Magnetic Susceptibility Source Separation Solely from Gradient Echo Data: Histological Validation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. MR Signal Modeling for
2.2. Postmortem Tissue Imaging
2.3. Data Processing
2.4. Immunohistochemistry
2.5. Histology Optical Density Estimation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
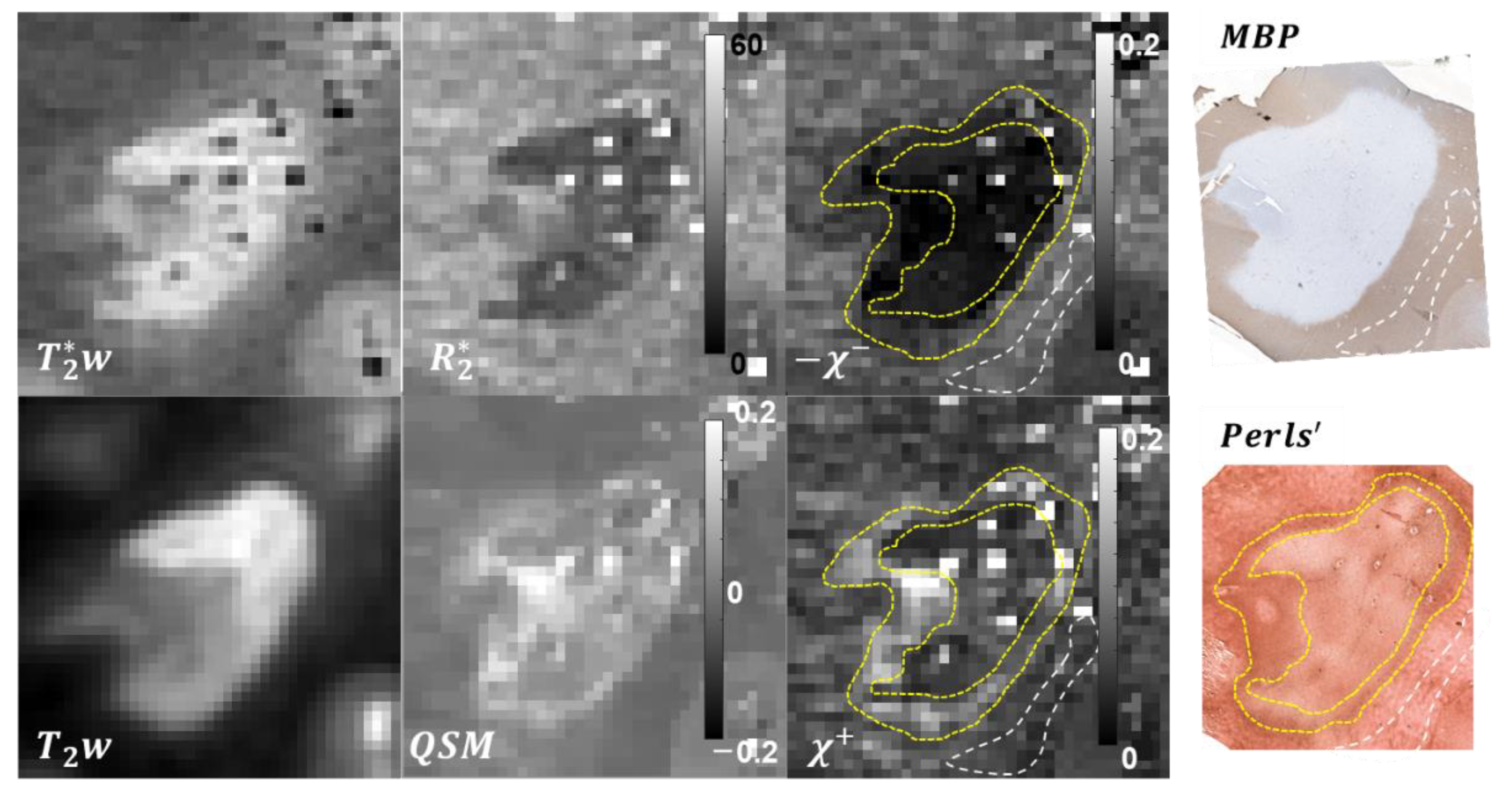
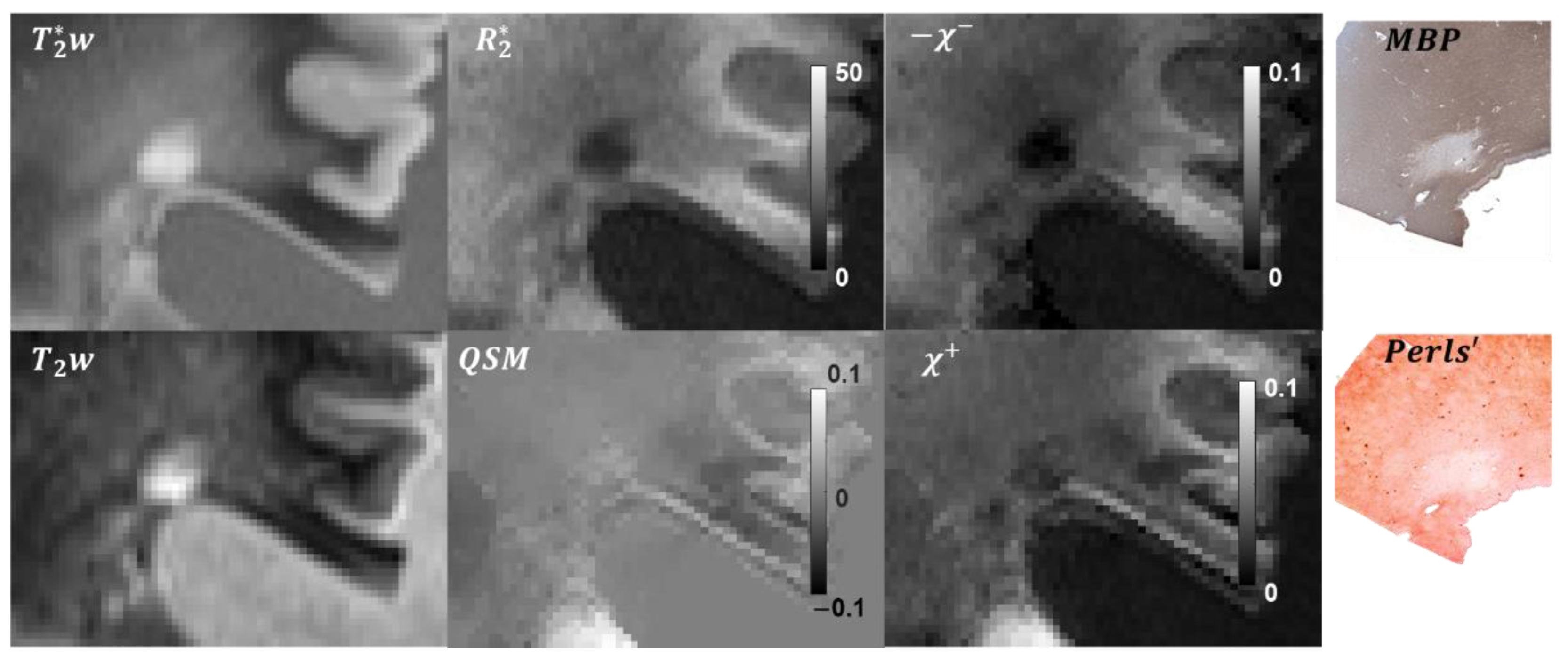
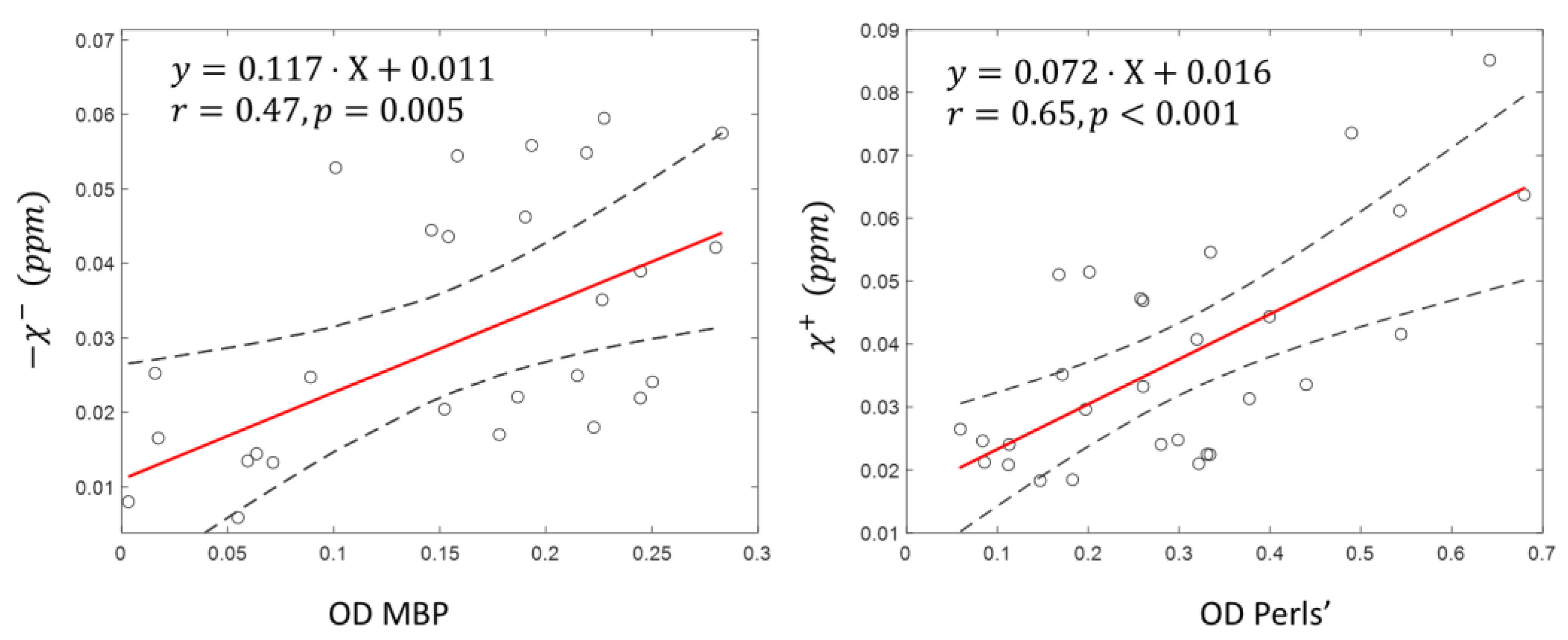
3.1. Tissue Composition
3.2. Lesion ROIs
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- MacKay, A.; Whittall, K.; Adler, J.; Li, D.; Paty, D.; Graeb, D. In Vivo Visualization of Myelin Water in Brain by Magnetic Resonance. Magn. Reson. Med. 1994, 31, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laule, C.; Leung, E.; Lis, D.K.; Traboulsee, A.L.; Paty, D.W.; MacKay, A.L.; Moore, G.R. Myelin Water Imaging in Multiple Sclerosis: Quantitative Correlations with Histopathology. Mult. Scler. 2006, 12, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Wisnieff, C.; Cooper, M.A.; Kumar, D.; Raj, A.; Spincemaille, P.; Wang, Y.; Vartanian, T.; Gauthier, S.A. T2 Prep Three-Dimensional Spiral Imaging with Efficient Whole Brain Coverage for Myelin Water Quantification at 1.5 Tesla. Magn. Reson. Med. 2012, 67, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Spincemaille, P.; Gauthier, S.A.; Wang, Y. Rapid Whole Brain Myelin Water Content Mapping without an External Water Standard at 1.5T. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 39, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmanzadeh, R.; Lu, P.J.; Barakovic, M.; Weigel, M.; Maggi, P.; Nguyen, T.D.; Schiavi, S.; Daducci, A.; la Rosa, F.; Schaedelin, S.; et al. Myelin and Axon Pathology in Multiple Sclerosis Assessed by Myelin Water and Multi-Shell Diffusion Imaging. Brain 2021, 144, 1684–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, V.; Pei, W.; Yang, G.; Li, S.Y.; Swamy, E.; Boster, A.; Schmalbrock, P.; Pitt, D. Iron Is a Sensitive Biomarker for Inflammation in Multiple Sclerosis Lesions. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisnieff, C.; Ramanan, S.; Olesik, J.; Gauthier, S.; Wang, Y.; Pitt, D. Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM) of White Matter Multiple Sclerosis Lesions: Interpreting Positive Susceptibility and the Presence of Iron. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 74, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Absinta, M.; Sati, P.; Schindler, M.; Leibovitch, E.C.; Ohayon, J.; Wu, T.X.; Meani, A.; Filippi, M.; Jacobson, S.; Cortese, I.C.M.; et al. Persistent 7-Tesla Phase Rim Predicts Poor Outcome in New Multiple Sclerosis Patient Lesions. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 2597–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal-Bianco, A.; Grabner, G.; Kronnerwetter, C.; Weber, M.; Hoftberger, R.; Berger, T.; Auff, E.; Leutmezer, F.; Trattnig, S.; Lassmann, H.; et al. Slow Expansion of Multiple Sclerosis Iron Rim Lesions: Pathology and 7 T Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 133, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gillen, K.M.; Mubarak, M.; Nguyen, T.D.; Pitt, D. Significance and in Vivo Detection of Iron-Laden Microglia in White Matter Multiple Sclerosis Lesions. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Gauthier, S.A.; Gupta, A.; Comunale, J.; Chiang, G.C.; Zhou, D.; Chen, W.; Giambrone, A.E.; Zhu, W.; Wang, Y. Longitudinal Change in Magnetic Susceptibility of New Enhanced Multiple Sclerosis (Ms) Lesions Measured on Serial Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM). J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2016, 44, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rochefort, L.; Brown, R.; Prince, M.R.; Wang, Y. Quantitative MR Susceptibility Mapping Using Piece-Wise Constant Regularized Inversion of the Magnetic Field. Magn. Reson. Med. 2008, 60, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rochefort, L.; Liu, T.; Kressler, B.; Liu, J.; Spincemaille, P.; Lebon, V.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y. Quantitative Susceptibility Map Reconstruction from MR Phase Data Using Bayesian Regularization: Validation and Application to Brain Imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2010, 63, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinayagamani, S.; Sheelakumari, R.; Sabarish, S.; Senthilvelan, S.; Ros, R.; Thomas, B.; Kesavadas, C. Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping: Technical Considerations and Clinical Applications in Neuroimaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2021, 53, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, T.; Kudo, K.; Fujima, N.; Yoshikawa, M.; Ikebe, Y.; Sato, R.; Shirai, T.; Bito, Y.; Uwano, I.; Miyata, M. Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping: Basic Methods and Clinical Applications. Radiographics 2022, 210054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweser, F.; Deistung, A.; Lehr, B.W.; Sommer, K.; Reichenbach, J.R. Semi-Twins: Simultaneous Extraction of Myelin and Iron Using a T2*-Weighted Imaging Sequence. In Proceedings of the 19th Meeting of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, Montréal, QC, Canada, 7–13 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Stuber, C.; Morawski, M.; Schafer, A.; Labadie, C.; Wahnert, M.; Leuze, C.; Streicher, M.; Barapatre, N.; Reimann, K.; Geyer, S.; et al. Myelin and Iron Concentration in the Human Brain: A Quantitative Study of MRI Contrast. Neuroimage 2014, 93 Pt 1, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lin, H.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Prince, M.R.; Gillen, K.; Yan, X.; Song, Q.; Hua, T.; Zhao, X.; et al. Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM) Minimizes Interference from Cellular Pathology in R2* Estimation of Liver Iron Concentration. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 48, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.G.; Lee, J.; Yun, Y.H.; Yoo, S.H.; Jang, J.; Oh, S.H.; Nam, Y.; Jung, S.; Kim, S.; Fukunaga, M.; et al. Chi-Separation: Magnetic Susceptibility Source Separation toward Iron and Myelin Mapping in the Brain. Neuroimage 2021, 240, 118371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmerich, J.; Bachert, P.; Ladd, M.E.; Straub, S. On the Separation of Susceptibility Sources in Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping: Theory and Phantom Validation with an in Vivo Application to Multiple Sclerosis Lesions of Different Age. J. Magn. Reson. 2021, 330, 107033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gong, N.J.; Chaim, K.T.; Otaduy, M.C.G.; Liu, C. Decompose Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM) to Sub-Voxel Diamagnetic and Paramagnetic Components Based on Gradient-Echo MRI Data. Neuroimage 2021, 242, 118477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimov, A.V.; Nguyen, T.D.; Gillen, K.M.; Marceille, M.; Spincemaille, P.; Pitt, D.; Gauthier, S.; Wang, Y. Susceptibility Source Separation from Gradient Echo Data Using Magnitude Decay Modeling. J. Neuroimaging 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yablonskiy, D.A.; Haacke, E.M. Theory of NMR Signal Behavior in Magnetically Inhomogeneous Tissues: The Static Dephasing Regime. Magn. Reson. Med. 1994, 32, 749–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, T. Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM): Decoding MRI Data for a Tissue Magnetic Biomarker. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 73, 82–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Liu, T.; de Rochefort, L.; Ledoux, J.; Khalidov, I.; Chen, W.; Tsiouris, A.J.; Wisnieff, C.; Spincemaille, P.; Prince, M.R.; et al. Morphology Enabled Dipole Inversion for Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping Using Structural Consistency between the Magnitude Image and the Susceptibility Map. Neuroimage 2012, 59, 2560–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, T.; Wisnieff, C.; Lou, M.; Chen, W.; Spincemaille, P.; Wang, Y. Nonlinear Formulation of the Magnetic Field to Source Relationship for Robust Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping. Magn. Reson. Med. 2013, 69, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, M.; Nguyen, T.D.; Thimmappa, N.D.; Salustri, C.; Dong, F.; Cooper, M.A.; Li, J.; Prince, M.R.; Wang, Y. Algorithm for Fast Monoexponential Fitting Based on Auto-Regression on Linear Operations (ARLO) of Data. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 73, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cusack, R.; Papadakis, N. New Robust 3-D Phase Unwrapping Algorithms: Application to Magnetic Field Mapping and Undistorting Echoplanar Images. Neuroimage 2002, 16 Pt 1, 754–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, T.; Khalidov, I.; de Rochefort, L.; Spincemaille, P.; Liu, J.; Tsiouris, A.J.; Wang, Y. A Novel Background Field Removal Method for MRI Using Projection onto Dipole Fields (PDF). NMR Biomed. 2011, 24, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischl, B. Freesurfer. Neuroimage 2012, 62, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jenkinson, M.; Bannister, P.; Brady, M.; Smith, S. Improved Optimization for the Robust and Accurate Linear Registration and Motion Correction of Brain Images. Neuroimage 2002, 17, 825–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexopoulou, E.; Stripeli, F.; Baras, P.; Seimenis, I.; Kattamis, A.; Ladis, V.; Efstathopoulos, E.; Brountzos, E.N.; Kelekis, A.D.; Kelekis, N.L. R2 Relaxometry with MRI for the Quantification of Tissue Iron Overload in Beta-Thalassemic Patients. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2006, 23, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, J.C.; Otto-Duessel, M.; Aguilar, M.; Nick, H.; Nelson, M.D.; Coates, T.D.; Pollack, H.; Moats, R. Cardiac Iron Determines Cardiac T2*, T2, and T1 in the Gerbil Model of Iron Cardiomyopathy. Circulation 2005, 112, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jensen, J.H.; Chandra, R.; Yu, H. Quantitative Model for the Interecho Time Dependence of the Cpmg Relaxation Rate in Iron-Rich Gray Matter. Magn. Reson. Med. 2001, 46, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bloembergen, N.; Morgan, L.O. Proton Relaxation Times in Paramagnetic Solutions Effects of Electron Spin Relaxation. J. Chem. Phys. 1961, 34, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hardy, P.A.; Gash, D.; Yokel, R.; Andersen, A.; Ai, Y.; Zhang, Z. Correlation of R2 with Total Iron Concentration in the Brains of Rhesus Monkeys. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2005, 21, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.Q.; Martin, W.; Allen, P.S. Estimation of the Iron Concentration in Excised Gray Matter by Means of Proton Relaxation Measurements. Magn. Reson. Med. 1996, 35, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Spincemaille, P.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. MEDI+0: Morphology Enabled Dipole Inversion with Automatic Uniform Cerebrospinal Fluid Zero Reference for Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 79, 2795–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimov, A.V.; Nguyen, T.D.; Spincemaille, P.; Sweeney, E.M.; Zinger, N.; Kovanlikaya, I.; Kopell, B.H.; Gauthier, S.A.; Wang, Y. Global Cerebrospinal Fluid as a Zero-Reference Regularization for Brain Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping. J. Neuroimaging 2022, 32, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Spincemaille, P.; Liu, Z.; Dimov, A.; Deh, K.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Gillen, K.M.; Wilman, A.H.; et al. Clinical Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM): Biometal Imaging and Its Emerging Roles in Patient Care. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 46, 951–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravanfar, P.; Loi, S.M.; Syeda, W.T.; van Rheenen, T.E.; Bush, A.I.; Desmond, P.; Cropley, V.L.; Lane, D.J.R.; Opazo, C.M.; Moffat, B.A.; et al. Systematic Review: Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM) of Brain Iron Profile in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 618435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C. Susceptibility Tensor Imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2010, 63, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wisnieff, C.; Liu, T.; Wang, Y.; Spincemaille, P. The Influence of Molecular Order and Microstructure on the R2* and the Magnetic Susceptibility Tensor. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2016, 34, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wharton, S.; Bowtell, R. Fiber Orientation-Dependent White Matter Contrast in Gradient Echo MRI. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 18559–18564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yablonskiy, D.A.; Sukstanskii, A.L.; Luo, J.; Wang, X. Voxel Spread Function Method for Correction of Magnetic Field Inhomogeneity Effects in Quantitative Gradient-Echo-Based MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2013, 70, 1283–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, F.; Yang, W.; Mordes, D.A.; Wang, J.Y.; Salameh, J.S.; Mok, J.; Chew, J.; Sharma, A.; Leno-Duran, E.; Suzuki-Uematsu, S.; et al. Monitoring Peripheral Nerve Degeneration in Als by Label-Free Stimulated Raman Scattering Imaging. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.K.; Calligaris, D.; Olubiyi, O.I.; Norton, I.; Yang, W.; Santagata, S.; Xie, X.S.; Golby, A.J.; Agar, N.Y. Label-Free Neurosurgical Pathology with Stimulated Raman Imaging. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3451–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dimov, A.V.; Gillen, K.M.; Nguyen, T.D.; Kang, J.; Sharma, R.; Pitt, D.; Gauthier, S.A.; Wang, Y. Magnetic Susceptibility Source Separation Solely from Gradient Echo Data: Histological Validation. Tomography 2022, 8, 1544-1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8030127
Dimov AV, Gillen KM, Nguyen TD, Kang J, Sharma R, Pitt D, Gauthier SA, Wang Y. Magnetic Susceptibility Source Separation Solely from Gradient Echo Data: Histological Validation. Tomography. 2022; 8(3):1544-1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8030127
Chicago/Turabian StyleDimov, Alexey V., Kelly M. Gillen, Thanh D. Nguyen, Jerry Kang, Ria Sharma, David Pitt, Susan A. Gauthier, and Yi Wang. 2022. "Magnetic Susceptibility Source Separation Solely from Gradient Echo Data: Histological Validation" Tomography 8, no. 3: 1544-1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8030127
APA StyleDimov, A. V., Gillen, K. M., Nguyen, T. D., Kang, J., Sharma, R., Pitt, D., Gauthier, S. A., & Wang, Y. (2022). Magnetic Susceptibility Source Separation Solely from Gradient Echo Data: Histological Validation. Tomography, 8(3), 1544-1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8030127





