Identification and Quantitation of 14C-Labeled Catechol Metabolites in Rat Plasma After Intranasal Instillation of Smoldering Eucalyptus Wood Smoke Extract
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Smoldering Eucalyptus Wood Smoke Extracts
2.3. Animals
2.4. Animal Exposures
2.5. Plasma Preparation
2.6. Parallel Accelerator and Molecular Mass Spectrometry
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. 14C-Labeled Compound Identification
| Formula | [M-H]− | m/z Delta | RDB | Combined Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C9H17O5N | 218.1034 | 0.0000 | 2.0 | 84.52 |
| C8H11N8 | 218.1034 | 0.0000 | 7.5 | 83.83 |
| C10H21NS2 | 218.1043 | −0.0009 | 1.0 | 82.51 |
| H15O2N10S | 218.1027 | 0.0007 | −1.5 | 74.93 |
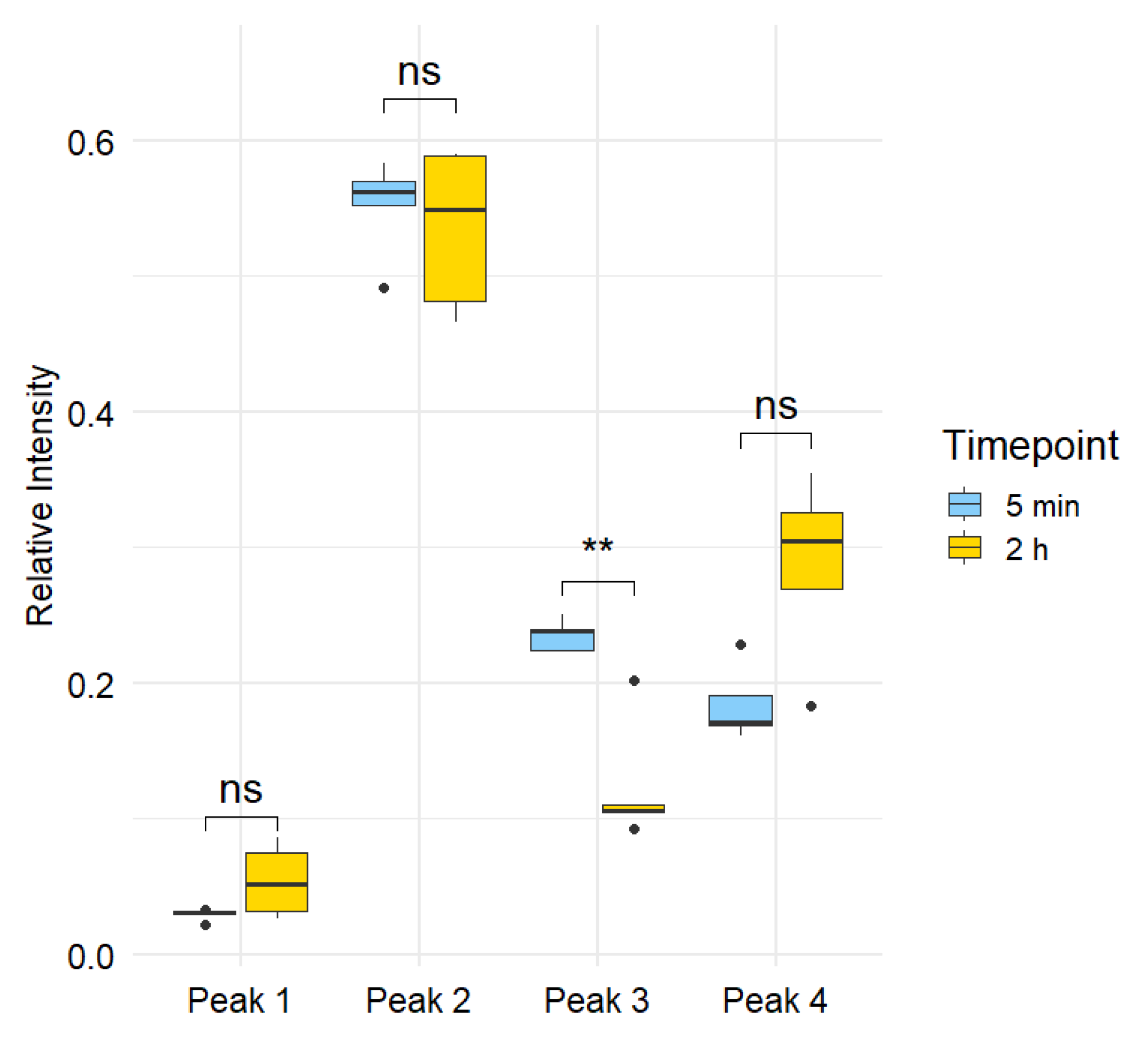
3.2. Differential Metabolite Expression
3.3. Summary
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAALAC | Association for Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care |
| ADME | Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism and Excretion |
| AMS | Accelerator Mass Spectrometry |
| APCI | Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization |
| AUC | Area Under Curve |
| CID | Collision-Induced Dissociation |
| ECD | Electron Capture Dissociation |
| EIC | Extracted Ion Chromatogram |
| EPA | Environmental Protection Agency |
| ETD | Electron Transfer Dissociation |
| FDR | False Discovery Rate |
| HCD | Higher-Energy Collision-Induced Dissociation |
| HESI | Heated Electrospray Ionization |
| HR | High-Resolution |
| IACUC | Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee |
| IRMPD | Infrared Multiphoton Dissociation |
| LC | Liquid Chromatography |
| LLNL | Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory |
| MAP | Mercapturic Acid Pathway |
| MS | Mass Spectrometry |
| NIGMS | National Institute of General Medical Sciences |
| NIH | National Institutes of Health |
| PAMMS | Parallel Accelerator and Molecular Mass Spectrometry |
| PK | Pharmacokinetic |
| PM | Particulate Matter |
| PM2.5 | Particulate matter less than 2.5 μm diameter |
| RDB | Rings plus Double Bonds |
| RF | Radio Frequency |
| RP | Reverse-Phase |
| RT | Retention Time |
| SPE | Solid-Phase Extraction |
| TIC | Total Ion Chromatogram |
| UVPD | Ultraviolet Photodissociation |
| WSE | Wood Smoke Extract |
References
- Xu, R.; Yu, P.; Abramson Michael, J.; Johnston Fay, H.; Samet Jonathan, M.; Bell Michelle, L.; Haines, A.; Ebi Kristie, L.; Li, S.; Guo, Y. Wildfires, Global Climate Change, and Human Health. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2173–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, E.; Runkle, J.D. Long-term health effects of wildfire exposure: A scoping review. J. Clim. Change Health 2022, 6, 100110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascio, W.E. Wildland fire smoke and human health. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Tong, H.; Xu, Y. Wildfire Smoke and Its Neurological Impact. JAMA Neurol. 2024, 81, 575–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornreich, M.R.; Issenberg, P. Determination of phenolic wood smoke components as trimethylsilyl ethers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1972, 20, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.K.; Nguyen, K.Q.; Karim, N.; Yang, Y.; Rice, R.H.; He, G.; Denison, M.S.; Nguyen, T.B. Relationship between the molecular composition, visible light absorption, and health-related properties of smoldering woodsmoke aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 539–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veres, P.; Roberts, J.M.; Burling, I.R.; Warneke, C.; de Gouw, J.; Yokelson, R.J. Measurements of gas-phase inorganic and organic acids from biomass fires by negative-ion proton-transfer chemical-ionization mass spectrometry. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D23302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, K.K.; Sonko, O.; Dansie, D.R.; Kouri, R.E.; Henry, C.J. Studies on the deposition and distribution of catechol from whole cigarette smoke in BC3F1Cum mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1982, 64, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-H.; Li, C.-W. Detection and Characterization of Catechol Quinone-Derived Protein Adducts Using Biomolecular Mass Spectrometry. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, J.L.; Pisha, E.; Shen, L.; Krol, E.S.; Iverson, S.L.; Huang, Z.; van Breemen, R.B.; Pezzuto, J.M. The reactivity of o-quinones which do not isomerize to quinone methides correlates with alkylcatechol-induced toxicity in human melanoma cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1997, 106, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, I.A. Analysis of endogenous glutathione-adducts and their metabolites. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2010, 24, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ognibene, T.J.; Thomas, A.T.; Daley, P.F.; Bench, G.; Turteltaub, K.W. An Interface for the Direct Coupling of Small Liquid Samples to AMS. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 2015, 361, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, A.T.; Stewart, B.J.; Ognibene, T.J.; Turteltaub, K.W.; Bench, G. Directly Coupled High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Accelerator Mass Spectrometry Measurement of Chemically Modified Protein and Peptides. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 3644–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baliu-Rodriguez, D.; Stewart, B.; Ognibene, T. HPLC-Parallel Accelerator and Molecular Mass Spectrometry Analysis of 14C-Labeled Amino Acids. J. Chrom. B 2023, 1216, 123590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.; Dingley, K.H.; Turteltaub, K.W. Accelerator mass spectrometry for biomedical research. Methods Enzymol. 2005, 402, 423–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enright, H.A.; Malfatti, M.A.; Zimmermann, M.; Ognibene, T.; Henderson, P.; Turteltaub, K.W. Use of Accelerator Mass Spectrometry in Human Health and Molecular Toxicology. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2016, 29, 1976–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fifield, L.K. The Methodology and Physics of Accelerator Mass Spectrometry: A Handbook for Students and Practitioners; Australia National University: Canberra, Australia, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Keck, B.D.; Ognibene, T.; Vogel, J.S. Analytical validation of accelerator mass spectrometry for pharmaceutical development. Bioanalysis 2010, 2, 469–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfatti, M.A.; Buchholz, B.A.; Enright, H.A.; Stewart, B.J.; Ognibene, T.J.; McCartt, A.D.; Loots, G.G.; Zimmermann, M.; Scharadin, T.M.; Cimino, G.D.; et al. Radiocarbon Tracers in Toxicology and Medicine: Recent Advances in Technology and Science. Toxics 2019, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turteltaub, K.W.; Vogel, J.S. Bioanalytical applications of accelerator mass spectrometry for pharmaceutical research. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2000, 6, 991–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, J.S.; Turteltaub, K.W.; Finkel, R.; Nelson, D.E. Accelerator mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 1995, 67, 353A–359A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, M.L.V.; Siddens, L.K.; Pennington, J.M.; Uesugi, S.L.; Labut, E.M.; Vertel, E.A.; Anderson, K.A.; Tidwell, L.G.; Tilton, S.C.; Ognibene, T.J.; et al. Impact of phenanthrene co-administration on the toxicokinetics of benzo[a]pyrene in humans. UPLC-accelerator mass spectrometry following oral microdosing. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2023, 382, 110608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.A.; Vicente, A.; Monteiro, C.; Gonçalves, C.; Evtyugina, M.; Pio, C. Emission of trace gases and organic components in smoke particles from a wildfire in a mixed-evergreen forest in Portugal. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1466–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Hurtado, E.; Pey, J.; Borrás, E.; Sánchez, P.; Vera, T.; Carratalá, A.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X.; Vallejo, V.R. Atmospheric PM and volatile organic compounds released from Mediterranean shrubland wildfires. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 89, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Jen, C.N.; Weber, R.J.; Misztal, P.K.; Goldstein, A.H. Chemical composition of PM2.5 in October 2017 Northern California wildfire plumes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 5719–5737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, A.; Alves, C.; Calvo, A.I.; Fernandes, A.P.; Nunes, T.; Monteiro, C.; Almeida, S.M.; Pio, C. Emission factors and detailed chemical composition of smoke particles from the 2010 wildfire season. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 71, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Warren, S.H.; Kooter, I.; Williams, W.C.; George, I.J.; Vance, S.A.; Hays, M.D.; Higuchi, M.A.; Gavett, S.H.; DeMarini, D.M.; et al. Chemistry, lung toxicity and mutagenicity of burn pit smoke-related particulate matter. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2021, 18, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.; Warren Sarah, H.; Krantz, Q.T.; King, C.; Jaskot, R.; Preston William, T.; George Barbara, J.; Hays Michael, D.; Landis Matthew, S.; Higuchi, M.; et al. Mutagenicity and Lung Toxicity of Smoldering vs. Flaming Emissions from Various Biomass Fuels: Implications for Health Effects from Wildland Fires. Environ. Health Perspect. 2018, 126, 017011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- California Air Resources Board. Camp Fire Air Quality Data Analysis; California Air Resources Board: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Pleil, J.D.; Ariel Geer Wallace, M.; Davis, M.D.; Matty, C.M. The physics of human breathing: Flow, timing, volume, and pressure parameters for normal, on-demand, and ventilator respiration. J. Breath Res. 2021, 15, 042002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.B.; Jacob, S. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J. Basic Clin. Pharm. 2016, 7, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, R.M.; Konduru, N.V.; Hirano, H.; Donaghey, T.C.; Adamo, B.; Laurenzi, B.; Pyrgiotakis, G.; Brain, J.D. Pulmonary distribution of nanoceria: Comparison of intratracheal, microspray instillation and dry powder insufflation. Inhal. Toxicol. 2016, 28, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baliu-Rodriguez, D.; Kucheriavaia, D.; Palagama, D.S.W.; Lad, A.; O’Neill, G.M.; Birbeck, J.A.; Kennedy, D.J.; Haller, S.T.; Westrick, J.A.; Isailovic, D. Development and Application of Extraction Methods for LC-MS Quantification of Microcystins in Liver Tissue. Toxins 2020, 12, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Ai, X.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, F. Determination of catechol in tobacco by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Se Pu 2015, 33, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talwar, D.; Williamson, C.; McLaughlin, A.; Gill, A.; O’Reilly, D.S.J. Extraction and separation of urinary catecholamines as their diphenyl boronate complexes using C18 solid-phase extraction sorbent and high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chrom. B 2002, 769, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, S.; Pang, B.; Yan, H.; Wu, B.; Li, M.; Xing, C.; Li, J. Using Urinary Biomarkers to Estimate the Benzene Exposure Levels in Individuals Exposed to Benzene. Toxics 2022, 10, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veningerová, M.; Prachar, V.; Uhnák, J.; Lukácsová, M.; Trnovec, T. Determination of chlorinated phenols and cresols in human urine using solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography. J. Chrom. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1994, 657, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.T.; Ognibene, T.; Daley, P.; Turteltaub, K.; Radousky, H.; Bench, G. Ultrahigh Efficiency Moving Wire Combustion Interface for Online Coupling of High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 9413–9417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrimpe-Rutledge, A.C.; Codreanu, S.G.; Sherrod, S.D.; McLean, J.A. Untargeted Metabolomics Strategies-Challenges and Emerging Directions. J. Am. Soc. Mass. Spectrom. 2016, 27, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, P.E.; Anders, M.W. The mercapturic acid pathway. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2019, 49, 819–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathias, P.I.; B’Hymer, C. Mercapturic acids: Recent advances in their determination by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry and their use in toxicant metabolism studies and in occupational and environmental exposure studies. Biomarkers 2016, 21, 293–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
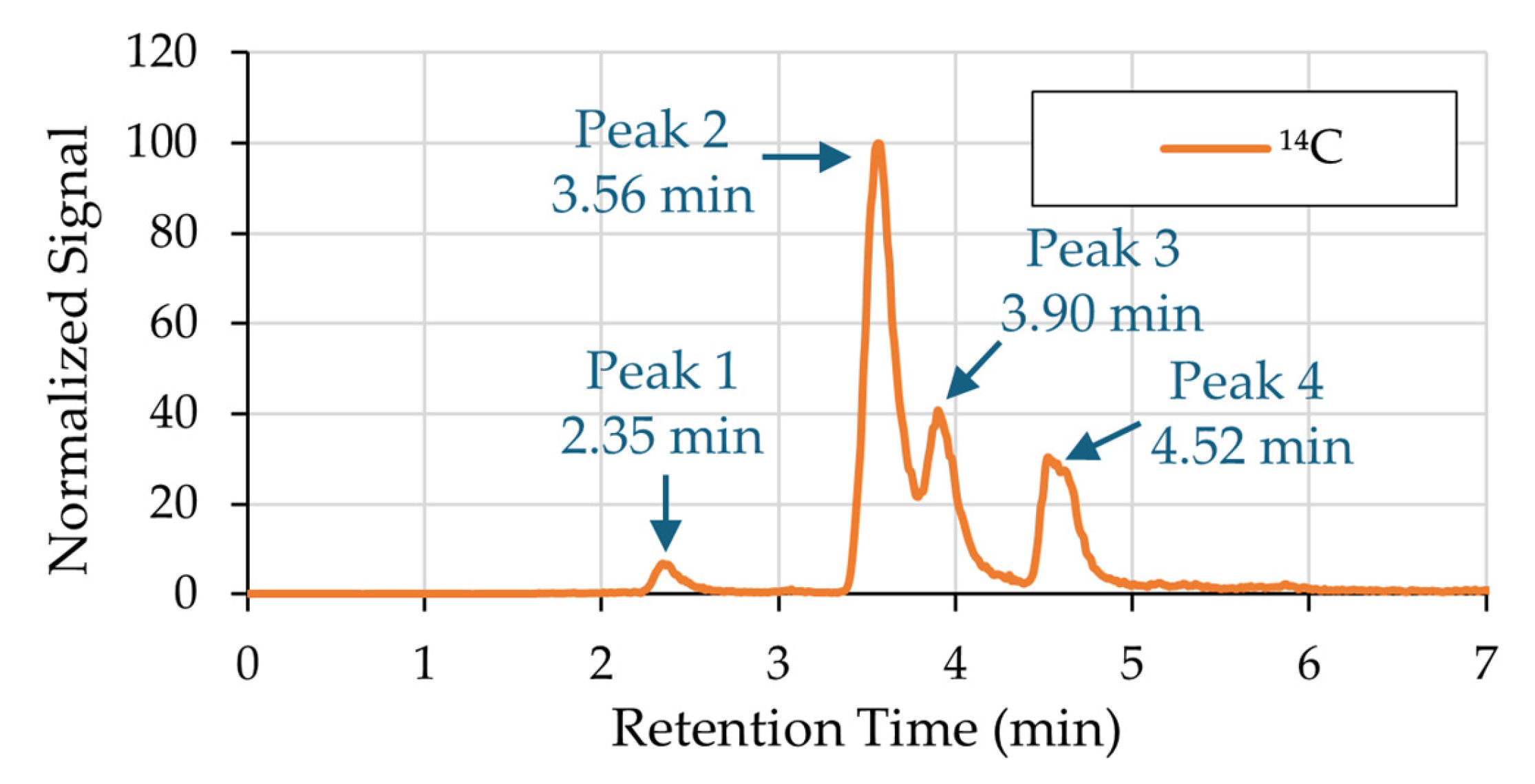
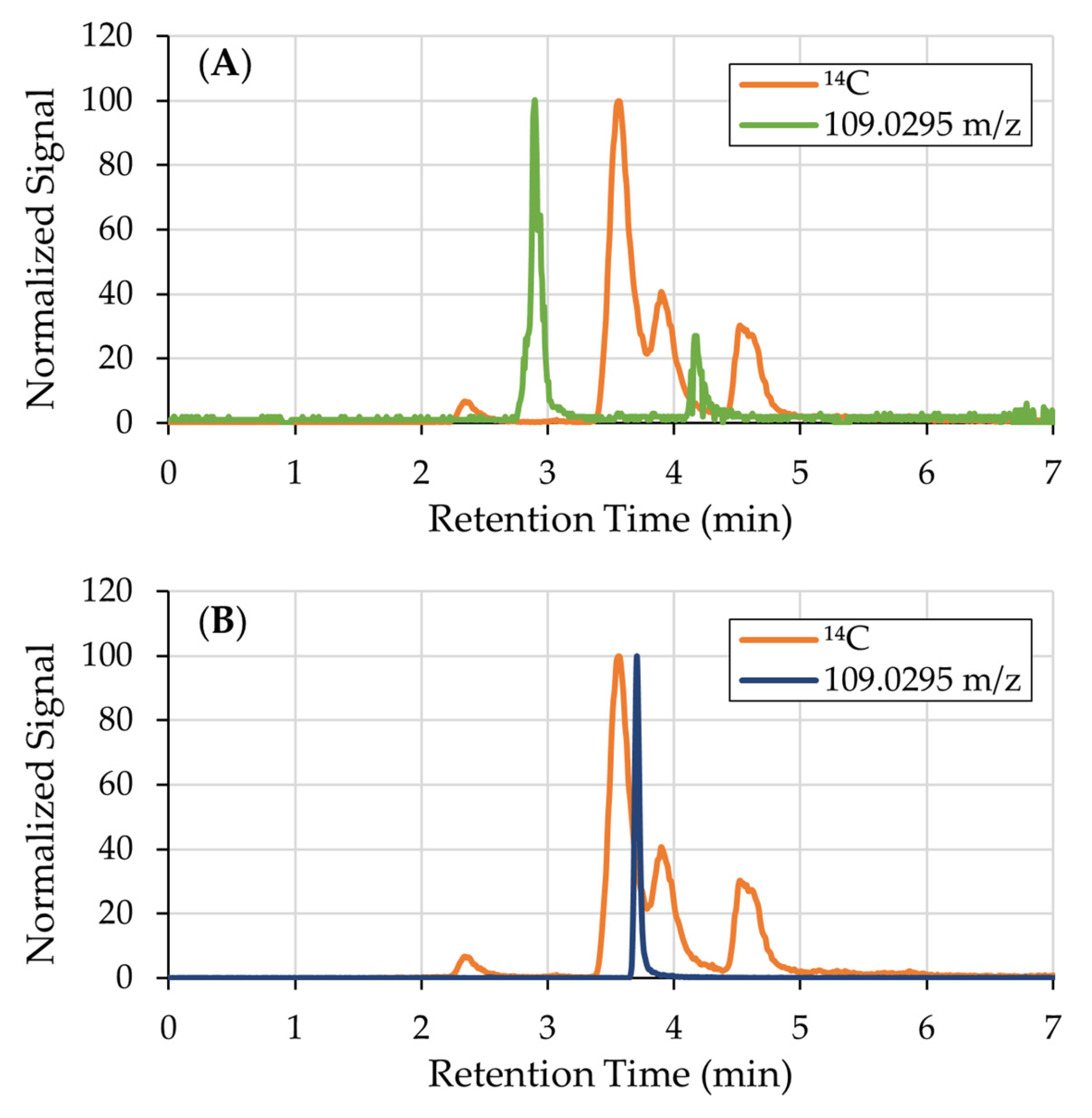
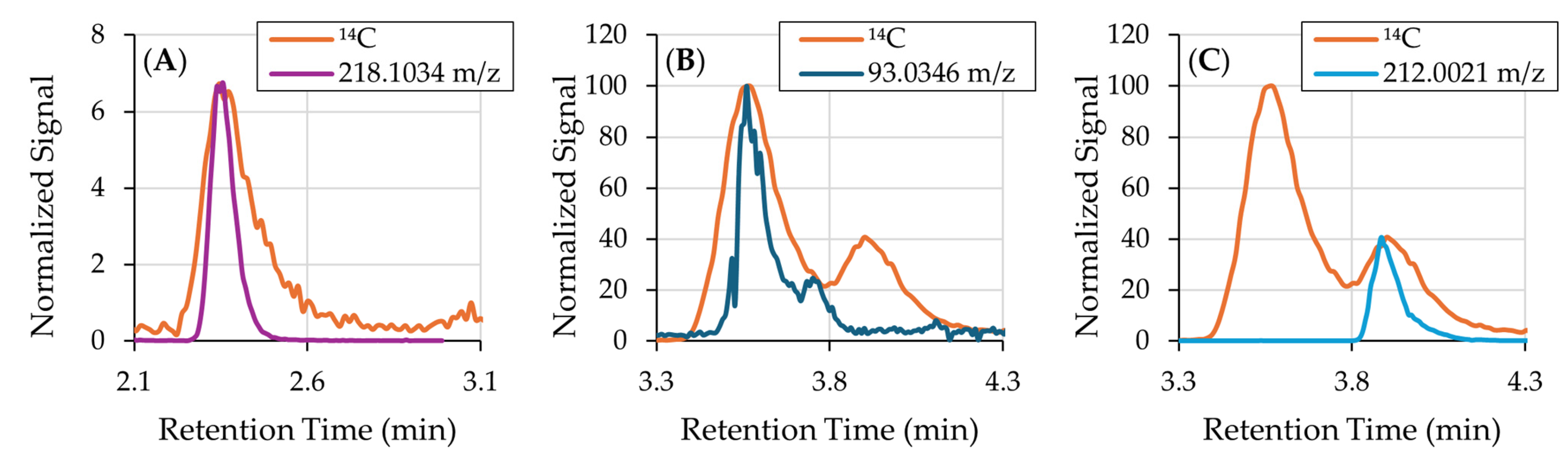
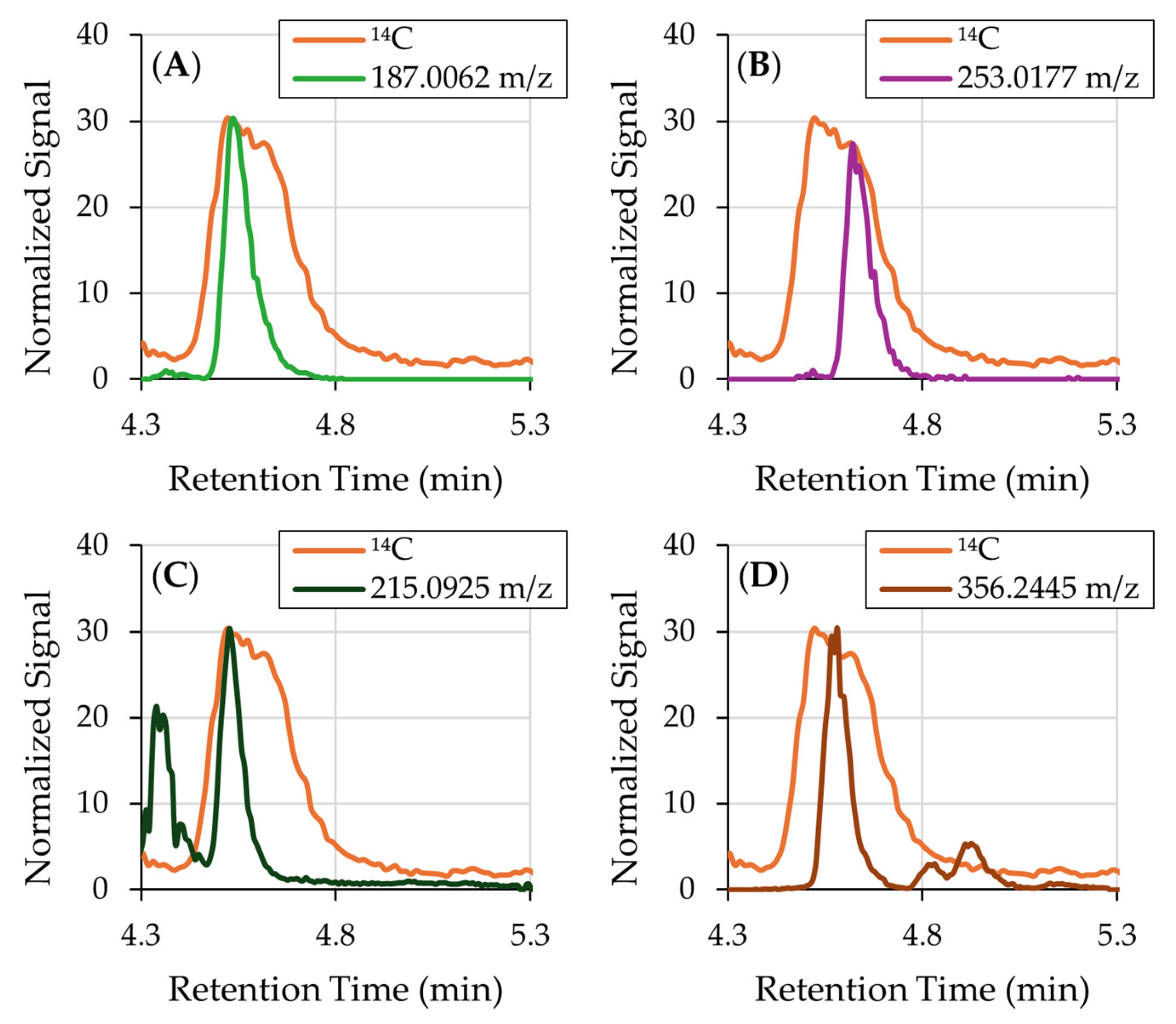
| Formula | [M-H]− | m/z Delta | RDB | Combined Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C6H6O | 93.0335 | 0.0011 | 4.0 | 89.71 |
| C4H4N3 | 93.0322 | 0.0024 | 4.5 | 87.60 |
| H7N4P | 93.0325 | 0.0021 | 0.0 | 86.29 |
| C2H9ONP | 93.0338 | 0.0008 | −0.5 | 83.26 |
| Formula | [M-H]− | m/z Delta | RDB | Combined Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C8H7O4NS | 212.00230 | −0.0002 | 6.0 | 89.14 |
| H3O7N7 | 212.00210 | 0.0000 | 3.0 | 76.99 |
| C14HON2 | 212.00160 | 0.0005 | 15.5 | 76.69 |
| CH7O2N7S2 | 212.00300 | −0.0009 | 2.5 | 76.52 |
| Peak | m/z | Formula | Proposed Identity | Confidence Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 218.1034 | C9H17O5N | catechol-glutamine conjugate | 4: Molecular Formula |
| 2 | 93.0346 | C6H6O | benzene oxide | 3: Tentative Structure |
| 3 | 212.0021 | C8H7O4NS | catechol-cysteine conjugate | 4: Molecular Formula |
| 4 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baliu-Rodriguez, D.; You, D.J.; Malfatti, M.A.; Ubick, E.A.; Kim, Y.H.; Buchholz, B.A. Identification and Quantitation of 14C-Labeled Catechol Metabolites in Rat Plasma After Intranasal Instillation of Smoldering Eucalyptus Wood Smoke Extract. Methods Protoc. 2025, 8, 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps8060147
Baliu-Rodriguez D, You DJ, Malfatti MA, Ubick EA, Kim YH, Buchholz BA. Identification and Quantitation of 14C-Labeled Catechol Metabolites in Rat Plasma After Intranasal Instillation of Smoldering Eucalyptus Wood Smoke Extract. Methods and Protocols. 2025; 8(6):147. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps8060147
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaliu-Rodriguez, David, Dorothy J. You, Michael A. Malfatti, Esther A. Ubick, Yong Ho Kim, and Bruce A. Buchholz. 2025. "Identification and Quantitation of 14C-Labeled Catechol Metabolites in Rat Plasma After Intranasal Instillation of Smoldering Eucalyptus Wood Smoke Extract" Methods and Protocols 8, no. 6: 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps8060147
APA StyleBaliu-Rodriguez, D., You, D. J., Malfatti, M. A., Ubick, E. A., Kim, Y. H., & Buchholz, B. A. (2025). Identification and Quantitation of 14C-Labeled Catechol Metabolites in Rat Plasma After Intranasal Instillation of Smoldering Eucalyptus Wood Smoke Extract. Methods and Protocols, 8(6), 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps8060147






