Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Seafood: Occurrence, Trophic Bioaccumulation, and Human Health Risks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Extraction and Quantitative Analysis
2.4. Toxicity Equivalent Concentration (TEP)
2.5. Carcinogenic Risks Assessment
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. PAHs Profile
3.2. PAHs Source Analysis
3.3. Bioaccumulation of PAHs
3.4. Risk Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akhbarizadeh, R.; Moore, F.; Keshavarzi, B. Investigating microplastics bioaccumulation and biomagnification in seafood from the Persian Gulf: A threat to human health? Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2019, 36, 1696–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, M.; Zanghì, G.; Cristaldi, A.; Copat, C.; Grasso, A.; Fiore, M.; Signorelli, S.S.; Zuccarello, P.; Conti, G.O. PAHs in seafood from the Mediterranean Sea: An exposure risk assessment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 115, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, M.; Luzardo, O.P.; Boada, L.D.; López Jurado, L.F.; Medina, M.; Zumbado, M.; Orós, J. Potential adverse health effects of persistent organic pollutants on sea turtles: Evidence from a cross-sectional study on Cape Verde loggerhead sea turtles. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 458–460, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, F.C.; Carreira, R.d.S.; Gramlich, K.C.; de Pinho, J.V.; Massone, C.G.; Vianna, M.; Hauser-Davis, R.A. A systematic review on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contamination in elasmobranchs and associated human health risks. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 195, 115535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, P.; Grimalt, J.O. On the Global Distribution of Persistent Organic Pollutants. Chim. Int. J. Chem. 2003, 57, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pala, N.; Vorkamp, K.; Bossi, R.; Ancora, S.; Ademollo, N.; Baroni, D.; Sarà, G.; Corsolini, S. Chemical threats for the sentinel Pygoscelis adeliae from the Ross Sea (Antarctica): Occurrence and levels of persistent organic pollutants (POPs), perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and mercury within the largest marine protected area worldwide. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 947, 174562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vagi, M.C.; Petsas, A.S.; Kostopoulou, M.N. Potential Effects of Persistent Organic Contaminants on Marine Biota: A Review on Recent Research. Water 2021, 13, 2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, M.G.; Vivian, D.N.; Heintz, R.A.; Yim, U.H. Long-Term Ecological Impacts from Oil Spills: Comparison of Exxon Valdez, Hebei Spirit, and Deepwater Horizon. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6456–6467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengtson Nash, S.; Bohlin-Nizzetto, P.; Galban-Malagon, C.; Corsolini, S.; Cincinelli, A.; Lohmann, R. Monitoring persistent organic chemicals in Antarctica in support of global chemical policy: A horizon scan of priority actions and challenges. Lancet Planet. Health 2023, 7, e435–e440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mearns, A.J.; Bissell, M.; Morrison, A.M.; Rempel-Hester, M.A.; Arthur, C.; Rutherford, N. Effects of pollution on marine organisms. Water Environ. Res. 2019, 91, 1229–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulster, E.L.; Gracia, A.; Snyder, S.M.; Romero, I.C.; Carr, B.; Toro-Farmer, G.; Murawski, S.A. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Baselines in Gulf of Mexico Fishes. In Scenarios and Responses to Future Deep Oil Spills: Fighting the Next War; Murawski, S.A., Ainsworth, C.H., Gilbert, S., Hollander, D.J., Paris, C.B., Schlüter, M., Wetzel, D.L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 253–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, S.M.; Pulster, E.L.; Murawski, S.A. Associations Between Chronic Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Health Indices in Gulf of Mexico Tilefish (Lopholatilus chamaeleonticeps) Post Deepwater Horizon. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2019, 38, 2659–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehm, P.D.; Pietari, J.; Cook, L.L.; Saba, T. Improving rigor in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon source fingerprinting. Environ. Forensics 2018, 19, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neff, J.M. Bioaccumulation in Marine Organisms: Effects of Contaminants from Oil Well Produced Water; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- NRC. Oil in the Sea: Inputs, Fates and Effects, 2nd ed.; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; Volume 1, p. 25057607. [Google Scholar]
- Savoca, D.; Pace, A. Bioaccumulation, Biodistribution, Toxicology and Biomonitoring of Organofluorine Compounds in Aquatic Organisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, N.; Martin, L.; Xu, W. Impact of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Accumulation on Oyster Health. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 734463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Li, Z. Multi-cascade physiologically based kinetic (PBK) matrix model: Simulating chemical bioaccumulation across food webs. Environ. Int. 2025, 198, 109376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, I.; Abdel-Shafy, M.; Mansour, S.M. A review on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Source, environmental impact, effect on human health and remediation. Egypt. J. Pet. 2016, 25, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomann, R.V.; Komlos, J. Model of biota-sediment accumulation factor for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. J. 1999, 18, 1060–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bay, B.; Wan, Y.; Jin, X.; Hu, J.; Jin, F. Trophic dilution of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in a marine food web from North China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 3109–3114. [Google Scholar]
- Meador, J.P.; Stein, J.E.; Reichert, W.L.; Varanasi, U. Bioaccumulation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by marine organisms. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1995, 143, 79–165. [Google Scholar]
- Carls, M.G.; Babcock, M.M.; Harris, P.M.; Irvine, G.V.; Cusick, J.A.; Rice, S.D. Persistence of oiling in mussel beds after the Exxon Valdez oil spill. Mar. Environ. Res. 2001, 51, 167–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, C.H.; Rice, S.D.; Short, J.W.; Esler, D.; Bodkin, J.L.; Ballachey, B.E.; Irons, D.B. Long-Term Ecosystem Response to the Exxon Valdez Oil Spill. Science 2003, 302, 2082–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struch, R.E.; Pulster, E.L.; Schreier, A.D.; Murawski, S.A. Hepatobiliary Analyses Suggest Chronic PAH Exposure in Hakes (Urophycis spp.) Following the Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2019, 38, 2740–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, T.T.; Milligan, R.J.; Daly, K.; Boswell, K.M.; Cook, A.B.; Cornic, M.; Frank, T.; Frasier, K.; Hahn, D.; Hernandez, F.; et al. The Open-Ocean Gulf of Mexico After Deepwater Horizon: Synthesis of a Decade of Research. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 753391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ylitalo, G.M.; Krahn, M.M.; Dickhoff, W.W.; Stein, J.E.; Walker, C.C.; Lassitter, C.L.; Garrett, E.S.; Desfosse, L.L.; Mitchell, K.M.; Noble, B.T.; et al. Federal seafood safety response to the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 20274–20279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, K.M.; Carreira, R.S.; Rosa Filho, J.S.; Rocha, P.P.; Santana, F.M.; Yogui, G.T. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in fishery resources affected by the 2019 oil spill in Brazil: Short-term environmental health and seafood safety. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 175, 113334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, I.C.; Sutton, T.; Carr, B.; Quintana-Rizzo, E.; Ross, S.W.; Hollander, D.J.; Torres, J.J. Decadal Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Mesopelagic Fishes from the Gulf of Mexico Reveals Exposure to Oil-Derived Sources. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10985–10996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Grist, S.; Nugegoda, D. The PAH body burdens and biomarkers of wild mussels in Port Phillip Bay, Australia and their food safety implications. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, S.; Kokushi, E.; Añasco, N.C.; Iwai, T.; Ito, K.; Koyama, J. Oil spill off the coast of Guimaras Island, Philippines: Distributions and changes of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in shellfish. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 962–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickliffe, J.K.; Simon-Friedt, B.; Howard, J.L.; Frahm, E.; Meyer, B.; Wilson, M.J.; Pangeni, D.; Overton, E.B. Consumption of Fish and Shrimp from Southeast Louisiana Poses No Unacceptable Lifetime Cancer Risks Attributable to High-Priority Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Risk Anal. 2018, 38, 1944–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Câmara, S.F.; Pinto, F.R.; da Silva, F.R.; Soares, M.O.; De Paula, T.M. Socioeconomic vulnerability of communities on the Brazilian coast to the largest oil spill (2019–2020) in tropical oceans. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2021, 202, 105506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Estevo, M.; Lopes, P.F.M.; de Oliveira Júnior, J.G.C.; Junqueira, A.B.; de Oliveira Santos, A.P.; da Silva Lima, J.A.; Malhado, A.C.M.; Ladle, R.J.; Campos-Silva, J.V. Immediate social and economic impacts of a major oil spill on Brazilian coastal fishing communities. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 164, 111984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, G.M.; Martins, D.A.; dos Santos, R.P.; de Santiago, I.S.; Nascimento, L.S.; Oliveira, A.H.B.; Yamamoto, F.Y.; Cavalcante, R.M. Levels, source appointment, and ecological risk of petroleum hydrocarbons in tropical coastal ecosystems (northeast Brazil): Baseline for future monitoring programmes of an oil spill area. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 296, 118709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, O.M.C.; Queiroz, A.F.d.S.; Cerqueira, J.R.; Soares, S.A.R.; Garcia, K.S.; Filho, A.P.; Rosa, M.d.L.d.S.; Suzart, C.M.; Pinheiro, L.; Moreira, Í.T.A. Environmental disaster in the northeast coast of Brazil: Forensic geochemistry in the identification of the source of the oily material. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 160, 111597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.N.; Junior, A.V.F.; Lamardo, E.Z.; Yogui, G.T.; Montes, M.D.J.F.; Silva, M.A.; Lima, E.J.A.C.; Rojas, L.A.V.; de Sales Jannuzzi, L.G.; da Silva, M.D.G.G.; et al. Finding the needle in a haystack: Evaluation of ecotoxicological effects along the continental shelf break during the Brazilian mysterious oil spill. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 357, 124422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.O.; Teixeira, C.E.P.; Bezerra, L.E.A.; Rabelo, E.F.; Castro, I.B.; Cavalcante, R.M. The most extensive oil spill registered in tropical oceans (Brazil): The balance sheet of a disaster. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 19869–19877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, H. Mystery oil spill threatens marine sanctuary in Brazil. Science 2019, 366, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magris, R.A.; Giarrizzo, T. Mysterious oil spill in the Atlantic Ocean threatens marine biodiversity and local people in Brazil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 153, 110961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, C.B.; Oleinik, P.H.; Leal, T.F.; Marques, W.C.; Nicolodi, J.L.; Lopes, B.d.C.F.L. Integrated environmental vulnerability to oil spills in sensitive areas. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.O.; Teixeira, C.E.P.; Bezerra, L.E.A.; Rossi, S.; Tavares, T.; Cavalcante, R.M. Brazil oil spill response: Time for coordination. Science 2020, 367, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brum, H.D.; Campos-Silva, J.V.; Oliveira, E.G. Brazil oil spill response: Government inaction. Science 2020, 367, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, A.D.C.; Fernandes, G.M.; Martins, D.A.; Cavalcante, R.M.; Chaves, M.R.B.; de Souza, A.A. Concentrations, sources and risks of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments from the Parnaiba Delta basin, Northeast Brazil. Chemosphere 2024, 349, 140889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BRASIL. 1996; Decreto de 28 de Agosto de 1996. Dispõe Sobre a Criação da Área de Proteção Ambiental Delta do Parnaíba, nos Estados do Piauí, Maranhão, e Ceará, e dá Outras Providências. Brasília. Available online: http://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/DNN/Anterior%20a%202000/1996/Dnn4368.htm (accessed on 15 January 2019).
- de Paula Filho, F.J.; Marins, R.V.; de Lacerda, L.D.; Aguiar, J.E.; Peres, T.F. Background values for evaluation of heavy metal contamination in sediments in the Parnaíba River Delta estuary, NE/Brazil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 2, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, T.A.; Gonçalves, T.S.; Nascimento, P.S.; Fernandes, C.A.F.; Cunha, F.E.A. Seasonal variation on diet of juvenile Elops saurus Linnaeus, 1766 (Ladyfish) in the Parnaiba River Delta. Acta Limnol. Bras. 2020, 32, e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Google Maps. 2025. Available online: https://www.google.com/maps/search/delta+do+parna%C3%ADba+estu%C3%A1rio+do+rio+parna%C3%ADba/@-2.8483786,-41.85092,13.19z?entry=ttu&g_ep=EgoyMDI1MTAwOC4wIKXMDSoASAFQAw%3D%3D (accessed on 26 October 2025).
- EPA. Method 8270D: Semivolatile Organic Compounds by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry. 2014; 16p. Available online: https://archive.epa.gov/epa/sites/production/files/2015-12/documents/8270d.pdf (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- Mauad, C.R.; Wagener, A.L.R.; Massone, C.G.; Aniceto, M.S.; Lazzari, L.; Carreira, R.S.; Farias, C.O. Urban rivers as conveyors of hydrocarbons to sediments of estuarine areas: Source characterization, flow rates and mass accumulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 506–507, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, P.-J.; Shih, T.-S.; Chen, H.-L.; Lee, W.-J.; Lai, C.-H.; Liou, S.-H. Assessing and predicting the exposures of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and their carcinogenic potencies from vehicle engine exhausts to highway toll station workers. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANVISA. Riscos a Saúde Humana Decorrentes do Consumo de Pescados Oriundos das Praias Contaminadas por óleo cru na Região Nordeste do Brasil, Nota Técnica n. 27/2019/SEI/GGALI/DIRE2/ANVISA. Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária: Brasília, DF, Brazil. 2019; 5p. Available online: https://portalcievs.saude.pe.gov.br/docs/SEI_ANVISA_-_0815698_-_Nota_T%C3%A9cnica_GGALI.pdf (accessed on 23 August 2025).
- Yender, R.; Michel, J.; Lord, C. Managing Seafood Safety After an Oil Spill; Hazardous Materials Response Division, Office of Response and Restoration, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: Seattle, WA, USA, 2002; 72p.
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological Statistics Software Package for Education and Data Analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Box, G.E.P.; Cox, D.R. An analysis of transformations. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1964, 26, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogasawara, E.; Martinez, L.C.; de Oliveira, D.; Zimbrão, G.; Pappa, G.L.; Mattoso, M. Adaptive Normalization: A novel data normalization approach for non-stationary time series. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Barcelona, Spain, 18–23 July 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Esteso, C.; Roselló-Carrió, A.; Carrasco-Correa, E.J.; Lerma-García, M.J. Bioaccumulation of environmental pollutants and marine toxins in bivalve molluscs: A review. Explor. Foods Foodomics 2024, 2, 788–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieves, R.; Colás-Ruiz, M.G.; Pintado-Herrera, M.S.; Salerno, B.; Tonini, F.; Lara-Martín, P.A.; Hampel, M. Bioconcentration, biotransformation, and transcriptomic impact of the UV-filter 4-MBC in the manila clam Ruditapes philippinarum. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 912, 169178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Cao, S.; Li, R.; Gao, H.; Na, G. Trophic Transfer of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons through the Food Web of the Fildes Peninsula, Antarctica. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 55057–55066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, R.A.; Francioni, E.; Silva, A.H.M.F.T.; Magalhães, C.A.; Gallotta, F.D.C.; Oliveira, F.F.; Souza, J.M.; Araújo, L.F.M.; Araújo, L.P.; Araújo Júnior, M.A.G.; et al. Bioaccumulation study of produced water discharges from Southeastern Brazilian offshore petroleum industry using feral fishes. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 74, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gewurtz, S.B.; Lazar, R.; Haffner, G.D. Comparison of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and polychlorinated biphenyl dynamics in benthic invertebrates of Lake Erie, USA. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 2000, 19, 2943–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaag, N.H.; Foekema, E.M.; Scholten, M.C.T.; Van Straalen, N.M. Comparison of contaminant accumulation in three species of marine invertebrates with different feeding habits. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 1997, 16, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monikh, F.A.; Hosseini, M.; Rahmanpour, S. The effect of size and sex on PCB and PAH concentrations in crab Portunus pelagicus. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 1575–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eke, C.D.; Anifowose, B.; Van De Wiel, M.; Lawler, D.; Knaapen, M. Influence of projected climatic conditions and varying lateral points of release on oil slock transport in a tide-dominated estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 254, 107341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.-Y.; Li, Y.-X.; Zhang, J.-Q.; Zhang, T.; Liu, G.-H.; Huang, M.-Z.; Li, X.; Ruan, J.-J.; Kannan, K.; Qiu, R.-L. Associations between polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) exposure and oxidative stress in people living near e-waste recycling facilities in China. Environ. Int. 2016, 94, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, W. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs): Environmental persistence and human health risks. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2025, 20, 1934578X241311451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwaichi, E.O.; Ntorgbo, S.A. Assessment of PAHs levels in some fish and seafood from different coastal waters in the Niger Delta. Toxicol. Rep. 2016, 13, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paik, Y.; Kim, H.S.; Joo, Y.S.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, K.W. Evaluation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contents in marine products in South Korea and risk assessment using the total diet study. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 33, 2377–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, R.; Yang, X.; Su, H.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Long, M. Levels, sources and probabilistic health risks of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the agricultural soils from sites neighboring suburban industries in Shanghai. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616, 1365–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zou, X.; Zou, S.; Li, P.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J. Pollution Status and Trophic Transfer of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Coral Reef Ecosystems of the South China Sea. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2021, 78, 2053–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ran, Y. Distribution and Bioconcentration of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Surface Water and Fishes. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 632910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shu, Y.; Kuang, Z.; Han, Z.; Wu, J.; Huang, X.; Song, X.; Yang, J.; Fan, Z. Bioaccumulation and Potential Human Health Risks of PAHs in Marine Food Webs: A Trophic Transfer Perspective. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 485, 136946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadeer, A.; Liu, M.; Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Khalil, S.K.; Huang, Y.; Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M.; Gao, D.; Yang, Y. Trophodynamics and Parabolic Behaviors of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in an Urbanized Lake Food Web, Shanghai. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 178, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, M.; Suzuki, N. Toxicities of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons for Aquatic Animals. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filatova, T.S.; Abramochkin, D.V. Physiological Effects of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Fish Organisms. Mosc. Univ. Biol. Sci. Bull. 2023, 78, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherr, G.N.; Fairbairn, E.; Whitehead, A. Impacts of Petroleum-Derived Pollutants on Fish Development. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2017, 5, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Yue, Z.; Samreen; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, J. Teratogenic Effects of Environmentally Relevant Concentrations of Phenanthrene on the Early Development of Marine Medaka (Oryzia melastigma). Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, E.R.; Mager, E.M. The Effects of Exposure to Crude Oil or PAHs on Fish Swim Bladder Development and Function. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 238, 108853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodson, P.V. The Toxicity to Fish Embryos of PAH in Crude and Refined Oils. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 73, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brander, S.; Hecht, S.; Kuivila, K. The Challenge: “Bridging the Gap” with Fish: Advances in Assessing Exposure and Effects across Biological Scales. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnuson, J.T.; Bautista, N.M.; Lucero, J.A.; Lund, A.K.; Xu, E.G.; Schlenk, D.; Burggren, W.W.; Roberts, A.P. Exposure to Crude Oil Induces Retinal Apoptosis and Impairs Visual Function in Fish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 2843–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser-Davis, R.A.; Lopes, R.M.; Ziolli, R.L. Inihibition of Mullet (M. Liza) Brain Acetylcholinesterase Activity by in Vitro Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Exposure. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 140, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, E.A.; Li, Y.; Zelikoff, J.T. Exposure of Japanese Medaka (Oryzias latipes) to Benzo [a] Pyrene Suppresses Immune Function and Host Resistance against Bacterial Challenge. Aquat. Toxicol. 2002, 56, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousin, X.; Cachot, J. PAHs and Fish—Exposure Monitoring and Adverse Effects—From Molecular to Individual Level. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 13685–13688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
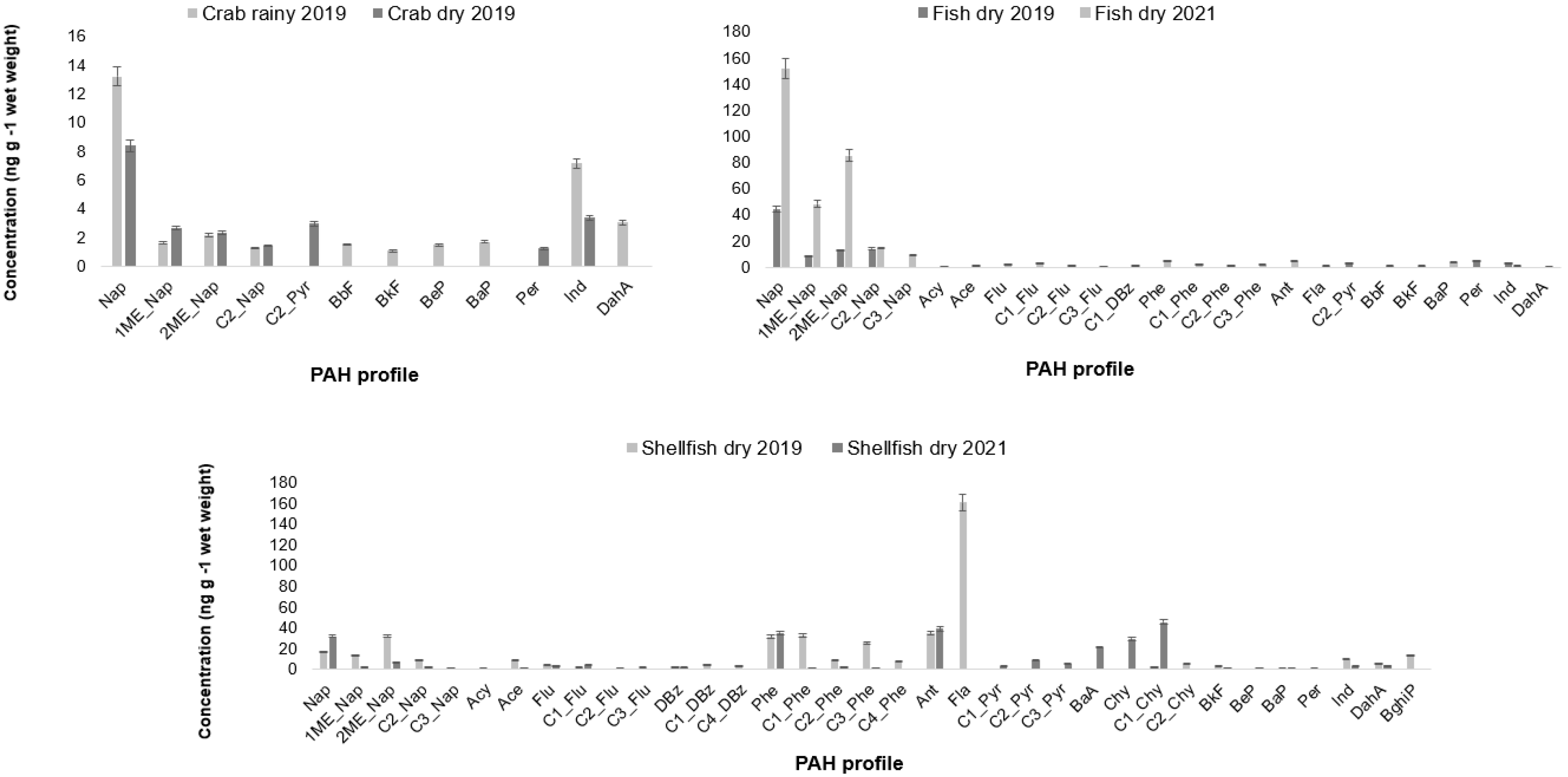
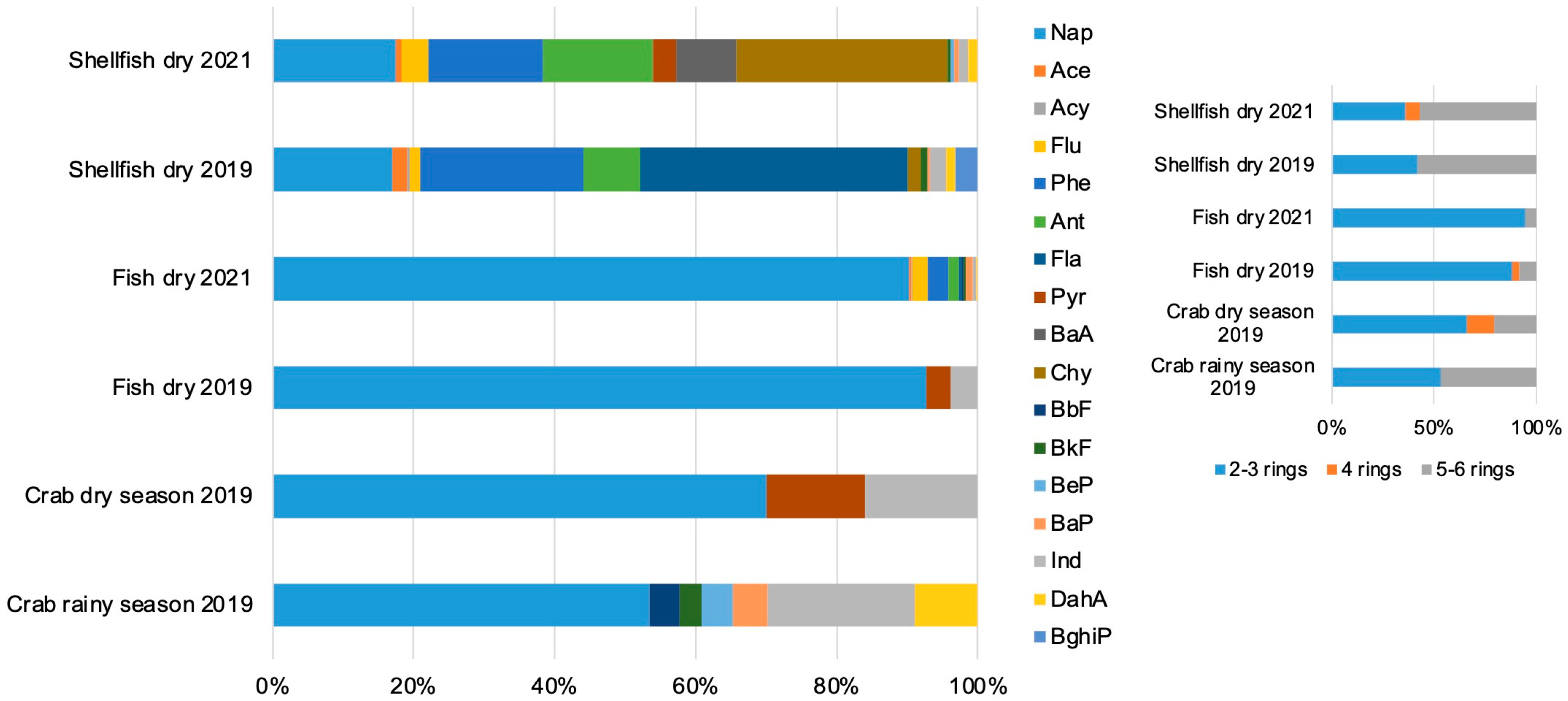
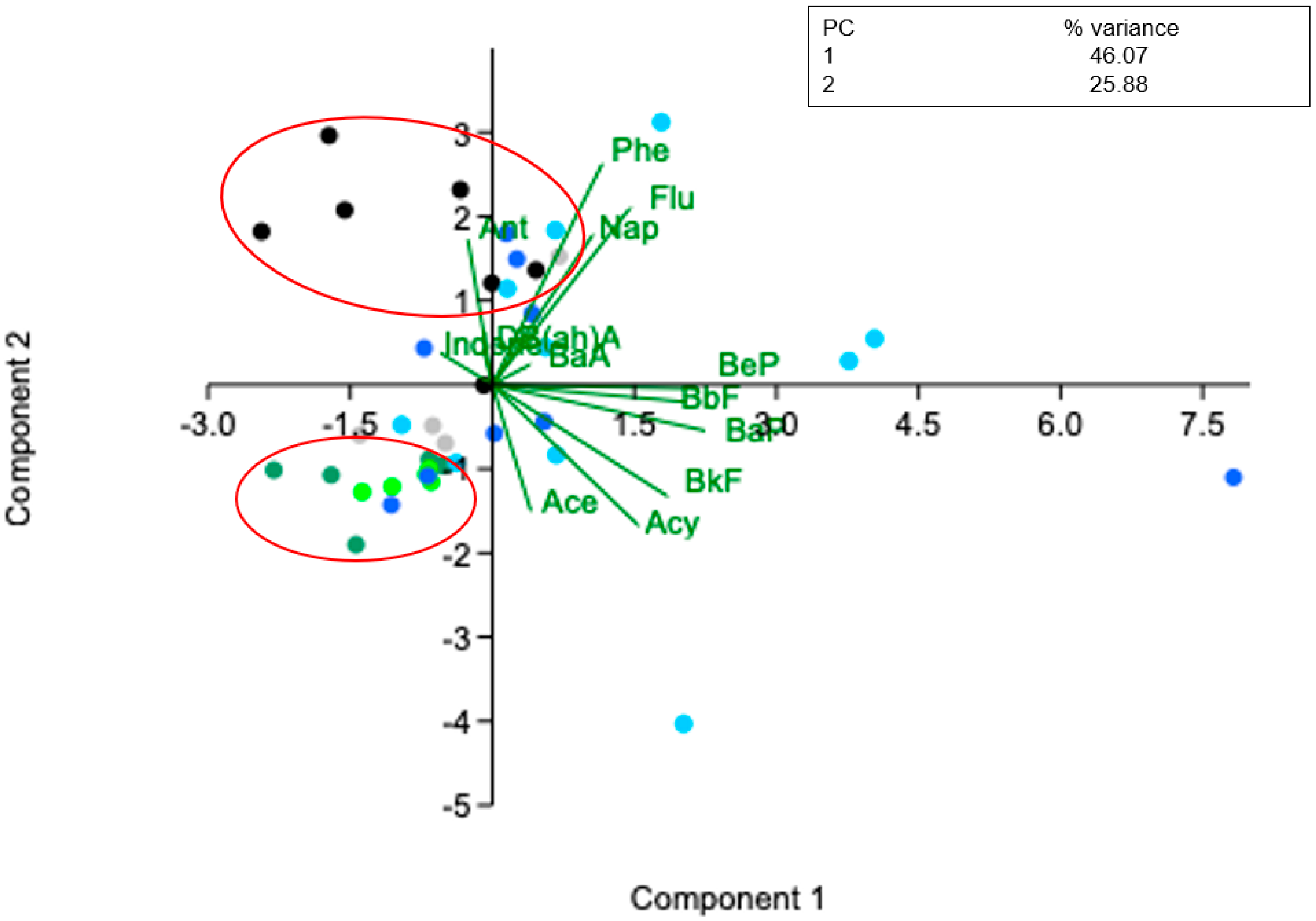


| ID | Species | Habitat/ Trophic Level | Season | Length (cm) | Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shellfish | Anomalocardia brasiliana | Sediment Filter | Rainy/2019 | 1.28 ± 0.26 | 4.19 ± 0.81 |
| Dry/2019 | 2.47 ± 0.26 | 3.41 ± 1.12 | |||
| Dry/2021 | 2.62 ± 2.22 | 5.91 ± 1.44 | |||
| Crab | Ucides cordatus | Mangrove Detritivore | Rainy/2019 | 6.94 + 3.74 | 139.34 + 19.49 |
| Dry/2019 | 7.16 + 0.31 | 158.30 + 21.37 | |||
| Dry/2021 | 6.50 + 2.64 | 114.42 + 17.20 | |||
| Fish | Mugil curema | Estuary Omnivore | Dry/2019 | 24.98 ± 1.77 | 150.63 ± 29.37 |
| Dry/2021 | 27.62 + 3.29 | 231.80 + 79.44 |
| PAH | RP |
|---|---|
| Benzo(a)anthracene | 0.145 |
| Chrysene | 0.0044 |
| Benzo(b)fluoranthene | 0.140 |
| Benzo(k)fluoranthene | 0.066 |
| Benzo(a)pyrene | 1.00 |
| Dibenz(a,h)anthracene | 1.11 |
| Indeno(1,2,3-cd)pyrene | 0.232 |
| Benzo(g,h,i)perylene | 0.022 |
| PAHs | TEFBap | TEQ Average (mg/kg) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 2021 | |||||
| Crab | Fish | Shellfish | Fish | Shellfish | ||
| Nap | 0.001 | 14.83 | 79.64 | 72.36 | 308.66 | 44.01 |
| Ace | 0.001 | 0 | 0 | 8.73 | 1.30 | 1.80 |
| Acy | 0.001 | 0 | 0 | 1.61 | 0.86 | 0 |
| Flu | 0.001 | 0 | 0 | 4.46 | 7.10 | 9.67 |
| Phe | 0.001 | 0 | 0 | 105.98 | 5.45 | 41.00 |
| Ant | 0.010 | 0 | 0 | 34.52 | 4.73 | 39.14 |
| Fla | 0.001 | 0 | 0 | 160.72 | 1.07 | 1.74 |
| Pyr | 0.001 | 2.96 | 2.96 | 0 | 0 | 17.50 |
| BaA | 0.100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 21.20 |
| Chy | 0.010 | 0 | 0 | 8.25 | 0 | 74.99 |
| BbF | 0.100 | 0 | 0 | 3.78 | 1.39 | 0 |
| BkF | 0.100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.96 | 1.44 |
| BaP | 1.000 | 0 | 0 | 1.34 | 3.65 | 1.61 |
| Ind | 0.100 | 0 | 3.37 | 10.19 | 1.34 | 2.98 |
| DahA | 1.000 | 3.37 | 0 | 5.21 | 0.91 | 3.64 |
| BghiP | 0.100 | 0 | 0 | 13.63 | 0 | 0 |
| PAHs | LOC * | LOC (ng/g ww) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 2021 | |||||
| Crab | Fish | Shellfish | Fish | Shellfish | ||
| Non-carcinogenic | ||||||
| Nap | 6670 | 944 | 58 | 193 | 15 | 318 |
| Ace | 20,000 | 0 | 0 | 1603 | 3588 | 7762 |
| Acy | - | 0 | 0 | 8697 | 5408 | 0 |
| Flu | 13,330 | 0 | 0 | 3141 | 657 | 1448 |
| Phe | - | 0 | 0 | 132 | 856 | 341 |
| Ant | 100,000 | 0 | 0 | 40 | 98 | 36 |
| Fla | 13,330 | 0 | 0 | 87 | 4352 | 8055 |
| Pyr | 10,000 | 4735 | 1578 | 0 | 0 | 800 |
| Carcinogenic | ||||||
| BaA | 41 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| Chy | 1364 | 0 | 0 | 169 | 0 | 18 |
| BbF | 43 | 0 | 0 | 37 | 33 | 0 |
| BkF | 91 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 48 | 97 |
| BaP | 6 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 1 | 8 |
| Ind | 5 | 0 | 13 | 14 | 38 | 47 |
| DahA | 26 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 4 |
| BghiP | 273 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fogaça, F.H.d.S.; Melo, P.T.d.S.; Massone, C.G.; Carreira, R.d.S.; Ramos, L.R.V.; Torres, J.P.M. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Seafood: Occurrence, Trophic Bioaccumulation, and Human Health Risks. Fishes 2025, 10, 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10110591
Fogaça FHdS, Melo PTdS, Massone CG, Carreira RdS, Ramos LRV, Torres JPM. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Seafood: Occurrence, Trophic Bioaccumulation, and Human Health Risks. Fishes. 2025; 10(11):591. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10110591
Chicago/Turabian StyleFogaça, Fabíola Helena dos Santos, Pamella Talita da Silva Melo, Carlos German Massone, Renato da Silva Carreira, Leonardo Rocha Vidal Ramos, and João Paulo Machado Torres. 2025. "Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Seafood: Occurrence, Trophic Bioaccumulation, and Human Health Risks" Fishes 10, no. 11: 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10110591
APA StyleFogaça, F. H. d. S., Melo, P. T. d. S., Massone, C. G., Carreira, R. d. S., Ramos, L. R. V., & Torres, J. P. M. (2025). Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Seafood: Occurrence, Trophic Bioaccumulation, and Human Health Risks. Fishes, 10(11), 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10110591








