Review of the Effects of Anesthetic Agents Used as Premedication for Patients Undergoing Electroconvulsive Therapy with Diagnoses of Bipolar Disorder or Major Depression on Convulsion, Recovery Period, and Hemodynamic Parameters
Highlights
- Premedication should be administered before the electroconvulsive therapy.
- Premedication may prevent hemodynamic responses that may occur as a response to this therapy. It also prevents the occurrence of side effects.
Highlights
- Premedication should be administered before the electroconvulsive therapy
- Premedication may prevent hemodynamic responses that may occur as a response to this therapy. It also prevents the occurrence of side effects.
Abstract
Introduction
Materials and Methods
- ○
- Questionnaire related to the descriptive characteristics of participants: This questionnaire included questions about the age, sex, height, weight, and the diagnosis of participants.
- ○
- Questionnaire related to ECT side effects and hemodynamic parameters: Data for this questionnaire were obtained from patient files and were related to (1) the current amount given (in joules), (2) the mean arterial blood pressure (MAP), (3) heart rate (HR) and peripheral oxygen saturation (SpO2) values, (4) the recovery period, (4) the convulsion period, and (5) the side effects that occurred.
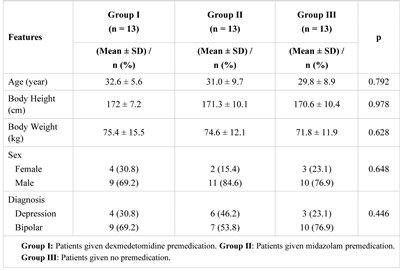
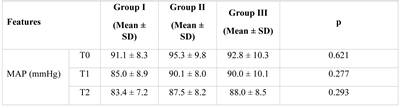
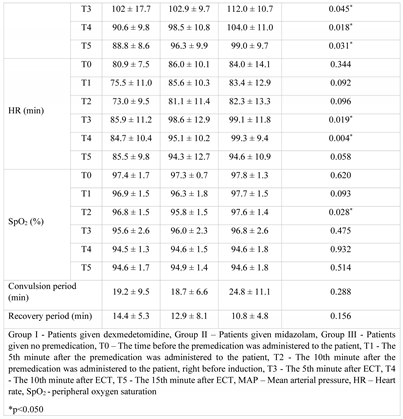
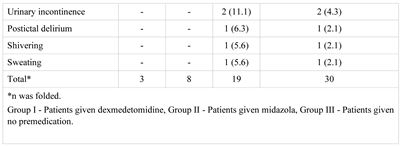
Results
Discussions
Conclusions
Conflict of interest disclosure
Compliance with ethical standards
References
- Algül, A.; Şen, H.; Ateş, M.A.; Yen, T.; Durmaz, O.; Özkan, S.; Başoğlu, C.; Semiz, Ü.B.; Ebrinç, S.; Dağlı, G.; Çetin, M. Propofol versus propofol-remifentanil combination anaesthesia in electroconvulsive therapy: Effects on seizure duration and hemodynamics. Bulletin of Clinical Psychopharmacology. 2009, 19, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Folk, J.W.; Kellner, C.H.; Beale, M.D.; Conroy, J.M.; Duc, T.A. Anesthesia for electroconvulsive therapy: a review. J ECT. 2000, 16, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.; White, P.F. Anesthesia for electroconvulsive therapy. Anesth Analg. 2002, 94, 1351–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizrak, A.; Koruk, S.; Ganidagli, S.; Bulut, M.; Oner, U. Premedication with dexmedetomidine and midazolam attenuates agitation after electroconvulsive therapy. J Anaesth. 2009, 23, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begeç, Z.; Köroğlu, A.; Gedik, E.; Yücel, A.; Toprak, H.I.; Karlıdağ, R.; Ersoy, M.Ö. Retrospective evaluation of our anesthetic applications for electroconvulsive therapy. Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim 2008, 36, 238–243. [Google Scholar]
- Aydogan, M.S.; Yücel, A.; Begec, Z.; Colak, Y.Z.; Durmus, M. The hemodynamic effects of dexmedetomidine and esmolol in electroconvulsive therapy: a retrospective comparison. J ECT. 2013, 29, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, P.J.; Dubey, K.P.; Watti, C.; Lalwani, J. Effectiveness of thiopentone, propofol and midazolam as an ideal intravenous anaesthetic agent for modified electroconvulsive therapy: A comparative study. Indian J Anaesth. 2010, 54, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Bot, A.; Michelet, D.; Hilly, J.; Maesani, M.; Dilly, M.P.; Brasher, C.; Mantz, J.; Dahmani, S. Efficacy of intraoperative dexmedetomidine compared with placebo for surgery in adults: a meta-analysis of published studies. Minerva Anestesiol. 2015, 81, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arain, S.R.; Ebert, T.J. The efficacy, side effects, and recovery characteristics of dexmedetomidine versus propofol when used for intraoperative sedation. Anesth Analg. 2002, 95, 461–466, table of contents. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozkose, Z.; Demir, F.S.; Pampal, K.; Yardim, S. Hemodynamic and anesthetic advantages of dexmedetomidine, an alpha 2-agonist, for surgery in prone position. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2006, 210, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begec, Z.; Toprak, H.I.; Demirbilek, S.; Erdil, F.; Onal, D.; Ersoy, M.O. Deksmedetomidine blunts acute hyperdynamic to responses Electroconvulsive therapy without altering seizure duration. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2008, 52, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, W.; Stool, L.A.; White, P.F.; Husain, M.M. Is oral clonidine effective in modifying the acute hemodynamic response during electroconvulsive therapy? Anesth Analg. 1998, 86, 1127–1130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Surve, R.; Bansal, S.; Sriganesh, K.; Subbakrishna, D.K.; Thirthalli, J.; Umamaheswara Rao, G.S. Incidence and risk factors for oxygen desaturation during recovery from modified electroconvulsive therapy: a prospective observational study. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2015, 31, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshiri, E.; Modir, H.; Bagheri, N.; Mohammadbeigi, A.; Jamilian, H.; Eshrati, B. Premedication effect of dexmedetomidine and alfentanil on seizure time, recovery duration, and hemodynamic responses in electroconvulsive therapy. Ann Card Anaesth. 2016, 19, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink, M. What is an adequate treatment in convulsive therapy? Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1991, 84, 424–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loimer, N.; Hofmann, P.; Chaudhry, H.R. Midazolam shortens seizure duration following electroconvulsive therapy. J Psychiatr Res. 1992, 26, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, H.Y.; Fragen, R.J.; Dunn, K. Dose-finding study of intramuscular midazolam preanesthetic medication in the elderly. Anesthesiology. 1991, 74, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisanby, S.H.; Morales, O.; Payne, N.; Kwon, E.; Fitzsimons, L.; Luber, B.; Nobler, M.S.; Sackeim, H.A. New developments in electroconvulsive therapy and magnetic seizure therapy. CNS Spectr. 2003, 8, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins Vincent, J. Principles of anesthesiology: general and regional anesthesia. Lea & Febiger, Philadelphia, 3th ed.; 1993. [Google Scholar]
 |
  |
  |
© 2019 by the author. 2019 Volkan Ozen, Mehmet Emin Orhan
Share and Cite
Ozen, V.; Orhan, M.E. Review of the Effects of Anesthetic Agents Used as Premedication for Patients Undergoing Electroconvulsive Therapy with Diagnoses of Bipolar Disorder or Major Depression on Convulsion, Recovery Period, and Hemodynamic Parameters. J. Mind Med. Sci. 2019, 6, 271-277. https://doi.org/10.22543/7674.62.P271277
Ozen V, Orhan ME. Review of the Effects of Anesthetic Agents Used as Premedication for Patients Undergoing Electroconvulsive Therapy with Diagnoses of Bipolar Disorder or Major Depression on Convulsion, Recovery Period, and Hemodynamic Parameters. Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences. 2019; 6(2):271-277. https://doi.org/10.22543/7674.62.P271277
Chicago/Turabian StyleOzen, Volkan, and Mehmet Emin Orhan. 2019. "Review of the Effects of Anesthetic Agents Used as Premedication for Patients Undergoing Electroconvulsive Therapy with Diagnoses of Bipolar Disorder or Major Depression on Convulsion, Recovery Period, and Hemodynamic Parameters" Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences 6, no. 2: 271-277. https://doi.org/10.22543/7674.62.P271277
APA StyleOzen, V., & Orhan, M. E. (2019). Review of the Effects of Anesthetic Agents Used as Premedication for Patients Undergoing Electroconvulsive Therapy with Diagnoses of Bipolar Disorder or Major Depression on Convulsion, Recovery Period, and Hemodynamic Parameters. Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences, 6(2), 271-277. https://doi.org/10.22543/7674.62.P271277



