Abstract
Aquaculture plays a crucial role in China’s agricultural sector, with improved growth performance and feed efficiency in cultured species representing key industry challenges. Among nutritional strategies, feed attractants have received increasing attention for their ability to stimulate feeding behavior and enhance feed utilization. This study hypothesized that dietary supplementation with a formulated feed attractant would enhance feeding activity, improve physiological condition, and modulate antioxidant and immune responses in juvenile largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). A total of 270 fish (initial weight: 12.5 ± 2.5 g) were randomly assigned to three groups: CON (basal diet), YXX0.05 (basal diet + 0.05% attractant), and YXX0.1 (basal diet + 0.10% attractant). After 56 days of feeding, no significant differences were observed in final body weight (FBW) or whole-body composition (p > 0.05). However, feed intake (FI) increased by 5.1%, and the condition factor (CF) improved significantly by 7.6% (p < 0.05) in the YXX0.05 group, while the viscerosomatic index (VSI) was reduced by 3.6% (p < 0.05), suggesting enhanced feeding motivation and improved body compactness. In terms of physiological responses, compared to the control group, the YXX0.05 group exhibited a significant increase in liver total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC) (p < 0.05), a significant decrease in malondialdehyde (MDA) content (p < 0.05), an increase in serum lysozyme (LZM) activity (p < 0.05), and a significant decrease in aspartate aminotransferase (AST) activity (p < 0.05), reflecting enhanced immune status and potential liver protection. In conclusion, although growth performance metrics such as FBW and specific growth rate (SGR) remained unchanged, the feed attractant at 0.05% inclusion significantly improved feed intake, body condition, and physiological health markers. These results suggest the attractant has practical value in improving fish welfare and nutrient utilization efficiency, providing a functional dietary strategy for sustainable largemouth bass farming.
Key Contribution:
In this study, we found that the fishy attractant had no effect on the growth performance or body composition of the largemouth bass, but significantly increased feed intake and condition factor, and significantly reduced the visceral somatic index. It also enhanced liver antioxidant capacity and serum immunity. This study provides a theoretical basis for the application of fish attractants in aquaculture.
1. Introduction
With the increasing scale and intensification of aquaculture, various stressors such as environmental, metabolic, and crowding stresses have led to immune dysfunction and frequent disease outbreaks in aquatic animals. These factors severely restrict the healthy and sustainable development of the aquaculture industry. According to recent estimates, global aquaculture losses due to disease alone can exceed billions of dollars annually, with significant impacts on fish survival, growth rates, and economic returns [1]. Additionally, suboptimal feed conversion ratios (FCRs) contribute to increased production costs and environmental burden. As a result, significant efforts have been devoted to developing effective nutritional strategies that can mitigate these challenges and enhance the overall performance of farmed aquatic species. Among these strategies, the use of feed attractants has gained considerable attention due to their ability to improve the palatability of artificial feed for fish and shrimp. Feed attractants, which are special additives included in aquaculture diets, play a crucial role in stimulating feeding behavior, increasing feed intake and feed conversion efficiency, promoting growth, reducing water pollution, lowering disease incidence and mortality, and ultimately enhancing economic profitability [1].
Common types of feed attractants used in aquaculture encompass a diverse range of compounds, including amino acids and peptides, nucleotides, herbal medicines, and plant- or animal-derived extracts such as betaine and allicin [2,3,4,5,6]. These compounds are strategically incorporated into aquafeeds to enhance palatability, stimulate feeding behavior, and optimize nutrient utilization in various aquatic species. The efficacy of different feed attractants depends on species-specific feeding preferences, physiological responses, and environmental conditions, making the selection and formulation of attractants a crucial aspect of aquafeed development [7,8]. Among them, free amino acids such as L-glutamine and glycine have been extensively studied for their potent appetite-stimulating effects, particularly in fish species like rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and Hoplias aimara (giant trahira) [9,10]. The presence of these amino acids in feed has been shown to trigger specific chemosensory receptors in fish, thereby enhancing feeding motivation and improving overall growth rates. These amino acids are thought to function by mimicking the taste of natural prey items, activating gustatory and olfactory receptors that elicit feeding responses [11].
In addition to amino acids, certain fatty acids, including butyric acid and octanoic acid, have been identified as highly effective attractants, particularly in crustaceans such as Litopenaeus vannamei (Pacific white shrimp) [12,13]. These compounds not only stimulate feed intake but also contribute to improved energy metabolism and intestinal health, which are essential for maintaining optimal growth performance. Fatty acids play a key role in modulating gut microbiota composition, enhancing nutrient absorption, and reducing intestinal inflammation, thereby improving feed efficiency and overall health status in farmed shrimp and other crustaceans. Furthermore, essential oils derived from natural sources such as garlic (e.g., those from garlic and ginger) have gained increasing attention due to their dual role as feeding stimulants and bioactive agents with antimicrobial and immunostimulatory properties [2,3]. The incorporation of these essential oils into aquafeeds has been reported to enhance both feed efficiency and disease resistance, making them valuable functional additives in sustainable aquaculture practices [14,15,16].
Notably, recent studies have highlighted the potential synergistic effects of combining multiple feed attractants within a single formulation. For instance, blends of amino acids, fatty acids, and plant extracts have been shown to exert superior effects on feed palatability and intake compared to individual compounds alone [17]. This synergy is thought to result from the activation of multiple chemosensory pathways, leading to a more pronounced stimulation of feeding behavior and improved nutrient absorption. Such findings underscore the importance of optimizing feed attractant combinations to maximize their effectiveness in aquaculture nutrition [18,19]. Beyond their role in enhancing feed intake, feed attractants also play a crucial role in aquaculture sustainability by reducing feed wastage and minimizing the environmental impact of uneaten feed. Improved feed palatability and intake efficiency result in better feed conversion ratios (FCRs), leading to reduced nutrient leaching into aquatic environments [20]. This reduction in organic waste output is particularly important in intensive aquaculture systems, where excessive nutrient loading can lead to eutrophication and deteriorated water quality [21]. Furthermore, some feed attractants, such as nucleotides and certain plant-derived compounds, have been reported to exert immunomodulatory effects, strengthening the resilience of aquatic animals against infectious diseases [22]. The incorporation of immunostimulatory attractants into aquafeeds can enhance the innate and adaptive immune responses of fish and shrimp, thereby reducing the reliance on antibiotics and chemical treatments, which aligns with the growing demand for sustainable and responsible aquaculture practices [23].
Largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) has emerged as one of the most economically important freshwater carnivorous fish species in China and other parts of Asia due to its fast growth, high market value, and consumer demand. However, its aggressive nature, high protein requirements, and sensitivity to feed palatability present challenges for intensive aquaculture. Largemouth bass are particularly responsive to feed formulation, and improving their feed intake and utilization efficiency is essential for enhancing production performance. Based on this background, we selected a complex fish attractant—comprising 8.3% isovaleric acid, 4.9% decanoic acid, 2.8% hexanoic acid, 2.4% octanoic acid, 1.4% butyric acid, and 6% phenylacetic acid—as a dietary supplement. Juvenile largemouth bass (M. salmoides) were chosen as the model species due to their commercial importance in freshwater aquaculture. The present study aimed to evaluate the effects of this attractant on the growth performance, antioxidant capacity, and immune status of juvenile largemouth bass. We hypothesized that the inclusion of the attractant would enhance feed intake, improve feed efficiency, and modulate oxidative stress and immune parameters without inducing negative impacts on tissue health.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Ethics
The research on the culture and management of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) was carried out in full adherence to the “Management Rule of Laboratory Animals” (Chinese Order No. 676, State Council, revised on 1 March 2017). The study received ethical approval from the Animal Care and Use Committee at the Fisheries College of Jimei University (Ethics Approval No. 1067). Every precaution was taken to ensure the animals were treated humanely and that any potential suffering was minimized throughout the course of the experiment.
2.2. Diet Preparation
The fish attractant used in this study was sourced from Dadi Hanke Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Chengdu, China), and consisted primarily of the following components: 8.3% isovaleric acid, 4.9% capric acid, 2.8% caproic acid, 2.4% caprylic acid, 1.4% butyric acid, and 6% phenylacetic acid. The experimental feed was formulated with fish meal and soybean meal as the primary protein sources, while fish oil and soybean oil were used as fat sources. All diets were formulated to be isonitrogenous and isolipidic, with protein and lipid levels verified through proximate composition analysis prior to the experiment. The attractant was first homogenized with a small amount of oil and then mixed evenly with the feed ingredients using a feed mixer. Pellets were produced with a pelletizer to a diameter of approximately 2 mm, suitable for juvenile largemouth bass. Three experimental feed types were prepared by incorporating 0.0% YXX (control), 0.05% YXX, and 0.1% YXX of the fish attractant (The dosage of YXX used in this study was determined based on preliminary trials conducted in our laboratory (unpublished data), as well as the application experience of Dadi Hanke Biotechnology Co. with other aquatic species). Once prepared, the feed was stored at −20 °C until needed. The detailed diet formulation and its chemical composition are provided in Table 1.

Table 1.
Formulation and chemical proximate composition of the experimental diets (dry matter basis, %).
2.3. Fish Rearing
The largemouth bass used in this study were obtained from an aquaculture facility located in Zhangzhou, Fujian, China. The experiment took place at the Institute of Fisheries, Jimei University, Xiamen, China. Following a 2-week acclimation period, 270 healthy largemouth bass with an average initial weight of 5.71 ± 0.02 g were selected and randomly allocated into three experimental groups. Each group contained three replicates, with 30 fish per replicate. The culture trial lasted for 56 days. Fish were fed twice daily at 9:00 AM and 5:30 PM, with feeding discontinued once the fish were visibly satiated. After 30 min, any residual feed was removed, and the water was changed. To maintain water quality, 40% of the culture water was replaced daily, ensuring the removal of dissolved waste. Biomass per tank was calculated weekly, and feeding amounts were adjusted accordingly to ensure consistent satiation. The water temperature was maintained between 25 and 28 °C, dissolved oxygen (DO): ≥6.0 mg/L, pH: 7.0–7.5, ammonia-N (NH3–N): <0.2 mg/L, nitrite (NO2−): <0.02 mg/L, photoperiod was maintained at 12 h light:12 h dark. Water temperature and dissolved oxygen were measured twice daily, while ammonia and nitrite levels were checked every two days. These parameters ensured a stable and stress-free environment for fish growth and health.
2.4. Sample Collection
After a 56-day feeding period, the experimental largemouth bass were fasted for 24 h, followed by anesthesia using eugenol (1:100) [24]. Once anesthetized, the number, weight, and length of the fish in each tank were recorded. From each tank, three fish were randomly selected to estimate the overall nutritional composition of the entire fish. Blood samples were drawn from 12 fish per tank. Each sample was placed into a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube and refrigerated at 4 °C for 24 h. The blood was then centrifuged at 4 °C, and the resulting upper serum layer was collected and stored at −80 °C for subsequent biochemical analysis. Additionally, the livers of 12 fish from each experimental tank were placed in sterile cryovials, quickly frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at −80 °C for further antioxidant capacity evaluation. For morphological examination of liver and intestinal tissues, the livers and intestines of three fish per tank were fixed in a 4% paraformaldehyde solution.
2.5. Performance and Nutritional Content Measurement
The initial body weight (IBW) and final body weight (FBW) of each fish in all treatments were recorded at the beginning and end of the experiment. From these measurements, the growth performance and morphological indices were computed as follows:
Feed intake (FI, g/fish) = (Feed consumption, g)/Final fish number;
Specific growth rate (SGR, %/day) = 100 × [Ln (Final fish body weight, g) − Ln (Initial fish body weight, g)]/Days of the experiment;
Feed conversion ratio (FCR) = (total feed intake on a dry basis, g)/(weight gain, g);
Weight gain rate (WGR, %) = 100 × [(Final fish body weight, g) − (Initial fish body weight, g)]/(Initial fish body weight, g);
Hepatosomatic index (HSI, %) = 100 × (liver weight, g)/(whole body weight, g);
Viscerosomatic index (VSI, %) = 100 × (viscera weight, g)/(body weight);
Survival rate (SR, %) = 100 × (Final fish number/Initial fish number);
Condition factor (CF, g/cm3) = 100 × (body wet weight, g)/(body length, cm)3.
The moisture, crude lipid, crude protein, and ash contents of the whole fish were measured following standard protocols [25]. Each sample was analyzed in triplicate, with approximately 5 g of homogenized whole fish used per replicate. To determine moisture content, the samples were dried at 105 °C until they reached a constant weight. The Kjeldahl method was used to assess crude protein, while crude lipid content was extracted using Soxhlet extraction with ether. Ash content was measured by heating the samples in a muffle furnace at 550 °C for 8 h. A Kjeltec™ 2300 Analyzer Unit (FOSS, Hillerød, Denmark) and Soxtec™ 8000 (FOSS, Hillerød, Denmark) were used. Instruments were calibrated using certified standards.
2.6. Analysis of Biochemical Indices
The upper serum layer, which had been stored, was used to measure the levels of aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), lysozyme (LZM), alkaline phosphatase (AKP), and acid phosphatase (ACP) using commercial kits (C010-2-1, C009-2-1, A050-1-1, A059-2-2, A060-2-2; Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, Nanjing, China). Each assay was performed in triplicate using a BioTek Synergy H1 microplate reader (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA), and absorbance values were recorded at specified wavelengths. Quality control standards and blanks were included in each run.
2.7. Analysis of Antioxidant Capacity
Liver tissue was first homogenized in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) at a 1:9 ratio. The resulting homogenate was then centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 20 min at 4 °C, and the supernatant was carefully collected. Superoxide dismutase (SOD), total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC), and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels were measured using commercial kits (A001-3-2, A015-2-1, A003-1-2; Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, Nanjing, China). Glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) content was determined using a separate kit (BC1195; Solarbio, Beijing, China). All experimental steps were carried out in accordance with the manufacturer’s guidelines.
2.8. Histopathological Analysis of Liver and Intestine
Fixed tissues were dehydrated through graded alcohols, embedded in paraffin, and sectioned at a thickness of 5 μm using a rotary microtome. Sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and examined under a light microscope (Nikon Eclipse E100, Tokyo, Japan). Morphological changes were recorded, and digital images were analyzed using ImageJ software (version 1.53k; NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA) to quantify histological parameters such as mucosal fold height and hepatocyte vacuolation.
2.9. Statistical Analysis
Data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (n = 3). One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s multiple range test was conducted using SPSS 22.0 software to assess significant differences among treatments, with statistical significance set at p < 0.05. All data met normality and homogeneity of variance assumptions prior to analysis (tested using Shapiro–Wilk and Levene’s tests, respectively).
3. Results
3.1. The Effects of Fishy Attractant on Growth Performance and Organ Indexes
Compared with the control group, supplementation with 0.05% and 0.10% fishy attractant in the feed significantly increased feed intake (FI) and condition factor (CF) and significantly reduced the viscerosomatic index (VSI) (p < 0.05; Table 2). However, no significant differences were observed in weight gain ratio (WGR), specific growth rate (SGR), feed conversion ratio (FCR), final body weight (FBW), hepatosomatic index (HSL), or survival rate (SR) between the essential oil-supplemented groups and the control (p > 0.05; Table 2). However, the FI and WGR of the group supplemented with 0.05% fish attractant showed a certain degree of increase. Moreover, no significant differences were found in moisture, crude fat, crude protein, or ash content in each group (p > 0.05; Table 3). The results indicate that the addition of fish attractant did not have any negative effects on the growth of juvenile largemouth bass, and it exhibited a certain degree of feeding stimulation.

Table 2.
Growth performance in different treatment groups.

Table 3.
Body composition in different treatment groups.
3.2. The Effects of Fish Attractant on Serum Biochemistry and Tissue Morphology
The liver and intestine are critical immune organs in fish. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining results showed that the addition of fish attractant in the diet had no effect on the liver (Figure 1) and intestinal tissue morphology (Figure 2 and Table 4) of juvenile largemouth bass. Serum biochemical analysis (Table 5) showed that aspartate aminotransferase (AST) activity was significantly lower in the YXX0.05 group compared to the control group (p < 0.05), and lysozyme (LZM) activity in the YXX0.05 group was significantly higher than in the control group (p < 0.05). No significant differences were observed in alanine aminotransferase (ALT), alkaline phosphatase (AKP), or acid phosphatase (ACP) activity between the experimental and control groups (p > 0.05). Our results indicate that the fish attractant had no significant effect on the phenotype of the immune organs in juvenile largemouth bass. However, blood immune markers suggest that the fish attractant may enhance the immune response in these fish.
Figure 1.
Liver morphology HE staining in different treatment groups (100 μm). (A) CON (0.0% fish attractant YXX); (B) YXX0.05 (0.05% fish attractant YXX); (C) YXX0.1 (0.1% fish attractant YXX).
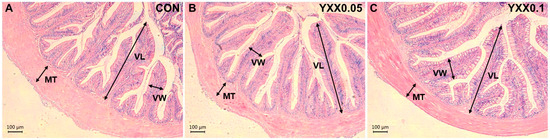
Figure 2.
Intestinal morphology in different treatment groups (A–C) (VL, villus length; VW, villus width; MT, muscular thickness, 100 μm).

Table 4.
Intestinal villus length, villus width, and muscular thickness in different treatment groups.

Table 5.
Serum biochemical parameters in different treatment groups.
3.3. The Effects of Fish Attractant on Oxidative Stress in the Liver
The blood marker analysis showed that the fish attractant reduced the AST levels in juvenile largemouth bass, indicating a potential protective effect on the liver (p < 0.05; Table 5). To further investigate, we assessed the antioxidant capacity of the liver. The results (Table 6) showed that total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC) levels were significantly higher (p < 0.05), and malondialdehyde (MDA) content was significantly lower (p < 0.05) in the experimental groups compared to the control group. No significant differences were found in the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) (p > 0.05). These results suggest that supplementing the diet with a certain proportion of fish attractant can enhance the hepatic antioxidant stress capacity of juvenile largemouth bass.

Table 6.
Liver antioxidant index in different treatment groups.
4. Discussion
Our experimental conditions, including the controlled rearing environment and carefully formulated feed composition, were specifically optimized to support the growth and development of juvenile largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Under these favorable conditions, and given the relatively short experimental duration of 60 days, it is plausible that the absence of significant differences in final body weight (FBW) following fish attractant supplementation may be attributed to these factors. Previous studies have indicated that the growth-promoting effects of dietary attractants often require a longer-term application to become evident, particularly in juvenile fish with limited initial growth potential [26].
Despite the lack of significant changes in final body weight (FBW), it is noteworthy that dietary supplementation with the fish attractant tended to enhance weight gain rate (WGR), and more importantly, resulted in significant improvements in feed intake (FI) and condition factor (CF), suggesting enhanced feeding motivation and improved physiological status. The YXX groups showed a significantly higher CF (p < 0.05), indicating improved body robustness and compactness. Both 0.05% and 0.10% attractant supplementation resulted in similar changes in FI and antioxidant parameters, suggesting a possible plateau effect. The absence of further benefits at 0.10% may imply that 0.05% is a sufficient dose under these conditions, though long-term or higher-dose studies are needed to assess safety and sustained effects. Meanwhile, the viscerosomatic index (VSI) significantly decreased, suggesting reduced visceral fat accumulation and altered nutrient partitioning. This pattern implies a possible shift in energy allocation from visceral fat deposition toward somatic (muscle) growth and improved structural development. Such changes in body composition may not be fully captured by conventional growth performance metrics such as FBW or specific growth rate (SGR), but they indicate more efficient nutrient utilization. These effects may be attributed to the functional components present in the YXX group, such as bioactive compounds that influence lipid metabolism, energy distribution, or hormonal regulation, which have been reported to promote lean tissue deposition and improve feed efficiency [27,28].
However, no improvement in feed efficiency was observed. Although FI increased in the YXX groups, the feed conversion ratio (FCR) remained stable among all treatments (0.94–0.95), indicating that the additional feed intake did not result in proportional weight gain. This phenomenon has been previously observed in other aquaculture studies, where increased feed intake beyond a certain threshold failed to improve FCR or overall growth performance due to metabolic limitations or inefficient nutrient utilization [26,29]. One possible explanation is that, in juvenile fish, a considerable portion of dietary energy is allocated to non-growth physiological functions such as maintenance, basal metabolism, or immune activity, especially when nutrient intake exceeds the growth capacity of the organism [30].
Furthermore, the existing literature has reported that the effects of dietary attractants—including compounds such as limonene, allicin, and betaine—on Micropterus salmoides follow a time-dependent pattern [31]. This raises the possibility that the beneficial impacts of fish attractants may require extended feeding durations or more advanced developmental stages to become fully manifest. Thus, further long-term studies are warranted to explore the potential cumulative benefits of attractant supplementation on growth performance, body composition, and feed utilization in Micropterus salmoides. While the present study confirms the biological efficacy of YXX supplementation under controlled warm-water conditions, its effectiveness may vary with seasonal changes in water temperature and fish metabolism. Further research across different seasons and commercial aquaculture settings is needed to assess the attractant’s year-round applicability and cost-effectiveness under variable environmental and operational conditions.
The fish attractant we used contains 8.3% isovaleric acid, 4.9% decanoic acid, 2.8% hexanoic acid, 2.4% octanoic acid, 1.4% butyric acid, and 6% phenylacetic acid. These compounds have been shown to stimulate appetite, influence energy metabolism, possess antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects, and support gut health [32,33,34,35,36,37,38]. Specifically, these organic acids and aromatic compounds have been reported to stimulate appetite by interacting with chemoreceptors in the olfactory and gustatory systems of fish, thereby enhancing feed intake and promoting growth performance [39]. In addition, they play a critical role in modulating energy metabolism, which is essential for optimizing feed efficiency and ensuring sustainable fish production [40]. Isovaleric acid is also recognized as a safe flavoring agent for human consumption [41]. This compound has been identified as an effective feeding stimulant in various fish species, further supporting its application in aquaculture nutrition. Additionally, previous studies have shown that adding 0.5 g/kg sodium butyrate (the product of butyric acid and sodium) significantly reduces VSI and improves growth performance in juvenile tilapia [42]. Furthermore, X. Meng et al. found that feeding juvenile Micropterus salmoides with 5–20% butyrate-producing clostridia fermentation products for two months led to increases in CF and reductions in VSI [43]. These results are consistent with our findings and indicate that the incorporation of fish attractants containing these bioactive acids can exert positive effects on growth performance without compromising the health and well-being of juvenile largemouth bass. The potential mechanism underlying these beneficial effects may involve enhanced nutrient absorption, improved gut microbial balance, and reduced intestinal inflammation, all of which contribute to optimized metabolic efficiency and better overall fish health.
Hematoxylin–eosin staining results showed no significant effects of the fish attractant on the morphology of immune organs (liver and intestine) in juvenile largemouth bass. This finding suggests that the fish attractant does not exert cytotoxic or adverse structural effects on these organs, indicating its safety for use in aquafeed formulations. In addition to histological analysis, serum biochemical assays revealed that the inclusion of the fish attractant led to a notable increase in LZM activity, a crucial biomarker of innate immune function in fish. Lysozyme plays a pivotal role in host defense mechanisms by hydrolyzing bacterial cell walls and enhancing the overall immune response [44]. This observation is consistent with previous research by Longzhen Liu, who reported a similar increase in LZM content when feeding Apostichopus japonicus with 1% butyric acid-producing additives [45]. Supplementing Micropterus salmoides feed with tributyrin (a butyric acid derivative) also increased LZM content [46]. Furthermore, our study demonstrated that fish attractant supplementation significantly reduced serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST) activity, which serves as a key enzymatic indicator of hepatic function and integrity [47]. Elevated AST activity is often associated with hepatocellular damage and metabolic stress, implying that the reduction observed in our study suggests a hepatoprotective effect of the fish attractant [48]. This protective function aligns with previous findings on butyric acid, which has been documented to mitigate liver injury in various animal models, including chickens [49], quails [50], and aquatic organisms such as Pacific shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) [51]. These findings collectively highlight the potential benefits of incorporating fish attractants into aquafeeds, not only for improving palatability but also for enhancing immune competence and liver health in farmed fish species. Future studies should focus on elucidating the precise molecular mechanisms underlying these protective effects and evaluating the long-term impacts of fish attractant supplementation on fish health and growth performance.
Blood biomarker results further indicate that fish attractant supplementation provides significant hepatic protection. To comprehensively evaluate this protective effect, we measured liver antioxidant capacity by assessing key oxidative stress markers. The findings revealed that dietary supplementation with the fish attractant led to a marked enhancement in total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC) and a concurrent reduction in malondialdehyde (MDA) levels, suggesting an overall improvement in hepatic oxidative balance. Elevated T-AOC levels indicate an increased ability to neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby mitigating oxidative damage, while decreased MDA levels suggest reduced lipid peroxidation, a critical factor in maintaining liver health and function [52].
These improvements may be attributed to the bioactive compounds present in YXX, such as polysaccharides, peptides, and phenolic compounds, which have been shown to modulate oxidative stress and immune pathways through the Nrf2/Keap1 and NF-κB signaling pathways [53]. Activation of these signaling cascades can enhance the expression of antioxidant enzymes and suppress inflammatory responses, thereby contributing to improved hepatic antioxidant defenses.
Previous studies have reported similar protective effects of specific dietary components on hepatic oxidative status. For instance, M. Zhao demonstrated that incorporating an optimal amount of octanoic acid into the diet effectively alleviated the detrimental impacts of high soybean oil intake on liver lipid metabolism and oxidative stress in large yellow croaker. This was evidenced by significant increases in T-AOC, superoxide dismutase (SOD), and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) activities, along with a notable decline in MDA concentrations [54]. Similarly, Aalamifar et al. reported that feeding barramundi (Lates calcarifer) with 2.5–10.0 g/kg butyric acid for 6 weeks reduced liver MDA levels [55], aligning with our findings.
Collectively, these results suggest that YXX supplementation enhances hepatic antioxidant capacity through the action of bioactive constituents that engage cellular defense pathways. This hepatoprotective effect is particularly relevant under intensive aquaculture conditions, where fish are frequently exposed to oxidative stress. In conclusion, our results demonstrate that fish attractants, when used at the appropriate dosage, can enhance FI and CF, improve immune response, and mitigate oxidative stress in juvenile M. salmoides without negatively affecting growth or health. Future studies should investigate the efficacy of this attractant at earlier developmental stages, where growth and immune responses may be more plastic. Given its promising effect on liver antioxidant status, it may also benefit fish reared in high-density RAS systems where oxidative stress is common. Moreover, potential synergies with probiotics or essential oils could be explored to further enhance palatability and gut health.
5. Conclusions
In summary, dietary supplementation with 0.05% fishy attractant significantly increased feed intake and condition factor, significantly reduced the viscerosomatic index, and enhanced liver antioxidant capacity and serum immune responses in juvenile largemouth bass under controlled experimental conditions. However, these physiological benefits were not accompanied by significant improvements in growth performance or detectable histological alterations within the 56-day feeding trial. In future studies, we aim to clarify the underlying mechanisms of action of this attractant by investigating its effects on intestinal microbiota composition and key oxidative stress-related signaling pathways.
Author Contributions
G.C.: methodology, writing, funding acquisition, and manuscript critical revision. Z.L., M.Y. and M.H.: project administration and funding acquisition. P.L., X.T. and Q.H.: investigation and data curation. Z.G.: data analysis. Y.S.: validation, reviewing, and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32303022) and Chengdu Dadihanke Biotechnology Co., Ltd. Technology Project (S24012).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The experiments on fish in this study were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee at the Fisheries College of Jimei University (No. 1067, 2024-01-03).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank the reviewers for their insightful comments to improve the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that this study received funding from Chengdu Dadihanke Biotechnology Co. The funder was not involved in the study design; the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data; the writing of the manuscript; or the decision to submit it for publication.
References
- Carr, W.E. The molecular nature of chemical stimuli in the aquatic environment. In Sensory Biology of Aquatic Animals; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1988; pp. 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Abdelkhalek, N.K.; Hassan, A.M. Antagonistic activity of dietary allicin against deltamethrin-induced oxidative damage in freshwater Nile tilapia; Oreochromis niloticus. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 111, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajiboye, O.; Yakubu, A.; Simpa, J.; Balogun, S. Effect of garlic-supplemented diets on growth response, survival, nutrient utilization and body composition of monosex Tilapia zillii. World J. Fish Mar. Sci. 2016, 8, 115–122. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, T.; Hegazi, E.; Dawood, M.A.; Nassef, E.; Bakr, A.; Paray, B.A.; Van Doan, H. Using of betaine to replace fish meal with soybean or/and corn gluten meal in nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) diets: Histomorphology, growth, fatty acid, and glucose-related gene expression traits. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 17, 100376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Jiang, W.-D.; Wu, P.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Yang, Q.-H.; Kuang, S.-Y.; Tang, L.; Zhou, X.-Q.; Feng, L. Betaine supplementations enhance the intestinal immunity of on-growing grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella): Partly related to TOR and NF-κB signaling pathways. Aquaculture 2020, 518, 734846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JP, D. Mixture interactions of glutamate and betaine in single squid olfactory receptor neurons. J. Comp. Physiol. 2000, 186, 57–67. [Google Scholar]
- Aaqillah-Amr, M.; Hidir, A.; Azra, M.; Ahmad-Ideris, A.; Abualreesh, M.; Noordiyana, M.; Ikhwanuddin, M. Use of pelleted diets in commercially farmed decapods during juvenile stages: A review. Animals 2021, 11, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, A.; Majeed, W.; Naveed, M.; Ramzan, U.; Bordiga, M.; Hameed, M.; Ur Rehman, S.; Rana, N. Success of aquaculture industry with new insights of using insects as feed: A review. Fishes 2022, 7, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öz, M.; Inanan, B.E.; Karasahin, T.; Dikel, S. Effects of glutamine on growth performance, nutrient content, fatty acid profile, and blood parameters of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J. Fish Biol. 2024, 104, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.R.P.; Campelo, D.A.V.; da Silva Carneiro, C.L.; Zuanon, J.A.S.; da Matta, S.L.P.; Furuya, W.M.; Salaro, A.L. Optimal dietary L-glutamine level improves growth performance and intestinal histomorphometry of juvenile giant trahira (Hoplias lacerdae), a Neotropical carnivorous fish species. Aquaculture 2022, 547, 737469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, S. The physiology of taste in fish: Potential implications for feeding stimulation and gut chemical sensing. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2017, 25, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.A.K.; Song, H.; Liu, Y.; Bunod, J.-D.; Dong, X.-H. Effects of microencapsulated organic acid and their salts on growth performance, immunity, and disease resistance of Pacific White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, A.J.; Sá, M.V.; Andriola-Neto, F.F.; Lemos, D. Behavioral response to selected feed attractants and stimulants in Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2006, 260, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.; Afzal, G.; Siddique, A.B.; Afzal, M.; Shahid, M.; Ramzan, A.; Iqbal, Z.; Ali, H.M.; Ahsan, H.; Hussain, R. Essential Oil-Based Functional Feeds for Promoting Growth in Aquaculture Species. Complement. Altern. Med. Essent. Oils 2024, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onomu, A.J.; Okuthe, G.E. The role of functional feed additives in enhancing aquaculture sustainability. Fishes 2024, 9, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.; El Basuini, M.F.; Yilmaz, S.; Abdel-Latif, H.M.; Alagawany, M.; Kari, Z.A.; Abdul Razab, M.K.A.; Hamid, N.K.A.; Moonmanee, T.; Van Doan, H. Exploring the roles of dietary herbal essential oils in aquaculture: A review. Animals 2022, 12, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Deng, L.; Chen, M.; Che, Y.; Li, L.; Zhu, L.; Chen, G.; Feng, T. Phytogenic feed additives as natural antibiotic alternatives in animal health and production: A review of the literature of the last decade. Anim. Nutr. 2024, 17, 244–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, K.; He, G.; Shi, M.; Chen, X.; Zhu, W.; Chen, Z.; Tan, B.; Xie, S. Effects of compound feed attractants on the growth rate, feed consumption, intestinal histology, protein synthesis, and immune response of black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon). Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2024, 311, 115952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, G.; Yong, A.S.-K.; Au, H.-L.; Doison, A.; Ooi, S.-Y.; Lim, L.-S.L.-S. Malaysian herbs as feeding attractants and enhancers for the giant freshwater prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii) and the whiteleg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Borneo J. Mar. Sci. Aquac. (BJoMSA) 2019, 3, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, J.P.; Mailloux, N.A.; Love, D.C.; Milli, M.C.; Cao, L. Feed conversion efficiency in aquaculture: Do we measure it correctly? Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 024017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rijn, J. Waste treatment in recirculating aquaculture systems. Aquac. Eng. 2013, 53, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.; Koshio, S.; Esteban, M.Á. Beneficial roles of feed additives as immunostimulants in aquaculture: A review. Rev. Aquac. 2018, 10, 950–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barad, R.R.; Verma, D.K.; Yusufzai, S.; Shrivastava, V.; Ram, A.R. Herbal Feed Additives: Natural Boost for Aquatic Health and Growth. In Sustainable Feed Ingredients and Additives for Aquaculture Farming: Perspectives from Africa and Asia; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 405–431. [Google Scholar]
- He, R.; Lei, B.; Su, Y.; Wang, A.; Cui, K.; Shi, X.; Chen, X. Effectiveness of eugenol as an anesthetic for adult spotted sea bass (Lateolabrax maculatus). Aquaculture 2020, 523, 735180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldsine, P.; Abeyta, C.; Andrews, W.H. AOAC International methods committee guidelines for validation of qualitative and quantitative food microbiological official methods of analysis. J. AOAC Int. 2002, 85, 1187–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, D.; Yi, M.; Li, X.; Li, Y. Effects of feeding rate and frequency on growth performance, digestion and nutrients balances of A tlantic salmon (Salmo salar) in recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS). Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadifar, E.; Pourmohammadi Fallah, H.; Yousefi, M.; Dawood, M.A.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Adineh, H.; Yilmaz, S.; Paolucci, M.; Doan, H.V. The gene regulatory roles of herbal extracts on the growth, immune system, and reproduction of fish. Animals 2021, 11, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faheem, M.; Rao, Z.A.; Liaqat, I.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Maneepitaksanti, W.; Van Doan, H. Bio-active components in medicinal plants: A mechanistic review of their effects on fish growth and physiological parameters–A review. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2022, 22, 1127–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abwao, J.; Jung’a, J.; Barasa, J.E.; Kyule, D.; Opiyo, M.; Awuor, J.F.; Ogello, E.; Munguti, J.M.; Keya, G.A. Selective breeding of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus: A strategy for increased genetic diversity and sustainable development of aquaculture in Kenya. J. Appl. Aquac. 2023, 35, 237–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, A.J. Effects of different feeding frequency on the growth, survival and feed conversion ratio of the Asian sea bass Lates calcarifer juveniles reared under hypersaline seawater of the Red Sea. Aquac. Res. 2008, 39, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Chen, M.; Bao, X.; Yu, Y.; Shi, W.; Kumkhong, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yu, H. Effects of three feed attractants on the growth performance and meat quality of the largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1029969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Huang, W.; Zhao, H.; Sun, Y.; Chen, B. Dietary condensed tannins improved growth performance and antioxidant function but impaired intestinal morphology of Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 21, 100853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Latif, H.M.; Abdel-Tawwab, M.; Dawood, M.A.; Menanteau-Ledouble, S.; El-Matbouli, M. Benefits of dietary butyric acid, sodium butyrate, and their protected forms in aquafeeds: A review. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2020, 28, 421–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Peng, D.; Liang, X.-F.; Li, J.; Luo, H.; Tang, S.; Chai, F. Intracerebroventricular injection with octanoic acid activates hypothalamic fatty acid sensing systems and regulates appetite in Chinese perch Siniperca chuatsi. Fish. Sci. 2022, 88, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.M.; Christensen, M.S.; Høy, C.-E. Intestinal absorption of octanoic, decanoic, and linoleic acids: Effect of triglyceride structure. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 1994, 38, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuiyan, M.S.; Ellett, F.; Murray, G.L.; Kostoulias, X.; Cerqueira, G.M.; Schulze, K.E.; Mahamad Maifiah, M.H.; Li, J.; Creek, D.J.; Lieschke, G.J. Acinetobacter baumannii phenylacetic acid metabolism influences infection outcome through a direct effect on neutrophil chemotaxis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9599–9604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.K.; Koh, C.B. The utilization and mode of action of organic acids in the feeds of cultured aquatic animals. Rev. Aquac. 2017, 9, 342–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasidi, R.; Pamungkas, W.; Handajani, H.; Puspaningsih, D.; Taqwa, F.H.; Hartami, P. Sustaining Aquaculture: Organic Acid as Feed Additives in Aquaculture. In Sustainable Feed Ingredients and Additives for Aquaculture Farming: Perspectives from Africa and Asia; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 481–500. [Google Scholar]
- Hancz, C. Feed efficiency, nutrient sensing and feeding stimulation in aquaculture: A review. Acta Agrar. Kaposváriensis 2020, 24, 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X. Optimizing Animal Energy Metabolism: Nutritional Strategies in Agricultural Production. Int. J. Mol. Zool. 2025, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Api, A.; Belmonte, F.; Belsito, D.; Botelho, D.; Bruze, M.; Burton, G., Jr.; Buschmann, J.; Dagli, M.; Date, M.; Dekant, W. RIFM fragrance ingredient safety assessment, isovaleric acid, CAS Registry Number 503-74-2. Food Chem Toxicol. 2019, 130, 110570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Figueirêdo Urach, B.; de Souza Ramos, A.P.; Luz, J.R.; de Magalhães Júnior, F.O.; Schorer, M.; Braga, L.G.T. Sodium butyrate improves the performance of juvenile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (Linneaus, 1758). Res. Soc. Dev. 2020, 9, e551997535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Cai, H.; Li, H.; You, F.; Jiang, A.; Hu, W.; Li, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, X. Clostridium butyricum-fermented Chinese herbal medicine enhances the immunity by modulating the intestinal microflora of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Aquaculture 2023, 562, 738768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragland, S.A.; Criss, A.K. From bacterial killing to immune modulation: Recent insights into the functions of lysozyme. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Wei, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Mao, Y.; Tian, X. A Comparative Study on Effects of Three Butyric Acid-Producing Additives on the Growth Performance, Non-specific Immunity, and Intestinal Microbiota of the Sea Cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Aquac. Nutr. 2024, 2024, 6973951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Shu, H.; Kou, Y.; Dang, H.; Ai, C. Beneficial effects of the butanoic acid derivative tributyrin on the growth, immunity and intestinal health of large mouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Aquaculture 2024, 590, 741007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalas, M.A.; Chavez, L.; Leon, M.; Taweesedt, P.T.; Surani, S. Abnormal liver enzymes: A review for clinicians. World J. Hepatol. 2021, 13, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Peng, B.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, H.; Xiao, Q.; Tang, S.; Liang, X.-F. Effects of three feed attractants on the growth, biochemical indicators, lipid metabolism and appetite of Chinese perch (Siniperca chuatsi). Aquac. Rep. 2022, 23, 101075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepa, K.; Purushothaman, M.; Vasanthakumar, P.; Sivakumar, K. Butyric acid as an antibiotic substitute for broiler chicken–A review. Adv. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2018, 6, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdeldayem, F.A.; Lestingi, A.; Abol-Ela, S.S.; Alagawany, M.; Ismail, T.A.; Mostafa, N.G.; El-Shall, N.A. Application of butyric acid as a feed additive for improving quail performance and health. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 104109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yohana, M.A.; Ray, G.W.; Yang, Q.; Shiyu, K.; Tan, B.; Wu, J.; Mao, M.; Feng, L. Comprehensive analysis of butyric acid impact on immunology, histopathology, gene expression, and metabolomic responses in pacific shrimp experiencing cold stress. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2024, 52, 101293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Gao, M.; Yang, N.; Ai, L.; Guo, L.; Xue, X.; Sheng, Z. Trimethyltin chloride induces apoptosis and DNA damage via ROS/NF-κB in grass carp liver cells causing immune dysfunction. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 142, 109082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, D.-D.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, X.-R.; Tang, W.-H.; Peng, Q.; Chen, Y.-H.; Wang, G.; Zhang, D.-Z.; Tang, B.-P.; Liu, Q.-N. The Nrf2-Keap1/ARE signaling pathway in aquatic animals. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 308, 142595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Gong, Y.; Tang, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhang, J.; Liu, G.; Zhang, H. Effects of supplemental octanoate on hepatic lipid metabolism, serum biochemical indexes, antioxidant capacity and inflammation-related genes expression of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) fed with high soybean oil diet. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1162633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalamifar, H.; Soltanian, S.; Vazirzadeh, A.; Akhlaghi, M.; Morshedi, V.; Gholamhosseini, A.; Torfi Mozanzadeh, M. Dietary butyric acid improved growth, digestive enzyme activities and humoral immune parameters in Barramundi (Lates calcarifer). Aquac. Nutr. 2020, 26, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).