D-Dimer Levels and Acute Pulmonary Embolism Development in COVID-19 Patients
Abstract
:Introduction
Materials and Methods
Patient group
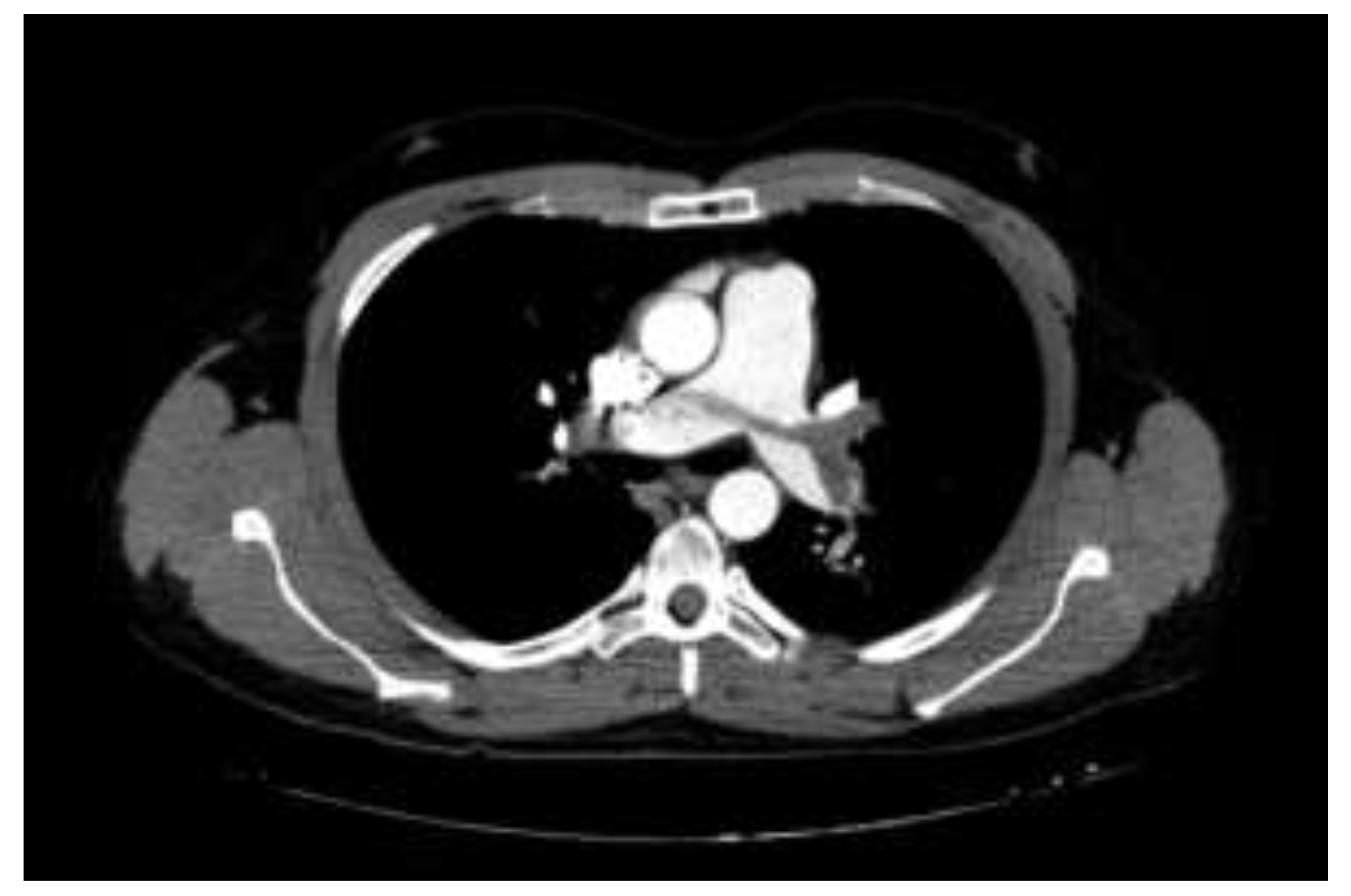
Pulmonary CT Angiography
Laboratory analysis
Statistical Analysis
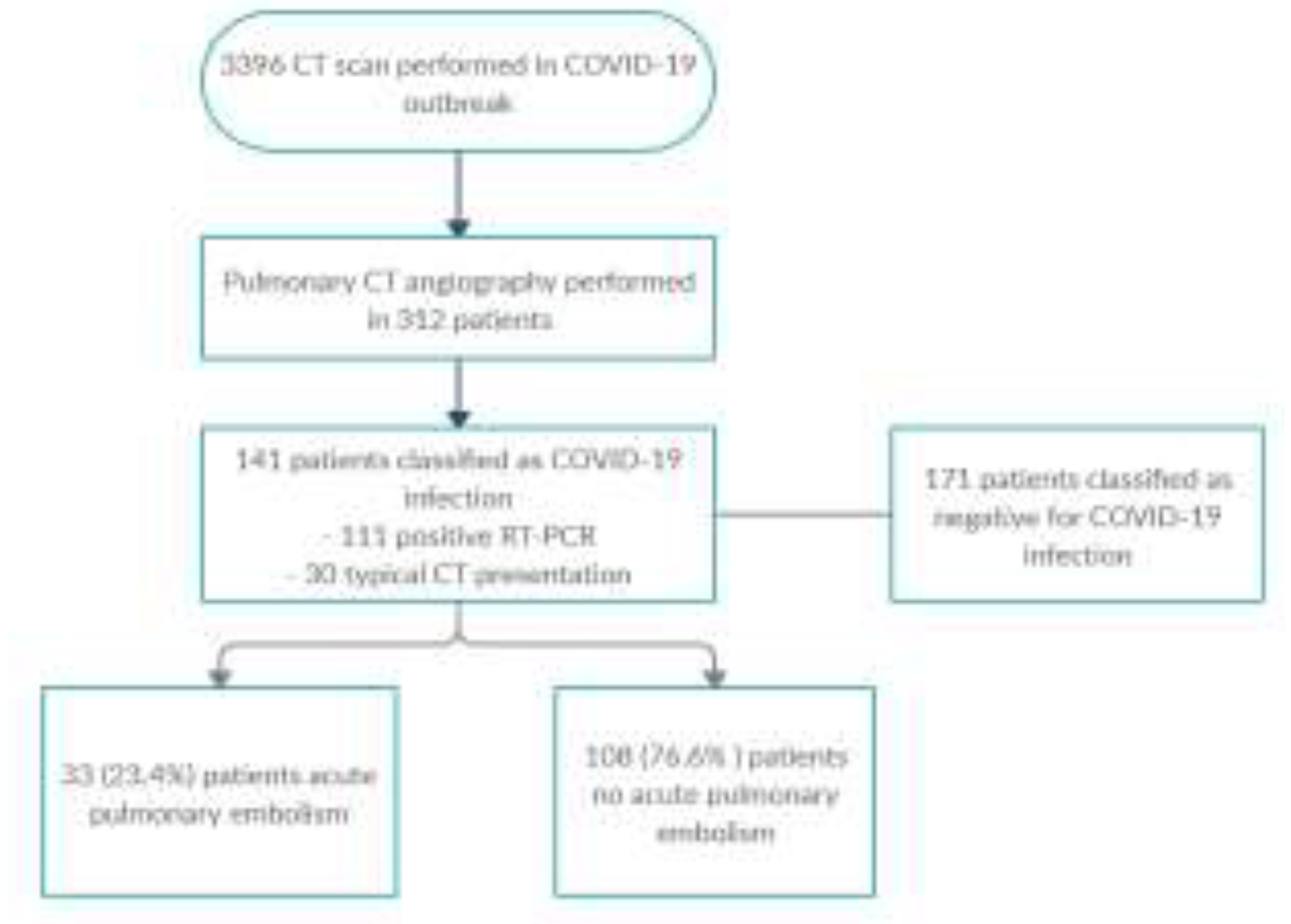
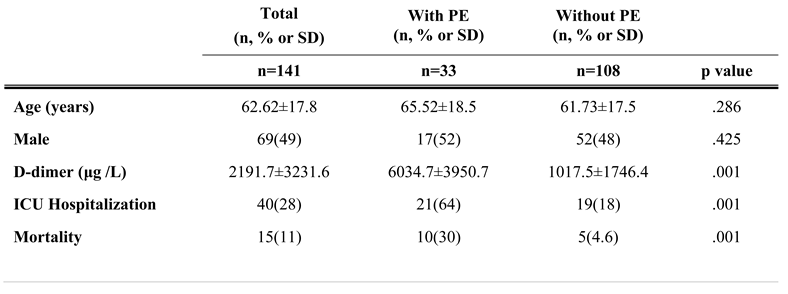
Results
Discussions
Highlights
- ✓
- Increased D-dimer levels are often seen in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia.
- ✓
- There appears to be a strong association between high D-dimer levels and thrombotic complications in COVID-19 patients.
- ✓
- Prophylaxis with anticoagulant agents may improve prognosis in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia.
Conclusions
Conflict of interest disclosure
Compliance with ethical standards
References
- Guan, W.J.; Ni, Z.Y.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.H.; Ou, C.Q.; et al. China Medical Treatment Expert Group for Covid-19. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danzi, G.B.; Loffi, M.; Galeazzi, G.; Gherbesi, E. Acute pulmonary embolism and COVID-19 pneumonia: a random association? Eur Heart J. 2020, 41, 1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, P.; Zhang, S. COVID-19 Complicated by Acute Pulmonary Embolism. Radiol Cardiothorac Imaging. 2020, 2, e200067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goeijenbier, M.; van Wissen, M.; van de Weg, C.; Jong, E.; Gerdes, V.E.; Meijers, J.C.; Brandjes, D.P.; van Gorp, E.C. Review: Viral infections and mechanisms of thrombosis and bleeding. J Med Virol. 2012, 84, 1680–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Zhou, M.; Dong, X.; Qu, J.; Gong, F.; Han, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Xia, J.; Yu, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet. 2020, 395, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, T.; Han, M.; Li, X.; Wu, D.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, L. Diagnostic utility of clinical laboratory data determinations for patients with the severe COVID-19. J Med Virol. 2020, 92, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Han, X.; Jiang, N.; Cao, Y.; Alwalid, O.; Gu, J.; Fan, Y.; Zheng, C. Radiological findings from 81 patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020, 20, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, D.O.; Jensen, A.; Khan, M.; Chin, J.; Chin, K.; Saad, J.; Parnell, R.; Awwad, C.; Patel, D. Pulmonary Embolism and Increased Levels of d-Dimer in Patients with Coronavirus Disease. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020, 26, 1941–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Fan, Y.; Chen, M.; Wu, X.; Zhang, L.; He, T.; Wang, H.; Wan, J.; Wang, X.; Lu, Z. Cardiovascular Implications of Fatal Outcomes of Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). JAMA Cardiol. 2020, 5, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; Guan, L.; Wei, Y.; Li, H.; Wu, X.; Xu, J.; Tu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Cao, B. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, N.; Li, D.; Wang, X.; Sun, Z. Abnormal coagulation parameters are associated with poor prognosis in patients with novel coronavirus pneumonia. J Thromb Haemost. 2020, 18, 844–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danzi, G.B.; Loffi, M.; Galeazzi, G.; Gherbesi, E. Acute pulmonary embolism and COVID-19 pneumonia: a random association? Eur Heart J. 2020, 41, 1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuckier, L.S.; Moadel, R.M.; Haramati, L.B.; Freeman, L.M. Diagnostic Evaluation of Pulmonary Embolism During the COVID-19 Pandemic. J Nucl Med. 2020, 61, 630–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Bai, H.; Chen, X.; Gong, J.; Li, D.; Sun, Z. Anticoagulant treatment is associated with decreased mortality in severe coronavirus disease 2019 patients with coagulopathy. J Thromb Haemost. 2020, 18, 1094–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revel, M.P.; Parkar, A.P.; Prosch, H.; Silva, M.; Sverzellati, N.; Gleeson, F.; Brady, A. European Society of Radiology (ESR) and the European Society of Thoracic Imaging (ESTI). COVID-19 patients and the radiology department - advice from the European Society of Radiology (ESR) and the European Society of Thoracic Imaging (ESTI). Eur Radiol. 2020, 30, 4903–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESC Guidance for the Diagnosis and Management of CV Disease during the COVID-19 Pandemic [Internet]. Available online: https://www.escardio.org/Education/COVID-19-and-Cardiology/ESC-COVID-19-Guidance (accessed on 26 May 2020).
- Bunce, P.E.; High, S.M.; Nadjafi, M.; Stanley, K.; Liles, W.C.; Christian, M.D. Pandemic H1N1 influenza infection and vascular thrombosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2011, 52, e14–e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schouten, H.J.; Geersing, G.J.; Koek, H.L.; Zuithoff, N.P.; Janssen, K.J.; Douma, R.A.; van Delden, J.J.; Moons, K.G.; Reitsma, J.B. Diagnostic accuracy of conventional or age adjusted D-dimer cut-off values in older patients with suspected venous thromboembolism: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2013, 346, f2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léonard-Lorant, I.; Delabranche, X.; Séverac, F.; Helms, J.; Pauzet, C.; Collange, O.; Schneider, F.; Labani, A.; Bilbault, P.; Molière, S.; Leyendecker, P.; Roy, C.; Ohana, M. Acute Pulmonary Embolism in Patients with COVID-19 at CT Angiography and Relationship to d-Dimer Levels. Radiology. 2020, 296, E189–E191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.; Meade, M.; Lauzier, F.; et al. Failure of anticoagulant thromboprophylaxis: risk factors in medical-surgical critically ill patients*. Crit Care Med. 2015, 43, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrigan, D.; Prucnal, C.; Kabrhel, C. Pulmonary embolism: the diagnosis, risk-stratification, treatment and disposition of emergency department patients. Clin Exp Emerg Med. 2016, 3, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, S.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, F. Prevalence of venous thromboembolism in patients with severe novel coronavirus pneumonia. J Thromb Haemost. 2020, 18, 1421–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douma, R.A.; Tan, M.; Schutgens, R.E.; Bates, S.M.; Perrier, A.; Legnani, C.; Biesma, D.H.; Ginsberg, J.S.; Bounameaux, H.; Palareti, G.; Carrier, M.; Mol, G.C.; Le Gal, G.; Kamphuisen, P.W.; Righini, M. Using an age-dependent D-dimer cut-off value increases the number of older patients in whom deep vein thrombosis can be safely excluded. Haematologica. 2012, 97, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

 |
 |
© 2021 by the author. 2021 Vural Ahmet, Kahraman Ahmet Nedim
Share and Cite
Ahmet, V.; Nedim, K.A. D-Dimer Levels and Acute Pulmonary Embolism Development in COVID-19 Patients. J. Mind Med. Sci. 2021, 8, 133-138. https://doi.org/10.22543/7674.81.P133138
Ahmet V, Nedim KA. D-Dimer Levels and Acute Pulmonary Embolism Development in COVID-19 Patients. Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences. 2021; 8(1):133-138. https://doi.org/10.22543/7674.81.P133138
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmet, Vural, and Kahraman Ahmet Nedim. 2021. "D-Dimer Levels and Acute Pulmonary Embolism Development in COVID-19 Patients" Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences 8, no. 1: 133-138. https://doi.org/10.22543/7674.81.P133138
APA StyleAhmet, V., & Nedim, K. A. (2021). D-Dimer Levels and Acute Pulmonary Embolism Development in COVID-19 Patients. Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences, 8(1), 133-138. https://doi.org/10.22543/7674.81.P133138



