Curved Planar Reformation: A Useful Method for Screening Dental Pathologies in Chronic Rhinosinusitis via Paranasal Sinus Computed Tomography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
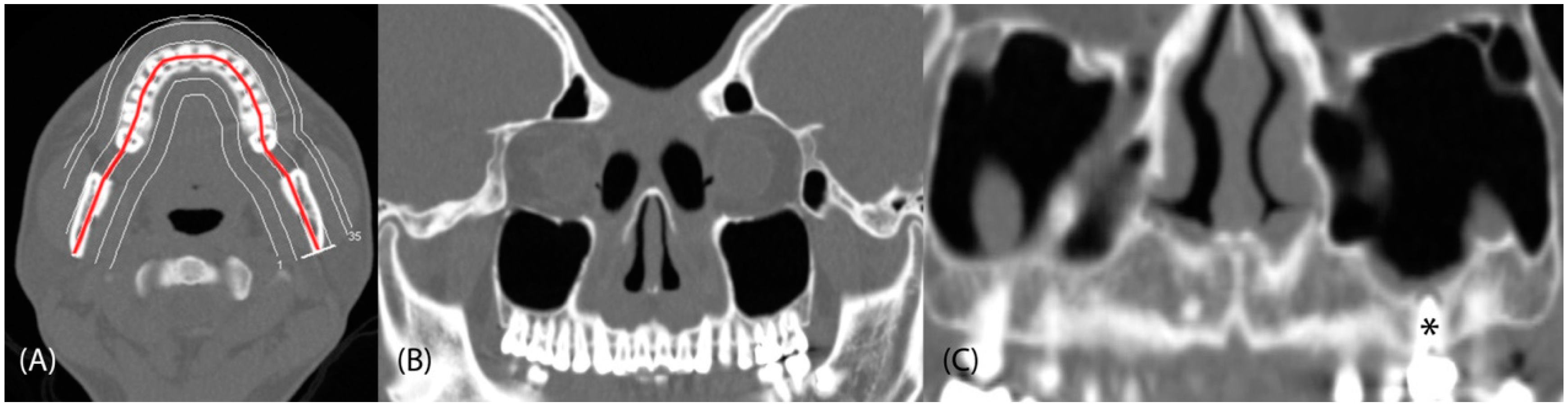
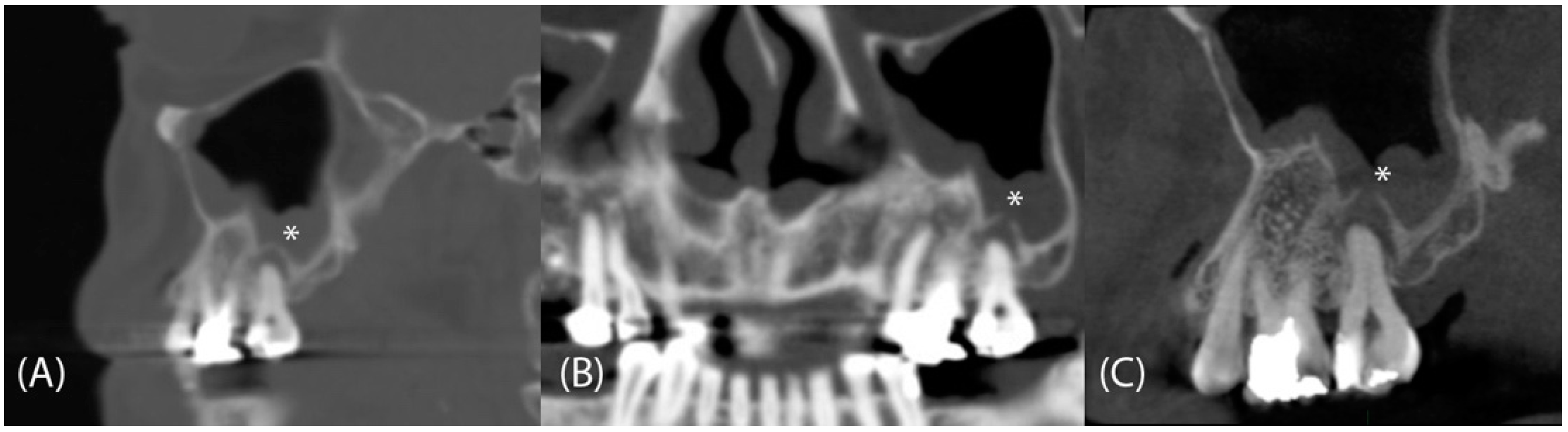
2.2. Assessment of Dental Pathologies and Sinus Conditions
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hastan, D.F.W.J.; Fokkens, W.J.; Bachert, C.; Newson, R.B.; Bislimovska, J.; Bockelbrink, A.; Bousquet, P.J.; Brozek, G.; Bruno, A.; Dahlén, S.E.; et al. Chronic rhinosinusitis in Europe: An underestimated disease. A GA2LEN study. Allergy 2011, 66, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackwell, D.L.; Lucas, J.W.; Clarke, T.C. Summary health statistics for U.S. adults: National health interview survey, 2012. Vital Health Stat. 10 2014, 260, 1–161. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, K.K.; Jolly, K.; Bhamra, N.; Osborne, M.S.; Ahmed, S.K. The evolution of sinus surgery in England in the last decade—An observational study. World J. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2020, 7, 240246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, V. The evolution of surgery on the maxillary sinus for chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope 2002, 112, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longhini, A.B.; Ferguson, B.J. Clinical aspects of odontogenic maxillary sinusitis: A case series. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2011, 1, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albu, S.; Baciut, M. Failures in endoscopic surgery of the maxillary sinus. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2010, 142, 196201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troeltzsch, M.; Pache, C.; Troeltzsch, M.; Kaeppler, G.; Ehrenfeld, M.; Otto, S.; Probst, F. Etiology and clinical characteristics of symptomatic unilateral maxillary sinusitis: A review of 174 cases. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2015, 43, 1522–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Yokoi, H.; Kohno, N. Association between odontogenic infections and unilateral sinus opacification. Auris Nasus Larynx 2015, 42, 288293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.C.; Lee, S.J. Clinical features and treatments of odontogenic sinusitis. Yonsei Med. J. 2010, 51, 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.L.; Nichols, B.G.; Poetker, D.M.; Loehrl, T.A. Odontogenic sinusitis: A case series studying diagnosis and management. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015, 5, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, M.M.; Platzgummer, H.; Unterhumer, S.; Weber, M.; Mistelbauer, G.; Groeller, E.; Loewe, C.; Schernthaner, R.E. Multipath curved planar reformations of peripheral CT angiography: Diagnostic accuracy and time efficiency. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2018, 41, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshioka, F.; Shimokawa, S.; Koguchi, M.; Ito, H.; Ogata, A.; Inoue, K.; Takase, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Nakahara, Y.; Masuoka, J.; et al. Curved planar reformation for the evaluation of hydromyelia in patients with scoliosis associated with spinal dysraphism. Spine 2018, 43, E177–E184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, B.W.; Jeong, S.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, C.H.; Cho, S.G.; Jeon, Y.S. Curved planar reformatted images of MDCT for differentiation of biliary stent occlusion in patients with malignant biliary obstruction. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 194, 1509–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehrschuetz, M.; Galle, G.; Wehrschuetz, E.; Sorantin, E.; Schaffler, G. Thick curved planar reformation of unenhanced multislice computed tomography demonstrating urolithiasis. Urology 2009, 74, 528–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, B.; Kamburoglu, K. Use of cone beam computed tomography in periodontology. World J. Radiol. 2014, 6, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, G.P.; Joy, T.E.; Mathew, J.; Kumar, V.R. Fundamentals of cone beam computed tomography for a prosthodontist. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2015, 15, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Patil, N.; Solanki, J.; Singh, R.; Laller, S. Oral implant imaging: A review. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 22, 7–17. [Google Scholar]
- Lund, V.J.; Mackay, I.S. Staging in rhinosinusitis. Rhinology 1993, 31, 183–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psaltis, A.J.; Li, G.; Vaezeafshar, R.; Cho, K.S.; Hwang, P.H. Modification of the Lund- Kennedy endoscopic scoring system improves its reliability and correlation with patient-reported outcome measures. Laryngoscope 2014, 124, 22162223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazian, M.; Vandewoude, C.; Wyatt, J.; Jacobs, R. Comparative assessment of panoramic radiography and CBCT imaging for radiodiagnostics in the posterior maxilla. Clin. Oral Investig. 2014, 18, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziebolz, D.; Szabadi, I.; Rinke, S.; Hornecker, E.; Mausberg, R.F. Initial periodontal screening and radiographic findings--a comparison of two methods to evaluate the periodontal situation. BMC Oral Health 2011, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechien, J.R.; Filleul, O.; Costa de Araujo, P.; Hsieh, J.W.; Chantrain, G.; Saussez, S. Chronic maxillary rhinosinusitis of dental origin: A systematic review of 674 patient cases. Int. J. Otolaryngol. 2014, 2014, 465173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuligowski, P.; Jaroń, A.; Preuss, O.; Gabrysz-Trybek, E.; Bladowska, J.; Trybek, G. Association between odontogenic and maxillary sinus conditions: A retrospective cone-beam computed tomographic study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elani, H.W.; Starr, J.R.; Da Silva, J.D.; Gallucci, G.O. Trends in Dental Implant Use in the U.S.; 19992016, and Projections to 2026. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 1424–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.M.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, H.M.; Park, I.H. Changing Trends in the Clinical Characteristics and Treatment Strategies for Odontogenic Sinusitis Over the Past 10 Years. Ear Nose Throat J. 2022, 01455613221080918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allevi, F.; Fadda, G.L.; Rosso, C.; Martino, F.; Pipolo, C.; Cavallo, G.; Felisati, G.; Saibene, A.M. Diagnostic criteria for odontogenic sinusitis: A systematic review. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2021, 35, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Workman, A.D.; Granquist, E.J.; Adapp, N.D. Odontogenic sinusitis: Developments in diagnosis, microbiology, and treatment. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 26, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Yokoi, H.; Ikeda, T.; Kawada, M.; Saito, K. The Prevalence of odontogenic pathology in patients with bilateral Rhinosinusitis. Allergy Rhinol. 2021, 12, 1177_2152656721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Dawood, A.; Mannocci, F.; Wilson, R.; Pitt Ford, T. Detection of periapical bone defects in human jaws using cone beam computed tomography and intraoral radiography. Int. Endod. J. 2009, 42, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos Junior, O.; Pinheiro, L.R.; Umetsubo, O.S.; Cavalcanti, M.G. CBCT-based evaluation of integrity of cortical sinus close to periapical lesions. Braz. Oral Res. 2015, 29, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M. Definition and management of odontogenic maxillary sinusitis. Maxillofac. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 41, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, R.E.; Long, C.M.; Loehrl, T.A.; Poetker, D.M. Odontogenic sinusitis: A review of the current literature. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2018, 3, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, B.J.; Jung, S.M.; Lee, H.N.; Kim, H.G.; Chung, J.H.; Jeong, J.H. Treatment strategy for odontogenic sinusitis. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2021, 35, 206212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simuntis, R.; Kubilius, R.; Tušas, P.; Leketas, M.; Vaitkus, J.; Vaitkus, S. Chronic odontogenic rhinosinusitis: Optimization of surgical treatment indications. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2020, 34, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longhini, A.B.; Branstetter, B.F.; Ferguson, B.J. Unrecognized odontogenic maxillary sinusitis: A cause of endoscopic sinus surgery failure. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2010, 24, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longhini, A.B.; Branstetter, B.F.; Ferguson, B.J. Otolaryngologists’ perceptions of odontogenic maxillary sinusitis. Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 1910–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokkens, W.J.; Lund, V.J.; Hopkins, C.; Hellings, P.; Kern, R.; Reitsma, S.; Toppila-Salmi, S.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Mullol, J.; Alobid, I.; et al. European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2020. Rhinology 2020, 58, 1–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patient Characteristics | Mean ± SD | n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 47.3 ± 13.7 | |
| Sex | ||
| Male (%) | 45 (54.9%) | |
| Female (%) | 37 (45.1%) | |
| CRS side | ||
| Right (%) | 25 (30.5%) | |
| Left (%) | 21 (25.6%) | |
| Bilateral (%) | 36 (43.9%) | |
| CRS with nasal polyp | 27 (32.9%) | |
| Lund–Mackay CT score | 7.3 ± 5.9 | |
| Modified Lund–Kennedy endoscopic score | 3.2 ± 2.5 | |
| Dental CBCT | 23 (28.1%) |
| Dental Pathology | Paranasal Sinus CT, n (%) | CPR, n (%) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| All pathologies | 136 (12.9%) | 217 (20.5%) | <0.001 * |
| Molars | 75 (55.1%) | 114 (52.5%) | <0.001 * |
| Premolars | 29 (21.3%) | 52 (24.0%) | <0.001 * |
| Anterior teeth | 32 (23.5%) | 51 (23.5%) | 0.001 * |
| Periapical lesions | 53 (39.0%) | 89 (41%) | <0.001 * |
| Molars | 17 | 26 | 0.029 * |
| Premolars | 15 | 30 | 0.004 * |
| Anterior teeth | 21 | 33 | 0.002 * |
| Caries | 24 (17.6%) | 61 (28.1%) | <0.001 * |
| Molar | 16 | 41 | 0.001 * |
| Premolar | 5 | 12 | 0.020 * |
| Anterior teeth | 3 | 8 | 0.059 |
| Periodontal lesions | 39 (28.7%) | 40 (18.4%) | 0.317 |
| Molars | 28 | 28 | 1.000 |
| Premolars | 4 | 4 | 1.000 |
| Anterior teeth | 7 | 8 | 0.317 |
| Fistulae | 9 (6.6%) | 15 (6.9%) | 0.014 * |
| Molars | 9 | 14 | 0.025 * |
| Premolars | 0 | 1 | 0.317 |
| Anterior teeth | 0 | 0 | 1.000 |
| Fractures | 2 (1.5%) | 3 (1.4%) | 0.317 |
| Molars | 1 | 1 | 1.000 |
| Premolars | 1 | 1 | 1.000 |
| Anterior teeth | 0 | 1 | 0.317 |
| Implants | 9 (6.6%) | 9 (4.1%) | 1.000 |
| Molars | 4 | 4 | 1.000 |
| Premolars | 4 | 4 | 1.000 |
| Anterior teeth | 1 | 1 | 1.000 |
| Dental Pathology | Dental CBCT, n (%) | CPR, n (%) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| All pathologies | 96 (30.9%) | 72 (23.2%) | 0.018 * |
| Molars | 46 (47.9%) | 38 (52.8%) | 0.303 |
| Premolars | 37 (38.5%) | 23 (31.9%) | 0.008 * |
| Anterior teeth | 13 (13.5%) | 11 (15.3%) | 0.577 |
| Periapical lesions | 27 (28.1%) | 27 (37.5%) | 1.000 |
| Molars | 11 | 13 | 0.414 |
| Premolars | 8 | 10 | 0.414 |
| Anterior teeth | 8 | 4 | 0.046 * |
| Caries | 28 (29.2%) | 17 (23.6%) | 0.140 |
| Molar | 7 | 6 | 0.915 |
| Premolar | 19 | 8 | 0.002 * |
| Anterior teeth | 2 | 3 | 0.705 |
| Periodontal lesions | 31 (32.3%) | 16 (22.2%) | |
| Molars | 20 | 10 | 0.161 |
| Premolars | 8 | 3 | 0.059 |
| Anterior teeth | 3 | 3 | 1.000 |
| Fistulae | 9 (9.4%) | 10 (13.9%) | 0.705 |
| Molars | 8 | 9 | 0.564 |
| Premolars | 1 | 1 | 1.000 |
| Anterior teeth | 0 | 0 | 1.000 |
| Fractures | 1 (1.0%) | 2 (2.8%) | 0.317 |
| Molars | 0 | 0 | 1.000 |
| Premolars | 1 | 1 | 1.000 |
| Anterior teeth | 0 | 1 | 0.317 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, W.-C.; Hwang, L.A.; Lin, W.-C.; Wu, C.-N.; Su, W.-C.; Fang, K.-C.; Luo, S.-D. Curved Planar Reformation: A Useful Method for Screening Dental Pathologies in Chronic Rhinosinusitis via Paranasal Sinus Computed Tomography. Tomography 2022, 8, 2330-2338. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8050194
Chen W-C, Hwang LA, Lin W-C, Wu C-N, Su W-C, Fang K-C, Luo S-D. Curved Planar Reformation: A Useful Method for Screening Dental Pathologies in Chronic Rhinosinusitis via Paranasal Sinus Computed Tomography. Tomography. 2022; 8(5):2330-2338. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8050194
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Wei-Chih, Lisa Alice Hwang, Wei-Che Lin, Ching-Nung Wu, Wei-Chia Su, Kuan-Chung Fang, and Sheng-Dean Luo. 2022. "Curved Planar Reformation: A Useful Method for Screening Dental Pathologies in Chronic Rhinosinusitis via Paranasal Sinus Computed Tomography" Tomography 8, no. 5: 2330-2338. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8050194
APA StyleChen, W.-C., Hwang, L. A., Lin, W.-C., Wu, C.-N., Su, W.-C., Fang, K.-C., & Luo, S.-D. (2022). Curved Planar Reformation: A Useful Method for Screening Dental Pathologies in Chronic Rhinosinusitis via Paranasal Sinus Computed Tomography. Tomography, 8(5), 2330-2338. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8050194







