Neonatal Screening for SCID: The French Experience
Abstract
:1. Introduction
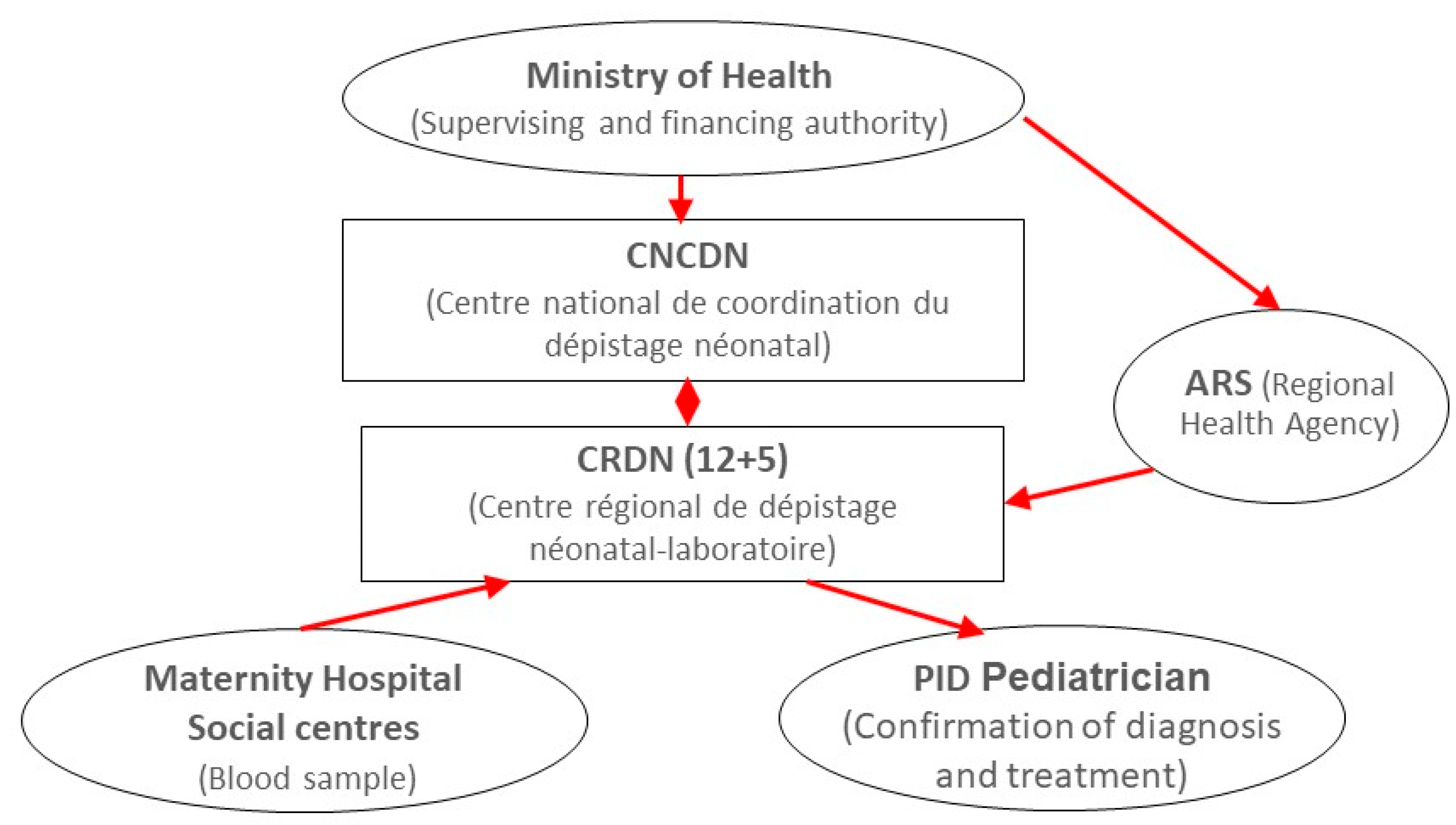
2. Overview of the DEPISTREC Pilot Study
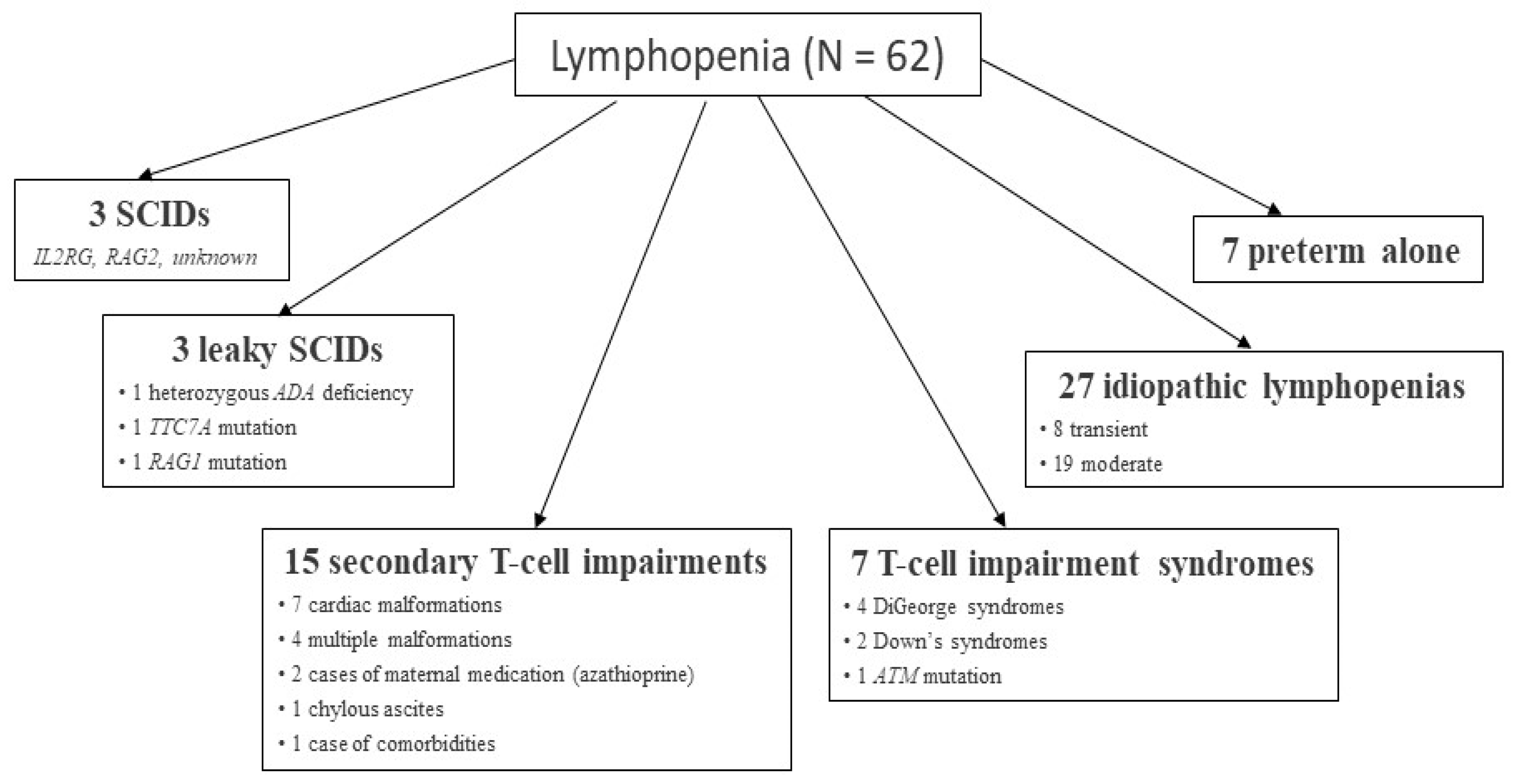
3. Initial Findings of the NeoSKID Program
4. DEPISTREC and NeoSKID: Lessons Learned
4.1. Feasibility and Clinical Utility
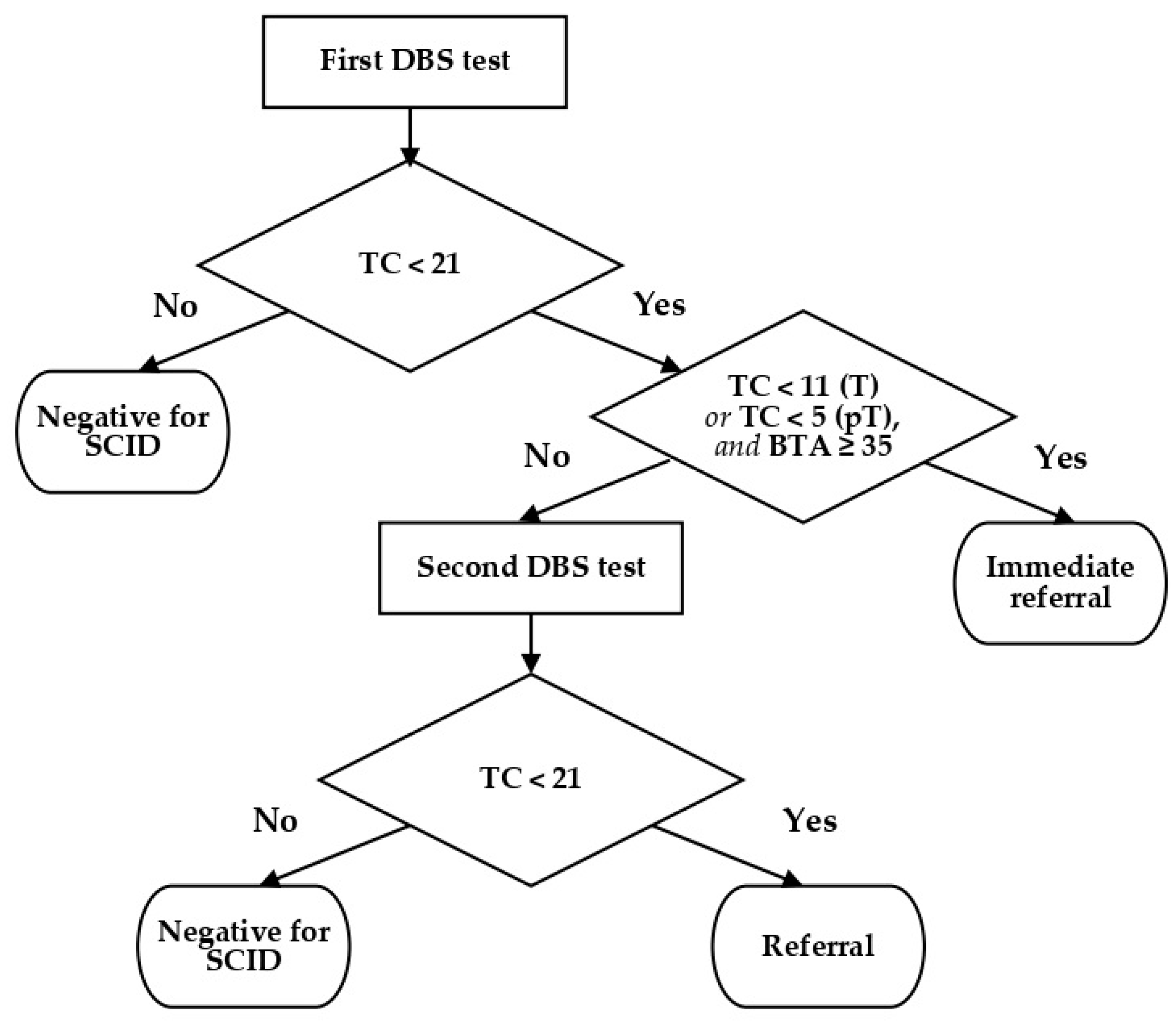
4.2. Reagents and Cut Off Values
4.3. Preterm Babies
4.4. Conclusions
5. Where Are We Now?
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chan, K.; Puck, J.M. Development of Population-Based Newborn Screening for Severe Combined Immunodeficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Routes, J.M.; Grossman, W.J.; Verbsky, J.; Laessig, R.H.; Hoffman, G.L.; Brokopp, C.D.; Baker, M.W. Statewide Newborn Screening for Severe T-Cell Lymphopenia. JAMA 2009, 302, 2465–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Comeau, A.M.; Hale, J.E.; Pai, S.-Y.; Bonilla, F.A.; Notarangelo, L.D.; Pasternack, M.S.; Meissner, H.C.; Cooper, E.R.; DeMaria, A.; Sahai, I.; et al. Guidelines for Implementation of Population-Based Newborn Screening for Severe Combined Immunodeficiency. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2010, 33, S273–S281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Advisory Committee on Heritable Disorders in Newborns and Children, Summary of 20th Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 21–22 January 2010. Available online: https://www.hrsa.gov/sites/default/files/hrsa/advisory-committees/heritable-disorders/meetings/Heritable%20Disorders%202004-2015/2010/January%2021-22,%202010/minutes.pdf (accessed on 24 May 2021).
- PID Life Index: Map. Available online: https://pidlifeindex.ipopi.org/#/en/principles/world-map (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- Buckley, R.H.; Schiff, S.E.; Schiff, R.I.; Markert, M.L.; Williams, L.W.; Roberts, J.L.; Myers, L.A.; Ward, F.E. Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation for the treatment of severe combined immunodeficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 340, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, S.-Y.; Logan, B.R.; Griffith, L.M.; Buckley, R.H.; Parrott, R.E.; Dvorak, C.C.; Kapoor, N.; Hanson, I.C.; Filipovich, A.H.; Jyonouchi, S.; et al. Transplantation outcomes for severe combined immunodeficiency, 2000–2009. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ministère des Solidarités et de la Santé [French Ministry of Solidarity and Health]. Programme National de Dépistage Néonatal [French National Newborn Screening Program]. Available online: https://solidarites-sante.gouv.fr/soins-et-maladies/prises-en-charge-specialisees/maladies-rares/DNN (accessed on 24 May 2021).
- CEREDIH. Available online: https://www.ceredih.fr/ (accessed on 24 May 2021).
- Gerstel-Thompson, J.L.; Wilkey, J.F.; Baptiste, J.C.; Navas, J.S.; Pai, S.-Y.; Pass, K.A.; Eaton, R.B.; Comeau, A.M. High-Throughput Multiplexed T-Cell-Receptor Excision Circle Quantitative PCR Assay with Internal Controls for Detection of Severe Combined Immunodeficiency in Population-Based Newborn Screening. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 1466–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Audrain, M.; Thomas, C.; Mirallie, S.; Bourgeois, N.; Sebille, V.; Rabetrano, H.; Durand-Zaleski, I.; Boisson, R.; Persyn, M.; Pierres, C.; et al. Evaluation of the T-Cell Receptor Excision Circle Assay Performances for Severe Combined Immunodeficiency Neonatal Screening on Guthrie Cards in a French Single Centre Study. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 150, 137–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clément, M.C.; Mahlaoui, N.; Mignot, C.; Le Bihan, C.; Rabetrano, H.; Hoang, L.; Neven, B.; Moshous, D.; Cavazzana, M.; Blanche, S.; et al. Systematic Neonatal Screening for Severe Combined Immunodeficiency and Severe T-Cell Lymphopenia: Analysis of Cost-Effectiveness Based on French Real Field Data. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 1589–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audrain, M.A.P.; Léger, A.J.C.; Hémont, C.A.F.; Mirallié, S.M.; Cheillan, D.; Rimbert, M.G.M.; Le Thuaut, A.M.-P.; Sébille-Rivain, V.A.; Prat, A.; Pinel, E.M.Q.; et al. Newborn Screening for Severe Combined Immunodeficiency: Analytic and Clinical Performance of the T Cell Receptor Excision Circle Assay in France (DEPISTREC Study). J. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 38, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C.; Durand-Zaleski, I.; Frenkiel, J.; Mirallié, S.; Léger, A.; Cheillan, D.; Picard, C.; Mahlaoui, N.; Riche, V.-P.; Roussey, M.; et al. Clinical and Economic Aspects of Newborn Screening for Severe Combined Immunodeficiency: DEPISTREC Study Results. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 202, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trück, J.; Prader, S.; Natalucci, G.; Hagmann, C.; Brotschi, B.; Kelly, J.; Bassler, D.; Steindl, K.; Rauch, A.; Baumgartner, M. Swiss newborn screening for severe T and B cell deficiency with a combined TREC/KREC assay—Management recommendations. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2020, 150, w20254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorsey, M.; Puck, J. Newborn Screening for Severe Combined Immunodeficiency in the US: Current Status and Approach to Management. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2017, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blom, M.; Pico-Knijnenburg, I.; Sijne-van Veen, M.; Boelen, A.; Bredius, R.G.M.; van der Burg, M.; Schielen, P.C.J.I. An evaluation of the TREC assay with regard to the integration of SCID screening into the Dutch newborn screening program. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 180, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argudo-Ramírez, A.; Martín-Nalda, A.; Marín-Soria, J.L.; López-Galera, R.M.; Pajares-García, S.; González de Aledo-Castillo, J.M.; Martínez-Gallo, M.; García-Prat, M.; Colobran, R.; Riviere, J.G.; et al. First Universal Newborn Screening Program for Severe Combined Immunodeficiency in Europe: Two-Years’ Experience in Catalonia (Spain). Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Spek, J.; Groenwold, R.H.; van der Burg, M.; van Montfrans, J.M. TREC Based Newborn Screening for Severe Combined Immunodeficiency Disease: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 35, 416–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rechavi, E.; Lev, A.; Saraf-Levy, T.; Etzioni, A.; Almashanu, S.; Somech, R. Newborn Screening for Severe Combined Immunodeficiency in Israel. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2017, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwan, A.; Abraham, R.S.; Currier, R.; Brower, A.; Andruszewski, K.; Abbott, J.K.; Baker, M.; Ballow, M.; Bartoshesky, L.E.; Bonilla, F.A.; et al. Newborn Screening for Severe Combined Immunodeficiency in 11 Screening Programs in the United States. JAMA 2014, 312, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jyonouchi, S.; Jongco, A.M.; Puck, J.; Sullivan, K.E. Immunodeficiencies Associated with Abnormal Newborn Screening for T Cell and B Cell Lymphopenia. J. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 37, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.; Monteil-Ganiere, C.; Mirallié, S.; Hémont, C.; Dert, C.; Léger, A.; Joyau, C.; Caldari, D.; Audrain, M. A Severe Neonatal Lymphopenia Associated with Administration of Azathioprine to the Mother in a Context of Crohn’s Disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2018, 12, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, K.; Davis, J.; Pai, S.-Y.; Bonilla, F.A.; Puck, J.M.; Apkon, M. A Markov Model to Analyze Cost-Effectiveness of Screening for Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID). Mol. Genet. Metab. 2011, 104, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, C.; Hubert, G.; Catteau, A.; Danielo, M.; Riche, V.P.; Mahlaoui, N.; Moshous, D.; Audrain, M. Review: Why Screen for Severe Combined Immunodeficiency Disease? Arch. Pediatr. 2020, 27, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haute Autorité de Santé [French National Authority for Health]. Feuille de Route: Evaluation a Priori de l’Extension du Dépistage Néonatal au Déficit Immunitaire Combiné Sévère (DICS) [Roadmap: Preliminary Evaluation of Extension of Newborn Screening Coverage to SCID]. 2018. Available online: https://www.has-sante.fr/upload/docs/application/pdf/2018-08/feuille_de_route_evaluation_a_priori_de_lextension_du_depistage_neonatal_au_deficit_immunitaire_combine_severe_dics.pdf (accessed on 24 May 2021).
- Haute Autorité de Santé. Programme de Travail. 2020. Available online: https://www.has-sante.fr/upload/docs/application/pdf/2020-07/programme_de_travail_has_2020.pdf (accessed on 24 May 2021).
| DEPISTREC Study | NeoSKID Program | |
|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 72,411 | 58,645 |
| Recall rate for a 2nd DBS | 0.16% | 0.22% |
| Recall rate for appointments | 0.023% | 0.026% |
| Recall rate for appointment after 2nd DBS | 0.017% | 0.005% |
| Total recall rate for appointment and flow cytometry | 0.04% | 0.03% |
| Kit Lot Code | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median TREC count | 110 | 153 | 88 | 118 | 111 | 122 |
| 0.5th percentile | 21 | 25 | 19 | 25 | 24 | 26 |
| Positive samples (%) | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.13 | 0.12 |
| Lab 1 | Lab 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| N | 49,145 | 23,266 |
| Abnormal results, % | 0.15 | 0.25 |
| Second DBS test, % | 0.13 | 0.22 |
| Immediate referral, % | 0.022 | 0.026 |
| Referral—immediate or after the second DBS, % | 0.039 | 0.043 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Audrain, M.; Thomas, C. Neonatal Screening for SCID: The French Experience. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2021, 7, 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns7030042
Audrain M, Thomas C. Neonatal Screening for SCID: The French Experience. International Journal of Neonatal Screening. 2021; 7(3):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns7030042
Chicago/Turabian StyleAudrain, Marie, and Caroline Thomas. 2021. "Neonatal Screening for SCID: The French Experience" International Journal of Neonatal Screening 7, no. 3: 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns7030042
APA StyleAudrain, M., & Thomas, C. (2021). Neonatal Screening for SCID: The French Experience. International Journal of Neonatal Screening, 7(3), 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns7030042






