Assessment of Spinal Muscular Atrophy Carrier Status by Determining SMN1 Copy Number Using Dried Blood Spots
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Objectives and Ethics
2.1.1. DBS Samples for Validation of SMN1 Copy Number Analysis
2.1.2. DBS Samples from Mongolian and Indonesian SMA Families
2.2. Detection of Homozygous SMN1 Deletion in DBS Samples
2.3. Detection of Heterozygous SMN1 Deletion in DBS Samples
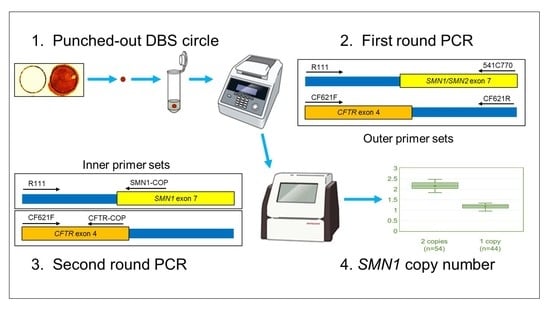
2.3.1. Outline
2.3.2. First Round PCR
2.3.3. Second Round PCR
2.3.4. Calculation of SMN1 Copy Number
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Detection of Homozygous SMN1 Deletion in the DBS Samples on Guthrie Cards
3.2. Detection of Heterozygous SMN1 Deletion in the DBS Samples
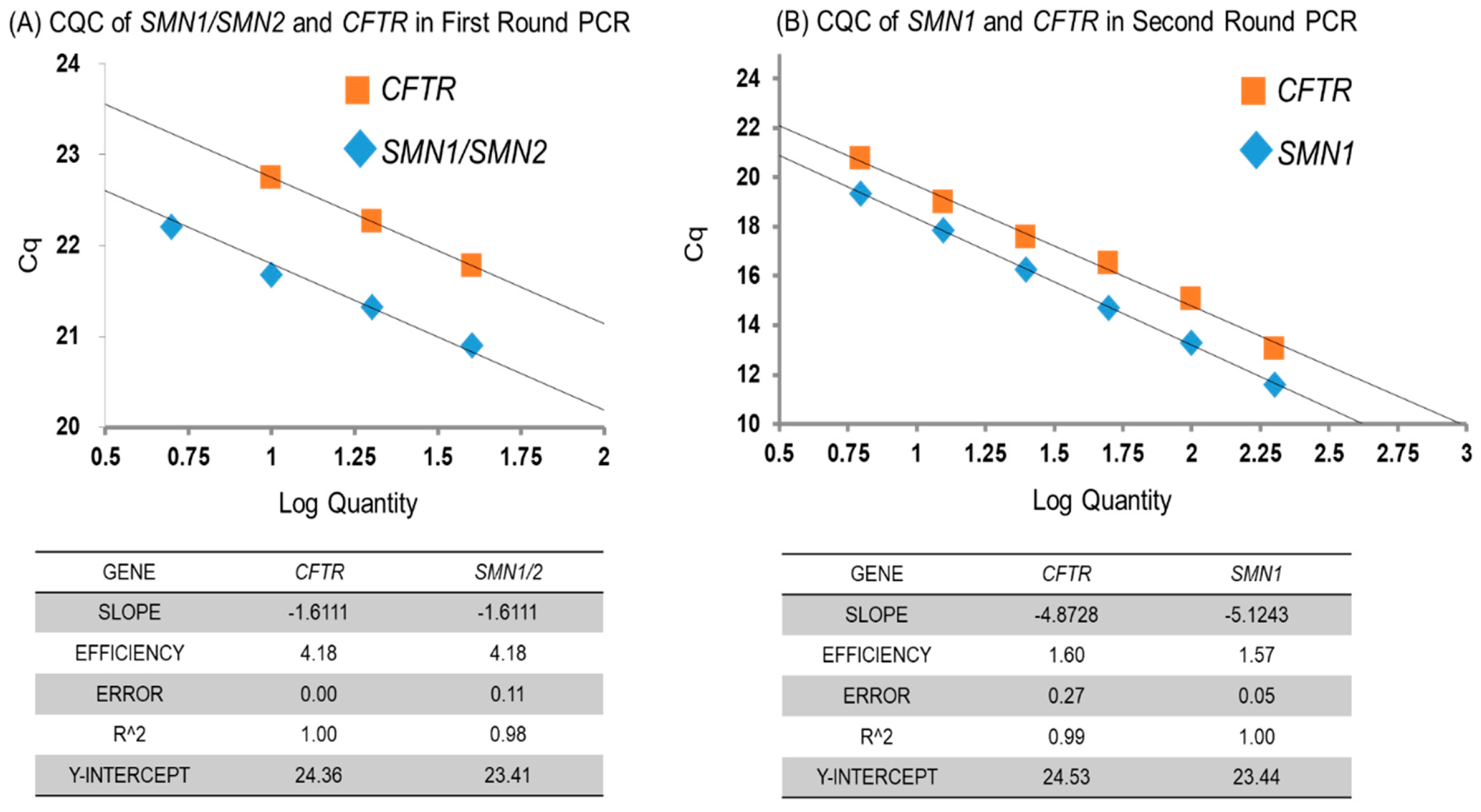
3.2.1. Amplification Efficiency of SMN1 and CFTR Genes
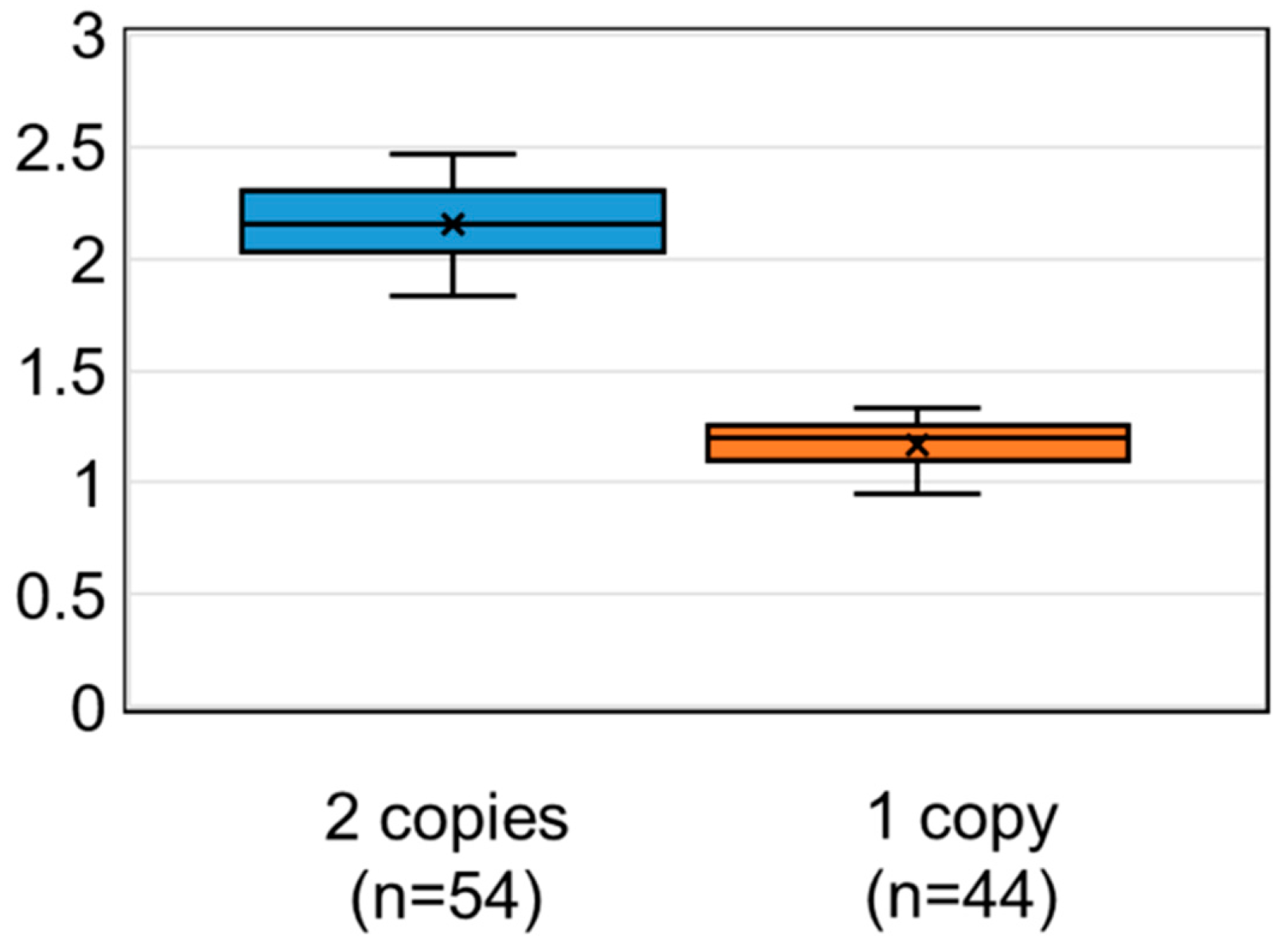
3.2.2. Calculated SMN1 Copy Number Values Using DBS on FTA Cards
3.2.3. Calculated SMN1 Copy Number Values Using DBS on Guthrie Cards
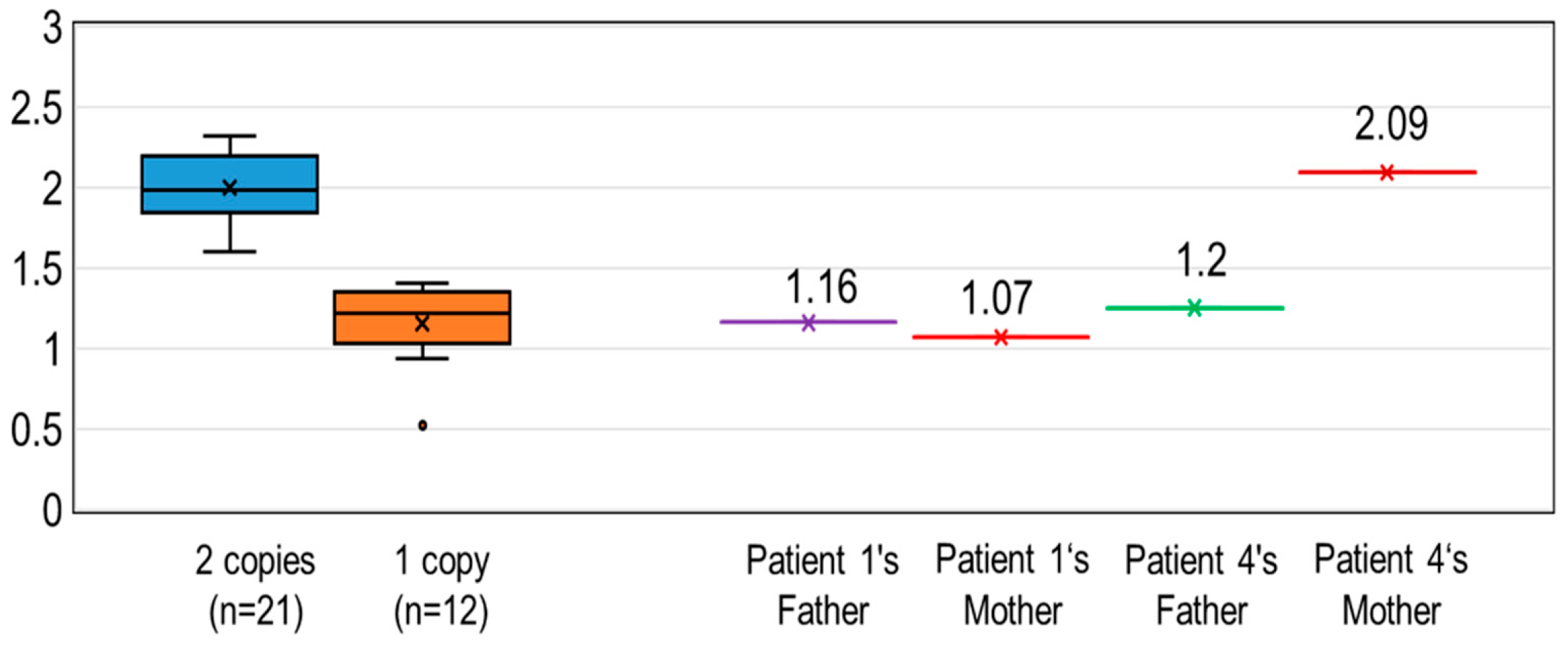
3.3. Determination of SMA Carrier Status from Analysis of SMN1 Copy Number
4. Discussion
4.1. Simple Method: Using Filter Paper Commonly Used for Newborn Screening
4.2. Robust Method: Adopting Nested Quantitative PCR Technology
4.3. Accurate Method: Adopting Calibrator-Normalized Relative Quantification Assay with Multiplex PCR
4.4. Inexpensive Method: No Requirement for DNA Extraction or Fluorescence-Labeled Probes
4.5. Limitation of Assigning SMA Carrier Status Based on the SMN1 Copy Number Assay
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nurputra, D.K.; Lai, P.S.; Harahap, N.I.F.; Morikawa, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Nishimura, N.; Kubo, Y.; Takeuchi, A.; Saito, T.; Takeshima, Y.; et al. Spinal muscular atrophy: From gene discovery to clinical trials. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2013, 77, 435–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefebvre, S.; Burglen, L.; Reboullet, S.; Clermont, O.; Burlet, P.; Viollet, L.; Bénichou, B.; Cruaud, C.; Millasseau, P.; Zeviani, M.; et al. Identification and characterization of a spinal muscular atrophy-determining gene. Cell 1995, 80, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, B. An update of the mutation spectrum of the survival motor neuron gene (SMN1) in autosomal recessive spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). Hum. Mutat. 2000, 15, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, W.D.; Kassar, D.; Kissel, J.T. Spinal muscular atrophy: Diagnosis and management in a new therapeutic era. Muscle Nerve 2014, 51, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, R.S.; Mercuri, E.; Darras, B.; Connolly, A.; Kuntz, N.; Kirschner, J.; Chiriboga, C.A.; Saito, K.; Servais, L.; Tizzano, E.; et al. Nusinersen versus sham control in Infantile-Onset spinal muscular atrophy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1723–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendell, J.R.; Al-Zaidy, S.; Shell, R.; Arnold, W.D.; Rodino-Klapac, L.R.; Prior, T.W.; Lowes, L.P.; Alfano, L.; Berry, K.; Church, K.; et al. Single-Dose Gene-Replacement therapy for spinal muscular atrophy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vivo, D.C.; Bertini, E.; Swoboda, K.J.; Hwu, W.-L.; Crawford, T.O.; Finkel, R.S.; Kirschner, J.; Kuntz, N.L.; Parsons, J.A.; Ryan, M.M.; et al. Nusinersen initiated in infants during the presymptomatic stage of spinal muscular atrophy: Interim efficacy and safety results from the Phase 2 NURTURE study. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2019, 29, 842–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, T.W. Carrier screening for spinal muscular atrophy. Genet. Med. 2008, 10, 840–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, T.W.; Snyder, P.J.; Rink, B.D.; Pearl, D.K.; Pyatt, R.E.; Mihal, D.C.; Conlan, T.; Schmalz, B.; Montgomery, L.; Ziegler, K.; et al. Newborn and carrier screening for spinal muscular atrophy. Am. J. Med Genet. Part A 2010, 152, 1608–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, Y.-H.; Chiang, S.-C.; Weng, W.-C.; Lee, N.-C.; Lin, C.-J.; Hsieh, W.-S.; Lee, W.-T.; Jong, Y.-J.; Ko, T.-M.; Hwu, W.-L. Presymptomatic diagnosis of spinal muscular atrophy through newborn screening. J. Pediatr. 2017, 190, 124–129.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraszewski, J.N.; Kay, D.M.; Stevens, C.F.; Koval, C.; Haser, B.; Ortiz, V.; Albertorio, A.; Cohen, L.L.; Jain, R.; Andrew, S.P.; et al. Pilot study of Population-Based newborn screening for spinal muscular atrophy in New York state. Genet. Med. 2017, 20, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czibere, L.; Burggraf, S.; Fleige, T.; Glück, B.; Keitel, L.M.; Landt, O.; Durner, J.; Röschinger, W.; Hohenfellner, K.; Wirth, B.; et al. High-Throughput genetic newborn screening for spinal muscular atrophy by rapid nucleic acid extraction from dried blood spots and 384-Well qPCR. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 28, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinohara, M.; Niba, E.T.E.; Wijaya, Y.O.S.; Takayama, I.; Mitsuishi, C.; Kumasaka, S.; Kondo, Y.; Takatera, A.; Hokuto, I.; Morioka, I.; et al. A novel system for spinal muscular atrophy screening in newborns: Japanese pilot study. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2019, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vill, K.; Kölbel, H.; Schwartz, O.; Blaschek, A.; Olgemöller, B.; Harms, E.; Burggraf, S.; Röschinger, W.; Durner, J.; Gläser, D.; et al. One year of newborn screening for SMA-Results of a german pilot project. J. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2019, 6, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, S.E.; Janakiraman, V.; Kaimal, A.; Musci, T.; Ecker, J.; Caughey, A.B. The Cost-Effectiveness of prenatal screening for spinal muscular atrophy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 202, 253.e1–253.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, J.K.; Kothary, R.; Parks, R.J. Opening the window: The case for carrier and perinatal screening for spinal muscular atrophy. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2016, 26, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tran, V.K.; Sasongko, T.H.; Hong, D.D.; Hoan, N.T.; Dung, V.C.; Lee, M.J.; Takeshima, Y.; Matsuo, M.; Nishio, H. SMN2 and NAIP gene dosages in Vietnamese patients with spinal muscular atrophy. Pediatr. Int. 2008, 50, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochmah, M.A.; Harahap, N.I.F.; Niba, E.T.E.; Nakanishi, K.; Awano, H.; Morioka, I.; Iijima, K.; Saito, T.; Saito, K.; Lai, P.S.; et al. Genetic screening of spinal muscular atrophy using a Real-Time modified COP-PCR technique with dried Blood-Spot DNA. Brain Dev. 2017, 39, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAndrew, P.; Parsons, D.; Simard, L.; Rochette, C.; Ray, P.; Mendell, J.; Prior, T.; Burghes, A. Identification of proximal spinal muscular atrophy carriers and patients by analysis of SMNT and SMNC gene copy number. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1997, 60, 1411–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvers, B.; Loeber, J.G.; Dhondt, J.-L.; Fukushi, M.; Hannon, W.H.; Torresani, T.; Webster, D. First ISNS reference preparation for neonatal screening for thyrotropin, phenylalanine and 17α-hydroxyprogesterone in blood spots. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2007, 30, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrott, P.; Smith, G.; Ristovski, Z.; Harding, R.M.; Hargreaves, M. A nested Real-Time PCR assay has an increased sensitivity suitable for detection of viruses in aerosol studies. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 106, 1438–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.M.; Aghili, A.; Li, S.; Ongoiba, A.; Kayentao, K.; Doumbo, S.; Traore, B.; Crompton, P.D. A nested Real-Time PCR assay for the quantification of Plasmodium falciparum DNA extracted from dried blood spots. Malar. J. 2014, 13, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passon, N.; Pozzo, F.; Molinis, C.; Bregant, E.; Gellera, C.; Damante, G.; Lonigro, R.I. A simple multiplex Real-Time PCR methodology for the SMN1 gene copy number quantification. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2009, 13, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, Y.; Sutomo, R.; Sadewa, A.H.; Akutsu, T.; Takeshima, Y.; Wada, H.; Matsuo, M.; Nishio, H. Correlation between SMN2 copy number and clinical phenotype of spinal muscular atrophy: Three SMN2 copies fail to rescue some patients from the disease severity. J. Neurol. 2002, 249, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anhuf, D.; Eggermann, T.; Rudnik-Schöneborn, S.; Zerres, K. Determination of SMN1 and SMN2 Copy Number Using TaqManTM Technology. Hum. Mutat. 2003, 22, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maranda, B.; Fan, L.; Soucy, J.-F.; Simard, L.; Mitchell, G.A. Spinal muscular atrophy: Clinical validation of a Single-Tube multiplex real time PCR assay for determination of SMN1 and SMN2 copy numbers. Clin. Biochem. 2012, 45, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Pyatt, R.; Prior, T.W. A feasibility study for the newborn screening of spinal muscular atrophy. Genet. Med. 2006, 8, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.L.; Lee, F.K.; Yazdanpanah, G.K.; Staropoli, J.F.; Liu, M.; Carulli, J.P.; Sun, C.; Dobrowolski, S.F.; Hannon, W.H.; Vogt, R.F. Newborn Blood Spot Screening Test Using Multiplexed Real-Time PCR to simultaneously screen for spinal muscular atrophy and severe combined immunodeficiency. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strunk, A.; Abbes, A.; Stuitje, A.R.; Hettinga, C.; Sepers, E.M.; Snetselaar, R.; Schouten, J.; Asselman, F.-L.; Cuppen, I.; Lemmink, H.; et al. Validation of a Fast, Robust, Inexpensive, Two-Tiered neonatal screening test algorithm on dried blood spots for spinal muscular atrophy. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2019, 5, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strom, C.M.; Anderson, B.; Peng, M.; Patel, U.; Braastad, C.D.; Sun, W. 1000 sample comparison of MLPA and RT-PCR for carrier detection and diagnostic testing for spinal muscular atrophy type 1. Open J. Genet. 2013, 3, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boemer, F.; Caberg, J.-H.; Dideberg, V.; Dardenne, D.; Bours, V.; Hiligsmann, M.; Dangouloff, T.; Servais, L. Newborn screening for SMA in Southern Belgium. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2019, 29, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochmah, M.A.; Awano, H.; Awaya, T.; Harahap, N.I.F.; Morisada, N.; Bouike, Y.; Saito, T.; Kubo, Y.; Saito, K.; Lai, P.S.; et al. Spinal muscular atrophy carriers with two SMN1 copies. Brain Dev. 2017, 39, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Tan, H.; Yang, P.; Zhang, R.; Tan, B.; Zhang, Y.; Mei, L.; Liang, D.; Wu, L. Notable carrier risks for individuals having two copies of SMN1 in spinal muscular atrophy families with 2-Copy Alleles: Estimation based on chinese meta-analysis data. J. Genet. Couns. 2016, 26, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogino, S.; Wilson, R.B. SMN dosage analysis and risk assessment for spinal muscular atrophy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2002, 70, 1596–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, M.; Liu, L.; Peter, I.; Zhu, J.; Scott, S.A.; Zhao, G.; Eversley, C.; Kornreich, R.; Desnick, R.J.; Edelmann, L. An ashkenazi jewish SMN1 haplotype specific to duplication alleles improves Pan-Ethnic carrier screening for spinal muscular atrophy. Genet. Med. 2013, 16, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alías, L.; Bernal, S.; Calucho, M.; Martínez, E.; March, F.; Gallano, P.; Fuentes-Prior, P.; Abulí, A.; Serra-Juhé, C.; Tizzano, E.F. Utility of two SMN1 variants to improve spinal muscular atrophy carrier diagnosis and genetic counselling. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 26, 1554–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dangouloff, T.; Burghes, A.; Tizzano, E.F.; Servais, L.; Bertini, E.; Boemer, F.; Hiligsmann, M.; Mueller-Felber, W.; Tiziano, D.; Young, P.; et al. 244th ENMC international workshop: Newborn screening in spinal muscular atrophy May 10–12, 2019, Hoofdorp, The Netherlands. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2020, 30, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wijaya, Y.O.S.; Purevsuren, J.; Harahap, N.I.F.; Niba, E.T.E.; Bouike, Y.; Nurputra, D.K.; Rochmah, M.A.; Thursina, C.; Hapsara, S.; Yamaguchi, S.; et al. Assessment of Spinal Muscular Atrophy Carrier Status by Determining SMN1 Copy Number Using Dried Blood Spots. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2020, 6, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns6020043
Wijaya YOS, Purevsuren J, Harahap NIF, Niba ETE, Bouike Y, Nurputra DK, Rochmah MA, Thursina C, Hapsara S, Yamaguchi S, et al. Assessment of Spinal Muscular Atrophy Carrier Status by Determining SMN1 Copy Number Using Dried Blood Spots. International Journal of Neonatal Screening. 2020; 6(2):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns6020043
Chicago/Turabian StyleWijaya, Yogik Onky Silvana, Jamiyan Purevsuren, Nur Imma Fatimah Harahap, Emma Tabe Eko Niba, Yoshihiro Bouike, Dian Kesumapramudya Nurputra, Mawaddah Ar Rochmah, Cempaka Thursina, Sunartini Hapsara, Seiji Yamaguchi, and et al. 2020. "Assessment of Spinal Muscular Atrophy Carrier Status by Determining SMN1 Copy Number Using Dried Blood Spots" International Journal of Neonatal Screening 6, no. 2: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns6020043
APA StyleWijaya, Y. O. S., Purevsuren, J., Harahap, N. I. F., Niba, E. T. E., Bouike, Y., Nurputra, D. K., Rochmah, M. A., Thursina, C., Hapsara, S., Yamaguchi, S., Nishio, H., & Shinohara, M. (2020). Assessment of Spinal Muscular Atrophy Carrier Status by Determining SMN1 Copy Number Using Dried Blood Spots. International Journal of Neonatal Screening, 6(2), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns6020043