Morphological and Histological Changes of Experimental Pseudomonas fluorescens Infection in Zebrafish (Danio rerio)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strain and Growth Conditions
2.2. Animal Model and Maintenance
2.3. Experimental Design and Infectious Challenge
2.4. Histopathological Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Findings
3.2. Histopathology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATCC | American Type Culture Collection |
| BHIA | Brain Heart Infusion Agar |
| CFU | Colony Forming Units |
| FHA | Filamentus Haemagglutinin |
| HPI | Hours Post Inoculation |
| H | Hours |
| OD | Optical Density |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| pH | Potential of hydrogen |
References
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2024; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024; ISBN 9789251387634. [Google Scholar]
- Garlock, T.; Asche, F.; Anderson, J.; Ceballos-Concha, A.; Love, D.C.; Osmundsen, T.C.; Pincinato, R.B.M. Aquaculture: The Missing Contributor in the Food Security Agenda. Glob. Food Secur. 2022, 32, 100620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kinkelin, P.; Michel, C.; Ghittino, P. Tratado de Las Enfermedades de Los Peces; Acribia: Zaragoza, Spain, 1991; ISBN 8420006866. [Google Scholar]
- Pridgeon, J.W.; Klesius, P.H. Major Bacterial Diseases in Aquaculture and Their Vaccine Development. CAB Rev. Perspect. Agric. Vet. Sci. Nutr. Nat. Resour. 2012, 7, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado-Miranda, J.J.; Castillo-Pérez, L.J.; Ponce-Hernández, A.; Carranza-Álvarez, C. Summary of Economic Losses Due to Bacterial Pathogens in Aquaculture Industry. In Bacterial Fish Diseases; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 399–417. ISBN 9780323856249. [Google Scholar]
- Vanamala, P.; Sindhura, P.; Sultana, U.; Vasavilatha, T.; Gul, M.Z. Chapter 14—Common Bacterial Pathogens in Fish: An Overview. In Bacterial Fish Diseases; Dar, G.H., Bhat, R.A., Qadri, H., Al-Ghamdy, K.M., Hakeem, K.R.B.T.-B.F.D., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 279–306. ISBN 978-0-323-85624-9. [Google Scholar]
- Dey, M.M. Strategies and Options for Increasing and Sustaining Fisheries and Aquaculture Production to Benefit Poorer Households in Asia; WorldFish Center: Penang, Malaysia, 2008; ISBN 9789832346661. [Google Scholar]
- Attia, M.M.; Abdelsalam, M.; Elgendy, M.Y.; Sherif, A.H. Dactylogyrus extensus and Pseudomonas fluorescens Dual Infection in Farmed Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio). Microb. Pathog. 2022, 173, 105867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Zhang, L. The Hierarchy Quorum Sensing Network in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Protein Cell 2014, 6, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, R.J. Fish Pathology, 4th ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK, 2012; ISBN 9781444332827. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.-R.; Hu, Y.-H.; Zhang, W.-W.; Sun, L. Construction of an Attenuated Pseudomonas fluorescens Strain and Evaluation of Its Potential as a Cross-Protective Vaccine. Vaccine 2009, 27, 4047–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvey, M.I.; Bradley, C.W.; Holden, E. Waterborne Pseudomonas aeruginosa Transmission in a Hematology Unit? Am. J. Infect. Control 2018, 46, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algammal, A.M.; Mabrok, M.; Sivaramasamy, E.; Youssef, F.M.; Atwa, M.H.; El-kholy, A.W.; Hetta, H.F.; Hozzein, W.N. Emerging MDR-Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Fish Commonly Harbor OprL and ToxA Virulence Genes and Bla TEM, Bla CTX-M, and TetA Antibiotic-Resistance Genes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panpatte, D.G.; Jhala, Y.K.; Shelat, H.N.; Vyas, R.V. Pseudomonas fluorescens: A Promising Biocontrol Agent and PGPR for Sustainable Agriculture. In Microbial Inoculants in Sustainable Agricultural Productivity: Vol. 1: Research Perspectives; Springer: New delhi, India, 2016; pp. 257–270. ISBN 9788132226475. [Google Scholar]
- Gołaś, I. The Influence of Aquaculture Efluents on the Prevalence and Biocides Resistance of Opportunistic Pseudomonas fluorescens Bacteria in the Drweca River Protected under the Natura 2000 Network. Water 2020, 12, 1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, T.; Kubota, S.; Miyashita, T. A Histopathological Study of Pseudomonas fluorescens Infection in Tilapia. Fish. Pathol. 1984, 19, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picot, L.; Abdelmoula, S.M.; Merieau, A.; Leroux, P.; Cazin, L.; Orange, N.; Feuilloley, M.G.J. Pseudomonas fluorescens as a Potential Pathogen: Adherence to Nerve Cells. Microbes Infect. 2001, 3, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinçtürk, E.; Tanrıkul, T.T. Yersinia ruckeri and Pseudomonas fluorescens Co-Infection in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum, 1792). Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 4858–4866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darak, O.; Dhondiraj Barde, R. Pseudomonas fluorescens Associated with Bacterial Disease in Catla catla in Marathwada Region of Maharashtra 1. Int. J. Adv. Biotechnol. Res. (IJBR) 2015, 6, 189–195. [Google Scholar]
- Gołaś, I.; Szmyt, M.; Potorski, J.; Łopata, M.; Gotkowska-Płachta, A.; GlińZska-Lewczuk, K. Distribution of Pseudomonas fluorescens and Aeromonas hydrophila Bacteria in a Recirculating Aquaculture System during Farming of European Grayling (Thymallus thymallus L.) Broodstock. Water 2019, 11, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pȩkala-Safińska, A. Contemporary Threats of Bacterial Infections in Freshwater Fish. J. Vet. Res. 2018, 62, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Foysal, M.J.; Rahman, M.M.; Alam, M. Antibiotic Sensitivity and In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity of Plant Extracts to Pseudomonas fluorescens Isolates Collected from Diseased Fish. Int. J. Nat. Sci. 2011, 1, 82–88. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, S.A.; Khalil, R.H. Studies on Pseudomonas Septicemia among Cultured Oreochromis niloticus. J. Arab. Aquac. Soc. 2010, 5, 55–64. [Google Scholar]
- Sierra, E.M.; Espinosa de Los Monteros, A.; Real, F.; Herráez, P.; Rodríguez, P.; Fernández, A. Histología y Patología de Los Peces Parte II: Infecciones Víricas, Bacterianas y Micoticas. Rev. Canar. De Las Cienc. Vet. 2011, 46–57. Available online: https://accedacris.ulpgc.es/bitstream/10553/8168/2/0280574_00002_0008.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- Zhang, W.W.; Hu, Y.H.; Wang, H.L.; Sun, L. Identification and Characterization of a Virulence-Associated Protease from a Pathogenic Pseudomonas fluorescens Strain. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 139, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.Y.; Sun, L. Pseudomonas fluorescens: Iron-Responsive Proteins and Their Involvement in Host Infection. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 176, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikandar, A. Histopathology: An Old Yet Important Technique in Modern Science. In Histopathology—An Update; InTech: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- González-Renteria, M.; del Carmen Monroy-Dosta, M.; Guzmán-García, X.; Hernández-Calderas, I.; Ramos-Lopez, Y.M.A. Antibacterial Activity of Lemna minor Extracts against Pseudomonas fluorescens and Safety Evaluation in a Zebrafish Model. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 3465–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Gersdorff, J.L. Zebrafish as a Model for Fish Diseases in Aquaculture. Pathogens 2020, 9, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neely, M.N. The Zebrafish as a Model for Human Bacterial Infections. In Bacterial Pathogenesis: Methods and Protocols, Methods in Molecular Biology; Nordenfelt, P., Ed.; Springer Science: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; Volume 1535, pp. 245–266. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa Borges, R.; César Matias Pereira, A.; Custodio de Souza, G.; Carlos Tavares Carvalho, J. Histopathology of Zebrafish (Danio rerio) in Nonclinical Toxicological Studies of New Drugs. In Zebrafish in Biomedical Research; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, C.; Matty, M.A.; Jurczyszak, D.; Gabor, K.A.; Millard, P.J.; Tobin, D.M.; Kim, C.H. Infectious Disease Models in Zebrafish. Methods Cell Biol. 2017, 138, 101–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleström, P.; Winther-Larsen, H.C. Zebrafish Offer Aquaculture Research Their Services. In Genomics in Aquaculture; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 165–194. ISBN 9780128016909. [Google Scholar]
- Ehsannia, S.; Ahari, H.; Kakoolaki, S.; Anvar, S.A.; Yousefi, S. Effects of Probiotics on Zebrafish Model Infected with Aeromonas hydrophila: Spatial Distribution, Antimicrobial, and Histopathological Investigation. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogaret, P.; El Garah, F.; Blanc-Potard, A.B. A Novel Infection Protocol in Zebrafish Embryo to Assess Pseudomonas aeruginosa Virulence and Validate Efficacy of a Quorum Sensing Inhibitor in Vivo. Pathogens 2021, 10, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakus, K.; Adamek, M.; Mojżesz, M.; Podlasz, P.; Chmielewska-Krzesińska, M.; Naumowicz, K.; Kasica-Jarosz, N.; Kłak, K.; Rakers, S.; Way, K.; et al. Evaluation of Zebrafish (Danio rerio) as an Animal Model for the Viral Infections of Fish. J. Fish. Dis. 2019, 42, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, Q.; Qu, J.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Y. A Live Attenuated Combination Vaccine Evokes Effective Immune-Mediated Protection against Edwardsiella tarda and Vibrio anguillarum. Vaccine 2014, 32, 5937–5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Fu, S.; Li, R.; Dang, H.; Gao, D.; Ye, S.; Jiang, Z. Identification and Histopathological and Pathogenicity Analysis of Aeromonas Salmonicida salmonicida from Goldfish (Carassius auratus) in North China. Aquac. Fish. 2020, 5, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulucan, A.; Yüksel, H.; Dörtbudak, M.B.; Yüksel, S. Comparative Examination of Commonly Used Some Fixatives with Routine Histochemical Staining’s for The Optimal Histological Appearance in The Gill Tissue of Zebrafish. Kocatepe Vet. J. 2019, 12, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza, K.; Inami, M.; Dalum, A.S.; Lund, H.; Bjelland, A.M.; Sørum, H.; Løvoll, M. Comparative Evaluation of Experimental Challenge by Intraperitoneal Injection and Cohabitation of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.) after Vaccination against Piscirickettsia salmonis (EM90-Like). J. Fish Dis. 2019, 42, 1713–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, S.O.; Baxter, E.J.; Holland, C.; Rodger, H.D. Development of a Novel Histopathological Gill Scoring Protocol for Assessment of Gill Health during a Longitudinal Study in Marine-Farmed Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar). Aquac. Int. 2012, 20, 813–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnevia, D.; Letamendía, M.; Perretta, A.; Delgado, E. Caracterización de Septicemia Hemorrágica Bacteriana (SHB), Diagnosticadas En Peces Ornamentales de Uruguay. Veterinaria 2010, 46, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmawaty, A.; Cheng, L.W.; Wang, P.C.; Chen, S.C. Comparative Pathogenicity and Histopathological Analysis of Edwardsiella anguillarum Intraperitoneal Infection in Milkfish (Chanos chanos), Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and Asian Seabass (Lates calcarifer). J. Fish Dis. 2024, 47, e13982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SigmaPlot, version 14.0; Systat Software, Inc.: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2019. Available online: https://systatsoftware.com (accessed on 5 January 2019).
- Kim, H.-Y. Statistical Notes for Clinical Researchers: Chi-Squared Test and Fisher’s Exact Test. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2017, 42, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clatworthy, A.E.; Lee, J.S.W.; Leibman, M.; Kostun, Z.; Davidson, A.J.; Hung, D.T. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection of Zebrafish Involves Both Host and Pathogen Determinants. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 1293–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torraca, V.; Mostowy, S. Zebra Fish Infection: From Pathogenesis to Cell Biology. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahne, W.; Popp, W.; Hoffmann, R. Pseudomonas fluorescens as a Pathogen of Tench (Tinca tinca). Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 1982, 4, 56–57. [Google Scholar]
- Solís, C.J.; Poblete-morales, M.; Cabral, S.; Valdés, J.A.; Reyes, A.E.; Avendaño-Herrera, R.; Feijóo, C.G. Neutrophil Migration in the Activation of the Innate Immune Response to Different Flavobacterium psychrophilum Vaccines in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 515187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.; Thanigaivel, S.; Vijayakumar, S.; Acharya, K.; Shinge, D.; Seelan, T.S.J.; Mukherjee, A.; Chandrasekaran, N. Pathogenecity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Oreochromis mossambicus and Treatment Using Lime Oil Nanoemulsion. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 116, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, J.; Gibson, S. Bacterial and Mycotic Diseases of Nonhuman Primates. In Nonhuman Primates in Biomedical Research; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 105–172. ISBN 9780123813664. [Google Scholar]
- Mokhtar, D.M.; Zaccone, G.; Alesci, A.; Kuciel, M.; Hussein, M.T.; Sayed, R.K.A. Main Components of Fish Immunity: An Overview of the Fish Immune System. Fishes 2023, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diab, A.S.; Aly, S.M.; John, G.; Abde-hadi, Y.; Mohamed, F. Effect of Garlic, Black Seed and Biogen as Immunostimulants on the Growth and Survival of Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (Teleostei: Cichlidae), and Their Response to Artificial Infection with Pseudomonas fluorescens. Afr. J. Aquat. Sci. 2010, 5914, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hal, A.M.; El-Barbary, M.I. Gene Expression and Histopathological Changes of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Infected with Aeromonas hydrophila and Pseudomonas fluorescens. Aquaculture 2020, 526, 735392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magi, G.E.; Lopez-Romalde, S.; Magariños, B.; Lamas, J.; Toranzo, A.E.; Romalde, J.L. Experimental Pseudomonas anguilliseptica Infection in Turbot Psetta maxima (L.): A Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Study. Eur. J. Histochem. 2009, 53, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


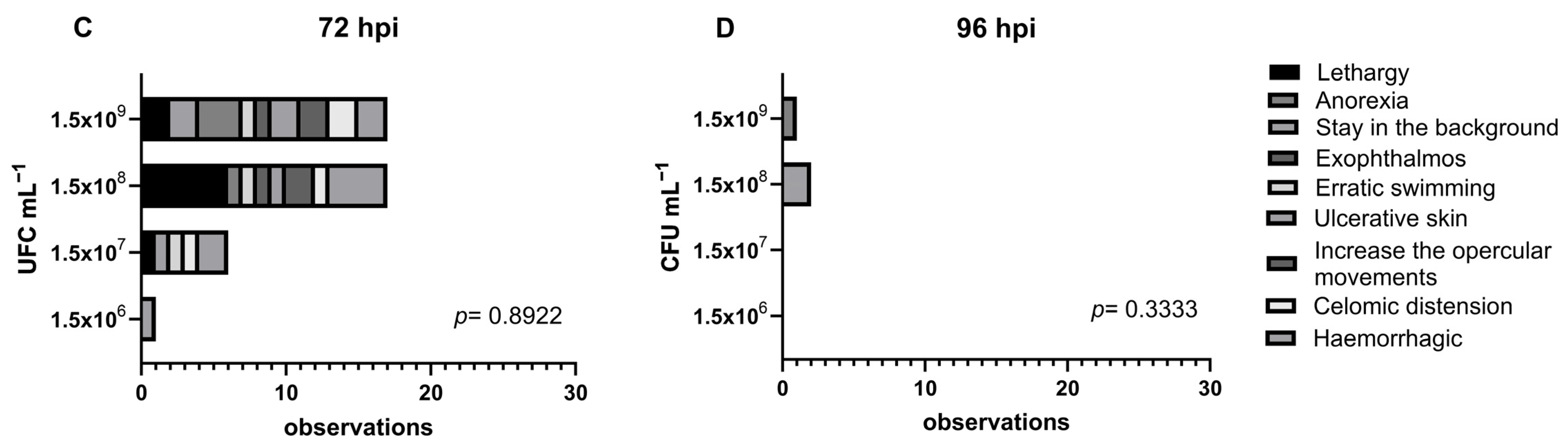
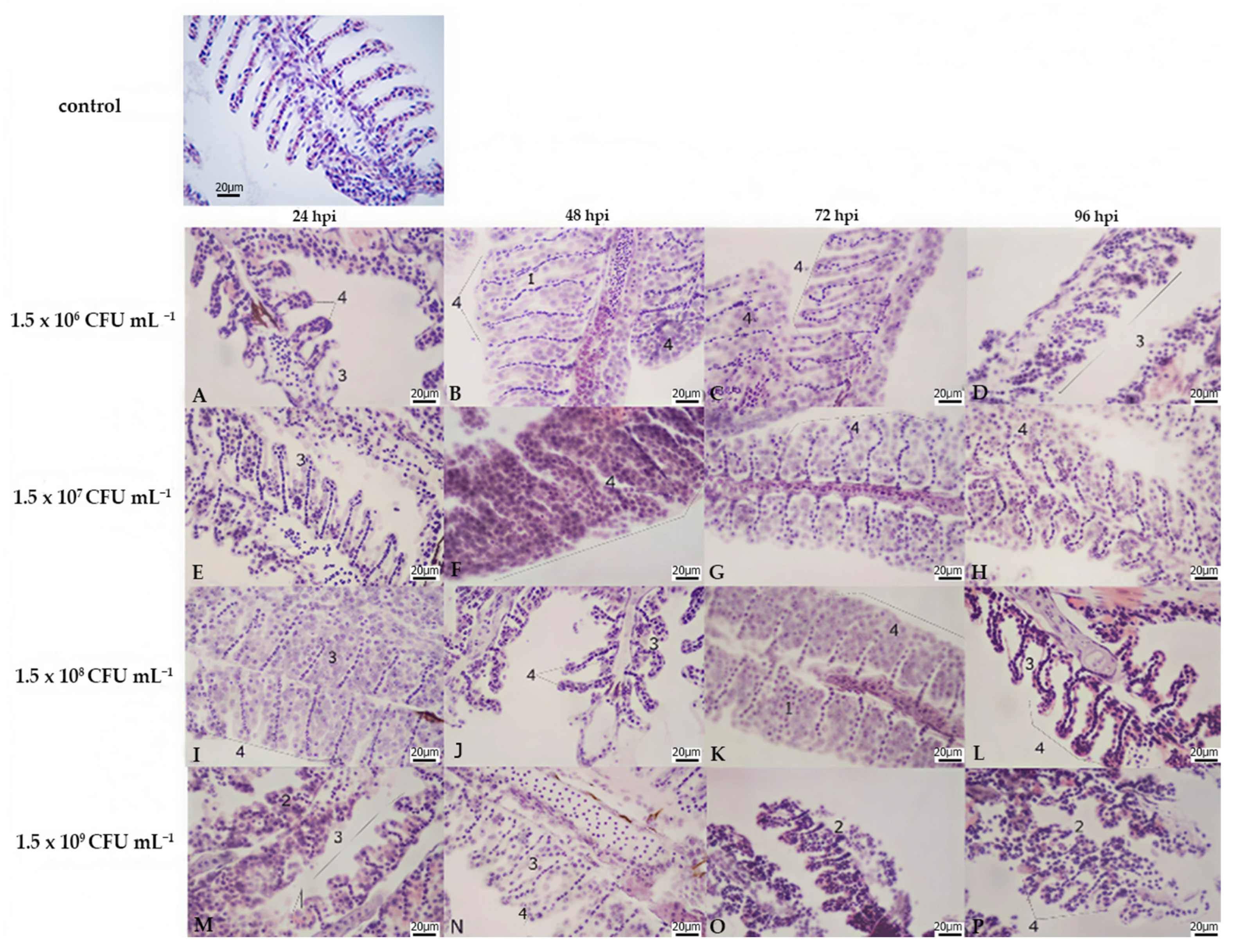
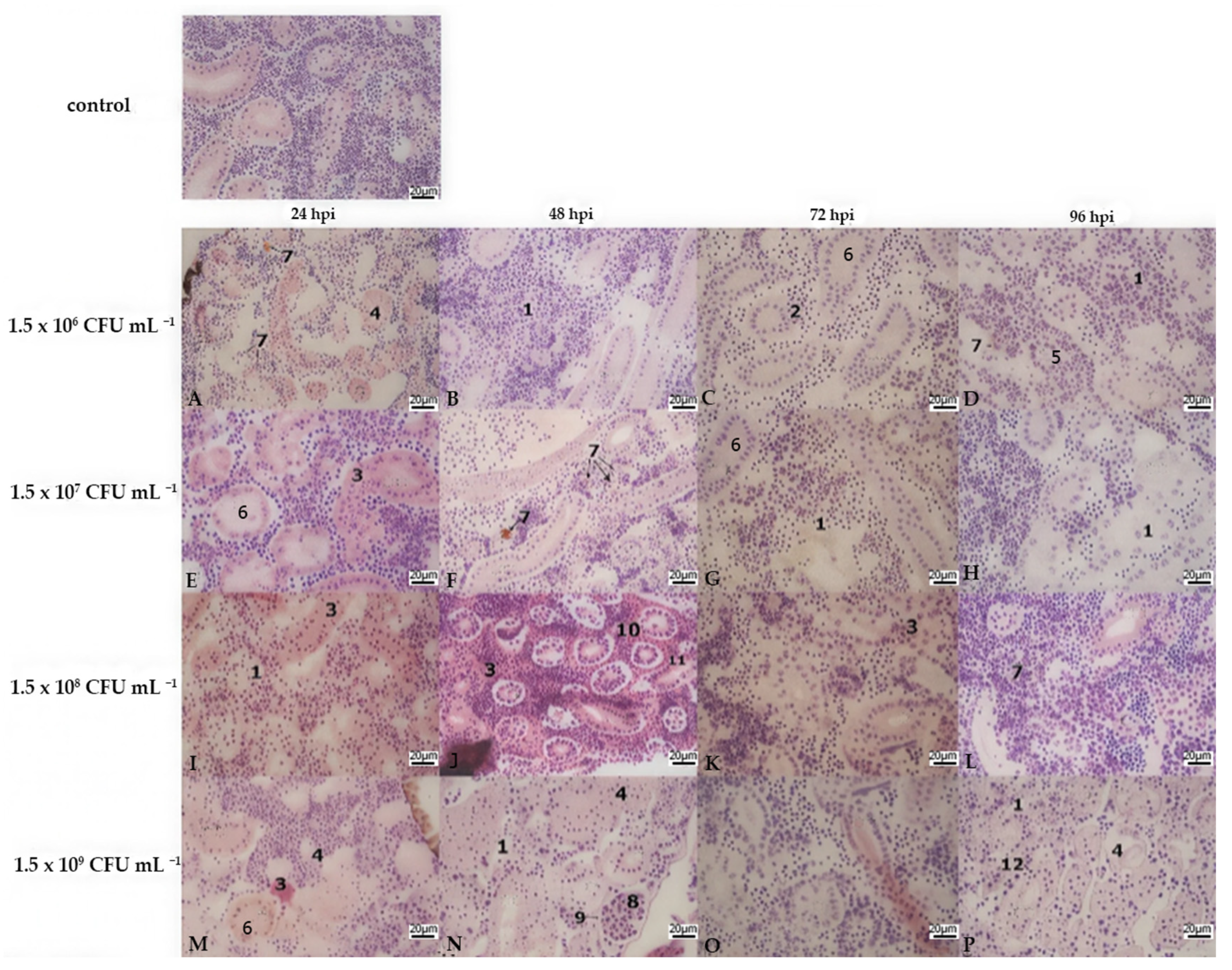
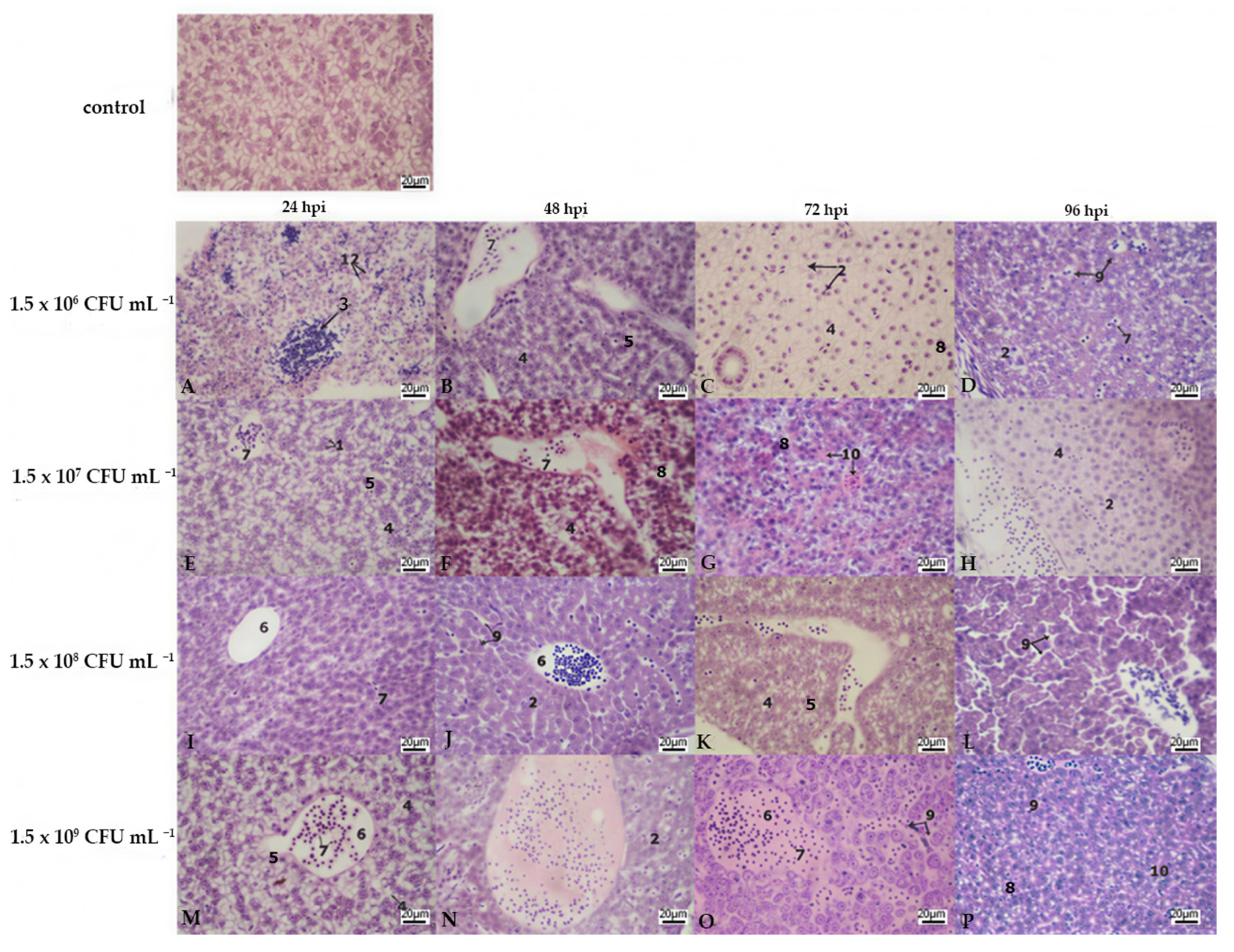
| Treatment | Bacterial Concentration (CFU mL−1) | Stocking Density (no./Treatment) | Number of Aquaria per Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tc (control) | 0 | 15 | 2 |
| Tcm (manipulation control) | PBS | 15 | 2 |
| T1 | 1.5 × 106 | 15 | 2 |
| T2 | 1.5 × 107 | 15 | 2 |
| T3 | 1.5 × 108 | 15 | 2 |
| T4 | 1.5 × 109 | 15 | 2 |
| Challenge Dosage | Number of Zebrafish (Organisms) by Duplicated | % Mortality (hpi) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | 96 h | ||
| Control | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Control intraperitoneal injection (PBS) | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1.5 × 106 CFU mL−1 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1.5 × 107 CFU mL−1 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1.5 × 108 CFU mL−1 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 6.66 | 6.66 |
| 1.5 × 109 CFU mL−1 | 15 | 0 | 20 | 20 | 33.33 |
| Liver | Kidney | Gills | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lamellar Hyperplasia | Lamellar Fusion | Cell Abnormalities | Lamellar Oedema | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bacterial Concentration | A | B | C | D | A | B | C | D | A | B | C | D | A | B | C | D | A | B | C | D | A | B | C | D | |
| hours post infection | 24 hpi | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 48 hpi | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 72 hpi | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 96 hpi | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González-Renteria, M.; Monroy-Dosta, M.d.C.; Ramos-López, M.A.; Campos-Guillén, J.; Bustamante-González, J.D.; González-Núñez, L.; Ávalos-Rodríguez, A.; Quintana-Obregón, E.A.; Perera-García, M.A. Morphological and Histological Changes of Experimental Pseudomonas fluorescens Infection in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fishes 2025, 10, 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10110551
González-Renteria M, Monroy-Dosta MdC, Ramos-López MA, Campos-Guillén J, Bustamante-González JD, González-Núñez L, Ávalos-Rodríguez A, Quintana-Obregón EA, Perera-García MA. Morphological and Histological Changes of Experimental Pseudomonas fluorescens Infection in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fishes. 2025; 10(11):551. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10110551
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález-Renteria, Mariela, María del Carmen Monroy-Dosta, Miguel Angel Ramos-López, Juan Campos-Guillén, Jesús Dámaso Bustamante-González, Leticia González-Núñez, Alejandro Ávalos-Rodríguez, Eber Addí Quintana-Obregón, and Martha Alicia Perera-García. 2025. "Morphological and Histological Changes of Experimental Pseudomonas fluorescens Infection in Zebrafish (Danio rerio)" Fishes 10, no. 11: 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10110551
APA StyleGonzález-Renteria, M., Monroy-Dosta, M. d. C., Ramos-López, M. A., Campos-Guillén, J., Bustamante-González, J. D., González-Núñez, L., Ávalos-Rodríguez, A., Quintana-Obregón, E. A., & Perera-García, M. A. (2025). Morphological and Histological Changes of Experimental Pseudomonas fluorescens Infection in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fishes, 10(11), 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10110551










