Assessment of Computed Tomography Perfusion Research Landscape: A Topic Modeling Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pan, R.K.; Petersen, A.M.; Pammolli, F.; Fortunato, S. The Memory of Science: Inflation, Myopia, and the Knowledge Network. J. Informetr. 2018, 12, 656–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.-W. Topic Modeling. Osong Public Health Res. Perspect. 2019, 10, 115–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, C.Y.; Hu, R.; Peterson, R.B.; Allen, J.W. Automated Processing of Head CT Perfusion Imaging for Ischemic Stroke Triage: A Practical Guide to Quality Assurance and Interpretation. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2021, 217, 1401–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliwicka, O.; Sechopoulos, I.; Baggiano, A.; Pontone, G.; Nijveldt, R.; Habets, J. Dynamic Myocardial CT Perfusion Imaging—State of the Art. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 5509–5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbino, N.; Brancato, V.; Salvatore, M.; Cavaliere, C. A Systematic Review on the Role of the Perfusion Computed Tomography in Abdominal Cancer. Dose-Response 2021, 19, 155932582110561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grootendorst, M. BERTopic: Neural Topic Modeling with a Class-Based TF-IDF Procedure. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.05794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.-W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-Training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natural Language Processing with Python: Analyzing Text with the Natural Language Toolkit: Bird, Steven, Klein, Ewan, Loper, Edward: 9780596516499: Amazon.Com: Books. Available online: https://www.amazon.com/Natural-Language-Processing-Python-Analyzing/dp/0596516495 (accessed on 17 May 2023).
- Bittermann, A.; Fischer, A. How to Identify Hot Topics in Psychology Using Topic Modeling. Z. Psychol. 2018, 226, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petralia, G.; Bonello, L.; Viotti, S.; Preda, L.; d’Andrea, G.; Bellomi, M. CT Perfusion in Oncology: How to Do It. Cancer Imaging 2010, 10, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegadło, A.; Różyk, A.; Żabicka, M.; Więsik–Szewczyk, E.; Maliborski, A. Dual-Energy Computed Tomography as a Lower Radiation Dose Alternative to Perfusion Computed Tomography in Tumor Viability Assessment. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisdas, S.; Baghi, M.; Smolarz, A.; Pihno, N.C.; Lehnert, T.; Knecht, R.; Mack, M.G.; Vogl, T.J.; Tuerkay, S.; Koh, T.S. Quantitative Measurements of Perfusion and Permeability of Oropharyngeal and Oral Cavity Cancer, Recurrent Disease, and Associated Lymph Nodes Using First-Pass Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography Studies. Investig. Radiol. 2007, 42, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumboldt, Z.; Al-Okaili, R.; Deveikis, J.P. Perfusion CT for Head and Neck Tumors: Pilot Study. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2005, 26, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bisdas, S.; Baghi, M.; Wagenblast, J.; Knecht, R.; Thng, C.H.; Koh, T.S.; Vogl, T.J. Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Parotid Tumors Using Deconvolution-Based Perfusion CT Imaging: Feasibility of the Method and Initial Results. Eur. J. Radiol. 2007, 64, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, V.; Halligan, S.; Wellsted, D.M.; Bartram, C.I. Can Perfusion CT Assessment of Primary Colorectal Adenocarcinoma Blood Flow at Staging Predict for Subsequent Metastatic Disease? A Pilot Study. Eur. Radiol. 2009, 19, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyle, S.D.; Law, W.P.; Miles, K.A. Predicting Tumour Response. Cancer Imaging 2013, 13, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Wu, N.; Cham, M.D.; Song, Y. Tumor Response in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Perfusion CT Evaluation of Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2009, 193, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, S.; Horger, T.; Oelker, A.; Beck, S.; Schulze, M.; Nikolaou, K.; Ketelsen, D.; Horger, M. Volume Perfusion Computed Tomography (VPCT)-Based Evaluation of Response to TACE Using Two Different Sized Drug Eluting Beads in Patients with Nonresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Impact on Tumor and Liver Parenchymal Vascularisation. Eur. J. Radiol. 2015, 84, 2548–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Wu, D.; Tang, M.; Sun, H.; Ji, Y.; Huang, C.; Zeng, M. Liver Computed Tomographic Perfusion for Monitoring the Early Therapeutic Response to Sorafenib in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2018, 14, 1556–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, D.; Chepeha, D.B.; Miller, T.; Carlos, R.C.; Bradford, C.R.; Karamchandani, R.; Worden, F.; Eisbruch, A.; Teknos, T.N.; Wolf, G.T.; et al. Correlation between Initial and Early Follow-up CT Perfusion Parameters with Endoscopic Tumor Response in Patients with Advanced Squamous Cell Carcinomas of the Oropharynx Treated with Organ-Preservation Therapy. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2006, 27, 101–106. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, I.R.; Olesen, R.; Boysen, A.K.; Jensen, L.H.; Mortensen, F.V.; Nielsen, D.T.; Rasmussen, F. Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography as a Potential Biomarker in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Treated with Regorafenib. Acta Radiol. 2019, 60, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisdas, S.; Rumboldt, Z.; Šurlan-Popovič, K.; Baghi, M.; Koh, T.S.; Vogl, T.J.; Mack, M.G. Perfusion CT in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Upper Aerodigestive Tract: Long-Term Predictive Value of Baseline Perfusion CT Measurements. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2010, 31, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spampinato, M.V.; Bisdas, S.; Sharma, A.K.; McDonald, D.; Strojan, P.; Rumboldt, Z. Computed Tomography Perfusion Assessment of Radiation Therapy Effects on Spinal Cord Hemodynamics. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 77, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Benjamin, E.J.; Go, A.S.; Arnett, D.K.; Blaha, M.J.; Cushman, M.; De Ferranti, S.; Després, J.-P.; Fullerton, H.J.; Howard, V.J.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2015 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2015, 131, e29–e322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heit, J.J.; Wintermark, M. Perfusion Computed Tomography for the Evaluation of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2016, 47, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, S.; Lansberg, M.G. CT Perfusion in Acute Stroke: Practical Guidance for Implementation in Clinical Practice. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2019, 39, 1664–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, W.J.; Rabinstein, A.A.; Ackerson, T.; Adeoye, O.M.; Bambakidis, N.C.; Becker, K.; Biller, J.; Brown, M.; Demaerschalk, B.M.; Hoh, B.; et al. 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2018, 49, e46–e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, G.W.; Marks, M.P.; Kemp, S.; Christensen, S.; Tsai, J.P.; Ortega-Gutierrez, S.; McTaggart, R.A.; Torbey, M.T.; Kim-Tenser, M.; Leslie-Mazwi, T.; et al. Thrombectomy for Stroke at 6 to 16 Hours with Selection by Perfusion Imaging. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, R.G.; Jadhav, A.P.; Haussen, D.C.; Bonafe, A.; Budzik, R.F.; Bhuva, P.; Yavagal, D.R.; Ribo, M.; Cognard, C.; Hanel, R.A.; et al. Thrombectomy 6 to 24 Hours after Stroke with a Mismatch between Deficit and Infarct. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, T.E.; Hamann, G.F.; Baranczyk, J.; Rosengarten, B.; Klotz, E.; Wiesmann, M.; Missler, U.; Schulte-Altedorneburg, G.; Brueckmann, H.J. Dynamic CT Perfusion Imaging of Acute Stroke. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2000, 21, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Geng, D.; Li, Y.; Song, D.; Gu, Y. Whole-Brain CT Perfusion and CT Angiography Assessment of Moyamoya Disease before and after Surgical Revascularization: Preliminary Study with 256-Slice CT. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, J. A Novel Staging System to Evaluate Cerebral Hypoperfusion in Patients with Moyamoya Disease. Stroke 2018, 49, 2837–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitun, S.; De Lorenzi, C.; Cademartiri, F.; Buscaglia, A.; Travaglio, N.; Balbi, M.; Bezante, G.P. CT Myocardial Perfusion Imaging: A New Frontier in Cardiac Imaging. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, e7295460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cademartiri, F.; Seitun, S.; Clemente, A.; La Grutta, L.; Toia, P.; Runza, G.; Midiri, M.; Maffei, E. Myocardial Blood Flow Quantification for Evaluation of Coronary Artery Disease by Computed Tomography. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2017, 7, 129–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.R.; Bamberg, F.; Branch, K.; Carrascosa, P.; Chen, M.; Cury, R.C.; Ghoshhajra, B.; Ko, B.; Nieman, K.; Pugliese, F.; et al. Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography Expert Consensus Document on Myocardial Computed Tomography Perfusion Imaging. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2020, 14, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wykrzykowska, J.J.; Arbab-Zadeh, A.; Godoy, G.; Miller, J.M.; Lin, S.; Vavere, A.; Paul, N.; Niinuma, H.; Hoe, J.; Brinker, J.; et al. Assessment of In-Stent Restenosis Using 64-MDCT: Analysis of the CORE-64 Multicenter International Trial. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 194, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbab-Zadeh, A.; Miller, J.M.; Rochitte, C.E.; Dewey, M.; Niinuma, H.; Gottlieb, I.; Paul, N.; Clouse, M.E.; Shapiro, E.P.; Hoe, J.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of Computed Tomography Coronary Angiography According to Pre-Test Probability of Coronary Artery Disease and Severity of Coronary Arterial Calcification. The CORE-64 (Coronary Artery Evaluation Using 64-Row Multidetector Computed Tomography Angiography) International Multicenter Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 59, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisdas, S.; Foo, C.Z.; Thng, C.H.; Vogl, T.J.; Koh, T.S. Optimization of Perfusion CT Protocol for Imaging of Extracranial Head and Neck Tumors. J. Digit. Imaging 2009, 22, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vats, N.; Mayer, P.; Kortes, F.; Klauß, M.; Grenacher, L.; Stiller, W.; Kauczor, H.-U.; Skornitzke, S. Evaluation and Timing Optimization of CT Perfusion First Pass Analysis in Comparison to Maximum Slope Model in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstas, A.A.; Goldmakher, G.V.; Lee, T.-Y.; Lev, M.H. Theoretic Basis and Technical Implementations of CT Perfusion in Acute Ischemic Stroke, Part 2: Technical Implementations. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 30, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouchi, T.; Tanabe, Y.; Smit, E.J.; Kido, T.; Kurata, A.; Kouchi, Y.; Nishiyama, H.; Uetani, T.; Ikeda, S.; Yamaguchi, O.; et al. Clinical Application of Four-Dimensional Noise Reduction Filtering with a Similarity Algorithm in Dynamic Myocardial Computed Tomography Perfusion Imaging. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 36, 1781–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendrik, A.M.; Vonken, E.; van Ginneken, B.; de Jong, H.W.; Riordan, A.; van Seeters, T.; Smit, E.J.; Viergever, M.A.; Prokop, M. TIPS Bilateral Noise Reduction in 4D CT Perfusion Scans Produces High-Quality Cerebral Blood Flow Maps. Phys. Med. Biol. 2011, 56, 3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukas, S.; Feger, S.; Rief, M.; Zimmermann, E.; Dewey, M. Noise Reduction and Motion Elimination in Low-Dose 4D Myocardial Computed Tomography Perfusion (CTP): Preliminary Clinical Evaluation of the ASTRA4D Algorithm. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 4572–4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rava, R.A.; Snyder, K.V.; Mokin, M.; Waqas, M.; Allman, A.B.; Senko, J.L.; Podgorsak, A.R.; Bhurwani, M.M.S.; Davies, J.M.; Levy, E.I.; et al. Effect of Computed Tomography Perfusion Post-Processing Algorithms on Optimal Threshold Selection for Final Infarct Volume Prediction. Neuroradiol. J. 2020, 33, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Gu, S.; Yao, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Ren, H.; Luo, T. Comparison of Two Computed Tomography Perfusion Post-Processing Software to Assess Infarct Volume in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1151823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muehlen, I.; Borutta, M.; Siedler, G.; Engelhorn, T.; Hock, S.; Knott, M.; Hoelter, P.; Volbers, B.; Schwab, S.; Doerfler, A. Prognostic Accuracy of CTP Summary Maps in Patients with Large Vessel Occlusive Stroke and Poor Revascularization after Mechanical Thrombectomy—Comparison of Three Automated Perfusion Software Applications. Tomography 2022, 8, 1350–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austein, F.; Riedel, C.; Kerby, T.; Meyne, J.; Binder, A.; Lindner, T.; Huhndorf, M.; Wodarg, F.; Jansen, O. Comparison of Perfusion CT Software to Predict the Final Infarct Volume After Thrombectomy. Stroke 2016, 47, 2311–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Most Popular Topics in Radiology 2023. Available online: https://www.rsna.org/news/2023/april/popular-topics-radiology-2023 (accessed on 21 August 2023).
- Zhang, R.; Wang, P.; Bian, Y.; Fan, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Shen, J.; Hu, Y.; Liao, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Establishment and Validation of an AI-Aid Method in the Diagnosis of Myocardial Perfusion Imaging. BMC Med. Imaging 2023, 23, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tozer, D.J.; Liu, W.; Peake, E.J.; Markus, H.S. Prediction of Response to Thrombolysis in Acute Stroke Using Neural Network Analysis of CT Perfusion Imaging. Eur. Stroke J. 2023, 8, 23969873231183206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werdiger, F.; Parsons, M.W.; Visser, M.; Levi, C.; Spratt, N.; Kleinig, T.; Lin, L.; Bivard, A. Machine Learning Segmentation of Core and Penumbra from Acute Stroke CT Perfusion Data. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1098562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gava, U.A.; D’Agata, F.; Tartaglione, E.; Renzulli, R.; Grangetto, M.; Bertolino, F.; Santonocito, A.; Bennink, E.; Vaudano, G.; Boghi, A.; et al. Neural Network-Derived Perfusion Maps: A Model-Free Approach to Computed Tomography Perfusion in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke. Front. Neuroinform. 2023, 17, 852105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhurwani, M.M.S.; Boutelier, T.; Davis, A.; Gautier, G.; Swetz, D.; Rava, R.A.; Raguenes, D.; Waqas, M.; Snyder, K.V.; Siddiqui, A.H.; et al. Identification of Infarct Core and Ischemic Penumbra Using Computed Tomography Perfusion and Deep Learning. J. Med. Imaging 2023, 10, 014001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisdas, S.; Hartel, M.; Cheong, L.H.; Koh, T.S. Detection of Early Vessel Leakiness in Acute Ischemic Stroke Using Computed Tomography Perfusion May Indicate Hemorrhagic Transformation. Acta Radiol. 2007, 48, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.M.; Kim, D.S.; Kim, M. Hemorrhagic Transformation After Ischemic Stroke: Mechanisms and Management. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 703258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sussman, E.; Connolly, E., Jr. Hemorrhagic Transformation: A Review of the Rate of Hemorrhage in the Major Clinical Trials of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Front. Neurol. 2013, 4, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorelli, M.; Bastianello, S.; von Kummer, R.; del Zoppo, G.J.; Larrue, V.; Lesaffre, E.; Ringleb, A.P.; Lorenzano, S.; Manelfe, C.; Bozzao, L. Hemorrhagic Transformation within 36 Hours of a Cerebral Infarct: Relationships with Early Clinical Deterioration and 3-Month Outcome in the European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study I (ECASS I) Cohort. Stroke 1999, 30, 2280–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, C.H.; Jung, S.C.; Cho, S.J.; Kim, D.; Lee, J.B.; Woo, D.-C.; Oh, W.Y.; Lee, J.G.; Kim, K.W. Perfusion CT for Prediction of Hemorrhagic Transformation in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 4077–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassi, N.; Parsons, M.W.; Christensen, S.; Sharma, G.; Bivard, A.; Donnan, G.A.; Levi, C.R.; Desmond, P.M.; Davis, S.M.; Campbell, B.C.V. Prediction of Poststroke Hemorrhagic Transformation Using Computed Tomography Perfusion. Stroke 2013, 44, 3039–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, L.C.S.; Payabvash, S.; Wang, Y.; Kamalian, S.; Schaefer, P.; Gonzalez, R.G.; Furie, K.L.; Lev, M.H. Admission CT Perfusion Is an Independent Predictor of Hemorrhagic Transformation in Acute Stroke with Similar Accuracy to DWI. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2011, 33, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.R.; Jain, M.; Kanthala, A.R.; Damania, D.; Stead, L.G.; Wang, H.Z.; Jahromi, B.S. Association of CT Perfusion Parameters with Hemorrhagic Transformation in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 1895–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinoyama, M.; Nakagawara, J.; Yoneda, H.; Suzuki, M.; Ono, H.; Kunitsugu, I.; Kamiyama, K.; Osato, T.; Nakamura, H. Initial “TTP Map-Defect” of Computed Tomography Perfusion as a Predictor of Hemorrhagic Transformation of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Cerebrovasc. Dis. Extra 2013, 3, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderrama-Zurián, J.-C.; Aguilar-Moya, R.; Melero-Fuentes, D.; Aleixandre-Benavent, R. A Systematic Analysis of Duplicate Records in Scopus. J. Informetr. 2015, 9, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
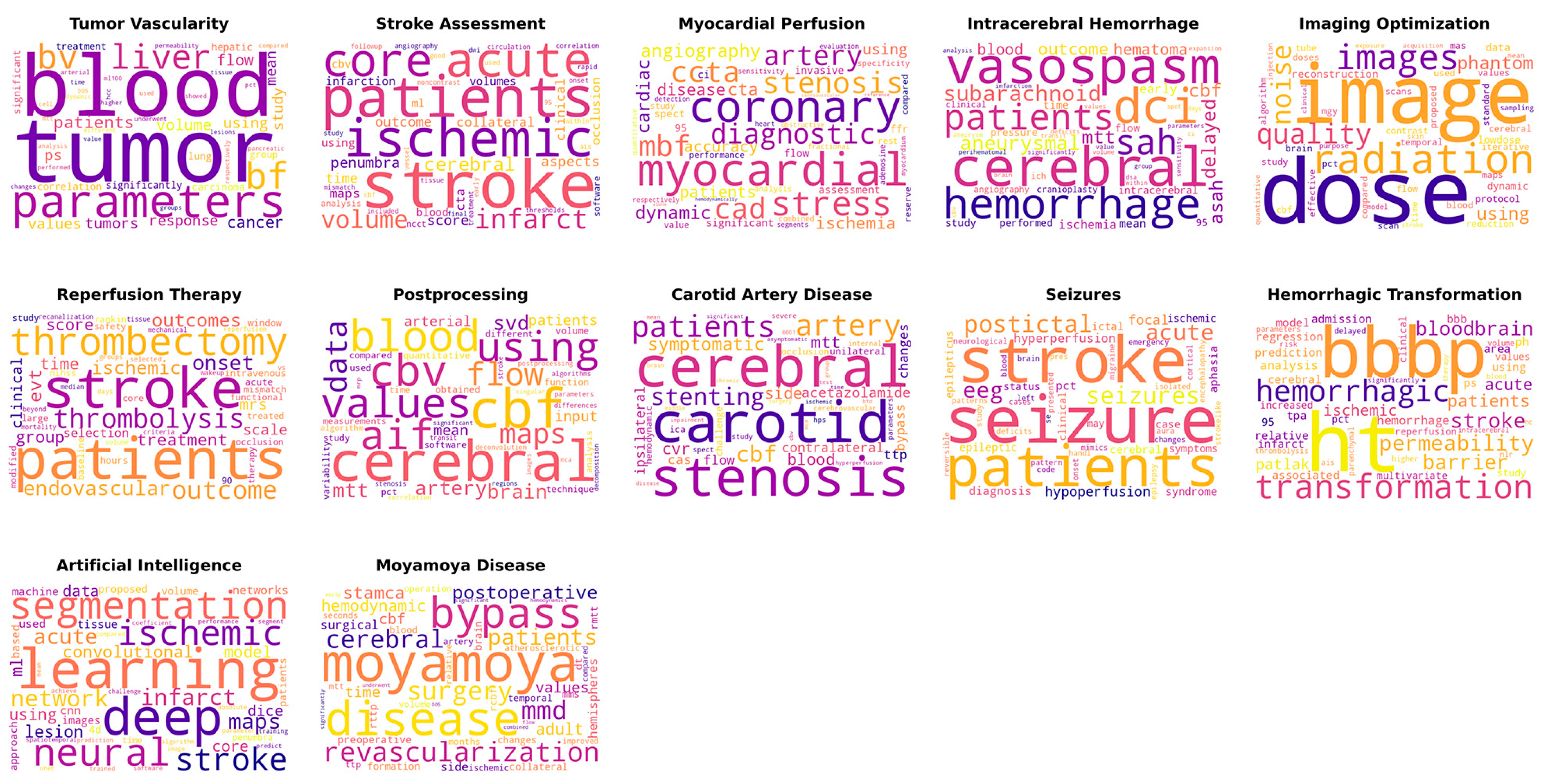
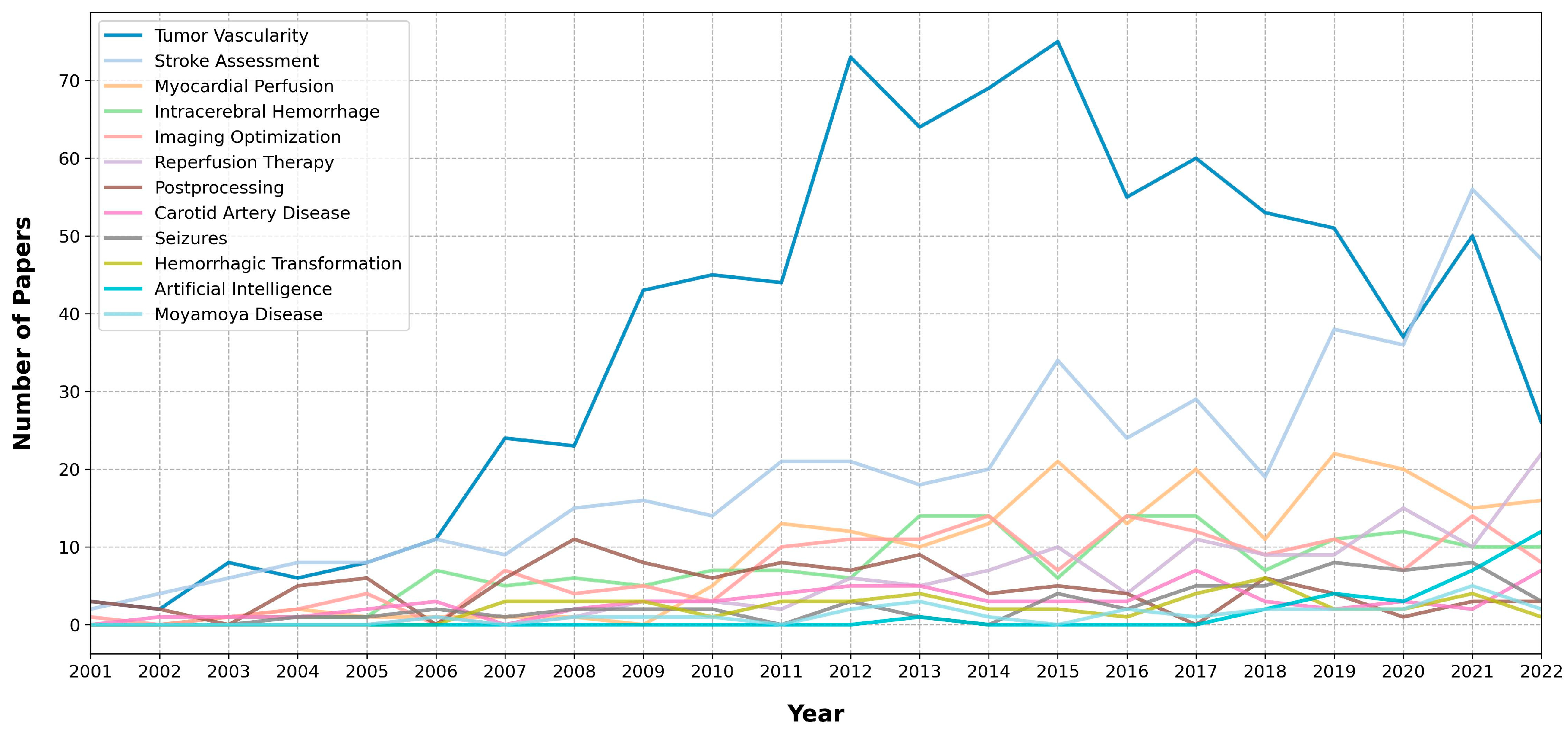
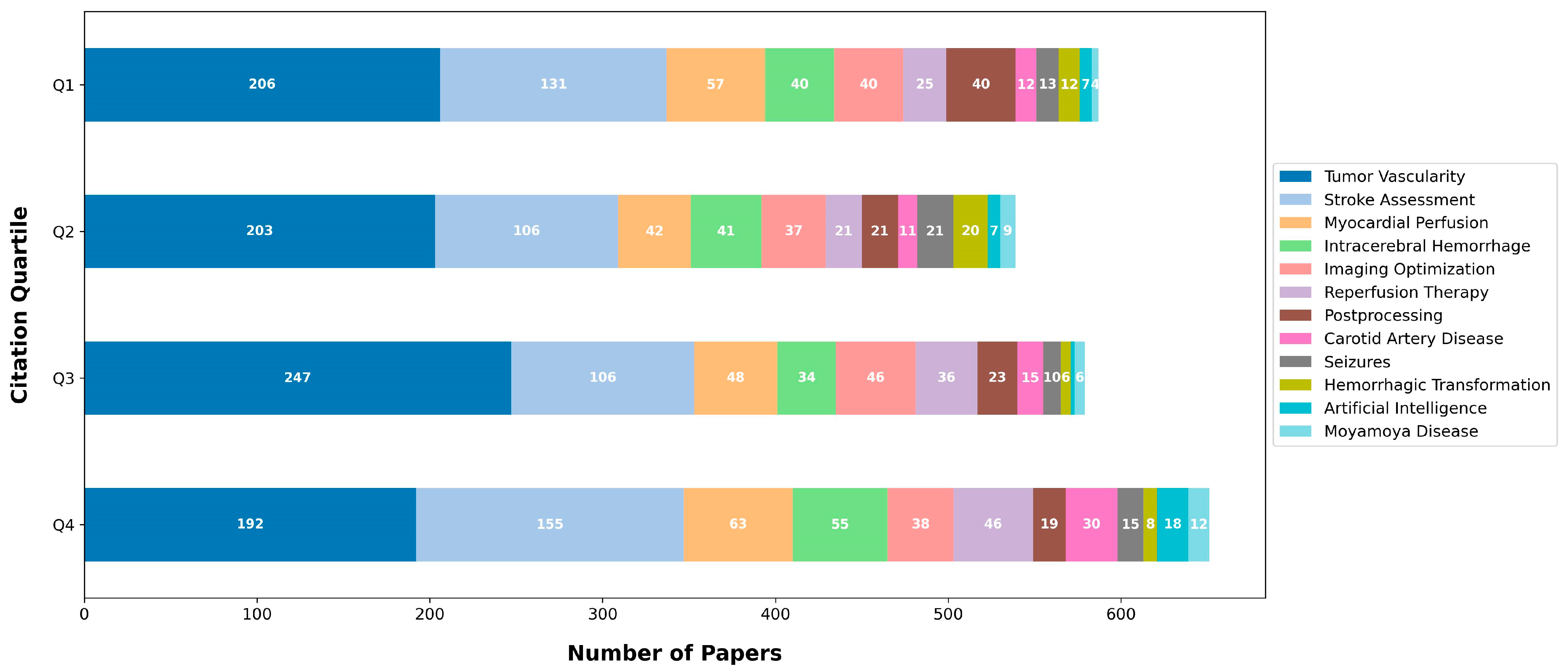

| Topic Label | Key Words | Number of Articles | Representative Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor Vascularity | tumor, blood, parameters, bf, liver, bv, patients, cancer, volume, flow, values, using, tumors, study, mean, ps, response, significantly, hepatic, significant, correlation, lung, carcinoma, treatment, group, permeability, compared, hcc, analysis, time, arterial, respectively, pancreatic, higher, value, ml100, performed, tissue, pct, lesions, changes, mtt, cell, showed, different, 005, dynamic, used, underwent, groups | 848 | Title: Perfusion computed tomography for monitoring induction chemotherapy in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the upper aerodigestive tract: Correlation between changes in tumor perfusion and tumor volume |
| Stroke Assessment | stroke, patients, ischemic, acute, core, infarct, volume, cerebral, penumbra, aspects, score, outcome, time, collateral, clinical, occlusion, maps, cta, infarction, using, volumes, ml, cbv, blood, analysis, ncct, software, angiography, followup, circulation, tissue, mismatch, thresholds, ais, early, dwi, noncontrast, rapid, 95, onset, used, study, cbf, final, included, treatment, within, vessel, good, correlation | 498 | Title: Quantifying infarct core volume in ischemic stroke: What is the optimal threshold and parameters of computed tomography perfusion? |
| Myocardial Perfusion | myocardial, coronary, stress, stenosis, cad, ccta, mbf, diagnostic, artery, angiography, dynamic, cardiac, cta, ischemia, disease, patients, accuracy, using, significant, 95, assessment, spect, invasive, ffr, ci, flow, performance, rest, reserve, value, compared, study, specificity, analysis, adenosine, combined, sensitivity, fractional, respectively, heart, evaluation, detection, segments, myocardium, quantitative, obstructive, hemodynamically, cardiovascular, reference, alone | 210 | Title: Dynamic myocardial CT perfusion imaging-state of the art |
| Intracerebral Hemorrhage | cerebral, vasospasm, dci, hemorrhage, patients, sah, subarachnoid, aneurysmal, delayed, cbf, asah, mtt, outcome, blood, hematoma, early, ischemia, mean, time, intracerebral, flow, study, 95, pressure, performed, angiography, cranioplasty, clinical, ich, perihematomal, brain, ci, group, aneurysm, spot, value, infarction, parameters, days, analysis, values, cbv, sensitivity, significantly, volume, within, expansion, dsa, deficits, transit | 170 | Title: Relationship between vasospasm, cerebral perfusion, and delayed cerebral ischemia after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage |
| Imaging Optimization | dose, image, radiation, images, quality, noise, phantom, using, reconstruction, lowdose, data, dynamic, protocol, maps, reduction, cerebral, contrast, scan, algorithm, brain, temporal, tube, values, doses, mgy, study, proposed, compared, time, scans, pct, mas, iterative, effective, cbf, flow, blood, used, standard, sampling, model, purpose, skin, quantitative, injection, mean, acquisition, clinical, stroke, exposure | 161 | Title: Temporal feature prior-aided separated reconstruction method for low-dose dynamic myocardial perfusion computed tomography |
| Reperfusion Therapy | patients, stroke, thrombectomy, thrombolysis, outcome, endovascular, onset, ischemic, evt, outcomes, treatment, time, group, score, mrs, scale, clinical, selection, intravenous, hours, window, acute, large, treated, modified, functional, core, rankin, occlusion, nihss, study, mismatch, 90, therapy, baseline, safety, reperfusion, wakeup, mechanical, days, volume, criteria, median, recanalization, selected, mortality, beyond, tissue, groups, vs | 128 | Title: Utilization of CT perfusion patient selection for mechanical thrombectomy irrespective of time: A comparison of functional outcomes and complications |
| Postprocessing | cerebral, cbf, blood, cbv, values, using, aif, flow, data, maps, artery, svd, mtt, brain, patients, mean, input, arterial, quantitative, function, obtained, volume, technique, pct, study, analysis, time, compared, different, measurements, variability, used, software, algorithm, postprocessing, algorithms, stenosis, deconvolution, parameters, correlation, differences, transit, stroke, significant, mca, regions, singular, images, mrp, decomposition | 103 | Title: Differences in CT perfusion maps generated by different commercial software: Quantitative analysis by using identical source data of acute stroke patients |
| Carotid Artery Disease | cerebral, carotid, stenosis, patients, artery, stenting, cbf, symptomatic, mtt, cvr, blood, side, acetazolamide, ipsilateral, bypass, contralateral, cas, ttp, flow, changes, unilateral, challenge, ica, occlusion, hemodynamic, cerebrovascular, internal, spect, study, hps, parameters, severe, asymptomatic, time, middle, impairment, test, group, disease, mean, surgery, bto, mca, chronic, hyperperfusion, cbv, significant, 0001, brain, ischemic | 68 | Title: Carotid artery stenting and blood–brain barrier permeability in subjects with chronic carotid artery stenosis |
| Seizures | seizure, stroke, patients, postictal, acute, eeg, hypoperfusion, focal, hyperperfusion, pct, diagnosis, aphasia, ictal, epileptic, syndrome, cerebral, epilepticus, case, ischemic, symptoms, status, clinical, may, neurological, emergency, cortical, mimics, left, blood, brain, aura, se, patterns, isolated, handl, cases, pres, deficits, pattern, encephalopathy, migraine, code, changes, onset, epilepsy, presented, study, reversible, strokelike | 59 | Title: Acute Ischemic Stroke or Epileptic Seizure? Yield of CT Perfusion in a “Code Stroke” Situation |
| Hemorrhagic Transformation | ht, bbbp, transformation, hemorrhagic, permeability, stroke, barrier, bloodbrain, patients, acute, ischemic, patlak, hemorrhage, analysis, ph, regression, model, using, ps, area, prediction, relative, 95, associated, admission, tpa, infarct, bbb, cerebral, multivariate, values, pct, clinical, increased, study, reperfusion, thrombolysis, volume, delayed, risk, ais, parenchymal, higher, nlr, parameters, significantly, therapy, intracerebral, blood, hc | 46 | Title: Hemorrhagic transformation of ischemic stroke: Prediction with CT perfusion |
| Artificial Intelligence | learning, deep, segmentation, neural, ischemic, stroke, network, infarct, maps, acute, convolutional, lesion, using, model, ml, core, data, dice, networks, cnn, machine, based, tissue, used, images, proposed, volume, patients, approach, 4d, penumbra, time, spatiotemporal, image, prediction, unet, trained, coefficient, performance, predict, absolute, algorithm, training, mean, software, parameter, segment, achieve, compared, challenge | 34 | Title: Prediction of Stroke Infarct Growth Rates by Baseline Perfusion Imaging |
| Moyamoya Disease | moyamoya, disease, bypass, revascularization, surgery, mmd, cerebral, patients, postoperative, stamca, hemodynamic, adult, cbf, values, time, surgical, hemispheres, side, preoperative, dt, rttp, mms, brain, rcbf, collateral, rmtt, formation, changes, temporal, blood, ttp, volume, operation, months, atherosclerotic, seconds, artery, ischemic, mtt, relative, improved, compared, hemodynamics, significant, flow, wbctp, underwent, 005, significantly, combined | 31 | Title: CT perfusion assessment of Moyamoya syndrome before and after direct revascularization (superficial temporal artery to middle cerebral artery bypass) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ozkara, B.B.; Karabacak, M.; Margetis, K.; Yedavalli, V.S.; Wintermark, M.; Bisdas, S. Assessment of Computed Tomography Perfusion Research Landscape: A Topic Modeling Study. Tomography 2023, 9, 2016-2028. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9060158
Ozkara BB, Karabacak M, Margetis K, Yedavalli VS, Wintermark M, Bisdas S. Assessment of Computed Tomography Perfusion Research Landscape: A Topic Modeling Study. Tomography. 2023; 9(6):2016-2028. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9060158
Chicago/Turabian StyleOzkara, Burak B., Mert Karabacak, Konstantinos Margetis, Vivek S. Yedavalli, Max Wintermark, and Sotirios Bisdas. 2023. "Assessment of Computed Tomography Perfusion Research Landscape: A Topic Modeling Study" Tomography 9, no. 6: 2016-2028. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9060158
APA StyleOzkara, B. B., Karabacak, M., Margetis, K., Yedavalli, V. S., Wintermark, M., & Bisdas, S. (2023). Assessment of Computed Tomography Perfusion Research Landscape: A Topic Modeling Study. Tomography, 9(6), 2016-2028. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9060158








