Abstract
The growing global demand for fish necessitates the exploration of sustainable aquaculture practices. This has led to a focus on the quality and sustainable production of fish products with minimal environmental impact. Thus, the objective of this review is to study and evaluate how different aquaculture systems impact the quality and nutritional profile of fish. Fish are rich sources of protein, containing almost 20% protein and essential amino acids and vitamins. The nutritional value and quality of fish products are directly related to the conditions under which they are produced through aquaculture. This article considers various aquaculture systems, including closed-loop systems, pond farming, marine aquaculture, and aquaponic systems. The operating principles, advantages, and inherent limitations of each fish-rearing system are subjected to rigorous critical analysis in this review. Such practices are necessary to meet the growing demand for fish and to maintain the integrity of aquatic ecosystems for future generations.
Key Contribution:
This review provides a comprehensive analysis of sustainable aquaculture practices, emphasizing their role in ensuring high-quality fish production while minimizing environmental impact. It critically examines the nutritional composition of fish, the microbial processes involved in water purification, disinfection strategies, and various aquaculture systems, evaluating their operational principles, benefits, and challenges, as well as the potential solutions for sustainable fisheries management and their impact on fish quality.
1. Introduction
In recent decades, healthy eating has been emphasized in routine human life. Nutritional behavior significantly influences a person’s physical and mental well-being. Nutrients and their metabolites in the human body provide the fundamental building blocks for cellular structures and primary energy sources [1,2,3]. Additionally, they function as direct regulators of protein activity, potent signaling molecules, and inducers and repressors of gene expression [2]. A deficiency in specific nutrients could increase disease risk, particularly due to reduced immunity [4]. Consequently, it is important to select foodstuffs that are rich in nutritional value.
Fish meat is a precious product that contains many nutrients. The global consumption of fish meat is increasing annually [5]. Fish meat is recognized globally for its high nutritional value, particularly as an important source of omega-3 fatty acids, iodine, and vitamin D [6]. Global fish consumption has significantly increased, with 89% of the total aquatic animal production—approximately 157 million tons in 2020—allocated for human consumption [5]. This rising demand for fish protein highlights its critical role in global food security [5]. However, many countries still experience fish deficiency in their diets for various reasons, including cultural and ethnic characteristics, geographic location, and economic status [7,8,9]. Fish consumption deficits may increase over time due to population growth, the decline of declining ocean fish stocks, and water pollution [10]. A lack of fish consumption results in deficiencies of certain nutrients. The most prevalent deficiencies are omega-3 and iodine, which are primarily sourced from fish [11]. In the future, countries with high fish consumption may see an increase in various cases of iodine, vitamin D, and omega-3 deficiency, which could lead to a deterioration in quality of life [10,12].
It is worth noting that the credibility of commercial fishing is decreasing every year [13,14,15]. This is because water resource pollution entails a decrease in the quality of fish products [13,14]. In addition, fishing greatly reduces the ecological diversity of fish [15]. Additionally, fisheries in freshwater rivers are losing their credibility due to water resource pollution and an increase in helminthiasis in fish [16,17]. However, various measures are being taken to reduce risks and ensure stable fish production, such as monitoring aquatic ecosystems and breeding fish under controlled conditions [18,19].
Despite these efforts, contemporary aquaculture systems encounter considerable obstacles concerning sustainability, efficiency, and nutrition. Sustainable aquaculture must tackle challenges such water overexploitation, nutrient contamination, and the substantial dependence on fishmeal and fish oil sourced from wild populations, which jeopardize marine biodiversity [20,21]. Furthermore, stressors produced by climate change and antibiotic resistance persist in undermining fish health and productivity [22].
Innovative solutions are emerging to address these restrictions. This encompasses the utilization of precision aquaculture instruments, such as automated feeding mechanisms, water quality sensors, and artificial intelligence for real-time surveillance, to improve production efficiency and environmental management [23]. Sustainable feed alternatives like insect meal, microbial protein, and algae-based ingredients are being explored to reduce dependence on marine resources while maintaining high levels of omega-3 fatty acids [24,25]. Furthermore, advances in selective breeding and genome editing are being investigated to improve fish resistance to disease and enhance nutritional traits [26]. The integration of aquaculture with hydroponics (aquaponics) and bioremediation techniques signifies a promising advancement in circular, resource-efficient fish farming [27]. Despite these advancements, there remain significant knowledge gaps regarding how various farming methods specifically influence the nutritional composition of farmed fish. Addressing these gaps through targeted research can substantially enhance productivity, sustainability, and the nutritional benefits of aquaculture products, ultimately contributing to improved global nutrition and public health outcomes.
The following section will examine the role and importance of various components of fish with respect to their effects on the human body. The benefits of fish products and the deficiency of some nutrients serve to highlight the relevance of fish farming worldwide.
2. Nutritional Benefits of Fish to Humans
The seafood and products of freshwater ecosystems are vital components of a healthy diet and lifestyle [28,29]. In particular, fish are the most consumed aquatic product [30]. Consuming fish meat has a beneficial effect on the human body, providing it with essential nutrients [5]. This is because fish meat is rich in high-quality proteins, essential amino acids, vitamins (especially A, B, and D), phosphorus, and other minerals (Figure 1) [31,32]. Fish play a central role in sustainable food systems due to their high feed conversion efficiency, low environmental footprint compared to terrestrial livestock, and their ability to deliver dense nutritional benefits in relatively small servings [33]. Compared to red meats, fish offer more favorable lipid profiles and lower levels of saturated fats, making them ideal for cardiovascular and metabolic health [34]. Comparing plant-based proteins to fish proteins, fish deliver a more complete amino acid profile and offer higher bioavailability of key nutrients such as vitamin B12, iodine, and long-chain omega-3s—nutrients typically lacking or present in limited forms in plant-based sources [35,36]. The importance and nutritional profile of fish were discussed in this review.
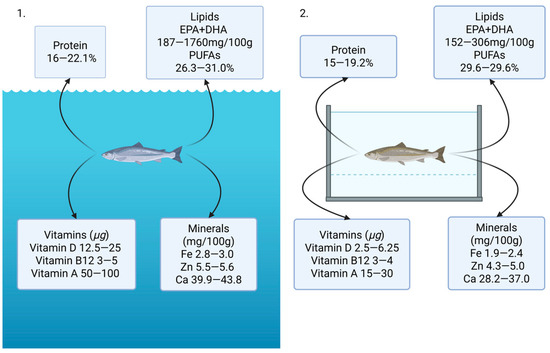
Figure 1.
Main nutrients found in wild fish (1) and farmed fish (2) [31,37,38,39,40,41]. EPA—eicosapentaenoic acid; DHA—docosahexaenoic acid. Values reflect ranges reported in recent literature and may vary with species, diet and environment. Created by BioRender (v3.45.0).
2.1. Fatty Acids
Fish are the most valuable source of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids as the human body is unable to produce these essential nutrients [42,43]. Therefore, they must be obtained through food [5]. Seafood is the sole source of long-chain omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), including eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) [31,32]. EPA and DHA play significant roles in preventing cardiovascular disease, inflammation, and cancer [44,45]. These fatty acids have been demonstrated to exert a favorable effect on several cardiovascular risk factors, including blood lipid levels, blood pressure, heart rate, and platelet aggregation. In this context, blood concentrations of EPA and DHA are associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and coronary heart disease [46]. Omega-3 PUFAs also possess anti-inflammatory properties, which may be beneficial in the treatment of diseases such as psoriasis, asthma, and rheumatoid arthritis [47]. Furthermore, omega-3-derived metabolites (resolvin and maresin) are employed in the treatment of inflammatory skin diseases [47].
Omega-3 and omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids are essential for the normal function of neurons and cell membranes [48]. In this regard, various neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s disease and schizophrenia) and emotional distress have been linked to HUFA deficiency [49]. Furthermore, blood concentrations of EPA, DHA, and arachidonic acid (AA) have been linked to the development of mental illness. Children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) have been observed to have lower blood concentrations of these fatty acids than control children. Consequently, the clinical application of omega-3 PUFAs is frequently regarded as a promising approach for the treatment of brain diseases [46]. A diet rich in omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids has been demonstrated to be an effective treatment for depression [50].
However, the potential risks of fish oil supplementation include hypervitaminosis A and D, vitamin E deficiency, increased bleeding times, and decreased platelet counts [51]. Long-term supplementation may also be linked to increased cancer risk, possibly due to oxidation products or the addition of vitamin E [52,53]. Common side effects include gastrointestinal disturbances, nausea, and a fishy taste [51,52]. While moderate consumption appears relatively safe, caution is advised for high-dose, long-term supplementation, especially during vulnerable life stages. Further research is needed to determine the therapeutic benefits and potential risks of omega-3 fatty acid supplementation [53].
2.2. Proteins and Essential Amino Acids
Fish are a rich source of protein, containing between 18 and 20% protein and essential amino acids such as lysine, methionine, and cysteine [54]. These amino acids possess antioxidant and antihypertensive properties that maintain blood quality, repair muscle tissue, and regulate the human body system [55]. For instance, asparagine, glycine, and glutamic acid facilitate the process of regeneration. Tyrosine, lysine, and methionine are reactive radicals in oxidative reactions [56]. Furthermore, the consumption of fish protein has been demonstrated to have a beneficial effect on reducing hypertension. This is due to the alteration of amino acid sequences, which, in turn, affects blood glucose metabolism. This is achieved by inhibiting dipeptidyl peptidase-4 and altering the intestinal microbiota, which, in turn, promotes increased conjugation of bile acids [57].
Fish protein hydrolysates (FPHs) are derived from fish and are frequently utilized as active ingredients in the production of food products. The extraction of proteins from fish is a key step in the production of hydrolysates. This process involves the removal of proteins from the skin, flesh, and waste (head, fins, etc.) of fish [58]. In addition to its antioxidant and antimicrobial activities, FPHs also exhibit antitumor and ACE inhibitory properties. Notably, ACE plays a pivotal role in regulating blood pressure and maintaining normal heart function [59]. FPH has shown promise in promoting skin, bone, and cartilage health, improving blood lipid profiles and aiding in weight management [60].
Fish consumption has both positive and negative health implications. While fish provide essential nutrients such as omega-3 fatty acids, proteins, vitamins, and minerals, they also accumulate persistent bioaccumulative and toxic substances (PBTS), such as methylmercury and organohalogenated pollutants [61,62]. Fish protein consumption has been linked to increased circulating levels of trimethylamine-N-oxide and accelerated aortic lesion formation in mice [63]. Moreover, fish eaters have shown greater cardiometabolic risk than those following plant-based diets [64]. Given these complex factors, a reassessment of the health risk-benefit ratio and sustainability of fish consumption is warranted [64].
2.3. Vitamins
Fish are a rich source of various vitamins [31,32]. The following vitamins have been identified in fish: vitamins A, D, B, and E [54]. Vitamins are organic, low-molecular-weight substances that are essential for the normal functioning of the body [65]. Most vitamins are not synthesized within the human body, which can result in vitamin deficiency. It is therefore of great importance that these substances enter the body through food [66].
Vitamin A, or retinol, is a vital nutrient for maintaining optimal vision and the integrity of epithelial cells [67]. This is accomplished by stimulating the development of new cells and by exerting a protective effect against infections. Fish are the most readily available source of vitamin A, which is deposited in the liver. The highest concentration of vitamin A is found in the livers of sea bass, swordfish, and lingcods. In comparison to regular cod, these species can exhibit up to a hundredfold the amount of retinol in their livers [68].
The next essential substance that can be derived from fish is vitamin D [69]. A notable quantity of vitamin D is found in the liver of fish, with fatty fish (e.g., salmon and tuna) exhibiting particularly high levels. Vitamin D plays a pivotal role in the regulation of calcium and phosphate metabolism [69]. These functions are of significant importance for the development of bone tissue and other biological processes [70]. Furthermore, vitamin D deficiency has been linked to cardiovascular health [71]. In addition to being an essential substance, fish also contain vitamin B12 and folic acid. Fish tissues and viscera are significant sources of folic acid, which is essential for the normal formation of red blood cells. Vitamin B12 is extracted from fishmeal, fish viscera, liver, kidney, and glandular tissues [68]. It is important to consume an adequate amount of vitamin E to prevent the development of cardiovascular disease and immune and neurodegenerative disorders. Vitamin E is a fat-soluble antioxidant that plays a role in the function and protection of lipids within the body [72]. It is derived from the germ oils of plants, including sunflower and olive. Furthermore, fish oil contains this substance, which is why fish are recommended for use in modern diets [73].
2.4. Minerals
Fish are rich in various minerals, including iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), calcium (Ca), phosphorus (P), and selenium (Se), among others [5,74]. The elements are of significance for the equilibrium of various bodily functions. The concentration of minerals in fish varies considerably depending on factors such as the species of fish, the source of accumulation, and the habitat (Table 1).

Table 1.
Some minerals are extracted from fish.
Consequently, the consumption of fish can be regarded as a beneficial prophylactic measure against a range of ailments. A diet comprising fish is beneficial for maintaining both physical and mental health. The benefits of fish make it one of the most consumed types of animal meat. According to the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), the average global consumption of fish in 2020 was 20.2 kg per capita. This figure has more than doubled since the 1960s. These calculations indicate that the consumption of fish and fish products is projected to reach 21.4 kg per capita by 2030 [5].
3. Methods for Growing Fish for Food Purposes
Aquatic pollution poses significant threats to fish quality and human health. Environmental toxicants, including heavy metals, can accumulate in fish tissues, affecting their physiological state and biochemical parameters [77]. These pollutants can lead to changes in antioxidant defense enzymes, liver enzymes, and other biochemical markers in fish, ultimately impacting meat quality and fish production [77]. The contamination of water bodies with industrial, agricultural, and domestic waste contributes to the increasing pollution of aquatic ecosystems [78]. In particular, heavy metal pollution can weaken the immune system of fish, increasing their susceptibility to parasitic, bacterial, and fungal diseases [78]. Furthermore, the consumption of contaminated fish can result in various human health issues, including food poisoning, gastroenteritis, diarrhea, and severe conditions such as typhoid and paratyphoid [79]. Environmental concerns are also associated with fish consumption, as increasing demand is damaging marine biodiversity [64]. While fish farming may reduce some contaminants, such as methylmercury, it may introduce other substances and have detrimental ecological impacts [64]. These findings underscore the urgent need for effective pollution control measures and fish farming methods to protect both aquatic ecosystems and human health.
The high demand for fish of various species of high value in both food and trade has led to the development and improvement of artificial rearing systems (Table 2) [5]. Aquaculture systems exhibit a considerable degree of diversity regarding breeding methods, practices, equipment, and integration with other agricultural activities. Ponds represent the most prevalent type of facility utilized for freshwater aquaculture. Nevertheless, in recent years, there have been notable advancements in the development of integrated breeding systems for freshwater aquaculture, which have been optimized to function alongside agricultural systems. This has resulted in increased productivity, more efficient resource use, and reduced environmental impacts [80].
To achieve optimal performance, it is necessary to create optimal conditions for the fish. The condition of the fish is largely dependent on the rearing environment [81]. These include water parameters (pH, salinity, and other organic compounds), physical parameters (light, temperature, and water flow), and the influence of feeding and fish density in aquaculture. Regardless of the method of fish farming, it is imperative to consider these factors to ensure the optimal performance of fish and fish products. There are numerous techniques employed in the practice of fish culture. The methods differ according to the specific characteristics of the facilities, the frequency of water exchange, and the intensity of the culture. When selecting a method, consideration is given to the regional context, local climate, and fish species (Table 2) [82]. The availability of different aquaculture systems is contingent upon the objective of creating optimal conditions and increasing fish production. This review describes the principal methods of fish farming, namely, closed water devices (CWDs), pond farming, aquaponic farming, and marine farms.

Table 2.
Comparative analysis of fish rearing systems. It has advantages and disadvantages.
Table 2.
Comparative analysis of fish rearing systems. It has advantages and disadvantages.
| System Type | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structure | |||
| Ponds | Built a dam across a natural watercourse or dug a hole in the ground. May have little or flow-through water exchange, depending on the construction method [83]. |
|
|
| Cages | Enclosed natural bay where shoreline forms all but one side, typically closed by net/mesh barrier [86]. |
|
|
| Tanks | Fish tank aquaculture involves rearing fish in controlled, artificial tank systems, which can be indoor (recirculating aquaculture systems, RAS) or outdoor [88]. |
|
|
| Water Exchange | |||
| Static (Static Ponds) | Involves fish production in earthen or lined ponds without continuous water flow. These systems rely on natural processes (e.g., photosynthesis, microbial activity) to maintain water quality [94]. |
|
|
| Closed (RAS) | Closed water exchange aquaculture, also known as recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS), is a highly controlled production method where water is continuously filtered and reused within the system. Recirculating systems with <10% daily water exchange, using mechanical and biological filtration [88]. |
|
|
| Semi-closed (Mariculture + RAS) | Replaces 10–50% water daily, blending seawater and recirculation [100]. Hybrid systems now use 15–30% exchange with tidal synchronization. |
|
|
| Open (Sea Cages) | Net pens rely entirely on natural water exchange via currents [103]. |
|
|
| Culture Intensification | |||
| Intensive | High stocking density with 20–100% daily exchange [81]. |
|
|
| Semi-intensive | Moderate stocking density with 5–20% daily exchange [94]. |
|
|
| Extensive | Minimal intervention with <5% daily exchange [97]. |
| Very low productivity [97]. |
| Integrated Fish Farming | |||
| Rice+fish (Paddy fields) | Fish (e.g., carp) reared in flooded paddies. Water exchange via monsoon rains [107]. |
|
|
| Duck+fish (Ponds) | Duck waste fertilizes ponds with natural exchange [110]. |
|
|
| Aquaponics | Combines RAS with hydroponics; <5% daily exchange [27]. |
|
|
3.1. RAS Cultivation
A recirculating aquaculture system (RAS) or closed-loop aquaculture unit (CLU) is a covered land-based facility for the rearing of fish in a controlled environment [113]. This method of fish farming does not necessitate a constant supply of water, thereby markedly reducing water consumption. In contrast to pond and marine aquaculture, closed-loop aquaculture has only recently emerged, with the first documented instances occurring in the 1950s. Efforts have been made to purify and reuse water [27]. The fundamental operational principle of the RAS is the continuous re-circulation of water (Figure 2). The water must be kept free of fish waste at all times. Furthermore, it is essential to provide fish with an adequate supply of oxygen to ensure their optimal health and well-being [81].

Figure 2.
Simplified scheme of the closed water supply device: the water comes from the outlet of the aquarium to the mechanical filter (1), and then biofiltration (2) is carried out. Subsequently, the water is degassed and purified from carbon dioxide (3) and oxygenated (4). Before being returned to the aquarium, the water was treated with ultraviolet light (5). Various devices (6), such as ozone treatment, heat exchange, automatic pH regulation, and denitrification devices, are added to the RAS as required [81]. Created by BioRender.
The utilization of mechanical filters is a fundamental aspect of the process of eliminating solid waste. These compounds are generated from fish waste, feed, colloids, and other organic solids. Mechanical filters may be distinguished according to the material from which they are constructed, their dimensions, and the mechanism by which they operate. For example, they include rotary drum filters, quick-acting sand filters, and others [114]. The mandatory mechanical treatment occurs upstream of the biofilter.
One of the most crucial elements in the reuse of water in the RAS is biofilters. Biological filters are essential for the conversion of ammonium to nitrate. This is because the ammonia released from the gills of fish becomes toxic at elevated concentrations. The concentration of ammonium/ammonia in water is contingent upon the most minute fluctuations in pH [115]. To achieve a balance of ammonia and ammonium, aerobic ammonia-oxidizing and nitrite-oxidizing bacteria, such as Nitrosomonas sp. and Nitrospira sp., are employed. These bacteria form colonies with specific substrates, thereby creating biofilters (e.g., a fixed-bed filter) [116,117].
Before the water is returned to the aquarium, it must be aerated to remove the accumulated gases. The most common and reliable method of oxygenation is the use of aerators to oxygenate the water [118]. The use of chemical components in this stage of water treatment has been on the rise in recent years. The use of hydrogen peroxide not only enhances the oxygen concentration but also has disinfectant effects [119]. Subsequently, ultraviolet (UV) disinfection is employed to reduce the bacterial density of the water without adversely affecting the aquatic microbiota [120]. In certain instances, photochemical treatment with ultraviolet light and hydrogen peroxide is employed. This method is more efficient than UV LEDs [121].
Beyond these essential elements, a range of optional components can be integrated into RAS to further optimize water quality parameters, including temperature, pH, and nitrogen compound levels, ultimately enhancing fish health, growth rates, and overall system efficiency [122]. An ozone generator is a device that produces ozone (O3), a highly reactive and potent oxidizing agent, from oxygen (O2) present in the air. Once dissolved in the water, ozone engages in a variety of reactions. Its strong oxidizing properties allow it to break down organic waste products, ammonia, and nitrites present in the system [123]. Optimization of temperature and pH in aquaculture plays an essential role in fish welfare. Most freshwater fish species thrive in water with a pH range of 6.5 to 9.0, while marine species typically require a more alkaline environment, with pH levels between 7.5 and 8.4 [122]. Therefore, it is important to monitor these parameters [124]. Recent advances in sensor technology and Internet of Things (IoT) systems enable real-time monitoring of critical water quality factors such as dissolved oxygen, temperature and pH [125]. The principal advantage of RAS systems is water capacity reuse of up to 90–99%. The production of a substantial quantity of fish products with minimal water consumption is ecologically beneficial for humanity. Moreover, land-based closed-water supply systems can be implemented in diverse geographical regions with varying climatic conditions. Nevertheless, such systems have the potential to contribute to the greenhouse effect and result in high energy costs [113]. Recirculating aquaculture systems are characterized by high energy consumption, mainly due to the continuous operation of pumps for water circulation, sophisticated filtration systems and environmental control mechanisms such as temperature regulation and aeration. For example, the production of one tone of Atlantic salmon in a RAS facility can require over 7500 kilowatt-hours of electricity [126].
Some RAS facilities may also employ diesel generators, particularly as a means of backup power in case of grid outages. Consequently, the carbon footprint of RAS is intrinsically linked to the carbon intensity of the local electricity grid or the specific fuel source being utilized [127]. Despite the energy intensity of RAS operations, a potential advantage in terms of carbon footprint lies in the possibility of locating these facilities closer to consumer markets, especially within urban environments. This strategic placement can lead to a reduction in the transportation-related emissions associated with the distribution of the final seafood product [128]. Adding to this, if RAS facilities can effectively source their energy needs from these cleaner alternatives, the greenhouse gas emissions associated with their operation could be substantially reduced, positioning them as a more environmentally sound option for aquaculture.
The controlled environmental conditions of RAS cultivation significantly influence the nutritional composition of fish, enhancing their nutritional quality. Specifically, RAS allows for precise management of dietary inputs and water quality parameters, leading to improved fatty acid profiles characterized by higher concentrations of beneficial polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), such as omega-3 fatty acids, which are crucial for human health [129,130]. Additionally, stable and optimized feeding conditions in RAS can result in fish with elevated protein content and improved amino acid profiles compared to traditional aquaculture systems [131]. Furthermore, precise nutrient supplementation in controlled RAS environments facilitates higher retention and consistent levels of essential micronutrients like selenium, iodine, and vitamins, thereby augmenting the overall nutritional value of the fish produced [132]. Thus, the RAS approach offers clear benefits in producing nutritionally superior fish products that address both consumer health and sustainable aquaculture objectives.
3.2. Pond Farming
Pond farming is also widely recognized as “organic aquaculture”, which is considered to be a developed practice and refers to open systems of fish farming [133]. The practice of raising fish in a pond is rather ancient, yet it remains an effective method. Those engaged in agricultural pursuits are more likely to be interested in this method. The construction of a pond on a plot of land allows the owner to not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of the landscape but also engage in fish production. The most common fish species are tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus), carp (Cyprinus carpio), and white amur (Ctenopharingodon idella) [134].
One of the defining characteristics of pond aquaculture is the influence of soil on water parameters, which subsequently affects fish [135]. The composition of the soil at the bottom of the pond has a significant impact on the concentration of nitrogen (N), the carbon-to-nitrogen (C/N) ratio, and the presence of other organic matter [136]. In this context, the quality of the soil is a factor to be considered when establishing an aquaculture operation. The most favorable conditions for establishing aquaculture are found on land with a neutral or slightly alkaline pH [135]. Once pond aquaculture is established, the soil reaches the bottom of the pond, where various organic and inorganic compounds fall and accumulate. Subsequently, favorable conditions are established for the proliferation of bacteria that decompose these substances [137,138].
The microbiota also plays a significant role in the field of pond aquaculture. Plankton, zooplankton, and various bacteria consume dead organic matter in water. When nutrients are scarce, fish consume plankton, thereby initiating a food chain. Nevertheless, this microbial community can also have a detrimental effect on fish. They reproduce at night and consume dissolved oxygen, which can result in a lack of oxygen in the water [138].
The next crucial parameter in pond aquaculture is dissolved oxygen (DO), which is typically produced in freshwater. The concentration of dissolved oxygen can be used to assess the degree of water pollution. A reduction in the concentration of DO results in increased stress for fish, which in turn increases the risk of mortality [139]. A reduction in DO is typically accompanied by an increase in water temperature and salinity. Furthermore, the use of herbicides for plants in ponds and the nighttime photosynthesis process can also influence the level of dissolved oxygen [140]. At present, several studies are being conducted to predict the trend of dissolved oxygen fluctuations. One such study employs the application of a neural network. By taking action in advance, it is possible to prevent the total loss of an entire farm [140].
Compared with other agricultural systems, pond farming is more closely integrated with the surrounding environment. In addition, the accumulation of unnecessary waste in water is a further consequence of this practice. Eutrophication (nutrient saturation) can have a detrimental impact on fish health. To circumvent such issues, the implementation of ecological engineering in pond farming is imperative [84]. To guarantee the hydrodynamic circulation of water, artificial reservoir schemes have been developed. Furthermore, it is essential to guarantee uninterrupted water filtration. To this end, specialized accumulation and filtration systems are installed at the terminus of drainage channels [101]. Conversely, the presence of sediment from fishponds can also be beneficial. The sediments at the bottom of the ponds are known to contain significant quantities of organic elements, including sodium, potassium, and phosphorus [141]. A series of fish waste treatment activities can be employed to derive plant fertilizer [142]. This fact serves to enhance the value of pond farming from an ecological standpoint.
Furthermore, pond aquaculture is significant in the context of biodiversity conservation. Ponds can be represented by habitats for a variety of animals, including fish and birds [143]. In this context, while pond aquaculture may be less efficient in terms of fish production, it plays a significant role in landscape conservation.
Pond farming often presents the advantage of lower initial investment costs when compared to more technologically advanced aquaculture systems such as RAS or offshore mariculture operations [144]. The availability and cost of labor are also important economic considerations that influence the location and scale of pond farming operations [145]. The nutritional quality of fish cultivated in pond farming can fluctuate considerably due to environmental interactions characteristic of open systems. Natural feeding behaviors, encompassing the ingestion of phytoplankton, zooplankton, and other microorganisms, frequently result in advantageous fatty acid compositions, notably elevated concentrations of omega-3 fatty acids such as EPA and DHA, in contrast to highly cultivated fish [146]. Inconsistencies in feeding practices and variations in environmental conditions might lead to inconsistent protein content and amino acid profiles, thereby impacting overall nutritional quality [147]. Pond farming generally provides fish with improved access to natural micronutrients, including carotenoids, selenium, and vitamins, hence enhancing the nutritional and sensory quality of the caught fish [78,148]. Consequently, notwithstanding certain discrepancies, pond aquaculture frequently enhances the nutritional attributes and consumer appeal of fish products.
3.3. Aquaponic Fish Breeding
An aquaponic system is an integrated combination of a closed water supply device and soilless organic crop production. The primary objective is to utilize the fish waste generated as a source of nutrients for plant growth, thereby producing two marketable products. Aquaponics is a combination of a closed water supply device and hydroponics. This system has the potential to achieve economically and environmentally beneficial production [149]. The fundamental principle of aquaponics is the integration of three distinct classes of organisms: aquatic organisms, bacteria, and plants (Figure 3).
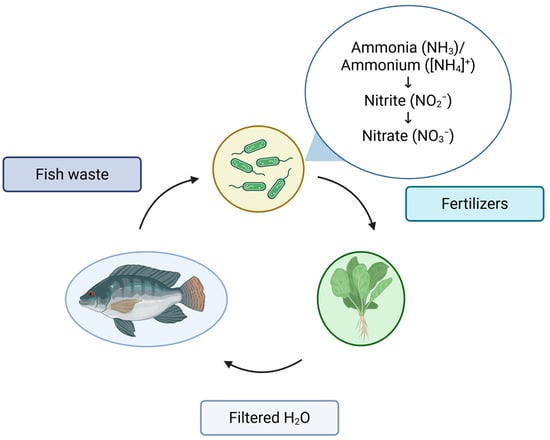
Figure 3.
Nutrient cycle in an aquaponic system [27,150]. Created by BioRender.
In a closed system with water recirculation, these organisms mutually enrich each other. Water serves as a medium for the transfer of nutrients, primarily from dissolved fish waste. Bacteria transform these wastes into nutrients that facilitate plant growth. Ammonia is oxidized by specific bacteria, such as Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter, to nitrite and then to nitrate [27].
The processes of nitrification and denitrification are highly important for addressing nitrogen toxicity in recirculating aquaculture systems [151]. As illustrated in Figure 3, the conversion of NH3/NH4 to NO2 (the initial step) and then to NO3 (the subsequent step) occurs during the nitrification process. Each of these steps is influenced by different microorganisms. In the initial stage, bacteria such as Nitrosomonas, Nitrobacter, and Nitrosococcus, among others, are involved. In the second step, bacteria such as Nitrobacter, Nitrococcus, and Nitrospira convert NO2 into NO3 [117,152]. Notably, denitrification results in a 50% reduction in nitrogen in the system. Microorganisms capable of converting nitrate to nitrogen include Achromobacter, Aerobacter, Acinetobacter, Bacillus, Brevibacterium, Flavobacterium, and others [153].
The quality of water is of paramount importance in aquaponics. It is essential to regulate a few parameters, including pH, temperature, NH3/NH4, NO2/NO3, and oxygen concentration. However, one challenge is the discrepancy in pH requirements between plants and fish. The optimal pH for plants is 6.0, while the pH range for fish is 7.0–8.0. Additionally, the optimal pH for the growth of nitrifying bacteria is 6.5–8.0 [27,154]. Consequently, a variety of technologies are employed to regulate the pH at an optimal level [155].
In addition to the pH, temperature can also negatively affect water quality. To create conditions that are equally conducive to the growth of plants and fish, an average temperature is set for both. For instance, tilapia are cultivated at a temperature of 25 degrees Celsius, which is conducive to optimal basal growth [27].
Not all fish and plant species can adapt to aquaponic farming. The most popular fish species are tilapia, trout, and perch. Depending on the density of the fish and the saturation of the water with organic compounds, plants are selected. Among them, greens (basil, mint, spinach) and vegetables such as peppers, cucumbers, and tomatoes are more commonly grown [156,157].
From an environmental perspective, aquaponics represents a promising technology. Aquaponics represents an alternative method of food production that contributes to sustainable development and prevents the release of aquaculture waste that pollutes water bodies and causes eutrophication [158]. However, aquaponic systems, especially those that are implemented indoors or as vertically integrated farms, can be energy-intensive in certain aspects. The overall carbon footprint of an aquaponic system is therefore heavily influenced by the energy efficiency of its design and the source of the electricity used to power it. Optimizing energy use through strategies such as implementing energy-efficient lighting systems (e.g., LEDs) and designing systems that minimize pumping requirements, along with transitioning to renewable energy sources, are critical for realizing the low-carbon potential of aquaponics [159]. Nevertheless, in comparison to other methods of fish farming, aquaponics represents a novel approach. The production of fish and plant products with minimal water inputs renders this method the most popular [112].
Aquaponic systems have been shown to enhance the nutritional quality of fish, especially their fatty acid composition, protein content, and micronutrient profiles. Aquaponically grown tilapia, for example, showed far greater polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) levels (30.45%) than their conventionally grown equivalents (18.64%) and lower saturated fatty acid (SFA) levels, hence producing a nutritionally better lipid profile [98]. Aquaponically bred fish typically exhibit a more advantageous omega-6 to omega-3 fatty acid ratio, offering cardiovascular health benefits to customers [160]. The protein content in aquaponically produced fish is usually optimized through regulated dietary practices, typically ranging from 25% to 35%, and can rise to about 45% in carnivorous species, thus ensuring balanced amino acid profiles, including essential amino acids such as lysine and methionine [161,162]. Moreover, aquaponic integration might result in increased micronutrient accumulation, such as elevated levels of vitamin C and carotenoids, hence enhancing the nutritional quality and consumer appeal of fish products [163]. Aquaponics presents a sustainable approach that enhances the nutritional qualities of cultivated fish, benefiting both producers and consumers.
For commercial aquaponics operations, strategic proximity to key sales channels such as local farmers’ markets, restaurants that prioritize fresh and sustainable ingredients, and opportunities for direct-to-consumer sales are particularly important factors that influence their location decisions [164]. The economic viability of commercial aquaponics ventures is significantly influenced by their ability to effectively access markets that place a high value on locally sourced and sustainably produced food.
3.4. Sea Farming
Marine farms and pond aquaculture are classified as “organic aquaculture”. Mariculture, also known as marine aquaculture, refers to the cultivation of aquatic species at sea, either throughout the entire production cycle or solely during the cultivation phase. Alternatively, mariculture is defined as the rearing phase of the production cycle, during which the species is grown in land-based hatcheries and, on occasion, even in freshwater, as exemplified by the Atlantic salmon [5].
Most marine fish farms are situated in shallow, sheltered, and coastal waters. This is primarily to ensure the safe operation of the facility and the accessibility of necessary service facilities for the feeding, incubation, storage, maintenance, and processing of harvested fish [165]. The establishment of coastal sea farms is also beneficial for water conservation. In recent years, there has been a growing application of the “Strategic Programme for Climate Resilience” principle in marine aquaculture. This approach is based on water purification with nitrifying bacteria and subsequent reuse [166].
As with pond aquaculture, mariculture farms produce effluents with high levels of fish waste and chemicals. The discharge of mariculture effluents can cause several significant environmental problems, including hypoxia, eutrophication, heavy metal pollution, and habitat destruction [167]. The primary objective of mariculture wastewater treatment is the removal of organic carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus. The separation of organic solid wastes can be effectively achieved using sedimentation or filtration techniques. The residual organic carbon and nutrients must be removed by functional microorganisms and/or algae [168].
The next significant challenge in marine farming is biofouling, which refers to the accumulation of undesired aquatic species. The introduction of these organisms alters the hydrodynamics within and surrounding the cage, which has a significant impact on water quality. Furthermore, the probability of disease transmission is elevated due to the introduction of additional aquatic species and their associated pathogens [169]. For instance, the probability of biofouling by anemones and hydroids is considerable on salmon farms. Furthermore, farmed fish are at risk of Cnidaria stings due to the accumulation of these organisms on farms [170].
A multitude of factors are considered during the design of offshore fish farms. These include water depth, current velocity, seabed conditions, and favorable conditions for fish. The design of flexible/solid floating, semisubmersible, and submerged cages is informed by this consideration [165].
Mariculture substantially impacts the nutritional quality of fish, specifically their fatty acid profiles, protein levels, and micronutrient concentrations. Marine-farmed dentex (Dentex dentex) demonstrated omega-3 fatty acid concentrations, including eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), nearly double those observed in other prevalent aquaculture species such as sea bream (Sparus aurata) and sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) [171]. The protein content in mariculture-produced fish generally varies from 18% to 22%, with essential amino acids comprising approximately 50% of the total amino acid profile; species like Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) and axillary seabream (Pagellus acarne) exemplify these high-quality protein characteristics [25,172]. Furthermore, fish cultivated in marine environments typically demonstrate increased concentrations of vital micronutrients, such as vitamin D (approximately 8–20 µg per 100 g), vitamin B12 (up to 10 µg per 100 g), selenium (30–50 µg per 100 g), and iodine (100–300 µg per 100 g), thereby substantially enhancing nutritional sufficiency and human health [173,174]. Consequently, mariculture significantly improves the nutritional attributes of cultivated fish, establishing it as a vital element of global food security initiatives.
4. Impact of Fish Farming Methods on Fish Nutritional Value
Aquaculture practices significantly influence the nutritional value and quality of farmed fish. Some studies have demonstrated that the flavor, chemical composition, and texture of fish fillets can be influenced by the culturing practices employed [175]. Intensive aquaculture practices may result in increased lipid content in fish, whereas extensive methods may result in the development of different flavors [175]. The fatty acid profile of farmed fish can be modified through dietary manipulation, which may enhance nutritional quality [175,176]. Pond-raised fish typically exhibit higher levels of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), especially omega-3 fatty acids, than cage-raised or wild fish [177,178]. Additionally, pond-raised fish exhibit elevated levels of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in comparison to other cultivation methods [131,177]. Amino acid profiles have been observed to vary between culture systems, with pond-raised fish potentially exhibiting higher levels of certain amino acids [131]. While studies have demonstrated that fish reared in the RAS may exhibit elevated dry matter, fat, and calorie content relative to their pond-raised counterparts, they may also display reduced levels of beneficial fatty acids, including EPA and DHA [131]. Nevertheless, the integration of seaweeds, such as Ulva sp., into an RAS has been demonstrated to enhance fish growth, elevate protein and lipid content, and augment EPA and DHA levels in fish while also improving water quality [130]. The cultivation of microalgae in RAS wastewater has the potential to produce valuable biomass for use as aquaculture feed, with the filtration process capable of influencing the fatty acid content of certain species [179]. These integrated systems can utilize metabolic byproducts from fish production to facilitate the growth of secondary crops with economic value, thereby creating a more efficient and sustainable aquaculture system.
The integration of fish and plant culture in aquaponic systems affects the approximate composition and fatty acid profiles of fish fillets [180]. Furthermore, alterations to the fatty acid profile may be achieved. For instance, freshwater aquaponic systems have the potential to reduce the levels of saturated fatty acids in certain fish species [180]. An aquaponic system has the potential to produce fish of comparable or higher quality than that achieved by conventional methods while simultaneously growing plants [181,182]. The efficiency of the system is contingent upon maintaining an optimal ratio between daily feed intake and the area devoted to plant growth [183]. The feasibility of cultivating marine species, such as the European sea bass, in aquaponic systems, encompassing both freshwater and saltwater environments, has been substantiated. This suggests the viability of maintaining product quality across diverse ecosystems [180]. Additionally, increasing dietary levels of EPA and DHA in Atlantic salmon reared in sea cages has been shown to enhance growth performance and overall quality. Recent research indicate that intensive aquaculture systems, particularly those employing high-energy meals, might elevate total lipid content in fish fillets by as much as 25% and may diminish omega-3 levels when plant-based feeds are overly utilized [184]. Organic farming methods, characterized by reduced stocking densities and natural feed inputs, are linked to leaner fish with elevated protein levels (up to 22% in fillet muscle) and improved fatty acid ratios [185]. In sea cage systems, environmental factors like water velocity and temperature influence fat deposition and texture, frequently resulting in fish with enhanced muscle growth and reduced intramuscular fat [186]. Feed is essential in determining fish nutrition; conventional fishmeal-based diets increase protein content and omega-3 levels as well as plant-based feeds may increase these advantages unless augmented with marine oils or microalgae [187].
Moreover, research shows that the use of a fish-intensive culture (sea farming) method also affects the nutritional composition of farmed fish. Compared with their wild counterparts, cultured sea bream showed greater total lipid content, with differences in fatty acid profiles [175]. Similarly, compared with wild fish, farmed sea bass exhibit altered protein and fatty acid compositions [188]. The fatty acid profile of cultured red sea bream was found to be directly influenced by the feed composition, with fish-fed sardines showing higher levels of EPA and DHA [25,189]. Proteomic and chemical analyses have revealed significant differences between farmed and wild fish, emphasizing the impact of aquaculture on food quality [188]. Furthermore, nutritional supplements and functional ingredients are being investigated as potential means of enhancing fish health, stress resistance, and disease resilience in aquaculture settings [176].
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Fish, as a food source, offer a range of health benefits to humans. As previously stated, fish meat is a rich source of essential fatty acids that support cognitive development, improve health indicators, and enhance overall immunity [190]. Furthermore, fish consumption has been demonstrated to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease [191]. Fish meat proteins are well digested and have high biological value [192]. Fish contain biomolecules that enhance physical and mental health [193]. The vitamins and minerals present in fish have been demonstrated to exert a beneficial influence on several cellular processes within the body [194]. These findings confirm that fish are a valuable source of nutrients essential for human health.
The practice of fish farming will continue to be relevant in terms of the production of fish products for human consumption [5]. A variety of fish farming techniques are employed to maximize production and efficient rearing. These include pond farming, confined rearing, aquaponics, and marine aquaculture. Importantly, selecting sustainable aquaculture system is a context-dependent process, shaped by structural features of the system, water exchange frequency, crop intensity, and integration with other organisms [82]. In addition, it is highly dependent on a range of factors, including the specific geographical location, the prevailing climate, the availability of critical resources such as land, water and energy, and the specific management practices that are employed. For instance, recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS) may be the optimal choice in urban areas where water scarcity is prevalent but renewable energy is accessible, while mariculture may be the most sustainable option in coastal regions where environmental conditions are conducive. Regardless of the rearing method employed, maintaining optimal water quality parameters remains essential. Fish behavior and stress responses are intimately linked to the quality of their aquatic environment [195]. In closed and open water exchange systems, the pH, salinity, temperature, NH3/NH4 ratio, NO2/NO3 ratio, and other substances are considered to be uniform, contingent upon the specific characteristics of the growing environment [196].
Consequently, the significance of fish as a source of sustenance for humans and the optimal methods for their cultivation have been subjected to rigorous investigation. An understanding of fish characteristics and their associated benefits is essential for selecting the most appropriate aquaculture techniques. An examination of the various rearing methods reveals the necessity for the continuous improvement of the qualities of aquaculture. The advancement of ecological knowledge and the development of technological innovations are facilitating the evolution of fish farming practices. Importantly, there is a need for research scientists to explore the relationship between diet and the lipid profile in different rearing systems. Understanding this connection can contribute to improving the nutritional quality of fish products and support the design of optimized feed strategies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.T., K.M.A. and Z.A.; formal analysis, N.T., M.K. and Z.N.; investigation, N.T. and Z.N.; data curation, N.T., A.M. and B.B.; writing—original draft preparation, N.T. and Z.N.; writing—review and editing, N.T., Z.N., A.M., B.B., M.K., K.M.A. and Z.A.; visualization, N.T. and K.M.A.; supervision, Z.A.; project administration, K.M.A., M.K. and Z.A.; funding acquisition, Z.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Science Committee of the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Republic of Kazakhstan, grant number AP19680579.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All the data are available in the text.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Balami, S.; Sharma, A.; Karn, R. Significance of Nutritional Value of Fish for Human Health. Malays. J. Halal Res. 2019, 2, 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Michalak, M.; Agellon, L.B. Importance of Nutrients and Nutrient Metabolism on Human Health. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2018, 91, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Serna, J.; Bergwitz, C. Importance of Dietary Phosphorus for Bone Metabolism and Healthy Aging. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A.C.; Caballero, B.; Cousins, R.J.; Tucker, K.L. Modern Nutrition in Health and Disease; Jones & Bartlett Learning: Burlington, MA, USA, 2020; 1645p. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture. 2022. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/cc0461en/online/cc0461en.html (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Pal, J.; Shukla, B.N.; Maurya, A.K.; Verma, H.O.; Pandey, G.; Amitha, A. A review on role of fish in human nutrition with special emphasis to essential fatty acid. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2018, 6, 427–430. [Google Scholar]
- Tacon, A.G.J.; Metian, M. Food Matters: Fish, Income, and Food Supply—A Comparative Analysis. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2018, 26, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beveridge, M.C.M.; Thilsted, S.H.; Phillips, M.J.; Metian, M.; Troell, M.; Hall, S.J. Meeting the food and nutrition needs of the poor: The role of fish and the opportunities and challenges emerging from the rise of aquaculturea. J. Fish Biol. 2013, 83, 1067–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, K.E.; Russell, J.; Gorman, E.; Hanich, Q.; Delisle, A.; Campbell, B.; Bell, J. Fish, food security and health in Pacific Island countries and territories: A systematic literature review. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golden, C.D.; Allison, E.H.; Cheung, W.W.L.; Dey, M.M.; Halpern, B.S.; McCauley, D.J.; Smith, M.; Vaitla, B.; Zeller, D.; Myers, S.S. Nutrition: Fall in fish catch threatens human health. Nature 2016, 534, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beisbekova, A.; Raushanova, A.; Juszkiewicz, K.; Kainarbayeva, M.; Chuyenbekova, A.; Khassenova, G.; Kozhakhmetova, A.; Kenessary, D. Medico-social effectiveness of biological monitoring of iodine deficiency status (IDS) among women of reproductive age in Kazakhstan. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2019, 26, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sioen, I.; De Henauw, S.; Van Camp, J.; Volatier, J.-L.; Leblanc, J.-C. Comparison of the nutritional–toxicological conflict related to seafood consumption in different regions worldwide. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 55, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merten, W.; Reyer, A.; Savitz, J.; Amos, J.; Woods, P.; Sullivan, B. Global Fishing Watch: Bringing Transparency to Global Commercial Fisheries. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.08756. [Google Scholar]
- Anna, Z.; Hindayani, P. The Cost of Pollution to Dam’s Fisheries. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2022, 31, 4539–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, G.M.; Arenas, F.; Neto, A.I.; Jenkins, S.R. Effects of Fishing and Regional Species Pool on the Functional Diversity of Fish Communities. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishery Management; Inland Fisheries: Rome, Italy, 2001; pp. 195–216.
- Cowx, I.G.; Portocarrero Aya, M. Paradigm shifts in fish conservation: Moving to the ecosystem services concept. J. Fish Biol. 2011, 79, 1663–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atalah, J.; Sanchez-Jerez, P. Global assessment of ecological risks associated with farmed fish escapes. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 21, e00842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, W.M.; Hostetler, W.M. Transgenic Fish: Production, Testing, and Risk Assessment. In Biotechnology in Animal Husbandry; Renaville, R., Burny, A., Eds.; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 261–281. [Google Scholar]
- Naylor, R.L.; Hardy, R.W.; Buschmann, A.H.; Bush, S.R.; Cao, L.; Klinger, D.H.; Little, D.C.; Lubchenco, J.; Shumway, S.E.; Troell, M. A 20-year retrospective review of global aquaculture. Nature 2021, 591, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacon, A.G.J.; Metian, M. Feed Matters: Satisfying the Feed Demand of Aquaculture. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2015, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defoirdt, T.; Sorgeloos, P.; Bossier, P. Alternatives to antibiotics for the control of bacterial disease in aquaculture. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Føre, M.; Frank, K.; Norton, T.; Svendsen, E.; Alfredsen, J.A.; Dempster, T.; Eguiraun, H.; Watson, W.; Stahl, A.; Sunde, L.M.; et al. Precision fish farming: A new framework to improve production in aquaculture. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 173, 176–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, M.; Gasco, L.; Piccolo, G.; Fountoulaki, E. Review on the use of insects in the diet of farmed fish: Past and future. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2015, 203, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprague, M.; Dick, J.R.; Tocher, D.R. Impact of sustainable feeds on omega-3 long-chain fatty acid levels in farmed Atlantic salmon, 2006–2015. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houston, R.D.; Bean, T.P.; Macqueen, D.J.; Gundappa, M.K.; Jin, Y.H.; Jenkins, T.L.; Selly, S.L.C.; Martin, S.A.; Stevens, J.R.; Santos, E.M.; et al. Harnessing Genomics to Fast-Track Genetic Improvement in Aquaculture. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 21, 389–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goddek, S.; Joyce, A.; Kotzen, B.; Burnell, G.M. Aquaponics Food Production Systems: Combined Aquaculture and Hydroponic Production Technologies for the Future; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hosomi, R.; Yoshida, M.; Fukunaga, K. Seafood Consumption and Components for Health. Glob. J. Health Sci. 2012, 4, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funge-Smith, S.; Bennett, A. A fresh look at inland fisheries and their role in food security and livelihoods. Fish Fish. 2019, 20, 1176–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, N.; Samat, N.; Lee, L.K. Insight into the Relation Between Nutritional Benefits of Aquaculture Products and Its Consumption Hazards: A Global Viewpoint. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 925463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacon, A.G.J.; Lemos, D.; Metian, M. Fish for Health: Improved Nutritional Quality of Cultured Fish for Human Consumption. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2020, 28, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasa Gopal, T.K. Chapter 9—Foods from the ocean for nutrition, health, and wellness. In Nutritional and Health Aspects of Food in South Asian Countries; Prakash, J., Waisundara, V., Prakash, V., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 113–122. [Google Scholar]
- Fry, J.P.; Mailloux, N.A.; Love, D.C.; Milli, M.C.; Cao, L. Feed conversion efficiency in aquaculture: Do we measure it correctly? Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 024017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Harris, W.S.; Appel, L.J. Fish Consumption, Fish Oil, Omega-3 Fatty Acids, and Cardiovascular Disease. Circulation 2002, 106, 2747–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaafsma, G. The Protein Digestibility–Corrected Amino Acid Score. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1865S–1867S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, F.; Yabuta, Y.; Bito, T.; Teng, F. Vitamin B12-containing plant food sources for vegetarians. Nutrients 2014, 6, 1861–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, I.J.; Eilertsen, K.E.; Otnæs, C.H.A.; Mæhre, H.K.; Elvevoll, E.O. An Update on the Content of Fatty Acids, Dioxins, PCBs and Heavy Metals in Farmed, Escaped and Wild Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.) in Norway. Foods 2020, 9, 1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molversmyr, E.; Devle, H.M.; Naess-Andresen, C.F.; Ekeberg, D. Identification and quantification of lipids in wild and farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar), and salmon feed by GC-MS. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 3117–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food Search|USDA FoodData Central. Available online: https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/food-search?query=fish%20 (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Mohanty, B.P.; Ganguly, S.; Mahanty, A.; Sankar, T.V.; Anandan, R.; Chakraborty, K.; Paul, B.N.; Sarma, D.; Syama Dayal, J.; Venkateshwarlu, G.; et al. DHA and EPA Content and Fatty Acid Profile of 39 Food Fishes from India. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 027437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladyshev, M.I.; Sushchik, N.N.; Makhutova, O.N.; Glushchenko, L.A.; Rudchenko, A.E.; Makhrov, A.A.; Borovikova, E.A.; Dgebuadze, Y.Y. Fatty Acid Composition and Contents of Seven Commercial Fish Species of Genus Coregonus from Russian Subarctic Water Bodies. Lipids 2017, 52, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balouei, F.; Stefanon, B.; Martello, E.; Atuahene, D.; Sandri, M.; Meineri, G. Supplementation with Silybum marianum Extract, Synbiotics, Omega-3 Fatty Acids, Vitamins, and Minerals: Impact on Biochemical Markers and Fecal Microbiome in Overweight Dogs. Animals 2024, 14, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshdaifat, M.M.; Serbester, U.; Obeidat, B.S.; Gorgulu, M. Fish Oil Supplementation as an Omega-3 Fatty Acid Source during Gestation: Effects on the Performance of Awassi Ewes and Their Offspring. Animals 2023, 13, 3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kok, B.; Malcorps, W.; Tlusty, M.F.; Eltholth, M.M.; Auchterlonie, N.A.; Little, D.C.; Harmsen, R.; Newton, R.W.; Davies, S.J. Fish as feed: Using economic allocation to quantify the Fish In: Fish Out ratio of major fed aquaculture species. Aquaculture 2020, 528, 735474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, P.C. Very long-chain n-3 fatty acids and human health: Fact, fiction and the future. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2018, 77, 52–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innes, J.K.; Calder, P.C. Marine Omega-3 (N-3) Fatty Acids for Cardiovascular Health: An Update for 2020. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, Y.; Saito-Sasaki, N.; Nakamura, M. Omega 3 Fatty Acid and Skin Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 623052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.; Xu, Q.; Chen, J.; Xu, Y.; Pang, J.; Peng, X.; Tang, Z.; Sun, W.; Sun, Z. Effects of Different Combinations of Sodium Butyrate, Medium-Chain Fatty Acids and Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on the Reproductive Performance of Sows and Biochemical Parameters, Oxidative Status and Intestinal Health of Their Offspring. Animals 2023, 13, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, J. Diet in Brain Health and Neurological Disorders: Risk Factors and Treatments. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, J.D.; Moazzami, K.; Wittbrodt, M.T.; Nye, J.A.; Lima, B.B.; Gillespie, C.F.; Rapaport, M.H.; Pearce, B.D.; Shah, A.J.; Vaccarino, V. Diet, Stress and Mental Health. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, B.A.; Talbert, R.L. Biological mechanisms and cardiovascular effects of omega-3 fatty acids. Clin. Pharm. 1988, 7, 795–807. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.P.-C.; Tseng, P.-T.; Zeng, B.-S.; Chang, C.-H.; Su, H.; Chou, P.-H.; Su, K.-P. Safety of Supplementation of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Adv. Nutr. 2023, 14, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, K.W.; Nakamura, Y.; Gosslau, A.M.; Li, S. Are there serious adverse effects of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplements? J. Food Bioact. 2019, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulu, S.; Nawanzi, K.; Abdel-Tawwab, M.; Khalil, H.S. Fish Nutritional Value as an Approach to Children’s Nutrition. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 780844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczak, M.; Panicz, R.; Eljasik, P.; Sadowski, J.; Tórz, A.; Żochowska-Kujawska, J.; Barbosa, V.; Dias, J.; Marques, A. Nutritional value and sensory properties of common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) fillets enriched with sustainable and natural feed ingredients. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 152, 112197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, B.; Shin, K.-H.; Kim, S.-K. Muscle Protein Hydrolysates and Amino Acid Composition in Fish. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, H.F.; Madsen, L.; Lied, G.A. Fish–derived proteins and their potential to improve human health. Nutr. Rev. 2019, 77, 572–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Rehman, A.; Shah, H.; Aadil, R.M.; Ali, A.; Shehzad, Q.; Ashraf, W.; Yang, F.; Karim, A.; Khaliq, A.; et al. Fish Protein and Its Derivatives: The Novel Applications, Bioactivities, and Their Functional Significance in Food Products. Food Rev. Int. 2022, 38, 1607–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idowu, A.T.; Igiehon, O.O.; Idowu, S.; Olatunde, O.O.; Benjakul, S. Bioactivity Potentials and General Applications of Fish Protein Hydrolysates. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2021, 27, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmal, N.P.; Santivarangkna, C.; Benjakul, S.; Maqsood, S. Fish protein hydrolysates as a health-promoting ingredient—Recent update. Nutr. Rev. 2022, 80, 1013–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili Tilami, S.; Sampels, S. Nutritional Value of Fish: Lipids, Proteins, Vitamins, and Minerals. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2018, 26, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dórea, J.G. Persistent, bioaccumulative and toxic substances in fish: Human health considerations. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 400, 93–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdekhasti, N.; Brandsch, C.; Schmidt, N.; Schloesser, A.; Huebbe, P.; Rimbach, G.; Stangl, G.I. Fish protein increases circulating levels of trimethylamine-N-oxide and accelerates aortic lesion formation in apoE null mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, G.; Baroni, L. Health and ecological implications of fish consumption: A deeper insight. Mediterr. J. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 9, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, K.; Semba, R.D.; Eggersdorfer, M.; Schaumberg, D.A. Introduction: The Diverse and Essential Biological Functions of Vitamins. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 61, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, G.F.M. Vitamins: Their Role in the Human Body; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; 451p. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, E.H. Vitamin A. In Reference Module in Biomedical Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Halver, J.E. The Vitamins. In Fish Nutrition; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 61–141. [Google Scholar]
- Charoenngam, N.; Shirvani, A.; Holick, M.F. Vitamin D for skeletal and non-skeletal health: What we should know. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma. 2019, 10, 1082–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cashman, K.D. Vitamin D Deficiency: Defining, Prevalence, Causes, and Strategies of Addressing. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2020, 106, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Guía-Galipienso, F.; Martínez-Ferran, M.; Vallecillo, N.; Lavie, C.J.; Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Pareja-Galeano, H. Vitamin D and cardiovascular health. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 2946–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torquato, P.; Marinelli, R.; Bartolini, D.; Galli, F. Vitamin E: Nutritional aspects. In Molecular Nutrition; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 447–485. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, A.; Lee, J.C.-Y. Vitamin E: Where Are We Now in Vascular Diseases? Life 2022, 12, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lall, S.P.; Kaushik, S.J. Nutrition and Metabolism of Minerals in Fish. Animals 2021, 11, 2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwasek, K.; Thorne-Lyman, A.L.; Phillips, M. Can human nutrition be improved through better fish feeding practices? A review paper. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 3822–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprague, M.; Chau, T.C.; Givens, D.I. Iodine Content of Wild and Farmed Seafood and Its Estimated Contribution to UK Dietary Iodine Intake. Nutrients 2022, 14, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.S.; El-Desoky, M.A.; El-Lahamy, A.A.; Gad, N.S. Influence of Environmental Pollutants on Water Quality and Biochemical Parameters of Fish Tissue. Adv. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. 2020, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, S.A.; Al-Rudainy, A.J.; Salman, N.M. Effect of environmental pollutants on fish health: An overview. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2024, 50, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obasohan, E.E.; Agbonlahor, D.E.; Obano, E.E. Water pollution: A review of microbial quality and health concerns of water, sediment and fish in the aquatic ecosystem. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 423–427. [Google Scholar]
- Brandão, M.L.; Dorigão-Guimarães, F.; Bolognesi, M.C.; Gauy, A.C.D.S.; Pereira, A.V.S.; Vian, L.; Carvalho, T.B.; Gonçalves-de-Freitas, E. Understanding behaviour to improve the welfare of an ornamental fish. J. Fish Biol. 2021, 99, 726–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bregnballe, J. A Guide to Recirculation Aquaculture: An Introduction to the New Environmentally Friendly and Highly Productive Closed Fish Farming Systems; Food & Agriculture Org.: Rome, Italy, 2022; 120p. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, A.; Sheikh Abdullah, S.R.; Hasan, H.A.; Othman, A.R.; Ismail, N. Izzati Aquaculture industry: Supply and demand, best practices, effluent and its current issues and treatment technology. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 287, 112271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egna, H.S.; Boyd, C.E. Dynamics of Pond Aquaculture; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997; 476p. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Shao, Z.; Cheng, G.; Lu, S.; Gu, Z.; Zhu, H.; Shen, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, X. Ecological engineering in pond aquaculture: A review from the whole-process perspective in China. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 1060–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Guang, C.; Xu, H.; Chen, Z.; Xu, P.; Yan, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J. A review of cage and pen aquaculture: China. FAO Fish. Tech. Pap. 2008, 498, 53. [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge, M.C.M. Cage Aquaculture; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; 379p. [Google Scholar]
- Nyakeya, K.; Masese, F.O.; Gichana, Z.; Nyamora, J.M.; Getabu, A.; Onchieku, J.; Odoli, C.; Nyakwama, R. Cage farming in the environmental mix of Lake Victoria: An analysis of its status, potential environmental and ecological effects, and a call for sustainability. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2022, 25, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.I.M.; Eding, E.H.; Verdegem, M.C.J.; Heinsbroek, L.T.N.; Schneider, O.; Blancheton, J.P.; d’Orbcastel, E.R.; Verreth, J.A.J. New developments in recirculating aquaculture systems in Europe: A perspective on environmental sustainability. Aquac. Eng. 2010, 43, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakocy, J. Tank Culture of Tilapia; Division of Agricultural Sciences and Natural Resources, Oklahoma State University: Stillwater, OK, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra Mal, B. Raceways and Tanks; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 239–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, E. Fish tank color: An overview. Aquaculture 2021, 530, 735750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losordo, T.; Delong, D.; Guerdat, T. 31—Advances in technology and practice for land-based aquaculture systems: Tank-based recirculating systems for finfish production. In New Technologies in Aquaculture; Burnell, G., Allan, G., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2009; pp. 945–983. [Google Scholar]
- Bostock, J.; McAndrew, B.; Richards, R.; Jauncey, K.; Telfer, T.; Lorenzen, K.; Little, D.; Ross, L.; Handisyde, N.; Gatward, I.; et al. Aquaculture: Global status and trends. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 2897–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E. Handbook for Aquaculture Water Quality; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; 454p. [Google Scholar]
- Diana, J.S. Aquaculture Production and Biodiversity Conservation. BioScience 2009, 59, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E. Chapter 6—General Relationship Between Water Quality and Aquaculture Performance in Ponds. In Fish Diseases; Jeney, G., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 147–166. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, P. Aquaculture environment interactions: Past, present and likely future trends. Aquaculture 2015, 447, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badiola, M.; Mendiola, D.; Bostock, J. Recirculating Aquaculture Systems (RAS) analysis: Main issues on management and future challenges. Aquac. Eng. 2012, 51, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalsgaard, J.; Lund, I.; Thorarinsdottir, R.; Drengstig, A.; Arvonen, K.; Pedersen, P.B. Farming different species in RAS in Nordic countries: Current status and future perspectives. Aquac. Eng. 2013, 53, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, S.; Skern-Mauritzen, R.; Saito, T.; Thompson, C. Optimising delousing strategies: Developing best practice recommendations for maximal efficacy and positive welfare—Final Report. Rapp. Fra Havforskningen 2023, 5–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Shang, K. Eco-Engineering Technologies and Achievements of Projects for Reconstructing Landscape Water from Aquaculture Ponds in Shanghai. Water 2023, 15, 2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerenciano, M.G.C.; Rombenso, A.N.; Vieira, F.D.N.; Martins, M.A.; Coman, G.J.; Truong, H.H.; Noble, T.H.; Simon, C.J. Intensification of Penaeid Shrimp Culture: An Applied Review of Advances in Production Systems, Nutrition and Breeding. Animals 2022, 12, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopin, T. Cage Aquaculture. Third Edition. By Malcolm C M Beveridge. Ames (Iowa): Blackwell Publishing Professional. $114.99 (paper). viii + 368 p; ill.; index. ISBN: 1–4051–0842–8. 2004. Q. Rev. Biol. 2006, 81, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, L.-H.; Jensen, I.; Mikkelsen, H.; Bjørn, P.-A.; Jansen, P.A.; Bergh, Ø. Disease interaction and pathogens exchange between wild and farmed fish populations with special reference to Norway. Aquaculture 2011, 315, 167–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E. Guidelines for aquaculture effluent management at the farm-level. Aquaculture 2003, 226, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebeling, J.M.; Timmons, M.B. Recirculating Aquaculture Systems. In Aquaculture Production Systems; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 245–277. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Fisheries and Aquaculture Department—Culture of Fish in Rice Fields. Available online: https://www.fao.org/4/a0823e/a0823e00.htm (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Berg, H. Rice monoculture and integrated rice-fish farming in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam—Economic and ecological considerations. Ecol. Econ. 2002, 41, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, P.; Mallick, U.K. Modeling the Analysis for the Exploitation of Fertilizers and Pesticides on Rice Production in Bangladesh. Org. Farming 2024, 10, 13–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, D.; Edwards, P. Integrated Livestock Fish Farming Systems; Food & Agriculture Org.: Rome, Italy, 2003; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/259999240_Integrated_Livestock_Fish_Farming_Systems (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Bondad-Reantaso, M.G.; Subasinghe, R.P.; Arthur, J.R.; Ogawa, K.; Chinabut, S.; Adlard, R.; Tan, Z.; Shariff, M. Disease and health management in Asian aquaculture. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 132, 249–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Ding, K.; Xu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Liu, D.; Li, G. States, Trends, and Future of Aquaponics Research. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Turchini, G.M. Recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS): Environmental solution and climate change adaptation. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, H.S. Recirculating Aquaculture Systems (RAS) for Zebrafish Culture. In The Zebrafish in Biomedical Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 337–356. [Google Scholar]
- Holan, A.B.; Good, C.; Powell, M.D. Health management in recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS). In Aquaculture Health Management; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 281–318. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, P.; Vidal, J.M.; Sepúlveda, D.; Torres, C.; Villouta, G.; Carrasco, C.; Aguilera, F.; Ruiz-Tagle, N.; Urrutia, H. Overview and future perspectives of nitrifying bacteria on biofilters for recirculating aquaculture systems. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 1478–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubakirova, K.; Satkanov, M.; Kulataeva, M.; Assylbekova, G.; Kambarbekova, A.; Alikulov, Z. Molybdoenzymes isolated from S. glanis liver can produce nitric oxide from nitrates and nitrites. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2023, 68, 222–230. [Google Scholar]
- Whangchai, N.; Klahan, R.; Balakrishnan, D.; Unpaprom, Y.; Ramaraj, R.; Pimpimol, T. Development of aeration devices and feeding frequencies for oxygen concentration improvement in 60-tones freshwater recirculating aquaculture and biofloc ponds of Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer) rearing. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bögner, D.; Bögner, M.; Schmachtl, F.; Bill, N.; Halfer, J.; Slater, M.J. Hydrogen peroxide oxygenation and disinfection capacity in recirculating aquaculture systems. Aquac. Eng. 2021, 92, 102140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahle, S.W.; Attramadal, K.J.K.; Vadstein, O.; Hestdahl, H.I.; Bakke, I. Disease and health management in Asian aquaculture. Aquaculture 2022, 546, 737382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Andrés, J.; Rueda-Márquez, J.J.; Homola, T.; Vielma, J.; Moríñigo, M.Á.; Mikola, A.; Sillanpää, M.; Acevedo-Merino, A.; Nebot, E.; Levchuk, I. A comparison of photolytic, photochemical and photocatalytic processes for disinfection of recirculation aquaculture systems (RAS) streams. Water Res. 2020, 181, 115928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- pH in Fish Farming|Yokogawa America. Available online: https://www.yokogawa.com/us/library/resources/application-notes/ph-in-fish-farming/ (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Bögner, D.; Schmachtl, F.; Mayr, B.; Franz, C.P.; Strieben, S.; Jaehne, G.; Lorkowski, K.; Slater, M.J. Sludge Pre-Treatment through Ozone Application: Alternative Sludge Reuse Possibilities for Recirculating Aquaculture System Optimization. Ozone: Sci. Eng. 2019, 41, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, T.; Naik, S.; Shaikh, A.; Pereira, W.; Ingle, B.; Rao, Y.S. Aquaculture Monitoring and Feedback System. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Smart Electronic Systems (iSES) (Formerly iNiS), Rourkela, India, 16–18 December 2019; pp. 326–330. [Google Scholar]
- Cordova-Rozas, M.; Aucapuri-Lecarnaque, J.; Shiguihara-Juárez, P. A Cloud Monitoring System for Aquaculture using IoT. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Sciences and Humanities International Research Conference (SHIRCON), Lima, Peru, 13–15 November 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- CSong, X.; Liu, Y.; Pettersen, J.B.; Brandão, M.; Ma, X.; Røberg, S.; Frostell, B. Life cycle assessment of recirculating aquaculture systems: A case of Atlantic salmon farming in China. J. Ind. Ecol. 2019, 23, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherry, J.; Koester, J. Life Cycle Assessment of Aquaculture Stewardship Council Certified Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar). Sustainability 2020, 12, 6079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, J.; Vaishnav, A.; Deb, S.; Kashyap, S.; Debbarma, P.; Devati; Gautam, P.; Pavankalyan, M.; Kumari, K.; Verma, D.K. Re-Circulatory Aquaculture Systems: A Pathway to Sustainable Fish Farming. Arch. Curr. Res. Int. 2024, 24, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhai, H.; Peng, Z.; Yu, J.; Yan, L.; Wang, W.; Ren, T.; Han, Y. Comparison of nutritional quality, flesh quality, muscle cellularity, and expression of muscle growth-related genes between wild and recirculating aquaculture system (RAS)-farmed black rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii). Aquacult Int. 2023, 31, 2263–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzoglou, E.; Kechagia, P.; Tsopelakos, A.; Miliou, H. Co-culture of Ulva sp. and Dicentrarchus labrax in Recirculating Aquaculture System: Effects on growth, retention of nutrients and fatty acid profile. Aquat. Living Resour. 2020, 33, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stejskal, V.; Matousek, J.; Podhorec, P.; Prokesova, M.; Zajic, T.; Mraz, J. The Effect of Culture System on Proximate Composition and Amino and Fatty Acid Profiles of Peled Coregonus peled Fillets. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2019, 28, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, V.; Maulvault, A.L.; Anacleto, P.; Santos, M.; Mai, M.; Oliveira, H.; Delgado, I.; Coelho, I.; Barata, M.; Araújo-Luna, R.; et al. Enriched feeds with iodine and selenium from natural and sustainable sources to modulate farmed gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) and common carp (Cyprinus carpio) fillets elemental nutritional value. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 140, 111330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François, N.R.L.; Jobling, M.; Carter, C. Finfish Aquaculture Diversification; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2010; 703p. [Google Scholar]
- Chakroff, M. Freshwater Fish Pond Culture and Management; The Corps: Quantico, VA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, C.E. Pond Bottom Soil Analyses. In Bottom Soils, Sediment, and Pond Aquaculture; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 1995; pp. 304–340. [Google Scholar]
- Hasibuan, S.; Syafriadiman, S.; Aryani, N.; Fadhli, M.; Hasibuan, M. The age and quality of pond bottom soil affect water quality and production of Pangasius hypophthalmus in the tropical environment. Aquac. Fish. 2023, 8, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E. Bottom Soils, Sediment, and Pond Aquaculture; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012; 366p. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, C.E. Water Quality Management for Pond Fish Culture; Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1982; 524p. [Google Scholar]
- Eze, E.; Ajmal, T. Dissolved Oxygen Forecasting in Aquaculture: A Hybrid Model Approach. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Dabrowski, J.; McCulloch, J. Dissolved oxygen prediction in prawn ponds from a group of one step predictors. Inf. Process. Agric. 2020, 7, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozdz, D.; Malinska, K.; Mazurkiewicz, J.; Kacprzak, M.; Mrowiec, M.; Szczypior, A.; Postawa, P.; Stachowiak, T. Fish pond sediment from aquaculture production—Current practices and the potential for nutrient recovery: A Review. Int. Agrophysics 2020, 34, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dróżdż, D.; Malińska, K.; Kacprzak, M.; Mrowiec, M.; Szczypiór, A.; Postawa, P.; Stachowiak, T. Potential of Fish Pond Sediments Composts as Organic Fertilizers. Waste Biomass Valor. 2020, 11, 5151–5163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett-Walker, J.; Collier, K.J.; Daniel, A.; Hicks, B.J.; Klee, D. Design features of constructed floodplain ponds influence waterbird and fish communities in northern New Zealand. Freshw. Biol. 2020, 65, 2066–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recirculating Aquaculture Systems (RAS)—Pros and Cons—Arab World Agribusiness 2021. Available online: https://www.fanarpublishing.net/arabworldagribusiness/aquaculture-37-2/recirculating-aquaculture-systems-ras-pros-and-cons/ (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Ghamkhar, R.; Boxman, S.E.; Main, K.L.; Zhang, Q.; Trotz, M.A.; Hicks, A. Life cycle assessment of aquaculture systems: Does burden shifting occur with an increase in production intensity? Aquac. Eng. 2021, 92, 102130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigorakis, K.; Rigos, G. Aquaculture effects on environmental and public welfare—The case of Mediterranean mariculture. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 899–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidwell, J.H. Functions and Characteristics of All Aquaculture Systems. In Aquaculture Production Systems; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 51–63. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, C.E.; Tucker, C.S. Pond Aquaculture Water Quality Management; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 1998; 732p. [Google Scholar]
- Colt, J.; Schuur, A.M.; Weaver, D.; Semmens, K. Engineering Design of Aquaponics Systems. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2022, 30, 33–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkmen, G.; Güner, Y. Aquaponic (Integrating Fish and Plant Culture) Systems. In International Symposium on Sustainable Development, Science Book; Wiley: London, UK, 2000; pp. 657–666. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, K.; Kuthiala, T.; Singh, G.; Arya, S.K.; Iwai, C.B.; Ravindran, B.; Khoo, K.S.; Chang, S.W.; Awasthi, M.K. An alternative approach towards nitrification and bioremediation of wastewater from aquaponics using biofilm-based bioreactors: A review. Chemosphere 2023, 316, 137849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagopian, D.S.; Riley, J.G. A closer look at the bacteriology of nitrification. Aquac. Eng. 1998, 18, 223–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasozi, N.; Abraham, B.; Kaiser, H.; Wilhelmi, B. The complex microbiome in aquaponics: Significance of the bacterial ecosystem. Ann. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satkanov, M.; Tazhibay, D.; Zhumabekova, B.; Assylbekova, G.; Abdukarimov, N.; Nurbekova, Z.; Kulatayeva, M.; Aubakirova, K.; Alikulov, Z. Method for assessing the content of molybdenum enzymes in the internal organs of fish. MethodsX 2024, 12, 102576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supriadi, O.; Sunardi, A.; Baskara, H.A.; Safei, A. Controlling pH and temperature aquaponics use proportional control with Arduino and Raspberry. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; Volume 550, p. 012016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosh, K.; Chowdhury, S. Review of aquaponics system: Searching for a technically feasible and economically profitable aquaponics system. J. Agric. Environ. Consum. Sci. 2019, 19, 5–13. [Google Scholar]
- Aitlessov, K.; Zhumabekova, B.; Sagyndykov, U.; Tuyakbayeva, A.; Bitkeyeva, A.; Bazarbaeva, K.Z.; Mukhtarov, A.; Nurbekova, Z.; Satkanov, M.; Kulatayeva, M.; et al. Foliar Fertilization with Molybdate and Nitrate Up-Regulated Activity of Nitrate Reductase in Lemon Balm Leaves. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasdravanidis, C.; Alvanou, M.V.; Lattos, A.; Papadopoulos, D.K.; Chatzigeorgiou, I.; Ravani, M.; Liantas, G.; Georgoulis, I.; Feidantsis, K.; Ntinas, G.K.; et al. Aquaponics as a Promising Strategy to Mitigate Impacts of Climate Change on Rainbow Trout Culture. Animals 2022, 12, 2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NDCs, F.F. Implementing Sustainable Aquaculture Management Systems. Available online: https://foodforwardndcs.panda.org/food-production/implementing-sustainable-aquaculture-management-systems/ (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Robaina, L.; Pirhonen, J.; Mente, E.; Sánchez, J.; Goosen, N. Fish diets in aquaponics. In Aquaponics Food Production Systems: Combined Aquaculture and Hydroponic Production Technologies for the Future; SpringerLink: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-15943-6_13 (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Eck, M.; Körner, O.; Jijakli, M.H. Nutrient Cycling in Aquaponics Systems. In Aquaponics Food Production Systems: Combined Aquaculture and Hydroponic Production Technologies for the Future; Goddek, S., Joyce, A., Kotzen, B., Burnell, G.M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 231–246. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, C.; Knopf, K.; Kloas, W. Fish Feeds in Aquaponics and Beyond: A Novel Concept to Evaluate Protein Sources in Diets for Circular Multitrophic Food Production Systems. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.J.; Shaw, C.; Chen, T.W.; Staß, C.M.; Ulrichs, C.; Riewe, D.; Kloas, W.; Geilfus, C.M. Plant nutritional value of aquaculture water produced by feeding Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) alternative protein diets: A lettuce and basil case study. Plants People Planet. 2024, 6, 362–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- What Is Aquaponics and How Does It Work?—Go Green Aquaponics. Available online: https://gogreenaquaponics.com/blogs/news/what-is-aquaponics-and-how-does-it-work (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Chu, Y.I.; Wang, C.M.; Park, J.C.; Lader, P.F. Review of cage and containment tank designs for offshore fish farming. Aquaculture 2020, 519, 734928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lounas, R.; Kasmi, H.; Chernai, S.; Nadia Amarni; Ghebriout, L.; Meslem-Haoui, N.; Hamdi, B. Towards Sustainable Mariculture: Some Global Trends. Thalassas 2020, 36, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cuthbertson, A.; Gualtieri, C.; Shao, D. A Review on Mariculture Effluent: Characterization and Management Tools. Water 2020, 12, 2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Liu, Q.; Liu, J.; Xiao, J.; Xu, G. Pollution Control of Industrial Mariculture Wastewater: A Mini-Review. Water 2022, 14, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannister, J.; Sievers, M.; Bush, F.; Bloecher, N. Biofouling in marine aquaculture: A review of recent research and developments. Biofouling 2019, 35, 631–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, L.M.; Davidson, I.C.; Bucknall, B.G.; Atalah, J. Salmon farm biofouling and potential health impacts to fish from stinging cnidarians. Aquaculture 2023, 568, 739315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleadin, J.; Lesic, T.; Kresic, G.; Baric, R.; Bogdanovic, T.; Oraic, D.; Vulic, A.; Legac, A.; Zrncic, S. Nutritional Quality of Different Fish Species Farmed in the Adriatic Sea. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2017, 29, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerezo-Valverde, J.; Martínez-Llorens, S.; Tomas-Vidal, A.; Jover, M.; Rodríguez, C.; Estefanell, J.; Gairín, J.I.; Rodrigues-dos-Santos-Domingues, P.M.; Rodríguez, C.; García-García, B. Amino acids composition and protein quality evaluation of marine species and meals for feed formulations in cephalopods. Aquac. Int. 2013, 21, 413–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, E.K. Health benefits of seafood; is it just the fatty acids? Food Chem. 2013, 140, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thilsted, S.H.; Thorne-Lyman, A.; Webb, P.; Bogard, J.R.; Subasinghe, R.; Phillips, M.J.; Allison, E.H. Sustaining healthy diets: The role of capture fisheries and aquaculture for improving nutrition in the post-2015 era. Food Policy 2016, 61, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orban, E.; Sinesio, F.; Paoletti, F.; Casini, N.S.; Caproni, R.; Moneta, E. Caratteristiche nutrizionali ed organolettiche di orate (Sparus aurata) da acquacoltura: Un esempio di come le differenti tecniche di allevamento possono influenzare la qualità del pesce. Riv. Sci. Aliment. 1996, 25, 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Oliva-Teles, A. Nutrition and health of aquaculture fish. J. Fish. Dis. 2012, 35, 83–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Ma, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, J. Comparison of proximate composition, amino acid and fatty acid profiles in wild, pond- and cage-cultured longsnout catfish (Leiocassis longirostris). Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 1772–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Mahecha, H.; de Francisco, A.; Beirão, L.H. Importância de ácidos graxos poliinsaturados presentes em peixes de cultivo e de ambiente natural para a nutrição humana. Bol. Inst. Pesca 2002, 28, 101–110. [Google Scholar]
- Calderini, M.L.; Stevčić, Č.; Taipale, S.; Pulkkinen, K. Filtration of Nordic recirculating aquaculture system wastewater: Effects on microalgal growth, nutrient removal, and nutritional value. Algal Res. 2021, 60, 102486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozzi, V.; Parisi, G.; Di Crescenzo, D.; Giordano, M.; Carnevali, O. Evaluation of Dicentrarchus labrax Meats and the Vegetable Quality of Beta vulgaris var. cicla Farmed in Freshwater and Saltwater Aquaponic Systems. Water 2016, 8, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakocy, J.; Shultz, R.C.; Bailey, D.S.; Thoman, E.S. Aquaponic production of tilapia and basil: Comparing a batch and staggered cropping system. In Proceedings of the South Pacific Soilless Culture Conference-SPSCC 648, Palmerston North, New Zealand, 10–13 February 2003; pp. 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebauer, R.; Brügmann, A.; Folorunso, E.A.; Goldhammer, T.; Gebauer, T.; Schöning, V.; Bittmann, S.; Knopf, K.; Mráz, J.; Kloas, W. Species- and diet-specific aquaculture wastewater nutrient profile: Implications for aquaponics and development of sustainable aquaponics diet. Aquaculture 2023, 568, 739307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beem, M.; Rakocy, J.; Masser, M.; Losordo, T. Recirculating Aquaculture Tank Production Systems: Aquaponics—Integrating Fish and Plant Culture—Oklahoma State University. Available online: https://extension.okstate.edu/fact-sheets/recirculating-aquaculture-tank-production-systems-aquaponics-integrating-fish-and-plant-culture.html (accessed on 24 May 2024).
- Glencross, B.D. A feed is still only as good as its ingredients: An update on the nutritional research strategies for the optimal evaluation of ingredients for aquaculture feeds. Aquac. Nutr. 2020, 6, 1871–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mente, E.; Stratakos, A.; Boziaris, I.S.; Kormas, K.A.; Karalazos, V.; Karapanagiotidis, I.T.; Catsiki, V.A.; Leondiadis, L. The effect of organic and conventional production methods on sea bream growth, health and body composition: A field experiment. Sci. Mar. 2022, 76, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmerhaus, G.; Lazado, C.C.; Cabillon, N.A.R.; Reiten, B.K.M.; Johansen, L.-H. The optimum velocity for Atlantic salmon post-smolts in RAS is a compromise between muscle growth and fish welfare. Aquaculture 2021, 532, 736076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, R.W. 13—Alternative marine sources of fish feed and farmed fish quality. In Improving Farmed Fish Quality and Safety; Lie, Ø., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2008; pp. 328–342. [Google Scholar]
- Monti, G.; De Napoli, L.; Mainolfi, P.; Barone, R.; Guida, M.; Marino, G.; Amoresano, A. Monitoring Food Quality by Microfluidic Electrophoresis, Gas Chromatography, and Mass Spectrometry Techniques: Effects of Aquaculture on the Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Anal. Chem. Soc. 2005, 77, 2587–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishita, T.; Uno, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Takahashi, T. Comparison of the Proximate Compositions in Cultured Red Sea Bream Differing the Localities and Culture Methods, and of the Wild Fish. Nippon. Suisan Gakkaishi 1988, 54, 1965–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchtman, D.W.; Song, C. Cognitive enhancement by omega-3 fatty acids from child-hood to old age: Findings from animal and clinical studies. Neuropharmacology 2013, 64, 550–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, A.; Basurto, X.; Virdin, J.; Lin, X.; Betances, S.J.; Smith, M.D.; Allison, E.H.; Best, B.A.; Brownell, K.D.; Campbell, L.M.; et al. Recognize fish as food in policy discourse and development funding. Ambio 2021, 50, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurdiani, R.; Prihanto, A.A.; Firdaus, M. Seafood as Source of Protein-based Functional Foods. In Encyclopedia of Marine Biotechnology; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 2987–2997. [Google Scholar]
- Hei, A. Mental Health Benefits of Fish Consumption. Clin. Schizophr. Relat. Psychoses 2020, 1, 19–225. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/343557862_Mental_Health_Benefits_of_Fish_Consumption (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Lagouri, V. Functional Foods; BoD—Books on Demand; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; 139p. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Li, R.; Xia, X.; Yu, C.; Fan, X.; Zhao, Y. A method overview in smart aquaculture. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindholm-Lehto, P. Water quality monitoring in recirculating aquaculture systems. Aquac. Fish. Fish. 2023, 3, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).