Functional Algal Feeds for Aquaculture: Micro- and Macroalgae Promote Gut Recovery in Gilthead Seabream
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Diets
2.2. Fish Rearing
2.2.1. Assisted-Feeding to Provoke an Insult
2.2.2. Nutritional Trial
2.3. Sampling and Analytical Procedures
2.3.1. Metabolic Enzyme Analysis
2.3.2. Histology Analysis
2.3.3. Gene Expression Analysis
RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
Real-Time PCR (RT-PCR)
2.4. Disruption Assessment
2.5. Dietary Recovery Assessment
2.6. Statistical and Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Disruption Assessment
3.2. Dietary Recovery Assessment
3.2.1. Metabolic Enzymes Analysis
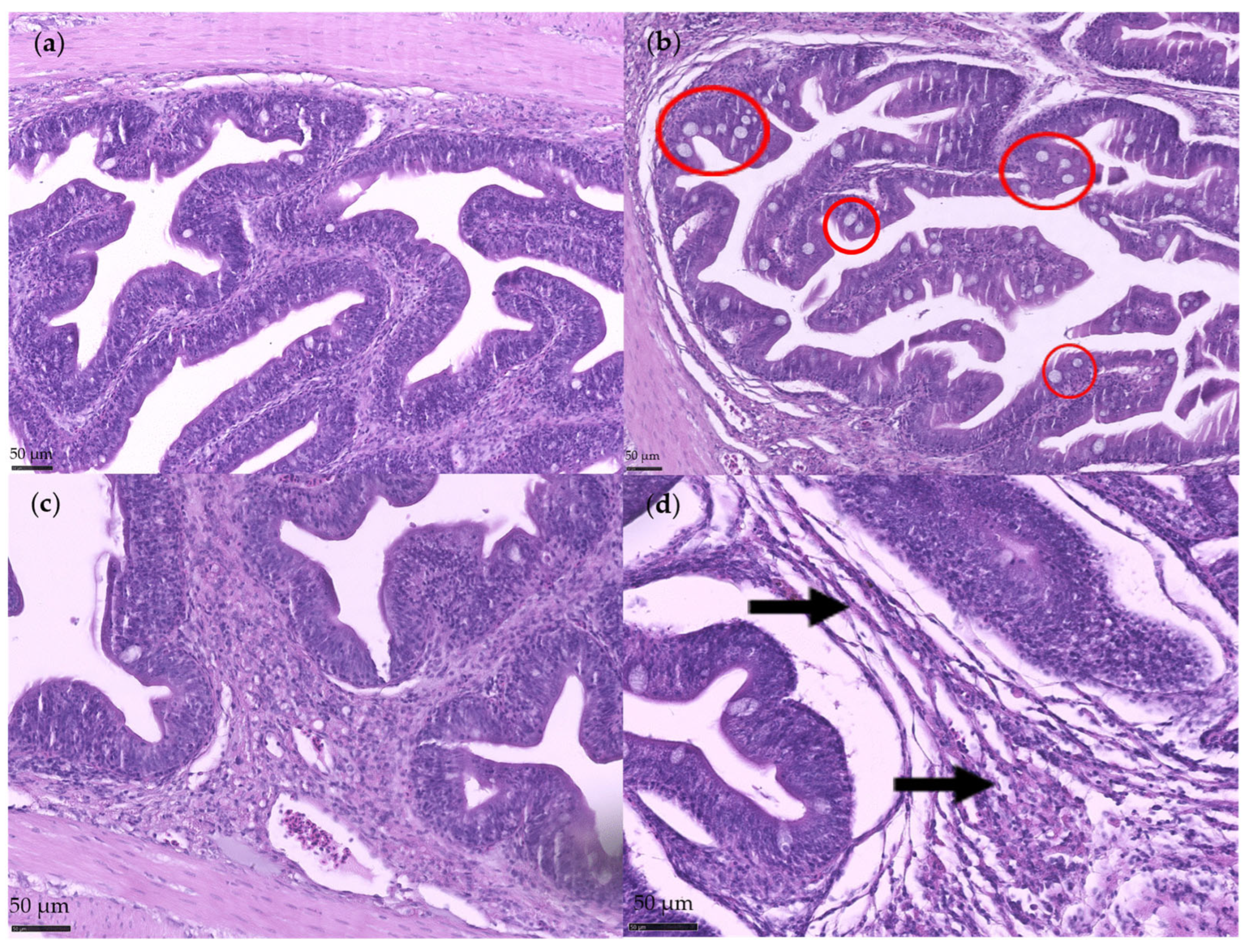
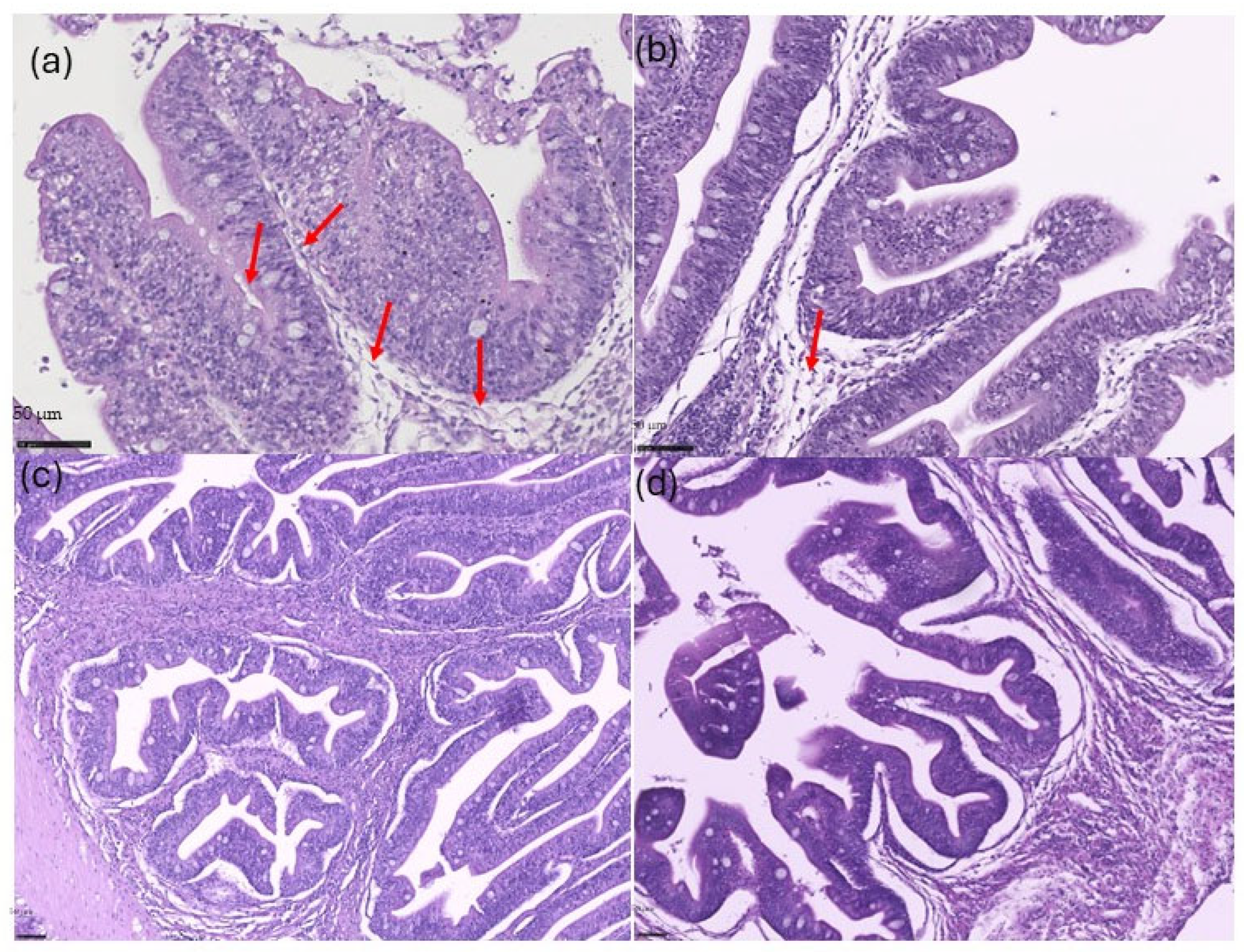
3.2.2. Histological Analysis
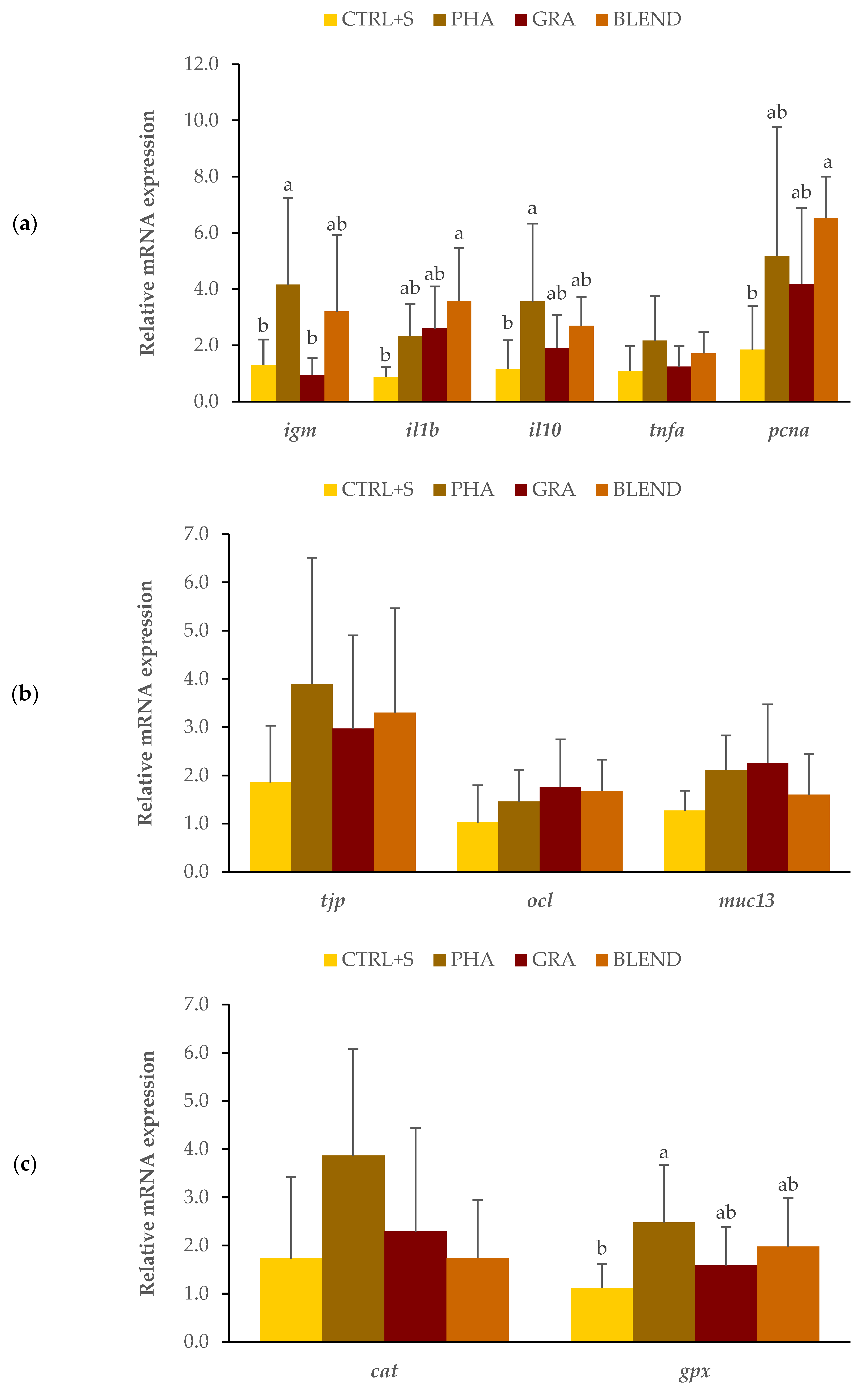
3.2.3. Gene Expression Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Disruption Assessment
4.2. Recovery Assessment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, Q.; Liu, H.; Jin, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Han, D.; Zhou, Z.; Xie, S. Potential Functions of the Gut Microbiome and Modulation Strategies for Improving Aquatic Animal Growth. Rev. Aquac. 2025, 17, e12959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Hossain Md., S.; Ragaza, J.A.; Benito, M.R. The Potential Impacts of Soy Protein on Fish Gut Health. Soybean Hum. Consum. Anim. Feed 2020, 10, 91–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, R.W. History of fish nutrition. In Nutrition and Physiology of Fish and Shellfish: Feed Regulation, Metabolism, and Digestion; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2025; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2024; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaharisis, L.; Tsironi, T.; Dimitroglou, A.; Taoukis, P.; Pavlidis, M. Stress assessment, quality indicators and shelf life of three aquaculture important marine fish, in relation to harvest practices, water temperature and slaughter method. Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 2608–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciji, A.; Akhtar, M.S. Stress management in aquaculture: A review of dietary interventions. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 2190–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, X.; Qiao, D.; Pei, C.; Kong, X. Signalling regulation of reactive oxygen species in fish inflammation. Rev. Aquac. 2024, 16, 1266–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egerton, S.; Wan, A.; Murphy, K.; Collins, F.; Ahern, G.; Sugrue, I.; Busca, K.; Egan, F.; Muller, N.; Whooley, J.; et al. Replacing fishmeal with plant protein in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) diets by supplementation with fish protein hydrolysate. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onomu, A.J.; Okuthe, G.E. The Role of Functional Feed Additives in Enhancing Aquaculture Sustainability. Fishes 2024, 9, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhulika Meinam, M.; Deepti, M.; Ngasotter, S.; Gupta, S.S.; Varghese, T. Functional Feed Additives in Aquaculture to Improve Food Security. Food Security, Nutrition and Sustainability Through Aquaculture Technologies; Springer Nature: Berlin, Germany, 2025; pp. 375–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaram, S.; Ringø, E.; Ghafarifarsani, H.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Ahani, S.; Chou, C.C. Use of Algae in Aquaculture: A Review. Fishes 2024, 9, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakky, M.A.H.; Tran, N.T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S. Utilization of marine macroalgae-derived sulphated polysaccharides as dynamic nutraceutical components in the feed of aquatic animals: A review. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 5787–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringø, E.; Ashour, M.; Ahmed, S.; Sharawy, Z.; Goda, A.; El-Haroun, E.; Ringø, E.; Ashour, M.; Ahmed, S.; Sharawy, Z.; et al. Microalgae and Seaweeds as Feed Additives for Aquatic Animals: Effects on Growth, Immunity, and Disease Resistance. Algae-Science and Applications; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerezuela, R.; Fumanal, M.; Tapia-Paniagua, S.T.; Meseguer, J.; Morinigo, M.Á.; Esteban, M.Á. Histological alterations and microbial ecology of the intestine in gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.) fed dietary probiotics and microalgae. Cell Tissue Res. 2012, 350, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerezuela, R.; Guardiola, F.A.; Meseguer, J.; Esteban, M.Á. Enrichment of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.) diet with microalgae: Effects on the immune system. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 38, 1729–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, B.; Gonçalves, A.T.; Santos, P.; Sardinha, M.; Conceição, L.E.C.; Serradeiro, R.; Pérez-sánchez, J.; Calduch-giner, J.; Schmid-staiger, U.; Frick, K.; et al. Immune status and hepatic antioxidant capacity of gilthead seabream sparus aurata juveniles fed yeast and microalga derived β-glucans. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.T.; Simões, M.; Costa, C.; Passos, R.; Baptista, T. Modulatory effect of Gracilaria gracilis on European seabass gut microbiota community and its functionality. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biotechnology, B.; Khandwal, D.; Maniar, J.N.; Pandey, A.K.; Gupta, N.K.; Mishra, A. Proximate, physicochemical, bioactive and antiproliferative characteristics of Gracilaria debilis extract reveal its nutraceutical potential. Blue Biotechnol. 2025, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, M.J.; Ferraz, R.; Magnoni, L.J.; Pereira, R.; Gonçalves, J.F.; Calduch-Giner, J.; Pérez-Sánchez, J.; Ozório, R.O.A. Protective effects of seaweed supplemented diet on antioxidant and immune responses in European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) subjected to bacterial infection. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, R.; Correia, A.P.; Ferreira, I.; Pires, P.; Pires, D.; Gomes, E.; do Carmo, B.; Santos, P.; Simões, M.; Afonso, C.; et al. Effect on health status and pathogen resistance of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) fed with diets supplemented with Gracilaria gracilis. Aquaculture 2021, 531, 735888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, C.S.C.; Pinto, O.; Sá, T.; Ferreira, M.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Cabrita, A.R.J.; Almeida, A.; Abreu, H.; Silva, J.; Fonseca, A.J.M.; et al. A commercial blend of macroalgae and microalgae promotes digestibility, growth performance, and muscle nutritional value of European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) juveniles. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1165343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, M.; Abdelhafiz, Y.; Abreu, H.; Silva, J.; Valente, L.M.P.; Kiron, V. Gracilaria gracilis and Nannochloropsis oceanica, singly or in combination, in diets alter the intestinal microbiota of European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1001942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, S.; Pereira, R.; Oliveira, B.; Baião, L.F.; Jessen, F.; Tulli, F.; Messina, M.; Silva, J.L.; Abreu, H.; Valente, L.M.P. Exploring the potential of seaweed Gracilaria gracilis and microalga Nannochloropsis oceanica, single or blended, as natural dietary ingredients for European seabass Dicentrarchus labrax. J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 32, 2041–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.; Montero, D.; Betancor, M.; Kaur, K.; Serradell, A.; Izquierdo, M.; Ginés, R.; Claeyssens, V.; Torrecillas, S. Benefits of dietary krill meal inclusion towards better utilization of nutrients, and response to oxidative stress in gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) juveniles. Aquaculture 2025, 598, 741957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, R.; Rema, P.; Dias, J.; Gonçalves, A.T.; Teodósio, R.; Engrola, S.; Sánchez-Vázquez, F.J.; Conceição, L.E.C. Socially Acceptable Feed Formulations May Impact the Voluntary Feed Intake and Growth, but Not Robustness of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fishes 2024, 9, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragão, C.; Colen, R.; Teodósio, R.; Cabano, M.; Antelo, L.T.; Vázquez, J.A.; Engrola, S. Fish Protein Hydrolysates Mitigate the Adverse Effects of No-Fishmeal Diets in Gilthead Seabream Juveniles. Aquac. Nutr. 2025, 2025, 1352251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arechavala-Lopez, P.; Nazzaro-Alvarez, J.; Jardí-Pons, A.; Reig, L.; Carella, F.; Carrassón, M.; Roque, A. Linking stocking densities and feeding strategies with social and individual stress responses on gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata). Physiol. Behav. 2020, 213, 112723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodósio, R.; Engrola, S.; Dias, J.; Gonçalves, A.T. Evaluation of Potential Disruptors of Intestinal Homeostasis in Gilthead Seabream Juveniles. In Aquaculture Europe 2022 Abstract Book, Proceedings of Aquaculture Europe 2022, Rimini, Italy, 27–30 September 2022; European Aquaculture Society: Oostende, Belgium, 2022; pp. 477–478. [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffl, M.W. Quantification strategies in real-time PCR. AZ Quant. PCR 2004, 1, 89–113. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, F.; Xiao, P.; Chen, D.; Xu, L.; Zhang, B. miRDeepFinder: A miRNA analysis tool for deep sequencing of plant small RNAs. Plant Mol. Biol. 2012, 80, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ran, C.; Teame, T.; Ding, Q.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Xie, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Olsen, R.E.; Gatlin, D.M.; et al. Research progress on gut health of farmers teleost fish: A viewpoint concerning the intestinal mucosal barrier and the impact of its damage. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2020, 30, 569–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, A.; Kortner, T.M.; Penn, M.; Østby, G.; Bakke, A.M.; Krogdahl, A.; Oliva-Teles, A. Saponins and phytosterols in diets for European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) juveniles: Effects on growth, intestinal morphology and physiology. Aquac. Nutr. 2015, 21, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, A.I.; dos Santos Azevedo, R.; Reyes, M.E.; Figueiredo, B.X.; dos Santos Flores, I.; Anni, L.S.A.; Silveira, T.; Tesser, M.B.; Jardim, R.D.; Junior, A.S.V.; et al. Impact of dietary supplementation with Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942 expressing a β-glucosidase from Amazonian soil on the physiology of zebrafish (Danio rerio) fed a soybean meal-rich diet. J. Appl. Phycol. 2025, 37, 2577–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wen, J.; Hou, X.; Wu, H.; Zhou, Q.; Fu, X.; Cui, C.; Lin, S.-M.; Chen, Y.; Luo, L.; et al. Effects of Dietary Soya-Saponins on Growth Performance and Intestinal Health in Juvenile Largemouth Bass (Micropterus Salmoides). Aquac. Rep. 2025, 45, 103142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.; Oliva-Teles, A.; Couto, A. Tracking Biomarkers for the Health and Welfare of Aquaculture Fish. Fishes 2024, 9, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, G.M.; Ismael, S.; Morais, J.; Araújo, J.R.; Faria, A.; Calhau, C.; Marques, C. Intestinal Alkaline Phosphatase: A Review of This Enzyme Role in the Intestinal Barrier Function. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacchetta, C.; Cazenave, J.; Mora, C.; Michlig, M.P.; Repetti, M.R.; Rossi, A.S. Non-lethal biomarkers as promising tools for fish health assessment: In situ exposure to bifenthrin as a case study. Aquat. Toxicol. 2024, 276, 107083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, F.; Wen, H.; Dong, L.; Tian, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, C.; Xiao, J.; Duan, X.; et al. Schizochytrium sp. can improve feed utilization, fillet DHA content, and non-specific immunity of juvenile Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fed fish oil free diet. J. Appl. Phycol. 2024, 36, 3341–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadel, A.; Mahmoud, M.A.; Abdelsalam, M.; Eissa, E.S.H.; Sherif, A.H. Aeromonas veronii infection in cultured Oreochromis niloticus: Prevalence, molecular and histopathological characterization correlated to water physicochemical characteristics, with the protective autochthonous probiotic. Aquac. Int. 2025, 33, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Hu, P.; Wen, Z.; Wang, J.; Zou, Y. Ameliorative effects of Sargassum kjellmanianum on hexavalent chromium-induced growth inhibition, immune suppression, and oxidative stress in yellow catfish. J. Appl. Phycol. 2024, 36, 2225–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, A.K.; Araujo, A.S.M.L.; da Silva, T.M.L.; de Sousa de Lima, F.M.; dos Santos Ferreira, J.; de Brito, T.V.; dos Reis Barbosa, A.L. Polysaccharides from macro algae: Anti-inflammatory actions against systemic inflammatory process and in the gastrointestinal tract. J. Appl. Phycol. 2023, 35, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldessouki, E.A.A.; Elshopakey, G.E.; Elbahnaswy, S.; Shakweer, M.S.; Abdelwarith, A.A.; Younis, E.M.; Davies, S.J.; Mili, A.; Abd El-Aziz, Y.M.; Abdelnour, S.A.; et al. Influence of astaxanthin-enriched Haematococcus pluvialis microalgae on the growth efficacy, immune response, antioxidant capacity, proinflammatory cytokines, and tissue histomorphology of hybrid red tilapia. Aquac. Int. 2024, 32, 7447–7468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.R.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, J.Y. Therapeutic potential of seaweed extracts: In vitro and in vivo studies on alleviating inflammation and enhancing intestinal barrier function. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 103774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creasey, E.A.; Isberg, R.R. Maintenance of vacuole integrity by bacterial pathogens. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2014, 17, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emilian, O.; Ioan, S.; Irina, P.; Raul, P.; Adriana, C.; Dorin, C.; Ciprian, S. Cytological Applications of the Vacuolization Phenomenon as a Means of Determining Saline Cytotoxicity. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, V.; Teixeira, V. Vacuolar ATPase-mediated regulation of neutral lipid dynamics: Insights into lipid droplet homeostasis and stress response mechanisms. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2024, 1869, 159465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Secombes, C.J. The Function of Fish Cytokines. Biology 2016, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, M.; Hikima, J.I.; Kono, T. Fish cytokines: Current research and applications. Fish. Sci. 2021, 87, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, I.; Zhang, Y.A.; Sunyer, J.O. Mucosal immunoglobulins and B cells of teleost fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 1346–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilal, S.; Etayo, A.; Hordvik, I. Immunoglobulins in teleosts. Immunogenetics 2021, 73, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, M.; Sousa, V.; Oliveira, B.; Canadas-Sousa, A.; Abreu, H.; Dias, J.; Kiron, V.; Valente, L.M.P. An in-depth characterisation of European seabass intestinal segments for assessing the impact of an algae-based functional diet on intestinal health. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maga, G.; Hübscher, U. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA): A dancer with many partners. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 3051–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezfuli, B.S.; Giari, L.; Lui, A.; Squerzanti, S.; Castaldelli, G.; Shinn, A.P.; Manera, M.; Lorenzoni, M. Proliferative cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) expression in the intestine of Salmo trutta trutta naturally infected with an acanthocephalan. Parasites Vectors 2012, 5, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Bao, Q.; Ma, K.; Li, X.; Jia, J.; Wu, H. Antioxidant and innate immunity of Danio rerio against Edwardsiella tarda in response to diets including three kinds of marine microalgae. Algal Res. 2022, 64, 102689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, J.M.; Lin, P.H.; Yao, Q.; Chen, C. Chemical and molecular mechanisms of antioxidants: Experimental approaches and model systems. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 840–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biller, J.D.; Takahashi, L.S. Oxidative stress and fish immune system: Phagocytosis and leukocyte respiratory burst activity. An. Acad. Bras. Ciências 2018, 90, 3403–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chang, H.; Han, D.; Lu, S.; Lv, W.; Guo, K.; Wang, C.; Li, S.; Han, S.; Liu, H. Effects of dietary chrysophyte (Poterioochromonas malhamensis) rich in beta-glucan on the growth performance, intestinal health, lipid metabolism, immune gene expression, and disease resistance against Aeromonas salmonicida in juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2022, 561, 738589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhzadeh, N.; Ahmadifar, E.; Soltani, M.; Tayefi-Nasrabadi, H.; Mousavi, S.; Naiel, M.A.E. Brown Seaweed (Padina australis) Extract can Promote Performance, Innate Immune Responses, Digestive Enzyme Activities, Intestinal Gene Expression and Resistance against Aeromonas hydrophila in Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio). Animals 2022, 12, 3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Diets | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ingredients (%) | CTRL | PHA | GRA | BLEND |
| Fishmeal Super Prime a | 8.00 | 8.00 | 8.00 | 8.00 |
| Poultry meal b | 7.50 | 7.50 | 7.50 | 7.50 |
| Poultry blood meal c | 4.70 | 4.70 | 4.70 | 4.70 |
| Feather meal hydrolysate d | 7.50 | 7.50 | 7.50 | 7.50 |
| Phaeodactylum tricornutum e | 0.00 | 2.50 | 0.00 | 2.50 |
| Gracilaria gracilis f | 0.00 | 0.00 | 2.50 | 2.50 |
| Corn gluten meal g | 10.00 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 10.00 |
| Soybean meal 44 h | 15.00 | 15.00 | 15.00 | 15.00 |
| Sunflower meal i | 15.00 | 15.00 | 15.00 | 15.00 |
| Wheat meal j | 13.00 | 10.50 | 10.50 | 8.00 |
| Vitamin and mineral premix k | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Antioxidant l | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 |
| Monocalcium phosphate m | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 |
| L-Lysine n | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 |
| Fish oil o | 7.00 | 7.00 | 7.00 | 7.00 |
| Rapeseed oil p | 9.30 | 9.30 | 9.30 | 9.30 |
| Proximate composition (% as fed) | ||||
| Dry matter | 93.17 | 95.49 | 95.49 | 94.88 |
| Ash | 6.52 | 6.91 | 7.10 | 7.50 |
| Crude protein | 41.64 | 45.87 | 44.69 | 45.65 |
| Crude lipid | 18.69 | 18.89 | 19.29 | 19.43 |
| Gross energy (MJ kg−1) | 21.31 | 21.62 | 21.71 | 21.55 |
| Gene | Forward Sequence (5′-3′) | Reverse Sequence (5′-3′) | Accession Number (GenBank) | Annealing Temperature (°C) | Primer Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ef1a | GGAGATGCACCACGAGTCTC | GCGTTGAAGTTGTCAGCTCC | AF184170 | 59 | 103 |
| cat | CGACATGGTGTGGGACTTCT | CGCTCACCATTGGCATTGAC | JQ308823 | 57 | 93 |
| gpx | TTTACGCCCTGACAGCCAAT | AGTAACGACTGTGGAGCTCG | KC201352 | 59 | 95 |
| igm | GACAACCTCAGCGTCCTTCA | CTTTTGAGTCTGCAGCGTCG | JQ811851 | 55 | 115 |
| il1b | TCCAAGCTTGCATCTGGAGG | GCTGAAGGGAACAGACACGA | AJ277166 | 55 | 106 |
| il10 | TCTTTCAAAACAGCGTTCGCC | TGGACTGCATGTGAGGCTTT | JX976621 | 57 | 83 |
| tnfa | CAGGATCTCGCGCTACTCAG | GCCCAGGTAGATGGTGTTGT | AJ413189 | 55 | 94 |
| pcna | TCATGATCTCCTGCGCCAAG | CAAAGATCAGCTGGACGGGT | KF857335 | 57 | 73 |
| tjp | CTGCTGGATGTGACACCCAA | GGCGATCCTCTGTCTCAAGG | XM_030417304.1 | 59 | 84 |
| ocl | TACGGTGGAATCGGAGGGAA | CTGGTGAGACACGACGATGA | JQ692876 | 55 | 89 |
| muc13 | CTGTCTACTGAACGGGGCAA | ATTCTGTCACTGAACGCCGT | JQ277713 | 57 | 79 |
| Enzyme | Treatments | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activity (U L−1) | CTRL + S | PHA | GRA | BLEND |
| ALP | 97.40 ± 14.77 a | 95.53 ± 15.50 a | 96.73 ± 21.45 a | 65.71 ± 24.99 b |
| ALT | 1.92 ± 0.90 | 2.07 ± 1.03 | 1.99 ± 1.23 | 2.30 ± 1.15 |
| AST | 15.37 ± 10.08 | 15.44 ± 7.97 | 13.15 ± 9.37 | 13.39 ± 5.96 |
| ALT:AST | 0.16 ± 0.10 | 0.14 ± 0.09 | 0.16 ± 0.10 | 0.19 ± 0.11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Gallego, I.; Aragão, C.; Teodósio, R.; Gonçalves, A.T.; Engrola, S. Functional Algal Feeds for Aquaculture: Micro- and Macroalgae Promote Gut Recovery in Gilthead Seabream. Fishes 2025, 10, 588. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10110588
García-Gallego I, Aragão C, Teodósio R, Gonçalves AT, Engrola S. Functional Algal Feeds for Aquaculture: Micro- and Macroalgae Promote Gut Recovery in Gilthead Seabream. Fishes. 2025; 10(11):588. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10110588
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Gallego, Ibon, Cláudia Aragão, Rita Teodósio, Ana Teresa Gonçalves, and Sofia Engrola. 2025. "Functional Algal Feeds for Aquaculture: Micro- and Macroalgae Promote Gut Recovery in Gilthead Seabream" Fishes 10, no. 11: 588. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10110588
APA StyleGarcía-Gallego, I., Aragão, C., Teodósio, R., Gonçalves, A. T., & Engrola, S. (2025). Functional Algal Feeds for Aquaculture: Micro- and Macroalgae Promote Gut Recovery in Gilthead Seabream. Fishes, 10(11), 588. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10110588











