Using Deep-Learning-Based Artificial Intelligence Technique to Automatically Evaluate the Collateral Status of Multiphase CTA in Acute Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Subjects
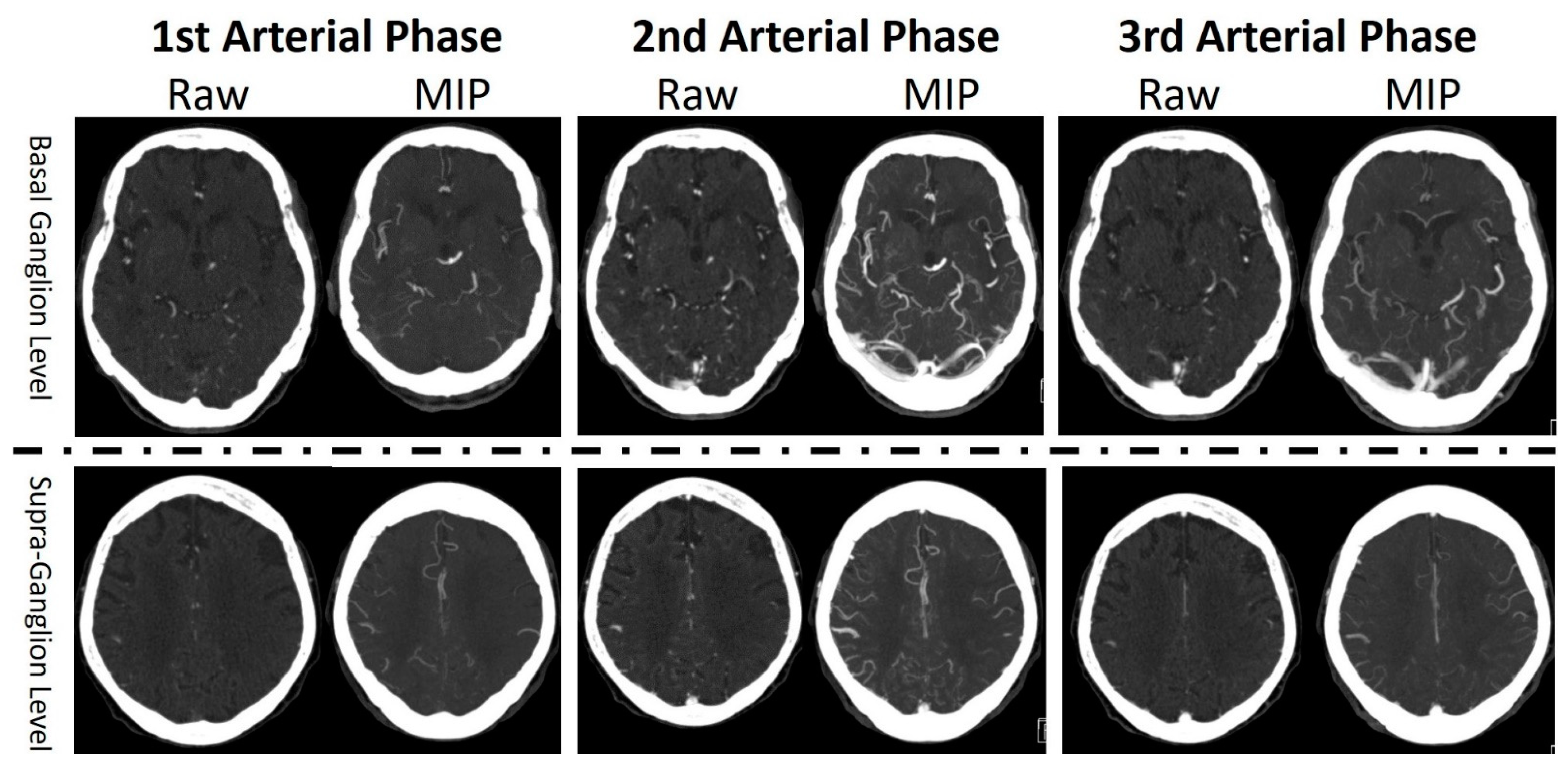
2.2. Imaging Studies
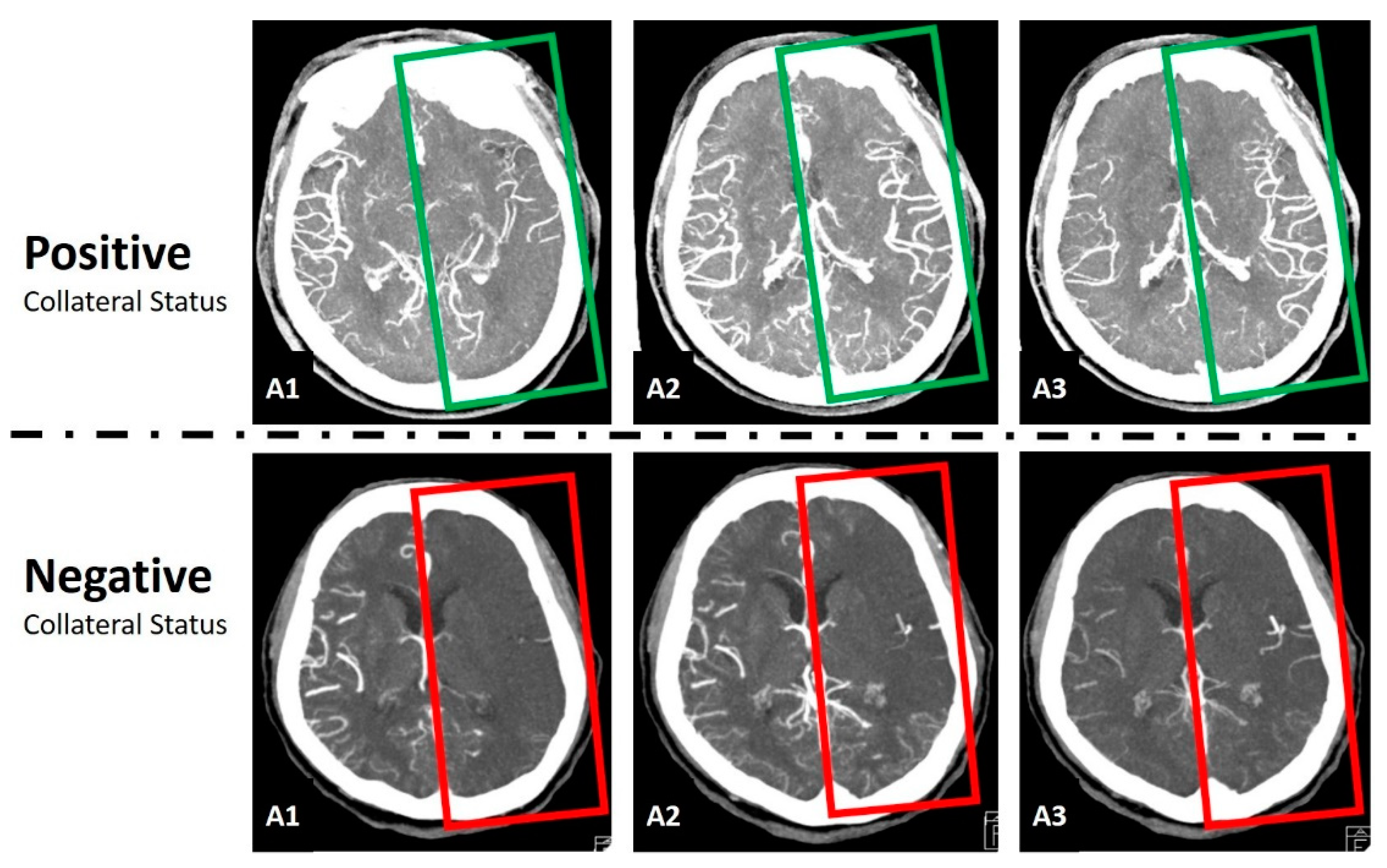
2.3. Data Preprocessing and Normalization
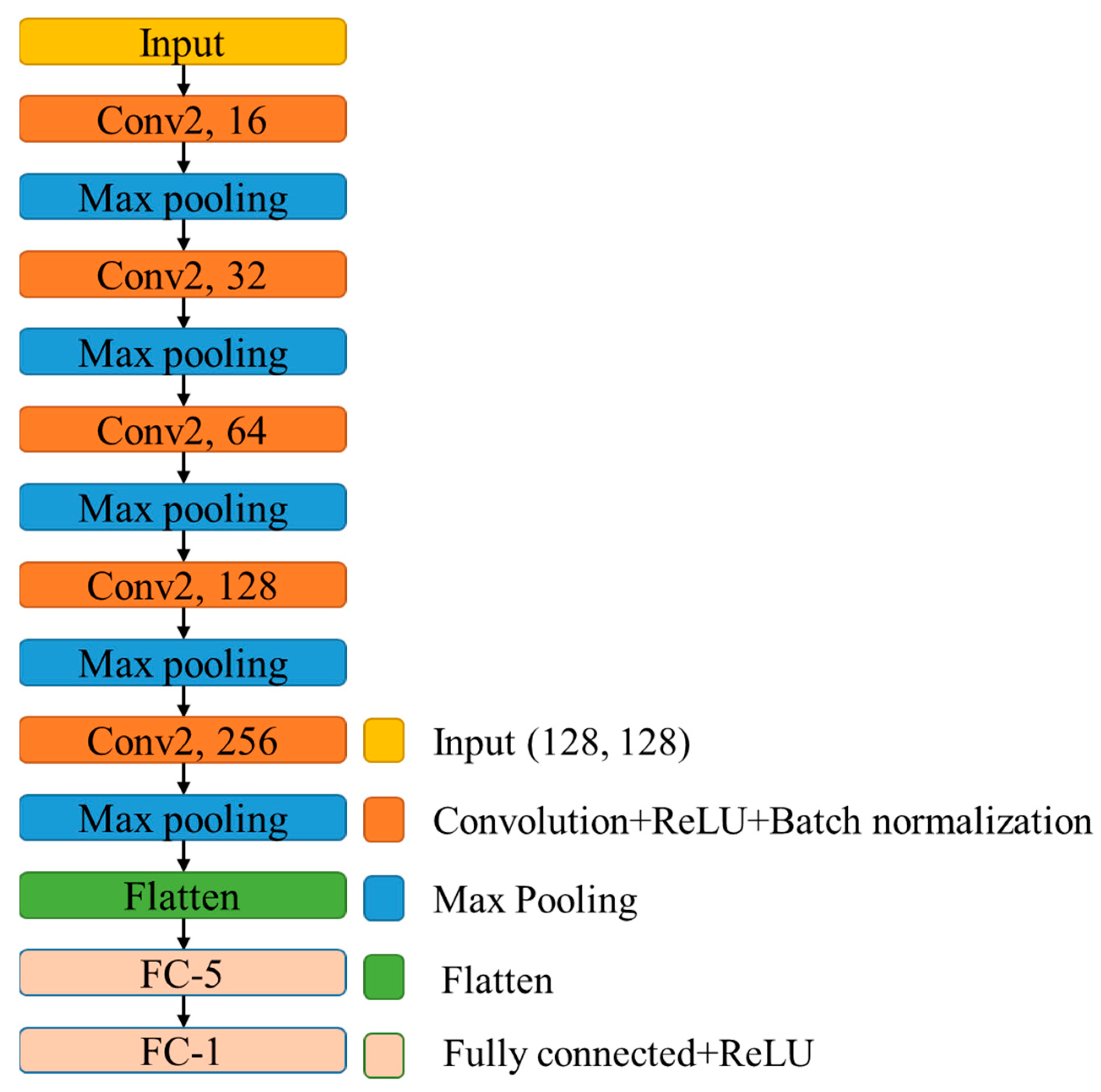
2.4. Convolutional Neural Network
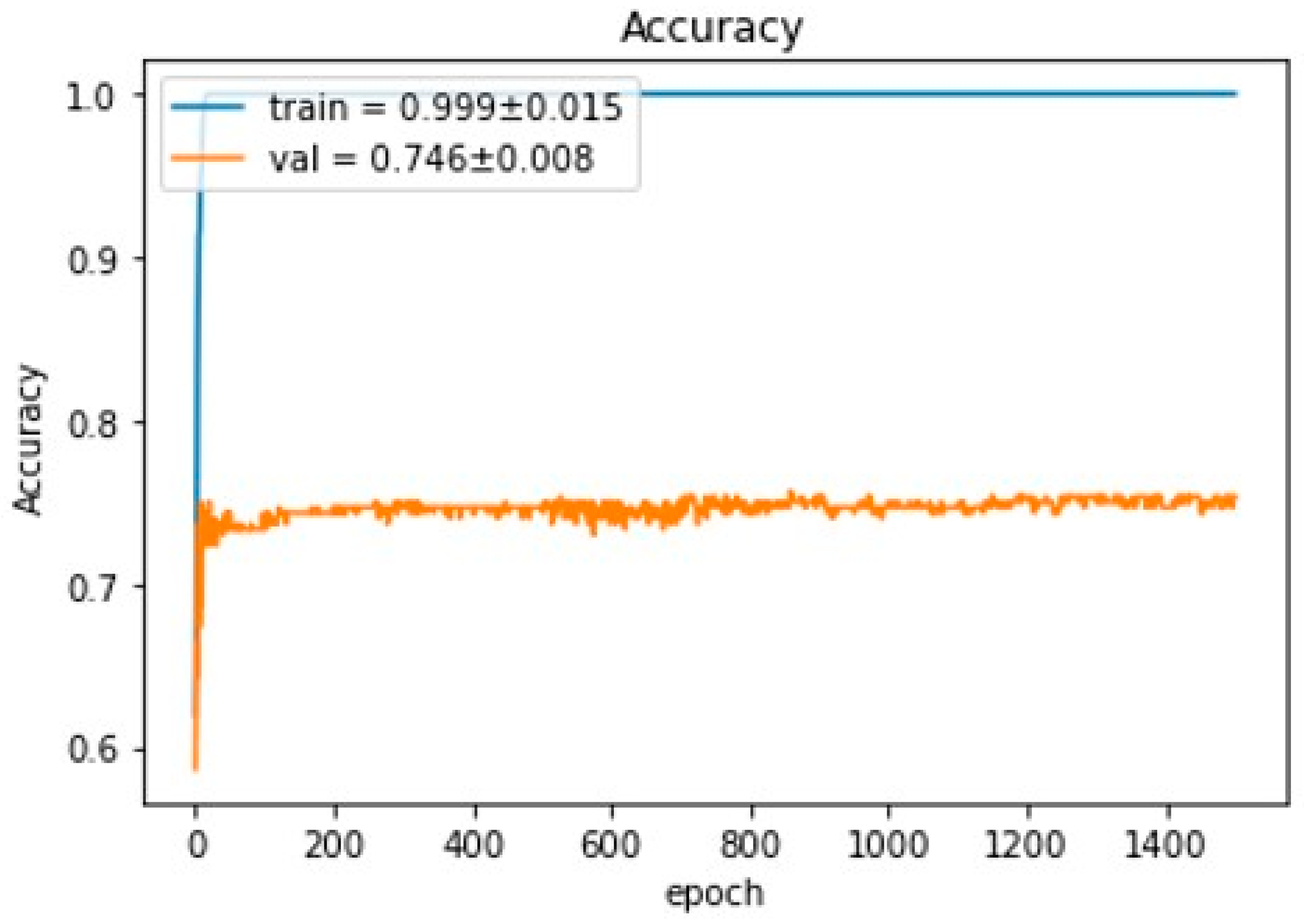
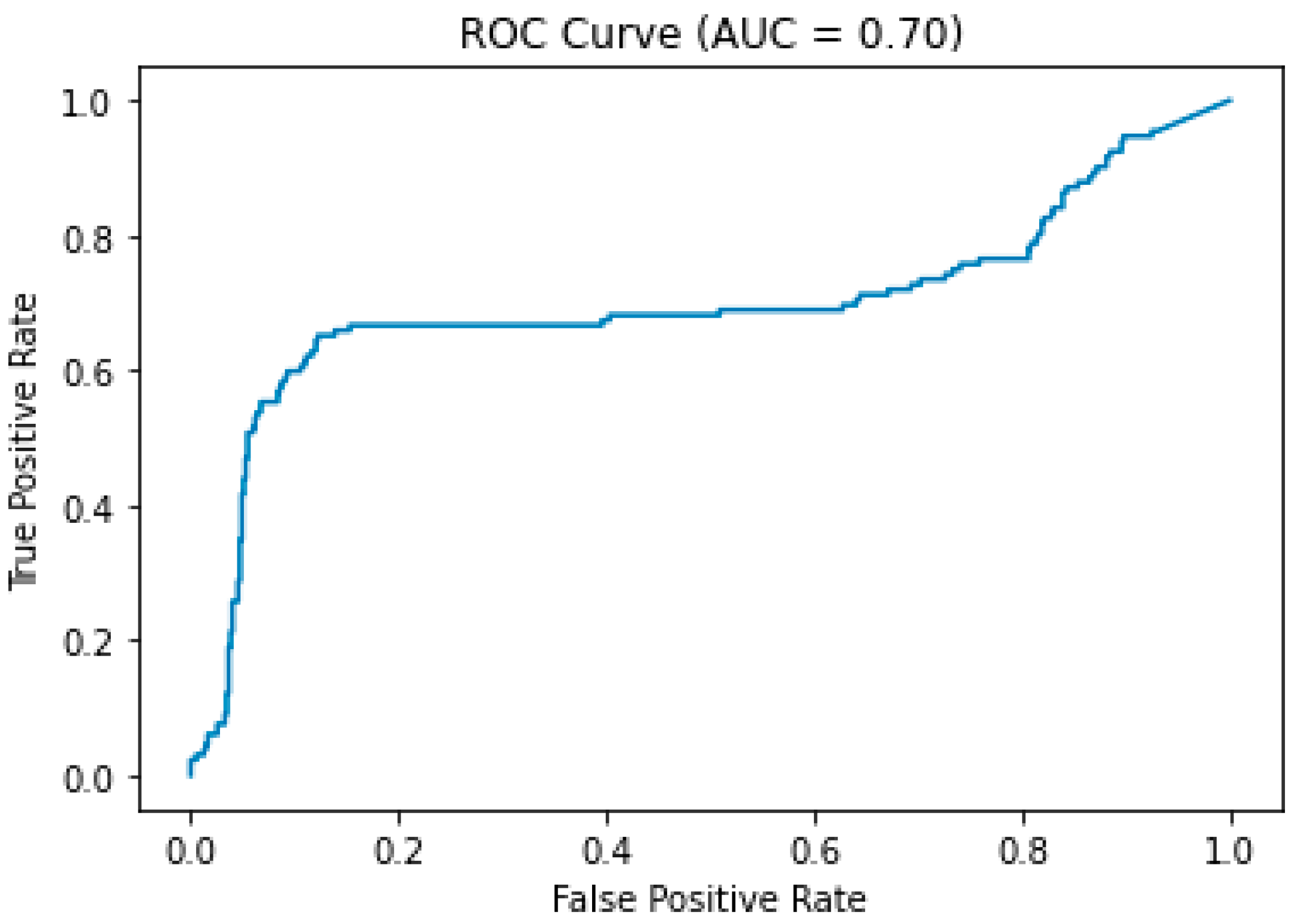
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cipolla, M.J.; Liebeskind, D.S.; Chan, S.L. The importance of comorbidities in ischemic stroke: Impact of hypertension on the cerebral circulation. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2018, 38, 2129–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Chou, C.; Huang, W.; Jhou, Z.; Hwang, Y.; Lin, H.; Tsai, Y.; Lin, C. Imaging findings of multiphase ct angiography of acute internal carotid artery occlusion within 6-hour time-window after thrombectomy and its clinical implication. Iran. J. Radiol. 2020, 17, e102948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dundamadappa, S.; Iyer, K.; Agrawal, A.; Choi, D.J. Multiphase ct angiography: A useful technique in acute stroke imaging-collaterals and beyond. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2021, 42, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, R.G.; Jadhav, A.P.; Haussen, D.C.; Bonafe, A.; Budzik, R.F.; Bhuva, P.; Yavagal, D.R.; Ribo, M.; Cognard, C.; Hanel, R.A.; et al. Thrombectomy 6 to 24 hours after stroke with a mismatch between deficit and infarct. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Parsons, M.; Bivard, A.; Sharma, G.; Mitchell, P.; Dowling, R.; Bush, S.; Churilov, L.; Xu, A.; Yan, B. Comparison of computed tomography perfusion and multiphase computed tomography angiogram in predicting clinical outcomes in endovascular thrombectomy. Stroke 2022, 53, 2926–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajpurkar, P.; Irvin, J.; Ball, R.L.; Zhu, K.; Yang, B.; Mehta, H.; Duan, T.; Ding, D.; Bagul, A.; Langlotz, C.P.; et al. Deep learning for chest radiograph diagnosis: A retrospective comparison of the chexnext algorithm to practicing radiologists. PLoS Med. 2018, 15, e1002686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayer, T.; Chen, Q.; Burnside, E.S. Artificial neural networks in mammography interpretation and diagnostic decision making. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2013, 2013, 832509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyser, C.D.; Dosenbach, N.U.; Smyser, T.A.; Snyder, A.Z.; Rogers, C.E.; Inder, T.E.; Schlaggar, B.L.; Neil, J.J. Prediction of brain maturity in infants using machine-learning algorithms. Neuroimage 2016, 136, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fartaria, M.J.; Bonnier, G.; Roche, A.; Kober, T.; Meuli, R.; Rotzinger, D.; Frackowiak, R.; Schluep, M.; Du Pasquier, R.; Thiran, J.P.; et al. Automated detection of white matter and cortical lesions in early stages of multiple sclerosis. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2016, 43, 1445–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yan, L.F.; Hu, Y.C.; Li, G.; Yang, Y.; Han, Y.; Sun, Y.Z.; Liu, Z.C.; Tian, Q.; Han, Z.Y.; et al. Optimizing a machine learning based glioma grading system using multi-parametric mri histogram and texture features. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 47816–47830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, B.K.; d’Esterre, C.D.; Qazi, E.M.; Almekhlafi, M.; Hahn, L.; Demchuk, A.M.; Goyal, M. Multiphase ct angiography: A new tool for the imaging triage of patients with acute ischemic stroke. Radiology 2015, 275, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, K. Neocognitron: A self organizing neural network model for a mechanism of pattern recognition unaffected by shift in position. Biol. Cybern. 1980, 36, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Dasuqi, K.; Payabvash, S.; Torres-Flores, G.A.; Strander, S.M.; Nguyen, C.K.; Peshwe, K.U.; Kodali, S.; Silverman, A.; Malhotra, A.; Johnson, M.H.; et al. Effects of collateral status on infarct distribution following endovascular therapy in large vessel occlusion stroke. Stroke 2020, 51, e193–e202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, O.Y.; Saver, J.L.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, G.M.; Chung, C.S.; Ovbiagele, B.; Lee, K.H.; Liebeskind, D.S.; Collaborators, U.C.-S.S. Collateral flow averts hemorrhagic transformation after endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2011, 42, 2235–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, X.; Fang, H.; Leung, T.W.; Mao, C.; Miao, Z.; Liu, L.; Wong, K.S.; Liebeskind, D.S. Impact of collaterals on the efficacy and safety of endovascular treatment in acute ischaemic stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2016, 87, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, W.J.; Rabinstein, A.A.; Ackerson, T.; Adeoye, O.M.; Bambakidis, N.C.; Becker, K.; Biller, J.; Brown, M.; Demaerschalk, B.M.; Hoh, B.; et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: A guideline for healthcare professionals from the american heart association/american stroke association. Stroke 2019, 50, e344–e418. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Potreck, A.; Scheidecker, E.; Weyland, C.S.; Neuberger, U.; Herweh, C.; Mohlenbruch, M.A.; Chen, M.; Nagel, S.; Bendszus, M.; Seker, F. Rapid ct perfusion-based relative cbf identifies good collateral status better than hypoperfusion intensity ratio, cbv-index, and time-to-maximum in anterior circulation stroke. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2022, 43, 960–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seker, F.; Pfaff, J.; Potreck, A.; Mundiyanapurath, S.; Ringleb, P.A.; Bendszus, M.; Mohlenbruch, M.A. Correlation of t(max) volumes with clinical outcome in anterior circulation stroke. Brain Behav. 2017, 7, e00772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenego, A.; Fahed, R.; Albers, G.W.; Kuraitis, G.; Sussman, E.S.; Martin, B.W.; Marcellus, D.G.; Olivot, J.M.; Marks, M.P.; Lansberg, M.G.; et al. Hypoperfusion intensity ratio correlates with angiographic collaterals in acute ischaemic stroke with m1 occlusion. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenillas, J.F.; Cortijo, E.; Garcia-Bermejo, P.; Levy, E.I.; Jahan, R.; Liebeskind, D.; Goyal, M.; Saver, J.L.; Albers, G.W. Relative cerebral blood volume is associated with collateral status and infarct growth in stroke patients in swift prime. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2018, 38, 1839–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potreck, A.; Seker, F.; Mutke, M.A.; Weyland, C.S.; Herweh, C.; Heiland, S.; Bendszus, M.; Mohlenbruch, M. What is the impact of head movement on automated ct perfusion mismatch evaluation in acute ischemic stroke? J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2022, 14, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, J.J.; Lum, C. Whole brain ct perfusion on a 320-slice ct scanner. Indian J. Radiol. Imaging 2011, 21, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Tan, D.; Liu, J.; Wu, J.; Huang, F.; Xiong, H.; Luo, T.; Chen, S.; Li, Y. Merging multiphase cta images and training them simultaneously with a deep learning algorithm could improve the efficacy of ai models for lateral circulation assessment in ischemic stroke. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rava, R.A.; Seymour, S.E.; Snyder, K.V.; Waqas, M.; Davies, J.M.; Levy, E.I.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Ionita, C.N. Automated collateral flow assessment in patients with acute ischemic stroke using computed tomography with artificial intelligence algorithms. World Neurosurg. 2021, 155, e748–e760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktar, M.; Tampieri, D.; Rivaz, H.; Kersten-Oertel, M.; Xiao, Y. Automatic collateral circulation scoring in ischemic stroke using 4d ct angiography with low-rank and sparse matrix decomposition. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2020, 15, 1501–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Garg, P.K.; Khera, P.S.; Panda, S.; Bohra, G.K.; Yadav, T.; Garg, M.K.; Tiwari, S. Multiphase computed tomography angiography (mcta) derived source images in acute ischemic stroke: Beyond collaterals. Can it obviate the need for computed tomography perfusion (ctp)? Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2022, 222, 107421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
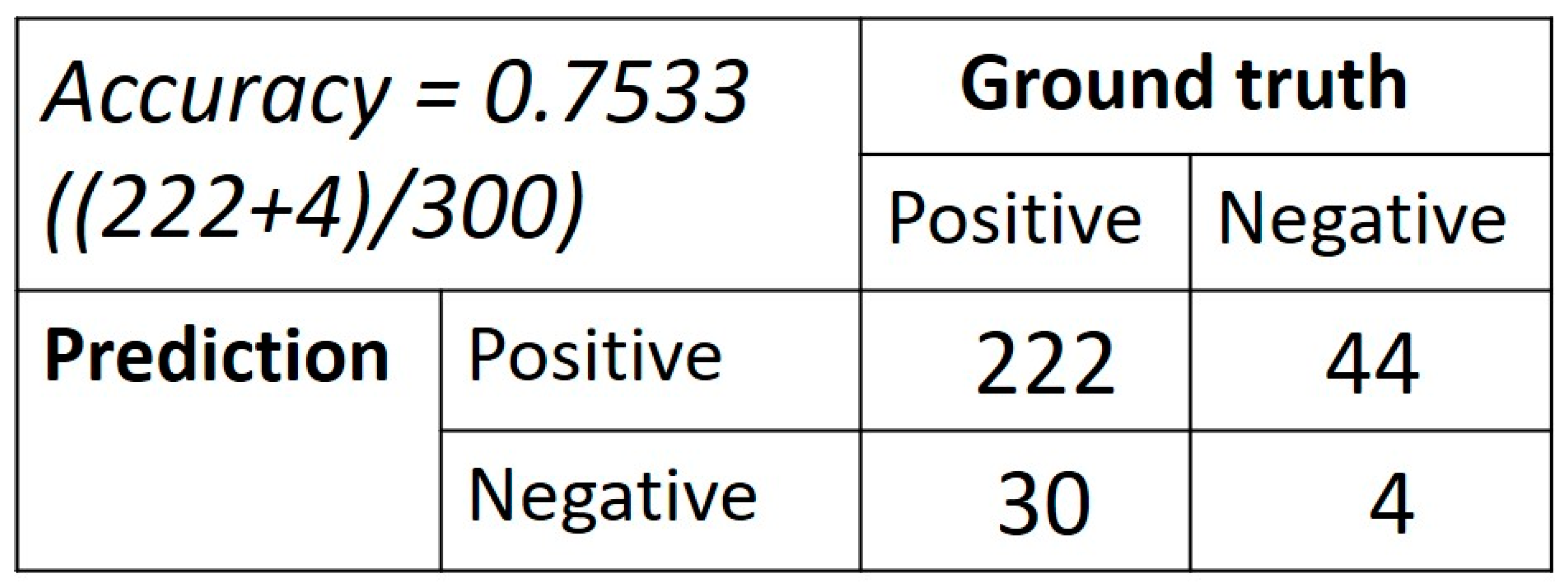
| Collateral Status | Positive (n = 61) | Negative (n = 21) |
|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD (Range) n (%) Median (Range) | ||
| Age (years) | 72.5 ± 13.5 (43–98) | 65.4 ± 14.8 (35–96) |
| Sex (male) | 28 (45.9) | 13 (61.9) |
| National Institute of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) | 17 (8–31) | 19 (13–23) |
| Glasgow Coma Scale | 14 (5–15) | 11 (7–15) |
| Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECTS) | 8 (5–10) | 8 (6–10) |
| Occlusion site | ICA: 20 (32.8) M1: 31 (50.8) M2: 10 (16.4) | ICA: 8 (38.1) M1: 10 (47.6) M2: 3 (14.3) |
| Modified treatment in cerebral infarction (mTICI) | 0–2a: 16 (26.2) 2b–3: 45 (73.8) | 0–2a: 8 (38.1) 2b–3: 13 (61.9) |
| Onset to Reperfusion time (minutes) | 316.3 ± 83.5 (152–528) | 317.6 ± 95.4 (189–519) |
| Symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage | 9 (14.8) | 5 (23.8) |
| Modified Rankin Scale | 0–2: 18 (29.5) 3–6: 43 (70.5) | 0–2: 3 (14.3) 3–6: 18 (85.7) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, C.-C.; Chiang, H.-F.; Hsieh, C.-C.; Chou, C.-L.; Jhou, Z.-Y.; Hou, T.-Y.; Shaw, J.-S. Using Deep-Learning-Based Artificial Intelligence Technique to Automatically Evaluate the Collateral Status of Multiphase CTA in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Tomography 2023, 9, 647-656. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9020052
Huang C-C, Chiang H-F, Hsieh C-C, Chou C-L, Jhou Z-Y, Hou T-Y, Shaw J-S. Using Deep-Learning-Based Artificial Intelligence Technique to Automatically Evaluate the Collateral Status of Multiphase CTA in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Tomography. 2023; 9(2):647-656. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9020052
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Chun-Chao, Hsin-Fan Chiang, Cheng-Chih Hsieh, Chao-Liang Chou, Zong-Yi Jhou, Ting-Yi Hou, and Jin-Siang Shaw. 2023. "Using Deep-Learning-Based Artificial Intelligence Technique to Automatically Evaluate the Collateral Status of Multiphase CTA in Acute Ischemic Stroke" Tomography 9, no. 2: 647-656. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9020052
APA StyleHuang, C.-C., Chiang, H.-F., Hsieh, C.-C., Chou, C.-L., Jhou, Z.-Y., Hou, T.-Y., & Shaw, J.-S. (2023). Using Deep-Learning-Based Artificial Intelligence Technique to Automatically Evaluate the Collateral Status of Multiphase CTA in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Tomography, 9(2), 647-656. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9020052








