- Review
Cryptographic Foundations of Pseudonymisation for Personal Data Protection
- Konstantinos Limniotis
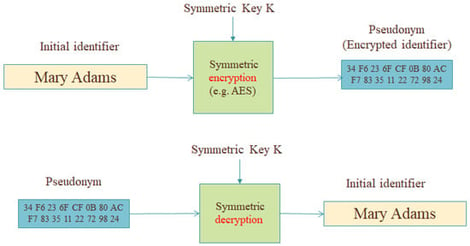
Pseudonymisation constitutes an essential technical and organisational measure for implementing personal data-protection safeguards. Its main goal is to hide identities of individuals, thus reducing data protection and privacy risks through facilitating the fulfilment of several principles such as data minimisation and security. However, selecting and deploying appropriate pseudonymisation mechanisms in a risk-based approach, tailored to the specific data processing context, remains a non-trivial task. This survey paper aims to present especially how cryptography can be used at the service of pseudonymisation, putting emphasis not only on traditional approaches but also on advanced cryptographic techniques that have been proposed to address special pseudonymisation challenges. To this end, we systematically classify existing approaches according to a taxonomy that captures key design dimensions that are relevant to specific data-protection challenges. Finally, since the notion of pseudonymisation adopted in this work is grounded in European data-protection law, we also discuss recent legal developments, in particular the CJEU’s latest judgment, which refined the interpretation of pseudonymous data.
11 March 2026