Abstract
Security in wireless sensor networks is commonly based on symmetric encryption and requires key-management systems to establish and exchange secret keys. A constraint that is common to many key-management approaches is an upper bound to the total number of nodes in the network. An example is represented by the schemes based on combinatorial design. These schemes use specific rules for the generation of sets of keys that are distributed to the nodes before deploying the network. The aim of these approaches is to improve the resilience of the network. However, the quantity of data that must be stored by each node is proportional to the number of nodes of the network, so the available memory affects the applicability of these schemes. This paper investigates the opportunity of reducing the storage overhead by distributing the same set of keys to more than one node. In addition, the presence of redundant sets of keys affects the resilience and the security of the network. A careful analysis is conducted to evaluate benefits and drawbacks of redundant key distribution approaches. The results show that the use of redundancy decreases the level of resilience, but it scales well on very large networks.
1. Introduction
A Wireless Sensor network (WSN) is a distributed computer network. The nodes that compose the WSN are autonomous devices which can collect data from the surrounding environment, perform some elaborations and communicate wirelessly with the other nodes of the network. The typical nodes are low-cost devices with limited power and computational capabilities. WSNs are currently applied in many fields, from military applications [1] to cold chain monitoring [2,3].
Symmetric cryptography is normally used to protect the communications. Since WSNs have specific characteristics, such as low computational capabilities and a large quantity of autonomous distributed nodes, they require specific key-management schemes to generate and distribute the keys used to encrypt and/or authenticate the messages. Although there exist lightweight public key schemes [4], they are only applied if the involved devices are considered compliant with the additional overhead [5,6].
In literature, many key-management schemes based on different approaches have been proposed. Any kind of approach involves benefits and drawbacks that are compliant with specific characteristics (e.g., mobile nodes and deployment knowledge). Many approaches are based on predeployment key distribution. Some of these schemes involve a memory overhead proportional to the number of nodes in the network. Therefore, the size of available memory involves an upper bound to the maximum number of nodes in the network. An opportunity to remove this threshold is represented by the distribution of redundant sets of keys. i.e., the same set distributed to multiple nodes. For example, the network could be divided in two parts. A complete distribution is done among one half of the nodes, while each node of the other part has the copy of a set from one node of the first part. In this way the size of the network is the double, with the same memory overhead. In this paper, the predeployment distribution approaches are investigated and they are extended with the concept of security. The differences and similarities of the various approaches are analyzed to identify their effects on resilience. The results show that the use of redundancy decreases the level of resilience, but it scales well on very large networks.
2. Related Works
In this section, a brief description of the main state-of-the-art approaches is presented. For a more in-depth description it is possible to read existing surveys on key distribution in WSNs [7,8].
2.1. Global Key
In the class of schemes, based on a global key, all nodes share a master key that is used to establish the final pairwise keys.
Besides PGK, the main scheme based on a global master key is the Symmetric-key key establishment, which is adopted by ZigBee (ZigBee Specification 1.0, June 2005, ZigBee Alliance). In this scheme, a node A, with identification number ID, starts the key establishment by sending a random number (C). To generate a common secret, a node B with identification number ID, after receiving the initial message, computes a new random number (C) and executes a keyed hash function with the global master key on the concatenation of the subsequent data: ID, ID, C and C. After generating the common secret, node B executes a hash function on this secret to generate the pairwise key. Then, node B sends back its identifier ID, the random number C and the Message authentication code (MAC), calculated on the concatenation of the subsequent data: a constant number , ID, ID, C and C. Then, node A calculates the pairwise key, checks the MAC and sends to node B a new MAC generated from the same data concatenated to a second constant number .
2.2. Full Pairwise Keys
In the full pairwise keys scheme (FPWK) all the keys are distributed before deployment, and no additional operation is required. Each possible link has a specific key, so each node stores a key per each other node in the network.
2.3. Random Key Predistribution Approaches
Random key predistribution basically consists in the generation of a large quantity of secret material and in the random distribution of a part of this material to each node. The first random key predistribution approach has been proposed by Eschenauer and Gligor [9]. In this approach, a pool containing keys is generated before deployment. Then, a ring containing r keys, that are randomly selected from the pool, is picked up by each node. During the network initialization, each node checks if there are shared keys with other neighboring nodes. The values of and r determine the probability of establishing a link between two nodes and the quantity of secret keys that an adversary can obtain by compromising a node.
A subsequent scheme based on random key predistribution is the q-composite random key predistribution [10]. With this scheme two nodes must share at least q starting keys to establish a link. They generate a pairwise key by performing a hash function on the concatenation of all shared starting keys. The main drawback of q-composite random key predistribution with respect to the scheme proposed by Eschenauer and Gligor is the larger quantity of memory required.
2.4. Combinatorial Design
In combinatorial design [11], and in particular in block design, it is possible to generate sets of elements that respect specific properties. These sets of elements can be used for various applications such as cryptography.
In the key-management schemes based on block design, the elements correspond to the keys and the sets correspond to the rings assigned to the nodes. Among block design a class often used for key management is the Symmetric Balanced Incomplete Block Design (SBIBD). This strategy allows to generate sets of keys with the following characteristics:
- a pool is composed of keys,
- the number of rings of keys, which corresponds to the maximum number of nodes, corresponds to ,
- each ring is composed by r keys,
- the same key is present in r rings, so it is shared by r nodes,
- the same set composed by more than one key cannot be present in more than one block.
Many papers adopt combinatorial design and in particular SBIBD for key management. A detailed description is included in [12]. In [13,14], the application of SBIBD and Generalized Quadrangles to key management is investigated and a hybrid proposal was presented. Srinivasa et al. [15] proposed an approach based on SBIBD and multiple key-space. Lee and Stinson [16] used Transversal designs. Ruj and Roy [17] used partially BIBDs, while Bechkit et al. [18] used unital design. In [19], Ruj et al. also managed the triple key distribution that protects against malicious nodes forwarding fake messages.
3. Redundant Key Management
PGK, FPWK and combinatorial design schemes can be defined deterministic schemes with predeployment key distribution. In this general approach, sets of keys are distributed to the nodes according to specific rules. The presence of redundant sets, distributed to more than one node, depends on the adopted strategy. However, all these options can be considered as specific configurations of the deterministic predeployment key distribution.
In the deterministic predeployment key distribution, the set of r keys loaded by a node is defined ring, while the set of all the keys in the network is defined pool. There are two kinds of redundancy: one related to the individual keys and another one to the rings. The redundancy of a key () corresponds to the quantity of nodes that know that key, while the redundancy of a ring () corresponds to the quantity of nodes that have that identical ring. The possible values of are between 2 and the number of nodes n. The values of are between 1 and n.
In PGK, there is only one key. This scheme corresponds to the deterministic predeployment key distribution with , , and . This configuration has the minimum quantity of keys and the maximum value of redundancy.
In FPWK there is a key per link. Therefore, the configuration is , , and . This configuration has the maximum quantity of keys and the minimum redundancy. However, FPWK requires that each node stores a quantity of keys equal to the size of the network. Therefore, the limit to the memory available for key storing also represents a limit for the number of nodes in the network.
The intermediate solutions between the global key scheme and FPWK can be obtained by applying ring redundancy to the latter scheme. If each ring, which is unique in FPWK, is loaded by two nodes, the new configuration is , , and . More in general, in the deterministic predeployment key distribution with ring redundancy , the parameters are:
and
A relevant element of the previous configuration corresponds to (3). This formula implies that each key is only included in two rings, and the whole redundancy depends on . Therefore, this configuration is called the minimum key redundancy configuration.
The schemes based on combinatorial design have key redundancy and no ring redundancy. Since , a scheme based on SBIBD corresponds to the deterministic predeployment key distribution with , , and . However, as with for FPWK, the total number of nodes in the network affects the size of the ring. Therefore, the maximum size of the storage available for the keys represents a limit to the size of the network.
The intermediate cases between combinatorial design and the global master key are characterized by equations that depend on specific combinatorial design strategy. With the SBIBD strategy, in the deterministic predeployment key distribution with ring redundancy , the parameters are:
and
4. Analysis and Evaluation
This section analyzes the properties of deterministic predeployment key distribution according to its configurations.
We shall assume that an adversary can perform a replay attack and eavesdrop on all the links of the network. An adversary can also capture a node and find all the secret information from its memory.
4.1. Resilience
One of the greatest risks in a WSN is that some nodes are compromised, and their secret material is used to attack other nodes. The strength of a scheme against this attack is called resilience. In particular, it is of special interest the resilience against eavesdropping, which is evaluated according to the quantity of links that an adversary can eavesdrop after compromising a specific amount of nodes.
The quantity of links that can be eavesdropped by an adversary with one key, is always . This value represents the quantity of links based on each key. The equations are more complicated if some nodes with their rings are compromised. The equations must consider how many keys can be present in more than one compromised ring, and that the links of the compromised nodes are no longer active and so they must not be considered. The formulas to compute the probability that a link is compromised, i.e., the average percentage of compromised links, in the deterministic predeployment key distribution scheme are (7) and (8), for the minimum key redundancy and for SBIBD configuration, respectively. With the introduction of redundancy, it is possible that an adversary compromises identical nodes. However, only different rings provide new secret material to the adversary. Therefore, by considering x compromised nodes, both formulas start with a summation from to which represents the minimum and the maximum quantity of compromised rings (k), respectively. In fact, corresponds to the quantity of nodes with the same ring. The first part inside the summation represents the probability that exactly k rings are compromised. It is computed as . The denominator of this fraction () represents the number of possible groups of x compromised nodes. The first binomial represents the number of possible groups of k different rings. The second element of the numerator computes the number of possible groups of x nodes with k different rings among the nodes that share those rings. This result is computed as a difference. Since this formula does not guarantee that at least a node per ring is present, the subtrahend is the summation of all the possible groups of x nodes that are included in less than k rings. The summation is alternatively positive and negative since each superior group redundantly includes all the smaller groups. The result of the described part of the formulas represents the probabilistic weight that will be multiplied by the corresponding quantity of compromised links. Therefore, always considering one compromised link, the results of (7) and (8) would be 1.
The subsequent part of the formulas depends on the considered scheme. With the minimum key redundancy configuration, represents the quantity of not-compromised nodes with a ring identical to a compromised one. Each of these nodes has possible links with a node with a not-compromised ring. All these links are compromised. Moreover, all the links among the not-compromised nodes with a compromised ring are compromised. Finally, computes the quantity of links among the nodes with the same ring that randomly selected a compromised key. In details, the quantity of not-compromised rings is multiplied by the number of links per ring , multiplied by the quantity of compromised keys per ring k, divided by the quantity of keys per ring . The final result is divided by which is the number of links among all the not-compromised nodes.
The first part of (8) is identical to the first part of (7). Also in this case the second part, on the second line, computes the number of compromised links.
The index of the initial summation is i, which represents the quantity of keys not compromised by the adversary. The part of the formula on the second line computes the probability that i has a specific value. The minimum value corresponds to , since the quantity of different rings and since with k compromised rings, the maximum number of compromised keys is the minimum between and , which represents the number of keys compromised by a set rings that share the same key (i.e., among all the compromised keys only one is repeated, and the number of different keys is maximum). The maximum value is (), which corresponds to the number of not-compromised keys when one ring is compromised. The first fraction within the summation computes the probability of the current value of i. The numerator is which is a function that computes the quantity of groups of k compromised rings compliant with i not-compromised keys. This value is divided by the total quantity of groups of k compromised rings. The value of function is computed through tables. The tables for are reported in Appendix A. The last part of the formula is the fraction of compromised links. The denominator computes the number of possible links between not-compromised nodes. The first part of the numerator is the total quantity of links multiplied by the number of compromised keys and divided by the total number of keys . The result corresponds to the quantity of compromised links, but it also counts the links with compromised nodes. Therefore, the links of the x compromised nodes, minus the links among the compromised nodes that would be counted two times, are subtracted.
4.2. Experimental Analysis
To provide a clear idea of the properties of the deterministic predeployment key distribution, the resilience of some configurations has been computed and plotted.
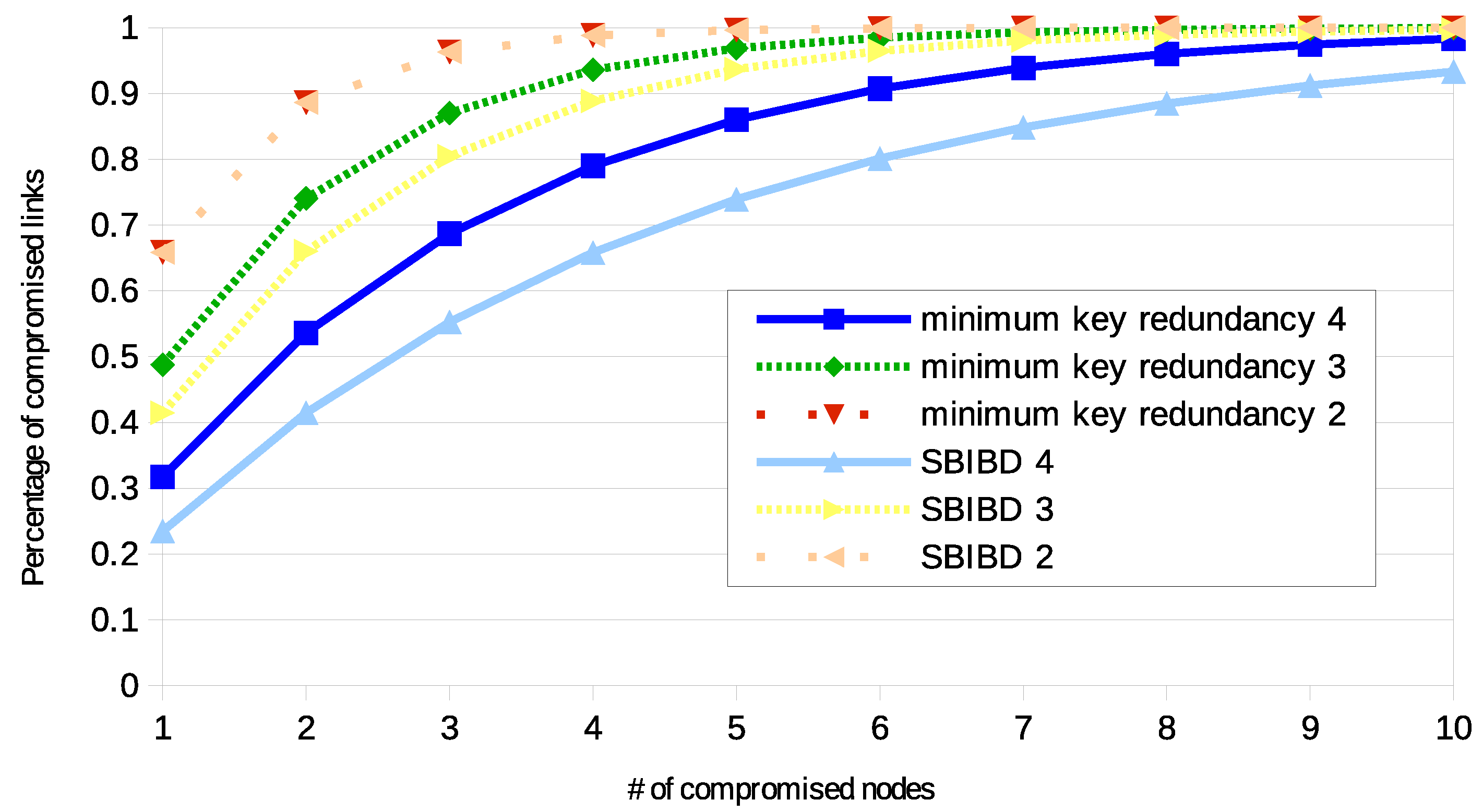
Figure 1 shows the level of resilience for a network composed by 84 nodes. The number 84 was selected since it is perfectly compliant with all the tested configurations. Each curve represents a configuration. The graph shows the [0,1] ratio of compromised links according to the number of compromised nodes. As expected, for all the curves, as the number of compromised nodes increases, the ratio of compromised links increases too. The continuous lines are referred to configurations with , fine dots are referred to , while sparse dots . The ring redundancy is computed according to r and n. Both for the minimum key redundancy and for SBIBD configuration, as r increases the ratio of compromised links decreases. By comparing the minimum key redundancy configuration to SBIBD configuration, it is observed that SBIBD always provides a better level of resilience. Only when the two curves are identical. However, this is a special case, such as for , since both the approaches generate the same key distribution.
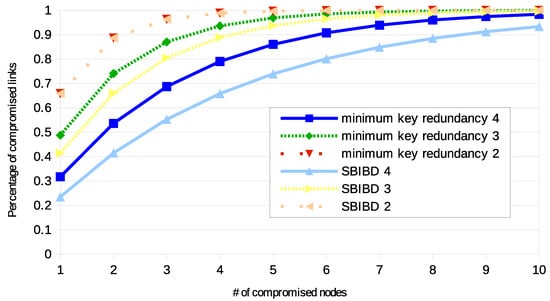
Figure 1.
Resilience of the two approaches with specific numbers of keys per ring (written in the label), with 84 nodes.
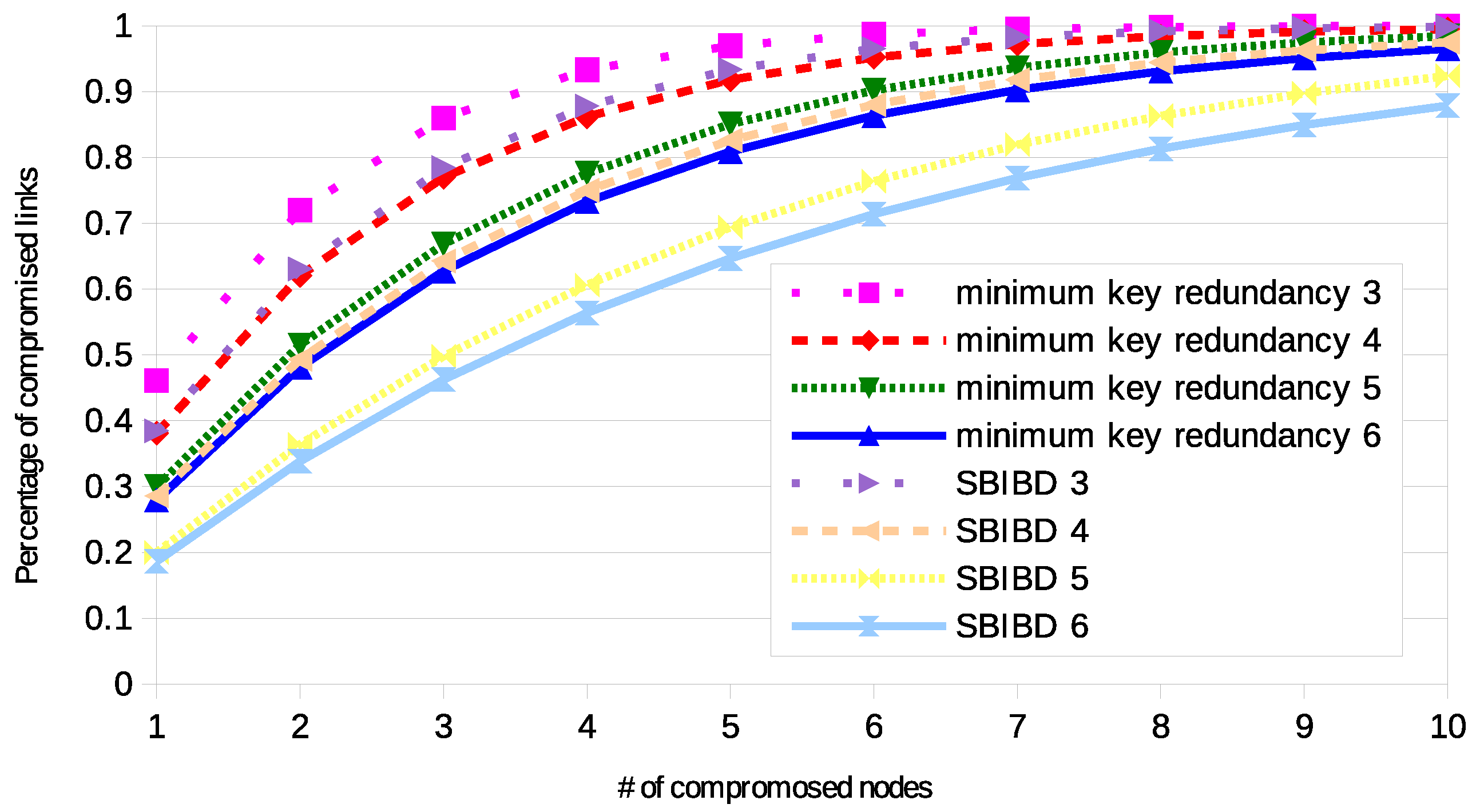
A representation similar to the previous one is presented in Figure 2. However, in this case, the size of the network is not constant. For each value of r, the minimum value of n compliant with the two approaches was selected. Therefore, it is not possible to directly compare the configurations with different values of r. However, it is possible to observe that all the general properties showed by the previous chart are confirmed.
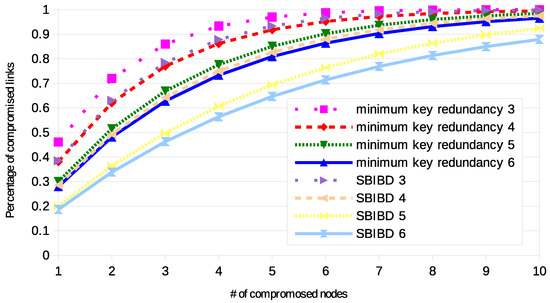
Figure 2.
Resilience with various networks, of the two approaches with specific numbers of keys per ring (written in the label).
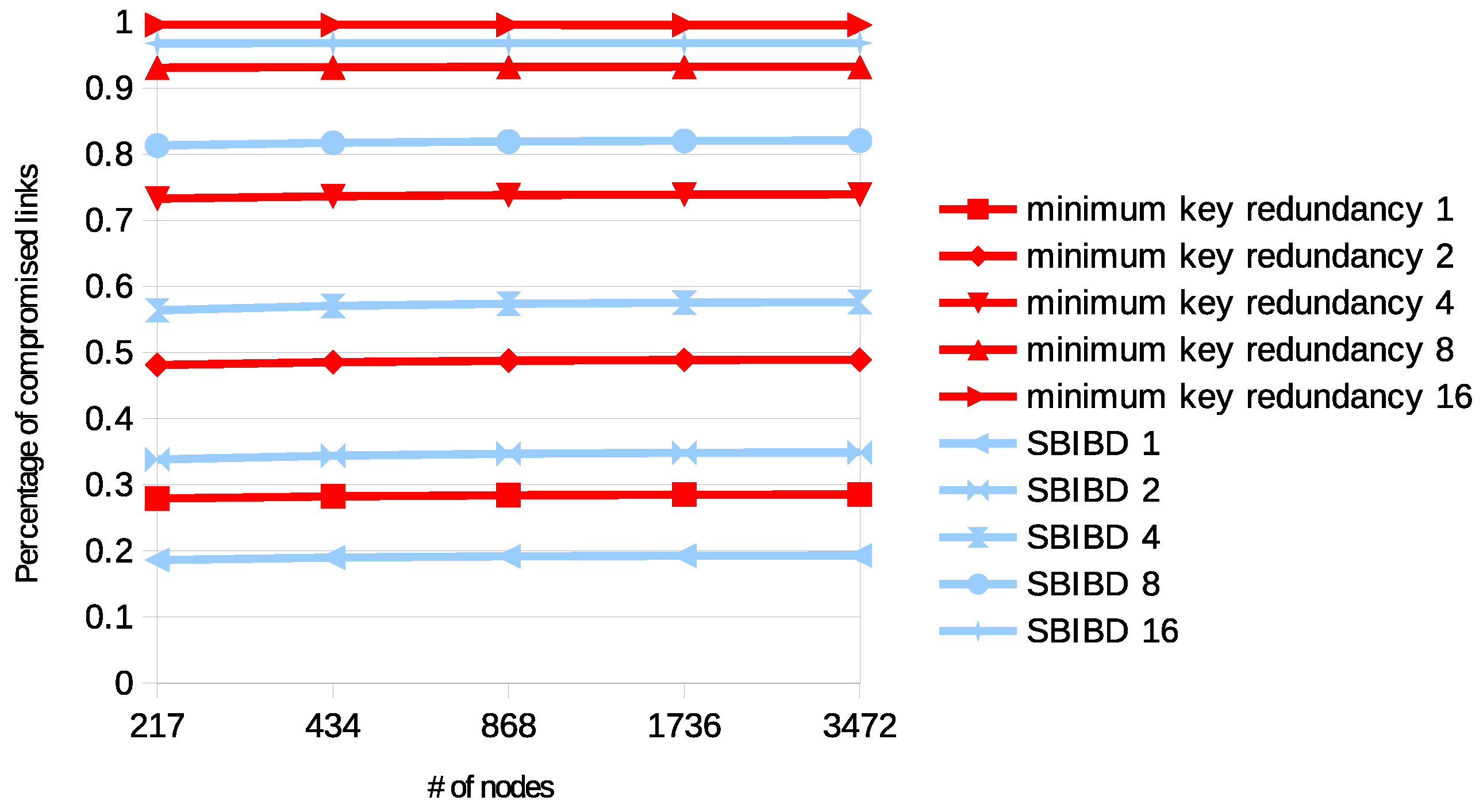
The resilience provided by a configuration with a fixed value of r on networks with various sizes is shown in Figure 3. Each curve is matched to a distribution strategy and to a specific number of compromised nodes. The graph shows the [0,1] ratio of compromised links according to the number of nodes in the network. It is observed that the size of the network only provides a slight decrease in the resilience, while each curve is quite stable.
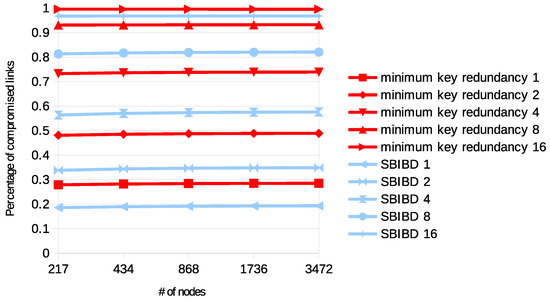
Figure 3.
Resilience with various networks, of the two approaches with 6 keys per ring according to specific numbers of compromised nodes (written in the label).
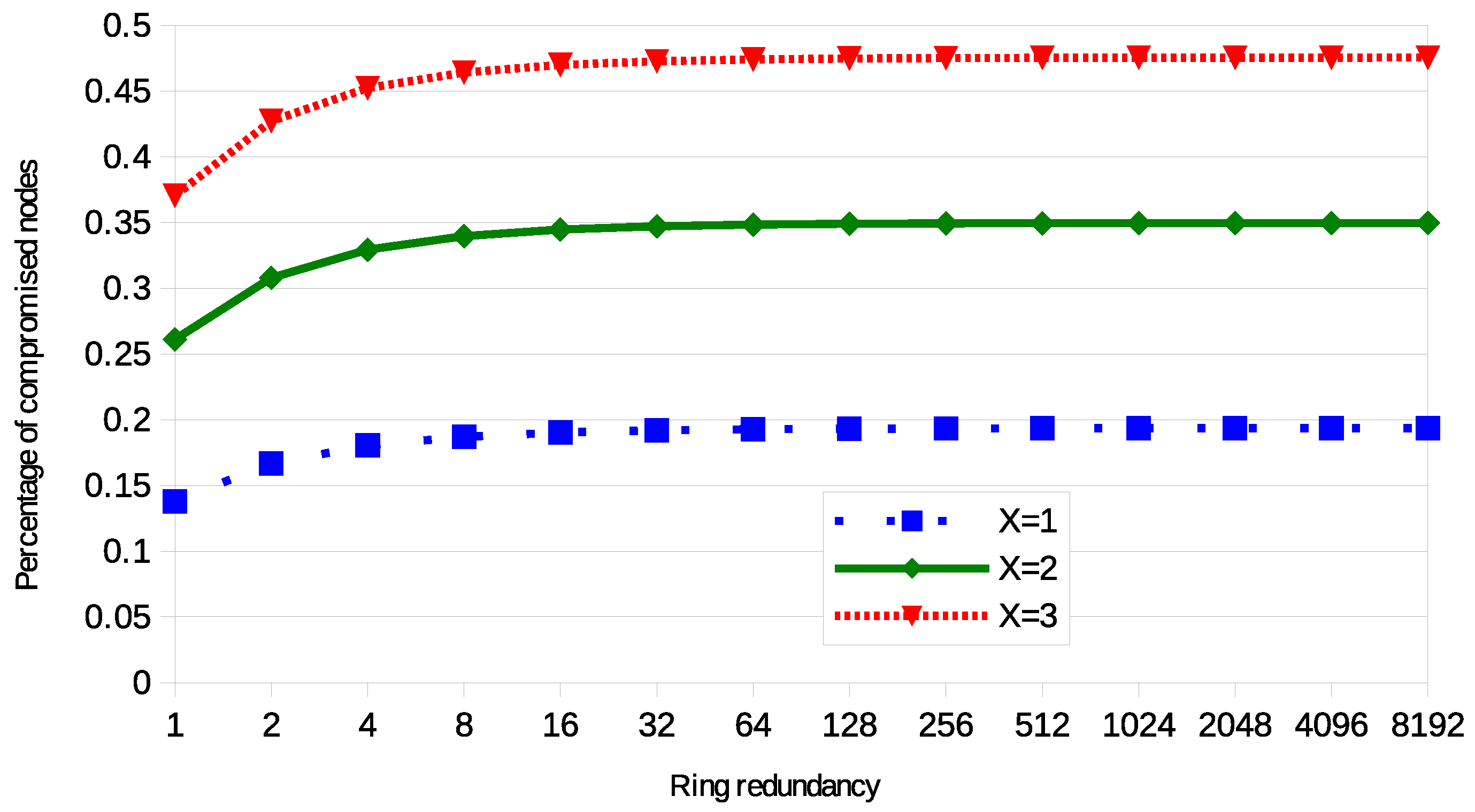
To provide a whole overview on the contribution of r and on the resilience, Figure 4 shows the [0,1] ratio of compromised links according to the value of . When the values of are very low, there is a visible variation in the level of resilience. However, the ratio of compromised links increases always more slowly and for high value of the difference is negligible. This result is because of the links of the compromised nodes. These links are considered not existing, since they are no more used by the nodes of the network, but they cannot be eavesdropped, since the adversary directly use them. When is high, the adversary gains an advantage by eavesdropping on all the links of the nodes identical to the compromised ones. However, if is small, the relative weight of the links of the compromised nodes is higher, and the other identical nodes are lower.
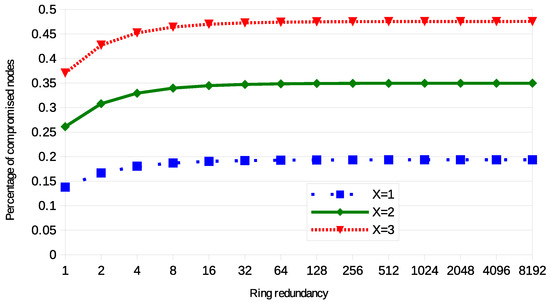
Figure 4.
Resilience with various networks, of SBIBD with 6 keys per ring with X compromised nodes.
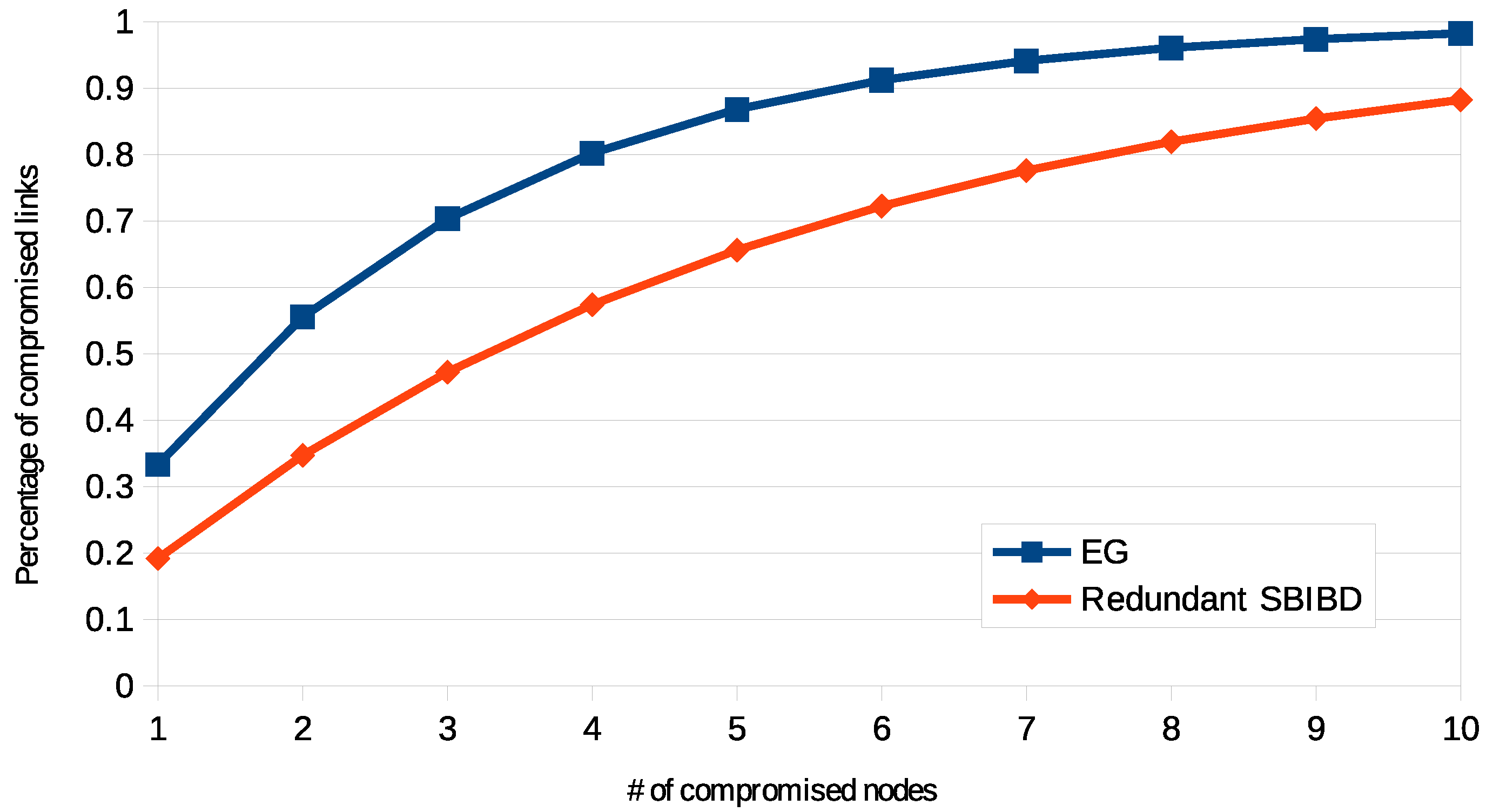
To evaluate the performance of a redundant scheme within the key-management scenario, SBIBD with is compared to EG with the same ring size. EG does not guarantee a full connectivity, since some nodes could share no common keys, so its connectivity is imposed higher than 0.99. In order to reach this connectivity level the value of p must be properly set. The formula that computes the connectivity of EG is (9).
According to the configuration of EG that guarantees the best resilience is , while in redundant SBIBD . By using the formula of resilience for EG presented in [20] it is possible to compare these schemes. The comparison is shown in Figure 5. It is possible to observe that the redundant scheme provides a better level of resilience.
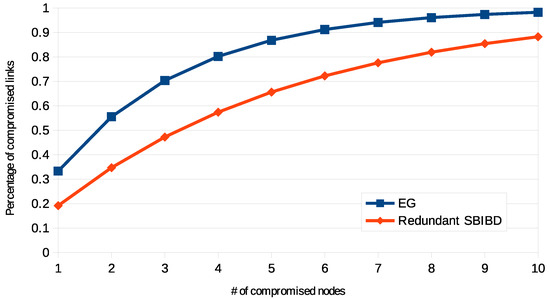
Figure 5.
Resilience with various networks, of SBIBD with 6 keys per ring with X compromised nodes.
4.3. Validation
A simulator has been developed to validate the proposed formulas. The simulator generates a set of rings of keys compliant with the requirements. Then, it randomly selects a specific quantity of nodes that are considered compromised. Finally, some links are checked to verify if the keys that they use are compromised.
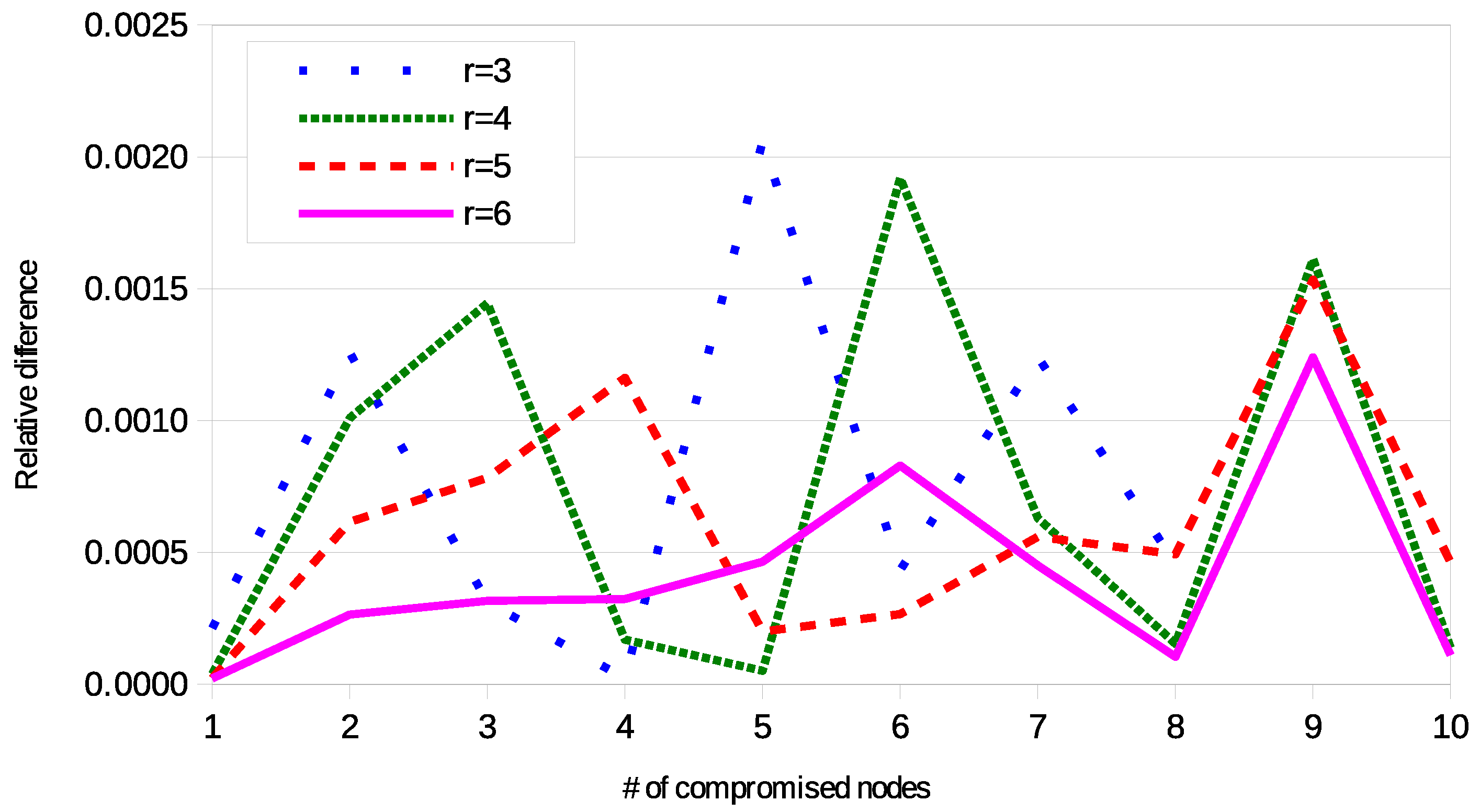
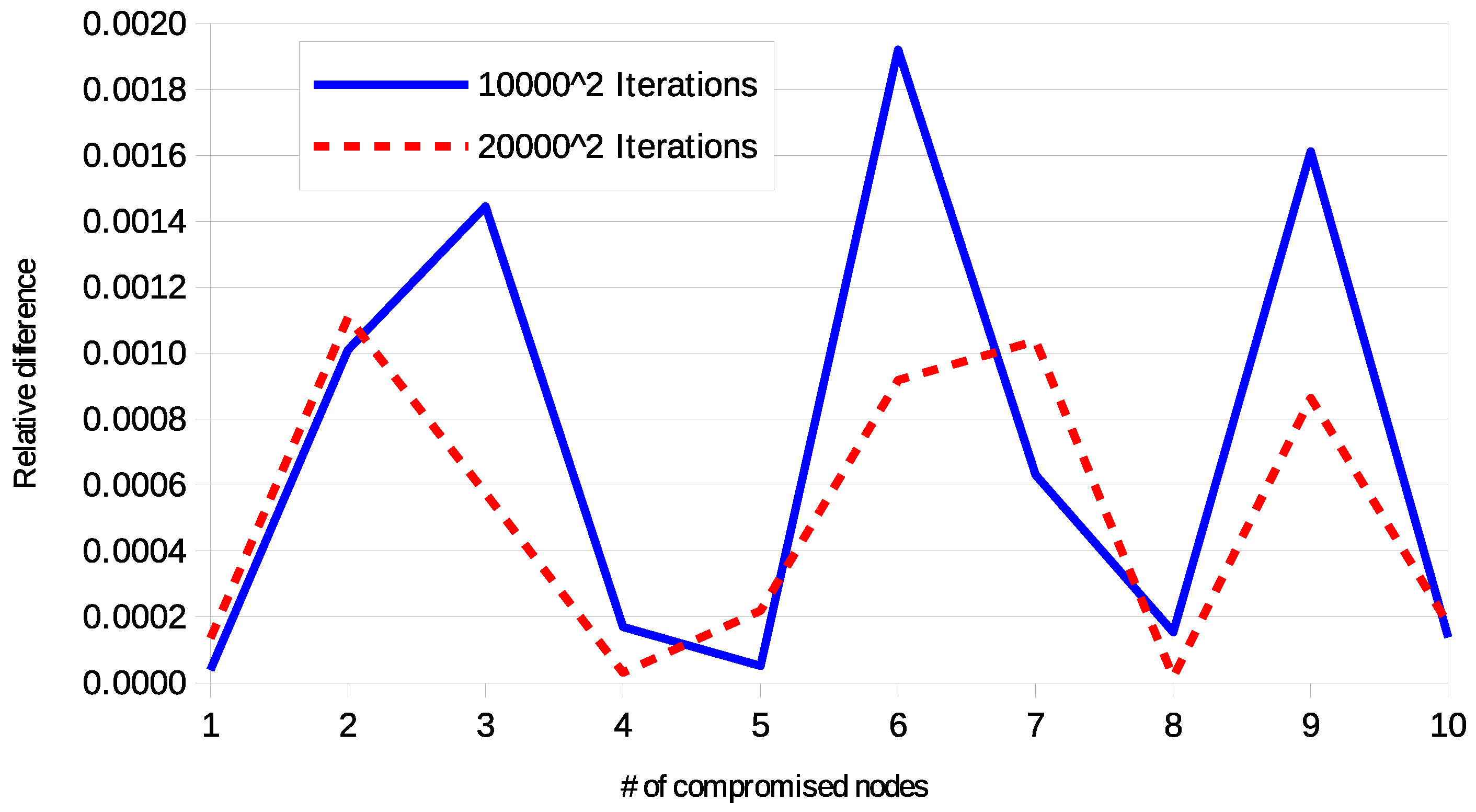
In particular, for every tested configuration sets of rings have been selected and links per selected set have been checked. The results validated the correctness of the formulas. Figure 6 shows some examples of comparison between the results provided by the theoretical formulas and the simulations. The relative difference is always lower than , and it is attributed to the statistical error. As a further proof, Figure 7 compares the curve obtained with , with the same configuration, but in this case the double of the sets of rings are selected and the double of the links per set are selected. It is possible to observe that the new curve is not steady, but the picks are strongly reduced.
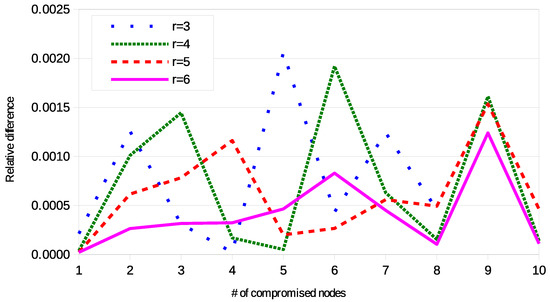
Figure 6.
Relative difference between theoretical formulas and simulations.
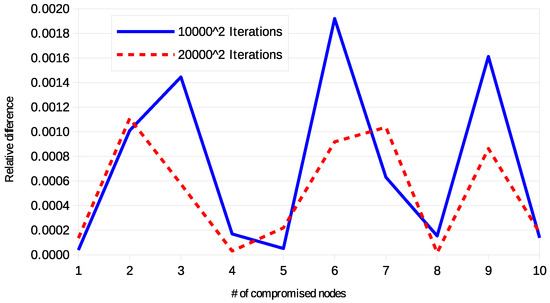
Figure 7.
Relative difference between theoretical formulas and simulations with r = 4.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, an investigation on the use of redundancy for key management in WSNs has been presented. Thanks to redundancy, an upper bound to the maximum quantity of nodes due to memory limit can be broken. The analysis provided analytical formulas to compute the effects of redundancy on resilience. Moreover, the proposed formulas can be also applied without redundancy. The correctness of the results has been validated through simulations. The analysis also showed that the minimum key redundancy configuration provides a lower level of resilience with respect to the SBIBD configuration. The initial increase of the level of redundancy produces a decrease in the resilience, but then the level becomes stable. Therefore, the redundant schemes scale well on very large networks.
Author Contributions
F.G. provided the main idea and conducting the research and investigation process. B.M. worked on the writing and editing of the paper, while M.R. supervised the whole activity.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| WSN | Wireless sensor network |
| PGK | Plain global key scheme |
| FPWK | Full pairwise keys scheme |
| SBIBD | Symmetric Balanced Incomplete Block Design |
Appendix A. Tables
The tables in this appendix correspond to formula . Each table reports the quantity of groups of k compromised rings compliant with i not-compromised keys for a specific value of r. Table A1, Table A2 and Table A3, correspond to , and , respectively. To improve the layout, the case with is split in two tables, Table A4 and Table A5. A small part of the last two tables is repeated.

Table A1.
r = 3.
Table A1.
r = 3.
| k ∖ i | 1 | 0 |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 28 | 7 |
| 4 | 7 | 28 |

Table A2.
r = 4.
Table A2.
r = 4.
| k ∖ i | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 234 | 52 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 0 | 234 | 468 | 0 | 13 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 468 | 702 | 117 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 78 | 936 | 702 |
| 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 468 | 1248 |
| 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 117 | 1170 |
| 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 702 |

Table A3.
r = 5.
Table A3.
r = 5.
| k ∖ i | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 1120 | 210 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 2520 | 3360 | 0 | 105 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1008 | 10,080 | 7560 | 1680 | 0 | 0 | 21 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 168 | 0 | 18,480 | 22,680 | 12,600 | 0 | 336 |
| 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2520 | 31,920 | 55,440 | 23,520 | 2880 |
| 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10,290 | 73,080 | 93,240 | 26,880 |
| 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1120 | 42,840 | 151,200 | 98,770 |
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13,860 | 140,448 | 198,408 |
| 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2520 | 86,688 | 263,508 |
| 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 210 | 37,800 | 255,920 |
| 13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11,760 | 191,730 |
| 14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2520 | 113,760 |
| 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 336 | 53,928 |
| 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 21 | 20,328 |
The rows of the tables corresponding to low values and high values of k are not reported. If , independently from the compromised ring, then . If , independently from the pair of compromised nodes, then . If the value of k is higher than the values reported in the tables, then .
As an example, we shall observe Table A1, corresponding to . If 3 rings are compromised, then among the 35 possible combinations of 3 rings over 7, there are 28 combinations of rings that involve one not-compromised key, and 7 combinations of rings that involve zero not-compromised keys.

Table A4.
r = 5, part I.
Table A4.
r = 5, part I.
| k ∖ i | 16 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 3875 | 620 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15,500 | 15,500 | 0 | 465 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 18,600 | 93,000 | 46,500 | 11,625 | 0 | 0 | 186 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3100 | 62,000 | 325,500 | 232,500 | 108,500 | 0 |

Table A5.
r = 5, part II.
Table A5.
r = 5, part II.
| k ∖ i | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 325,500 | 232,500 | 108,500 | 0 | 4650 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 31 |
| 7 | 46,500 | 434,000 | 1,100,500 | 744,000 | 257,300 | 46,500 | 0 | 0 | 775 |
| 8 | 0 | 46,500 | 697,500 | 2,522,625 | 2,938,800 | 1,302,000 | 372,000 | 0 | 9300 |
| 9 | 0 0 | 0 | 93,000 | 1,441,500 | 5,894,650 | 7,579,500 | 4,185,000 | 879,625 | 86,800 |
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 3100 | 279,000 | 4,014,965 | 13,981,000 | 17,042,250 | 7,830,600 | 1,201,250 |
| 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 18,600 | 1,302,000 | 12,378,300 | 32,968,500 | 29,806,500 | 8,198,415 |
| 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 217000 | 6,466,600 | 37,874,250 | 65,193,000 | 31,369,675 |
| 13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15,500 | 2,173,100 | 29,434,500 | 95,759,000 | 78,870,975 |
| 14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 474,300 | 16,600,500 | 103,555,500 | 144,552,225 |
| 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 62,620 | 7,021,500 | 87,100,700 | 206,355,375 |
| 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3875 | 2,241,300 | 58,838,000 | 239,457,020 |
| 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 530,100 | 32,468,625 | 232,183,800 |
| 18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 88,350 | 14,725,000 | 191,439,725 |
| 19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9300 | 5,471,500 | 135,639,725 |
| 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 465 | 1,646,100 | 83,025,750 |
| 21 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 392,150 | 43,960,015 |
| 22 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 71,300 | 20,088,775 |
| 23 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9300 | 7,879,425 |
| 24 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 775 | 2,628,800 |
| 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 31 | 736,250 |
References
- Ball, M.G.; Qela, B.; Wesolkowski, S. A Review of the Use of Computational Intelligence in the Design of Military Surveillance Networks. In Recent Advances in Computational Intelligence in Defense and Security; Abielmona, R., Falcon, R., Zincir-Heywood, N., Abbass, H.A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 663–693. [Google Scholar]
- Badia-Melis, R.; Ruiz-Garcia, L.; Garcia-Hierro, J.; Villalba, J.I.R. Refrigerated Fruit Storage Monitoring Combining Two Different Wireless Sensing Technologies: RFID and WSN. Sensors 2015, 15, 4781–4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Matetić, M.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, X.; Jemrić, T. Postharvest Quality Monitoring and Variance Analysis of Peach and Nectarine Cold Chain with Multi-Sensors Technology. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, R.; Caballero-Gil, C.; Santonja, J.; Zamora, A. Algorithms for Lightweight Key Exchange. Sensors 2017, 17, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, K. A Survey of Public-Key Cryptographic Primitives in Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 18, 577–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandino, F.; Celozzi, C.; Rebaudengo, M. A Key Management Scheme for Mobile Wireless Sensor Networks. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simplício, M.A., Jr.; Barreto, P.S.; Margi, C.B.; Carvalho, T.C. A survey on key management mechanisms for distributed Wireless Sensor Networks. Comput. Netw. 2010, 54, 2591–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Niedermeier, M.; de Meer, H. Dynamic key management in wireless sensor networks: A survey. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2013, 36, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschenauer, L.; Gligor, V. A key-management scheme for distributed sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 9th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security, CCS ’02, Washington, DC, USA, 18–22 November 2002; pp. 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.; Perrig, A.; Song, D. Random key predistribution schemes for sensor networks. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Security and Privacy, Berkeley, CA, USA, 11–14 May 2003; pp. 197–213. [Google Scholar]
- Colbourn, C.J.; Dinitz, J.H. Handbook of Combinatorial Designs; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, K.M. On the Applicability of Combinatorial Designs to Key Predistribution for Wireless Sensor Networks. In Coding and Cryptology; Chee, Y.M., Li, C., Ling, S., Wang, H., Xing, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 124–145. [Google Scholar]
- Çamtepe, S.A.; Yener, B. Combinatorial Design of Key Distribution Mechanisms for Wireless Sensor Networks. In Computer Security—ESORICS 2004; Samarati, P., Ryan, P., Gollmann, D., Molva, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 293–308. [Google Scholar]
- Camtepe, S.A.; Yener, B. Combinatorial Design of Key Distribution Mechanisms for Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2007, 15, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasa, K.G.; Poornima, V.; Archana, V.; Reshma, C.; Venugopal, K.R.; Patnaik, L.M. Combinatorial Approach to Key Generation using Multiple Key Spaces for Wireless Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of the 2008 16th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communications, Chennai, India, 14–17 December 2008; pp. 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Stinson, D.R. A combinatorial approach to key predistribution for distributed sensor networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, New Orleans, LA, USA, 13–17 March 2005; Volume 2, pp. 1200–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruj, S.; Roy, B. Key Predistribution Using Partially Balanced Designs in Wireless Sensor Networks. In Parallel and Distributed Processing and Applications; Stojmenovic, I., Thulasiram, R.K., Yang, L.T., Jia, W., Guo, M., de Mello, R.F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 431–445. [Google Scholar]
- Bechkit, W.; Challal, Y.; Bouabdallah, A.; Tarokh, V. A Highly Scalable Key Pre-Distribution Scheme for Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2013, 12, 948–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruj, S.; Nayak, A.; Stojmenovic, I. Pairwise and Triple Key Distribution in Wireless Sensor Networks with Applications. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2013, 62, 2224–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandino, F.; Ferrero, R.; Rebaudengo, M. A Key Distribution Scheme for Mobile Wireless Sensor Networks: q - s -Composite. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2017, 12, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).