Human-Cyber-Physical Systems for Energy Internet—A Review
Abstract
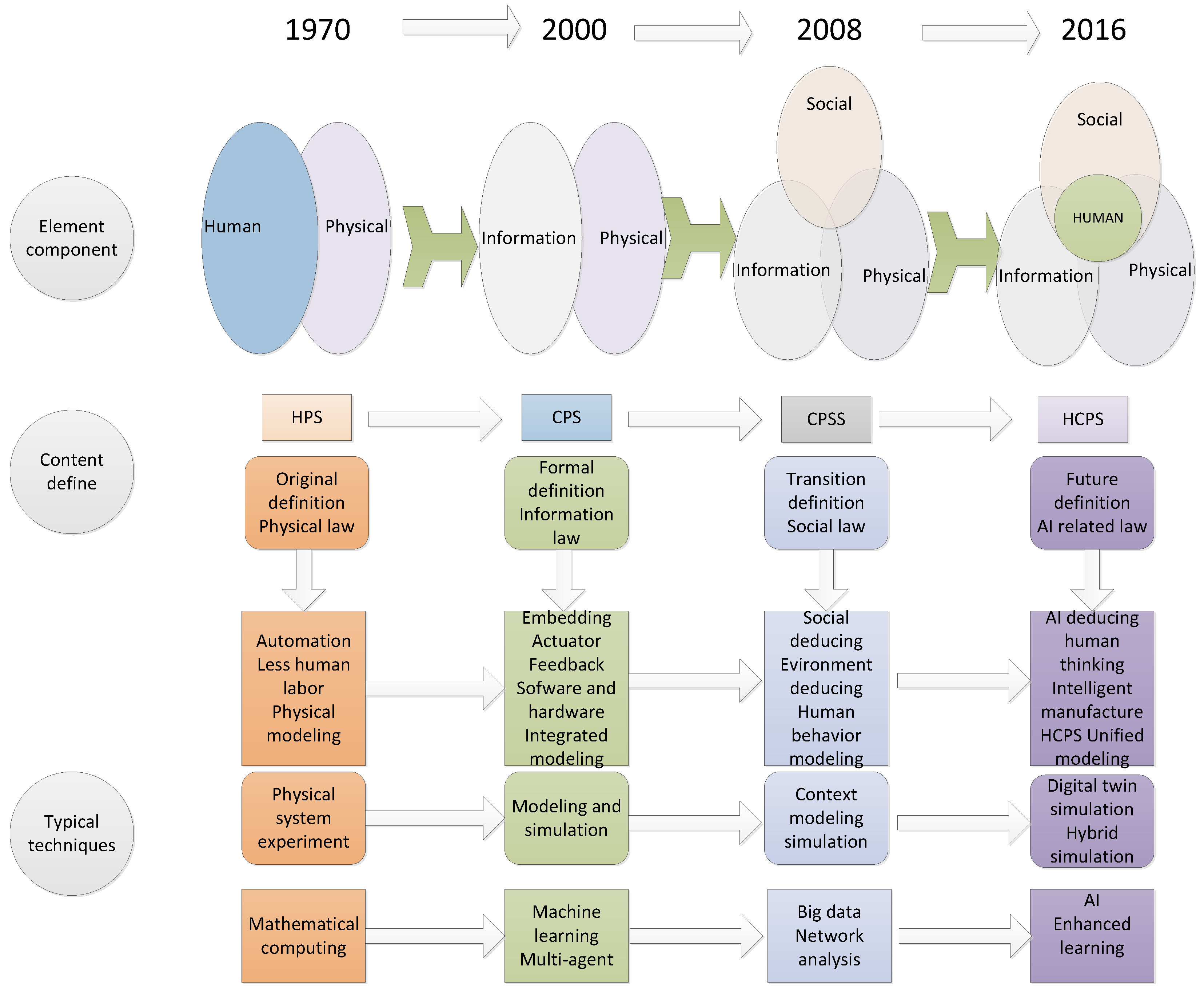
1. Introduction
- (1)
- HPS: the production system was formed by humans and machines, which emphasized the human control of the machine, reduced the labor intensity and improved the production efficiencies through electrification and automation.
- (2)
- CPS: the production system was made of an information system and machine, which emphasized the aid function of the information system in industry, which through sensor information gathering and actuator information feedback, improved the automatic level of the machine.
- (3)
- CPSS: developed from CPS, the production system is made of an information system, physical system and society, which emphasized the complementary nature of the information system and society system, and through information relay, improved the intelligence level of machines (give it a fish). As CPSS is the transition of CPS and HCPS, it is not reviewed in detail in this paper.
- (4)
- HCPS: based on CPSS, the production system is made of humans, cyber and physics, which emphasizes the leader role of humans in production. Based on the information relay and policies interaction, it can largely improve the system’s intelligence level (teach him to fish).
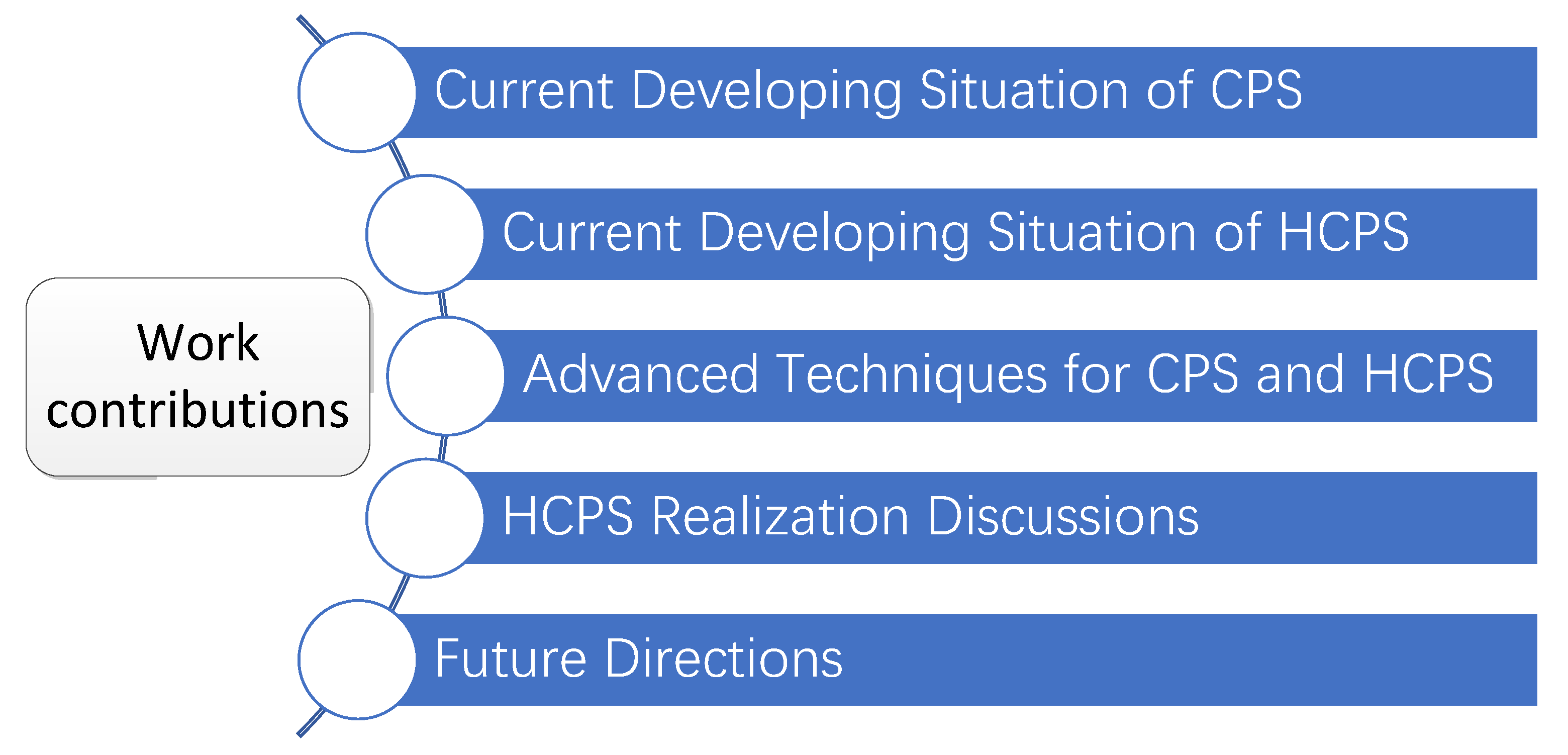
2. Current Developing Situation of CPS
2.1. CPS on Related Industries
2.2. CPS on Electricity Power System
2.2.1. CPS on Framework Design
2.2.2. CPS on Support Technologies and Algorithms
2.2.3. CPS on System Function
2.2.4. CPS on Power Ancillary Service
2.2.5. CPS on Energy Internet Realization
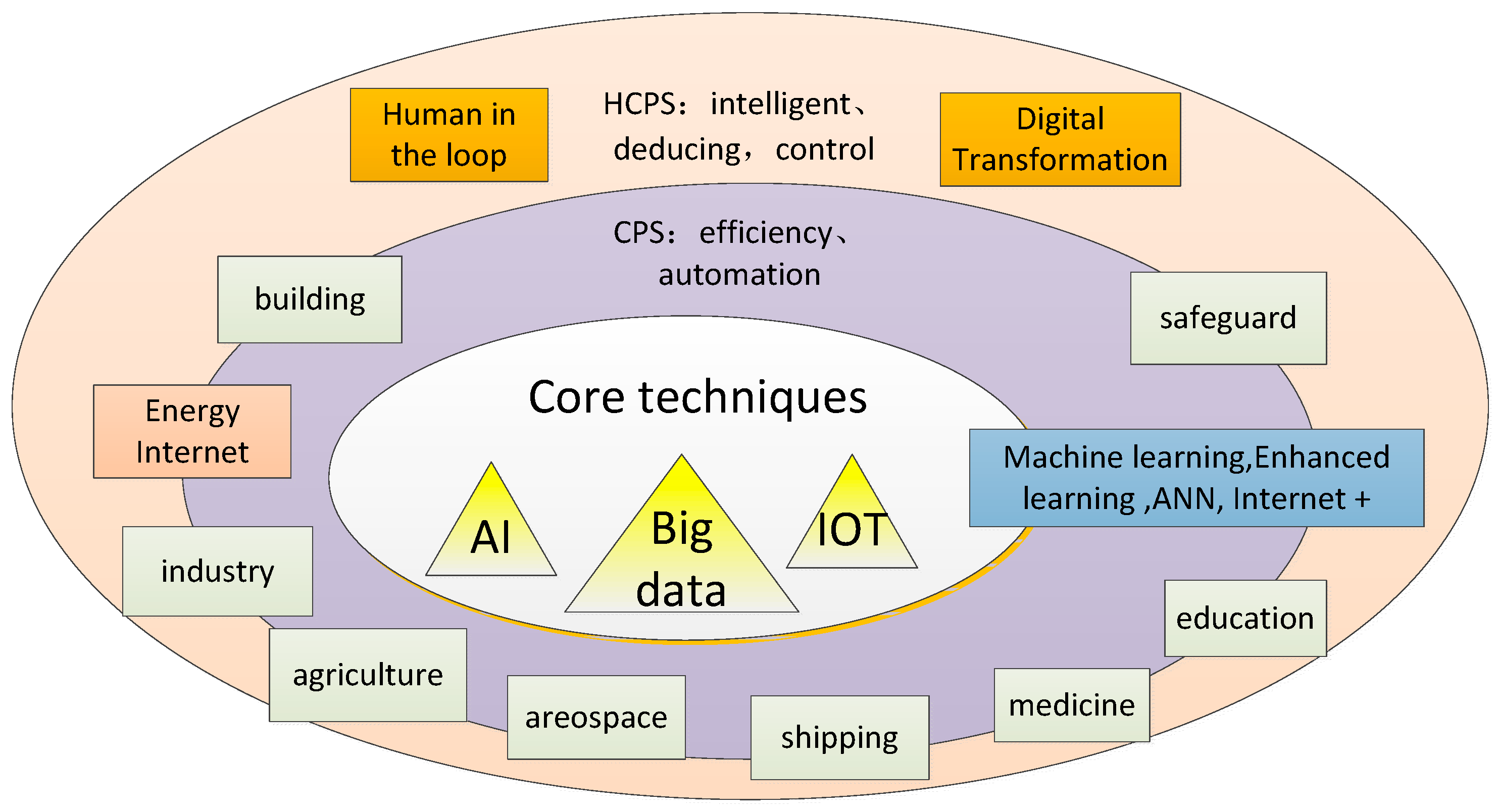
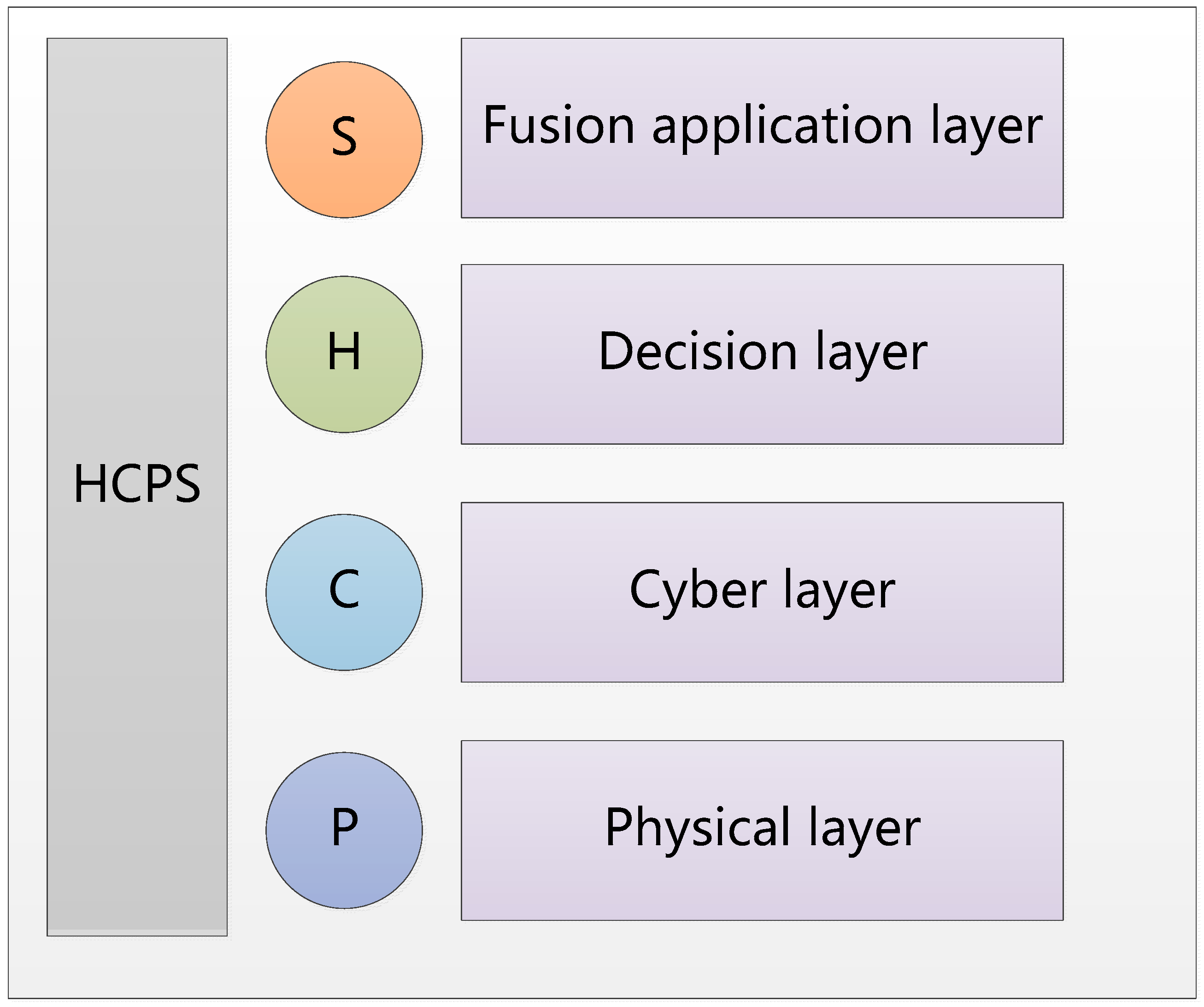
3. Current Developing Situation of HCPS
3.1. HCPS Framework
3.2. Related HCPS Research
3.3. HCPS on Energy Internet
3.3.1. System Modeling
3.3.2. Human-in-the-Loop
3.3.3. Digital Transformation
3.3.4. Technique Summary
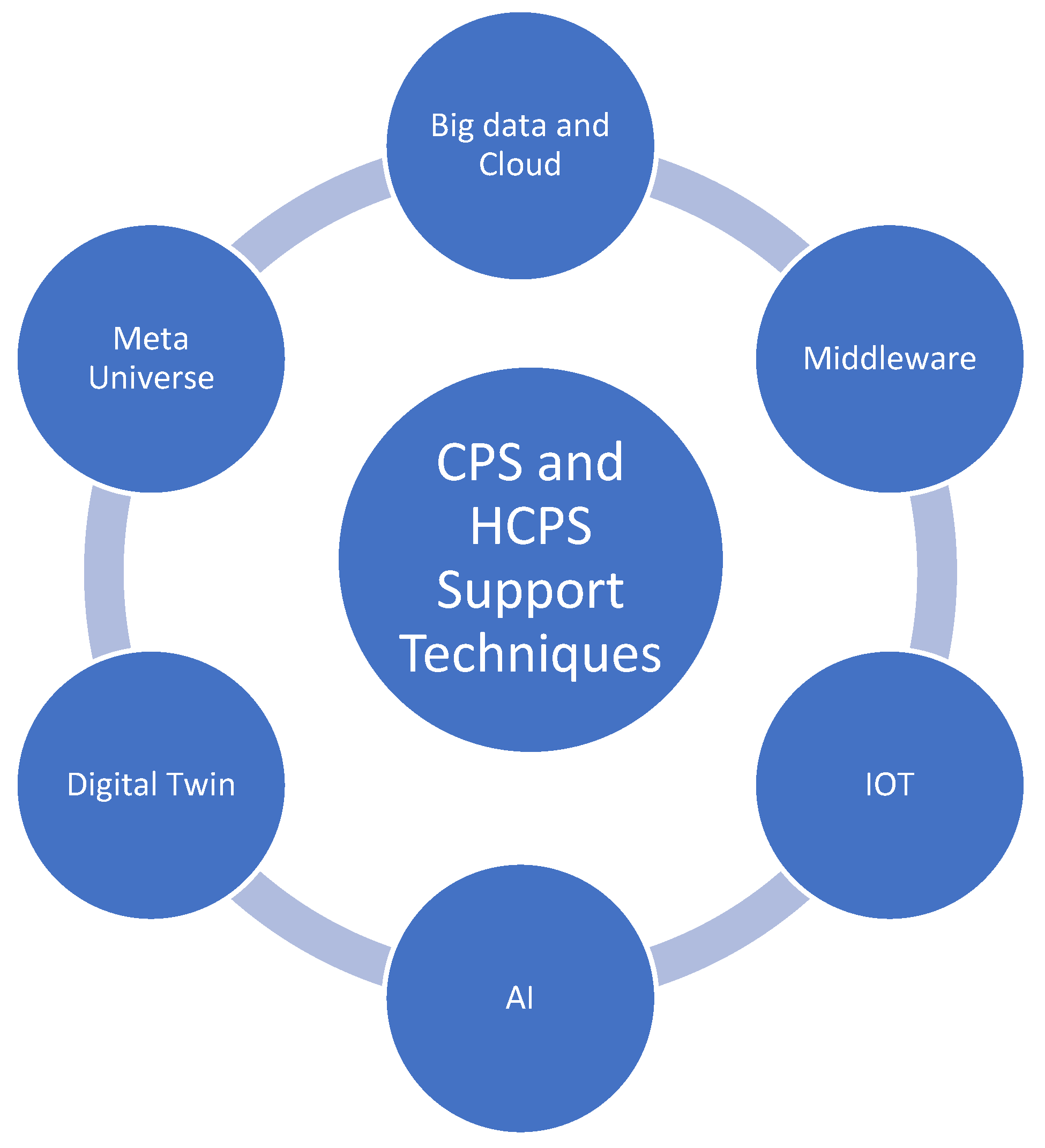
4. Advanced Techniques for CPS and HCPS
4.1. Big Data and Cloud
4.2. Middleware
4.3. IOT
4.4. AI
4.5. Digital Twin
4.6. Meta Universe
5. HCPS Realization Discussions
6. Conclusions
7. Future Directions
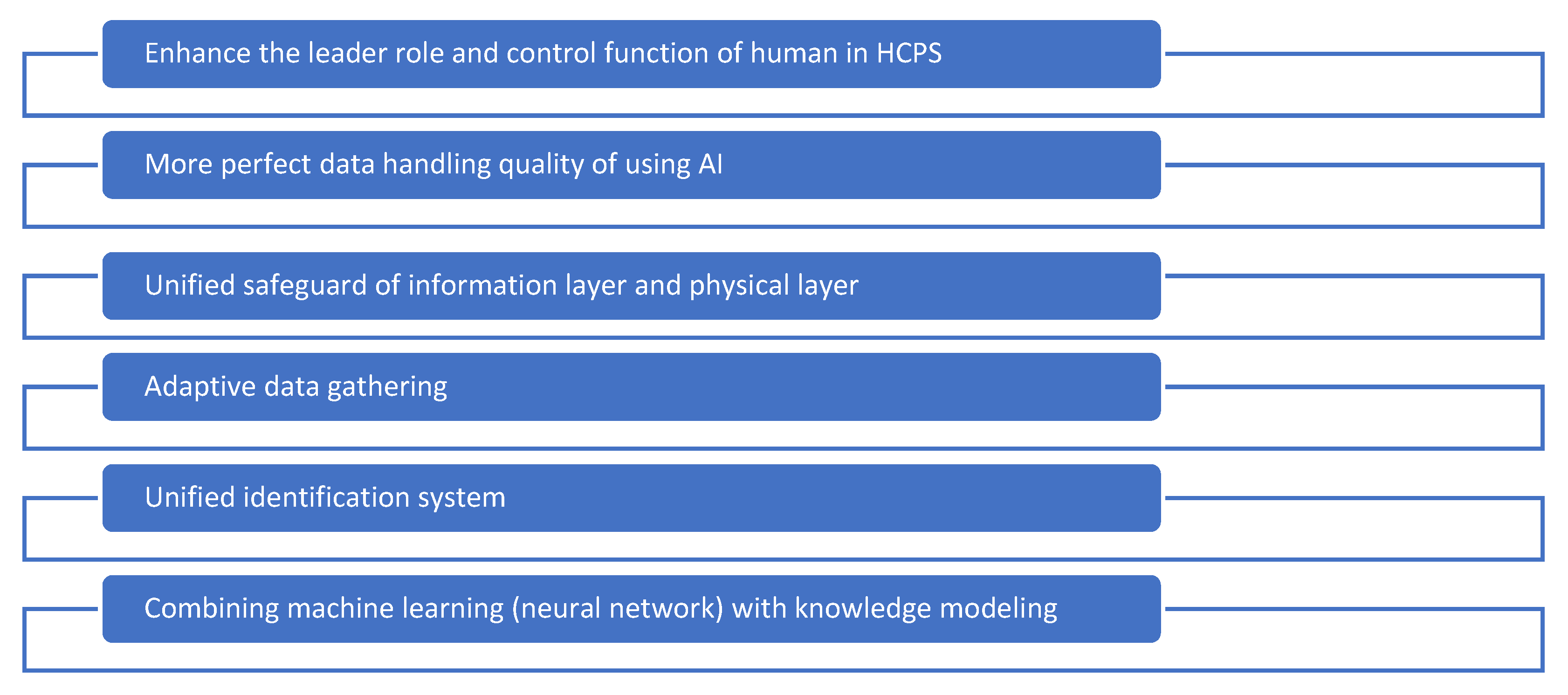
- (1)
- Enhance the leader role and control function of humans in HCPS. With the automation of HCPS, the problem with the need for human direction in fault and emergency situations becomes more complex and urgent. Humans should take the duty of directing, judging and control in HCPS; however, how to effectively use the knowledge of humans in HCPS cannot be effectively solved at present, such as in the EI domain, which requires the breakthrough of theory and techniques and the innovation of the concept. The leading role of humans in HCPS should be definitely ensured.
- (2)
- More perfect data handling quality of using AI. The AI technique is rapidly developing, with its typical product, Chat-GPT 4.0, becoming a research hot spot in recent months, whose thinking level can match that of humans. When the related AI device and software can further enhance its deducing ability and human-like ways of thinking, it will and can largely improve the performance of HCPS, and finally, the performance of EI.
- (3)
- Unified safeguarding of the information layer and physical layer. HCPS is a high fused system that tightly combines the physical layer with the information layer. An attack on one layer can be easily propagated to the other layer, such as the avalanche effect, which brought large challenges for the safeguard framework, simulation model and technique adoption, and this can be clearly observed in the EI system. It needs to set up a proper safe model, effectively utilize hybrid system safety simulation software and generate highly effective and low delay safeguarding policies to ensure the entire performance of HCPS. On the bases of passive defense, active and self-adaptive intelligent safeguarding techniques are necessary.
- (4)
- Adaptive data gathering. Based on the dynamic features of HCPS, the fault and emergency conditions may generate massive data, such as in EI. If the data cannot be gathered and handled in time, the operator cannot deeply mine the fault features, find timely resolutions and make highly effective safeguarding policies. Therefore, it needs to be based on the characters of the fault, activate the data gathering scheme when the fault occurs and modify the traditional sample policies and sample dimensions in time to ensure effective and reliable related data gathering, as well as correctly understand the fault from the system angle in order to win the time for fault handling and reduce the handling cost of HCPS operations.
- (5)
- Unified identification system. EIs are required to achieve a cross-domain mass bidirectional interaction for both the energy and information flow, whereupon the corresponding HCPS requires an effective identity authentication and authorization system to realize efficient operations among regions, nodes and/or businesses. Distributed digital identity, as a rising type of digital identity which decouples identity registration, management and verification, with its multi-center grant and multi-center authentication mechanism, echoes the bottom-up construction of the EI. The adoption of distributed digital identity technologies, including DID (Decentralized Identifier) and VC (Verifiable Credential), may help to improve the overall performance of HCPS in EI with a wide range of complex scenarios.
- (6)
- Combining machine learning (neural network) with knowledge modeling. Both techniques are broadly utilized in EI, but their interaction or integration are rare, which introduces some inherited shortcomings; for example, the neural network techniques cannot be effectively used in situations with less data, its result may not obey the physical laws, the parameters of modeling techniques need to be precisely estimated and its execution time may be long. Through the comprehensive utilization of the two means, the above problems can be effectively solved, which will open a new gate for high performance HCPS with its application in EI.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AADL | Architecture Analysis and Design Language |
| ADMM | The Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers |
| ADPSS | The Advanced Digital Power Simulator |
| BEMS | Building Energy Managing System |
| CC | Computational/Cyber Component |
| CPS | Cyber-Physical Systems |
| CPSOS | Cyber-Physical System of System |
| DER | Distributed Energy Resources |
| DFD | Data Flow Diagram |
| DID | Decentralized Identifier |
| EH | Energy Hub |
| EI | Energy Internet |
| EI-CPS | Energy Internet Cyber-Physical System |
| EISH | Energy Integrated Service Hub |
| EMS | Emergency Management System |
| EMS | Energy Management System |
| FPDS | Flexible Power Distribution System |
| FPDU | Flexible Power Distribution Unit |
| HC | Human Component |
| HCPI | Human-Cyber-Physical Intelligent |
| HCPS | Human-Cyber-Physical Systems |
| HF | Human Factors |
| HIL | Hardware-In-The-Loop |
| HVDC | High Voltage Discrete Current |
| ICPS | Industry CPS |
| ICT | Information Communication Technologies |
| IEMS | Integrated Energy Management System |
| IOB | Internet of Behaviors |
| IPS | Integrated Power System |
| ODEs | Ordinary Differential Equations |
| PC | Physical Component |
| PCPS | Power Cyber Physical System |
| PDEs | Partial Differential Equations |
| SCPIFS | Security Control Plan Incorporating Frequency Stability |
| UPIOT | Ubiquitous Power Internet of Things |
| VC | Verifiable Credential |
| VCPS | Vehicular Cyber-Physical System |
| WECSs | Wind Energy Conversion Systems |
References
- Zhou, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J. Human–Cyber–Physical Systems (HCPSs) in the Context of New-Generation Intelligent Manufacturing. Engineering 2019, 5, 624–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera-Rivera, A.; Ochoa, W.; Larrinaga, F.; Lasa, G. How-to conduct a systematic literature review: A quick guide for computer science research. MethodsX 2022, 9, 101895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.; Canedo, A.; Al Faruque, M.A. Cyber–Physical Codesign at the Functional Level for Multidomain Automotive Systems. IEEE Syst. J. 2017, 11, 2949–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerthi, C.K.; Jabbar, M.A.; Seetharamulu, B. Cyber Physical Systems (CPS): Security Issues. Challenges and Solutions. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Computing Research (ICCIC), Coimbatore, India, 14–16 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Maurice, O. A first Cyber-Physical Systems of Systems Modeling. In Proceedings of the 2018 13th Annual Conference on System of Systems Engineering, Paris, France, 19–22 June 2018; pp. 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Barrère, M.; Hankin, C.; Barboni, A.; Zizzo, G.; Parisini, T. CPS-MT: A Real-Time Cyber-Physical System Monitoring Tool for Security Research. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 24th International Conference on Embedded and Real-Time Computing Systems and Applications (RTCSA), Hakodate, Japan, 28–31 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rai, R.; Sahu, C.K. Driven by Data or Derived Through Physics? A Review of Hybrid Physics Guided Machine Learning Techniques with Cyber-Physical System (CPS) Focus. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 71050–71073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, E.; Xu, X.; Lu, Y. Human Cyber-Physical Systems: A Skill-Based Correlation Between Humans and Machines. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 16th International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE), Hong Kong, 20–21 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Beghi, A.; Marcuzzi, F.; Rampazzo, M.; Virgulin, M. Enhancing the Simulation-Centric Design of Cyber-Physical and Multi-physics Systems through Co-simulation. In Proceedings of the 2014 17th Euromicro Conference on Digital System Design, Verona, Italy, 27–29 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Vangheluwe, H. Multi-Paradigm Modelling of Cyber-Physical Systems. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/ACM 4th International Workshop on Software Engineering for Smart Cyber-Physical Systems (SEsCPS), Gothenburg, Sweden, 27 May–3 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Guo, R.; Hu, Y.; Yu, H.; Wu, H.; Peng, A. Research on the Architecture of Cyber-Physical Machine Tool System. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 4th International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 7–10 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Song, E.Y.; Burns, M.; Pandey, A.; Roth, T. IEEE 1451 Smart Sensor Digital Twin Federation for IoT/CPS Research. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Sensors Applications Symposium (SAS), Sophia Antipolis, France, 11–13 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Liu, G.; Wen, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Ma, W.; Sun, C.; Luo, G.; Huang, R. Industrial Safety Control System and Key Technologies of Digital Twin System Oriented to Human-Machine Interaction. Comput. Integr. Manuf. Syst. 2021, 27, 374–389. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Stary, C. Digital Twin Generation: Re-Conceptualizing Agent Systems for Behavior-Centered CPS Development. Sensors 2021, 21, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovhannisyan, D.; Kurdahi, F.; Eltawil, A.; Aghakouchak, A.; Al Faruque, M.A. Poster Abstract: Unifying Modeling Substrate for Irrigation Cyber-Physical Systems. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM/IEEE 7th International Conference on Cyber-Physical Systems (ICCPS), Vienna, Austria, 11–14 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.U.; Li, S.; Wang, Q.; Shao, Z. CPS Oriented Control Design for Networked Surveillance Robots with Multiple Physical Constraints. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2016, 35, 778–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, W.; Huang, W.; Cheng, J. A Collaborative Modeling Method for Multi -behavior Models of Electromechanical CPS Systems. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/ACIS 20th International Fall Conference on Computer and Information Science (ICIS Fall), Xi’an, China, 13–15 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cornejo, O.; Pastore, F.; Briand, L. MASS: A tool for Mutation Analysis of Space CPS. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/ACM 44th International Conference on Software Engineering: Companion Proceedings (ICSE-Companion), Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 22–27 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, C.; Bao, X.; Fu, L.; Xia, L.; Xu, X.; Xu, C. A Novel Key-Value Based Real-time Data Management Framework for Ship Integrated Power Cyber-Physical System. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Innovative Smart Grid Technologies—Asia (ISGT Asia), Chengdu, China, 21–24 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Chang, L.; Guo, L.; Wang, Y.; Jia, X. Application Research of ZigBee Protocol in CPS Based on Multi-agent. In Proceedings of the 2017 29th Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), Chongqing, China, 28–30 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yampolskiy, M.; Horvath, P.; Koutsoukos, X.D. Systematic Analysis of Cyber-Attacks on CPS-Evaluating Applicability of DFD-Based Approach. In Proceedings of the 2012 5th International Symposium on Resilient Control Systems IEEE, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 14–16 August 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Zhang, S. Modeling of Security Risk for Industrial Cyber-Physics System under Cyber-attacks. In Proceedings of the 2021 4th IEEE International Conference on Industrial Cyber-Physical Systems (ICPS), Victoria, BC, Canada, 10–12 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, K.; Sahoo, S.; Mohanty, R.; Panigrahi, B.K.; Blaabjerg, F. Decentralized Anomaly Characterization Certificates in Cyber-Physical Power Electronics Based Power Systems. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 22nd Workshop on Control and Modelling of Power Electronics (COMPEL), Cartagena, Colombia, 2–5 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mäkiö, J.; Mäkiö-Marusik, E.; Yablochnikov, E. Task-Centric Holistic Agile Approach on Teaching Cyber Physical Systems Engineering. In Proceedings of the IECON 2016—42nd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Florence, Italy, 23–26 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zabasta, A.; Peuteman, J.; Kunicina, N.; Fedotov, A.K.; Prylutskyy, Y.; Fedotov, A.S. Development of Industry Oriented Curricular on Cyber Physical Systems for Belarusian and Ukrainian Universities. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 6th Workshop on Advances in Information, Electronic and Electrical Engineering (AIEEE), Vilnius, Lithuania, 8–10 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, R.; Weimer, J.; Lee, I. Towards Context-Aware Cyber-Physical Systems. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Workshop on Monitoring and Testing of Cyber-Physical Systems (MT-CPS), Porto, Portugal, 10–13 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, X.; Wu, J.; Li, G.; Bashir, A.K.; Li, J.; AlZubi, A.A. Recurrent Semantic Learning-driven Fast Binary Vulnerability Detection in Healthcare Cyber Physical Systems. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Kong, D.; Pang, G.; Wang, B.; Yu, Z.; Pang, Z.; Yang, G. GuLiM: A Hybrid Motion Mapping Technique for Teleoperation of Medical Assistive Robot in Combating the COVID-19 Pandemic. IEEE Trans. Med. Robot. Bionics 2022, 4, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herkersdorf, A. Multicore Enablement for Cyber Physical Systems. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Embedded Computer Systems (SAMOS), Samos, Greece, 16–19 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Balasubramaniyan, S.; Subathra, B.; Hemesh, R.C.; Gurusamy, S.; Srinivasan, S. On Simulating Processor Schedules and Network Protocols within CPS Using TrueTime. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Computing Research (ICCIC), Madurai, India, 10–12 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dunets, R.; Klym, H.; Kochan, R. Models of Hardware Integration of Sensors Elements with Cyber-Physical Systems. In Proceedings of the 2016 13th International Conference on Modern Problems of Radio Engineering, Telecommunications and Computer Science (TCSET), Lviv, Ukraine, 23–26 February 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, N.; Lyshevski, S.E. Information Fusion and Data-Driven Processing in Inertial Measurement Units for Cyber-Physical Systems. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 37th International Conference on Electronics and Nanotechnology (ELNANO), Kyiv, Ukraine, 18–20 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, W. The Encapsulation Technology of CPS Node Sensor Based on UM-BUS. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Information Science, Parallel and Distributed Systems (ISPDS), Xi’an, China, 14–16 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Moness, M.; Moustafa, A.M. A Survey of Cyber-Physical Advances and Challenges of Wind Energy Conversion Systems: Prospects for Internet of Energy. IEEE Internet Things J. 2016, 3, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Xiang, K.; Du, Y.; Li, Y.; Lin, H. Research on the Energy Internet Under the Background of Ubiquitous Power Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 3rd Conference on Energy Internet and Energy System Integration (EI2), Changsha, China, 8–10 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, G.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y. Component Model of Grid Cyber Physical Systems Based on Finite Automata. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 4th Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IAEAC), Chengdu, China, 20–22 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.; Liu, L.; Cheng, C.; Wang, W.; Wei, J.; Wu, J. Multi-microgrids Transaction Model Based on Cyber Physical System. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Intelligent Technology and Embedded Systems (ICITES), Chengdu, China, 30 October–2 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, J.; Shi, P.; Mu, Q. Based on Random Game Petri Net Model CPS Risk Assessment and Defense Decision of Distribution Network. In Proceedings of the 2021 4th International Conference on Advanced Electronic Materials, Computers and Software Engineering (AEMCSE), Changsha, China, 26–28 March 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H. Entropy Analysis of CPS with Application in Smart Grids: From Discrete Network to Continuum Limit. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications (SmartGridComm), Miami, FL, USA, 2–5 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Li, K.; Meng, Z. CPS Optimal Control for Interconnected Power Grid Based on Model Predictive Control. In Proceedings of the 2018 2nd IEEE Conference on Energy Internet and Energy System Integration (EI2), Beijing, China, 20–22 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wei, J.; Liu, X.; Ye, S. The Study and Application of Security Control Plan Incorporating Frequency Stability (SCPIFS) in CPS-Featured Interconnected Asynchronous Grids. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Innovative Smart Grid Technologies—Asia (ISGT Asia), Chengdu, China, 21–24 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nejati, S. Testing Cyber-Physical Systems via Evolutionary Algorithms and Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/ACM 12th International Workshop on Search-Based Software Testing (SBST), Montreal, QC, Canada, 26–27 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.; Zhao, L.; Ni, M.; Li, M. Review of Cyber Physical System and Cyber Attack Modeling. In Proceedings of the 2020 12th IEEE PES Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference (APPEEC) IEEE, Nanjing, China, 20–23 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, N.; Guo, Q.; Sun, H.; Huang, J. A Synchronous Iterative Method of Power Flow in Inter-Connected Power Grids Considering Privacy Preservation: A CPS Perspective. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 4th Conference on Energy Internet and Energy System Integration (EI2), Wuhan, China, 3 October–1 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Z.; Xu, L.; Xin, S.; Li, W.; Shi, Z.; Guo, Q. A Future Outlook for Cyber-Physical Power System. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Energy Internet and Energy System Integration (EI2), Beijing, China, 26–28 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Xu, L.; Guo, Q.; Sheng, T.; Yang, T.; Huang, Y.; Wu, Z. Sensitivity-Based Critical Measurement Identification of State Estimation: From A CPS Perspective. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Control, and Computing Technologies for Smart Grids (SmartGridComm), Aalborg, Denmark, 29–31 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ravikumar, G.; Hyder, B.; Govindarasu, M. Efficient Modeling of HIL Multi-Grid System for Scalability & Concurrency in CPS Security Testbed. In Proceedings of the 2019 North American Power Symposium (NAPS), Wichita, KS, USA, 13–15 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ravikumar, G.; Hyder, B.; Govindarasu, M. Efficient Modeling of IEC-61850 Logical Nodes in IEDs for Scalability in CPS Security Testbed. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/PES Transmission and Distribution Conference and Exposition (T&D), Chicago, IL, USA, 12–15 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, K.; Li, H.; Liu, G.; Li, B.; Geng, S.; Lei, Y. Site Selection of Energy Integrated Hub Station Based on CPS. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 4th International Electrical and Energy Conference (CIEEC), Wuhan, China, 28–30 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Jiang, K. Research on Location Planning of Integrated Service Station of Integrated Energy System. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 5th International Electrical and Energy Conference (CIEEC), Nangjing, China, 27–29 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Faria, L.; Silva, A.; Ramos, C.; Vale, Z.; Marques, A. Cyber-Ambient Intelligent Training of Operators in Power Systems Control Centres. In Proceedings of the 2009 15th International Conference on Intelligent System Applications to Power Systems, Curitiba, Brazil, 8–12 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.L. Research of CPSNet Security Technology in Smart Grid. Ph.D. Thesis, Graduate School of National University of Defense Technology, Harbin, China, 2013. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.; Lian, H.; Na, C.; Li, X. Modeling and Vulnerability Analysis of Cyber-Physical Power Systems Based on Community Theory. IEEE Syst. J. 2020, 14, 3938–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumar, G.; Hyder, B.; Govindarasu, M. Hardware-in-the-Loop CPS Security Architecture for DER Monitoring and Control Applications. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Texas Power and Energy Conference (TPEC), College Station, TX, USA, 6–7 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- IEEE 2030.5-2013 SEP2; IEEE Standard for Smart Energy Profile Application Protocol. IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013.
- Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Xu, Y.; Mu, Q.; Zhang, X. The Research and Implementation of Power CPS Simulation Platform Based on ADPSS. In Proceedings of the 16th IET International Conference on AC and DC Power Transmission, Xi’an, China, 2–3 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, P. Characteristics and Technical Challenges in Energy Internet Cyber-Physical System. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference Europe (ISGT-Europe), Ljubljana, Slovenia, 9–12 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Q.; Ma, C.; Sha, G.; Zhao, C.; Li, Z. Research on Flexible Power Distribution Unit and Its Key Technologies for Energy Internet. In Proceedings of the 2018 13th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Wuhan, China, 31 May–2 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, B.; Shao, H.; Jiang, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Jing, Z. Key Technologies and Prospects for Planning Methods of Energy Internet. In Proceedings of the 2018 2nd IEEE Conference on Energy Internet and Energy System Integration (EI2), Beijing, China, 20–22 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L.; Yu, T.; Jiang, H.; Shi, S.; Tan, Z.; Zhang, Z. Energy Internet Access Equipment Integrating Cyber-Physical Systems: Concepts, Key Technologies, System Development, and Application Prospects. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 23127–23148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Xia, B.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, M.; Ma, Z. Research on Integrated Model and Interactive Influence of Energy Internet Cyber Physical System. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Sustainable Power and Energy Conference (iSPEC), Chengdu, China, 23–25 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Li, X.; Freiheit, T.; Epureanu, B.I. Learning and Intelligence in Human-Cyber-Physical Systems: Framework and Perspective. In Proceedings of the 2020 Second International Conference on Transdisciplinary AI (TransAI), Irvine, CA, USA, 21–23 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Qiao, F.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Kong, W. Human-Machine Cooperation Based Adaptive Scheduling for a Smart Shop Floor. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Toronto, ON, Canada, 11–14 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, W.; Zhou, X. Smart Factory Production and Operation Management Methods based on HCPS. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control (ICNSC), Nanjing, China, 30 October–2 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X. The New Development Direction of Artificial Intelligence—Human Cyber Physical Intelligence. In Proceedings of the 2021 10th International Conference on Educational and Information Technology (ICEIT), Chengdu, China, 18–20 January 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, P.; Bi, S.; Guan, Z.; Cheng, H. Cooperative Governance of Intelligent Society: Research Status and Development Trend. J. South China Norm. Univ. 2023, 55, 19–35. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, X. AIoT: The Concept, Architecture and Key Techniques. Chin. J. Comput. 2023, 1–20. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Munir, S.; Ahmed, M.; Stankovic, J. EyePhy: Detecting Dependencies in Cyber-Physical System Apps due to Human-in-the-Loop. In Proceedings of the 12th EAI International Conference on Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems: Computing, Networking and Services ICST (Institute for Computer Sciences, Social-Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering), Coimbra, Portugal, 22–24 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, S.; Guo, D.; Qian, C.; Ao, D.; Zhang, T.; Rong, Y.; Huang, G. Computer Vision-enabled HCPS Assembly Workstations Swarm for Enhancing Responsiveness in Mass Customization. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 16th International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE), Hong Kong, China, 20–21 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- An, D. Formal Modeling and Dynamic Verification for Human Cyber Physical Systems under Uncertain Environment. Ph.D. Thesis, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 2020. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Bellini, E.; Bagnoli, F.; Caporuscio, M.; Damiani, E.; Flammini, F.; Linkov, I.; Liò, P.; Marrone, S. Resilience Learning through Self Adaptation in Digital Twins of Human-Cyber-Physical Systems. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Cyber Security and Resilience (CSR), Rhodes, Greece, 26–28 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, M.; Chen, Z.; Xu, B. Human-cyber-physical Services Dispatch Approach for Data Characteristics. J. Softw. 2021, 32, 3404–3422. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Hu, P.; Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Zhou, B. A Digital-Twin Visualized Architecture for Flexible Manufacturing System. J. Manuf. Syst. 2021, 60, 176–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Eder, M.A.; Shihavuddin, A.; Zheng, D. A Human-Cyber-Physical System toward Intelligent Wind Turbine Operation and Maintenance. Sustainability 2021, 13, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoukat, M.U.; Yan, L.; Liu, W.; Hussain, F.; Nawaz, S.A.; Niaz, A. Digital Twin-Driven Virtual Control Technology of Home-Use Robot: Human-Cyber-Physical System. In Proceedings of the 2022 17th International Conference on Emerging Technologies (ICET), Swabi, Pakistan, 29–30 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Qiao, C.; Yu, X.; Wagh, A.; Sudhaakar, R.; Addepalli, S. Toward Effective Service Scheduling for Human Drivers in Vehicular Cyber-Physical Systems. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2012, 23, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirner, G.; Erdogmus, D.; Chowdhury, K.; Padir, T. The Future of Human-in-the-Loop Cyber-Physical Systems. Computer 2013, 46, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, M.; Xu, W.; Qi, Q. Theories and Technologies for Cyber-Physical Fusion in Digital Twin Shop-Floor. Comput. Integr. Manuf. Syst. 2017, 23, 1603–1611. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mei, H.; Cao, D.; Xie, T. Ubiquitous Operating System: Toward the Blue Ocean of Human-Cyber-Physical Ternary Ubiquitous Computing. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2022, 37, 30–37. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Song, L.; Xiang, T.; Liu, L. New Development Direction of Artificial Intelligence-Human Cyber Physical Ternary Fusion Intelligence. Comput. Sci. 2020, 47, 1–5+22. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yi, D.; Wang, X. Architecture and Key Techniques of Parallel Creation Through the Fusion of Human-Cyber-Physical Intelligence in CPSS. Chin. J. Intell. Sci. Technol. 2022, 4, 344–354. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Nagarajan, S.M.; Devarajan, G.G.; Mohammed, A.S.; Ramana, T.V.; Ghosh, U. Intelligent Task Scheduling Approach for IoT Integrated Healthcare Cyber Physical Systems. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Dai, F.; Qin, M. A Privacy-Preserving Deep Learning Scheme for Edge-Enhanced Smart Homes. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Dependable, Autonomic and Secure Computing, International Conference on Pervasive Intelligence and Computing, International Conference on Cloud and Big Data Computing, International Conference on Cyber Science and Technology Congress (DASC/PiCom/CBDCom/CyberSciTech), Falerna, Italy, 12–15 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Gelenbe, E.; Gorbil, G.; Wu, F.J. Emergency Cyber-Physical-Human Systems. In Proceedings of the 2012 21st International Conference on Computer Communications and Networks (ICCCN), Munich, Germany, 30 July–2 August 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zamfirescu, C.B.; Pirvu, B.C.; Gorecky, D.; Chakravarthy, H. Human-centred Assembly: A Case Study for an Anthropocentric Cyber-physical System. Procedia Technol. 2014, 15, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Guo, J.; Fan, S.; Huang, Y.; Shang, Y. Human-in-the-loop Hybrid-augmented Intelligence Method for Power System Dispatching, Basic Concept and Research Framework. Proc. CSEE 2023, 43, 1–15. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Munir, S.; Stankovic, J.A.; Liang, C.M.; Lin, S. Reducing Energy Waste for Computers by Human-in-the-Loop Control. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 2015, 2, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mona, B.; Alireza, A.; Saeed, T.; Farrokh, A.; Mehdi, k.; Mohammad, S. IoT-Enabled Humans in the Loop for Energy Management Systems: Promoting Building Occupants’ Participation in Optimizing Energy Consumption. IEEE Electrif. Mag. 2018, 6, 64–72. [Google Scholar]
- Eichler, A.; Darivianakis, G.; Lygeros, J. Humans-in-the-loop: A Game-Theoretic Perspective on Adaptive Building Energy Systems. In Proceedings of the 2018 17th European Control Conference (ECC), Limassol, Cyprus, 12–15 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Schutte, M.; Hota, A.; Eichler, A.; Lygeros, J. Dynamic Mechanism Design for Human-in-the-Loop Control of Building Energy Consumption. In Proceedings of the 2019 American Control Conference (ACC), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 10–12 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shimamoto, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Yamashita, Y. Stochastic Model Predictive Control of Energy Management Systems with Human in the Loop. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 9th Global Conference on Consumer Electronics (GCCE) IEEE, Kobe, Japan, 13–16 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Neumeyer, X.; Santos, S.C.; Morris, M.H. Overcoming Barriers to Technology Adoption When Fostering Entrepreneurship Among the Poor: The Role of Technology and Digital Literacy. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2021, 68, 1605–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neeley, T.; Leonardi, P. Developing a Digital Mindset. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2022, 100, 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Neumeyer, X.; Liu, M. Managerial competencies and development in the Digital Age. IEEE Eng. Manag. Rev. 2021, 49, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solberg, E.; Traavik, L.E.; Wong, S.I. Digital Mindsets: Recognizing and Leveraging Individual Beliefs for Digital Transformation. Calif. Manag. Rev. 2020, 62, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N. A Cloud-Based Platform for Big Data-Driven CPS Modeling of Robots. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 34667–34680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.J.; Kim, D.K.; Kim, W.-T.; Park, S.-M. Dynamic Software Updates in Cyber-Physical Systems. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 17–19 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Shekhar, S. Dynamic Data Driven Cloud Systems for Cloud-Hosted CPS. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Cloud Engineering Workshop (IC2EW), Berlin, Germany, 4–8 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Lu, Y.; Yan, D.; Xiao, J.; Wu, H. Scientometric mapping of smart building research: Towards a framework of human-cyber-physical system (HCPS). Autom. Constr. 2021, 129, 103776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrela, V.V.; Monteiro, A.C.B.; Frana, R.P.; Iano, Y.; Khelassi, A.; Razmjooy, N. Health 4.0: Applications, Management, Technologies and Review. Med. Technol. J. 2019, 2, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Sun, D.; Li, Y.; Zhao, M.; Liu, W. Hierarchical Human-vehicle Collaboration Control Strategy for Intelligent Vehicle under Human-cyber-physical System Architecture. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 25th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Macau, China, 8–12 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Roth, E.; Howell, D.; Beckwith, C.; Burden, S.A. Toward experimental validation of a model for human sensorimotor learning and control in teleoperation. In Micro-and Nanotechnology Sensors, Systems, and Applications IX; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2017; Volume 20194. [Google Scholar]
- Yamagami, M.; Howell, D.; Roth, E.; Burden, S.A. Contributions of feedforward and feedback control in a manual trajectory-tracking task. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2019, 51, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhou, H.; Yang, G.; Li, X.; Yang, H. Human Digital Twin (HDT)Driven Human-Cyber-Physical Systems:Key Technologies and Applications. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2022, 35, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Eder, M.A.; Shihavuddin, A. A concept for human-cyber-physical systems of future wind turbines towards Industry 5.0. TechRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. Super-metauniverse with cyber life as center in integrating cyber nature and cyber society sky-earth computing (III) beyond cloud computing. ITM Web Conf. 2022, 45, 01067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lie, Z. Study the Fundamental Principle of Metaseience-Metamathematies and Dialectical Logic about (Man—Machine-Universe) Pansystem Theory—[Bohr’s Correspoudence Principle and Aristotle’s Systems Logical Breaking and Dynamics for Develop Science]. J. Chang. Univ. 1986, 2, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.; Qiuye, S.; Dazhong, M. Storage Control Strategy for Energy Hub of We-Energy in the Energy Internet. In Proceedings of the 2017 CCDC, Chongqing, China, 28–30 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Li, C.; Tang, Y.; Xiao, Q. An Internet of Things based energy efficiency monitoring and management system for machining workshop. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 199, 957–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkwyn, C. Sanxing Garden Internet+ Smart Energy Demonstration Project. Metering Int. 2019, (Suppl. 2), 38. [Google Scholar]
- Hiremth, M.; Kumar, M. Internet of Things for Energy Management in the Home Power Supply. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2018, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Tentzeris, M.M.; Kawahara, Y. Novel Energy Harvesting Technologies for ICT Applications. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Symposium on Applications and the Internet, Turku, Finland, 28 July–1 August 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Shahzad, Y.; Javed, H.; Farman, H.; Ahmad, J.; BilalZubair, M. Internet of Energy: Opportunities, applications, architectures and challenges in smart industries. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2020, 86, 106739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
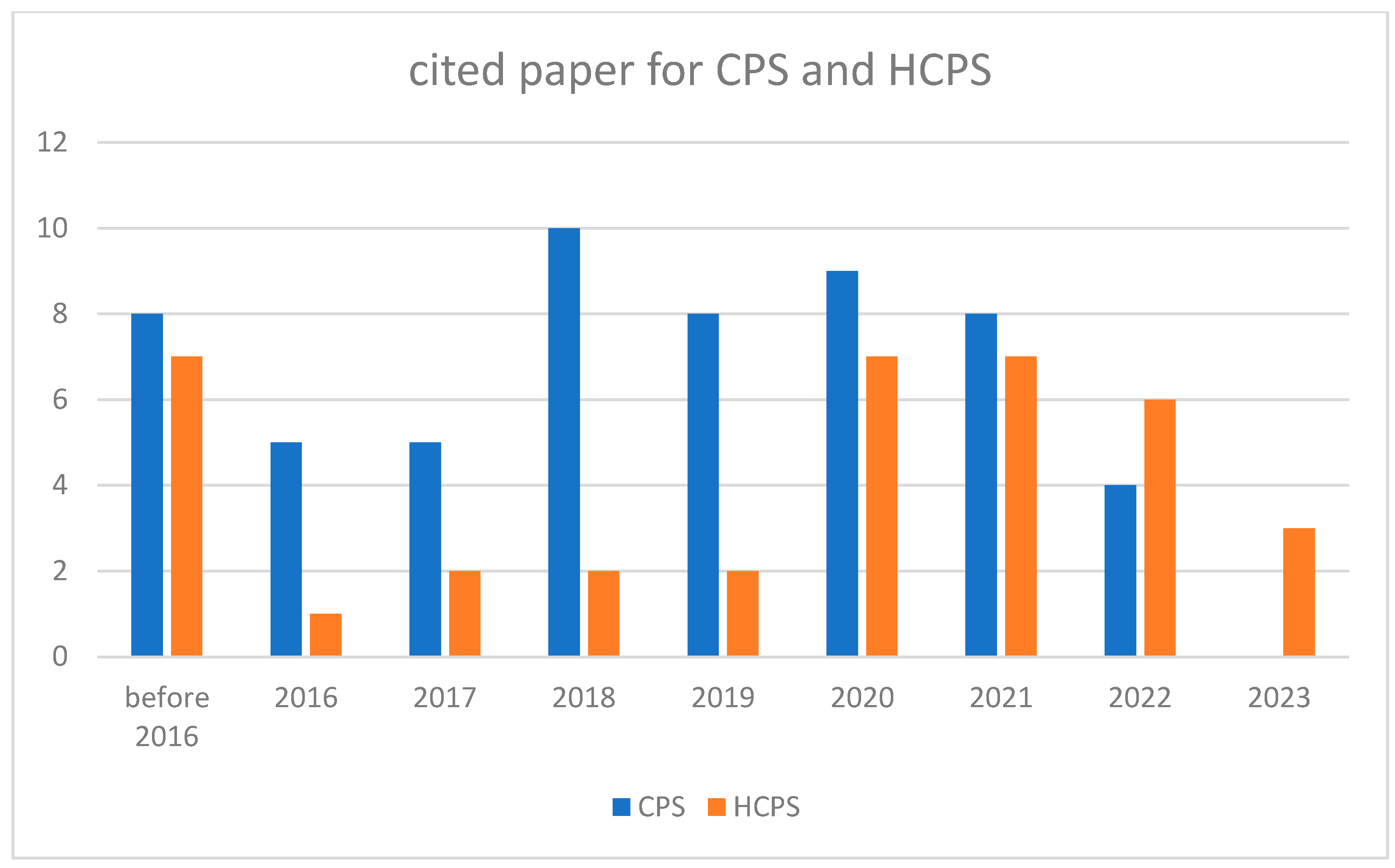
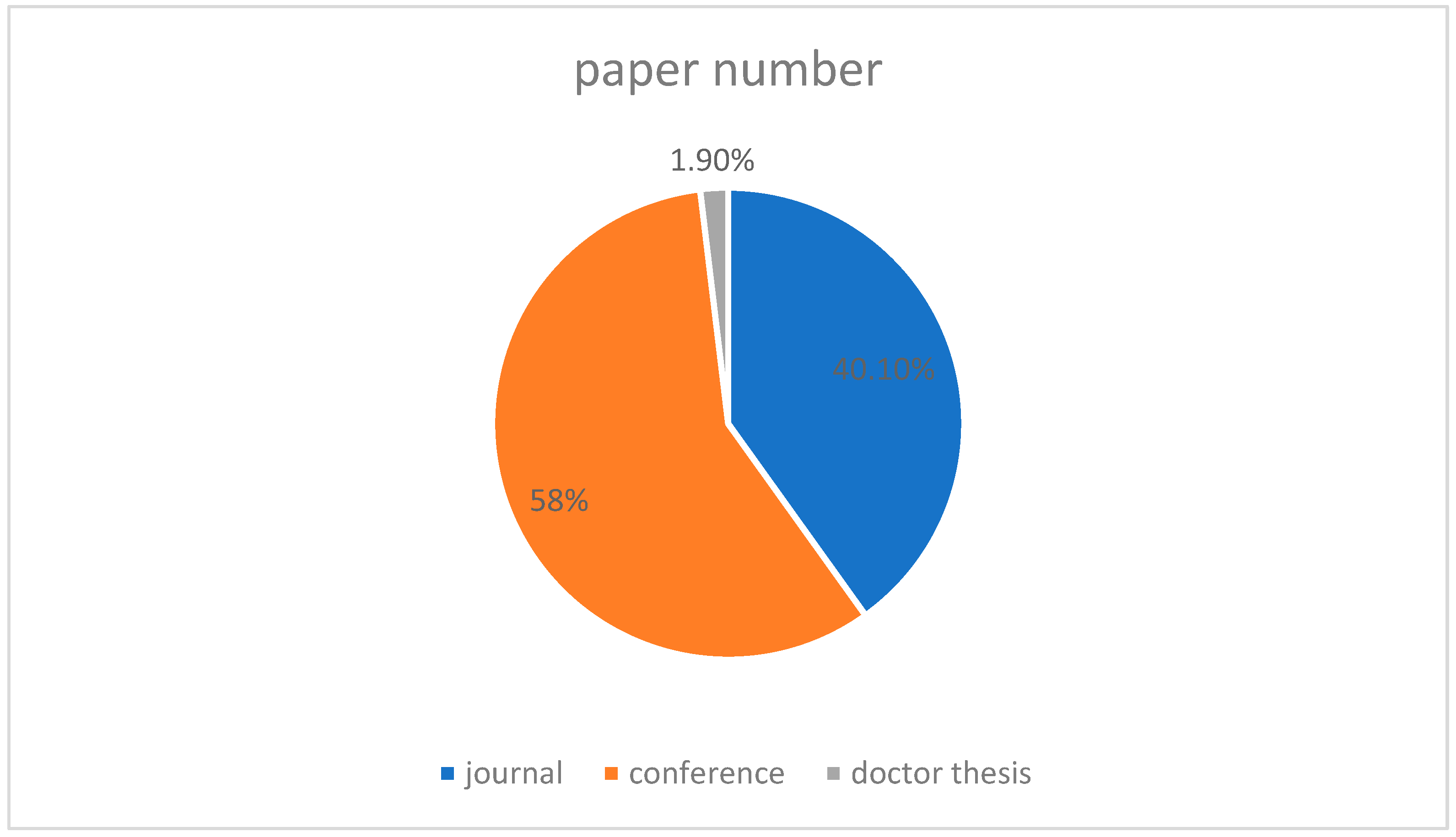

| Industry | Paper No. | Research Content | Main Object | Technique Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Theory analysis | [3] | Proposed a function level cyber-physical code design method. | Designed a function level cyber-physical code design method. | Using high-level combination algorithm. |
| [4] | Reviewed the development of CPS, discussed the related safety factors with the CPS, brought challenges, and its effects in healthcare. | Undertook a development review. | Conducted safety factor analysis and challenge analysis. | |
| [5] | Proposed the basic concepts of CPSOS modeling. | Created system model equations, exchanged data through ultra-long distance. | Set up neural networks, sensing networks and action actuate networks. | |
| [6] | Proposed an initial design of a flexible and real-time CPS monitor tool. | Founded related framework and main comprised components, and further researched related demos. | Designed a real-time CPS monitor tool. | |
| [7] | Advanced five standards for the model performance evaluation, and the model performance based on CPS modelling was discussed. | Undertook the hybrid modeling method research. | Using physical and equation modeling and machine learning. | |
| [8] | Discussed whether the machine and human can realize collaborate control in the CPS system. | Realized collaborate control in the CPS system. | Updated the difference list between the abilities of human and machine | |
| industry | [9] | Founded a pure simulation prototype on industry CPS. | Realized simulation integration of CPS and physic system. | Conducted firm ware and multi-physic control systems’ collaborative simulation. |
| [10] | Listed the faced challenges in CPS collaborative development. | Undertook the simulation demo in CPS design. | Using coherent management and collaborative simulation. | |
| [11] | Analyzed the need of industry 4.0 to CPS system and proposed detailed representation of CPS machine tool system. | Proposed a 4-layer framework. | Conducted detailed representation of CPS machine tool system. | |
| [12] | Proposed an intelligent sensor modeling and communication protocol based on digital twin. | Undertook intelligent collaboration in CPS. | Using digital twin. | |
| [13] | Focused on industry safety and control and proposed related schemes with digital twin system. | Realized industry safety and control. | Based on digital twin system. | |
| [14] | Proposed setting behavior models based on digital twin in IOB (Internet of Behaviors). | Increased the running efficiency and transparent extent of CPS, and improved the dynamic adjust abilities. | Using digital twin in IOB. | |
| agriculture | [15] | Developed an electrical circuit model for adjusting soil’s moisture in next generation of CPS irrigation. | Realized next generation of CPS irrigation. | Developed an electrical circuit model for soil’s moisture. |
| aerospace | [16] | Proposed corresponding CPS interactive model to realize formation control and tracked the emergence of other robots and the static hurdles. | Realize formation control, orbit tracing and obstacle avoiding. | Set up CPS interactive model. |
| [17] | Proposed an electromechanical event model and the co-simulation method based on CPS. | Illustrated related space and temporal information with this energy system, and proposed system modeling and handling method based on event response. | Founding unified model and top layer services across the domain of application and data resource. | |
| [18] | Proposed a mutation analysis tool for embedded software in CPS. | Realized mutation analysis in CPS environment and solved the extendable and precision problem. | Realized online software system management of satellite orbiting. | |
| shipping | [19] | Proposed a next generation of ship IPS (integrated power system), which realized high information level of every physical equipment, and would evolve into CPS. | Realized patch handling and distributed deploying to obtain time efficiency and system extensibility. | Proposed a new type of key-value model. |
| building | [20] | Proposed a multi-agent technology and corresponding ZigBee protocol for intelligent building CPS system. | Set up intelligent building CPS system. | Realized wireless network user level CPS based on multi-agent technology. |
| safeguard | [21] | Proposed some performance extensions on DFD (Data Flow Diagram) and used it in UAV quad-rotor to analyze its safety. | Constituted effective information and physical defense system. | Using DFD (data flow diagram) on related CPS interaction. |
| [22] | Proposed a safety threat quantization analysis method in ICPS (Industry CPS). | Founded the math model between physical factory and feedback controller. | Set up dynamic closed loop fusion model. | |
| [23] | Decide the boundary of the plane to distinguish grid fault and information attack based on CPS. | Distinguished the abnormal features of physical fault and information fault. | Proposed a distributed 2-dimensional plane mapping method based on local measured frequency and voltage. | |
| education | [24] | Proposed a new task-oriented real and flexible method to teach CPS. | Using a new task-oriented real and flexible method to teach CPS. | Summarized five types of teaching methods and realized on demand use. |
| [25] | Managed to create the CPS curriculum focusing on industry. | Made breakthrough on the gap between industry need and education output. | Taking institution cooperation. | |
| medicine | [26] | Used CPS to non-intrusive measure the patients’ blood oxygen content and reduce the error probability. | Realized CPS medicine operation. | Modelled the context probability based on system status and developed a context sensing filter. |
| [27] | Realized rapid binary vulnerability detect for healthcare CPS based on cycle semantic learning driven. | Improved the detect precision of robust properties. | Using the related technique with healthcare CPS. | |
| [28] | Used CPS related technologies to realize remote operation of medical robot to effectively resist COVID disease. | Resisted COVID disease. | Using CPS related technologies. | |
| Hardware/software | [29] | The usage of the general accelerator and related software and hardware to provide key non-function demand for covering offline multi-core and chip’s multi-handling system framework. | Used proper virtual and self-organizing technologies for CPS. | Set up offline multi-core and chip multi-handling system framework. |
| [30] | Described the role and function of True Time 2.0 software package in information packing simulation with the scheme of CPS handler and network protocol. | Undertook programming in CPS research by using toolbox to simulation and multi-module to initialization. | Designed the TrueTime tool. | |
| [31] | Proposed the fusion model of sensor element and hardware in CPS. | Adopted active resistor measurement and obtained higher measure precision. | Conducted multi-channel sensor interaction. | |
| [32] | Used CPS components to enhance the data quality and sensing precision of inertia sensors. | Developed physical coherent tools and algorithms of inertia measure units. | Using post-processing to reduce the noise and mistake of estimated physical value in the measurement. | |
| [33] | Designed the package scheme of sensor method by CPS. | Undertook on the optimal and package of function method. | Realized inter-layer calling between methods. |
| Industry | Paper No. | Research Content | Main Object | Technique Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPS on Framework Design | [34] | Proposed the WECSs (Wind Energy Conversion Systems) concept, analyzed its function need, and further applied CPS to improve its performance. | Proposed the research trend for energy applications, so CPS could be potentially integrated with WECS. | Realized demand-side management and smart building. |
| [35] | Proposed the UPIOT (Ubiquitous Power Internet of Things) concept. | CPS can deeply coordinate information and physical resources in UPIOT. | Using the techniques of computing, communication and control. | |
| [36] | Based on information and automation, and through deepening fusion of information system and physical system, electrical power system would gradually evolve into power CPS. | Researched the finite state automation model of electrical power components, and analyzed its state characters, state transfer rules and state transfer functions of related services. | The model was validated in the feeder terminal units. | |
| [37] | Proposed a multi-micro grid task model based on CPS. | Researched the CPS framework and model of multi-micro grid and set up the multi-micro grid CPS model based on multi-agent system. | Related demos verified the effect of proposed model. |
| Research Topic | Paper No. | Research Content | Main Object | Technique Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Support Technologies and Algorithms | [38] | Proposed a distributed network method for CPS risk evaluation and defense policy making. Through network risk level analysis, it could promote the attack and defense precision. | Promoted the attack and defense precision. | Fulfilling the task based on stochastic game Petri model. |
| [39] | In grid monitoring and operation, the key importance of interdependent of physical dynamics and communications in CPS was analyzed. | Information entropy estimation could be used in measuring its uncertainty and determined its communication need in monitoring. | ODEs (Ordinary Differential Equations) and PDEs (Partial Differential Equations) was used to describe the entropy evolution. | |
| [40] | Proposed that CPS standard can more objectively evaluate the effect of control behavior. | Realize optimal control and fulfill CPS standard at the same time. | Proposed a dynamic optimal CPS control method based on model predictive control in interconnect power grid. | |
| [41] | With the aid of cyber communication and handling, the SCPIFS (Security Control Plan Incorporating Frequency Stability) could ensure the safety and stability in both end of HVDC (High Voltage Discrete Current) tie-line and operate economically. | Ensuring that grid is within the limit of frequency stability domain. | With the aid of cyber communication and handling. | |
| [42] | Tested the performance of CPS based on exploring method. | Handled complex continuous method, expanded the big test input space, which was suited for black system. | Combined with the machine learning techniques to improve the search precision and effectiveness and expanded the test results in the form of information explanation. | |
| [43] | Introduced the related research of CPS power systems, it reviewed the development trend of info-attack means and summarized the modeling methods of CPS. | Had important theory and application value in the research of CPS power system. | Using relation matrix, graph theory, complex network theory, finite state machine, math programming and cell automation. | |
| [44] | Proposed that advanced ICT was the fundament of development power system into CPS network, which needed inter-connection and privacy preserve. | The CPS realization in power flow exchange needed the support of cyber interaction, to which ICT is the fundamental means. | Using ICT technologies. |
| Research Topic | Paper No. | Research Content | Main Object | Technique Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPS on System Function | [45] | Analyzed the CPS security modeling and its assessment in power grid. | IEMS (Integrated Energy Management System) was proposed, with the form of distributed EMS and cloud EMS. | Safety modeling and assessment were carried out. |
| [46] | Proposed that as the state estimation was a basic function of energy managing system in the power grid, and the disturbing data might affect its performance. | CPS should consider the cyber security, and a sensitive analysis method for CPS was proposed. | Identifying its critical measurement. | |
| [47,48] | Proposed the need of HIL (Hardware-In-the-Loop) for CPS security testbeds to handle the power system blackout. | Have zero overruns and low latency in computing and transmitting. | The performance was verified by a synthetic grid model and IEEE related bus grid models. | |
| [49] | Proposed the function of EH (Energy Hub), and its reasonable location could make smooth and reliable operating of CPS in power grid. | A comprehensive EH location model was proposed based on CPS. | Using Matlab/Simulink to show its effectiveness improvement of EH in power utilization. | |
| [50] | Proposed the EISH (Energy Integrated Service Hub) concept, which can be seen as the integration of data center, energy store device, EV charge station, and gas network for cold and hot energy. | Make a reliable CPS in multi-energy system. | Consider the communication efficiency, data transmission delay, and energy transmission efficiency, and carried out the simulation using Matlab/Simulink. |
| Research Topic | Paper No. | Research Content | Main Object | Technique Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPS on Power Ancillary Service | [51] | Proposed that renewable energy and power market will increase the dimensions of distributed power generating problem. | Realized the intelligent training of grid control center’s working staff, optimizing related factors such as in renewable energy, distributed generating and power market. | Fulfilling the target through CPS and edge intelligence. |
| [52] | Analyzed the correlation of smart grid with CPS and based on the analysis of locating the key safe node in cyber-power fusion network, it proposed some effective safeguards. | Proposed some effective safeguards. | Fulfilling the task through modeling and simulation. | |
| [53] | Discussed the vulnerabilities of CPPS in community attack type. The related models included power level, information level and their function linkage in the condition of topo consistency and non-scale information network. | Analyzed the effect of different attacks and different information networks on the proceeding of cascade failure. | The proposed minimum load cutting model was illustrated as a linear programming model. | |
| [54] | Proposed that deep interaction of massive cyber-physical interoperation in DER (Distributed Energy Resources) and overall remote monitoring and control made grid attack easier. | A DER monitoring and control architecture of CPS was proposed, with standard communication protocols, such as IEEE 2030.5-2013 SEP2 [55] (IEEE standard for Smart Energy Profile Application Protocol). | Related simulation showed 100% real-time performance and zero overruns. | |
| [56] | Proposed the PCPS (Power Cyber Physical System), which combining information flow and power flow. | A PCPS simulation platform based on ADPSS (the Advanced Digital Power Simulator) was proposed. | Related simulation results showed that this simulation could meet the needs of PCPS research. |
| Research Topic | Paper No. | Research Content | Main Object | Technique Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPS on Energy Internet Realization | [57] | Proposed EI-CPS (Energy Internet Cyber-Physical System) with deep couple of energy layer and information layer. | Proposed the future technique challenges of EI-CPS. | Paper analyzed core techniques in CPS, such as system modeling, data analysis and operation control and so on. |
| [58] | Proposed a FPDU (Flexible Power Distribution Unit) based on CPS in Energy Internet. | FPDS (Flexible Power Distribution System) is further proposed, with the equipment combinations of iPower + Router, iPower + Switcher and iPower + Hub. | Included four key technologies, such as port plug and play, multi-port energy routing, hierarchical information communication and layered energy managing. | |
| [59] | From system running perspective, existing problem of CPS in Energy Internet was systematic analyzed. | Proposed the key directions for future research with adaptive planning as the main view angle. | Adopted two-layer constraint for planning model, which combined with complex network construction and planning, and realized “source-network-load” collaboration. | |
| [60] | Proposed access equipment concept in Energy Internet based on CPS. | Its overall framework, designing functions, core hardware and software components and future development directions are comprehensively studied and analyzed. | Undertook the techniques used in monitoring of and coordinating with the distributed energy devices. | |
| [61] | Studied CPS in Energy Internet, which included the interaction between the cyber layer and physical layer and related flow matrix forming. | The influence of cyber data disturb (dislocation, delay and data error) in the proposed model was studied. | Corresponding simulation model was built and tested for its validity and influences. |
| Research Topic | Paper No. | Research Content | Main Object | Technique Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| system design | [62] | Proposed a unified framework used for further understanding the intelligent properties of HCPS. | Provided a more real and rational industry 4.0. | Realizing “human as center” concept. |
| [63] | Proposed a new HCPS framework, which can coordinate the task assignment between human and machine. | Proposed a new adaptive control and manage method for human-machine collaboration. | Undertook adaptive control, machine learning catered to intelligent shopping platform. | |
| [64] | Introduced HCPS into smart power plant. | Realized the cooperation of HCP and other elements of smart power factory. | Introduced HCPS into smart power factory. | |
| theory analysis | [65] | Focused on the originality of HCPI, summarized its basic concept, research content and the application in ternary fusion intelligent. | Produced a new research era: HCPI. | Adopted Human-cyber-physical intelligent (HCPI). |
| [66] | Treated HCPS highly fusion as the core features of intelligent society. | Realized collaboration management of intelligent society. | Using the main model and the method of collaborate computing. | |
| [67] | Treated HCPS swarm intelligent computing as the future research direction of AIOT. | Realized CHPS swarm intelligent computing. | Using self-organize, and self-adaption AIOT. | |
| technique development | [68] | Proposed a HCPS like App which could detect dependencies between interventions for medical effect in healthcare domain. | Proposed a CPS App. | Used a physiological simulator to model the complex interactions of human’s physiology. |
| [69] | Proposed a distributed group assembly system based on swarm intelligence and swarm robots in HCPS. | Increased the flexible and response property in focus on market change. | Set up a distributed group assembly system based on swarm intelligence and swarm robots. | |
| [70] | Used machine learning algorithm to analyze the space and temporal data in the environment, and conducted intelligent modelling on the system and environment, which founding a unified safety HCPS framework. | Founded a unified safety HCPS framework combining dynamic authentic. | Hybrid modeling was used which combining space-temporal driven with model driven means. | |
| [71] | Extended the multi-simulation method, which will combine with multi-equations and data driven method to set up AI modeling normal form and improving the resistance of HCPS. | Found optimal decision sequences to ensure that the system resist in non-determined conditions, and continuous HCPS evolving. | Using RESILTRON framework, AI modeling, and Digital twin. | |
| [72] | Conducted similarity analysis on traffic data, and considered the related physical characters which can influence HCPS and ensured rational assignment of related tasks. | Ensured service assign accuracy and safety. | Comprehensively considered every side’s data characters in HCPS and realized related features’ cross domain fusion. | |
| [73] | Proposed a HCPS flexible manufacture system based digital twin’s general visualize framework. | Realized product design and debug. | Constituting a digital twin C-P model using multi-source heterogeneous information. | |
| [74] | Proposed an intelligent and self-managed new generation wind rotor HCPS framework in the background of Industry 5.0. | Provide more precise and intelligent sensing and policing ability. | Through digital twin, the training speed and model precision was largely improved. | |
| [75] | Realized deep fusion of physical space and virtual space based on HCPS fusion and interaction, to solve the control problem of robots. | Proposed and set up digital-twin driven intelligent control system. | Realized HCPS fusion and interaction. | |
| application model | [76] | Proposed a VCPS (Vehicular Cyber-Physical System) concept, whose performance is analyzed depended on different information transmission conditions with especially considered HF (Human Factors). | Minimized the system-wide total utility loss due to unsuccessful delivery of some services. | Formulated the basic HFSS problem (BHFSSP) using Integer Linear Programming (ILP) and proved its NP-Completeness. |
| [77] | Proposed a novel platform and designed a related framework for human-in-the-loop application in robot aiding human operation. | Augmented human interaction with the physical world. | Set up a prototyping platform and a design framework for rapid exploration of a novel human-in-the-loop application. | |
| [78] | Digital twin was a potential method to realize intelligent interaction and information fusion in HCPS. | Realized real-time interaction and control and intelligent collaborating. | Classified CPS as four-dimensional scientific problems. | |
| [79] | Ubiquitous computing in HCPS would form new type computing modes, and generate killer applications, and traditional industry would face massive technique challenges and innovation opportunities. | Realized high-speed development of operation system. | Using ubiquitous computing. | |
| [80] | The crossing of AI and multi-disciplinary would produce new research directions: HCPS intelligent or ternary fusion intelligent. | Realized the organize fusion of physical space, information space and society space. | Taking HCPS intelligent or ternary fusion intelligent. | |
| [81] | Fused the innovation algorithm with human and AI, utilizing the advantages of robot, and promoted the role of HCPS in art collaboration innovation. | Promoted the development of HCPS art collaboration innovation. | Focused on parallel art innovation based on CPSS intelligent fusion. | |
| [82] | Applied CPS in IOT healthcare. | Realized the effective utilizing of fog/cloud level resources and minimized operation cost. | Utilized cloud resources utilizing in CPS. | |
| [83] | Applied HCPS in smart home’s related research. | Proposed a new deep learning training scheme and avoided privacy omitting. | Using HCPS related technology. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, J.; Jin, J.; Ming, Y.; Sun, C.; Zeng, X.; Jiao, Z.; Ai, S. Human-Cyber-Physical Systems for Energy Internet—A Review. Energies 2023, 16, 5624. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16155624
Cao J, Jin J, Ming Y, Sun C, Zeng X, Jiao Z, Ai S. Human-Cyber-Physical Systems for Energy Internet—A Review. Energies. 2023; 16(15):5624. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16155624
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Junwei, Jian Jin, Yangyang Ming, Chuang Sun, Xiping Zeng, Zhenzhen Jiao, and Songpu Ai. 2023. "Human-Cyber-Physical Systems for Energy Internet—A Review" Energies 16, no. 15: 5624. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16155624
APA StyleCao, J., Jin, J., Ming, Y., Sun, C., Zeng, X., Jiao, Z., & Ai, S. (2023). Human-Cyber-Physical Systems for Energy Internet—A Review. Energies, 16(15), 5624. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16155624








