Triaenophorus nodulosus (Cestoda: Bothriocephalidea) in Northern Pike (Esox lucius) and Pumpkinseed (Lepomis gibbosus) from the Mrežnica River: Pathological Effects of Adult Tapeworms and Intestinal Immune Response
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area, Sampling, and Data Analysis
2.2. Parasite Identification
2.3. Histopathology and Immunofluorescence Assay
3. Results
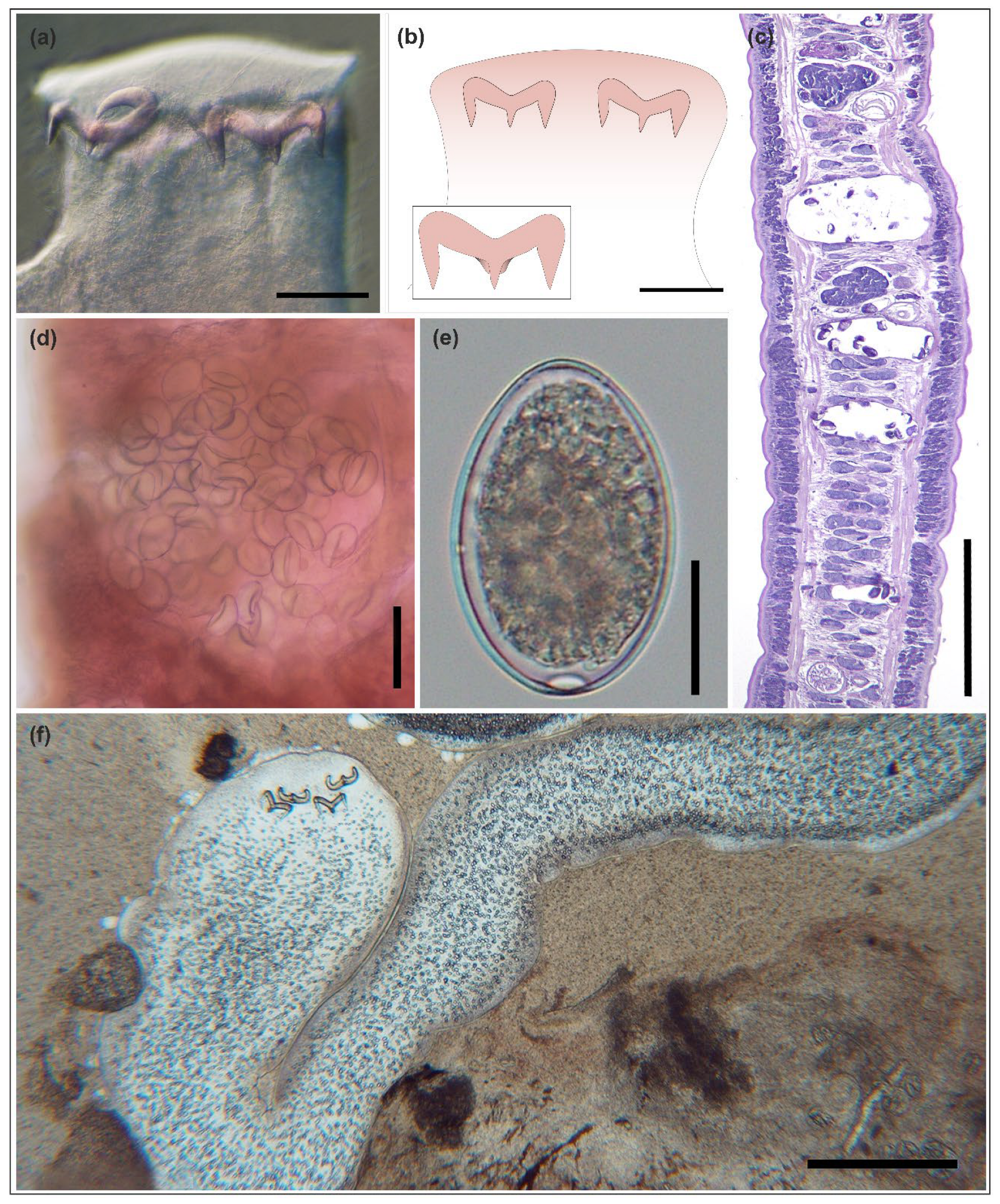
3.1. Parasite Identification and Infection Dynamics
3.2. Body Condition and Gross Pathology
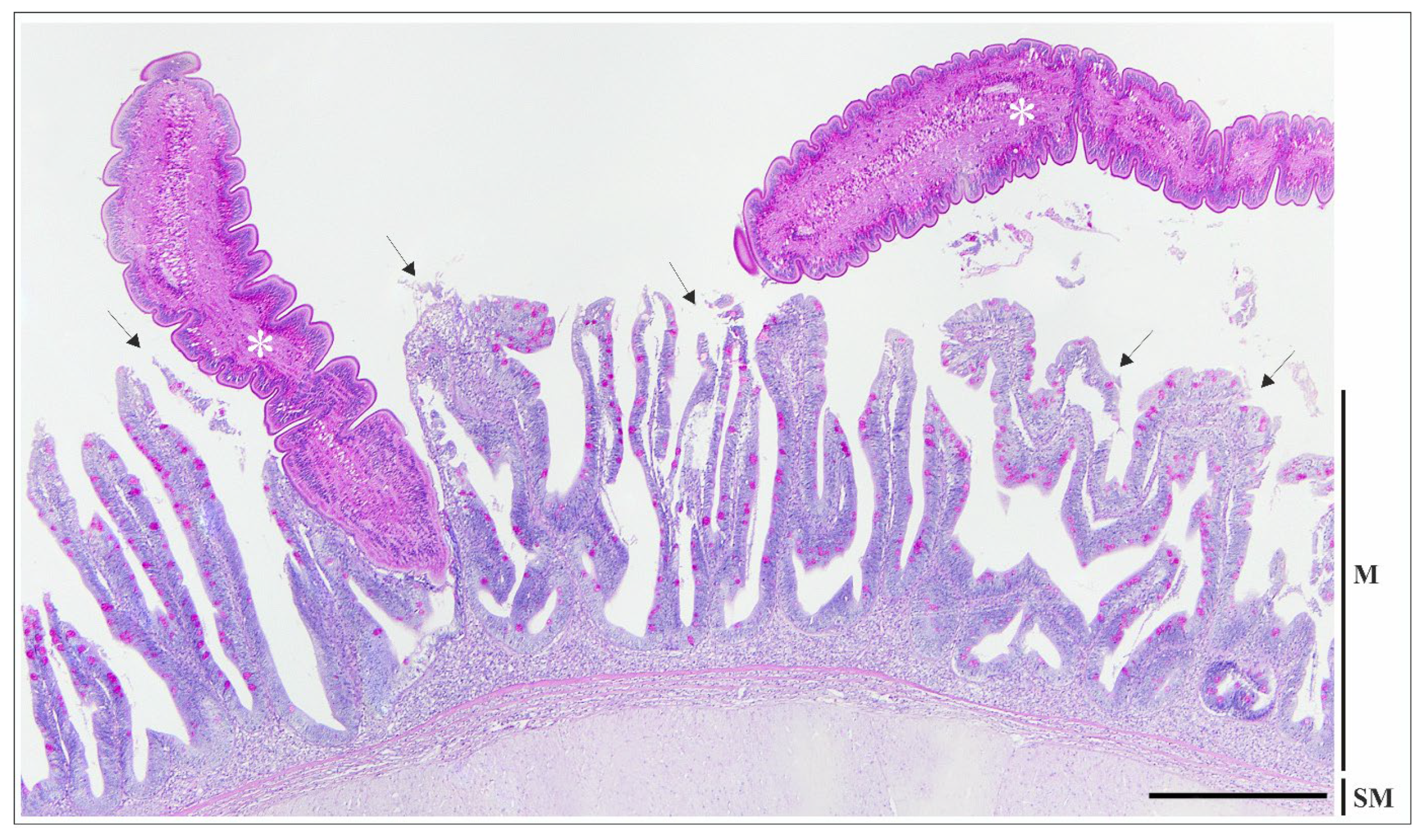
3.3. Histopathology and Immunofluorescence Assay
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuperman, B.I. Tapeworms of the Genus Triaenophorus. In Parasites of Fishes; Amerind Publishing Co. Pvt. Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Brabec, J.; Waeschenbach, A.; Scholz, T.; Littlewood, D.T.J.; Kuchta, R. Molecular phylogeny of the Bothriocephalidea (Cestoda): Molecular data challenge morphological classification. Int. J. Parasitol. 2015, 45, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasenko, P.G.; Sokolov, S.G.; Ieshko, E.P.; Frolov, E.V.; Kalmykov, A.P.; Parshukov, A.N.; Chugunova, Y.K.; Kashinskaya, E.N.; Shokurova, A.V.; Bochkarev, N.A.; et al. A re-evaluation of conflicting taxonomic structures of Eurasian Triaenophorus spp. (Cestoda, Bothriocephalidea: Triaenophoridae) based on partial cox1 mtDNA and 28S rRNA gene sequences. Can. J. Zool. 2022, 100, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, T.A.; Chambers, C.; Isinguzo, I. Cestoidea (Phylum Platyhelminthes). In Fish Diseases and Disorders, Protozoan and Metazoan Infections, 2nd ed.; Woo, P.T.K., Ed.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2006; Volume 1, pp. 391–416. [Google Scholar]
- Scholz, T.; Choudhury, A.; McAllister, C.T. A young parasite in an old fish host: A new genus for protocephalid tapeworms (Cestoda) of bowfin (Amia calva) (Holostei: Amiiformes), and a revised list of its cestodes. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2022, 18, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, U.; Molnár, K.; Cech, G.; Eiras, J.C.; Bandyopadhyay, P.K.; Ghosh, S.; Czeglédi, I.; Székely, C. Evidence of the American Myxobolus dechtiari was introduced along with its host Lepomis gibbosus in Europe: Molecular and histological data. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2021, 15, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischthal, J.H. Parasites of northwest Wisconsin fishes III. The 1946 survey. Trans. Wis. Acad. Sci. Arts Lett. 1952, 41, 17–58. [Google Scholar]
- Scholz, T.; Paggi, L.; Di Cave, D.; Orecchia, P. On some cestodes parasitizing freshwater fish in Italy. Parassitologia 1992, 34, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brinker, A.; Hamers, R. First Description of Pumpkinseed Lepomis gibbosus (L.) as a Possible Second Intermediate Host for Triaenophorus nodulosus (Pallas, 1781) (Cestoda, Pseudophyllidea) in Germany. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 2000, 20, 83–86. [Google Scholar]
- Košuthová, L.; Koščo, J.; Letková, V.; Košuth, P.; Manko, P. New records of endoparasitic helminths in alien invasive fishes from the Carpathian region. Biologia 2009, 64, 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, G.; Vanacker, M.; Fox, M.G.; Beisel, J.-N. Impact of the cestode Triaenophorus nodulosus on the exotic Lepomis gibbosus and the autochthonous Perca fluviatilis. Parasitology 2014, 142, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawler, G.H. Aspect of the Biology of Triaenophorus nodulosus in Yellow Perch, Perca flavescens, in Heming Lake, Manitoba. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1969, 26, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stromberg, P.C.; Crites, J.L. Triaenophoriasis in Lake Erie white bass, Morone chrysops. J. Wildl. Dis. 1974, 10, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechtiar, A.O.; Christie, W.J. Survey of the Parasite Fauna of Lake Ontario Fishes, 1961 to 1971. In Parasites of Fishes in the Canadian Waters of the Great Lakes; Technical Report No. 51; Nepszy, S.J., Ed.; Great Lakes Fishery Commission: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1988; pp. 66–95. [Google Scholar]
- Morley, N.J.; Lewis, J.W. Influence of Triaenophorus nodulosus plerocercoids (Cestoda: Pseudophyllidea) on the occurrence of intestinal helminths in the perch (Perca fluviatilis). J. Helminthol. 2017, 91, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, T.; Kuchta, R.; Oros, M. Tapeworms as pathogens of fish: A review. J. Fish Dis. 2021, 44, 1883–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dezfuli, B.S.; Giari, L.; Lorenzoni, M.; Manera, M.; Noga, E.J. Perch liver reaction to Triaenophorus nodulosus plerocercoids with an emphasis on piscidins 3, 4 and proliferative cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) expression. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 200, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronina, S.V.; Pronin, N.M. The effect of cestode (Triaenophorus nodulosus) infestation on the digestive tract of pike (Esox lucius). J. Ichthyol. 1982, 22, 641–648. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Shostak, A.W.; Dick, T.A. Intestinal pathology in northern pike, Esox lucius L., infected with Triaenophorus crassus Forel, 1868 (Cestoda: Pseudophyllidea). J. Fish Dis. 1986, 9, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashinskaya, E.N.; Vlasenko, P.G.; Kolmogorova, T.V.; Izotova, G.V.; Shokurova, A.V.; Romanenko, G.A.; Markevich, G.N.; Andree, K.B.; Solovyev, M.M. Metapopulation Structure of Two Species of Pikeworm (Triaenophorus, Cestoda) Parasitizing the Postglacial Fish Community in an Oligotrophic Lake. Animals 2023, 13, 3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frolova, T.V.; Izvekova, G.I. A comparative Analysis of the Effect on Intestinal Cestodes in Different Fish Species on Proteolytic Enzyme Activity. J. Evol. Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 58, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolova, T.V.; Izvekova, G.I. Metabolic Adaptation of Fish Intestinal Helminths: Anti-Protease Inhibitory Ability of Cestodes Triaenophorus nodulosus. J. Evol. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 59, 1488–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjurčević, E.; Kužir, S.; Valić, D.; Marino, F.; Benko, V.; Kuri, K.; Matanović, K. Pathogenicity of Clinostomum complanatum (Digenea: Clinostomidae) in naturally infected chub (Squalius cephalus) and common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Vet. Arh. 2022, 92, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, R.D.M.; Valencia, A.H.; Geffen, A.J. The Origin of Fulton’s Condition Factor—Setting the Record Straight. Fisheries 2006, 31, 236–238. [Google Scholar]
- Bush, A.O.; Lafferty, K.D.; Lotz, J.M.; Shostak, A.W. Parasitology meets ecology on its own terms: Margolis et al. revisited. J. Parasitol. 1997, 83, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchta, R.; Vlčková, R.; Poddubnaya, L.G.; Gustinelli, A.; Dzika, E.; Scholz, T. Invalidity of three Palaearctic species of Triaenophorus tapeworms (Cestoda: Pseudophyllidea): Evidence from morphometric analysis of scolex hooks. Folia Parasitol. 2007, 54, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandelj, P.; Žele Vengušt, D.; Vengušt, G.; Kušar, D. Case report: First report of potentially zoonotic Gongylonema pulchrum in a free-living roe deer (Capreolus capreolus) in Slovenia. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1444614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roelfsema, J.H.; Nozari, N.; Pinelli, E.; Kortbeek, L.M. Novel PCRs for differential diagnosis of cestodes. Exp. Parasitol. 2016, 161, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taube, K.; Noreikiene, K.; Kahar, S.; Gross, R.; Ozerov, M.; Vasemägi, A. Subtle transcriptomic response of Eurasian perch (Perca fluviatilis) associated with Triaenophorus nodulosus plerocercoid infection. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2023, 22, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boufana, B.; Žibrat, U.; Jehle, R.; Craig, P.S.; Gassner, H.; Schabetsberger, R. Differential diagnosis of Triaenophorus crassus and T. nodulosus experimental infection in Cyclops abyssorum praealpinus (Copepoda) from the Alpine Lake Grundlsee (Austria) using PCR-RFLP. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 109, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chervy, L. Manual for the study of tapeworms (Cestoda) parasitic in ray-finned fish, amphibians and reptiles. Folia Parasitol. 2024, 71, 001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alesci, A.; Capillo, G.; Mokhtar, D.M.; Fumia, A.; D’Angelo, R.; Cascio, P.L.; Albano, M.; Guerrera, M.C.; Sayed, R.K.A.; Spanò, N.; et al. Expression of Antimicrobic Peptide Piscidin1 in Gills Mast Cells of Giant Mudskipper Periophthalmodon schlosseri (Pallas, 1770). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsman, A.; Tibblin, P.; Berggren, H.; Nordahl, O.; Koch-Schmidt, P.; Larsson, P. Pike Esox lucius as an emerging model organism for studies in ecology and evolutionary biology: A review. J. Fish Biol. 2015, 87, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayyaf Dezfuli, B.; Giari, L.; Lorenzoni, M.; Carosi, A.; Manera, M.; Bosi, G. Pike intestinal reaction to Acanthocephalus lucii (Acanthocephala): Immunohistochemical and ultrastructural surveys. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosi, G.; Lorenzoni, M.; Carosi, A.; Sayyaf Dezfuli, B. Mucosal Hallmarks in the Alimentary Canal of Northern Pike Esox lucius (Linnaeus). Animals 2020, 10, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragun, Z.; Ivanković, D.; Tepić, N.; Filipović Marijić, V.; Šariri, S.; Mijošek Pavin, T.; Drk, S.; Gjurčević, E.; Matanović, K.; Kužir, S.; et al. Metal Bioaccumulation in the Muscle of the Northern Pike (Esox lucius) from Historically Contaminated River and the Estimation of the Human Health Risk. Fishes 2024, 9, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, J.R.; Pegg, J.; Williams, C.F. Pathological and Ecological Host Consequences of Infection by an Introduced Fish Parasite. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, T.; Kuchta, R.; Williams, C. Bothriocephalus acheilognathi. In Fish Parasites: Pathobiology and Protection; Woo, P.T.K., Buchmann, K., Eds.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2012; pp. 282–297. [Google Scholar]
- Dezfuli, B.S.; Giari, L.; Squerzanti, S.; Lui, A.; Lorenzoni, M.; Sakalli, S.; Shinn, A.P. Histological damage and inflammatory response elicited by Monobothrium wageneri (Cestoda) in the intestine of Tinca tinca (Cyprinidae). Parasites Vectors 2011, 4, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.F.; Poddubnaya, L.G.; Scholz, T.; Turnbull, J.F.; Ferguson, H.W. Histopathological and ultrastructural studies of the tapeworm Monobothrium wageneri (Caryophyllidea) in the intestinal tract of tench Tinca tinca. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2011, 97, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezfuli, B.S.; Lui, A.; Giari, L.; Castaldelli, G.; Shinn, A.P.; Lorenzoni, M. Innate immune defence mechanisms of tench, Tinca tinca (L.), naturally infected with the tapeworm Monobothrium wageneri. Parasite Immunol. 2012, 34, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackiewicz, J.S.; Cosgrove, G.E.; Gude, W.D. Relationship of Pathology to Scolex Morphology among Caryophyllid Cestodes. Z. Parasitenkd. 1972, 39, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayunga, E.G. Observations on the intestinal pathology caused by three caryophyllid tapeworms of the white sucker Catostomus commersoni Laécpède. J. Fish Dis. 1979, 2, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, T.; Waeschenbach, A.; Oros, M.; Brabec, J.; Littlewood, D.T.J. Phylogenetic reconstruction of early diverging tapeworms (Cestoda: Caryophyllidea) reveals ancient radiations in vertebrate hosts and biogeographic regions. Int. J. Parasitol. 2021, 51, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, O.M.; Rubtsova, N.Y. Revisiting Hunterella nodulosa Mackiewicz and McCrae, 1962 (Cestoda: Caryophyllidae) from Catostomus commersoni (Lacépède) with a Special Treatment of its Ecological Diversity in Wisconsin Waters. Int. J. Zool. Anim. Biol. 2023, 6, 000473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayyaf Dezfuli, B.; Franchella, E.; Bernacchia, G.; De Bastiani, M.; Lorenzoni, F.; Carosi, A.; Lorenzoni, M.; Bosi, G. Infection of endemic chub Squalius tenellus with the intestinal tapeworm Caryophyllaeus brachycollis (Cestoda): Histopathology and ultrastructural survey. Parasitology 2024, 151, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, H.; Jones, A. Parasitic Worms of Fish; Taylor & Francis Ltd.: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Gjurčević, E.; Beck, A.; Drašner, K.; Stanin, D.; Kužir, S. Pathogenicity of Atractolytocestus huronensis (Cestoda) from cultured common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Vet. Arh. 2012, 82, 273–282. [Google Scholar]
- Bosi, G.; Maynard, B.J.; Pironi, F.; Sayyaf Dezfuli, B. Parasites and the neuroendocrine control of fish intestinal function: An ancient struggle between pathogens and host. Parasitology 2022, 149, 1842–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayyaf Dezfuli, B.; Lorenzoni, M.; Carosi, A.; Bosi, G.; Franchella, E.; Poddubnaya, L.G. Glandular cell products in adult cestode: A new tale of tapeworm interaction with fish innate immune response. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2024, 25, 100991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoole, D.; Nisan, H. Ultrastructural studies on intestinal response of carp, Cyprinus carpio L., to the pseudophyllidean tapeworm, Bothriocephalus acheilognathi Yamaguti, 1934. J. Fish Dis. 1994, 17, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosi, G.; Shinn, A.P.; Giari, L.; Simoni, E.; Pironi, F.; Dezfuli, B.S. Changes in the neuromodulators of the diffuse endocrine system of the alimentary canal of farmed rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), naturally infected with Eubothrium crassum (Cestoda). J. Fish Dis. 2005, 28, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnár, K.; Majoros, G.; Csaba, G.; Székely, C. Pathology of Atractolytocestus huronensis Anthony, 1958 (Cestoda, Caryophyllaeidae) in Hungarian pond-farmed common carp. Acta Parasitol. 2003, 48, 222–228. [Google Scholar]
- Barčák, D.; Madžunkov, M.; Uhrovič, D.; Miko, M.; Brázová, T.; Oros, M. Khawia japonensis (Cestoda), the Asian parasite of common carp, continues to spread in Central European countries: Distribution, infection indices and histopathology. BioInvasions Rec. 2021, 10, 934–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, A.L.; Pittaway, C.E.; Sparrow, R.M.; Balkwill, E.C.; Coles, G.C.; Tilley, A.; Wilson, A.D. Analysis of caecal mucosal inflammation and immune modulation during Anoplocephala perfoliata infection of horses. Parasite Immunol. 2019, 41, e12667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochneva, A.; Drozdova, P.; Borvinskaya, E. The first transcriptomic resource for the flatworm Triaenophorus nodulosus (Cestoda: Bothriocephalidea), a common parasite of Holarctic freshwater fish. Mar. Genom. 2020, 51, 100702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazanec, H.; Koník, P.; Gardian, Z.; Kuchta, R. Extracellular vesicles secreted by model tapeworm Hymenolepis diminuta: Biogenesis, ultrastructure and protein composition. Int. J. Parasitol. 2021, 51, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutyrev, I.A.; Biserova, N.M.; Mazur, O.E.; Dugarov, Z.N. Experimental study of ultrastructural mechanisms and kinetics of tegumental secretion in cestodes parasitizing fish (Cestoda: Diphyllobothriidea). J. Fish Dis. 2021, 44, 1237–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlyuchenkova, A.N.; Kutyrev, I.A.; Fedorov, A.V.; Chelombitko, M.A.; Mazur, O.E.; Dugarov, Z.N. Investigation into Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Excretory/Secretory Products from Gull-Tapeworm Dibothriocephalus dendriticus and Ligula Ligula interrupta Plerocercoids. Mosc. Univ. Biol. Sci. Bull. 2023, 78, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, A.E. Histamine, mast cells and hypersensitivity responses in fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 1982, (Suppl. 2), 147–155. [Google Scholar]
- Reite, O.B.; Evensen, Ø. Inflammatory cells of teleostean fish: A review focusing on mast cells/eosinophilic granule cells and rodlet cells. Fish Shellfish Immun. 2006, 20, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezfuli, B.S.; Bosi, G.; DePasquale, J.A.; Manera, M.; Giari, L. Fish innate immunity against intestinal helminths. Fish Shellfish Immun. 2016, 50, 274–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hakeem, S.S.; Fadladdin, Y.A.J.; Khormi, M.A.; Abd-El-Hafeez, H.H. Modulation of the intestinal mucosal and cell-mediated response against natural helminth infection in the African catfish Clarias gariepinus. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayyaf Dezfuli, B.; Lorenzoni, M.; Carosi, A.; Giari, L.; Bosi, G. Teleost innate immunity, an intricate game between immune cells and parasites of fish organs: Who wins, who loses. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1250835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumsden, J.S. Gastrointestinal Tract, Swimbladder, Pancreas and Peritoneum. In Systemic Pathology of Fish: A Text and Atlas of Normal Tissues in Teleosts and Their Responses in Disease, 2nd ed.; Ferguson, H.W., Ed.; Scotian Press: London, UK, 2006; pp. 168–199. [Google Scholar]
- Dezfuli, B.S.; Manera, M.; Bosi, G.; DePasquale, J.A.; D’Amelio, S.; Castaldelli, G.; Giari, L. Anguilla anguilla intestinal immune response to natural infection with Contracaecum rudolphii A larvae. J. Fish Dis. 2016, 39, 1187–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dezfuli, B.S.; Giovinazzo, G.; Lui, A.; Giari, L. Inflammatory response to Dentitruncus truttae (Acanthocephala) in the intestine of brown trout. Fish Shellfish Immun. 2008, 24, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dezfuli, B.S.; Lui, A.; Giari, L.; Pironi, F.; Manera, M.; Lorenzoni, M.; Noga, E.J. Piscidins in the intestine of European perch, Perca fluviatilis, naturally infected with an enteric worm. Fish Shellfish Immun. 2013, 35, 1539–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayyaf Dezfuli, B.; Fernandes, C.E.; Galindo, G.M.; Castaldelli, G.; Manera, M.; DePasquale, J.A.; Lorenzoni, M.; Bertin, S.; Giari, L. Nematode infection in liver of the fish Gymnotus inaequilabiatus (Gymnotiformes: Gymnotidae) from the Pantanal Region in Brazil: Pathobiology and inflammatory response. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vukšić, M. Histological and Histochemical Identification of Mast Cells in Fish. Master’s Thesis, The University of Zagreb, Zagreb, Croatia, 2023. (In Croatian). [Google Scholar]
- Dezfuli, B.S.; Lui, A.; Boldrini, P.; Pironi, F.; Giari, L. The inflammatory response of fish to helminth parasites. Parasite 2008, 15, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezfuli, B.S.; Giari, L. Mast cells in the gills and intestines of naturally infected fish: Evidence of migration and degranulation. J. Fish Dis. 2008, 31, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silphaduang, U.; Noga, E.J. Peptide antibiotics in mast cells of fish. Nature 2001, 414, 268–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, S.V.; Sarkar, P.; Kumar, P.; Arockiaraj, J. Piscidin, Fish Antimicrobial Peptide: Structure, Classification, Properties, Mechanism, Gene Regulation and Therapeutical Importance. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2021, 27, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín-Parra, C.; Serna-Duque, J.A.; Espinosa-Ruiz, C.; Albadalejo-Riad, N.; Bardera, G.; Thompson, K.; Esteban, M.Á. Piscidin 1 and 2 of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata): New insights into their role as host defense peptides. Fish Shellfish Immun. 2025, 165, 110501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccone, G.; Capillo, G.; Fernandes, J.M.O.; Kiron, V.; Lauriano, E.R.; Alesci, A.; Cascio, P.L.; Guerrera, M.C.; Kuciel, M.; Zuwala, K.; et al. Expression of the Antimicrobial Peptide Piscidin 1 and Neuropeptides in Fish Gill and Skin: A Potential Participation in Neuro-Immune Interaction. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feist, S.W.; Longshaw, M. Histopathology of fish parasite infections—Importance for populations. J. Fish Biol. 2008, 73, 2143–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sampling Site | Species | No. of Fish | Prevalence | Mean Intensity * | Sampling Season (Month) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF | Esox lucius | 16 | 18.8 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | Spring (April–May) |
| 16 | - | - | Autumn (September) | ||
| DRF | Esox lucius | 17 | 76.5 | 1.3 ± 0.2 | Spring (April–May) |
| 13 | - | - | Autumn (September) | ||
| Lepomis gibbosus | 53 | 5.7 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | Spring (April–May) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gjurčević, E.; Benko, V.; Matanović, K.; Bandelj, P.; Alesci, A.; Marino, F.; Kužir, S.; Duka, L.; Abbate, J.M. Triaenophorus nodulosus (Cestoda: Bothriocephalidea) in Northern Pike (Esox lucius) and Pumpkinseed (Lepomis gibbosus) from the Mrežnica River: Pathological Effects of Adult Tapeworms and Intestinal Immune Response. Fishes 2025, 10, 640. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10120640
Gjurčević E, Benko V, Matanović K, Bandelj P, Alesci A, Marino F, Kužir S, Duka L, Abbate JM. Triaenophorus nodulosus (Cestoda: Bothriocephalidea) in Northern Pike (Esox lucius) and Pumpkinseed (Lepomis gibbosus) from the Mrežnica River: Pathological Effects of Adult Tapeworms and Intestinal Immune Response. Fishes. 2025; 10(12):640. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10120640
Chicago/Turabian StyleGjurčević, Emil, Valerija Benko, Krešimir Matanović, Petra Bandelj, Alessio Alesci, Fabio Marino, Snježana Kužir, Laura Duka, and Jessica Maria Abbate. 2025. "Triaenophorus nodulosus (Cestoda: Bothriocephalidea) in Northern Pike (Esox lucius) and Pumpkinseed (Lepomis gibbosus) from the Mrežnica River: Pathological Effects of Adult Tapeworms and Intestinal Immune Response" Fishes 10, no. 12: 640. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10120640
APA StyleGjurčević, E., Benko, V., Matanović, K., Bandelj, P., Alesci, A., Marino, F., Kužir, S., Duka, L., & Abbate, J. M. (2025). Triaenophorus nodulosus (Cestoda: Bothriocephalidea) in Northern Pike (Esox lucius) and Pumpkinseed (Lepomis gibbosus) from the Mrežnica River: Pathological Effects of Adult Tapeworms and Intestinal Immune Response. Fishes, 10(12), 640. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10120640







