Follow-Up Assessment of Intracranial Aneurysms Treated with Endovascular Coiling: Comparison of Compressed Sensing and Parallel Imaging Time-of-Flight Magnetic Resonance Angiography
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Image Acquisition
2.2. Image Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Population
3.2. Evaluation of Aneurysm Occlusion
3.3. Evaluation of Adjacent Vessels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vlak, M.H.M.; Algra, A.; Brandenburg, R.; Rinkel, G.J.E. Prevalence of unruptured intracranial aneurysms, with emphasis on sex, age, comorbidity, country, and time period: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caranci, F.; Briganti, F.; Cirillo, L.; Leonardi, M.; Muto, M. Epidemiology and genetics of intracranial aneurysms. Eur. J. Radiol. 2013, 82, 1598–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molyneux, A.; International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT) Collaborative Group. International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling in 2143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: A randomised trial. Lancet 2002, 360, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naggara, O.N.; White, P.M.; Guilbert, F.; Roy, D.; Weill, A.; Raymond, J. Endovascular Treatment of Intracranial Unruptured Aneurysms: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Literature on Safety and Efficacy. Radiology 2010, 256, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiex, R.; Norbash, A.M.; Frerichs, K.U. The Safety of Dedicated-Team Catheter-Based Diagnostic Cerebral Angiography in the Era of Advanced Noninvasive Imaging. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2010, 31, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goyal, M.; Demchuk, A.M.; Menon, B.K.; Eesa, M.; Rempel, J.L.; Thornton, J.; Roy, D.; Jovin, T.G.; Willinsky, R.A.; Sapkota, B.L.; et al. Randomized Assessment of Rapid Endovascular Treatment of Ischemic Stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Amerongen, M.J.; Boogaarts, H.D.; De Vries, J.; Verbeek, A.L.M.; Meijer, F.; Prokop, M.; Bartels, R. MRA Versus DSA for Follow-Up of Coiled Intracranial Aneurysms: A Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Menke, J.; Schramm, P.; Sohns, J.M.; Kallenberg, K.; Staab, W. Diagnosing flow residuals in coiled cerebral aneurysms by MR angiography: Meta-analysis. J. Neurol. 2013, 261, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, S.U.; Mocco, J.; Zhang, X.; Kelly, M.; Doshi, A.; Nael, K.; De Leacy, R. MRA versus DSA for the follow-up imaging of intracranial aneurysms treated using endovascular techniques: A meta-analysis. J. NeuroInterv. Surg. 2019, 11, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toni, F.; Marliani, A.F.; Cirillo, L.; Battaglia, S.; Princiotta, C.; Dall’Olio, M.; Simonetti, L.; Leonardi, M. 3T MRI in the Evaluation of Brain Aneurysms Treated with Flow-Diverting Stents: Preliminary Experience. Neuroradiol. J. 2009, 22, 588–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levent, A.; Yuce, I.; Eren, S.; Ozyigit, O.; Kantarci, M. Contrast-Enhanced and Time-of-Flight MR Angiographic Assessment of Endovascular Coiled Intracranial Aneurysms at 1.5 T. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2014, 20, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sprengers, M.E.S.; Schaafsma, J.D.; Van Rooij, W.J.; Berg, R.V.D.; Rinkel, G.J.E.; Akkerman, E.M.; Ferns, S.P.; Majoie, C.B.L.M. Evaluation of the Occlusion Status of Coiled Intracranial Aneurysms with MR Angiography at 3T: Is Contrast Enhancement Necessary? Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 30, 1665–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cho, W.-S.; Kim, S.S.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, S.H. The effectiveness of 3T time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography for follow-up evaluations after the stent-assisted coil embolization of cerebral aneurysms. Acta Radiol. 2014, 55, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marciano, D.; Soize, S.; Metaxas, G.; Portefaix, C.; Pierot, L. Follow-up of intracranial aneurysms treated with stent-assisted coiling: Comparison of contrast-enhanced MRA, time-of-flight MRA, and digital subtraction angiography. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 44, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierot, L.; Portefaix, C.; Gauvrit, J.-Y.; Boulin, A. Follow-Up of Coiled Intracranial Aneurysms: Comparison of 3D Time-of-Flight MR Angiography at 3T and 1.5T in a Large Prospective Series. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 33, 2162–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cirillo, M.; Scomazzoni, F.; Cirillo, L.; Cadioli, M.; Simionato, F.; Iadanza, A.; Kirchin, M.; Righi, C.; Anzalone, N. Comparison of 3D TOF-MRA and 3D CE-MRA at 3T for imaging of intracranial aneurysms. Eur. J. Radiol. 2013, 82, e853–e859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, S.; Fan, F.; Hu, P.; Yang, K.; Zhai, X.; Geng, J.; Ji, Z.; Lu, J.; Zhang, H. The sensitivity and specificity of TOF-MRA compared with DSA in the follow-up of treated intracranial aneurysms. J. NeuroInterv. Surg. 2021, 13, 1172–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griswold, M.A.; Jakob, P.M.; Heidemann, R.M.; Nittka, M.; Jellus, V.; Wang, J.; Kiefer, B.; Haase, A. Generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA). Magn. Reson. Med. 2002, 47, 1202–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, J.C. Compressed sensing MRI: A review from signal processing perspective. BMC Biomed. Eng. 2019, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geethanath, S.; Reddy, R.; Konar, A.S.; Imam, S.; Sundaresan, R.; Ramesh, R.B.D.; Venkatesan, R. Compressed Sensing MRI: A Review. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 41, 183–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Okada, T.; Fushimi, Y.; Yamamoto, A.; Fujimoto, K.; Okuchi, S.; Fukutomi, H.; Takahashi, J.C.; Funaki, T.; Miyamoto, S.; et al. Magnetic resonance angiography with compressed sensing: An evaluation of moyamoya disease. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0189493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fushimi, Y.; Okada, T.; Kikuchi, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Okada, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Schmidt, M.; Yoshida, K.; Miyamoto, S.; Togashi, K. Clinical evaluation of time-of-flight MR angiography with sparse undersampling and iterative reconstruction for cerebral aneurysms. NMR Biomed. 2017, 30, e3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sakata, A.; Fushimi, Y.; Okada, T.; Nakajima, S.; Hinoda, T.; Speier, P.; Schmidt, M.; Forman, C.; Yoshida, K.; Kataoka, H.; et al. Evaluation of cerebral arteriovenous shunts: A comparison of parallel imaging time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography (TOF-MRA) and compressed sensing TOF-MRA to digital subtraction angiography. Neuroradiology 2020, 63, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demerath, T.; Bonati, L.; El Mekabaty, A.; Schubert, T. High-resolution compressed-sensing time-of-flight MRA in a case of acute ICA/MCA dissection. Neuroradiology 2020, 62, 753–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Cao, Y.Z.; Mu, X.H.; Sun, Y.; Schmidt, M.; Forman, C.; Speier, P.; Lu, S.S.; Hong, X.N. Highly accelerated compressed sensing time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography may be reliable for diagnosing head and neck arterial steno-occlusive disease: A comparative study with digital subtraction angiography. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 3059–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascitelli, J.R.; Moyle, H.; Oermann, E.K.; Polykarpou, M.F.; Patel, A.A.; Doshi, A.H.; Gologorsky, Y.; Bederson, J.B.; Patel, A.B. An update to the Raymond–Roy Occlusion Classification of intracranial aneurysms treated with coil embolization. J. NeuroInterv. Surg. 2015, 7, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anzalone, N.; Scomazzoni, F.; Cirillo, M.; Righi, C.; Simionato, F.; Cadioli, M.; Iadanza, A.; Kirchin, M.; Scotti, G. Follow-Up of Coiled Cerebral Aneurysms at 3T: Comparison of 3D Time-of-Flight MR Angiography and Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2008, 29, 1530–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, J.; Duan, Y.; Zhuo, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, G.; Song, Q.; Gao, B.; Zhang, B.; Wang, M.; Yang, L.; et al. Acceleration of Brain TOF-MRA with Compressed Sensitivity Encoding: A Multicenter Clinical Study. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2021, 42, 1208–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behme, D.; Malinova, V.; Kallenberg, K.; Knauth, M.; Mohr, A. Unenhanced Time-of-Flight MR Angiography versus Gadolinium-Enhanced Time-of-Flight MR Angiography in the Follow-Up of Coil-Embolized Aneurysms. J. Neurol. Surg. Part A Cent. Eur. Neurosurg. 2016, 77, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, T.J.; Huston, J.; Cloft, H.J.; Mandrekar, J.; Gray, L.; Bernstein, M.; Atkinson, J.L.; Kallmes, D.F. A Prospective Trial of 3T and 1.5T Time-of-Flight and Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography in the Follow-Up of Coiled Intracranial Aneurysms. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 31, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanda, T.; Fukusato, T.; Matsuda, M.; Toyoda, K.; Oba, H.; Kotoku, J.; Haruyama, T.; Kitajima, K.; Furui, S. Gadolinium-based Contrast Agent Accumulates in the Brain Even in Subjects without Severe Renal Dysfunction: Evaluation of Autopsy Brain Specimens with Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectroscopy. Radiology 2015, 276, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, R.J.; McDonald, J.S.; Kallmes, D.F.; Jentoft, M.E.; Murray, D.L.; Thielen, K.R.; Williamson, E.E.; Eckel, L.J. Intracranial Gadolinium Deposition after Contrast-enhanced MR Imaging. Radiology 2015, 275, 772–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Songsaeng, D.; Sakarunchai, I.; Harmontree, S.; Mongkolnaowarat, S.; Charnchaowanish, P.; Zhang, S.; Krings, T. Black-blood vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging—A new imaging biomarker for regrowth of coiled saccular aneurysms? Interdiscip. Neurosurg. 2021, 23, 100920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitt, M.R.; Barbour, M.C.; Rolland Du Roscoat, S.; Geindreau, C.; Chivukula, V.K.; McGah, P.M.; Nerva, J.D.; Morton, R.P.; Kim, L.J.; Aliseda, A. Computational fluid dynamics of cerebral aneurysm coiling using high-resolution and high-energy synchrotron X-ray microtomography: Comparison with the homogeneous porous medium approach. J. NeuroInterv. Surg. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
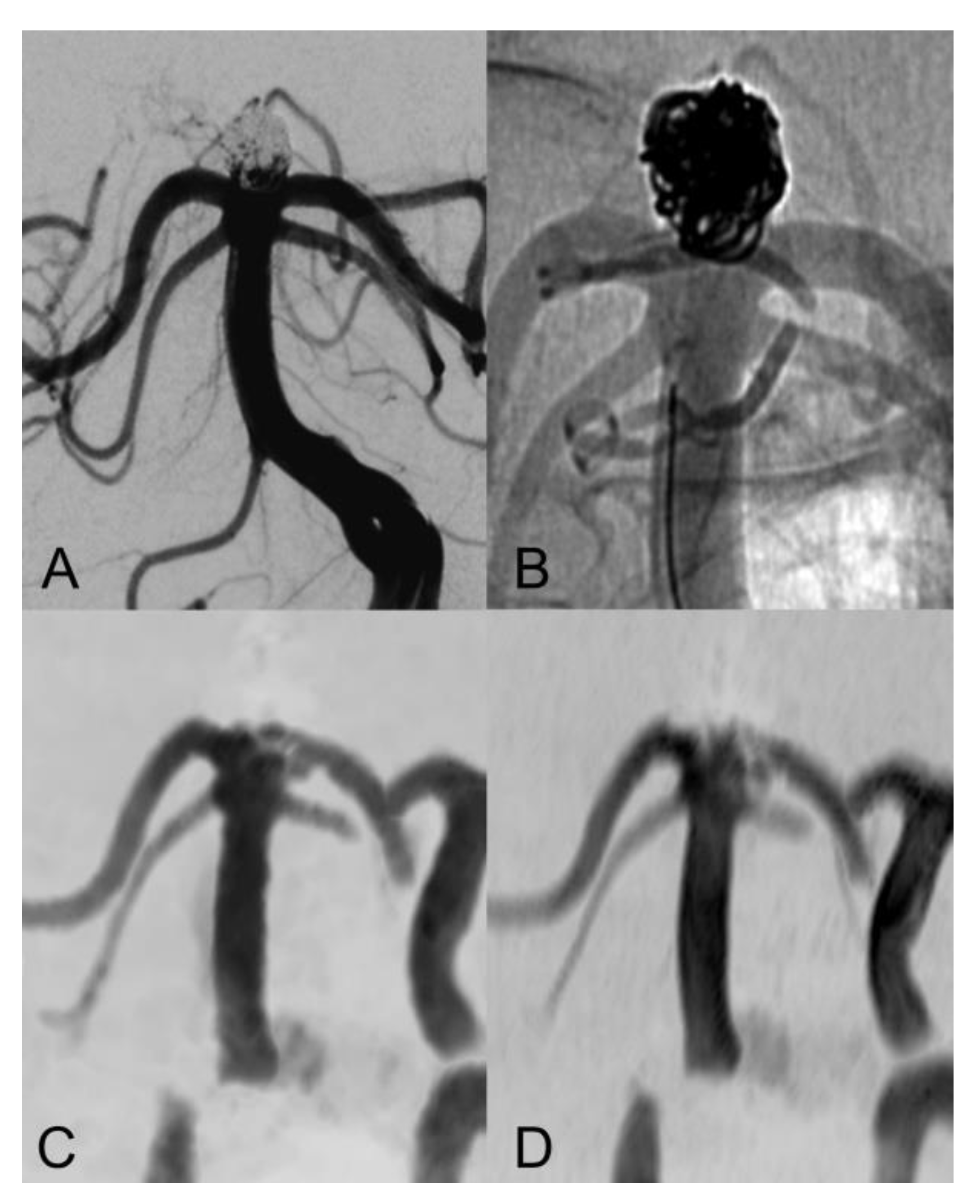
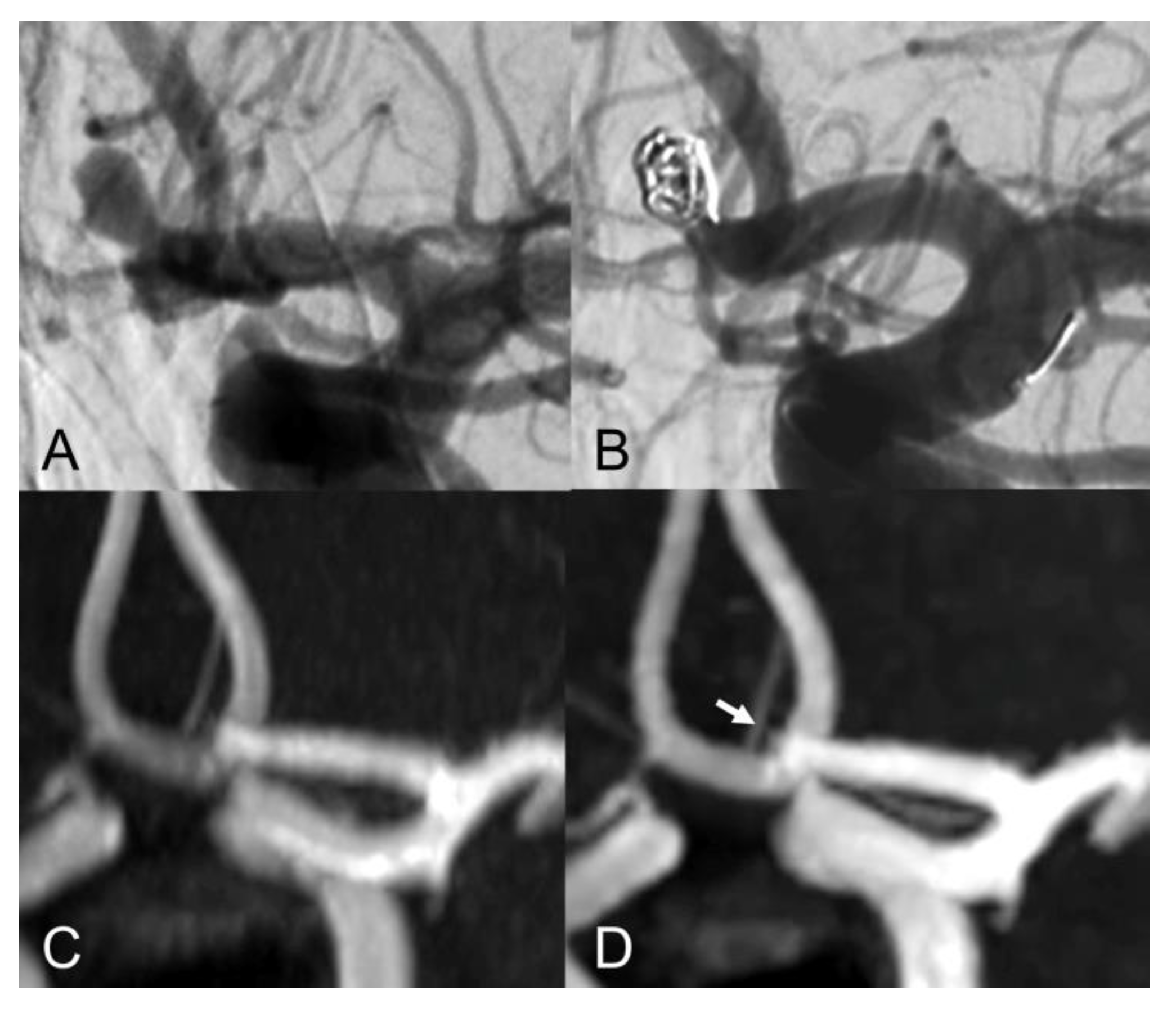
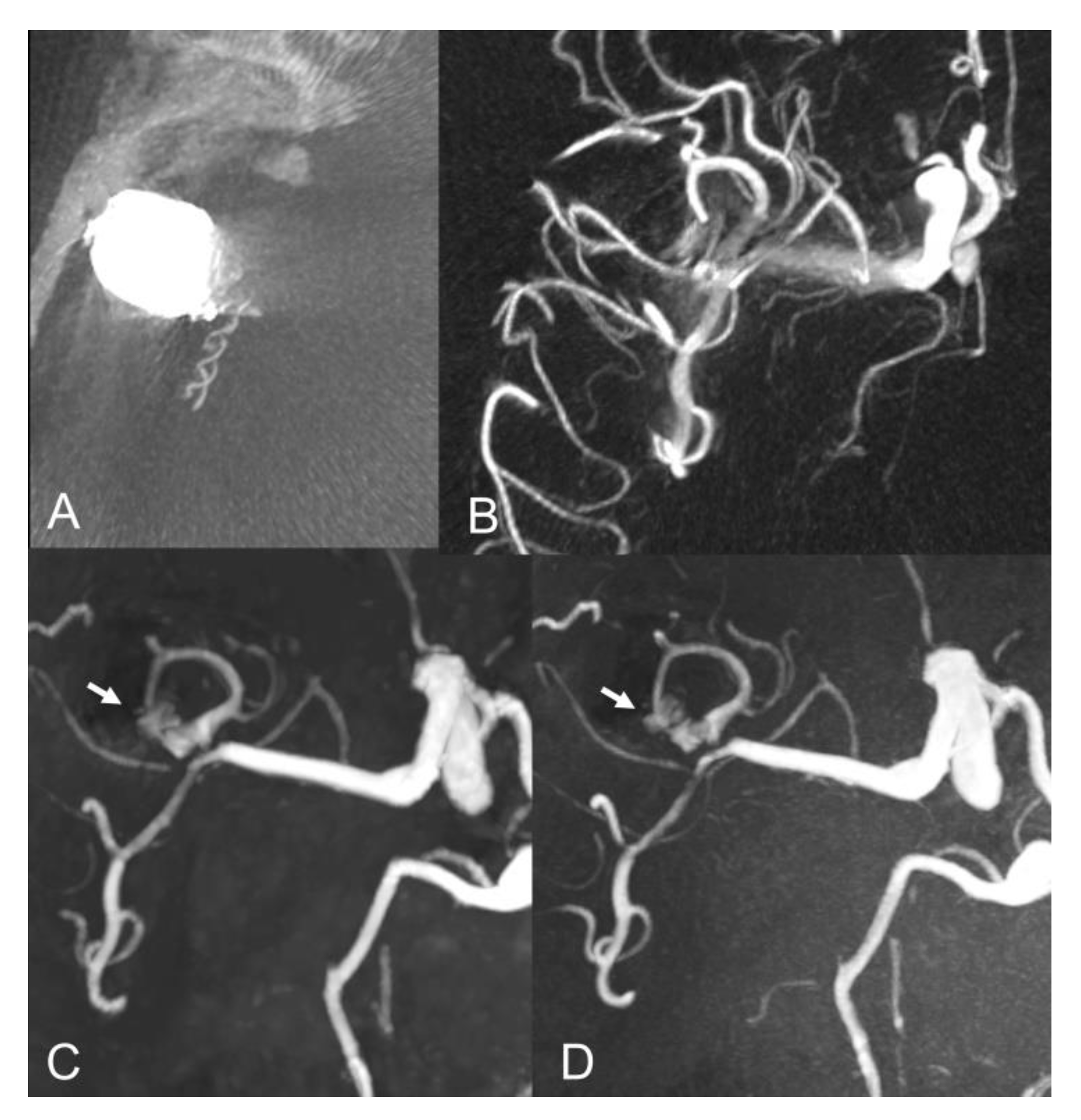
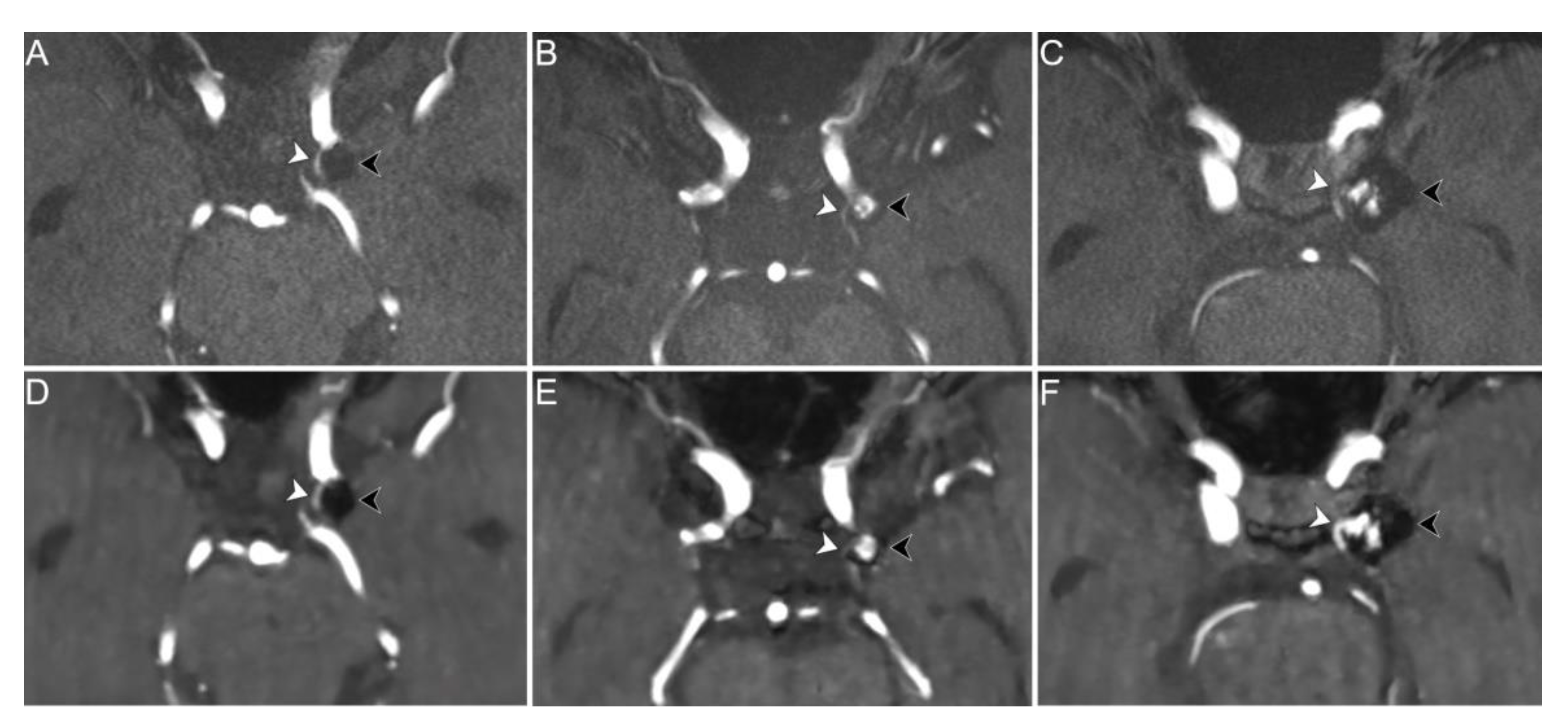
| Sex (female) | 16 (72.7%) |
| Age (years) | 63 (55–76) |
| Follow-up time (years) | 2.5 (0.9–4.7) |
| Subarachnoid hemorrhage | 5 (22.7%) |
| Stent placement | 7 (31.8%) |
| Aneurysm location | |
| ACA | 8 (36.4%) |
| Supraclinoid ICA | 6 (27.2%) |
| M1-M2 bifurcation | 3 (13.6%) |
| PCA | 2 (9.1%) |
| Basilar artery | 2 (9.1%) |
| Pericallosal artery | 1 (4.5%) |
| Aneurysm diameter (mm) | 7 (6–10) |
| Total Readings (n = 88) | Coil Embolization | Stent-Assisted Coiling | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parent vessel depiction | 0.051 | |||
| Better | 10 (11.4%) | 9 (15.0%) | 1 (3.6%) | |
| Equal | 76 (86.4%) | 51 (85.0%) | 25 (89.3%) | |
| Worse | 2 (2.3%) | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (7.1%) | |
| Adjacent vessels depiction | 1 | |||
| Better | 8 (9.1%) | 6 (10.0%) | 2 (7.1%) | |
| Equal | 70 (79.5%) | 47 (78.3%) | 23 (82.1%) | |
| Worse | 10 (11.4%) | 7 (11.7%) | 3 (10.7%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vornetti, G.; Bartiromo, F.; Toni, F.; Dall’Olio, M.; Cirillo, M.; Speier, P.; Princiotta, C.; Schmidt, M.; Tonon, C.; Zacà, D.; et al. Follow-Up Assessment of Intracranial Aneurysms Treated with Endovascular Coiling: Comparison of Compressed Sensing and Parallel Imaging Time-of-Flight Magnetic Resonance Angiography. Tomography 2022, 8, 1608-1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8030133
Vornetti G, Bartiromo F, Toni F, Dall’Olio M, Cirillo M, Speier P, Princiotta C, Schmidt M, Tonon C, Zacà D, et al. Follow-Up Assessment of Intracranial Aneurysms Treated with Endovascular Coiling: Comparison of Compressed Sensing and Parallel Imaging Time-of-Flight Magnetic Resonance Angiography. Tomography. 2022; 8(3):1608-1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8030133
Chicago/Turabian StyleVornetti, Gianfranco, Fiorina Bartiromo, Francesco Toni, Massimo Dall’Olio, Mario Cirillo, Peter Speier, Ciro Princiotta, Michaela Schmidt, Caterina Tonon, Domenico Zacà, and et al. 2022. "Follow-Up Assessment of Intracranial Aneurysms Treated with Endovascular Coiling: Comparison of Compressed Sensing and Parallel Imaging Time-of-Flight Magnetic Resonance Angiography" Tomography 8, no. 3: 1608-1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8030133
APA StyleVornetti, G., Bartiromo, F., Toni, F., Dall’Olio, M., Cirillo, M., Speier, P., Princiotta, C., Schmidt, M., Tonon, C., Zacà, D., Lodi, R., & Cirillo, L. (2022). Follow-Up Assessment of Intracranial Aneurysms Treated with Endovascular Coiling: Comparison of Compressed Sensing and Parallel Imaging Time-of-Flight Magnetic Resonance Angiography. Tomography, 8(3), 1608-1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8030133






