Integrative Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analyses Reveal the Impact of Methionine Supplementation to Gibel Carp (Carassius auratus gibelio)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Diets Formulation and Preparation
2.2. Rearing Conditions
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Proximate Composition of Whole Fish and Diets
2.5. Biochemical Assays
2.6. Metabolomics and Transcriptomics in the Hepatopancreas
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth Performance
3.2. Whole Body Composition and Intestinal Digestive Enzyme Activities
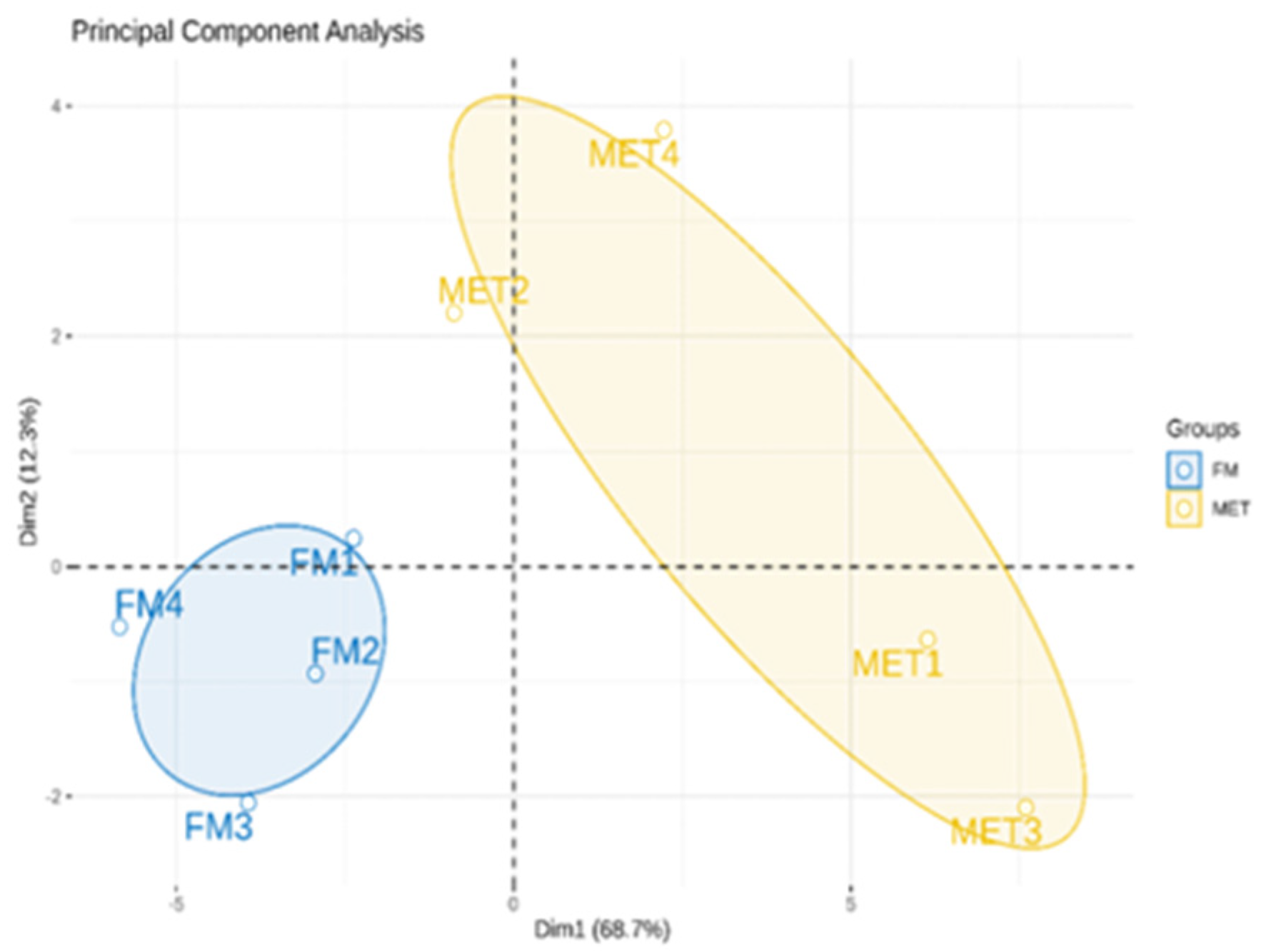
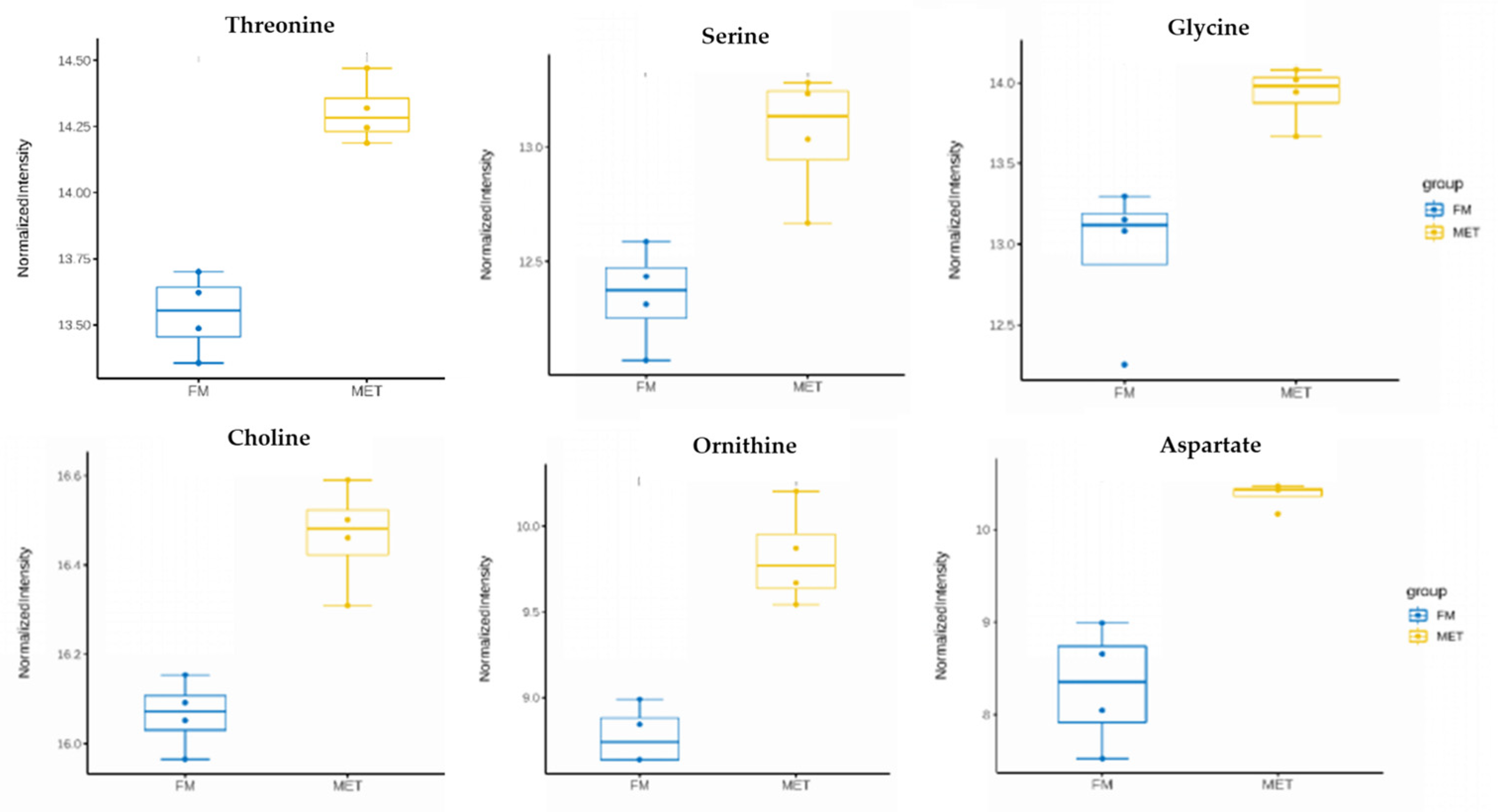
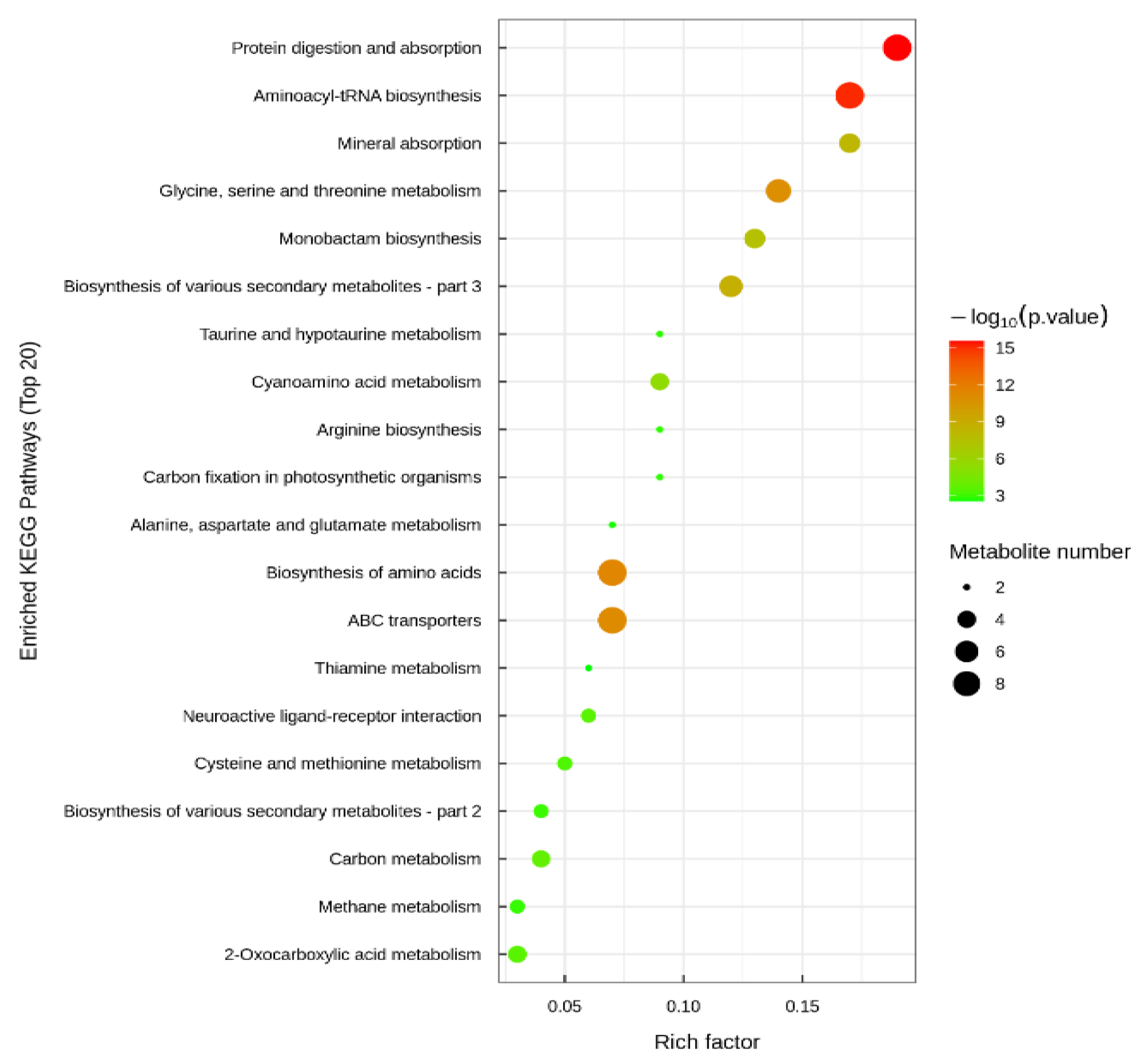
3.3. Metabolomics in the Hepatopancreas
3.4. Transcriptomics in the Hepatopancreas
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rolland, M.; Skov, P.V.; Larsen, B.K.; Holm, J.; Gómez-Requeni, P.; Dalsgaard, J. Increasing Levels of Dietary Crystalline Methionine Affect Plasma Methionine Profiles, Ammonia Excretion, and the Expression of Genes Related to the Hepatic Intermediary Metabolism in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 198, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, A.J.P.; Sá, M.V.C.; Browdy, C.L.; Vazquez-Anon, M. Practical Supplementation of Shrimp and Fish Feeds with Crystalline Amino Acids. Aquaculture 2014, 431, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolland, M.; Feekings, J.P.; Dalsgaard, J.; Skov, P.V. Modelling the Effects of Dietary Methionine Level and Form on Postprandial Plasma Essential Amino Acid Profiles in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquac. Nutr. 2016, 22, 1185–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agboola, J.O.; Overland, M.; Skrede, A.; Hansen, J.O. Yeast as major protein-rich ingredient in aquafeeds: A review of the implications for aquaculture production. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 13, 949–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espe, M.; Adam, A.C.; Saito, T.; Skjærven, K.H. Methionine: An Indispensable Amino Acid in Cellular Metabolism and Health of Atlantic Salmon. Aquac. Nutr. 2023, 2023, 5706177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gao, C.; Wang, B.; Wang, C.; Sagada, G.; Yan, Y. Methionine in Fish Health and Nutrition: Potential Mechanisms, Affecting Factors, and Future Perspectives. Aquaculture 2023, 568, 739310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espe, M.; Andersen, S.M.; Holen, E.; Rønnestad, I.; Veiseth-Kent, E.; Zerrahn, J.E.; Aksnes, A. Methionine Deficiency Does Not Increase Polyamine Turnover through Depletion of Hepatic S-Adenosylmethionine in Juvenile Atlantic Salmon. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 1274–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Séité, S.; Mourier, A.; Camougrand, N.; Salin, B.; Figueiredo-Silva, A.C.; Fontagné-Dicharry, S.; Panserat, S.; Seiliez, I. Dietary Methionine Deficiency Affects Oxidative Status, Mitochondrial Integrity and Mitophagy in the Liver of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Tang, L.; Jiang, W.D.; Hu, K.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Kuang, S.Y.; Tang, L.; Tang, W.N.; Zhang, Y.A.; et al. The Relationship between Dietary Methionine and Growth, Digestion, Absorption, and Antioxidant Status in Intestinal and Hepatopancreatic Tissues of Sub-Adult Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodósio, R.; Engrola, S.; Cabano, M.; Colen, R.; Masagounder, K.; Aragão, C. Metabolic and Nutritional Responses of Nile Tilapia Juveniles to Dietary Methionine Sources. Br. J. Nutr. 2022, 127, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, L.; Magalhaes, R.; Martins, N.; Fontinha, F.; Castro, C.; Peres, H.; Mercier, Y.; Mahmood, T.; Nuez-Ortín, W.G.; Oliva-Teles, A. Evaluation of Dietary Methionine Sources on Growth Performance and Antioxidant Potential of Gilthead Seabream Juveniles Reared at High Water Temperature. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2024, 55, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.Y.; Lin, X.W.; Shao, X.P.; Zhao, J.H.; Xu, H.; de Cruz, C.R.; Xu, Q.Y. Effects of Supplementing Coated Methionine in a High Plant-Protein Diet on Growth, Antioxidant Capacity, Digestive Enzymes Activity and Expression of TOR Signaling Pathway Associated Genes in Gibel Carp, Carassius auratus gibelio. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1319698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, M.; Moura, J.; Peixoto, D.; Castro-Cunha, M.; Conceição, L.E.C.; Dias, J.; Costas, B. Dietary Methionine as a Strategy to Improve Innate Immunity in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Juveniles. General. Comp. Endocrinol. 2021, 302, 113690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, M.; Engrola, S.; Colen, R.; Conceição, L.E.C.; Dias, J.; Costas, B. Dietary Methionine Supplementation Improves the European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Immune Status Following Long-Term Feeding on Fishmeal-Free Diets. Br. J. Nutr. 2020, 124, 890–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zheng, S.; Cheng, K.; Ma, X.; Wu, G. Use of Alternative Protein Sources for Fishmeal Replacement in the Diet of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Part II: Effects of Supplementation with Methionine or Taurine on Growth, Feed Utilization, and Health. Amino Acids 2021, 53, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.P.; Zhou, W.Y.; Liu, S.S.; Zhang, W.B.; Mai, K.S. Efficacy of Crystalline Methionine and Microencapsulation Methionine in Diets for Pacific White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 4206–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, S.Y.; Tan, B.P.; Dong, X.H.; Yang, Q.H.; Liu, H.Y. Effects of Supplemental Coated or Crystalline Methionine in Low-Fishmeal Diet on the Growth Performance and Body Composition of Juvenile Cobia Rachycentron Canadum (Linnaeus). Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2014, 32, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Gong, S.; Yang, H.; Lin, Y.; Yu, D.; Luo, Z. Effects of Supplementation of Crystalline or Coated Lysine and/or Methionine on Growth Performance and Feed Utilization of the Chinese Sucker, Myxocyprinus asiaticus. Aquaculture 2011, 316, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.C.; Shi, B.; Jiao, L.F.; Jin, M.; Sun, P.; Ding, L.Y.; Yuan, Y. Hepatopancreas and Ovarian Transcriptome Response to Different Dietary Soybean Lecithin Levels in Portunus trituberculatus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2019, 31, 100600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zou, X.; Zhao, M.; Guan, Q.Q.; Xuan, Z.Y.; Liu, L.S.; Gao, Z.X. Integrated transcriptome and metabolome analysis of liver reveals unsynchronized growth mechanisms in blunt-snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala). BMC Genom. 2025, 26, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. The Official Methods of Analysis, 18th ed.; AOAC International: Maryland, MD, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Alami-Durante, H.; Bazin, D.; Cluzeaud, M.; Fontagné-Dicharry, S.; Kaushik, S.; Geurden, I. Effect of Dietary Methionine Level on Muscle Growth Mechanisms in Juvenile Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2018, 483, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.J.; Yu, D.H.; Dong, G.F.; Gong, S.Y. Partial Replacement of Fish Meal by Soybean Meal with or without Methionine and Phytase Supplement in Diets for Juvenile Chinese Sucker, Myxocyprinus asiaticus. Aquac. Nutr. 2015, 22, 12318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo-Silva, C.; Lemme, A.; Sangsue, D.; Kiriratnikom, S. Effect of DL-Methionine Supplementation on the Success of Almost Total Replacement of Fish Meal with Soybean Meal in Diets for Hybrid Tilapia (Reochromis niloticus × Reochromis mossambicus). Aquac. Nutr. 2015, 21, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Figueiredo-Silva, C.; Dong, Y.; Yue, Y.R.; Lin, H.Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Xia, D.M.; Lu, X. Effect of Replacing Fish Meal with Soybean Meal and of DL-methionine or Lysine Supplementation in Pelleted Diets on Growth and Nutrient Utilization of Juvenile Golden Pompano (Trachinotus ovatus). Aquac. Nutr. 2015, 22, 12284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Ji, W.X.; Wu, Y.B.; Han, H.; Qin, J.G.; Wang, Y. Replacement of Dietary Fish Meal by Soybean Meal Supplemented with Crystalline Methionine for Japanese Seabass (Lateolabrax japonicus). Aquac. Res. 2014, 47, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, A.J.P.; Masagounder, K. Optimal Levels of Fish Meal and Methionine in Diets for Juvenile Litopenaeus vannamei to Support Maximum Growth Performance with Economic Efficiency. Animals 2022, 13, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Liang, H.; He, J.; Masagounder, K.; Yue, Y.; Yang, H.; Ge, X.; Xie, J.; Xi, B. Effects of DL-Methionine Supplementation on the Success of Fish Meal Replacement by Plant Proteins in Practical Diets for Juvenile Gibel Carp (Carassius auratus Gibelio). Aquac. Nutr. 2017, 23, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, S.Y.; Tan, B.P.; Lin, H.Z.; Mai, K.S.; Ai, Q.H.; Wang, X.J.; Zhang, W.B.; Xu, W.; LiuFu, Z.G. Effects of Supplementation of Crystalline or Coated Methionine on Growth Performance and Feed Utilization of the Pacific White Shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquac. Nutr. 2011, 17, e1–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, Z.; Noor, M.; Khan, S.A.; Younas, W.; Ualiyeva, D.; Hassan, Z.; Yousafzai, A.M. Dietary Supplementations of Methionine Improve Growth Performances, Innate Immunity, Digestive Enzymes, and Antioxidant Activities of Rohu (Labeo rohita). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 47, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccotti, C.; Biasato, I.; Gasco, L.; Caimi, C.; Oddon, S.B.; Rimoldi, S.; Brambilla, F.; Terova, G. How Different Dietary Methionine Sources Could Modulate the Hepatic Metabolism in Rainbow Trout? Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 3238–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Y.; He, J.Y.; Su, N.N.; Masagounder, K.; Xu, M.L.; Chen, L.L.; Liu, Q.Y.; Ye, H.Q.; Sun, Z.Z.; Ye, C.X. Effects of DL-Methionine and a Methionine Hydroxy Analogue (MHA-Ca) on Growth, Amino Acid Profiles and the Expression of Genes Related to Taurine and Protein Synthesis in Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio). Aquaculture 2021, 532, 735962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Wang, X.; Tan, C.; Zhou, H.; Mai, K.; He, G. Effect of Dietary Methionine Levels on Growth Performance, Amino Acid Metabolism and Intestinal Homeostasis in Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Aquaculture 2019, 498, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Lin, P.; Mai, H.; Chen, L.; Wei, Z.; Tan, B.; Ye, C. Metabolomics Profiles Revealed Potential Biomarkers of Pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) under Cold and Low Salinity Stress. Aquac. Rep. 2025, 40, 102633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, M.; Imanaka, T. Peroxisomal ABC Transporters: Structure, Function and Role in Disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Basis Dis. 2012, 1822, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Ingredients | FM | CM50 | CM100 | HM50 | HM100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fishmeal | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 |
| Soybean meal | 26.8 | 26.8 | 26.8 | 26.8 | 26.8 |
| Wheat middling | 31.6 | 31.6 | 31.6 | 31.6 | 31.6 |
| Rapeseed meal | 12.0 | 12.0 | 12.0 | 12.0 | 12.0 |
| Cottonseed protein | 10.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 |
| Soybean lecithin oil | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| Soybean oil | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Fish oil | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| DL-methionine | 0.0 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Coated methionine (10%) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.5 | 5.0 |
| Vitamin mixture a | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Mineral mixture b | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| Choline chloride | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Ca(H2PO4)2 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| Magnesium sulfate | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Coating materials | 6.0 | 5.75 | 5.5 | 3.5 | 1.0 |
| Total | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Nutrient level (%) | |||||
| Dry matter | 92.46 | 92.40 | 92.56 | 92.03 | 91.52 |
| Crude protein | 32.16 | 33.86 | 34.65 | 34.07 | 34.58 |
| Crude lipid | 5.53 | 5.50 | 5.51 | 5.52 | 5.50 |
| Ash | 6.54 | 6.71 | 6.65 | 6.64 | 6.61 |
| Groups | BWi | BWf | WG | SGR | FCR | SR | CF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FM | 9.22 ± 0.04 | 20.47 ± 0.42 ab | 119.97 ± 4.79 a | 1.14 ± 0.04 a | 1.98 ± 0.08 b | 96.00 ± 3.27 | 2.79 ± 0.20 |
| CM50 | 9.25 ± 0.01 | 19.88 ± 0.28 a | 113.95 ± 4.53 a | 1.09 ± 0.02 a | 2.10 ± 0.06 b | 99.00 ± 2.00 | 2.85 ± 0.21 |
| CM100 | 9.22 ± 0.03 | 20.27 ± 0.75 ab | 117.86 ± 7.81 a | 1.13 ± 0.06 a | 2.03 ± 0.14 b | 96.00 ± 0.00 | 2.85 ± 0.14 |
| HM50 | 9.19 ± 0.05 | 20.07 ± 0.20 a | 116.04 ± 1.04 a | 1.12 ± 0.01 a | 2.04 ± 0.03 b | 95.00 ± 2.00 | 2.75 ± 0.22 |
| HM100 | 9.18 ± 0.03 | 21.46 ± 0.81 b | 130.77 ± 11.27 b | 1.21 ± 0.06 b | 1.83 ± 0.12 a | 96.00 ± 5.66 | 2.83 ± 0.14 |
| Two-way ANOVA (p value) | |||||||
| Form | / | 0.330 | 0.056 | 0.022 | 0.023 | 0.230 | 0.321 |
| Level | / | 0.009 | 0.020 | 0.009 | 0.012 | 0.539 | 0.502 |
| Interactions | / | 0.110 | 0.162 | 0.146 | 0.173 | 0.230 | 0.500 |
| Groups | Moisture (%) | Crude Protein (%) | Crude Lipid (%) | Ash (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FM | 72.95 ± 0.37 | 15.99 ± 0.12 | 4.67 ± 0.12 b | 4.27 ± 0.07 |
| CM50 | 73.79 ± 0.55 | 16.07 ± 0.10 | 4.30 ± 0.12 a | 4.25 ± 0.04 |
| CM100 | 74.23 ± 1.25 | 15.95 ± 0.06 | 4.77 ± 0.23 b | 4.25 ± 0.06 |
| HM50 | 73.76 ± 0.97 | 16.15 ± 0.17 | 4.73 ± 0.08 b | 4.35 ± 0.06 |
| HM100 | 73.24 ± 0.32 | 16.14 ± 0.15 | 4.20 ± 0.26 a | 4.26 ± 0.05 |
| Two-way ANOVA (p value) | ||||
| Form | 0.254 | 0.100 | 0.210 | 0.123 |
| Level | 0.917 | 0.399 | 0.219 | 0.178 |
| Interactions | 0.287 | 0.468 | 0.147 | 0.164 |
| Groups | Lipase (U/mgprot) | Protease (U/mgprot) | Amylase (U/mgprot) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FM | 11.12 ± 0.25 a | 18.60 ± 4.10 a | 61.26 ± 1.89 a |
| CM50 | 11.05 ± 0.32 a | 21.96 ± 2.48 ab | 61.07 ± 1.43 a |
| CM100 | 11.23 ± 0.44 a | 24.66 ± 0.65 b | 61.16 ± 1.97 a |
| HM50 | 11.31 ± 0.50 a | 25.36 ± 1.32 b | 62.09 ± 1.26 a |
| HM100 | 14.81 ± 0.26 b | 25.67 ± 1.97 b | 65.03 ± 0.76 b |
| Two-way ANOVA (p value) | |||
| Form | <0.001 | 0.020 | 0.001 |
| Level | <0.001 | 0.094 | 0.022 |
| Interactions | <0.001 | 0.175 | 0.030 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Qian, R.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, J. Integrative Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analyses Reveal the Impact of Methionine Supplementation to Gibel Carp (Carassius auratus gibelio). Fishes 2025, 10, 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10050203
Liu Y, Qian R, Xu Q, Zhao J. Integrative Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analyses Reveal the Impact of Methionine Supplementation to Gibel Carp (Carassius auratus gibelio). Fishes. 2025; 10(5):203. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10050203
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yujie, Rendong Qian, Qiyou Xu, and Jianhua Zhao. 2025. "Integrative Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analyses Reveal the Impact of Methionine Supplementation to Gibel Carp (Carassius auratus gibelio)" Fishes 10, no. 5: 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10050203
APA StyleLiu, Y., Qian, R., Xu, Q., & Zhao, J. (2025). Integrative Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analyses Reveal the Impact of Methionine Supplementation to Gibel Carp (Carassius auratus gibelio). Fishes, 10(5), 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10050203







