Establishment of Gill-Derived Primary Cell Cultures from Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) as an Alternative Platform for Studying Host–Virus Interactions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Fish Rearing
2.2. Establishment of Largemouth Bass Gill-Derived Primary Cells
2.3. Viral Infection
2.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.5. qRT-PCR
2.6. Cellular Transfection
2.7. Statistics
3. Results
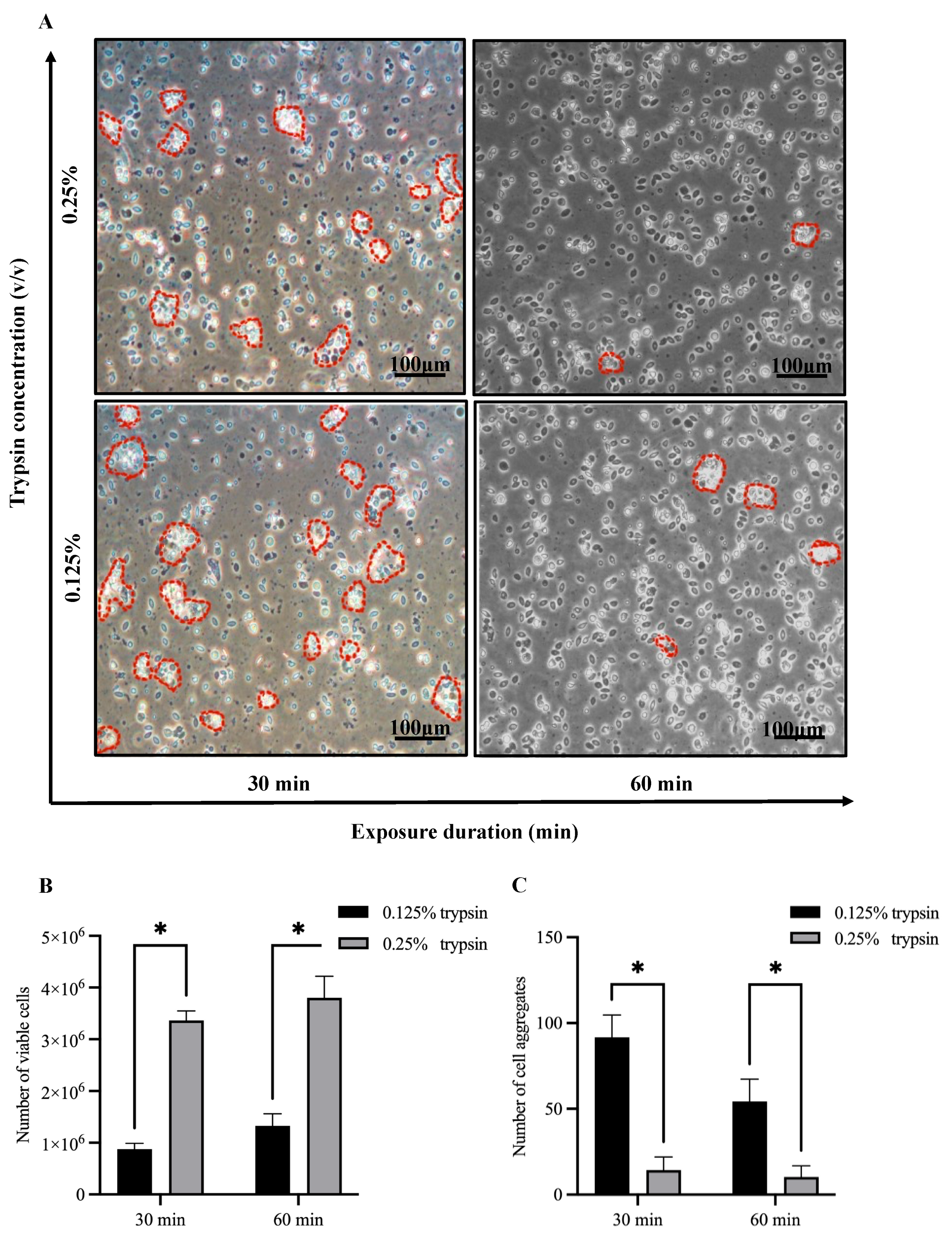
3.1. Establishment of Largemouth Bass Gill-Derived Primary Cells
3.2. Largemouth Bass Gill-Derived Primary Cells Are More Susceptible to MSRV Infections
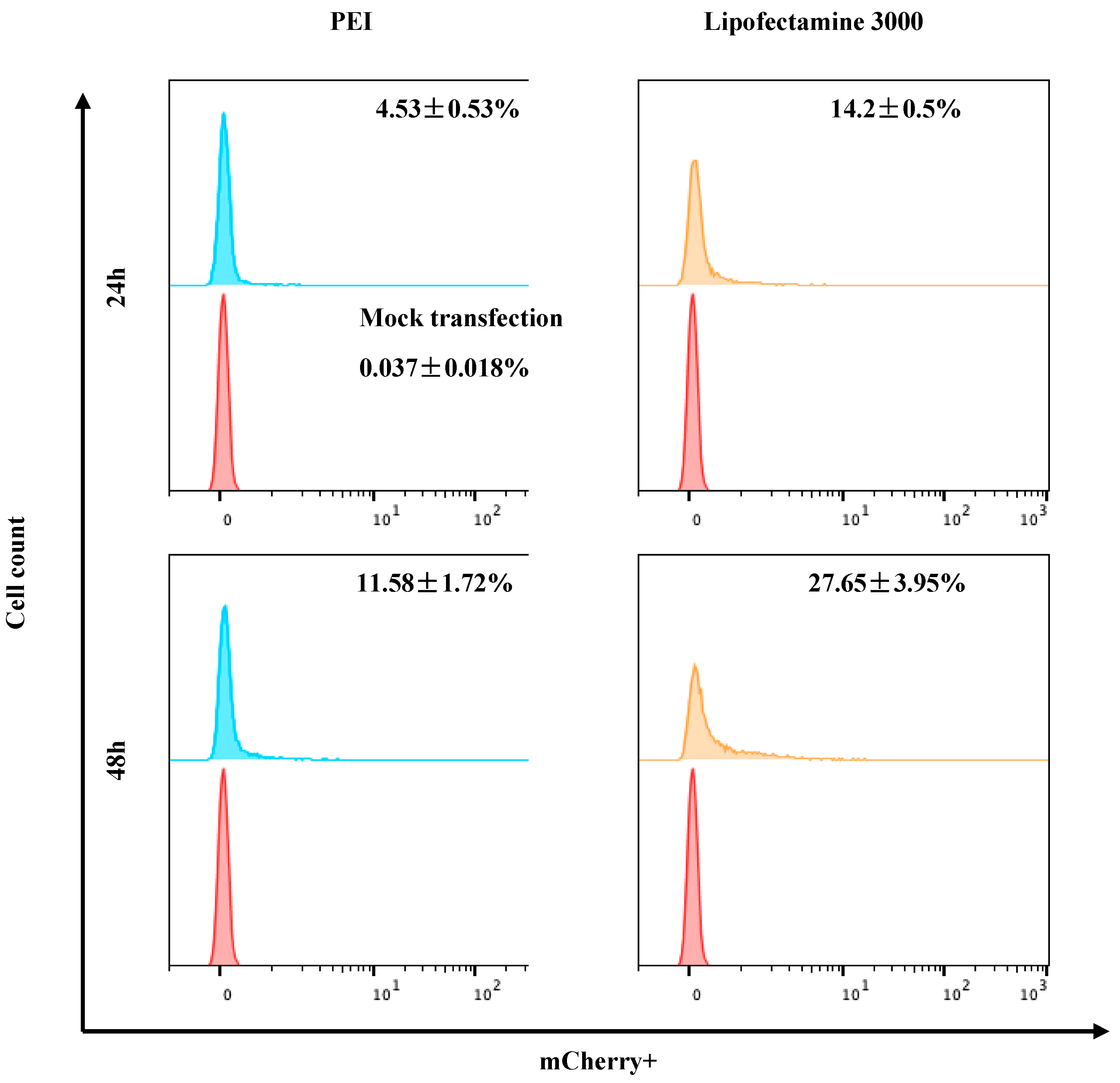
3.3. Optimization of Exogenous Transfection in Largemouth Bass Gill-Derived Primary Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qi, Z.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Mei, J.; Wang, D. Transcriptome analysis of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) challenged with LPS and polyI:C. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 133, 108534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhao, J.; An, N.; Li, D.C.; Huang, M.M.; Fei, H. Updates on infectious diseases of largemouth bass: A major review. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 154, 109976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Luo, M.; Zheng, G.; Liang, H.; Liu, L.; Lin, Q.; Niu, Y.; Luo, X.; Li, N. Determination and Characterization of a Novel Birnavirus Associated with Massive Mortality in Largemouth Bass. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0171621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Bergmann, S.M.; Mai, Q.; Yang, Y.; Liu, W.; Sun, D.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cai, W.; et al. Simultaneous Isolation and Identification of Largemouth Bass Virus and Rhabdovirus from Moribund Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Viruses 2022, 14, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mugimba, K.K.; Byarugaba, D.K.; Mutoloki, S.; Evensen, Ø.; Munang’andu, H.M. Challenges and Solutions to Viral Diseases of Finfish in Marine Aquaculture. Pathogens 2021, 10, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.; Deng, G.; Bai, J.; Li, S.; Yu, L.; Quan, Y.; Yang, X.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Ye, X. A strain of Siniperca chuatsi rhabdovirus causes high mortality among cultured Largemouth Bass in South China. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2013, 25, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, H.; Yi, S.F.; Zhang, H.M.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Yu, X.; Qian, S.C.; Huang, M.M.; Yang, S. Transcriptome and 16S rRNA analysis revealed the response of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) to Rhabdovirus infection. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 973422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Liang, J.; Yang, G.; Lu, J.; Chen, J. The laminin receptor is a receptor for Micropterus salmoides rhabdovirus. J. Virol. 2024, 98, e0069724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getchell, R.G.; Groocock, G.H.; Cornwell, E.R.; Schumacher, V.L.; Glasner, L.I.; Baker, B.J.; Frattini, S.A.; Wooster, G.A.; Bowser, P.R. Development and characterization of a largemouth bass cell line. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2014, 26, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, X.; Lu, Y.T.; Wang, B.; Guo, Z.Y.; Qian, A.D.; Li, Y.H. Infection of epithelioma papulosum cyprini (EPC) cells with spring viremia of carp virus (SVCV) induces autophagy and apoptosis through endoplasmic reticulum stress. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 183, 106293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Dong, H.; Chen, X.; Bergmann, S.M.; Yang, Y.; Wei, X.; Tong, G.; Li, H.; Yu, H.; Chen, Y. Establishment and characterization of a permanent heart cell line from largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides and its application to fish virology and immunology. Aquaculture 2022, 547, 737427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolskiy, A.A.; Grishchenko, I.V.; Yudkin, D.V. Cell Cultures for Virology: Usability, Advantages, and Prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maqsood, M.I.; Matin, M.M.; Bahrami, A.R.; Ghasroldasht, M.M. Immortality of cell lines: Challenges and advantages of establishment. Cell Biol. Int. 2013, 37, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Xu, W.; Wang, W.; Pan, Z.; Qin, Q.; Huang, X.; Huang, Y. Largemouth Bass Virus Infection Induced Non-Apoptotic Cell Death in MsF Cells. Viruses 2022, 14, 1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salybekov, A.A.; Kobayashi, S.; Asahara, T. Characterization of Endothelial Progenitor Cell: Past, Present, and Future. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Boström, C.; Franzenburg, S.; Bayer, T.; Dagan, T.; Reusch, T.B.H. Somatic genetic drift and multilevel selection in a clonal seagrass. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 4, 952–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.E.; Dayeh, V.R.; Schirmer, K.; Bols, N.C. Applications and potential uses of fish gill cell lines: Examples with RTgill-W1. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2009, 45, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weli, S.C.; Aamelfot, M.; Dale, O.B.; Koppang, E.O.; Falk, K. Infectious salmon anaemia virus infection of Atlantic salmon gill epithelial cells. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzi, M. Sampling variation of the fifty percent end-point, determined by the Reed-Muench (Behrens) method. Hum. Biol. 1950, 22, 151–190. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Guo, M.; Liu, J.; Li, C. circRNA432 enhances the coelomocyte phagocytosis via regulating the miR-2008-ELMO1 axis in Vibrio splendidus-challenged Apostichopus japonicus. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Li, X.; Tao, W.; Teng, F.; Li, C. Vibrio splendidus infection promotes circRNA-FGL1-regulated coelomocyte apoptosis via competitive binding to Myc with the deubiquitinase OTUB1 in Apostichopus japonicus. PLoS Pathog. 2024, 20, e1012463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Qiu, T.X.; Lu, J.F.; Liu, H.W.; Hu, L.; Liu, L.; Chen, J. Potential aquatic environmental risks of trifloxystrobin: Enhancement of virus susceptibility in zebrafish through initiation of autophagy. Zool. Res. 2021, 42, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Qiu, T.X.; Hu, Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, J. Antiviral effects of natural small molecules on aquatic rhabdovirus by interfering with early viral replication. Zool. Res. 2022, 43, 966–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matras, M.; Stachnik, M.; Borzym, E.; Maj-Paluch, J.; Reichert, M. Distribution of carp edema virus in organs of infected juvenile common carp. J. Vet. Res. 2023, 67, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotny, L. Respiratory Tract Disorders in Fishes. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2021, 24, 267–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheifler, M.; Magnanou, E.; Sanchez-Brosseau, S.; Desdevises, Y. Host specificity of monogenean ectoparasites on fish skin and gills assessed by a metabarcoding approach. Int. J. Parasitol. 2022, 52, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartor, H.; Dahle, M.K.; Gulla, S.; Weli, S.C.; Gjessing, M.C. Emergence of Salmon Gill Poxvirus. Viruses 2022, 14, 2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, M.; Guo, W.; Deng, S.; Liu, H.; Yao, L. Isolation and identification of a new strain Micropterus salmoides rhabdovirus (MSRV) from largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides in China. Aquaculture 2023, 572, 739538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Wu, Y.; Gu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Xie, H.; Qian, S.; Huang, M.; Fei, H.; et al. Infection dynamic of Micropterus salmoides rhabdovirus and response analysis of largemouth bass after immersion infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 139, 108922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazer, E.S.; Massey, K.L.; Curley, S.A. A protocol to effectively create single cell suspensions of adherent cells for multiparameter high-throughput flow cytometry. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2010, 46, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Kao, Y.C.; Ma, H.; Tsay, R.Y. An investigation on the correlation between the mechanical property change and the alterations in composition and microstructure of a porcine vascular tissue underwent trypsin-based decellularization treatment. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 86, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Godoy, R.S.; Cook, D.P.; Scott, A.L.; Nurse, C.A.; Jonz, M.G. Single-cell transcriptomic analysis of neuroepithelial cells and other cell types of the gills of zebrafish (Danio rerio) exposed to hypoxia. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmaratnam, A.; Kumar, R.; Valaparambil, B.S.; Sood, N.; Pradhan, P.K.; Das, S.; Swaminathan, T.R. Establishment and characterization of fantail goldfish fin (FtGF) cell line from goldfish, Carassius auratus for in vitro propagation of Cyprinid herpes virus-2 (CyHV-2). PeerJ 2020, 8, e9373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ager-Wick, E.; Hodne, K.; Fontaine, R.; von Krogh, K.; Haug, T.M.; Weltzien, F.A. Preparation of a High-quality Primary Cell Culture from Fish Pituitaries. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 28, 58159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avalos-Soriano, A.; García-Gasca, A.; Yáñez-Rivera, B. The Development and Evaluation of Brain and Heart Cell Lines from a Marine Fish for Use in Xenobiotic-Induced Cytotoxicity Testing. Altern. Lab. Anim. 2021, 49, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zheng, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Yin, J.; Ren, Y.; Shi, C.; Zhao, Z.; Jiang, Z.; et al. Susceptibilities of ten fish cell lines to infection with Tilapia lake virus. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 166, 105510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, E.B.; Chen, G. Micropterus salmoides rhabdovirus (MSRV) infection induced apoptosis and activated interferon signaling pathway in largemouth bass skin cells. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2018, 76, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xue, M.; Liu, L.; Wang, H.; Qiu, T.; Zhou, Y.; Shan, L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, G.; Hu, Y.; et al. Rhein: A potent immunomodulator empowering largemouth bass against MSRV infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 144, 109284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Shan, L.; Zhu, S.; Liu, G.; Liu, L.; Hu, Y.; Chen, J. Palmatine as a potent immunomodulator: Enhancing resistance to Micropterus salmoides rhabdovirus in largemouth bass through innate immune activation and viral suppression. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 154, 109928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadbent, L.; Villenave, R.; Guo-Parke, H.; Douglas, I.; Shields, M.D.; Power, U.F. In Vitro Modeling of RSV Infection and Cytopathogenesis in Well-Differentiated Human Primary Airway Epithelial Cells (WD-PAECs). Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1442, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettayebi, K.; Crawford, S.E.; Murakami, K.; Broughman, J.R.; Karandikar, U.; Tenge, V.R.; Neill, F.H.; Blutt, S.E.; Zeng, X.L.; Qu, L.; et al. Replication of human noroviruses in stem cell-derived human enteroids. Science 2016, 353, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonin, Y.; Loustalot, F.; Desmetz, C.; Foulongne, V.; Constant, O.; Fournier-Wirth, C.; Leon, F.; Molès, J.P.; Goubaud, A.; Lemaitre, J.M.; et al. Zika Virus Strains Potentially Display Different Infectious Profiles in Human Neural Cells. EBioMedicine 2016, 12, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.T.; Zou, J.; Holland, J.W.; Martin, S.A.; Collet, B.; Kanellos, T.; Secombes, C.J. Identification and characterisation of TLR18-21 genes in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 41, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.K.; Eberwine, J.H. Mammalian cell transfection: The present and the future. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 3173–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene Name | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | GCTATGTGGCTCTTGACTTCGA | CCGTCAGGCAGCTCATAGCT |
| MSRV-G | AAGAGCCCGAGAGAAAAAT | TGAATAGCGGTCCATCAAC |
| IFN1 | ATGAAAACTCAAATGTGGACGTA | GATAGTTTCCACCCATTTCCTTAA |
| ISG15 | GCCTGGTATCACAGACAG | ACATCTTGCACTGACATA |
| Mx1 | ATCTGGTGGATAAGGGAAC | CATCCTCTGTTAATGTGGC |
| Viperin | GCAAAGCGAGGGTTACGAC | CTGCCATTACTAACGATGCTGAC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Nie, L.; Fei, C.; Chen, J. Establishment of Gill-Derived Primary Cell Cultures from Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) as an Alternative Platform for Studying Host–Virus Interactions. Fishes 2025, 10, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10010018
Wang Z, Nie L, Fei C, Chen J. Establishment of Gill-Derived Primary Cell Cultures from Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) as an Alternative Platform for Studying Host–Virus Interactions. Fishes. 2025; 10(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10010018
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ziwen, Li Nie, Chenjie Fei, and Jiong Chen. 2025. "Establishment of Gill-Derived Primary Cell Cultures from Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) as an Alternative Platform for Studying Host–Virus Interactions" Fishes 10, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10010018
APA StyleWang, Z., Nie, L., Fei, C., & Chen, J. (2025). Establishment of Gill-Derived Primary Cell Cultures from Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) as an Alternative Platform for Studying Host–Virus Interactions. Fishes, 10(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10010018







