Function of the RNA Coliphage Qβ Proteins in Medical In Vitro Evolution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Concept and Consequence of Evolution in the Medical Field
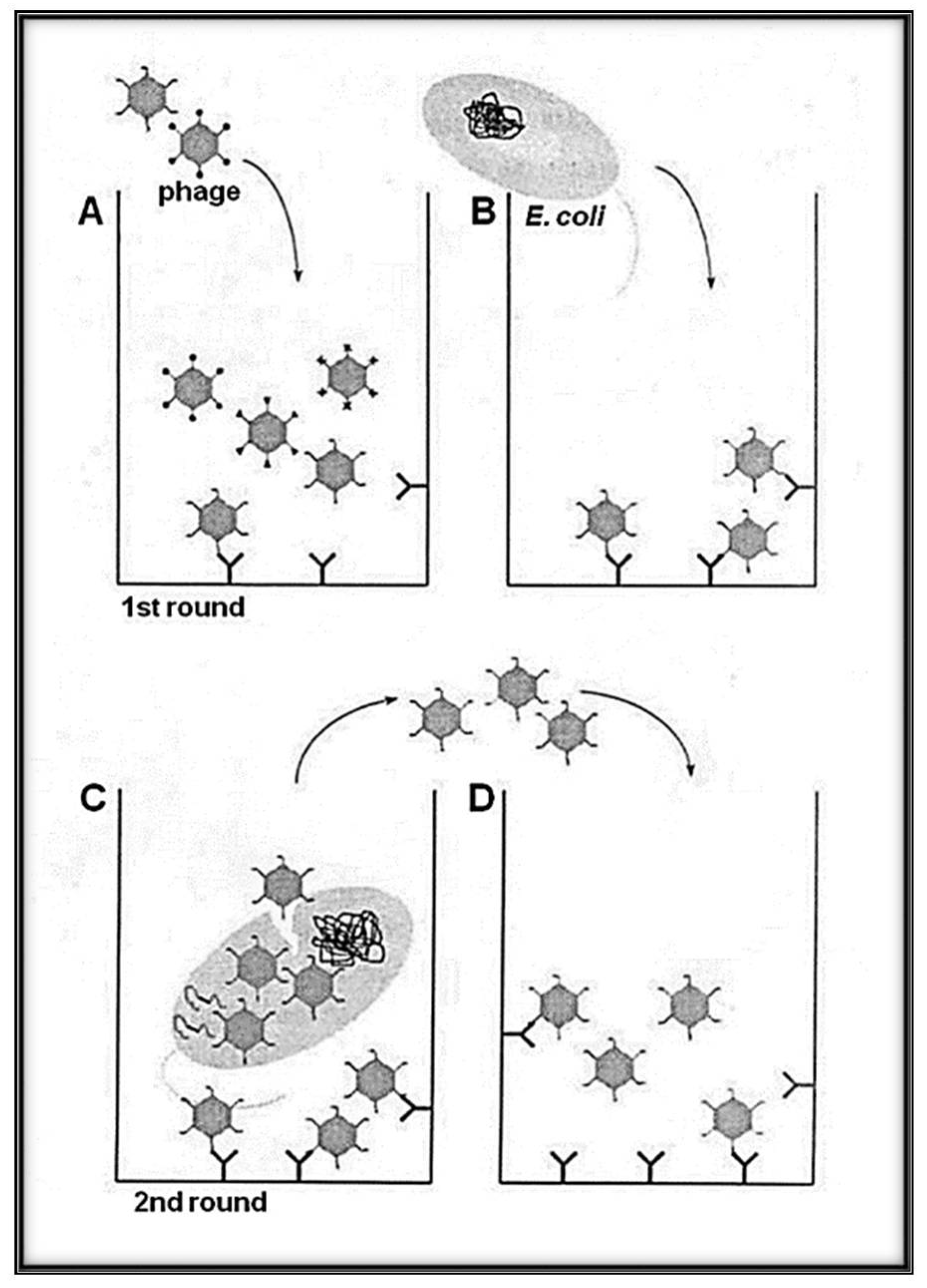
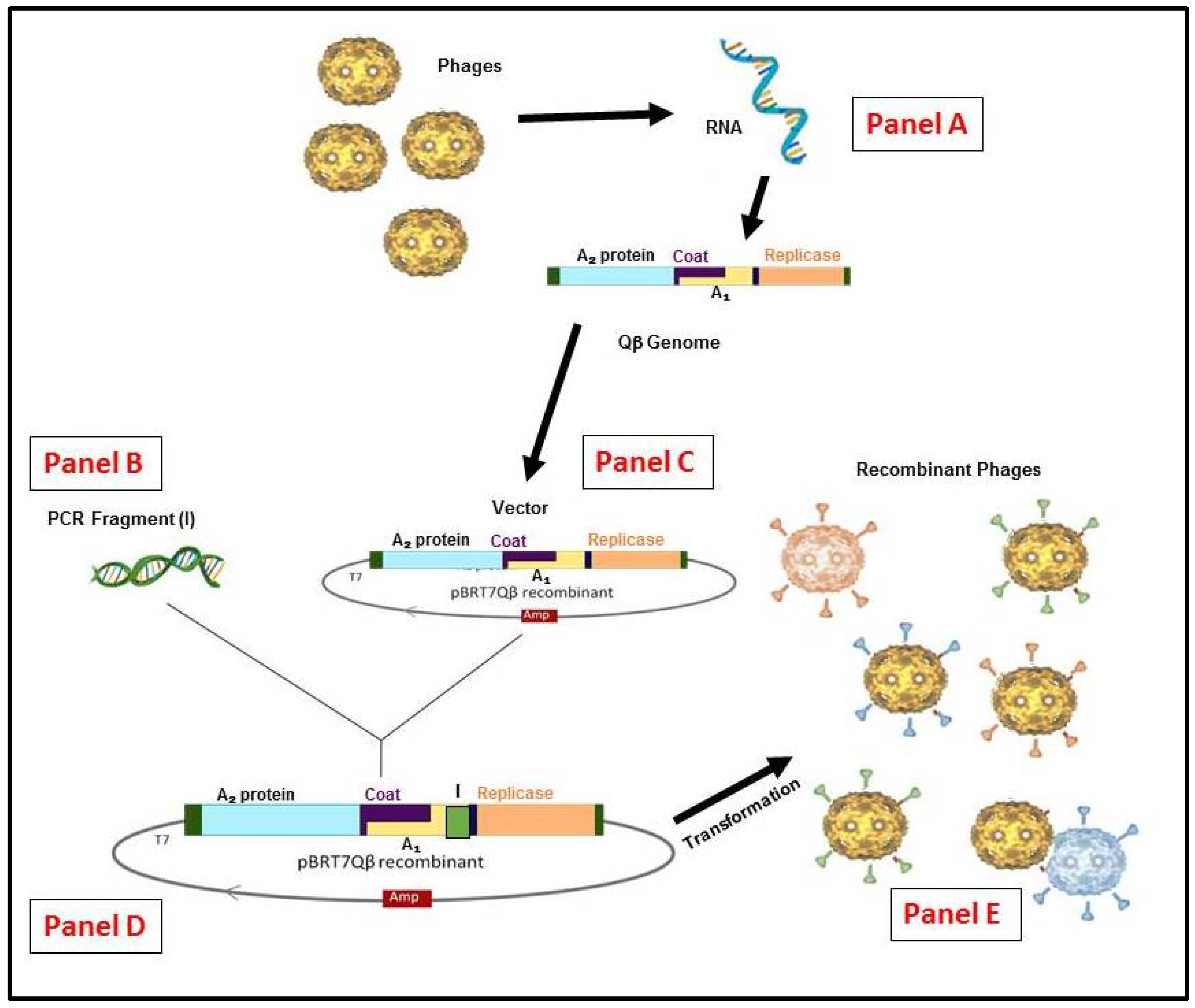
3. RNA-Coliphage Qβ Display
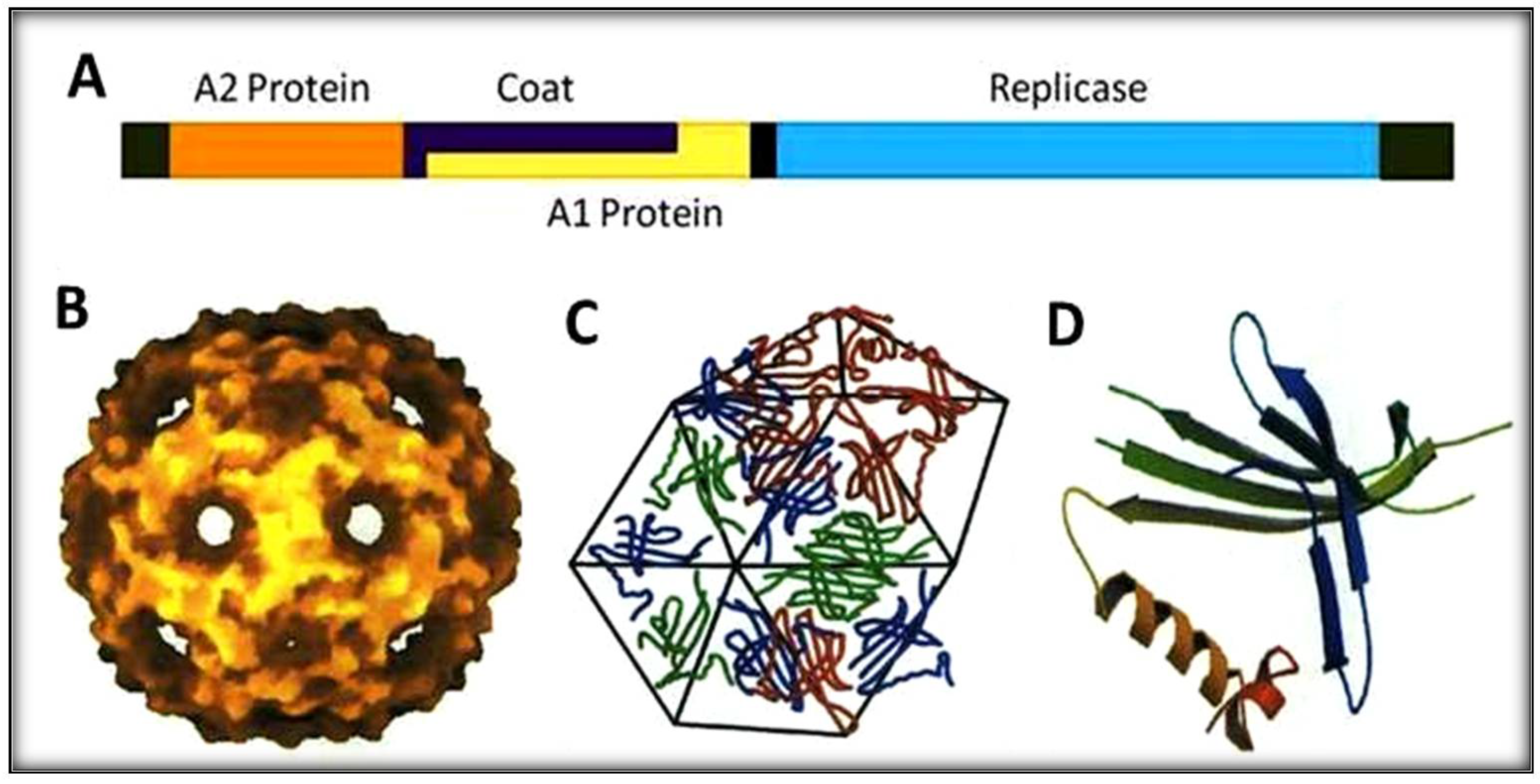
4. The Biology of RNA Qβ
4.1. The Maturation Protein or A2
4.2. The Read-Through Protein or A1
4.3. The Replicase Protein or REP
4.4. Qβ Life Cycle
5. Medical Applications of Qβ In Vitro Evolution
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woolhouse, M.E.J.; Brierley, L.; McCaffery, C.; Lycett, S. Assessing the epidemic potential of RNA and DNA viruses. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingo, E.; Sheldon, J.; Perales, C. Viral Quasispecies Evolution. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2012, 76, 159–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaminathan, G.; Martin-Garcia, J.; Navas-Martin, S. RNA viruses and microRNAs: Challenging discoveries for the 21st century. Physiol. Genom. 2013, 45, 1035–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, Y.; Ishiguro, A.; Miyakawa, S. RNA plasticity and selectivity applicable to therapeutics and novel biosensor development. Genes Cells 2012, 17, 344–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanjuán, R.; Domingo-Calap, P. Mechanisms of viral mutation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 4433–4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haller, S.L.; Peng, C.; McFadden, G.; Rothenburg, S. Poxviruses and the evolution of host range and virulence. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 21, 15–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Currin, A.; Swainston, N.; Day, P.J.; Kell, D.B. Synthetic biology for the directed evolution of protein biocatalysts: Navigating sequence space intelligently. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1172–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citorik, R.J.; Mimee, M.; Lu, T.K. Bacteriophage-based synthetic biology for the study of infectious diseases. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2014, 19, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Houten, N.E.; Henry, K.A.A.; Smith, G.P.; Scott, J.K. Engineering filamentous phage carriers to improve focusing of antibody responses against peptides. Vaccine 2010, 28, 2174–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skamel, C.; Aller, S.G.; Waffo, A.B. In vitro evolution and affinity-maturation with coliphage Qβ display. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113069. [Google Scholar]
- Waffo, A.B.; Singleton, R.L.; Ngu, L.N.; Egbo, T.; Simo, J.; Sanders, C.A.; Ambada, G.E.; Nji, N.N.; Ngoh, A.A.; Matthews, Q.L.; et al. Surface Engineering of Recombinant RNA Coliphage Qβ to Display gp41 Membrane-Proximal External-Region Epitopes from HIV-1. J. Clin. Exp. Immunol. J. Clin. Exp. 2017, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, D.; Gold, L. RNA replication by Qβ replicase: A working model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1196, 93, 11558–11562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, E.; Holland, J.J. RNA virus mutations and fitness for survival. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1197, 51, 151–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eigen, M.; Biebricher, C.K. Sequence Space and Quasispecies Distribution; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Biebricher, C.K.; Luce, R. Template-free generation of RNA species that replicate with bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 3458–3465. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Biebricher, C.K. Mutation, competition and selection as measured with small RNA molecules. Orig. Evol. Viruses 1999, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, J.W. A constant rate of spontaneous mutation in DNA-based microbes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 7160–7164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaklee, P.N.; Miglietta, J.J.J.; Palmenberg, A.C.; Kaesberg, P. Infectious positive- and negative-strand transcript RNAs from bacteriophage Qβ cDNA clones. Virology 1988, 163, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongsma, M.A.; Bakker, P.L.L.; Peters, J.; Bosch, D.; Stiekema, W.J. Adaptation of Spodoptera exigua larvae to plant proteinase inhibitors by induction of gut proteinase activity insensitive to inhibition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 8041–8045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlovska, T.M.; Cielens, I.; Vasiljeva, I.; Strelnikova, A.; Kazaks, A.; Dislers, A.; Dreilina, D.; Ose, V.; Gusars, I.; Pumpens, P. RNA phage Qβ coat protein as a carrier for foreign epitopes. Intervirology 1996, 39, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, D.R.; Priano, C.; Merz, P.A.; Binderow, B.D. Qβ RNA bacteriophage: Mapping cis-acting elements within an RNA genome. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 3872–3881. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moya, A.; Holmes, E.C.; González-Candelas, F. The population genetics and evolutionary epidemiology of RNA viruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paranchych, W. Attachment, Ejection and Penetration Stages of the RNA Phage Infectious Process. RNA Phages; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1975; pp. 85–111. [Google Scholar]
- Priano, C.; Arora, R.; Butke, J.; Mills, D.R. A complete plasmid-based complementation system for RNA coliphage Qβ: Three proteins of bacteriophages Qβ (group III) and SP (group IV) can be interchanged. J. Mol. Biol. 1995, 249, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priano, C.; Arora, R.; Jayant, L.; Mills, D.R. Translational activation in coliphage Qβ: On a polycistronic messenger RNA, repression of one gene can activate translation of another. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 271, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorzelnik, K.V.; Cui, Z.; Reed, C.A.A.; Jakana, J.; Young, R.; Zhang, J. Asymmetric cryo-EM structure of the canonical Allolevivirus Qβ reveals a single maturation protein and the genomic ssRNA in situ. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 11519–11524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumnieks, J.; Tars, K. Crystal structure of the read-through domain from bacteriophage Qβ A1 protein. Protein Sci. 2011, 20, 1707–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axelrod, V.D.; Brown, E.; Priano, C.; Mills, D.R. Coliphage Qβ RNA replication: RNA catalytic for single-strand release. Virology 1991, 184, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, R.W.; Cwirla, S.E.; Ackerman, M.S.; Olson, A.M.; Peters, E.A.; Dower, W.J. Selective enrichment and characterization of high affinity ligands from collections of random peptides on filamentous phage. Anal. Biochem. 1992, 204, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, C.A.; Langlais, C.; Kuznetsov, V.; Young, R. Inhibitory mechanism of the Qβ lysis protein A2. Mol. Microbiol. 2012, 86, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnier, J.; Kimura, M.; Foulaki, K.; Subramanian, A.-R.; Isono, K.; Wittmann-Liebold, B. Primary structure of Escherichia coli ribosomal protein S1 and of its gene rpsA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 1008–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhardt, T.G.; Wang, N.; Struck, D.K.; Young, R. Breaking free: ‘Protein antibiotics’ and phage lysis. Res. Microbiol. 2002, 153, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, T.G.; Wang, N.; Struck, D.K.; Young, R. A protein antibiotic in the phage Qβ virion: Diversity in lysis targets. Science 2001, 292, 2326–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumenthal, T.; Carmichael, G.G. RNA replication: Function and structure of Qβ-replicase. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1979, 48, 525–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karnik, S.; Billeter, M. The lysis function of RNA bacteriophage Qβ is mediated by the maturation (A2) protein. EMBO J. 1983, 2, 1521–1526. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bycroft, M.; Hubbard, T.J.; Proctor, M.; Freund, S.M.; Murzin, A.G. The solution structure of the S1 RNA binding domain: A member of an ancient nucleic acid-binding fold. Cell 1997, 88, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayant, L.; Priano, C.; Mills, D.R. In polycistronic Qβ RNA, single-strandedness at one ribosome binding site directly affects translational initiations at a distal upstream cistron. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 7199–7210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Smit, M.H.; van Duin, J. Control of translation by mRNA secondary structure in Escherichia coli: A quantitative analysis of literature data. J. Mol. Biol. 1994, 244, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adzhubei, A.A.; Sternberg, M.J.E.; Makarov, A.A. Polyproline-II helix in proteins: Structure and function. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 2100–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashiwagi, A.; Yomo, T. Ongoing phenotypic and genomic changes in experimental coevolution of RNA bacteriophage Qβ and Escherichia coli. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeshita, D.; Tomita, K. Assembly of Qβ viral RNA polymerase with host translational elongation factors EF-Tu and-Ts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15733–15738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidmose, R.T.; Vasiliev, N.N.; Chetverin, A.B.; Andersen, G.R.; Knudsen, C.R. Structure of the Qβ replicase, an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase consisting of viral and host proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 10884–10889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajitani, M.; Kato, A.; Wada, A.; Inokuchi, Y.; Ishihama, A. Regulation of the Escherichia coli hfq gene encoding the host factor for phage Q beta. J. Bacteriol. 1994, 176, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, E.M.; Gesteland, R.F. The adsorption of bacteriophage R-17. Virology 1964, 22, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klovins, J.; van Duin, J. A long-range pseudoknot in Qβ RNA is essential for replication. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 294, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poot, R.A.; Tsareva, N.V.; Boni, I.V.; van Duin, J. RNA folding kinetics regulates translation of phage MS2 maturation gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 10110–10115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gralla, J.; Steitz, J.A.; Crothers, D.M. Direct physical evidence for secondary structure in an isolated fragment of R17 bacteriophage mRNA. Nature 1974, 248, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Z.; Gorzelnik, K.V.; Chang, J.-Y.; Langlais, C.; Jakana, J.; Young, R.; Zhang, J. Structures of Qβ virions, virus-like particles, and the Qβ–MurA complex reveal internal coat proteins and the mechanism of host lysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11697–11702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiner, A.M.; Weber, K. Natural read-through at the UGA termination signal of Qβ coat protein cistron. Nat. New Biol. 1971, 234, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, G.P.; Petrenko, V.A. Phage display. Chem. Rev. 1997, 97, 391–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, C.A.; Aller, S.; Waffo, A.B. Nanobody exposed on phage Qβ as a blocker of P-glycoprotein for cancer therapy. Cancer Research, in preparation.
- Palasingam, K.; Shaklee, P.N. Reversion of Qβ RNA phage mutants by homologous RNA recombination. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 2435–2442. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singleton, R.L.; Sanders, C.A.; Jones, K.; Thorington, B.; Egbo, T.; Coats, M.T.; Waffo, A.B. Function of the RNA Coliphage Qβ Proteins in Medical In Vitro Evolution. Methods Protoc. 2018, 1, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps1020018
Singleton RL, Sanders CA, Jones K, Thorington B, Egbo T, Coats MT, Waffo AB. Function of the RNA Coliphage Qβ Proteins in Medical In Vitro Evolution. Methods and Protocols. 2018; 1(2):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps1020018
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingleton, Rana L., Carrie A. Sanders, Kevin Jones, Bobby Thorington, Timothy Egbo, Mamie T. Coats, and Alain Bopda Waffo. 2018. "Function of the RNA Coliphage Qβ Proteins in Medical In Vitro Evolution" Methods and Protocols 1, no. 2: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps1020018
APA StyleSingleton, R. L., Sanders, C. A., Jones, K., Thorington, B., Egbo, T., Coats, M. T., & Waffo, A. B. (2018). Function of the RNA Coliphage Qβ Proteins in Medical In Vitro Evolution. Methods and Protocols, 1(2), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps1020018




