Danger! Stay Alert: The Role of Skein Cells in the Evolution of the Sea Lamprey (Petromyzon marinus, Linnaeus 1758)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Collection
2.2. Tissue Preparation and Histological Analysis
2.3. Rationale for Antibody Selection
2.4. Peroxidase Immunohistochemistry
2.5. Immunofluorescence
2.6. Confocal Microscopy
2.7. Quantitative and Statistical Image Analysis
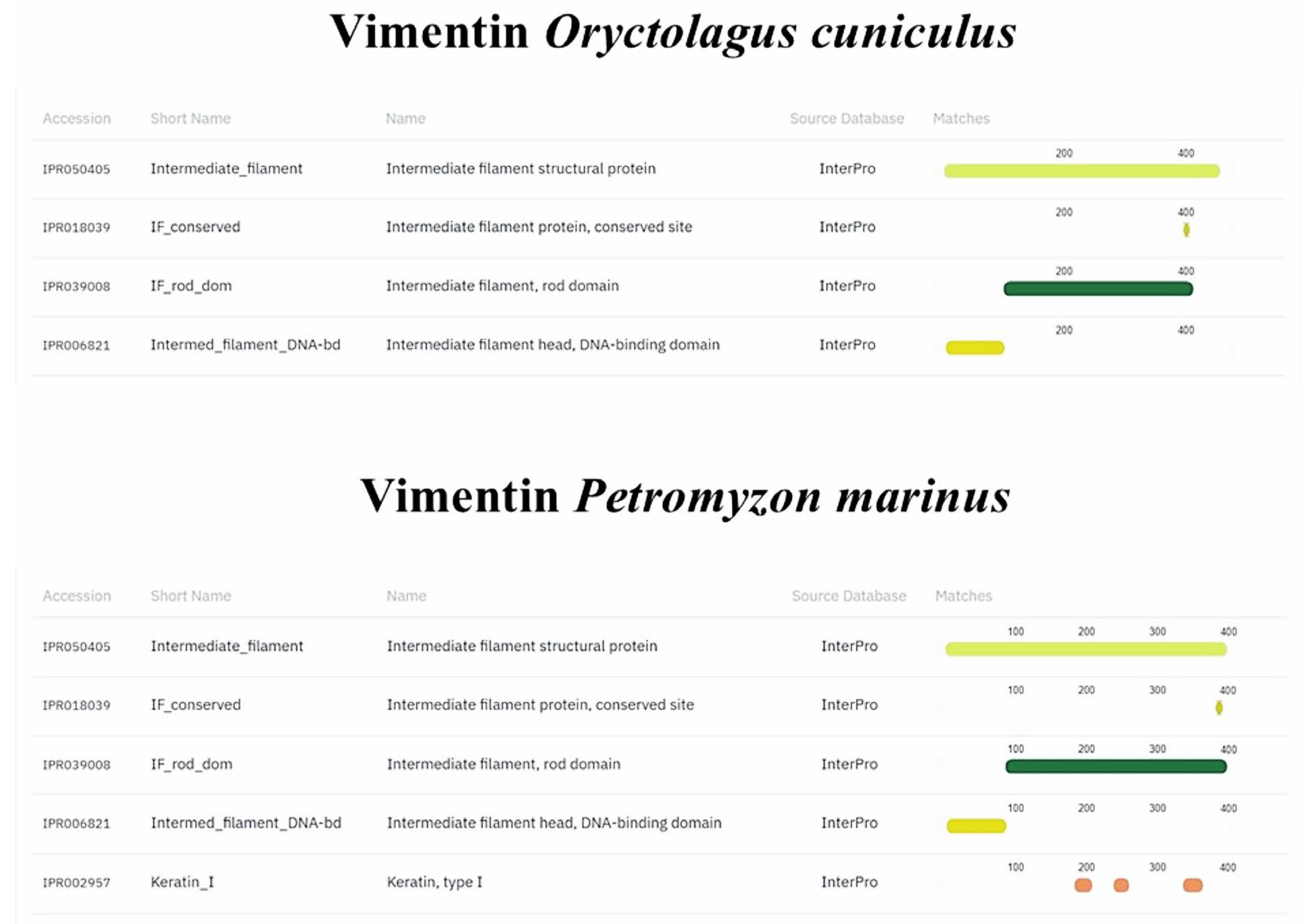
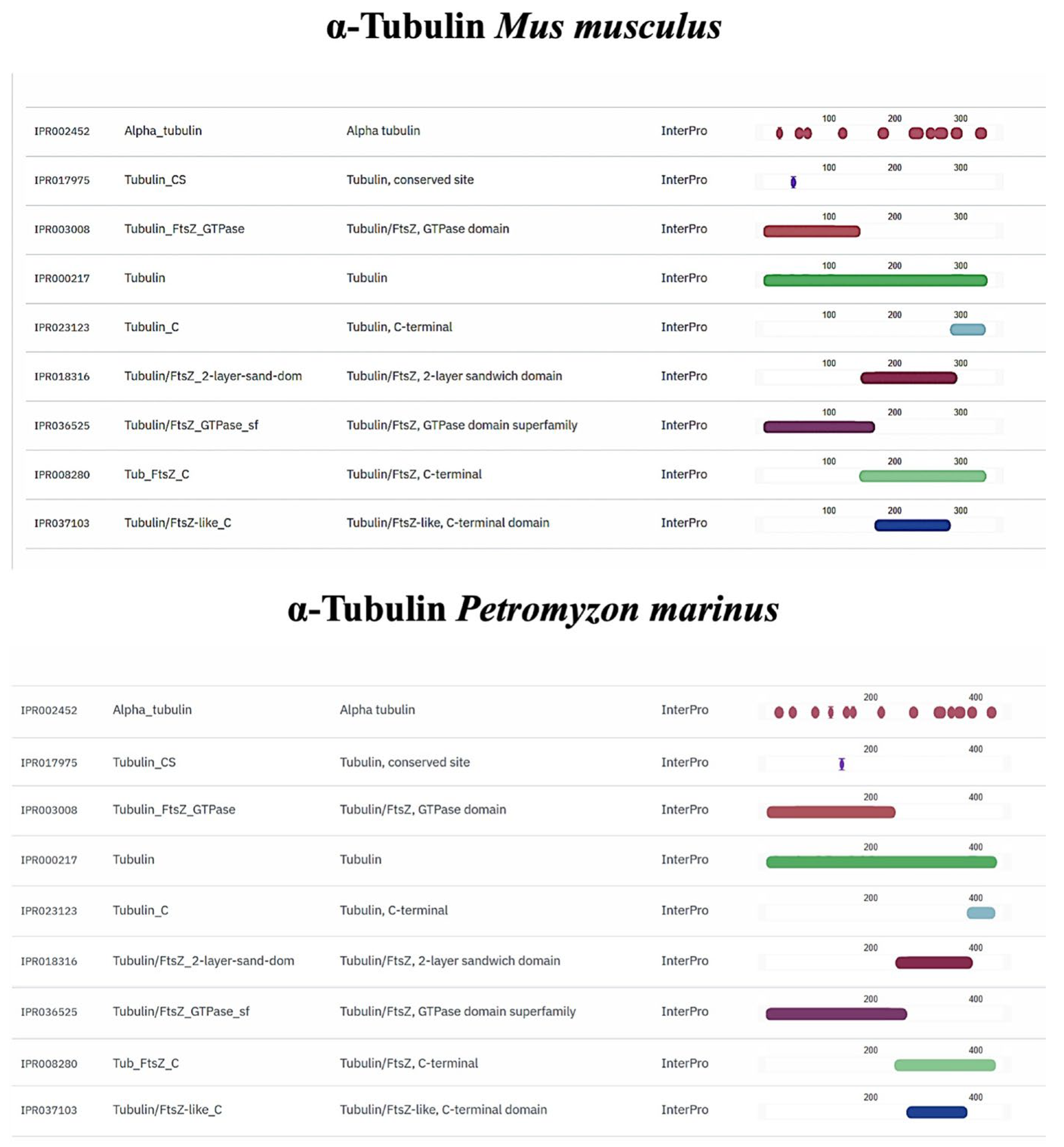
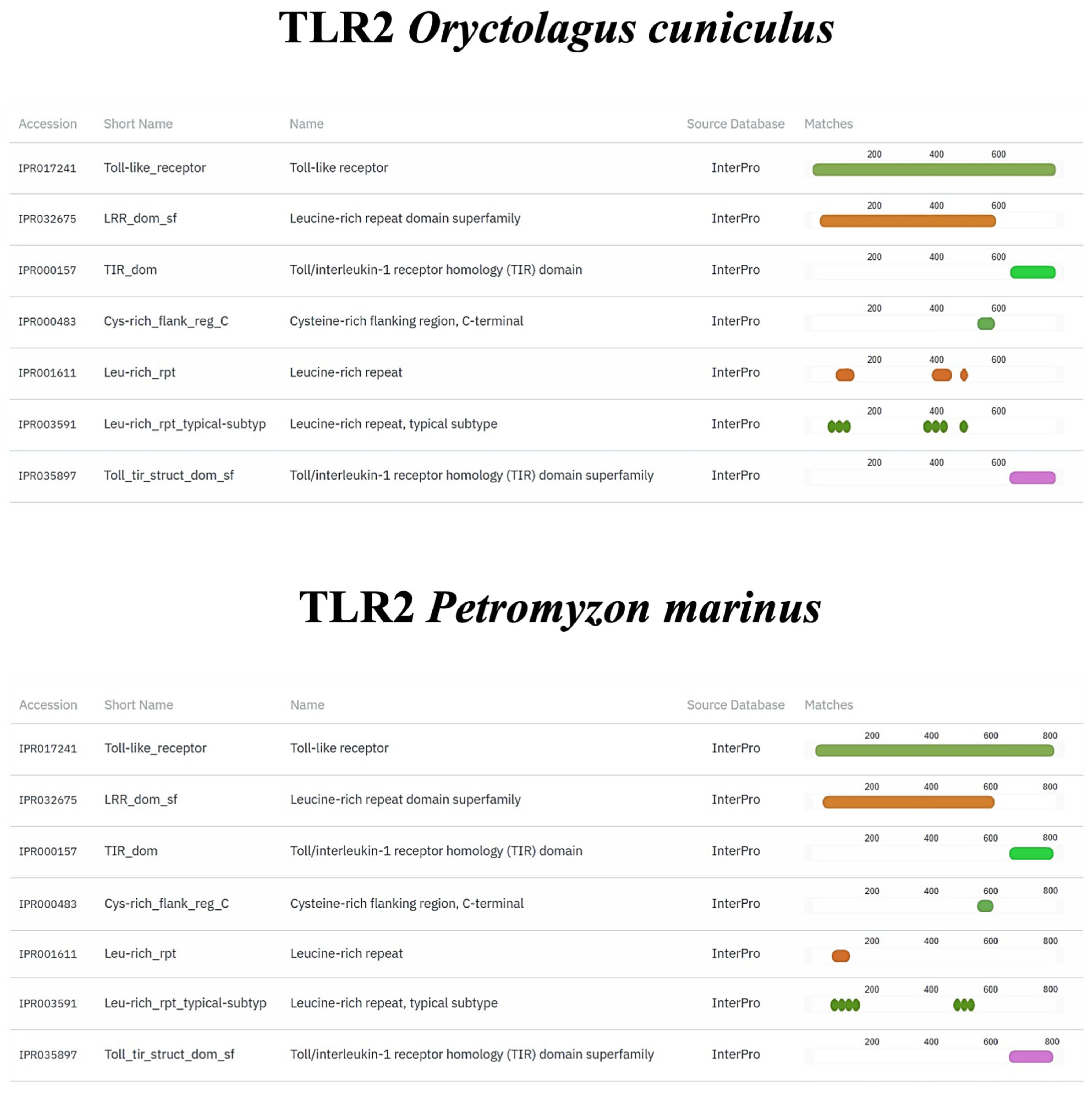
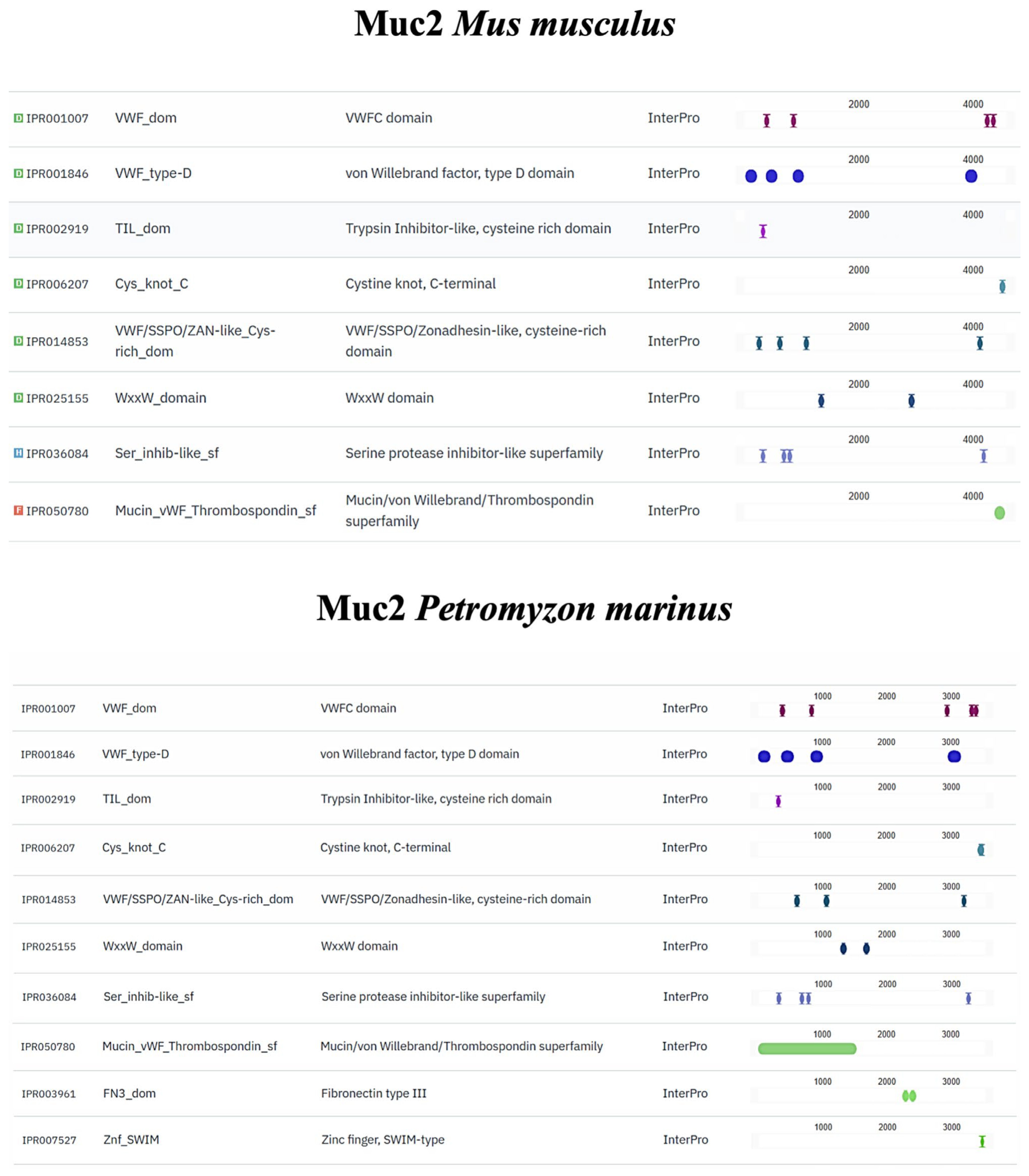
2.8. In Silico Comparison of Muc2, TLR2, Vimentin and α-Tubulin Protein Domains
3. Results
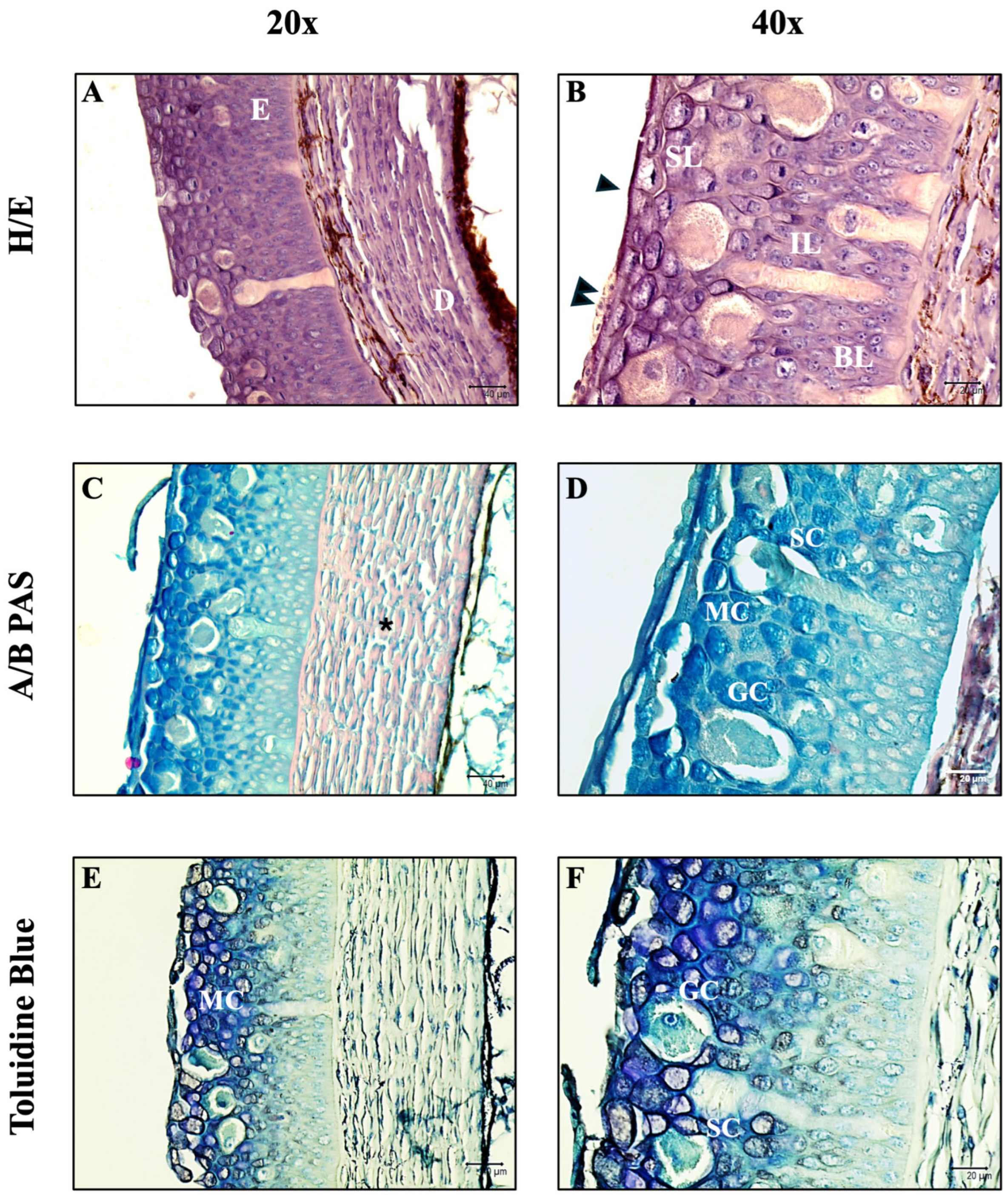
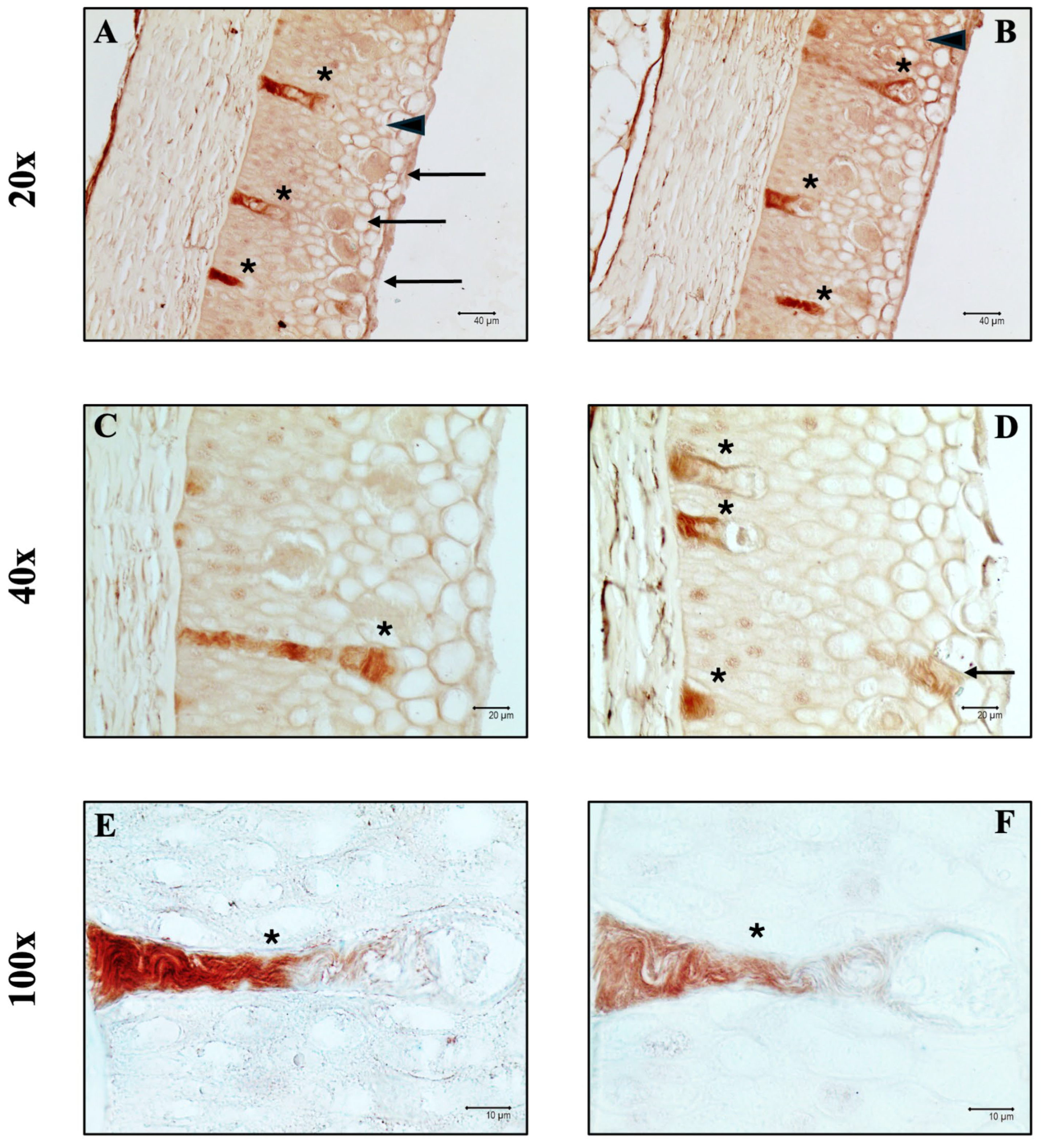
3.1. Histology and Histochemistry
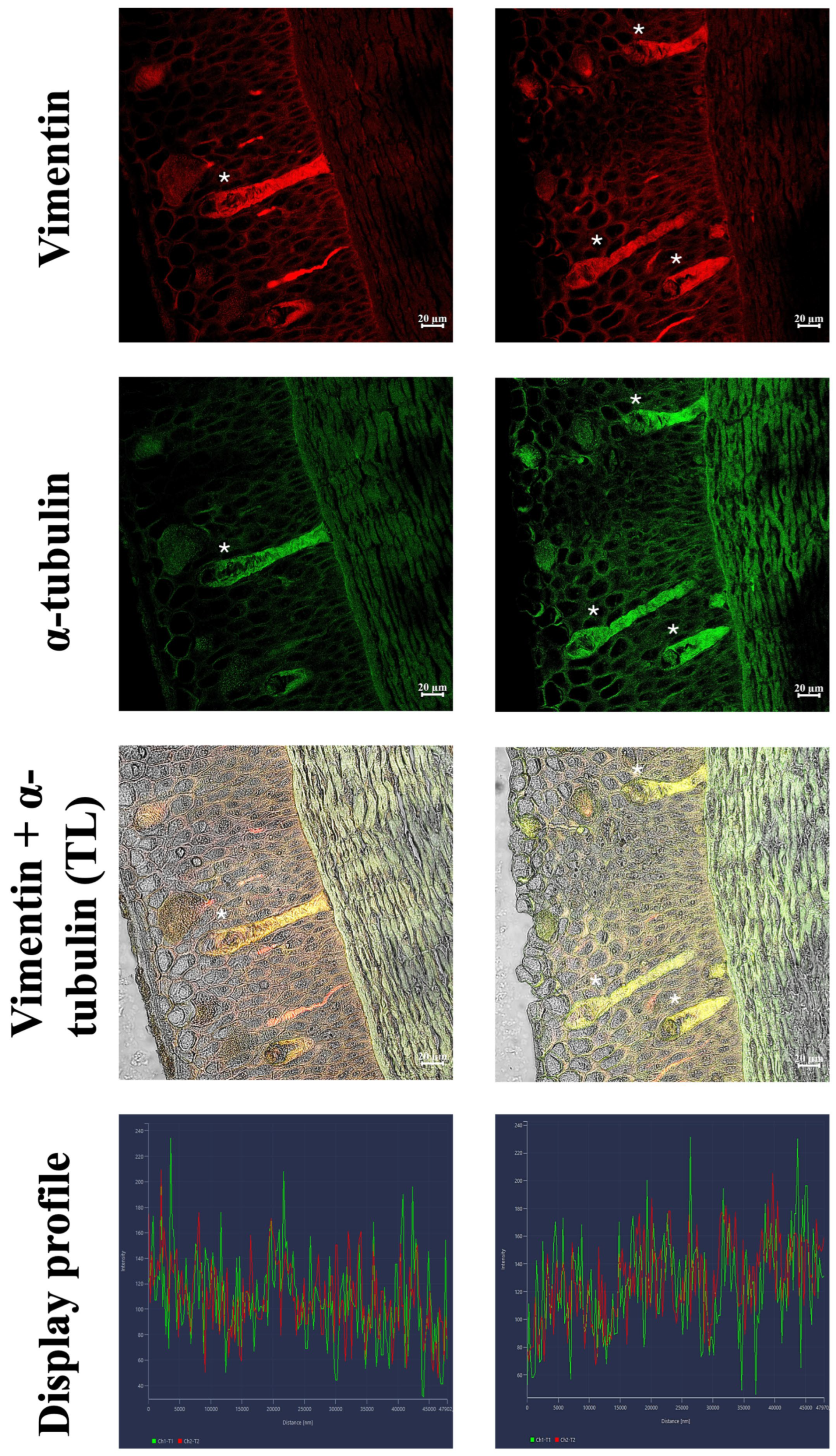
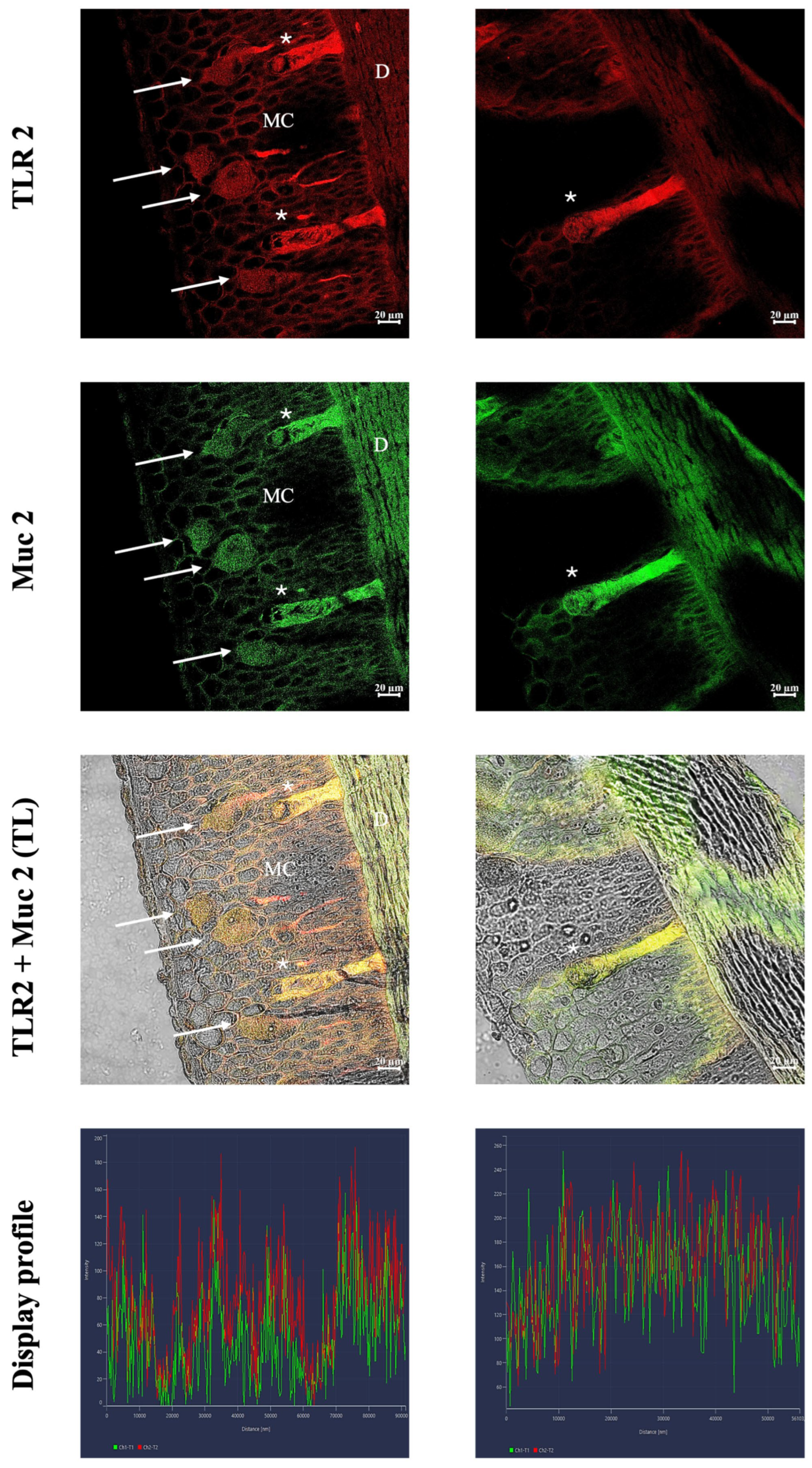
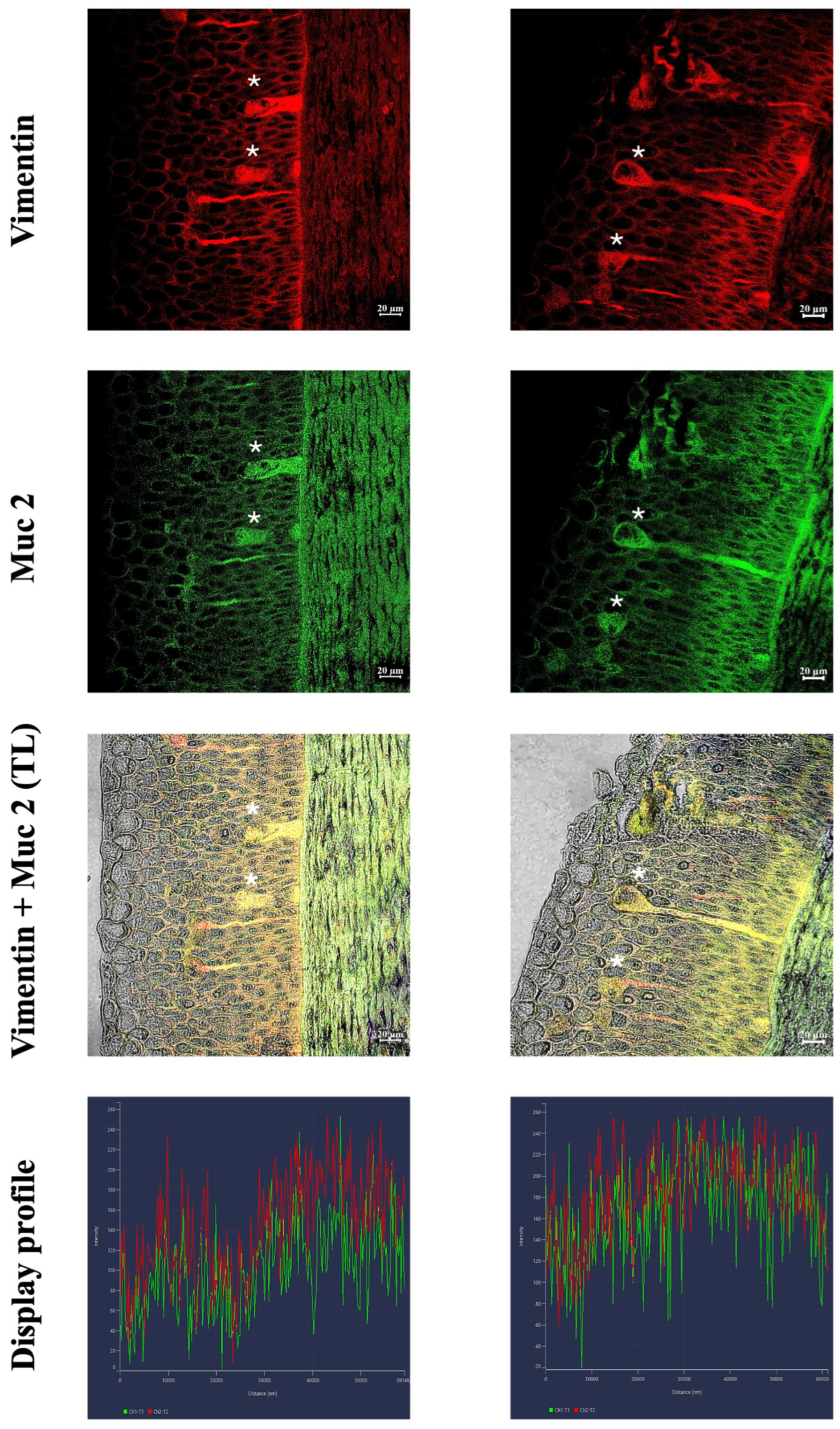
3.2. Immunofluorescence and Confocal Microscopy
3.3. Immunoperoxidase
3.4. In Silico Analyses
4. Discussion
4.1. Alarm Signaling: An Evolutionary Perspective
4.2. Morphological and Histochemical Profile of Skein Cells Within the Petromyzon marinus Epidermis
4.3. Evidence for the Possible Functional Role of Skein Cells: Immunity and Alarm Signaling
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hume, J.B.; Wagner, M. A Death in the Family: Sea Lamprey (Petromyzon marinus) Avoidance of Confamilial Alarm Cues Diminishes with Phylogenetic Distance. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 3751–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, R.E.; Miyai, C.A.; Sanches, F.H.C.; Giaquinto, P.C.; Delicio, H.C.; Volpato, G.L. Blood Cues Induce Antipredator Behavior in Nile Tilapia Conspecifics. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, M.C.O.; Elvidge, C.K.; Jackson, C.D.; Chivers, D.P.; Brown, G.E. The Responses of Prey Fish to Temporal Variation in Predation Risk: Sensory Habituation or Risk Assessment? Behav. Ecol. 2010, 21, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kicklighter, C.E.; Germann, M.; Kamio, M.; Derby, C.D. Molecular Identification of Alarm Cues in the Defensive Secretions of the Sea Hare Aplysia Californica. Anim. Behav. 2007, 74, 1481–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathuru, A.S.; Kibat, C.; Cheong, W.F.; Shui, G.; Wenk, M.R.; Friedrich, R.W.; Jesuthasan, S. Chondroitin Fragments Are Odorants That Trigger Fear Behavior in Fish. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majer, A.P.; Trigo, J.R.; Duarte, L.F.L. Evidence of an Alarm Signal in Ophiuroidea (Echinodermata). Mar. Biodivers. Rec. 2009, 2, e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daleo, P.; Alberti, J.; Avaca, M.S.; Narvarte, M.; Martinetto, P.; Iribarne, O. Avoidance of Feeding Opportunities by the Whelk Buccinanops Globulosum in the Presence of Damaged Conspecifics. Mar. Biol. 2012, 159, 2359–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemical Cues and Reducing the Risk of Predation. In Chemical Communication in Crustaceans; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 355–370. ISBN 978-0-387-77100-7.
- Persons, M.H.; Walker, S.E.; Rypstra, A.L.; Marshall, S.D. Wolf Spider Predator Avoidance Tactics and Survival in the Presence of Diet-Associated Predator Cues (Araneae: Lycosidae). Anim. Behav. 2001, 61, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llandres, A.L.; Gonzálvez, F.G.; Rodríguez-Gironés, M.A. Social but Not Solitary Bees Reject Dangerous Flowers Where a Conspecific Has Recently Been Attacked. Anim. Behav. 2013, 85, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.; Laland, K.; Krause, J. (Eds.) Fish Cognition and Behavior, 1st ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-1-4443-3221-6. [Google Scholar]
- Gherardi, F.; Mavuti, K.M.; Pacini, N.; Tricarico, E.; Harper, D.M. The Smell of Danger: Chemical Recognition of Fish Predators by the Invasive Crayfish Procambarus Clarkii: Chemical Recognition of Fish Predators by Invasive Crayfish. Freshw. Biol. 2011, 56, 1567–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, B.R.; Molis, M.; Scrosati, R.A. Predator Chemical Cues Affect Prey Feeding Activity Differently in Juveniles and Adults. Can. J. Zool. 2012, 90, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chivers, D.P.; Smith, R.J.F. Chemical Alarm Signalling in Aquatic Predator-Prey Systems: A Review and Prospectus. Écoscience 1998, 5, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, A.E.; Holstrom, I.E.; Molitor, S.A.; Hanson, M.E.; Shegrud, W.R.; Gillen, J.C.; Willard, S.J.; Wisenden, B.D. Field Verification of Chondroitin Sulfate as a Putative Component of Chemical Alarm Cue in Wild Populations of Fathead Minnows (Pimephales promelas). Chemoecology 2017, 27, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, P.W.; Wisenden, B.D. (Eds.) Fish Pheromones and Related Cues, 1st ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-0-8138-2386-7. [Google Scholar]
- Schoeppner, N.M.; Relyea, R.A. When Should Prey Respond to Consumed Heterospecifics? Testing Hypotheses of Perceived Risk. Copeia 2009, 2009, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Reis, M.; Thawornwattana, Y.; Angelis, K.; Telford, M.J.; Donoghue, P.C.J.; Yang, Z. Uncertainty in the Timing of Origin of Animals and the Limits of Precision in Molecular Timescales. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 2939–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, P.R.; Arakawa, H.; Aronsuu, K.; Baker, C.; Blair, S.-R.; Beaulaton, L.; Belo, A.F.; Kitson, J.; Kucheryavyy, A.; Kynard, B.; et al. Lamprey Fisheries: History, Trends and Management. J. Great Lakes Res. 2021, 47, S159–S185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchiori, C.H.; Santana, M.V.D.O.; Malheiros, K.D.P. Ecological and Medicinal Importance of Lampreys (Cyclostomata: Petromyzontiformes: Petromyzontidae). Middle East. Res. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 4, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docker, M.F. (Ed.) Lampreys: Biology, Conservation and Control; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 1, ISBN 978-94-017-9305-6. [Google Scholar]
- Fish & Fisheries Series. Available online: https://link.springer.com/series/5973 (accessed on 8 July 2025).
- Green, S.A.; Bronner, M.E. The Lamprey: A Jawless Vertebrate Model System for Examining Origin of the Neural Crest and Other Vertebrate Traits. Differentiation 2014, 87, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imre, I.; Di Rocco, R.T.; Belanger, C.F.; Brown, G.E.; Johnson, N.S. The Behavioural Response of Adult Petromyzon marinus to Damage-released Alarm and Predator Cues. J. Fish Biol. 2014, 84, 1490–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C.M.; Stroud, E.M.; Meckley, T.D. A Deathly Odor Suggests a New Sustainable Tool for Controlling a Costly Invasive Species. Can. J. Fish Aquat. Sci. 2011, 68, 1157–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hume, J.B.; Meckley, T.D.; Johnson, N.S.; Luhring, T.M.; Siefkes, M.J.; Wagner, C.M. Application of a Putative Alarm Cue Hastens the Arrival of Invasive Sea Lamprey (Petromyzon marinus) at a Trapping Location. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 72, 1799–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luhring, T.M.; Meckley, T.D.; Johnson, N.S.; Siefkes, M.J.; Hume, J.B.; Wagner, C.M. A Semelparous Fish Continues Upstream Migration When Exposed to Alarm Cue, but Adjusts Movement Speed and Timing. Anim. Behav. 2016, 121, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, W. The Distribution of Fright Reaction and Alarm Substance Cells in Fishes. Copeia 1977, 1977, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brönmark, C.; Hansson, L.-A. (Eds.) Chemical Ecology in Aquatic Systems; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; ISBN 978-0-19-958309-6. [Google Scholar]
- Carreau-Green, N.D.; Mirza, R.S.; MartÍnez, M.L.; Pyle, G.G. The Ontogeny of Chemically Mediated Antipredator Responses of Fathead Minnows Pimephales promelas. J. Fish Biol. 2008, 73, 2390–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Alonso, R.; Megías, M.; Pombal, M.A.; Molist, P. Morphological and Functional Aspects of the Epidermis of the Sea Lamprey Petromyzon marinus throughout Development. J. Fish Biol. 2017, 91, 80–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, E.B.; Whitear, M. Skein Cells in Lamprey Epidermis. Can. J. Zool. 1980, 58, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akat, E.; Yenmiş, M.; Pombal, M.A.; Molist, P.; Megías, M.; Arman, S.; Veselỳ, M.; Anderson, R.; Ayaz, D. Comparison of Vertebrate Skin Structure at Class Level: A Review. Anat. Rec. 2022, 305, 3543–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Q.; Li, J.; Pang, Y. Lamprey Wound Healing and Regenerative Effects: The Collaborative Efforts of Diverse Drivers. IJMS 2023, 24, 3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ángeles Esteban, M. An Overview of the Immunological Defenses in Fish Skin. ISRN Immunol. 2012, 2012, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsui, S.; Nakamura, O.; Watanabe, T. Lamprey (Lethenteron japonicum) IL-17 Upregulated by LPS-Stimulation in the Skin Cells. Immunogenetics 2007, 59, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rast, J.P.; Buckley, K.M. Lamprey Immunity Is Far from Primitive. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 5746–5747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chivers, D.P.; Zhao, X.; Brown, G.E.; Marchant, T.A.; Ferrari, M.C.O. Predator-Induced Changes in Morphology of a Prey Fish: The Effects of Food Level and Temporal Frequency of Predation Risk. Evol. Ecol. 2008, 22, 561–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pergolizzi, S.; Fumia, A.; D’Angelo, R.; Mangano, A.; Lombardo, G.P.; Giliberti, A.; Messina, E.; Alesci, A.; Lauriano, E.R. Expression and Function of Toll-like Receptor 2 in Vertebrate. Acta Histochem. 2023, 125, 152028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.; Das, S.K.; Samal, J.; Thatoi, H.N. Epidermal Mucus, a Major Determinant in Fish Health: A Review. IJVR 2018, 19, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrindell, J.; Desnues, B. Vimentin: From a Cytoskeletal Protein to a Critical Modulator of Immune Response and a Target for Infection. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1224352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilan-Ber, T.; Ilan, Y. The Role of Microtubules in the Immune System and as Potential Targets for Gut-Based Immunotherapy. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 111, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alesci, A.; Pergolizzi, S.; Savoca, S.; Fumia, A.; Mangano, A.; Albano, M.; Messina, E.; Aragona, M.; Lo Cascio, P.; Capillo, G.; et al. Detecting Intestinal Goblet Cells of the Broadgilled Hagfish Eptatretus Cirrhatus (Forster, 1801): A Confocal Microscopy Evaluation. Biology 2022, 11, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suprewicz, Ł.; Zakrzewska, M.; Okła, S.; Głuszek, K.; Sadzyńska, A.; Deptuła, P.; Fiedoruk, K.; Bucki, R. Extracellular Vimentin as a Modulator of the Immune Response and an Important Player during Infectious Diseases. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2024, 102, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Cófreces, N.B.; Sánchez-Madrid, F. Sailing to and Docking at the Immune Synapse: Role of Tubulin Dynamics and Molecular Motors. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birchenough, G.M.H.; Nyström, E.E.L.; Johansson, M.E.V.; Hansson, G.C. A Sentinel Goblet Cell Guards the Colonic Crypt by Triggering Nlrp6-Dependent Muc2 Secretion. Science 2016, 352, 1535–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcdonald, J.H.; Dunn, K.W. Statistical Tests for Measures of Colocalization in Biological Microscopy. J. Microsc. 2013, 252, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paysan-Lafosse, T.; Blum, M.; Chuguransky, S.; Grego, T.; Pinto, B.L.; Salazar, G.A.; Bileschi, M.L.; Bork, P.; Bridge, A.; Colwell, L.; et al. InterPro in 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D418–D427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leahy, D.J.; Hendrickson, W.A.; Aukhil, L.; Erickson, H.P. Structure of a Fibronectin Type III Domain from Tenascin Phased by MAD Analysis of the Selenomethionyl Protein. Science 1992, 258, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S.; McKnite, A.; Xie, Y.; Christian, J.L. Fibronectin Type III and Intracellular Domains of Toll-like Receptor 4 Interactor with Leucine-Rich Repeats (Tril) Are Required for Developmental Signaling. MBoC 2018, 29, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencharit, S.; Cui, C.B.; Siddiqui, A.; Howard-Williams, E.L.; Sondek, J.; Zuobi-Hasona, K.; Aukhil, I. Structural Insights into Fibronectin Type III Domain-Mediated Signaling. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 367, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laity, J.H.; Lee, B.M.; Wright, P.E. Zinc Finger Proteins: New Insights into Structural and Functional Diversity. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2001, 11, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feder, M.E.; Wagner, C.M. Building a Natural Repellent: Effects of Varying Alarm Cue Exposure on Swim Activity and Spatial Avoidance in an Invasive Fish. Conserv. Physiol. 2025, 13, coaf028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensch, E.L.; Dissanayake, A.A.; Nair, M.G.; Wagner, C.M. Sea Lamprey Alarm Cue Comprises Water- and Chloroform- Soluble Components. J. Chem. Ecol. 2022, 48, 704–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peckarsky, B.L.; Abrams, P.A.; Bolnick, D.I.; Dill, L.M.; Grabowski, J.H.; Luttbeg, B.; Orrock, J.L.; Peacor, S.D.; Preisser, E.L.; Schmitz, O.J.; et al. Revisiting the Classics: Considering Nonconsumptive Effects in Textbook Examples of Predator–Prey Interactions. Ecology 2008, 89, 2416–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Reader, S.M.; Sakata, J.T. Alarm Cues and Alarmed Conspecifics: Neural Activity during Social Learning from Different Cues in Trinidadian Guppies. Proc. R. Soc. B 2022, 289, 20220829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, T.R. A Review of Squirrel Alarm-Calling Behavior: What We Know and What We Do Not Know about How Predator Attributes Affect Alarm Calls. Anim. Behav. Cogn. 2020, 7, 168–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danchin, É.; Giraldeau, L.-A.; Valone, T.J.; Wagner, R.H. Public Information: From Nosy Neighbors to Cultural Evolution. Science 2004, 305, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucon-Xiccato, T.; Di Mauro, G.; Bisazza, A.; Bertolucci, C. Alarm Cue-Mediated Response and Learning in Zebrafish Larvae. Behav. Brain Res. 2020, 380, 112446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poisson, A.; Valotaire, C.; Borel, F.; Bertin, A.; Darmaillacq, A.-S.; Dickel, L.; Colson, V. Embryonic Exposure to a Conspecific Alarm Cue Triggers Behavioural Plasticity in Juvenile Rainbow Trout. Anim. Behav. 2017, 133, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feder, M.E.; Wisenden, B.D.; Luhring, T.; Wagner, C. Speed Kills? Migrating Sea Lamprey Increase Speed When Exposed to an Antipredator Cue but Make Worse Short-Term Decisions. J. Great Lakes Res. 2024, 50, 102398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hume, J.B.; Luhring, T.M.; Wagner, C.M. Push, Pull, or Push–Pull? An Alarm Cue Better Guides Sea Lamprey towards Capture Devices than a Mating Pheromone during the Reproductive Migration. Biol. Invasions 2020, 22, 2129–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bals, J.D.; Wagner, C.M. Behavioral Responses of Sea Lamprey (Petromyzon marinus) to a Putative Alarm Cue Derived from Conspecific and Heterospecific Sources. Behaviour 2012, 149, 901–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byford, G.J.; Wagner, C.M.; Hume, J.B.; Moser, M.L. Do Native Pacific Lamprey and Invasive Sea Lamprey Share an Alarm Cue? Implications for Use of a Natural Repellent to Guide Imperiled Pacific Lamprey into Fishways. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2016, 36, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Stockwell, C.A.; Snider, M.R.; Wisenden, B.D. Epidermal Club Cells in Fishes: A Case for Ecoimmunological Analysis. IJMS 2021, 22, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodall, J.; Rincón-Camacho, L.; Pozzi, A.G. Epidermal Club Cells in the Cardinal Tetra (Paracheirodon Axelrodi): Presence, Distribution, and Relationship to Antipredator Behavior. Zoology 2024, 164, 126170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, L.; Pan, P.; Yan, P.; Long, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Zhou, R.; Wen, B.; Xie, L.; Liu, D. Role of Vimentin in Modulating Immune Cell Apoptosis and Inflammatory Responses in Sepsis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alesci, A.; Fumia, A.; Mastrantonio, L.; Marino, S.; Miller, A.; Albano, M. Functional Adaptations of Hemocytes of Aplysia Depilans (Gmelin, 1791) and Their Putative Role in Neuronal Regeneration. Fishes 2024, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, D. The SKIN|Functional Morphology of the Integumentary System in Fishes. In Encyclopedia of Fish Physiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 476–488. [Google Scholar]
- Chia, J.S.M.; Wall, E.S.; Wee, C.L.; Rowland, T.A.J.; Cheng, R.-K.; Cheow, K.; Guillemin, K.; Jesuthasan, S. Bacteria Evoke Alarm Behaviour in Zebrafish. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, S.; Chen, F.; Gou, S. Microtubule Inhibitors Containing Immunostimulatory Agents Promote Cancer Immunochemotherapy by Inhibiting Tubulin Polymerization and Tryptophan-2,3-Dioxygenase. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 187, 111949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, L.; Cooper, T.A. Insights into Cell-Specific Functions of Microtubules in Skeletal Muscle Development and Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alesci, A.; Albano, M.; Savoca, S.; Mokhtar, D.M.; Fumia, A.; Aragona, M.; Lo Cascio, P.; Hussein, M.M.; Capillo, G.; Pergolizzi, S.; et al. Confocal Identification of Immune Molecules in Skin Club Cells of Zebrafish (Danio Rerio, Hamilton 1882) and Their Possible Role in Immunity. Biology 2022, 11, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, N.; Wang, B.; Su, B.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Tan, F.; Li, C. Characterization of Toll-like Receptor 1 (TLR1) in Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2021, 115, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alesci, A.; Di Paola, D.; Marino, S.; De Gaetano, F.; Albano, M.; Morgante, S.; Rigano, G.; Giuffrè, L.; Kotanska, M.; Spanò, N.; et al. Exploring the Internal Defense System of Cerastoderma glaucum (Bruguière, 1789) Exposed to Pristine Microplastics: The Sentinel Role of Haemocytes as Biomarkers. Fishes 2024, 9, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alesci, A.; Di Paola, D.; Fumia, A.; Marino, S.; D’Iglio, C.; Famulari, S.; Albano, M.; Spanò, N.; Lauriano, E.R. Internal Defense System of Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lamarck, 1819): Ecological Role of Hemocytes as Biomarkers for Thiacloprid and Benzo[a]Pyrene Pollution. Toxics 2023, 11, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alesci, A.; Capillo, G.; Fumia, A.; Albano, M.; Messina, E.; Spanò, N.; Pergolizzi, S.; Lauriano, E.R. Coelomocytes of the Oligochaeta Earthworm Lumbricus terrestris (Linnaeus, 1758) as Evolutionary Key of Defense: A Morphological Study. Zool. Lett. 2023, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alesci, A.; Marino, S.; Miller, A.; Giliberti, A.; Rigano, G.; Giuffrè, L.; Fernandes, J.M.O.; Savoca, S.; Capillo, G. Role of Mucous Cells in the Defence System of the Cnidarian Actinia equina (Linnaeus, 1758): The Keystone of Evolution. Acta Zool. 2024, 106, azo.12523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alesci, A.; Pergolizzi, S.; Lo Cascio, P.; Capillo, G.; Lauriano, E.R. Localization of Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide and Toll-like Receptor 2 Immunoreactive Cells in Endostyle of Urochordate Styela plicata (Lesueur, 1823). Microsc. Res. Tech. 2022, 85, 2651–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alesci, A.; Capillo, G.; Fumia, A.; Messina, E.; Albano, M.; Aragona, M.; Lo Cascio, P.; Spanò, N.; Pergolizzi, S.; Lauriano, E.R. Confocal Characterization of Intestinal Dendritic Cells from Myxines to Teleosts. Biology 2022, 11, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alesci, A.; Capillo, G.; Mokhtar, D.M.; Fumia, A.; D’Angelo, R.; Lo Cascio, P.; Albano, M.; Guerrera, M.C.; Sayed, R.K.A.; Spanò, N.; et al. Expression of Antimicrobic Peptide Piscidin1 in Gills Mast Cells of Giant Mudskipper Periophthalmodon schlosseri (Pallas, 1770). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, G.P.; Miller, A.; Aragona, M.; Messina, E.; Fumia, A.; Kuciel, M.; Alesci, A.; Pergolizzi, S.; Lauriano, E.R. Immunohistochemical Characterization of Langerhans Cells in the Skin of Three Amphibian Species. Biology 2024, 13, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alesci, A.; Marino, S.; Di Fresco, D.; Miller, A.; Saccardi, L.; Famulari, S.; Albano, M.; Di Paola, D.; Spanò, N.; Lauriano, E.R. Evolution of Snake Skin: Role of Cutaneous Tactile Corpuscles in Hierophis viridiflavus (Lacépède, 1789). Acta Zool. 2024, 106, azo.12499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.; Lombardo, G.P.; Guerrera, M.C.; Messina, E.; Marino, S.; Pellicanò, F.; Kotanska, M.; Pergolizzi, S.; Alesci, A.; Lauriano, E.R. Immunohistochemistry of the Nasal Cavity-associated Lymphoid Tissue in the Dolphin (Stenella coeruleoalba, Meyen 1833). Microsc. Res. Tech. 2024, 87, 2103–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuckin, M.A.; Hasnain, S.Z. Goblet Cells as Mucosal Sentinels for Immunity. Mucosal Immunol. 2017, 10, 1118–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoop, K.A.; Newberry, R.D. Goblet Cells: Multifaceted Players in Immunity at Mucosal Surfaces. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alesci, A.; Marino, S.; D’Iglio, C.; Morgante, S.; Miller, A.; Rigano, G.; Ferri, J.; Fernandes, J.M.O.; Capillo, G. Investigating Development and Defense Systems in Early Reproductive Stages of Male and Female Gonads in Black Scorpionfish Scorpaena porcus (Linnaeus, 1758). Biology 2024, 13, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Antibody | Supplier | Dilution (µL/µL) | Animal Source/Clone |
|---|---|---|---|
| Piscidin-1 | GenScript, Piscataway, NJ, USA | 1:200 | Rabbit |
| TLR2 | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA | 1:200 | Rabbit |
| α-tubulin | Sigma-Aldrich, Saint Louis, MO, USA | 1:300 | Mouse, clone 6-11B-1 |
| Muc2 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA | 1:200 | Mouse, clone F-2 |
| Vimentin | Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA | 1:200 | Rabbit |
| Alexa Fluor 488 donkey anti-mouse IgG FITC conjugated | Molecular Probes, Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA | 1:300 | Donkey |
| Alexa Fluor 594 donkey anti-rabbit IgG TRITC conjugated | Molecular Probes, Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA | 1:300 | Donkey |
| Antibody | Immunogen Sequence/Region from the Supplier Company | P. marinus Ortholog Accession (NCBI) | Host Accession (Closest Species) | Sequence Homology |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TLR2 | a.a. 180–196, 353–370, and 473–489 | XP_032835900.1 | XP_058522725.1 | 34.53% |
| α-tubulin | 15 S dynein fraction from sea urchinsperm axoneme | XP_032815810.1 | NP_001019507.1 | 84.70% |
| Muc2 | a.a. C-terminus 4880–5179 | XP_075913103.1 | NP_076055.4 | 35.28% |
| Vimentin | a.a. 63–90 (includes Ser82) | XP_032807738.1 | BAE29426.1 | 70.75% |
| Basal | Intermediate | Superficial | |
|---|---|---|---|
| H/E | 156.916 ± 21.956 | 150.512 ± 27.501 | 147.945 ± 22.427 |
| AB/PAS | 157.534 ± 18.372 | 142.850 ± 27.938 | 111.701 ± 26.746 |
| Toluidin Blue | 189.518 ± 16.514 | 162.610 ± 25.070 | 156.510 ± 26.332 |
| No. of Immunopositive Skein Cells | |
|---|---|
| Vimentin+ | 58 |
| α-tubulin+ | 60 |
| TLR2+ | 63 |
| Muc2+ | 57 |
| Piscidin-1+ | 61 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alesci, A.; Marino, S.; Fiorentino, S.; Miller, A.; Palato, S.; Famulari, S.; Lombardo, G.P.; Ferreira Artoni, R.; Lauriano, E.R. Danger! Stay Alert: The Role of Skein Cells in the Evolution of the Sea Lamprey (Petromyzon marinus, Linnaeus 1758). Fishes 2025, 10, 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10120605
Alesci A, Marino S, Fiorentino S, Miller A, Palato S, Famulari S, Lombardo GP, Ferreira Artoni R, Lauriano ER. Danger! Stay Alert: The Role of Skein Cells in the Evolution of the Sea Lamprey (Petromyzon marinus, Linnaeus 1758). Fishes. 2025; 10(12):605. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10120605
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlesci, Alessio, Sebastian Marino, Stefania Fiorentino, Anthea Miller, Simon Palato, Sergio Famulari, Giorgia Pia Lombardo, Roberto Ferreira Artoni, and Eugenia Rita Lauriano. 2025. "Danger! Stay Alert: The Role of Skein Cells in the Evolution of the Sea Lamprey (Petromyzon marinus, Linnaeus 1758)" Fishes 10, no. 12: 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10120605
APA StyleAlesci, A., Marino, S., Fiorentino, S., Miller, A., Palato, S., Famulari, S., Lombardo, G. P., Ferreira Artoni, R., & Lauriano, E. R. (2025). Danger! Stay Alert: The Role of Skein Cells in the Evolution of the Sea Lamprey (Petromyzon marinus, Linnaeus 1758). Fishes, 10(12), 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10120605












