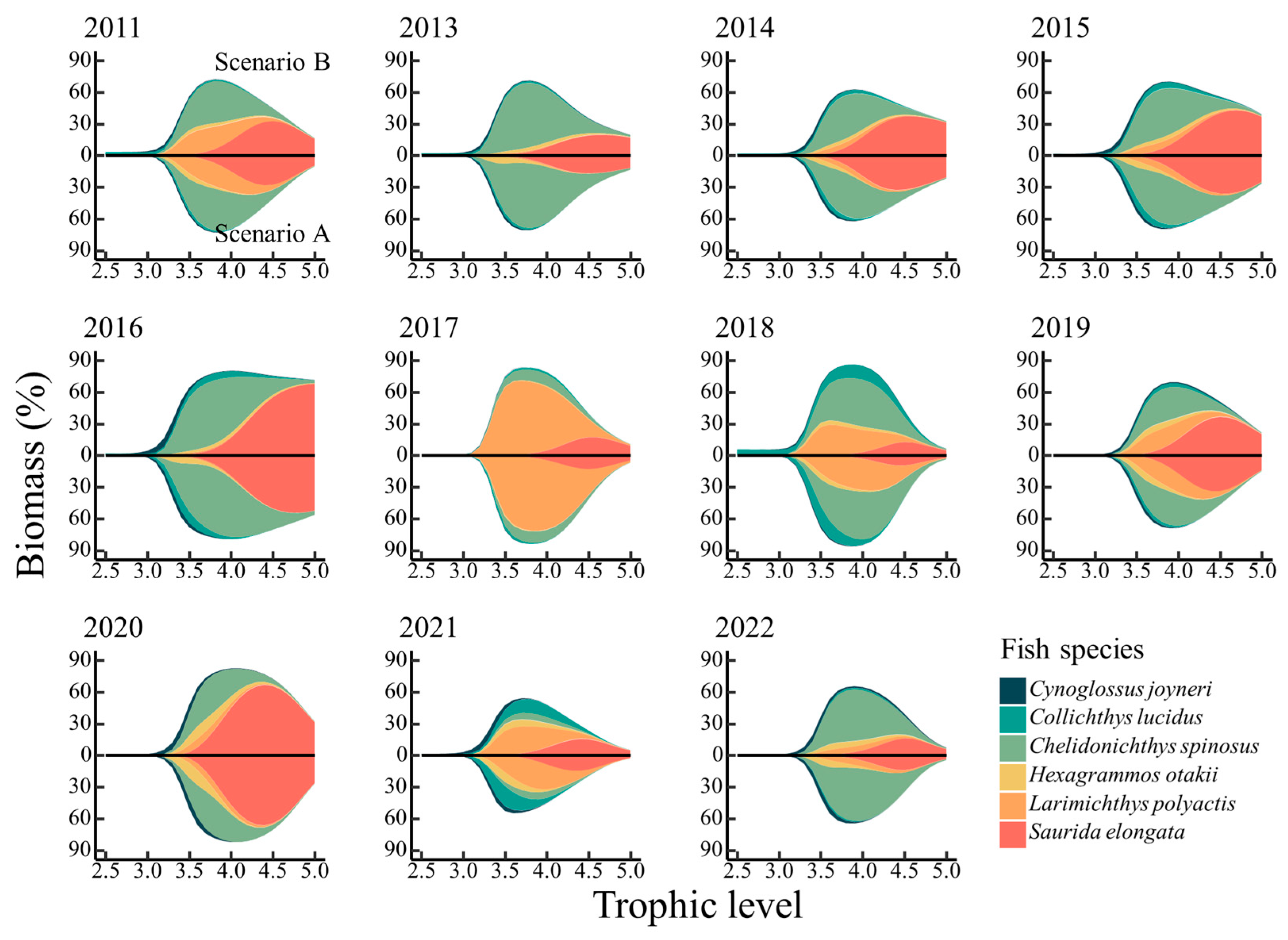
3.2. Effect of Ontogenetic Dietary Variations on the Trophic Spectrum
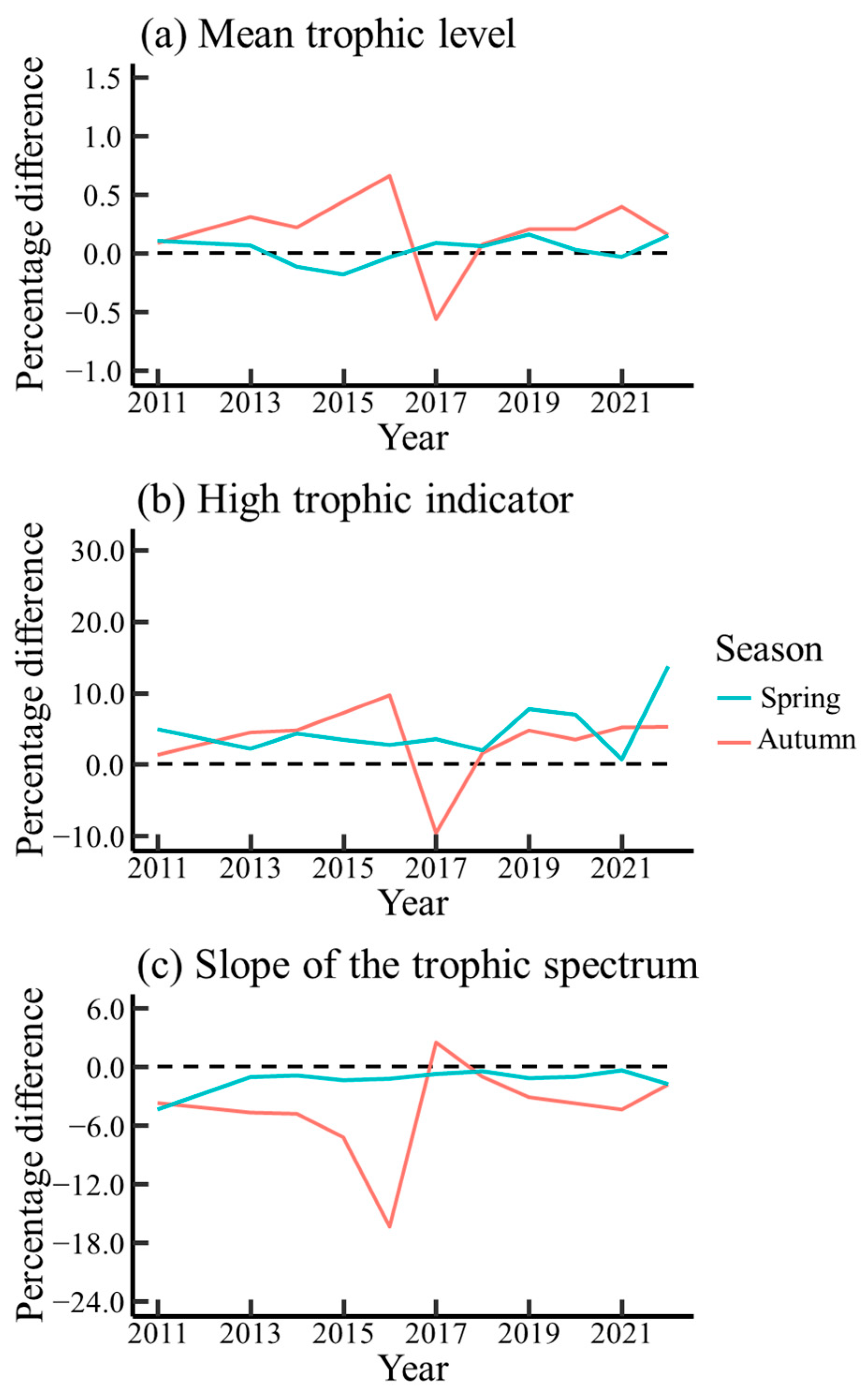
3.3. Temporal Variations in Trophic Indicators
4. Discussion
4.1. Stable Isotopic Values and Trophic Levels
4.2. Effect of Ontogenetic Dietary Shifts on the Trophic Spectrum
4.3. Effect of Ontogenetic Dietary Shifts on Trophic Indicators
4.4. Implications for Fishery Management
4.5. Limitations and Prospects
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MTL | Mean trophic level |
| HTI | High trophic indicator |
| Slope | Slope of the trophic spectrum |
Appendix A
| Fish Species | Number of Samples | δ15N (‰, Mean ± SD) |
|---|---|---|
| Chelidonichthys spinosus | 18 | 10.85 ± 0.64 |
| Larimichthys polyactis | 27 | 10.80 ± 0.86 |
| Saurida elongata | 27 | 11.67 ± 1.37 |
| Liparis sp. | 4 | 10.37 ± 1.02 |
| Hexagrammos otakii | 33 | 10.07 ± 1.58 |
| Collichthys lucidus | 41 | 9.81 ± 1.74 |
| Cynoglossus joyneri | 63 | 9.48 ± 1.41 |
| Callionymus valenciennei | 7 | 10.31 ± 1.06 |
| Collichthys niveatus | 6 | 9.03 ± 1.65 |
| Muraenesox cinereus | 6 | 10.17 ± 1.23 |
| Amblychaeturichthys hexanema | 7 | 10.84 ± 1.04 |
| Total | 239 | - |
| Species | Size Classes | Number of Samples | δ15N (‰, Mean ± SD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chelidonichthys spinosus | <111 | 3 | 11.05 ± 0.95 |
| 111–120 | 3 | 11.05 ± 0.62 | |
| 121–130 | 3 | 11.32 ± 0.51 | |
| 131–140 | 3 | 10.20 ± 0.47 | |
| 141–150 * | 3 | 10.89 ± 0.53 | |
| >151 | 3 | 10.59 ± 0.28 | |
| Subtotal | 18 | 10.85 ± 0.64 | |
| Collichthys lucidus | <41 | 1 | 7.98 |
| 41–50 | 3 | 8.11 ± 1.04 | |
| 51–60 | 6 | 8.60 ± 1.50 | |
| 61–70 * | 4 | 9.42 ± 0.70 | |
| 71–80 | 7 | 10.50 ± 1.02 | |
| 81–90 | 6 | 10.10 ± 0.40 | |
| 91–100 | 5 | 11.51 ± 1.31 | |
| 101–110 | 5 | 11.62 ± 1.14 | |
| 111–120 | 3 | 9.47 ± 0.53 | |
| >121 | 1 | 10.89 | |
| Subtotal | 41 | 9.81 ± 1.74 | |
| Cynoglossus joyneri | <65 | 3 | 8.69 ± 0.71 |
| 65–74 | 4 | 9.69 ± 0.40 | |
| 75–84 | 8 | 9.22 ± 1.22 | |
| 85–94 | 4 | 9.26 ± 1.48 | |
| 95–104 | 2 | 8.68 ± 0.55 | |
| 105–114 | 6 | 9.38 ± 1.04 | |
| 115–124 | 4 | 11.13 ± 1.11 | |
| 125–134 | 4 | 9.86 ± 0.93 | |
| 135–144 | 4 | 9.50 ± 0.28 | |
| 145–154 | 4 | 8.80 ± 1.79 | |
| 155–164 | 8 | 9.06 ± 1.21 | |
| 165–174 | 3 | 10.45 ± 1.47 | |
| 175–184 * | 3 | 10.80 ± 0.72 | |
| 185–194 | 3 | 11.43 ± 0.42 | |
| >195 | 3 | 11.65 ± 0.51 | |
| Subtotal | 63 | 9.48 ± 1.41 | |
| Hexagrammos otakii | <51 | 1 | 9.68 |
| 51–60 | 6 | 9.15 ± 1.40 | |
| 61–70 | 1 | 7.81 | |
| 71–80 * | 1 | 11.14 | |
| 81–90 | 3 | 11.56 ± 0.55 | |
| 91–100 | 3 | 9.65 ± 0.38 | |
| 101–110 | 4 | 10.61 ± 0.34 | |
| 111–120 | 3 | 10.68 ± 1.10 | |
| 121–130 * | 3 | 9.02 ± 1.03 | |
| 131–140 | 4 | 10.65 ± 2.29 | |
| 141–150 | 3 | 11.25 ± 0.31 | |
| >151 | 1 | 11.44 | |
| Subtotal | 33 | 10.07 ± 1.58 | |
| Larimichthys polyactis | <91 | 3 | 10.51 ± 0.47 |
| 91–100 | 3 | 11.00 ± 1.10 | |
| 101–110 * | 6 | 10.28 ± 0.78 | |
| 111–120 | 4 | 10.65 ± 1.24 | |
| 121–130 | 6 | 11.13 ± 0.81 | |
| >131 | 5 | 10.57 ± 1.65 | |
| Subtotal | 27 | 10.80 ± 0.86 | |
| Saurida elongata | <61 | 2 | 10.84 ± 1.81 |
| 61–70 | 2 | 12.34 ± 0.36 | |
| 71–80 | 2 | 11.17 ± 0.49 | |
| 81–90 | 3 | 11.87 ± 0.85 | |
| 91–100 | 3 | 11.15 ± 1.20 | |
| 101–110 | 3 | 11.94 ± 0.50 | |
| 111–120 | 1 | 11.99 | |
| 121–130 | 3 | 12.08 ± 1.12 | |
| 131–140 | 2 | 11.32 ± 1.33 | |
| 141–150 | 3 | 12.30 ± 0.19 | |
| 151–180 * | 1 | 12.51 | |
| >180 | 2 | 11.94 ± 0.80 | |
| Subtotal | 27 | 11.67 ± 1.37 | |
| Total | 209 | - | |
| Fish Species | This Study | Jiaozhou Bay [57] | Lingshan Island [58] | SCA of Haizhou Bay [25] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δ15N (‰) | TL | δ15N (‰) | TL | δ15N (‰) | TL | TL | |
| Chelidonichthys spinosus | 10.85 | 3.88 | 11.55 | 3.28 | 10.94 | 3.38 | 4.08 |
| Collichthys lucidus | 9.81 | 3.64 | - | - | 11.71 | 3.60 | 3.75 |
| Cynoglossus joyneri | 9.48 | 3.55 | 13.62 | 3.89 | 11.24 | 3.46 | 3.10 |
| Hexagrammos otakii | 10.07 | 3.69 | 13.54 | 3.86 | 12.86 | 3.94 | 3.83 |
| Larimichthys polyactis | 10.8 | 3.83 | 13.65 | 3.9 | 12.18 | 3.74 | 4.02 |
| Saurida elongata | 11.67 | 4.15 | 12.88 | 3.67 | 11.56 | 3.56 | 4.50 |
References
- Tang, Q. Strategies of Research on Marine Food Web and Trophodynamics between High Trophic Levels. Mar. Fish. Res. 1999, 20, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Libralato, S.; Pranovi, F.; Stergiou, K.; Link, J. Trophodynamics in Marine Ecology: 70 Years after Lindeman. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 512, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnetta, D.; Badalamenti, F.; Sweeting, C.J.; D’Anna, G.; Libralato, S.; Pipitone, C. Erosion of Fish Trophic Position: An Indirect Effect of Fishing on Food Webs Elucidated by Stable Isotopes. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2024, 379, 20230167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durante, L.M.; Beentjes, M.P.; Wing, S.R. Shifting Trophic Architecture of Marine Fisheries in New Zealand: Implications for Guiding Effective Ecosystem-based Management. Fish Fish. 2020, 21, 813–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombouts, I.; Beaugrand, G.; Fizzala, X.; Gaill, F.; Greenstreet, S.P.R.; Lamare, S.; Le Loc’h, F.; McQuatters-Gollop, A.; Mialet, B.; Niquil, N.; et al. Food Web Indicators under the Marine Strategy Framework Directive: From Complexity to Simplicity? Ecol. Indic. 2013, 29, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keramidas, I.; Dimarchopoulou, D.; Ofir, E.; Scotti, M.; Tsikliras, A.C.; Gal, G. Ecotrophic Perspective in Fisheries Management: A Review of Ecopath with Ecosim Models in European Marine Ecosystems. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1182921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arreguín-Sánchez, F. Holistic Approach to Ecosystem-Based Fisheries Management: Linking Biological Hierarchies for Sustainable Fishing; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; ISBN 978-3-030-96846-5. [Google Scholar]
- Berdnikov, S.V.; Selyutin, V.V.; Surkov, F.A.; Tyutyunov, Y.V. Modeling of Marine Ecosystems: Experience, Modern Approaches, Directions of Development (Review). Part 2. Population and Trophodynamic Models. Phys. Oceanogr. 2022, 38, 182–203. [Google Scholar]
- Crowder, L.B.; Hazen, E.L.; Avissar, N.; Bjorkland, R.; Latanich, C.; Ogburn, M.B. The Impacts of Fisheries on Marine Ecosystems and the Transition to Ecosystem-Based Management. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2008, 39, 259–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, J.H. The Structure of Marine Ecosystems; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1974; ISBN 978-0-674-36746-3. [Google Scholar]
- Polovina, J.J. Model of a Coral Reef Ecosystem: I. The ECOPATH Model and Its Application to French Frigate Shoals. Coral Reefs 1984, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Jiang, Z.; Zhou, L.; Dai, B.; Song, Z. A Functional Group Approach Reveals Important Fish Recruitments Driven by Flood Pulses in Floodplain Ecosystem. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 99, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanalderweireldt, L.; Albouy, C.; Le Loc’h, F.; Millot, R.; Blestel, C.; Patrissi, M.; Marengo, M.; Garcia, J.; Bousquet, C.; Barrier, C.; et al. Ecosystem Modelling of the Eastern Corsican Coast (ECC): Case Study of One of the Least Trawled Shelves of the Mediterranean Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2022, 235, 103798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanjari, R.N.; Shah, T.H.; Telvekar, P.; Bhat, F.A.; Abubakr, A.; Bhat, B.A.; Darve, S.I.; Ramteke, K.K.; Mathialagan, D.; Magloo, A.H.; et al. Assessing Ecosystem Health: A Preliminary Investigation of the Gosikhurd Dam Ecosystem Structure and Functioning, an Appraisal Based on Ecological Modelling, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gascuel, D.; Bozec, Y.-M.; Chassot, E.; Colomb, A.; Laurans, M. The Trophic Spectrum: Theory and Application as an Ecosystem Indicator. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2005, 62, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodland, R.J.; Secor, D.H. Benthic-pelagic Coupling in a Temperate Inner Continental Shelf Fish Assemblage. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2013, 58, 966–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galván, D.; Sweeting, C.; Reid, W. Power of Stable Isotope Techniques to Detect Size-Based Feeding in Marine Fishes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 407, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colléter, M.; Gascuel, D.; Ecoutin, J.-M.; Tito De Morais, L. Modelling Trophic Flows in Ecosystems to Assess the Efficiency of Marine Protected Area (MPA), a Case Study on the Coast of Sénégal. Ecol. Model. 2012, 232, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Pontavice, H.; Gascuel, D.; Reygondeau, G.; Stock, C.; Cheung, W.W.L. Climate-induced Decrease in Biomass Flow in Marine Food Webs May Severely Affect Predators and Ecosystem Production. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2021, 27, 2608–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiaw, M.; Gascuel, D.; Sadio, O.; Ndour, I.; Diadhiou, H.D.; Kantoussan, J.; Faye, S.; Thiam, M.; Meissa, B.; Brehmer, P. Efficiency of Two Contrasted Marine Protected Areas (MPA) in West Africa over a Decade of Fishing Closure. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2021, 210, 105655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y. (Ed.) Fishery Resources and Habitat Environment in Haizhou Bay; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2022; ISBN 978-7-109-29397-7. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X. (Ed.) Fisheries Resources and Fishery Oceangraphy; Marine Press: Beijing, China, 2004; ISBN 7-5027-6118-7. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J.; Xue, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xu, B.; Liu, Y.; Ren, Y.; Chen, Y. Evaluating the Efficacy of Fisheries Management Strategies in China for Achieving Multiple Objectives under Climate Change. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2023, 245, 106870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Xu, B.; Zhang, C.; Xue, Y.; Ren, Y. Spatio-temporal variations of functional diversity of fish communities in Haizhou Bay. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 3233–3244. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Ding, X.; Jiang, X.; Xu, B.; Zhang, C.; Ren, Y.; Xue, Y. Variations in the Mean Trophic Level and Large Fish Index of Fish Community in Haizhou Bay, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 2829–2836. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Ren, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wan, R. Optimization of Stratification Scheme for a Fishery-Independent Survey with Multiple Objectives. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2015, 34, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Zhao, X.; Meng, T.; Cui, Y. The Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea Biological Resources and Habitats; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2005; ISBN 978-7-03-015476-7. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Xue, Y.; Xu, B.; Ren, Y.; Dou, S. Feeding Ecology of Hexagrammos otakii in Haizhou Bay. J. Fish. Sci. China 2018, 25, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ren, X.; Xu, B.; Zhang, C.; Ren, Y.; Xue, Y. Understanding the Feeding Ecology of Cynoglossus joyneri in Haizhou Bay Based on Stable Isotope Analysis. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 32, 1080–1086. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X. Study on Feeding Ecology and Food Relations of Two High Trophic Level Fishes in Haizhou Bay. Master’s Thesis, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, C.; Xu, B.; Ren, Y.; Xue, Y. Feeding Strategy and Prey Selectivity of Chelidonichthys spinosus during Autumn in Haizhou Bay. J. Fish. Sci. China 2018, 25, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Jin, X.; Zhang, B.; Liang, Z. Seasonal, Diel and Ontogenetic Variation in Feeding Patterns of Small Yellow Croaker in the Central Yellow Sea. J. Fish Biol. 2005, 67, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, L.; Jin, H.; Zhou, Y. Seasonal and Ontogenetic Diet Composition Variation of Collichthys lucidus in Inshore Waters in the North of East China Sea. Mar. Fish. 2012, 34, 270–276. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Tang, Q. Study on Trophic Level of Important Resources Species at High Trophic Levels in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China. Adv. Mar. Sci. 2004, 22, 393–404. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Huang, L.; Sun, Y. Trophic Levels and Feeding Characters of Marine Fishes in the Yellow Sea and Northern East China Sea Based on Stable Isotope Analysis. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2021, 42, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, B.; Zhang, C.; Ren, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Xue, Y. Ecosystem Structure in the Haizhou Bay and Adjacent Waters Based on Ecopath Model. Haiyang Xuebao 2020, 42, 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- Post, D.M. Using Stable Isotopes to Estimate Trophic Position: Models, Methods, and Assumptions. Ecology 2002, 83, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guitton, J.; Colleter, M.; Gatti, P.; Gascuel, D. EcoTroph: An Implementation of the EcoTroph Ecosystem Modelling Approach. 2022. R Package Version 1.6.1. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=EcoTroph (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis, 2nd ed.; Use R! Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-24277-4. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, Y.-J.; Shannon, L.J. Using Indicators for Evaluating, Comparing, and Communicating the Ecological Status of Exploited Marine Ecosystems. 1. The IndiSeas Project. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2010, 67, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, K.; Xu, Y.; Xu, S.; Wang, K. Decadal-Scale Variation in Mean Trophic Level in Beibu Gulf Based on Bottom-Trawl Survey Data. Mar. Coast. Fish. 2021, 13, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdaud, P.; Gascuel, D.; Bentorcha, A.; Brind’Amour, A. New Trophic Indicators and Target Values for an Ecosystem-Based Management of Fisheries. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 61, 588–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehren, J.; Gascuel, D. Fishing Without a Trace? Assessing the Balanced Harvest Approach Using EcoTroph. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, N.; McCann, K.; Gellner, G.; Moore, J.C. Structural Asymmetry and the Stability of Diverse Food Webs. Nature 2006, 442, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindeman, R.L. The Trophic-Dynamic Aspect of Ecology. Ecology 1942, 23, 399–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric Tests Against Trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods; Charles Griffin: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Kale, S. Trend Analysis and Future Forecasting of Marine Capture Fisheries Production of Turkey. Res. Mar. Sci. 2020, 5, 773–794. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the Regression Coefficient Based on Kendall’s Tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amundsen, P.-A.; Gabler, H.-M.; Staldvik, F.J. A New Approach to Graphical Analysis of Feeding Strategy from Stomach Contents Data—Modification of the Costello (1990) Method. J. Fish Biol. 1996, 48, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerking, S.D. Feeding Ecology of Fish; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1994; ISBN 978-0-12-280780-0. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Li, J.; Dong, H.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, J. Application of Stable Isotope Technology in Feeding Habit Research of Aquatic Animals. Chin. J. Fish. 2023, 36, 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- Mittelbach, G.G.; Persson, L. The Ontogeny of Piscivory and Its Ecological Consequences. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1998, 55, 1454–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecquerie, L.; Nisbet, R.M.; Fablet, R.; Lorrain, A.; Kooijman, S.A.L.M. The Impact of Metabolism on Stable Isotope Dynamics: A Theoretical Framework. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2010, 365, 3455–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, S.W.; Buckley, B.A.; Granger, S.L.; Entsua-Mensah, M.; Ansa-Asare, O.; White, M.J.; McKinney, R.A.; Mensah, E. Anthropogenic Enrichment and Nutrients in Some Tropical Lagoons of Ghana, West Africa. Ecol. Appl. 2007, 17, S144–S164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Xue, Y.; Ren, Y.; Ma, Q. Spatial and Seasonal Variations in the Trophic Spectrum of Demersal Fish Assemblages in Jiaozhou Bay, China. Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 2015, 33, 934–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, J.; Sun, X.; Zhan, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X. Trophic Structure of Fishery Assemblage in Surrounding Waters of Lingshan Island Based on Stable Isotope Analysis. Period. Ocean Univ. China 2022, 52, 40–51. [Google Scholar]
- Vander Zanden, M.J.; Cabana, G.; Rasmussen, J.B. Comparing Trophic Position of Freshwater Fish Calculated Using Stable Nitrogen Isotope Ratios (δ15 N) and Literature Dietary Data. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1997, 54, 1142–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybczynski, S.M.; Walters, D.M.; Fritz, K.M.; Johnson, B.R. Comparing Trophic Position of Stream Fishes Using Stable Isotope and Gut Contents Analyses. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2008, 17, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Xu, Z. Abundance and Distribution of Shrimps in Different Seasons in the Southern Haizhou Bay of Jiangsu Province. Mar. Sci. Bull. 2012, 31, 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- Luan, J.; Zhang, C.; Xu, B.; Xue, Y.; Ren, Y. Modelling the Spatial Distribution of Three Portunidae Crabs in Haizhou Bay, China. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terborgh, J.; Lopez, L.; Nuñez, P.; Rao, M.; Shahabuddin, G.; Orihuela, G.; Riveros, M.; Ascanio, R.; Adler, G.H.; Lambert, T.D.; et al. Ecological Meltdown in Predator-Free Forest Fragments. Science 2001, 294, 1923–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasche, L.; Gascuel, D. EcoTroph: A Simple Model to Assess Fishery Interactions and Their Impacts on Ecosystems. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2013, 70, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, J.K.; Worm, B. Cascading Top-down Effects of Changing Oceanic Predator Abundances. J. Anim. Ecol. 2009, 78, 699–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, I.C.; Hansen, C.; Morzaria-Luna, H.N.; Girardin, R.; Marshall, K.N. Ecosystem-Based Harvest Control Rules for Norwegian and US Ecosystems. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellier, E.; Sæther, B.-E.; Engen, S. Sustainable Strategies for Harvesting Predators and Prey in a Fluctuating Environment. Ecol. Model. 2021, 440, 109350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.P.; Cox, S.P.; Hammill, M.O.; Den Heyer, C.E.; Swain, D.P.; Mosnier, A.; Benoît, H.P. Forecasting the Response of a Recovered Pinniped Population to Sustainable Harvest Strategies That Reduce Their Impact as Predators. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2021, 78, 1804–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, S.M.; Rice, J.; Charles, A. Balanced Harvesting in Fisheries: A Preliminary Analysis of Management Implications. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2016, 73, 1668–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, C.; Wabnitz, C.; Weijerman, M.; Woodworth-Jefcoats, P.; Polovina, J. Finding the Way to the Top: How the Composition of Oceanic Mid-Trophic Micronekton Groups Determines Apex Predator Biomass in the Central North Pacific. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2016, 549, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Pauly, D. Fisheries Impacts on China’s Coastal Ecosystems: Unmasking a Pervasive ‘Fishing down’ Effect. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srithong, N.; Jensen, K.R.; Jarernpornnipat, A. Application of the Ecopath Model for Evaluation of Ecological Structure and Function for Fisheries Management: A Case Study from Fisheries in Coastal Andaman Sea, Thailand. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 47, 101972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, P.; Cheung, W.W.L.; Chen, M.; Xian, W.; Yang, S.; Xiao, J. Comparing Marine Ecosystems of Laizhou and Haizhou Bays, China, Using Ecological Indicators Estimated from Food Web Models. J. Mar. Syst. 2020, 202, 103238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moullec, F.; Barrier, N.; Drira, S.; Guilhaumon, F.; Marsaleix, P.; Somot, S.; Ulses, C.; Velez, L.; Shin, Y.-J. An End-to-End Model Reveals Losers and Winners in a Warming Mediterranean Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caskenette, A.L.; McCann, K.S. Biomass Reallocation between Juveniles and Adults Mediates Food Web Stability by Distributing Energy Away from Strong Interactions. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, K.A.; McCann, K.S.; Caskenette, A.L. Interaction Strength and Stability in Stage-structured Food Web Modules. Oikos 2018, 127, 1494–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Hernández, J.; Nunn, A.D.; Adams, C.E.; Amundsen, P. Causes and Consequences of Ontogenetic Dietary Shifts: A Global Synthesis Using Fish Models. Biol. Rev. 2019, 94, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Dong, X.; Zhang, C.; Xu, B.; Ji, Y.; Ren, Y.; Xue, Y. Influencing Factors of Predation on Five Keystone Prey Species in Haizhou Bay Based on Delta-GAMMs. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 34, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar]
- Rudd, M.B.; Thorson, J.T. Accounting for Variable Recruitment and Fishing Mortality in Length-Based Stock Assessments for Data-Limited Fisheries. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2018, 75, 1019–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froese, R.; Stern-Pirlot, A.; Winker, H.; Gascuel, D. Size Matters: How Single-Species Management Can Contribute to Ecosystem-Based Fisheries Management. Fish. Res. 2008, 92, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, L.E.; Funk, H.G.; Palmieri, M.; Stafford, J.D.; Nichols, M.E. Length in Assessing Status of Freshwater Fish Populations: A Review. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2024, 44, 1092–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, B. (Ed.) Fishery Stock Assessment; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.; Chen, Y.; Dong, S.; Hanson, A.; Huang, B.; Leadbitter, D.; Little, D.C.; Pikitch, E.K.; Qiu, Y.; Sadovy De Mitcheson, Y.; et al. Opportunity for Marine Fisheries Reform in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, I.; Su, M.S.; Leaño, E.M. Status of Research in Stock Enhancement and Sea Ranching. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2003, 13, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Feng, J.; Lozano-Montes, H.M.; Loneragan, N.R.; Zhang, X.; Tian, T.; Wu, Z. Estimating Ecological Carrying Capacity for Stock Enhancement in Marine Ranching Ecosystems of Northern China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 936028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitada, S. Lessons from Japan Marine Stock Enhancement and Sea Ranching Programmes over 100 Years. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 1944–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Lin, H.; Wu, L.; Zhuang, X.; Ma, J.; Kang, B.; Ding, S. Resource Status and Effect of Long-Term Stock Enhancement of Large Yellow Croaker in China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 743836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, C.; Ovando, D.; Hilborn, R.; Gaines, S.D.; Deschenes, O.; Lester, S.E. Status and Solutions for the World’s Unassessed Fisheries. Science 2012, 338, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Xue, Y.; Ren, Y. Temporal and Spatial Variation in Taxonomic Diversity of Fish in Haizhou Bay: The Effect of Environmental Factors. J. Fish. Sci. China 2013, 20, 624–634. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, H.; Xue, Y.; Ren, Y.; Zou, Y.; Yu, L. Studies on the Ecological Groups of Fish Communities in Haizhou Bay, China. Period. Ocean Univ. China 2017, 47, 59–71. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, P.; Liang, Z.-L.; Yu, Y.; Tang, Y.-L.; Zhao, F.-F.; Huang, L.-Y. Trawl Selectivity-Induced Evolution Effects on Age Structure and Size-at-Age of Largehead Hairtail (Trichiurus Lepturus) Linnaeus, 1758 in the East China Sea, China. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2015, 31, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterworth, D. Experiences in the Evaluation and Implementation of Management Procedures. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 1999, 56, 985–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Smith, A.D.M.; Punt, A.E.; Richardson, A.J.; Gibbs, M.; Fulton, E.A.; Pascoe, S.; Bulman, C.; Bayliss, P.; Sainsbury, K. Ecosystem-Based Fisheries Management Requires a Change to the Selective Fishing Philosophy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9485–9489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; Sui, H.; Xu, B.; Zhang, C.; Ren, Y.; Xue, Y. Using Network Analysis to Identify Keystone Species in the Food Web of Haizhou Bay, China. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2020, 71, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, W. Study on the Feeding Habit and Trophic Level of Main Economic Invertebrates in the Huanghai Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 1999, 18, 117–126. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Xu, B.; Zhang, C.; Ren, Y.; Xue, Y. Identification of Keystone Prey Species in Haizhou Bay Food Web Based on SURF Index. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 9373–9378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, J.L.; Jennings, S.; Law, R.; Castle, M.D.; McCloghrie, P.; Rochet, M.; Benoît, E. How Does Abundance Scale with Body Size in Coupled Size-structured Food Webs? J. Anim. Ecol. 2009, 78, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 35892-2018; Laboratory Animal−Guideline for the Ethical Review of Animal Welfare. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection, and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2018.

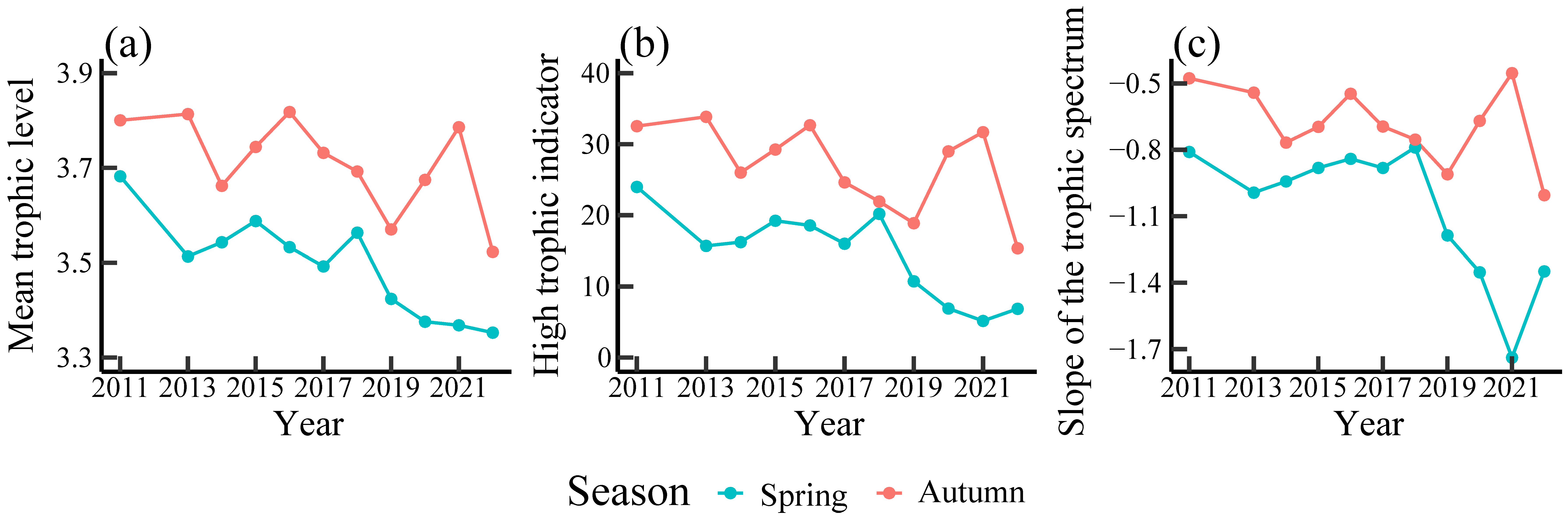
| Species | Size Thresholds of Dietary Shift (cm) | Equidistant Size Classes (cm) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Range of Size | Size Interval | ||
| Hexagrammos otakii | 80, 130 [28] | 50–150 | 10 |
| Cynoglossus joyneri | 184 [29] | 65–195 | 10 |
| Saurida elongata | 180 [30] | 60–180 | 10 |
| Chelidonichthys spinosus | 150 [31] | 110–150 | 10 |
| Larimichthys polyactis | 110 [32] | 90–130 | 10 |
| Collichthys lucidus | 70 [33] | 40–120 | 10 |
| Fish Species | Catchability Coefficient | Relative Biomass (%) | Trophic Level | Analytical Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chelidonichthys spinosus | 0.5 | 14.70% | 3.88 | SIA (this study) |
| Enedrias fangi | 0.5 | 13.59% | 3.24 | SCA [25] |
| Larimichthys polyactis | 0.5 | 11.73% | 3.83 | SIA (this study) |
| Thryssa kammalensis | 0.3 | 9.54% | 3.20 | SCA [34] |
| Pampus argenteus | 0.3 | 4.83% | 3.25 | SCA [25] |
| Saurida elongata | 0.5 | 4.34% | 4.15 | SIA (this study) |
| Liparis sp. | 0.5 | 4.00% | 3.86 | SIA (this study) |
| Hexagrammos otakii | 0.5 | 3.23% | 3.69 | SIA (this study) |
| Collichthys lucidus | 0.5 | 2.76% | 3.64 | SIA (this study) |
| Conger myriaster | 0.5 | 2.48% | 4.22 | SCA [25] |
| Lophius litulon | 0.8 | 2.11% | 4.36 | SCA [25] |
| Syngnathus acus | 0.5 | 1.83% | 3.20 | SCA [25] |
| Miichthys miiuy | 0.5 | 1.70% | 4.16 | SCA [25] |
| Engraulis japonicus | 0.3 | 1.58% | 3.60 | SCA [34] |
| Setipinna tenuifilis | 0.3 | 1.56% | 3.28 | SIA [35] |
| Cynoglossus joyneri | 1.0 | 1.50% | 3.55 | SIA (this study) |
| Callionymus valenciennei | 0.5 | 1.41% | 3.72 | SIA (this study) |
| Johnius belengeri | 0.5 | 1.28% | 3.83 | SCA [25] |
| Collichthys niveatus | 0.5 | 1.21% | 3.35 | SIA (this study) |
| Trichiurus lepturus | 0.5 | 0.96% | 4.78 | SCA [25] |
| Ammodytes personatus | 0.5 | 0.94% | 3.37 | SCA [25] |
| Argyrosomus argentatus | 0.5 | 0.87% | 4.13 | SCA [25] |
| Apogon lineatus | 0.5 | 0.85% | 3.40 | SCA [25] |
| Chaeturichthys stigmatias | 0.8 | 0.79% | 3.86 | SCA [25] |
| Platycephalus indicus | 0.5 | 0.75% | 3.93 | SIA [35] |
| Muraenesox cinereus | 0.5 | 0.65% | 3.68 | SIA (this study) |
| Callionymus beniteguri | 0.5 | 0.64% | 3.36 | SCA [25] |
| Callionymus kitaharae | 0.5 | 0.61% | 3.39 | SCA [25] |
| Pleuronichthys cornutus | 1.0 | 0.60% | 3.53 | SCA [25] |
| Amblychaeturichthys hexanema | 0.8 | 0.58% | 3.88 | SIA (this study) |
| Callionymus richardsoni | 0.5 | 0.50% | 3.53 | SCA [25] |
| Others | 0.5 | 5.89% | 3.70 | Ecopath [36] |
| Indicator | Seasons | Mann–Kendall Test | Sen’s Slope | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z | p-Value | |||
| Mean trophic level | Spring | −2.96 | 0.00 * | −0.03 |
| Autumn | −1.71 | 0.09 | −0.02 | |
| High trophic indicator | Spring | −2.34 | 0.02 * | −1.60 |
| Autumn | −1.87 | 0.06 + | −1.33 | |
| Slope of the trophic spectrum | Spring | −1.71 | 0.09 | −0.05 |
| Autumn | −1.09 | 0.28 | −0.03 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, J.; Yin, J.; Xu, B.; Zhang, C.; Ji, Y.; Ren, Y.; Xue, Y. The Effect of Ontogenetic Dietary Shifts on the Trophic Structure of Fish Communities Based on the Trophic Spectrum. Fishes 2025, 10, 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10050231
Xu J, Yin J, Xu B, Zhang C, Ji Y, Ren Y, Xue Y. The Effect of Ontogenetic Dietary Shifts on the Trophic Structure of Fish Communities Based on the Trophic Spectrum. Fishes. 2025; 10(5):231. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10050231
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Junwei, Jie Yin, Binduo Xu, Chongliang Zhang, Yupeng Ji, Yiping Ren, and Ying Xue. 2025. "The Effect of Ontogenetic Dietary Shifts on the Trophic Structure of Fish Communities Based on the Trophic Spectrum" Fishes 10, no. 5: 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10050231
APA StyleXu, J., Yin, J., Xu, B., Zhang, C., Ji, Y., Ren, Y., & Xue, Y. (2025). The Effect of Ontogenetic Dietary Shifts on the Trophic Structure of Fish Communities Based on the Trophic Spectrum. Fishes, 10(5), 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10050231







