The Influence of Data-Driven Compressed Sensing Reconstruction on Quantitative Pharmacokinetic Analysis in Breast DCE MRI
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
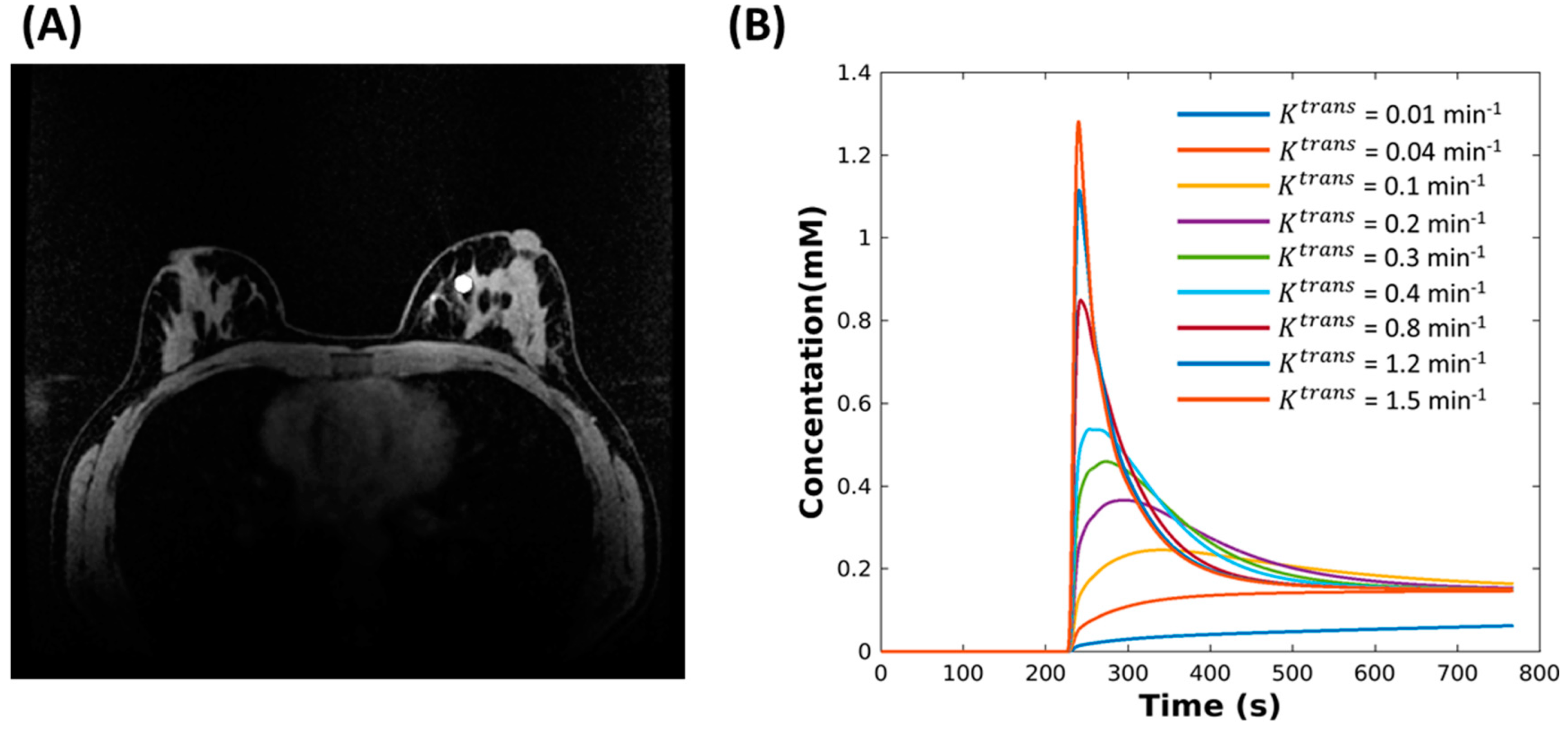
2.1. Digital Reference Object (DRO)
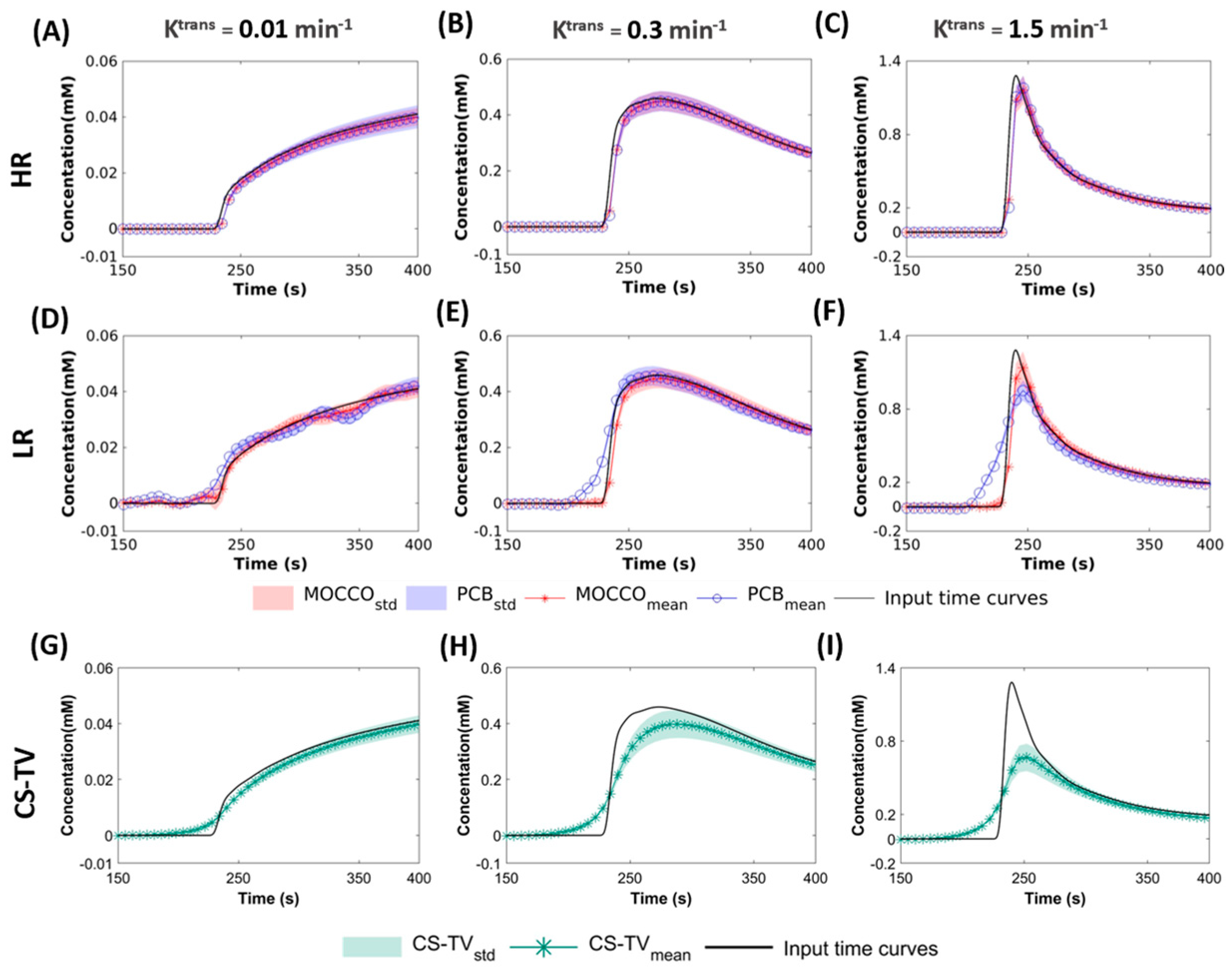
2.2. Reconstruction
- Behavior with temporal models derived from high resolution images (HR): the for this approach included two elements of the pre-estimated temporal matrix, which included the reference CTCs and temporal curve with constant value to simulate dynamic and static tissue signal changes.
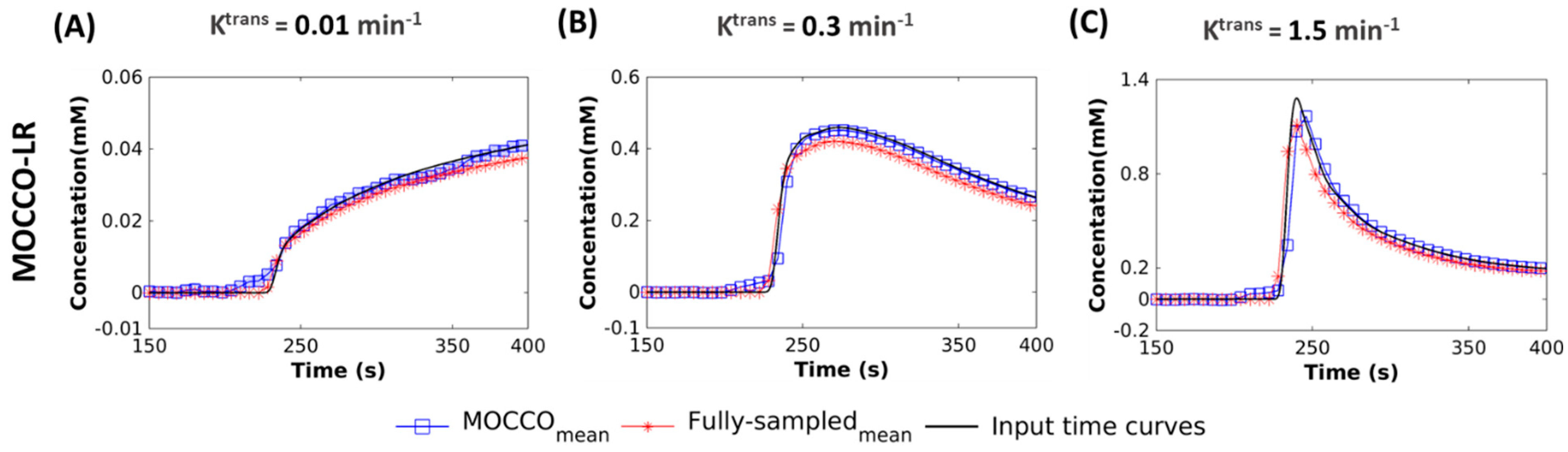
- Performance with temporal models derived from low resolution images (LR): in this approach, was learned through the low frequency region from fully-sampled central k-space data using progressive learning with cubic spline approximation [51,52] followed by complex independent component analysis (ICA) [53]. The ICA technique assumes that each component is statistically independent from the source signals, which has been shown to be a robust method to identify key components of the perfusion series and remove unwanted image-to-image fluctuations [54].
2.3. Analysis
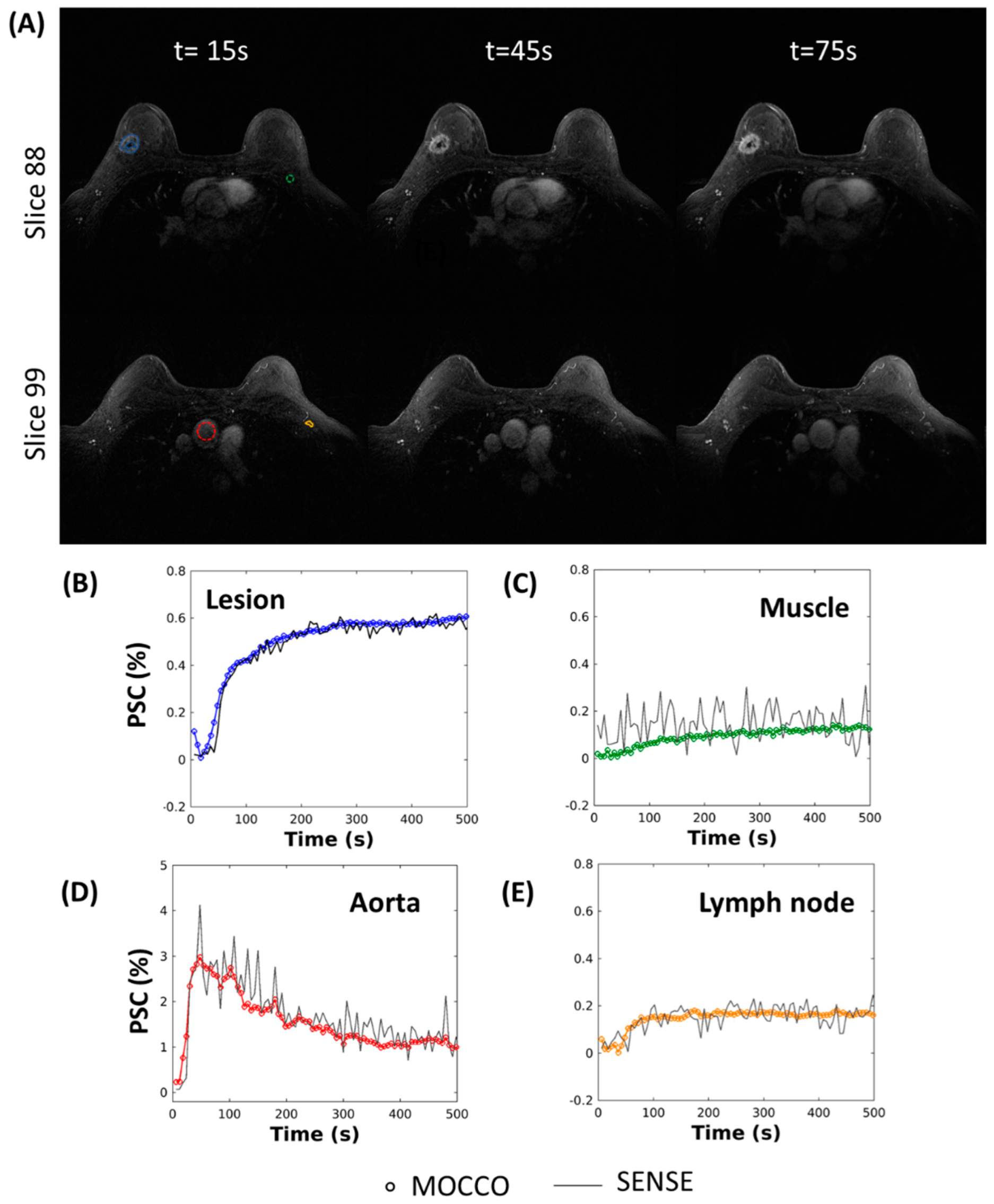
2.4. In Vivo Imaging
MRI Acquisition
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mann, R.M.; Cho, N.; Moy, L. Breast MRI: State of the Art. Radiology 2019, 292, 520–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinker-Domenig, K.; Bogner, W.; Gruber, S.; Bickel, H.; Duffy, S.; Schernthaner, M.; Dubsky, P.; Pluschnig, U.; Rudas, M.; Trattnig, S.; et al. High Resolution MRI of the Breast at 3 T: Which BI-RADS® Descriptors Are Most Strongly Associated with the Diagnosis of Breast Cancer? Eur. Radiol. 2012, 22, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harry, V.N.; Semple, S.I.; Parkin, D.E.; Gilbert, F.J. Use of New Imaging Techniques to Predict Tumour Response to Therapy. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobbes, M.B.I.; Prevos, R.; Smidt, M.; Tjan-Heijnen, V.C.G.; van Goethem, M.; Schipper, R.; Beets-Tan, R.G.; Wildberger, J.E. The Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Assessing Residual Disease and Pathologic Complete Response in Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: A Systematic Review. Insights Imaging 2013, 4, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Arlinghaus, L.R.; Ayers, G.D.; Chakravarthy, A.B.; Abramson, R.G.; Abramson, V.G.; Atuegwu, N.; Farley, J.; Mayer, I.A.; Kelley, M.C.; et al. DCE-MRI Analysis Methods for Predicting the Response of Breast Cancer to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: Pilot Study Findings. Magn. Reason. Med. 2014, 71, 1592–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mann, R.M.; Kuhl, C.K.; Kinkel, K.; Boetes, C. Breast MRI: Guidelines from the European Society of Breast Imaging. Eur. Radiol. 2008, 18, 1307–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morris, E.A.; Comstock, C.E.; Lee, C.H. ACR BI-RADS® Magnetic Resonance Imaging. In ACR BI-RADS® Atlas, Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System; American College of Radiology: Reston, VA, USA, 2013; p. 18. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhl, C.K.; Schild, H.H.; Morakkabati, N. Dynamic Bilateral Contrast-Enhanced MR Imaging of the Breast: Trade-off between Spatial and Temporal Resolution. Radiology 2005, 236, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosen, E.L.; Baker, J.A.; Soo, M.S. Malignant Lesions Initially Subjected to Short-Term Mammographic Follow-Up1. Radiology 2002, 223, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, D.M.; Baker, D.R.; Daniel, B.L. Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Breast Cancer: Clinical Indications and Breast MRI Reporting System. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2000, 12, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malich, A.; Boehm, T.; Facius, M.; Freesmeyer, M.G.; Fleck, M.; Anderson, R.; Kaiser, W.A. Differentiation of Mammographically Suspicious Lesions: Evaluation of Breast Ultrasound, MRI Mammography and Electrical Impedance Scanning as Adjunctive Technologies in Breast Cancer Detection. Clin. Radiol. 2001, 56, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissnitzer, M.; Dershaw, D.D.; Feigin, K.; Bernard-Davila, B.; Barra, F.; Morris, E.A. MRI Appearance of Invasive Subcentimetre Breast Carcinoma: Benign Characteristics Are Common. Br. J. Radiol. 2017, 90, 20170102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, R.; Sung, J.; Lee, C.; Comstock, C.; Wynn, R.; Morris, E. Characteristics and Outcome of Enhancing Foci Followed on Breast MRI with Management Implications. Clin. Radiol. 2014, 69, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mussurakis, S.; Buckley, D.L.; Drew, P.J.; Fox, J.N.; Carleton, P.J.; Turnbull, L.W.; Horsman, A. Dynamic MR Imaging of the Breast Combined with Analysis of Contrast Agent Kinetics in the Differentiation of Primary Breast Tumours. Clin. Radiol. 1997, 52, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, P.; Liney, G.P.; Lowry, M.; Kneeshaw, P.J.; Turnbull, L.W. Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Sub-1 Cm Breast Lesions Using Dynamic Contrast Enhanced MRI. Breast 2004, 13, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veltman, J.; Stoutjesdijk, M.; Mann, R.; Huisman, H.J.; Barentsz, J.O.; Blickman, J.G.; Boetes, C. Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Breast: The Value of Pharmacokinetic Parameters Derived from Fast Dynamic Imaging during Initial Enhancement in Classifying Lesions. Eur. Radiol. 2008, 18, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schabel, M.C.; Morrell, G.R.; Oh, K.Y.; Walczak, C.A.; Barlow, R.B.; Neumayer, L.A. Pharmacokinetic Mapping for Lesion Classification in Dynamic Breast MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2010, 31, 1371–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Litjens, G.J.S.; Heisen, M.; Buurman, J.; ter Haar Romeny, B.M. Pharmacokinetic Models in Clinical Practice: What Model to Use for DCE-MRI of the Breast? In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 14–17 April 2010; pp. 185–188. [Google Scholar]
- Garimella, V.; Qutob, O.; Fox, J.N.; Long, E.D.; Chaturvedi, A.; Turnbull, L.W.; Drew, P.J. Recurrence Rates after DCE-MRI Image Guided Planning for Breast-Conserving Surgery Following Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Locally Advanced Breast Cancer Patients. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. (EJSO) 2007, 33, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, R.M.; Mus, R.D.; van Zelst, J.; Geppert, C.; Karssemeijer, N.; Platel, B. A Novel Approach to Contrast-Enhanced Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Screening: High-Resolution Ultrafast Dynamic Imaging. Investig. Radiol. 2014, 49, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-H.; Yin, F.-F.; Horton, J.; Chang, Z. Review of Treatment Assessment Using DCE-MRI in Breast Cancer Radiation Therapy. World J. Methodol. 2014, 4, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieber, A.; Zeitler, H.; Rosenthal, H.; Görich, J.; Kreienberg, R.; Brambs, H.J.; Tomczak, R. MRI of Breast Cancer: Influence of Chemotherapy on Sensitivity. Br. J. Radiol. 1997, 70, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, Y.; Partovi, S.; Müller-Eschner, M.; Amarteifio, E.; Bäuerle, T.; Weber, M.-A.; Kauczor, H.-U.; Rengier, F. Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Fundamentals and Application to the Evaluation of the Peripheral Perfusion. Cardiovasc. Diagn. 2014, 4, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giovanni, P.; Azlan, C.A.; Ahearn, T.S.; Semple, S.I.; Gilbert, F.J.; Redpath, T.W. The Accuracy of Pharmacokinetic Parameter Measurement in DCE-MRI of the Breast at 3 T. Phys. Med. Biol. 2010, 55, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heisen, M.; Fan, X.; Buurman, J.; van Riel, N.A.W.; Karczmar, G.S.; Romeny, B.M. ter H. The Influence of Temporal Resolution in Determining Pharmacokinetic Parameters from DCE-MRI Data. Magn. Reson. Med. 2010, 63, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopata, R.G.P.; Backes, W.H.; van den Bosch, P.P.J.; Riel, N.A.W. van On the Identifiability of Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2007, 58, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaals, J.J.V.; Brummer, M.E.; Dixon, W.T.; Tuithof, H.H.; Engels, H.; Nelson, R.C.; Gerety, B.M.; Chezmar, J.L.; Boer, J.A.D. “Keyhole” Method for Accelerating Imaging of Contrast Agent Uptake. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1993, 3, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.A.; Haraldseth, O.; Müller, T.B.; Rinck, P.A.; Øksendal, A.N. K-Space Substitution: A Novel Dynamic Imaging Technique. Magn. Reson. Med. 1993, 29, 830–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saranathan, M.; Rettmann, D.W.; Hargreaves, B.A.; Clarke, S.E.; Vasanawala, S.S. DIfferential Subsampling with Cartesian Ordering (DISCO): A High Spatio-Temporal Resolution Dixon Imaging Sequence for Multiphasic Contrast Enhanced Abdominal Imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 35, 1484–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, H.K.; Dougherty, L. Dynamic MRI with Projection Reconstruction and KWIC Processing for Simultaneous High Spatial and Temporal Resolution. Magn. Reson. Med. 2004, 52, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z. Spatiotemporal imagingwith partially separable functions. In Proceedings of the 2007 4th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, Arlington, VA, USA, 12–15 April 2007; pp. 988–991. [Google Scholar]
- Lustig, M.; Donoho, D.; Pauly, J.M. Sparse MRI: The Application of Compressed Sensing for Rapid MR Imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2007, 58, 1182–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, K.T.; Uecker, M.; Frahm, J. Undersampled Radial MRI with Multiple Coils. Iterative Image Reconstruction Using a Total Variation Constraint. Magn. Reson. Med. 2007, 57, 1086–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, R.W.; Ramsay, E.A.; Cheung, E.Y.; Plewes, D.B. The Influence of Radial Undersampling Schemes on Compressed Sensing Reconstruction in Breast MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2012, 67, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velikina, J.V.; Alexander, A.L.; Samsonov, A. Accelerating MR Parameter Mapping Using Sparsity-Promoting Regularization in Parametric Dimension. Magn. Reson. Med. 2013, 70, 1263–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsao, J.; Kozerke, S. MRI Temporal Acceleration Techniques. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 36, 543–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Haldar, J.P.; Brinegar, C.; Liang, Z. Low Rank Matrix Recovery for Real-Time Cardiac MRI. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 14–17 April 2010; pp. 996–999. [Google Scholar]
- Brinegar, C.; Schmitter, S.S.; Mistry, N.N.; Johnson, G.A.; Liang, Z.-P. Improving Temporal Resolution of Pulmonary Perfusion Imaging in Rats Using the Partially Separable Functions Model. Magn. Reson. Med. 2010, 64, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Velikina, J.V.; Samsonov, A.A. Reconstruction of Dynamic Image Series from Undersampled MRI Data Using Data-Driven Model Consistency Condition (MOCCO). Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 74, 1279–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, P.N.; Velikina, J.V.; Strigel, R.M.; Bancroft, L.C.H.; Samsonov, A.A.; Cashen, T.A.; Wang, K.; Kelcz, F.; Johnson, K.M.; Korosec, F.R.; et al. Comparison of Data-Driven and General Temporal Constraints on Compressed Sensing for Breast DCE MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2021, 85, 3071–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Grimm, R.; Block, K.T.; Chandarana, H.; Kim, S.; Xu, J.; Axel, L.; Sodickson, D.K.; Otazo, R. Golden-Angle Radial Sparse Parallel MRI: Combination of Compressed Sensing, Parallel Imaging, and Golden-Angle Radial Sampling for Fast and Flexible Dynamic Volumetric MRI: IGRASP: Iterative Golden-Angle RAdial Sparse Parallel MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 72, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.G.; Feng, L.; Grimm, R.; Freed, M.; Block, K.T.; Sodickson, D.K.; Moy, L.; Otazo, R. Influence of Temporal Regularization and Radial Undersampling Factor on Compressed Sensing Reconstruction in Dynamic Contrast Enhanced MRI of the Breast: Temporal Regularization and Radial Undersampling Effects on DCE-MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2016, 43, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henze Bancroft, L.; Holmes, J.; Bosca-Harasim, R.; Johnson, J.; Wang, P.; Korosec, F.; Block, W.; Strigel, R. An Anthropomorphic Digital Reference Object (DRO) for Simulation and Analysis of Breast DCE MRI Techniques. Tomography 2022, 8, 1005–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofts, P.S. Modeling Tracer Kinetics in Dynamic Gd-DTPA MR Imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1997, 7, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, J.P.B.; Jackson, A.; Parker, G.J.M.; Jayson, G.C. DCE-MRI Biomarkers in the Clinical Evaluation of Antiangiogenic and Vascular Disrupting Agents. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 96, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barboriak, D.P.; MacFall, J.R.; Viglianti, B.L.; Dewhirst DVM, M.W. Comparison of Three Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Models for the Prediction of Contrast Agent Distribution Measured by Dynamic MR Imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2008, 27, 1388–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rakow-Penner, R.; Daniel, B.; Yu, H.; Sawyer-Glover, A.; Glover, G.H. Relaxation Times of Breast Tissue at 1.5T and 3T Measured Using IDEAL. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2006, 23, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohrer, M.; Bauer, H.; Mintorovitch, J.; Requardt, M.; Weinmann, H.-J. Comparison of Magnetic Properties of MRI Contrast Media Solutions at Different Magnetic Field Strengths. Investig. Radiol. 2005, 40, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fessler, J.A. On NUFFT-Based Gridding for Non-Cartesian MRI. J. Magn. Reson. 2007, 188, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pruessmann, K.P.; Weiger, M.; Scheidegger, M.B.; Boesiger, P. SENSE: Sensitivity Encoding for Fast MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 1999, 42, 952–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velikina, J.; Alexander, A.; Salmons, J.; Raimy, E.; Purnell, T.; Kecskemeti, S.; Samsonov, A. Ultrafast Speech Imaging at High Spatial Resolution Using Model-Consistency Condition Reconstruction with Progressive Temporal Basis Learning. In Proceedings of the 26th ISMRM Scientific Meeting, Paris, France, 16–21 June 2018. Abstract 0245. [Google Scholar]
- De Boor, C. A Practical Guide to Splines. In Applied Mathematical Sciences; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Novey, M.; Adali, T. On Extending the Complex FastICA Algorithm to Noncircular Sources. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2008, 56, 2148–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollny, G.; Kellman, P.; Santos, A.; Ledesma-Carbayo, M.J. Automatic Motion Compensation of Free Breathing Acquired Myocardial Perfusion Data by Using Independent Component Analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2012, 16, 1015–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bube, K.P.; Langan, R.T. Hybrid ℓ1/ℓ2 Minimization with Applications to Tomography. Geophysics 1997, 62, 1183–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, S.R.; Ng, T.S.C.; Santa-Maria, N.; Montagne, A.; Zlokovic, B.V.; Jacobs, R.E. ROCKETSHIP: A Flexible and Modular Software Tool for the Planning, Processing and Analysis of Dynamic MRI Studies. BMC Med. Imaging 2015, 15, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aharon, M.; Elad, M.; Bruckstein, A. K-SVD: An Algorithm for Designing Overcomplete Dictionaries for Sparse Representation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2006, 54, 4311–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
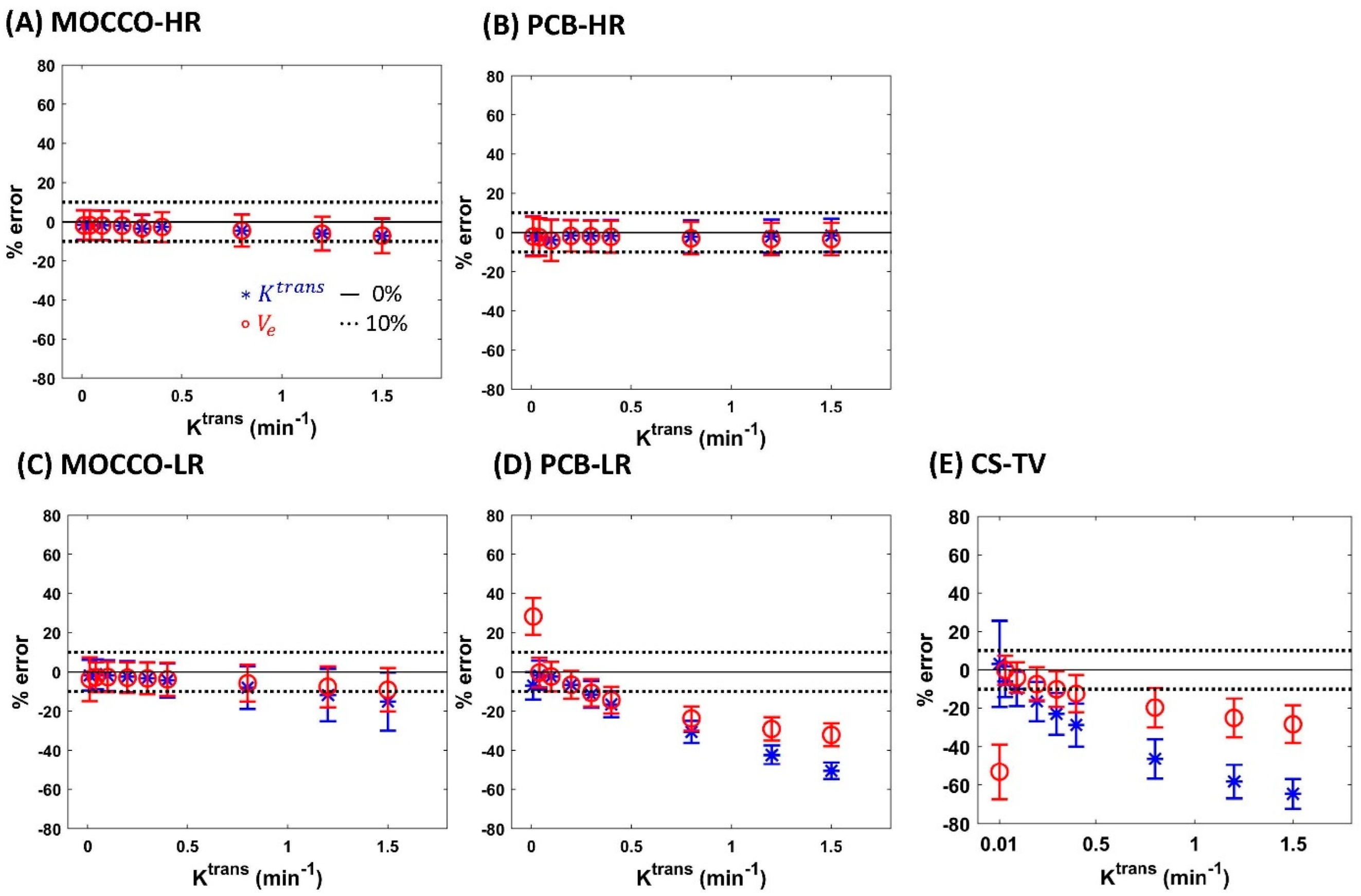
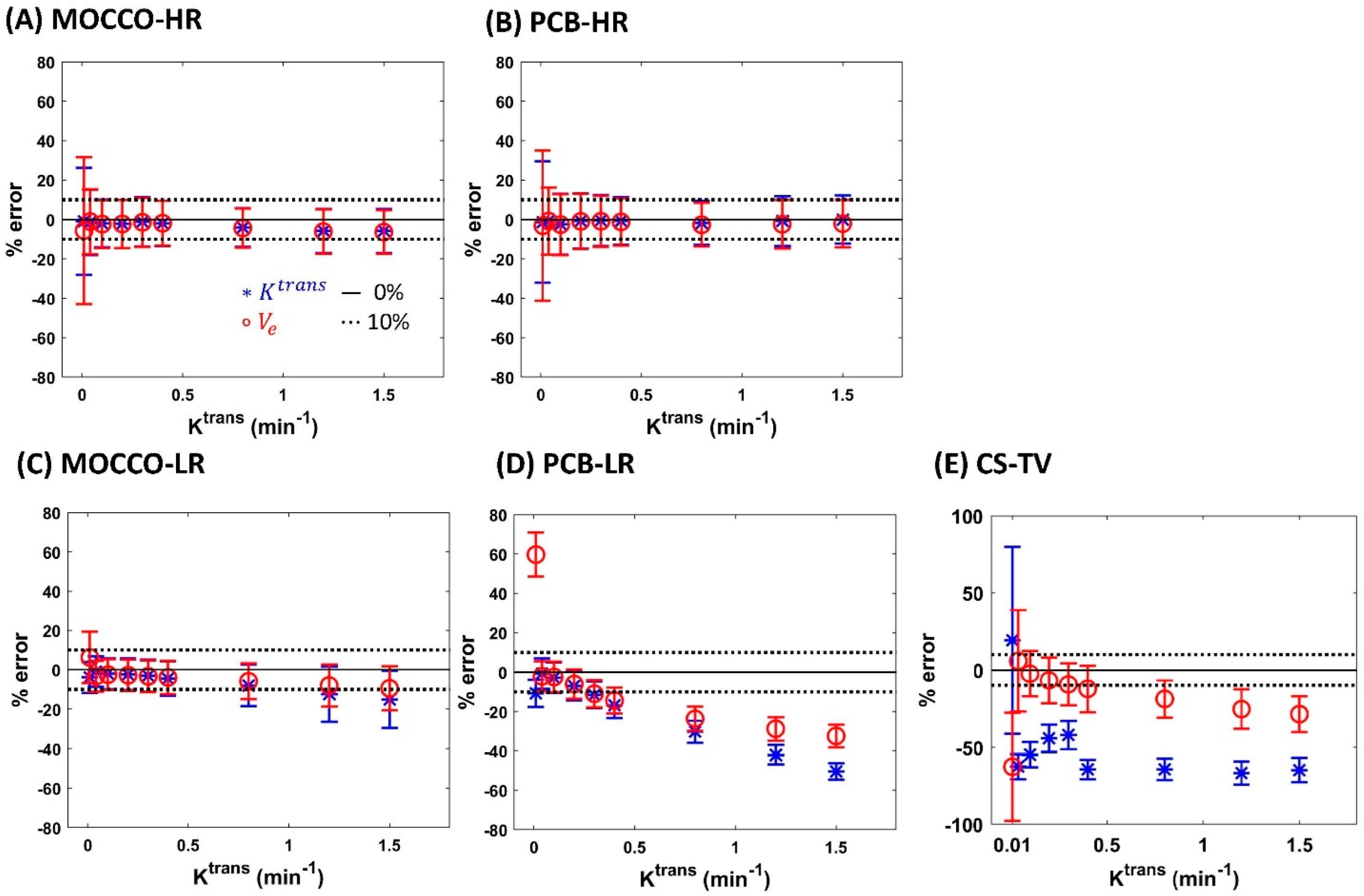
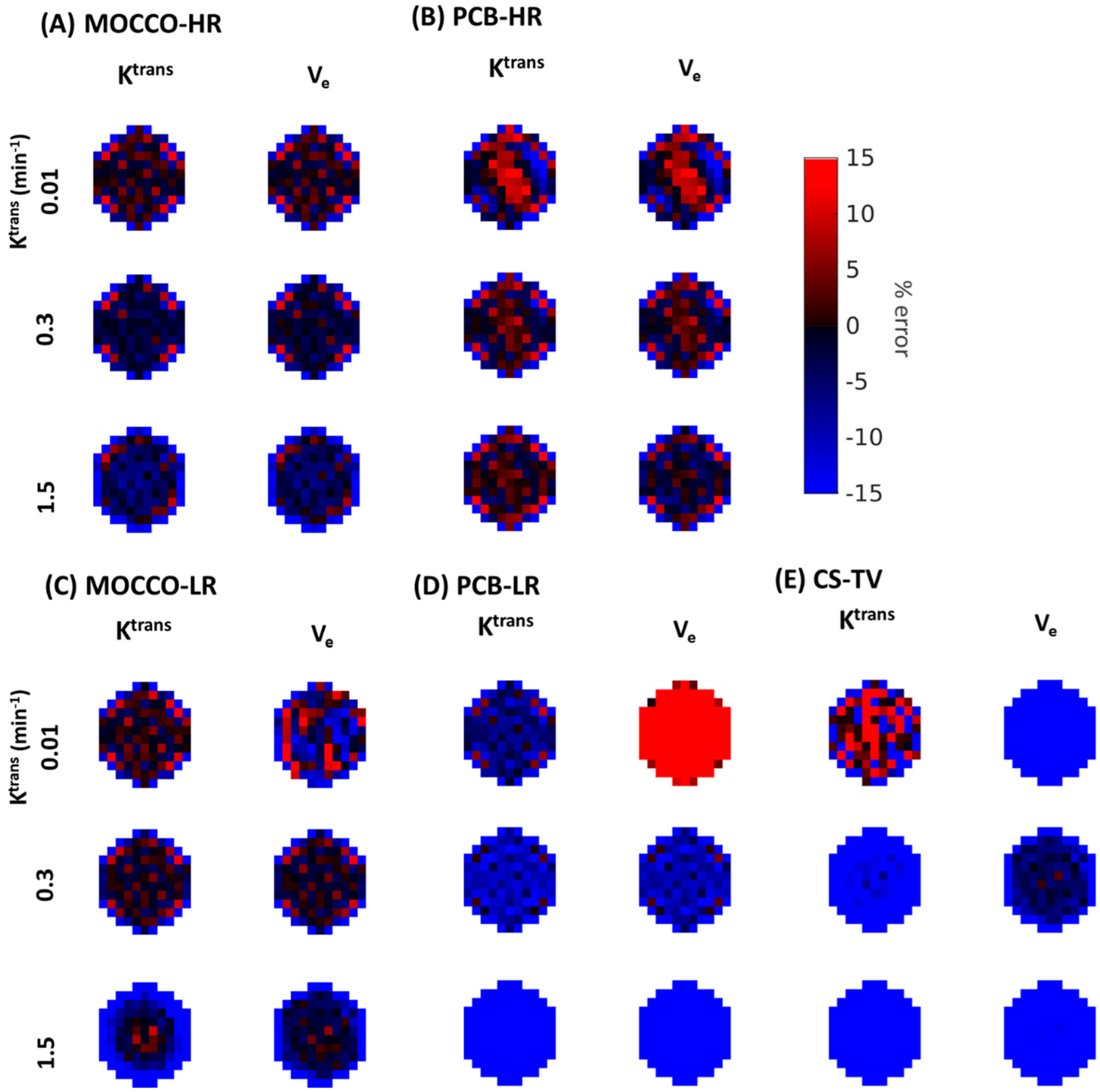
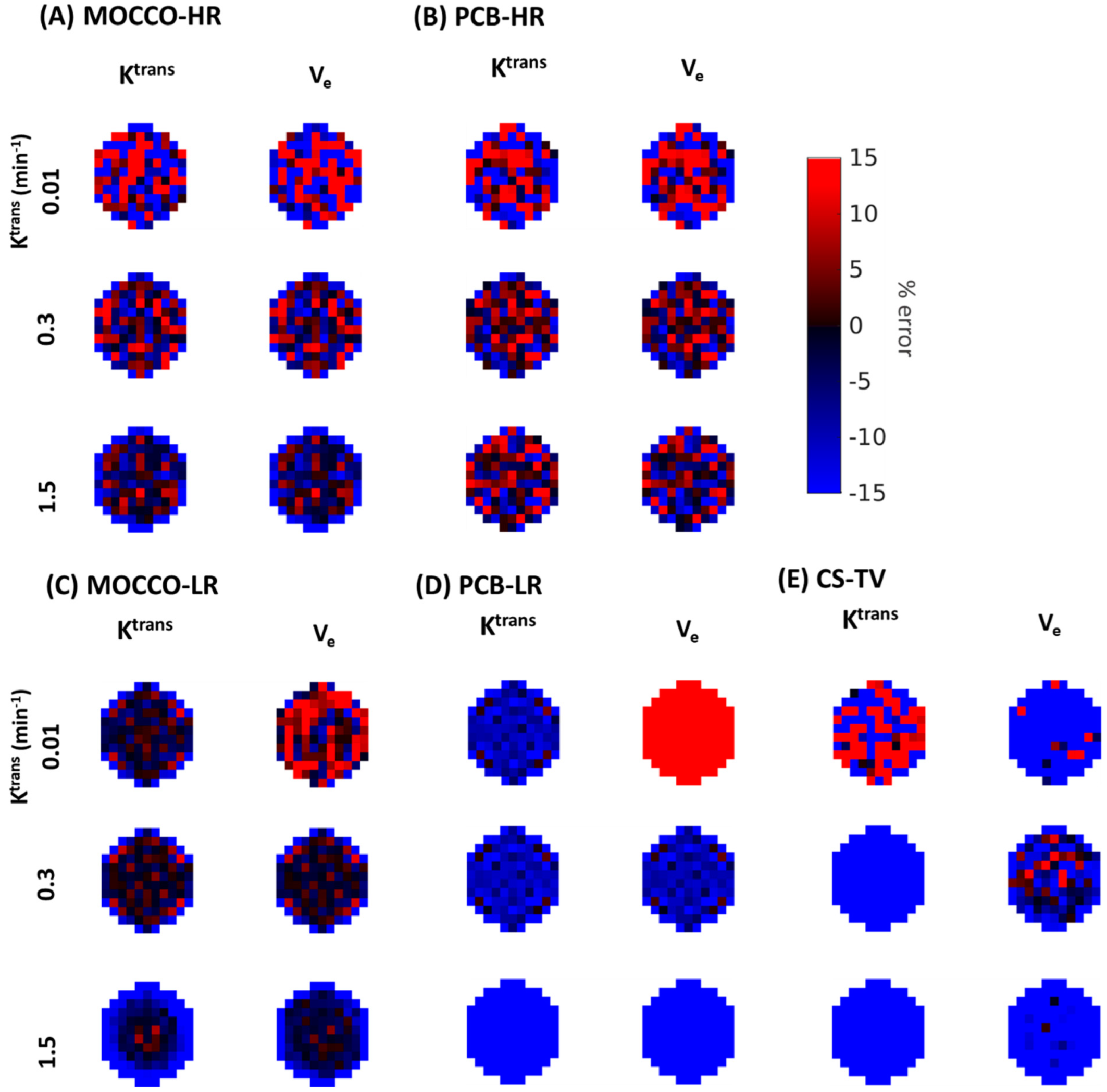
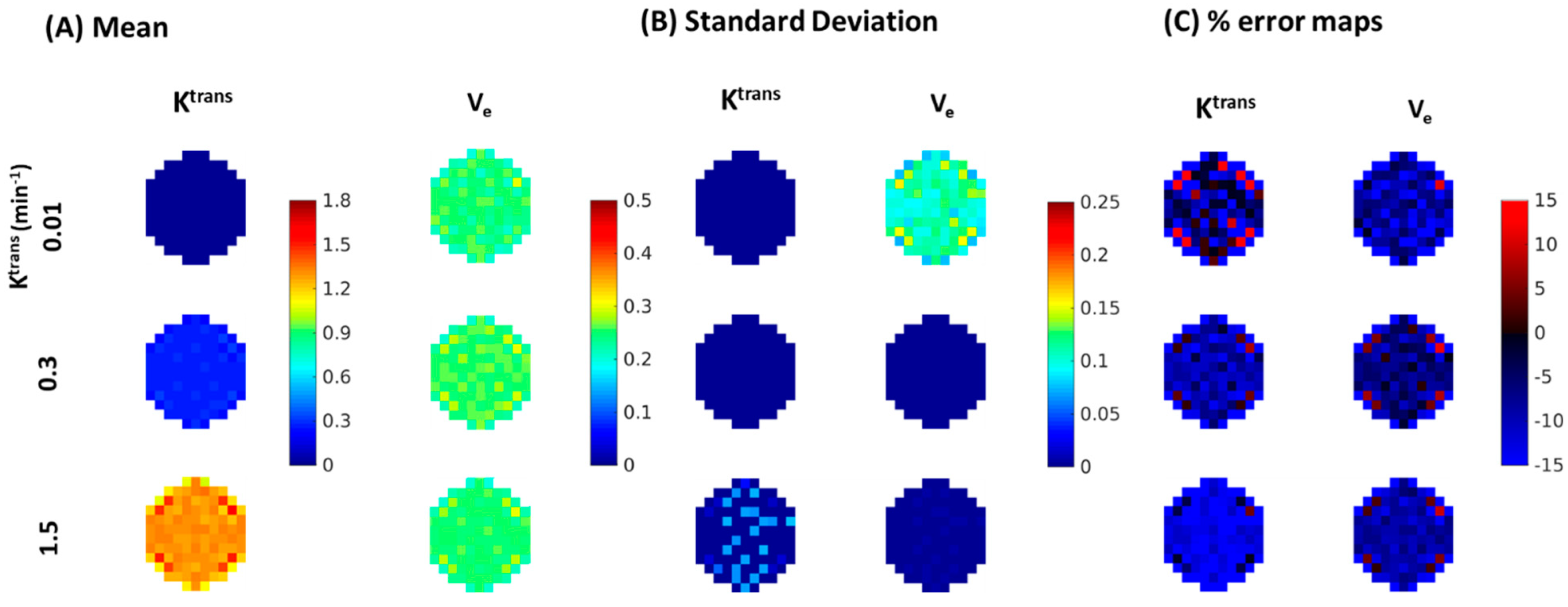
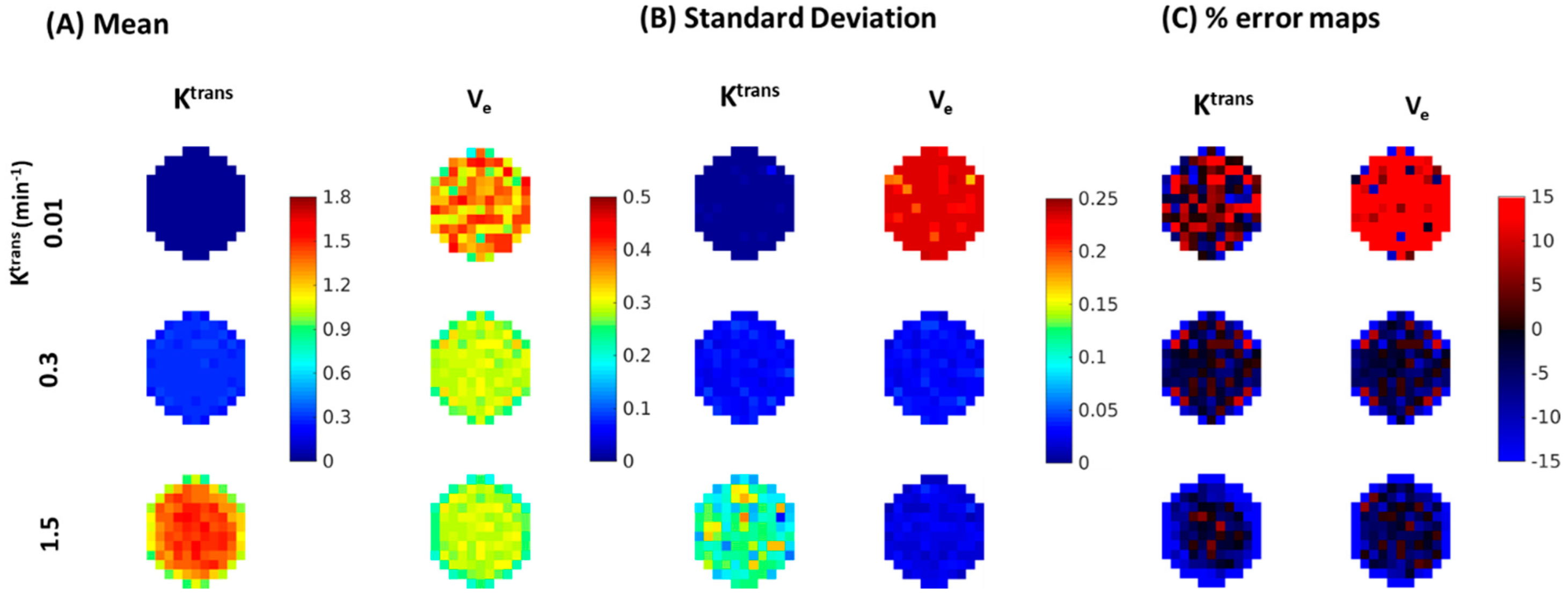
| Reference | MOCCO-HR | PCB-HR | MOCCO-LR | PCB-LR | CS-TV | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % error for Ktrans | Ktrans | 0% | 0% | 20% | 0% | 20% | 0% | 20% | 0% | 20% | 0% | 20% |
| 0.01 | −4.7 | −1.65 ± 7.52 | −0.99 ± 27.14 | −1.79 ± −7.04 | −1.32 ± 30.77 | −1.74 ± 7.81 | −3.91 ± 7.87 | −7.04 ± 7.02 | −10.77 ± 6.84 | 3.17 ± 22.67 | 19.24 ± 60.41 | |
| 0.04 | 0.06 | −1.72 ± 7.49 | −1.46 ± 16.54 | −2.36 ± −1.69 | −0.80 ± 17.04 | −1.21 ± 7.67 | −0.92 ± 7.75 | −1.69 ± 7.5 | −0.68 ± 7.71 | −6.15 ± 8.06 | −62.50 ± 8.11 | |
| 0.1 | 0.09 | −1.72 ± 7.51 | −2.03 ± 12.07 | −3.96 ± −2.3 | −2.40 ± 15.48 | −1.83 ± 7.78 | −2.07 ± 7.85 | −2.3 ± 7.52 | −2.79 ± 7.74 | −9.94 ± 9.05 | −54.77 ± 8.11 | |
| 0.2 | −0.13 | −2.04 ± 7.47 | −2.22 ± 12.2 | −1.64 ± −6.54 | −0.70 ± 13.96 | −2.38 ± 8.02 | −2.33 ± 8.1 | −6.54 ± 7.13 | −6.94 ± 7.3 | −16.52 ± 10.29 | −44.29 ± 9.00 | |
| 0.3 | −1.50 | −3.53 ± 6.9 | −1.15 ± 12.49 | −1.72 ± −11.51 | −0.59 ± 12.98 | −3.22 ± 8.19 | −3.09 ± 8.17 | −11.51 ± 6.86 | −11.5 ± 6.84 | −22.92 ± 10.95 | −42.09 ± 9.20 | |
| 0.4 | −1.91 | −2.7 ± 7.55 | −1.97 ± 11.43 | −1.87 ± −16.58 | −0.72 ± 12.05 | −4.35 ± 8.64 | −4.45 ± 8.74 | −16.58 ± 6.59 | −16.79 ± 6.46 | −28.79 ± 11.11 | −64.42 ± 6.31 | |
| 0.8 | −2.71 | −4.39 ± 8.16 | −4.04 ± 9.86 | −2.13 ± −30.54 | −1.67 ± 11.21 | −8.07 ± 10.85 | −7.94 ± 10.65 | −30.54 ± 5.6 | −30.43 ± 5.67 | −46.46 ± 10.21 | −64.26 ± 6.90 | |
| 1.2 | −3.64 | −6.03 ± 8.55 | −5.83 ± 11.23 | −1.90 ± −42.34 | −0.80 ± 12.58 | −11.76 ± 13.32 | −12.49 ± 13.97 | −42.34 ± 4.86 | −42.04 ± 4.88 | −58.19 ± 8.68 | −66.76 ± 7.46 | |
| 1.5 | −4.86 | −7.17 ± 8.76 | −5.81 ± 11.19 | −1.48 ± −50.6 | −0.05 ± 12.23 | −15.1 ± 14.86 | −15.04 ± 14.54 | −50.6 ± 4.28 | −50.44 ± 4.27 | −64.58 ± 7.63 | −64.75 ± 7.90 | |
| % error for Ve | Ktrans | 0% | 0% | 20% | 0% | 20% | 0% | 20% | 0% | 20% | 0% | 20% |
| 0.01 | −8.38 | −1.86 ± 7.55 | −5.65 ± 37.29 | −2.03 ± 10.10 | −3.18 ± 38.12 | −3.71 ± 11.14 | 6.22 ± 13 | 28.27 ± 9.47 | 59.68 ± 11.16 | −53.17 ± 14.28 | −64.65 ± 35.00 | |
| 0.04 | −0.36 | −1.74 ± 7.49 | −1.07 ± 16.49 | −2.44 ± 9.49 | −0.80 ± 17.04 | −2.72 ± 7.68 | −3.37 ± 7.77 | −0.35 ± 7.59 | −2.09 ± 7.59 | −0.12 ± 7.53 | 5.86 ± 32.90 | |
| 0.1 | −0.08 | −1.9 ± 7.51 | −2.35 ± 12.11 | −4.12 ± 10.46 | −2.60 ± 15.44 | −2.65 ± 7.68 | −2.51 ± 7.82 | −2.36 ± 7.51 | −2.46 ± 7.76 | −3.92 ± 7.82 | −2.45 ± 14.76 | |
| 0.2 | −0.13 | −1.95 ± 7.5 | −2.28 ± 12.25 | −1.79 ± 8.02 | −0.96 ± 13.92 | −2.98 ± 7.86 | −2.81 ± 7.88 | −6.56 ± 7.12 | −6.05 ± 7.37 | −7.40 ± 8.69 | −6.70 ± 14.90 | |
| 0.3 | −0.73 | −3.24 ± 7.02 | −1.44 ± 12.38 | −1.93 ± 7.95 | −0.90 ± 12.94 | −3.34 ± 8.03 | −3.36 ± 8.04 | −10.67 ± 6.93 | −10.96 ± 6.88 | −10.07 ± 9.31 | −9.32 ± 13.66 | |
| 0.4 | −0.95 | −2.66 ± 7.59 | −1.88 ± 11.39 | −2.23 ± 8.14 | −1.22 ± 12.00 | −3.79 ± 8.39 | −3.91 ± 8.49 | −14.4 ± 6.77 | −14.43 ± 6.64 | −12.43 ± 9.69 | −12.31 ± 15.04 | |
| 0.8 | −1.42 | −4.48 ± 8.15 | −4.34 ± 9.93 | −3.00 ± 8.28 | −2.68 ± 11.09 | −5.78 ± 9.37 | −5.86 ± 9.14 | −23.77 ± 6.15 | −23.73 ± 6.22 | −19.72 ± 10.23 | −18.81 ± 12.10 | |
| 1.2 | −1.67 | −6.04 ± 8.59 | −6.13 ± 11.23 | −3.34 ± 8.31 | −2.41 ± 12.36 | −7.57 ± 10.45 | −8.02 ± 10.58 | −29.09 ± 5.98 | −28.93 ± 5.99 | −25.12 ± 10.53 | −25.39 ± 12.70 | |
| 1.5 | −1.87 | −7.06 ± 8.86 | −6.39 ± 11.06 | −3.37 ± 8.25 | −2.10 ± 12.00 | −9.13 ± 11.03 | −9.45 ± 11.13 | −32.13 ± 5.89 | −32.57 ± 5.82 | −28.38 ± 9.78 | −28.62 ± 11.57 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, P.N.; Velikina, J.V.; Bancroft, L.C.H.; Samsonov, A.A.; Kelcz, F.; Strigel, R.M.; Holmes, J.H. The Influence of Data-Driven Compressed Sensing Reconstruction on Quantitative Pharmacokinetic Analysis in Breast DCE MRI. Tomography 2022, 8, 1552-1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8030128
Wang PN, Velikina JV, Bancroft LCH, Samsonov AA, Kelcz F, Strigel RM, Holmes JH. The Influence of Data-Driven Compressed Sensing Reconstruction on Quantitative Pharmacokinetic Analysis in Breast DCE MRI. Tomography. 2022; 8(3):1552-1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8030128
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ping Ni, Julia V. Velikina, Leah C. Henze Bancroft, Alexey A. Samsonov, Frederick Kelcz, Roberta M. Strigel, and James H. Holmes. 2022. "The Influence of Data-Driven Compressed Sensing Reconstruction on Quantitative Pharmacokinetic Analysis in Breast DCE MRI" Tomography 8, no. 3: 1552-1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8030128
APA StyleWang, P. N., Velikina, J. V., Bancroft, L. C. H., Samsonov, A. A., Kelcz, F., Strigel, R. M., & Holmes, J. H. (2022). The Influence of Data-Driven Compressed Sensing Reconstruction on Quantitative Pharmacokinetic Analysis in Breast DCE MRI. Tomography, 8(3), 1552-1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8030128






