The Effects of Two Different Aquaculture Methods on Water Quality, Microbial Communities, Production Performance, and Health Status of Penaeus monodon
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental P. monodon
2.2. Production of Nitrifying Biofloc
2.3. Experimental Design
2.3.1. Description of the Zero Water Exchange Systems
2.3.2. Description of the Clear Water Systems
2.4. Water Quality, Biofloc Volume and Morphostructure
2.5. Microbial Sampling, DNA Extraction and qPCR Analysis
2.6. P. monodon Growth Performance
2.7. Analysis of Digestive Enzymes and Antioxidant Enzyme
2.8. RNA Extraction and Gene Expression
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
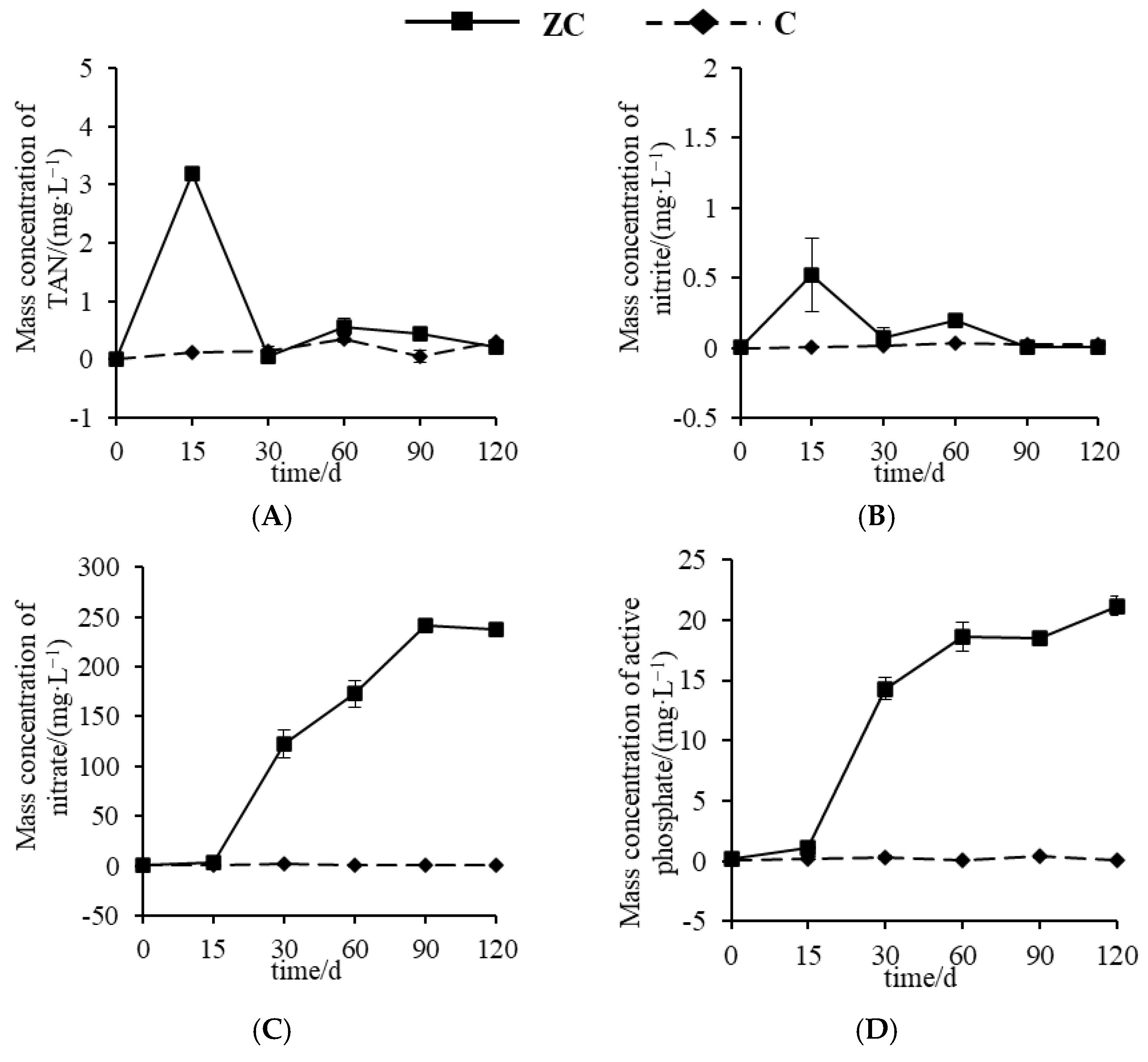
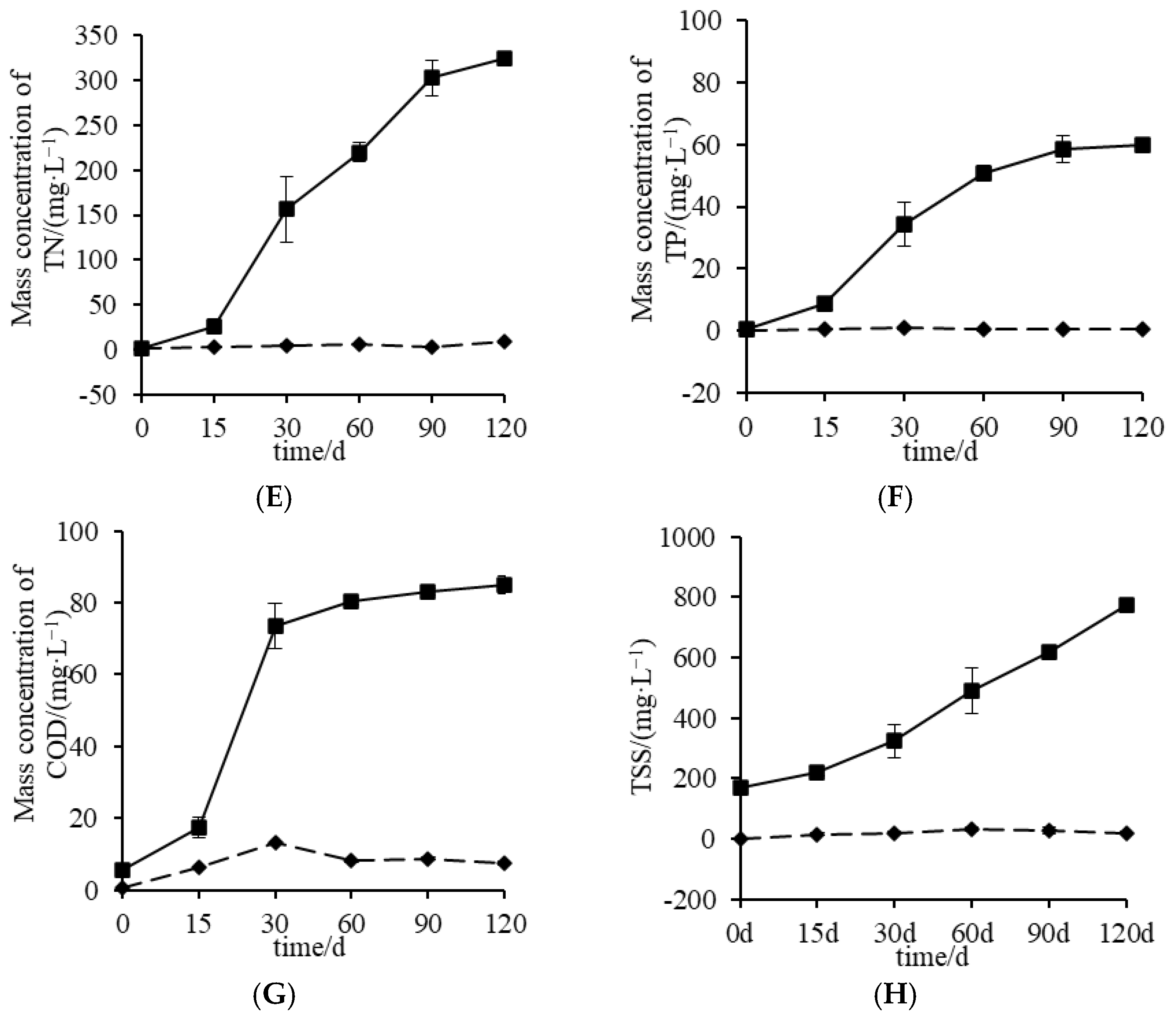
3.1. Characteristics of Water Environmental Factors in P. monodon Culture
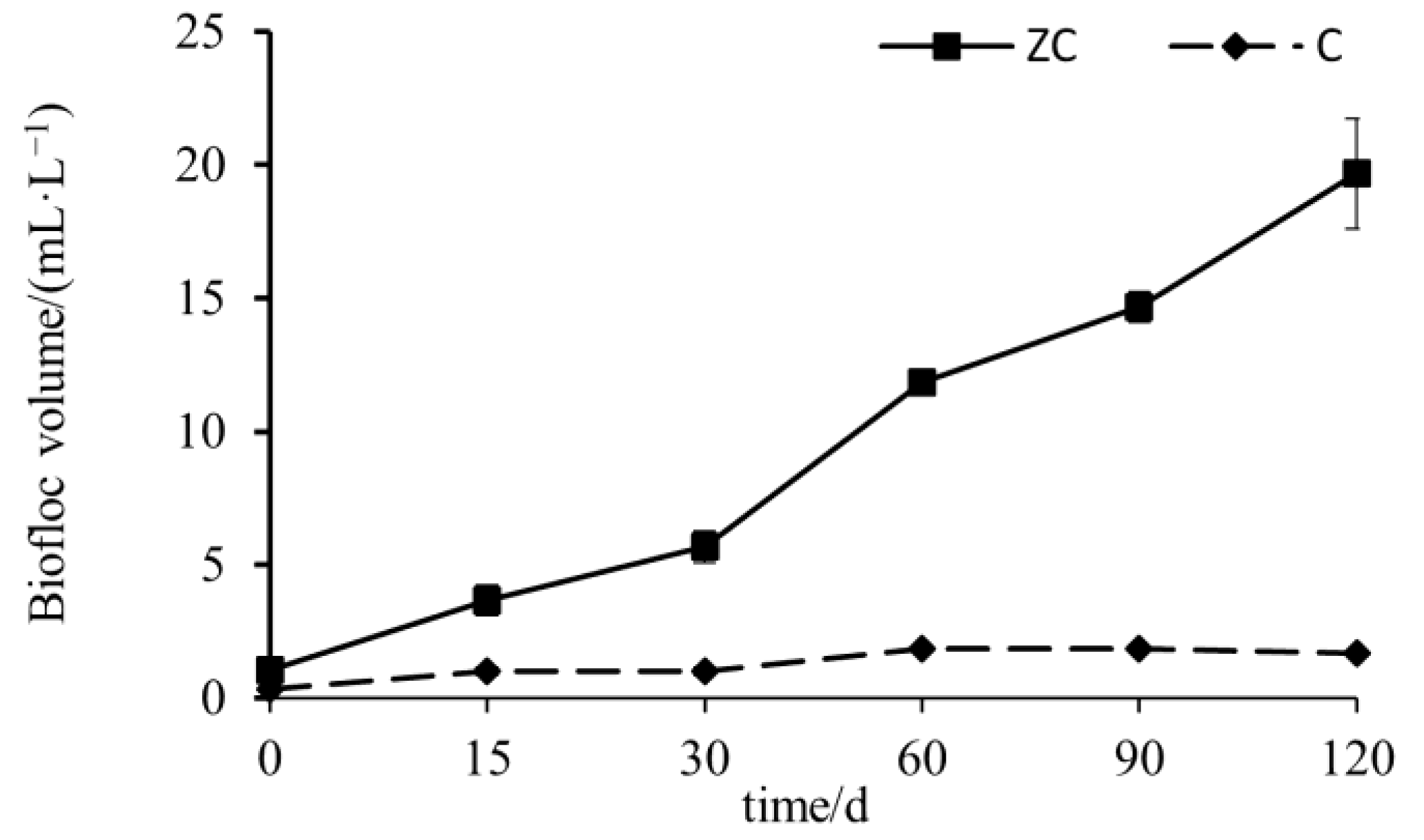
3.2. The Characteristics of Biofloc Volume Changes
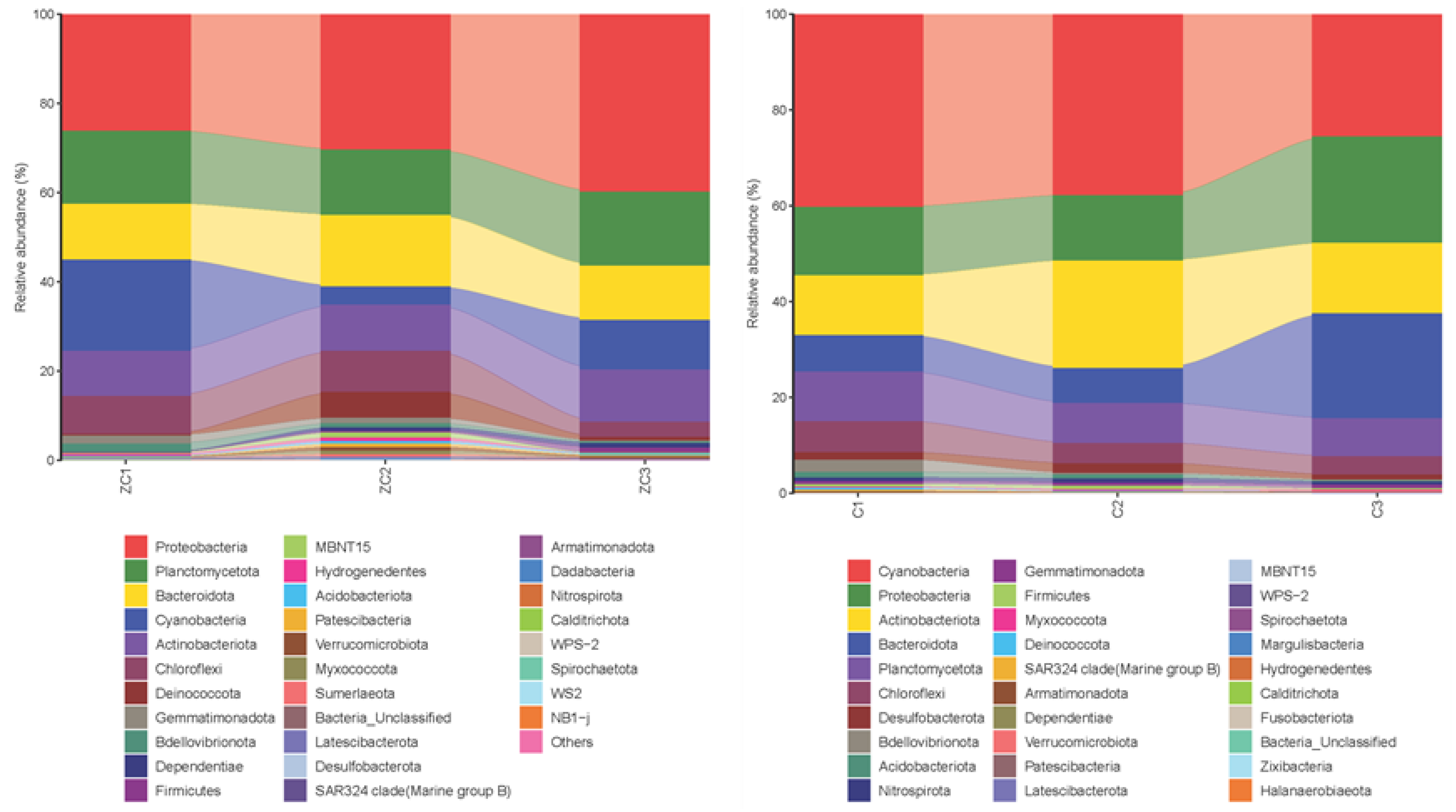
3.3. The Microbial Communities’ Diversity and Compositional Characteristics in P. monodon Farms
3.4. The Growth Performance of P. monodon
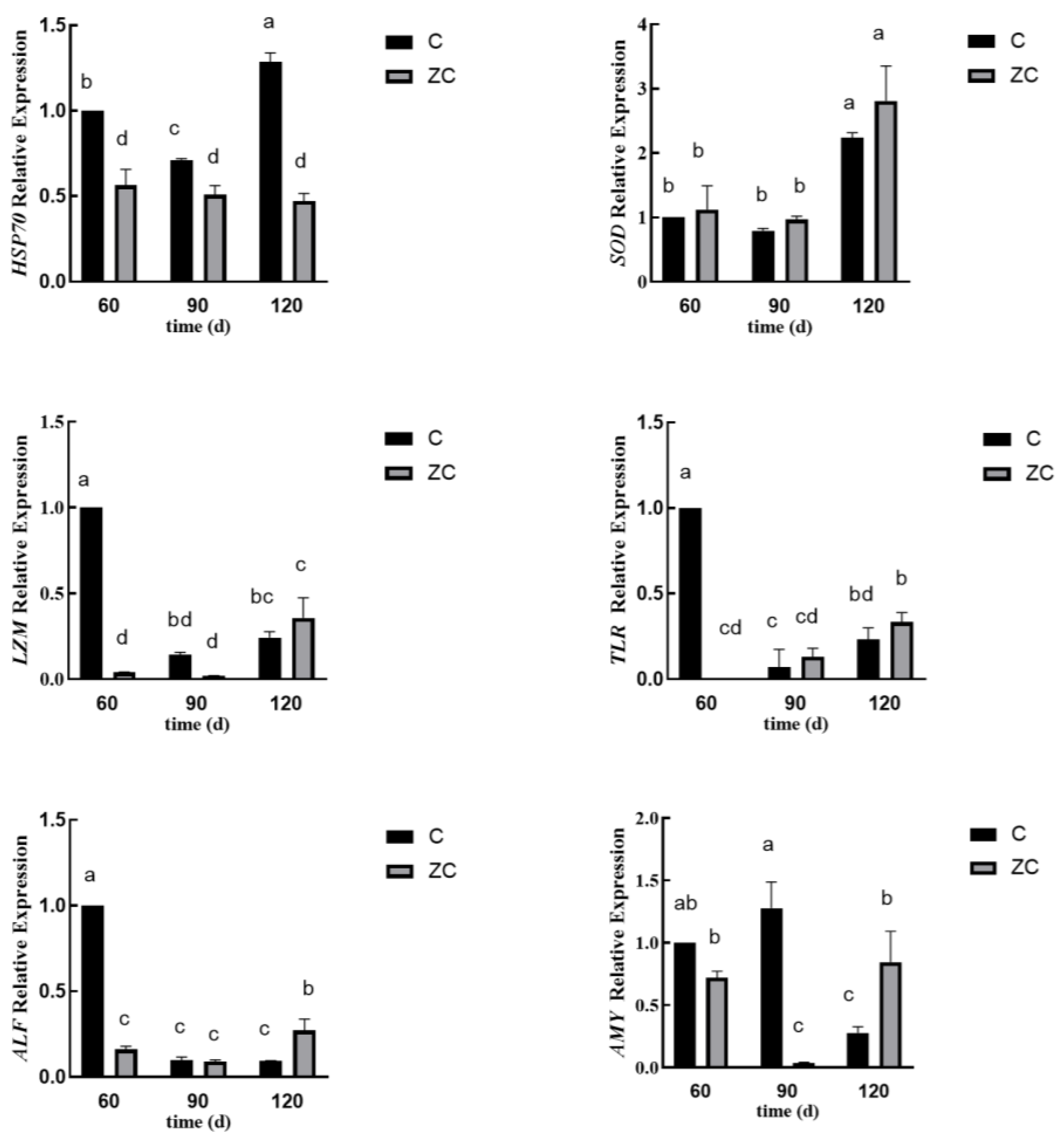
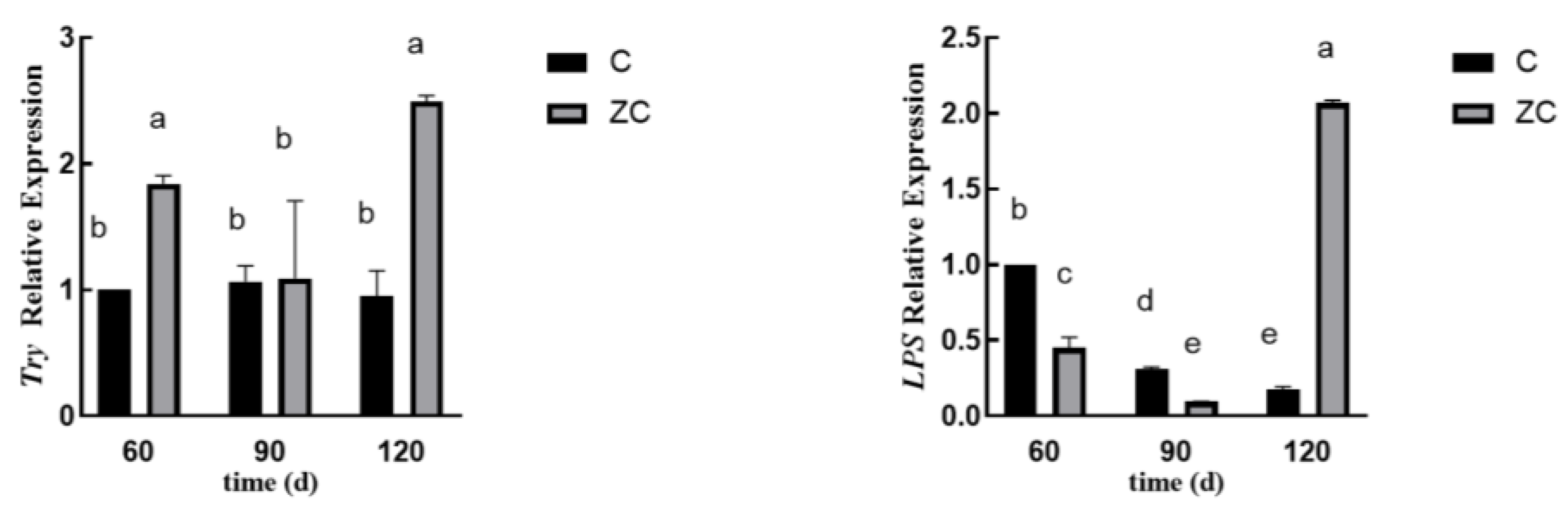
3.5. The Greatly Differential Expressed Genes Between Two Groups
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The state of world fisheries and aquaculture 2021. In Sustainability in Action; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Fisheries Administration Bureau, Ministry of Agriculture. China Fishery Statistics Year Book (2024); Beijing China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Khanjani, M.H.; Mohammadi, A.; Emerenciano, M.G.C. Microorganisms in biofloc aquaculture system. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 26, 101300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crab, R.; Defoirdt, T.; Bossier, P.; Verstraete, W. Biofloc technology in aquaculture: Beneficial effects and future challenges. Aquaculture 2012, 356, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Córdova, L.R.; Emerenciano, M.; Miranda-Baeza, A.; Martínez-Porchas, M. Microbial-based systems for aquaculture of fish and shrimp: An updated review. Rev. Aquac. 2014, 7, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.-J.; Morris, T.C.; Samocha, T.M. Effects of C/N ratio on biofloc development, water quality, and performance of Litopenaeus vannamei juveniles in a biofloc-based, high-density, zero-exchange, outdoor tank system. Aquaculture 2016, 453, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avnimelech, Y. Carbon/nitrogen ratio as a control element in aquaculture systems. Aquaculture 1999, 176, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebeling, J.M.; Timmons, M.B.; Bisogni, J.J. Engineering analysis of the stoichiometry of photoautotrophic, autotrophic, and heterotrophic removal of ammonia–nitrogen in aquaculture systems. Aquaculture 2006, 257, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.L.; Yang, X.L.; Xia, M.Q.; Chen, M. Co-metabolic degradation of steroid estrogens by heterotrophic bacteria and nitrifying bacteria in MBRs. J. Env. Sci. Health A 2017, 52, 778–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmautz, Z.; Espinal, C.A.; Bohny, A.M.; Rezzonico, F.; Junge, R.; Frossard, E.; Smits, T.H.M. Environmental parameters and microbial community profiles as indication towards microbial activities and diversity in aquaponic system compartments. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avnimelech, Y. Biofloc Technology: A Practical Guide Book; The World Aquaculture Society: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Burford, M.A.; Thompson, P.J.; McIntosh, R.P.; Bauman, R.H.; Pearson, D.C. The contribution of flocculated material to shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) nutrition in a high-intensity, zero-exchange system. Aquaculture 2004, 232, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Borewicz, K.; van Loo, J.; Olabarrieta, M.Z.; Kokou, F.; Sipkema, D.; Verdegem, M.C.J. In-Situ Biofloc Affects the Core Prokaryotes Community Composition in Gut and Enhances Growth of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Microb. Ecol. 2022, 84, 879–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanjani, M.H.; Sharifinia, M.; Emerenciano, M.G.C. Biofloc Technology (BFT) in Aquaculture: What Goes Right, What Goes Wrong? A Scientific-Based Snapshot. Aquac. Nutr. 2024, 2024, 7496572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Anand, P.S.S.; De, D.; Ghoshal, T.K.; Alavandi, S.V.; Vijayan, K.K. Integration of substrate in biofloc based system: Effects on growth performance, water quality and immune responses in black tiger shrimp, Penaeus monodon culture. Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 2986–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uawisetwathana, U.; Situmorang, M.L.; Arayamethakorn, S.; Haniswita; Suantika, G.; Panya, A.; Karoonuthaisiri, N.; Rungrassamee, W. Supplementation of Ex-Situ Biofloc to Improve Growth Performance and Enhance Nutritional Values of the Pacific White Shrimp Rearing at Low Salinity Conditions. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Anand, P.S.S.; De, D.; Sundaray, J.K.; Raja, R.A.; Biswas, G.; Ponniah, A.G.; Ghoshal, T.K.; Deo, A.D.; Panigrahi, A.; et al. Effects of carbohydrate supplementation on water quality, microbial dynamics and growth performance of giant tiger prawn (Penaeus monodon). Aquac. Int. 2014, 22, 901–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Z.Y.; Forster, I.; Conquest, L.; Dominy, W. Enhanced growth effects on shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) from inclusion of whole shrimp floc or floc fractions to a formulated diet. Aquac. Nutr. 2008, 14, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.-J.; Pan, L.-Q. Effects of bioflocs on growth performance, digestive enzyme activity and body composition of juvenile Litopenaeus vannamei in zero-water exchange tanks manipulating C/N ratio in feed. Aquaculture 2012, 356, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Roy, S.; Behera, B.K.; Swain, H.S.; Das, B.K. Biofloc Microbiome with Bioremediation and Health Benefits. Front Microbiol 2021, 12, 741164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyne Anand, P.S.; Kumar, S.; Kohli, M.P.S.; Sundaray, J.K.; Sinha, A.; Pailan, G.H.; Dam Roy, S. Dietary biofloc supplementation in black tiger shrimp, Penaeus monodon: Effects on immunity, antioxidant and metabolic enzyme activities. Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 4512–4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 17378.4-2007; Marine Monitoring Specifications—Part 4: Seawater Analysis. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Burian, A.; Pinn, D.; Peralta-Maraver, I.; Sweet, M.; Mauvisseau, Q.; Eyice, O.; Bulling, M.; Rothig, T.; Kratina, P. Predation increases multiple components of microbial diversity in activated sludge communities. ISME J. 2022, 16, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radley, J.A. Starch and Its Derivatives; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Winkler, U.K.; Stuckmann, M. Glycogen, hyaluronate, and some other polysaccharides greatly enhance the formation of exolipase by Serratia marcescens. J. Bacteriol. 1979, 138, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlanger, B.F.; Kokowsky, N.; Cohen, W. The preparation and properties of two new chromogenic substrates of trypsin. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1961, 95, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengal, K.; Kor, G.; Kozak, P.; Niksirat, H. Effects of environmental factors on the cellular and molecular parameters of the immune system in decapods. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A-Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2023, 276, 111332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Pan, L.; Chen, W.; Wang, C. Effect of using sodium bicarbonate to adjust the pH to different levels on water quality, the growth and the immune response of shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei reared in zero-water exchange biofloc-based culture tanks. Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 1194–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, M.T.; Broom, M.; Al-Mur, B.A.; Al Harbi, M.; Ghandourah, M.; Al Otaibi, A.; Haque, M.F. Biofloc Technology: Emerging Microbial Biotechnology for the Improvement of Aquaculture Productivity. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Fu, X.; He, J.; Wang, R.; Yan, M.; Wang, J.; Dong, P.; Huang, L.; Zhang, D. Gut bacterial consortium enriched in a biofloc system protects shrimp against Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection. Microbiome 2023, 11, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tảo, C.T.; Khoa TN, D.; Hòa, N.V.; Hải, T.N. Effects of carbon sources on nursing white-leg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) larvae applying biofloc technology. CTU J. 2020, 56, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Bandhana, R.S.; Sangotra, R. Comparison of water quality and composition of bioflocs reared in indoor and outdoor conditions. Int. Res. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.; Ren, W.; Li, L.; Dong, S.; Tian, X. Light and carbon sources addition alter microbial community in biofloc-based Litopenaeus vannamei culture systems. Aquaculture 2020, 515, 734572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irankhah, S.; Ali, A.A.; Soudi, M.R.; Gharavi, S.; Ayati, B. Highly efficient phenol degradation in a batch moving bed biofilm reactor: Benefiting from biofilm-enhancing bacteria. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 34, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordahi, M.A.; Ayoub, G.M.; Zayyat, R.M. A critical review of current research on cyanobacterial cells and associated toxins in aquatic environments: Occurrence, impact, and treatment methods. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øvreås, L.; Kallscheuer, N.; Calisto, R.; Bordin, N.; Storesund, J.E.; Jogler, C.; Devos, D.; Lage, O. Comparative genomic analyses of aerobic planctomycetes isolated from the deep sea and the ocean surface. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2025, 118, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.J.; Pan, L.Q.; Sun, X.H.; Huang, J. Effects of bioflocs on water quality, and survival, growth and digestive enzyme activities of Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone) in zero-water exchange culture tanks. Aquac. Res. 2013, 44, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, P.S.S.; Kohli, M.P.S.; Kumar, S.; Sundaray, J.K.; Roy, S.D.; Venkateshwarlu, G.; Sinha, A.; Pailan, G.H. Effect of dietary supplementation of biofloc on growth performance and digestive enzyme activities in Penaeus monodon. Aquaculture 2014, 418, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, A.; Das, R.R.; Sivakumar, M.R.; Saravanan, A.; Saranya, C.; Sudheer, N.S.; Kumaraguru Vasagam, K.P.; Mahalakshmi, P.; Kannappan, S.; Gopikrishna, G. Bio-augmentation of heterotrophic bacteria in biofloc system improves growth, survival, and immunity of Indian white shrimp Penaeus indicus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 98, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Outama, P.; Le Xuan, C.; Wannavijit, S.; Lumsangkul, C.; Linh, N.V.; Montha, N.; Tongsiri, S.; Chitmanat, C.; Van Doan, H. Modulation of growth, immune response, and immune-antioxidant related gene expression of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) reared under biofloc system using mango peel powder. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 131, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ren, Y.; Li, Y.; Xia, B. Regulation of growth, intestinal microbiota, non-specific immune response and disease resistance of sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus (Selenka) in biofloc systems. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 77, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junprung, W.; Supungul, P.; Tassanakajon, A. Litopenaeus vannamei heat shock protein 70 (LvHSP70) enhances resistance to a strain of Vibrio parahaemolyticus, which can cause acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND), by activating shrimp immunity. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2019, 90, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rungrassamee, W.; Leelatanawit, R.; Jiravanichpaisal, P.; Klinbunga, S.; Karoonuthaisiri, N. Expression and distribution of three heat shock protein genes under heat shock stress and under exposure to Vibrio harveyi in Penaeus monodon. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.S.; Lv, L.X.; Wang, J.X. Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor D from kuruma shrimp exhibits antiviral activity. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2022, 4, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Yuan, M.; Xu, L.; Lio, E.; Zhang, F.; Mou, H.; Secundo, F. Application of enzymes as a feed additive in aquaculture. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2022, 4, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Ren, Y.; Wang, G.; Xia, B.; Li, Y. Dietary supplementation of biofloc influences growth performance, physiological stress, antioxidant status and immune response of juvenile sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus (Selenka). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 72, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghani, M.U.; Chen, J.; Khosravi, Z.; Wu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhong, L.; Cui, H. Unveiling the multifaceted role of toll-like receptors in immunity of aquatic animals: Pioneering strategies for disease management. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1378111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Meng, S.; Xu, H.; Song, C.; Fan, L.; Qiu, L.; Li, D. Responses of Digestive, Antioxidant, Immunological and Metabolic Enzymes in the Intestines and Liver of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) under the Biofloc Model. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | Length | Tm (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PmEF1 | F-GGTGCTGGACAAGCTGAAGGC | 21 | 64.10 |
| R-CGTTCCGGTGATCATGTTCTTGATG | 25 | 62.41 | |
| PmSOD | F-GCTGCTACAAAGAAGTTGGT | 20 | 56.26 |
| R-GGACTGGAATGATCCAAAGC | 20 | 56.47 | |
| Hsp70 | F-CTTCGACAACCGCATGGTGA | 20 | 60.95 |
| R-GAAGAGGGAGCCGATCTCCA | 20 | 60.76 | |
| PmALF | F-GCCACCACAAGAACCTTAGA | 20 | 57.44 |
| R-ACTGCTCCGGTTTAGAGAAAG | 21 | 57.68 | |
| PmLZM | F-TGGTGTGGCAGCGATTATG | 19 | 58.22 |
| R-GATCGAGGTCGCGATTCTTAC | 21 | 58.69 | |
| PmTLR | F-CTTAGCCTTGGAGACAAC | 18 | 52.26 |
| R-GATGCTTAACAGCTCCTC | 18 | 52.46 | |
| PmAMY | F-TGTCGGATGCGATTGCTCC | 19 | 60.52 |
| R-TGAATGCCCTCGGTGATGC | 19 | 60.45 | |
| PmPTL | F-GCGTTTGAATGGAGGGTTGG | 20 | 59.76 |
| R-TGCGTGTTGTCACTCCGTAA | 20 | 59.90 | |
| PmTry | F-CAGGGCGATGACTTTGATAAT | 21 | 56.10 |
| R-ACTGATGGTGAAGCCGTTGTA | 21 | 59.65 |
| Factors | ZC | C |
|---|---|---|
| Temprature (°C) | 26.98 ± 1.97 | 26.11 ± 2.15 |
| pH | 7.67 ± 0.11 | 8.05 ± 0.05 |
| DO (mg·L−1) | 5.65 ± 0.32 | 6.10 ± 0.52 |
| Salinity (‰) | 15.61 ± 1.37 | 14.16 ± 4.24 |
| Sample ID | Sequences | ASVs | Chao1 | Goods Coverage | Pielou Evenness | Shannon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 56339 | 1152 | 1153.625 | 0.999 | 0.779 | 7.926 |
| C2 | 56339 | 1171 | 1172.052 | 0.999 | 0.767 | 7.816 |
| C3 | 56339 | 1180 | 1179.000 | 1.000 | 0.794 | 8.109 |
| ZC1 | 61458 | 733 | 733.234 | 0.999 | 0.709 | 6.753 |
| ZC2 | 61458 | 768 | 768.000 | 1.000 | 0.764 | 7.329 |
| ZC3 | 61458 | 675 | 672.942 | 0.999 | 0.701 | 6.590 |
| Indicator | ZC | C | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Final weight (g) | 11.46 ± 0.61 | 9.38 ± 0.12 | 0.004 |
| Weight gain (g) | 11.43 ± 0.61 | 9.33 ± 0.36 | 0.007 |
| Survival rate (%) | 75.90 ± 2.50 | 35.76 ± 4.83 | <0.001 |
| Unit yield (kg·m−3) | 1.31 ± 0.03 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | <0.001 |
| Specific growth rate (% day−1) | 4.95 ± 0.04 | 4.39 ± 0.03 | <0.001 |
| Feed conversion ratio | 1.90 ± 0.04 | 3.44 ± 0.35 | 0.002 |
| shrimp Water usage (m3·kg−1) | 0.98 ± 0.02 | 16.02 ± 1.63 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, H.; Xu, Y.; Jing, L.; Su, H.; Hu, X.; Cao, Y.; Wen, G. The Effects of Two Different Aquaculture Methods on Water Quality, Microbial Communities, Production Performance, and Health Status of Penaeus monodon. Fishes 2025, 10, 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10030106
Ren H, Xu Y, Jing L, Su H, Hu X, Cao Y, Wen G. The Effects of Two Different Aquaculture Methods on Water Quality, Microbial Communities, Production Performance, and Health Status of Penaeus monodon. Fishes. 2025; 10(3):106. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10030106
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Huan, Yu Xu, Lu Jing, Haochang Su, Xiaojuan Hu, Yucheng Cao, and Guoliang Wen. 2025. "The Effects of Two Different Aquaculture Methods on Water Quality, Microbial Communities, Production Performance, and Health Status of Penaeus monodon" Fishes 10, no. 3: 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10030106
APA StyleRen, H., Xu, Y., Jing, L., Su, H., Hu, X., Cao, Y., & Wen, G. (2025). The Effects of Two Different Aquaculture Methods on Water Quality, Microbial Communities, Production Performance, and Health Status of Penaeus monodon. Fishes, 10(3), 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10030106






