Longitudinal Assessment Using Optical Coherence Tomography in Patients with Friedreich’s Ataxia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Cohort Description
3.2. Ophthalmological Findings
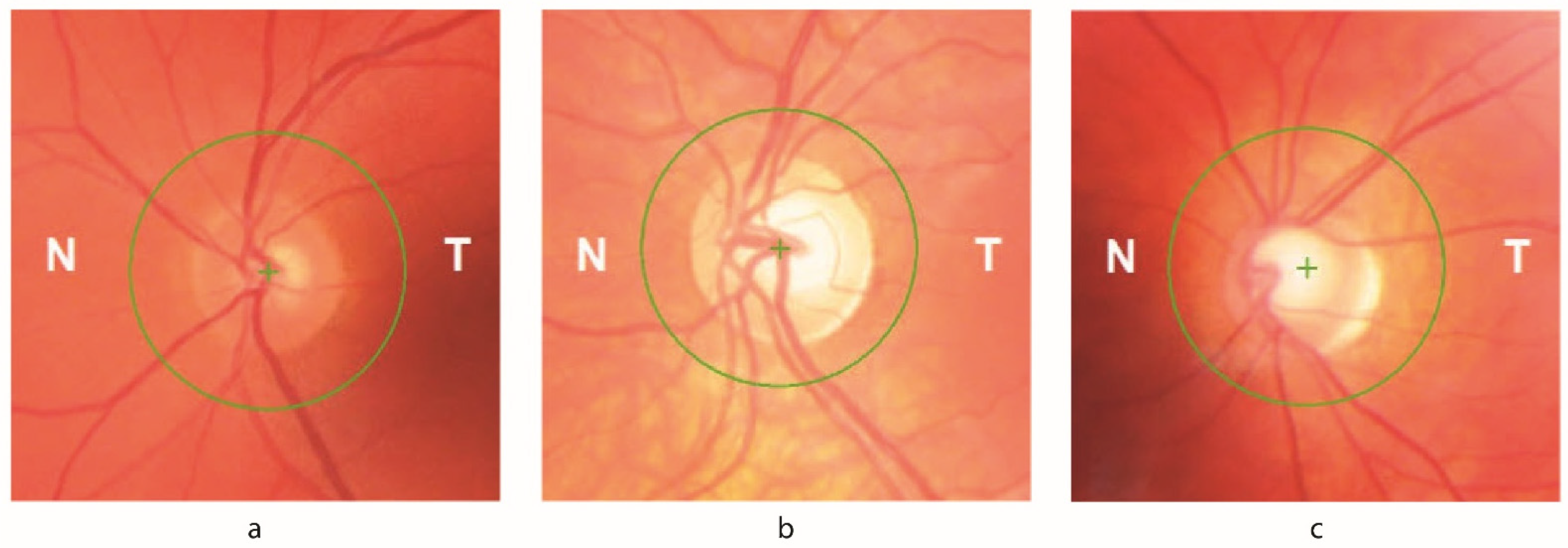
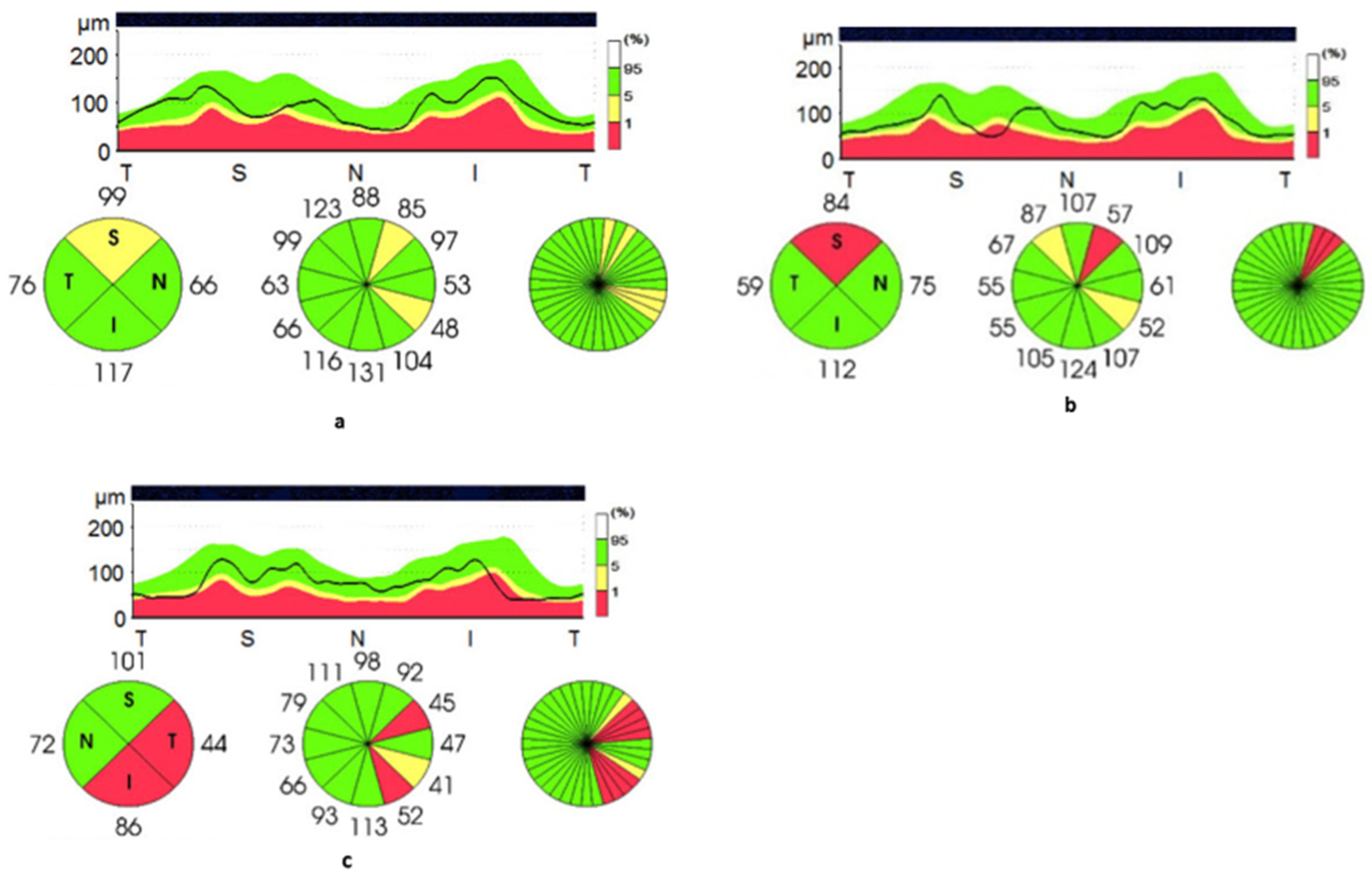
3.3. Optical Coherence Tomography
3.4. Correlation with Clinical Features
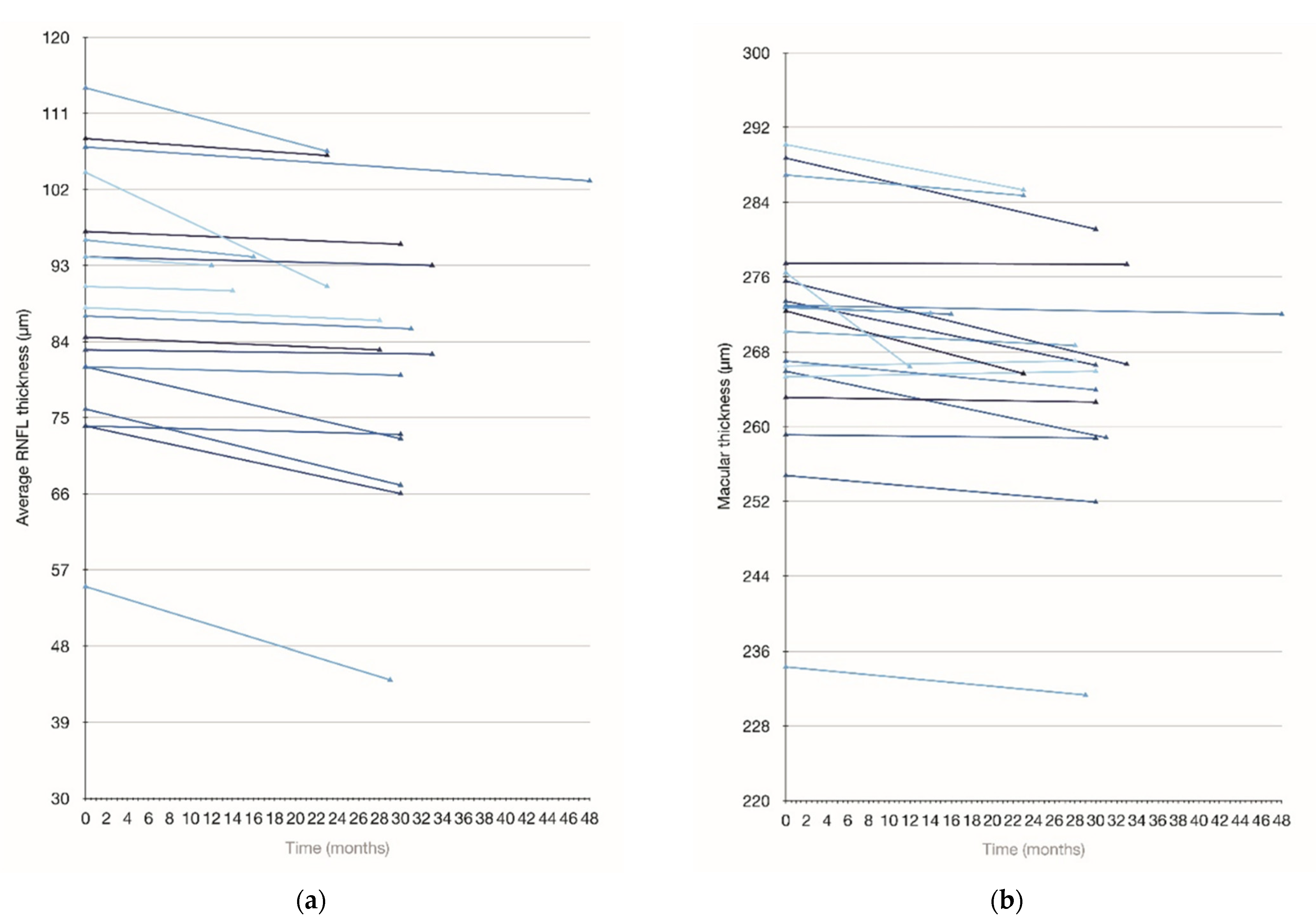
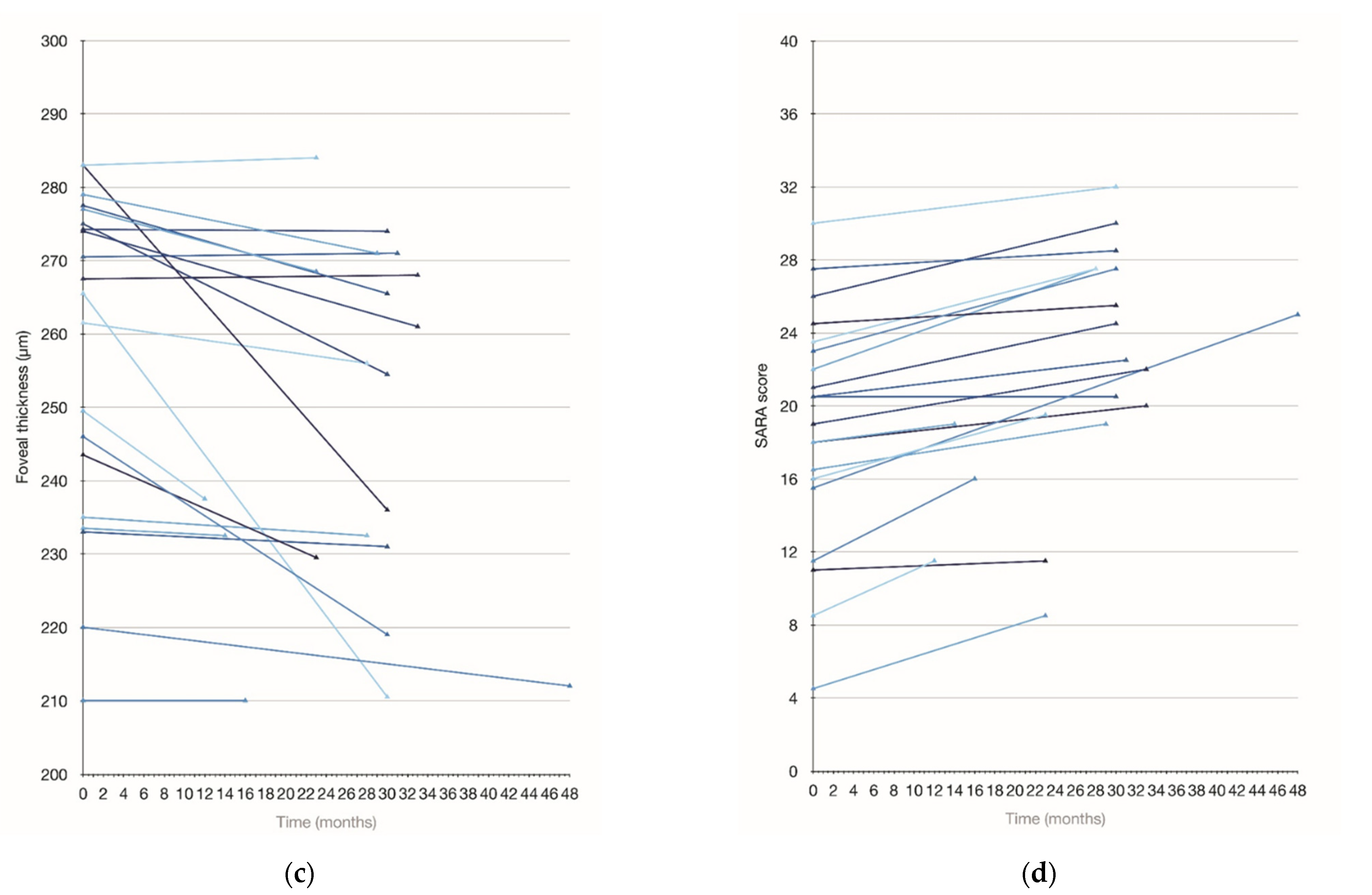
3.5. Longitudinal Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beaudin, M.; Matilla-Dueñas, A.; Soong, B.W.; Pedroso, J.L.; Barsottini, O.G.; Mitoma, H.; Tsuji, S.; Schmahmann, J.D.; Manto, M.; Rouleau, G.A.; et al. The Classification of Autosomal Recessive Cerebellar Ataxias: A Consensus Statement from the Society for Research on the Cerebellum and Ataxias Task Force. Cerebellum 2019, 18, 1098–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürk, K. Friedreich Ataxia: Current Status and Future Prospects. Cerebellum Ataxias 2017, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campuzano, V.; Montermini, L.; Moltò, M.D.; Pianese, L.; Cossée, M.; Cavalcanti, F.; Monros, E.; Rodius, F.; Duclos, F.; Monticelli, A.; et al. Friedreich’s ataxia: Autosomal recessive disease caused by an intronic GAA triplet repeat expansion. Science 1996, 271, 1423–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galea, C.A.; Huq, A.; Lockhart, P.J.; Tai, G.; Corben, L.A.; Yiu, E.M.; Gurrin, L.C.; Lynch, D.R.; Gelbard, S.; Durr, A.; et al. Compound heterozygous FXN mutations and clinical outcome in friedreich ataxia. Ann. Neurol. 2016, 79, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, D.J.H.; Wood, N.W.; Ryan, F.; Hanna, M.G.; Connolly, S.; Moore, D.P.; Redmond, J.; Barton, D.E.; Murphy, R.P. Intrafamilial phenotypic variability in Friedreich ataxia associated with a G130V mutation in the FRDA gene. Arch. Neurol. 2002, 59, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pandolfo, M. Friedreich ataxia: The clinical picture. J. Neurol. 2009, 256, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, M.H.; Boesch, S.; Nachbauer, W.; Mariotti, C.; Giunti, P. Clinical features of Friedreich’s ataxia: Classical and atypical phenotypes. J. Neurochem. 2013, 126, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dürr, A.; Cossee, M.; Agid, Y.; Campuzano, V.; Mignard, C.; Penet, C.; Mandel, J.-L.; Brice, A.; Koenig, M. Clinical and genetic abnormalities in patients with Friedreich’s ataxia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 335, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeppen, A.H.; Mazurkiewicz, J.E. Friedreich ataxia: Neuropathology revised. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 72, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harding, A.E. Friedreich’s ataxia: A clinical and genetic study of 90 families with an analysis of early diagnostic criteria and intrafamilial clustering of clinical features. Brain 1981, 104, 589–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourke, T.; Keane, D. Friedreich’s Ataxia: A review from a cardiology perspective. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2011, 180, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reetz, K.; Dogan, I.; Hohenfeld, C.; Didszun, C.; Giunti, P.; Mariotti, C.; Durr, A.; Boesch, S.; Klopstock, T.; Rodríguez de Rivera Garrido, F.J.; et al. Nonataxia symptoms in Friedreich Ataxia: Report from the registry of the European Friedreich’s Ataxia consortium for translational studies (EFACTS). Neurology 2018, 91, e917–e930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahey, M.C.; Cremer, P.D.; Aw, S.T.; Millist, L.; Todd, M.J.; White, O.B.; Halmagyi, M.; Corben, L.A.; Collins, V.; Churchyard, A.J.; et al. Vestibular, saccadic and fixation abnormalities in genetically confirmed Friedreich ataxia. Brain 2008, 131, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramat, S.; Leigh, R.J.; Zee, D.S.; Optican, L.M. What clinical disorders tell us about the neural control of saccadic eye movements. Brain 2007, 130, 10–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, J.M.; Perlman, S.; Baloh, R.W. Eye movements in Friedreich’s ataxia. Arch. Neurol. 1983, 40, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöls, L.; Amoiridis, G.; Przuntek, H.; Frank, G.; Epplen, J.T.; Epplen, C. Friedrcih’s ataxia: Revision of the phenotype according to molecular genetics. Brain 1997, 120, 2131–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschner, C.; Perlman, S.; Baloh, R.W. Comparison of oculomotor findings in the progressive ataxia syndromes. Brain 1994, 117, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyer, L.A.; Galetta, K.; Wilson, J.; Sakai, R.; Perlman, S.; Mathews, K.; Wilmot, G.R.; Gomez, C.M.; Ravina, B.; Zesiewicz, T.; et al. Analysis of the visual system in Friedreich ataxia. J. Neurol. 2013, 260, 2362–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortuna, F.; Barboni, P.; Liguori, R.; Valentino, M.L.; Savini, G.; Gellera, C.; Mariotti, C.; Rizzo, G.; Tonon, C.; Manners, D.; et al. Visual system involvement in patients with Friedreich’s ataxia. Brain 2009, 132, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noval, S.; Conteras, I.; Sanz-Gallego, I.; Manrique, R.K.; Arpa, J. Ophthalmic features of Friedreich’s ataxia. Eye 2012, 26, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, M.H.; Bartmann, A.P.; Clayton, L.M.S.; Nethisinghe, S.; Pfundt, R.; Paul Chapple, J.; Reilly, M.M.; Manji, H.; Wood, N.J.; Bremner, F.; et al. Optical Coherence Tomography and Visual Field Findings in Patients With Friedreich Ataxia. J. Neuro-Ophthalmol. 2014, 34, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, P.; Ramírez, A.I.; de Hoz, R.; Cadena, M.; Ferreras, A.; Monsalve, B.; Salobrar-García, E.; Muñoz-Blanco, J.L.; Urcelay-Segura, J.L.; Salazar, J.J.; et al. Ocular Involvement in Friedreich Ataxia Patients and Its Relationship with Neurological Disability, a Follow-Up Study. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkinson, M.H.; Bartmann, A.P.; Clayton, L.M.S.; Nethisinghe, S.; Pfundt, R.; Paul Chapple, J.; Reilly, M.M.; Manji, H.; Wood, N.J.; Bremner, F.; et al. Optical coherence tomography in autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay. Brain 2018, 141, 989–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkinson, M.H.; Bartmann, A.P.; Clayton, L.M.S.; Nethisinghe, S.; Pfundt, R.; Chapple, J.P.; Reilly, M.M.; Manji, H.; Wood, N.; Bremner, F.; et al. Scale for the assessment and rating of ataxia: Development of a new clinical scale. Neurology 2006, 66, 1717–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas-Black, G.J.; Parkinson, M.H.; Bremner, F.; Giunti, P. Peripapillary retinal nerve fibre layer thickness in Friedreich’s ataxia: A biomarker for trials? Brain 2019, 142, e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhi, M.; Aziz, S.; Muhammad, K.; Adhi, M.I. Macular Thickness by Age and Gender in Healthy Eyes Using Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topcon 3D OCT Series. In Normative Database-Summary; Topcon Medical Systems: Oakland, NJ, USA, 2011.
- Leung, C.K.S.; Yu, M.; Weinreb, R.N.; Ye, C.; Liu, S.; Lai, G.; Lam, D.S.C. Retinal nerve fiber layer imaging with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography: A prospective analysis of age-related loss. Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 731–737. [Google Scholar]
- Bogdanova-Mihaylova, P.; Chen, H.; Plapp, H.M.; Gorman, C.; Alexander, M.D.; McHugh, J.C.; Moran, S.; Early, A.; Cassidy, L.; Lynch, T.; et al. Neurophysiological and ophthalmological findings of SPG7-related spastic ataxia: A phenotype study in an Irish cohort. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 3897–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdanova-Mihaylova, P.; Alexander, M.D.; Murphy, R.P.; Chen, H.; Healy, D.G.; Walsh, R.A.; Murphy, S.M. Clinical spectrum of AIFM1-associated disease in an Irish family, from mild neuropathy to severe cerebellar ataxia with colour blindness. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2019, 24, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanova-Mihaylova, P.; Austin, N.; Alexander, M.D.; Cassidy, L.; Murphy, R.P.; Walsh, R.A.; Murphy, S.M. Spastic ataxia associated with colour vision deficiency due to DDHD2 mutations. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, e9–e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, D.; Bogdanova-Mihaylova, P.; McNamara, B.; Sweeney, B.; Costello, D.; Walsh, R. Childhood onset demyelinating neuropathy with late onset ataxia due to mutation in SAMD9L. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2020, 25, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carelli, V.; Ross-Cisneros, F.N.; Sadun, A.A. Mitochondrial dysfunction as a cause of optic neuropathies. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2004, 23, 53–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, B.X.; Ross-Cisneros, F.N.; Carelli, V.; Rue, K.S.; Salomao, S.R.; Moraes-Filho, M.N.; Moraes, M.N.; Berezovsky, A.; Belfort, R.; Sadun, A.A. Mathematically modeling the involvement of axons in Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 7608–7617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu-Wai-Man, P.; Griffiths, P.G.; Chinnery, P.F. Mitochondrial optic neuropathies–disease mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2011, 30, 81–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, J.A.; Biousse, V.; Newman, N.J. The Neuro-Ophthalmology of Mitochondrial Disease. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2010, 55, 299–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, R.M.; Griffiths, P.G.; Johnson, M.A.; Turnbull, D.M. Histochemical localization of mitochondrial enzyme activity in human optic nerve and retina. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1999, 83, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu-Wai-Man, C.Y.; Chinnery, P.F.; Griffiths, P.G. Optic neuropathies–importance of spatial distribution of mitochondria as well as function. Med. Hypotheses 2005, 65, 1038–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carelli, V.; La Morgia, C.; Valentino, M.L.; Barboni, P.; Ross-Cisneros, F.N.; Sadun, A.A. Retinal ganglion cell neurodegeneration in mitochondrial inherited disorders. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1787, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouault, T.A.; Tong, W.H. Iron-sulphur cluster biogenesis and mitochondrial iron homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotig, A.; de Lonlay, P.D.; Chretien, D.; Foury, F.; Koenig, M.; Sidi, D.; Munnich, A.; Rustin, P. Aconitase and mitochondrial iron-sulphur protein deficiency in Friedreich ataxia. Nat. Genet. 1997, 17, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, J.B.; Dehmer, T.; Schöls, L.; Mende, H.; Hardt, C.; Vorgerd, M.; Bürk, K.; Matson, W.; Dichgans, J.; Beal, M.F.; et al. Oxidative stress in patients with Friedreich ataxia. Neurology 2000, 55, 1719–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, E.; Johnson, J.; Dong, Y.N.; Mercado-Ayon, E.; Warren, N.; Zhai, M.; McMillan, E.; Salovin, A.; Lin, H.; Lynch, D.R. Role of frataxin protein deficiency and metabolic dysfunction in Friedreich ataxia, an autosomal recessive mitochondrial disease. Neuronal Signal. 2018, 2, NS20180060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmucker, S.; Puccio, H. Understanding the molecular mechanisms of Friedreich’s ataxia to develop therapeutic approaches. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, R103–R110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alldredge, C.D.; Schlieve, C.R.; Miller, N.R.; Levin, L.A. Pathophysiology of the optic neuropathy associated with Friedreich ataxia. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2003, 121, 1582–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cossée, M.; Dürr, A.; Schmitt, M.; Dahl, N.; Trouillas, P.; Allinson, P.; Kostrzewa, M.; Nivelon-ChevallierKarl, A.; Gustavson, H.; Kohlschütter, A.; et al. Friedreich’s ataxia: Point mutations and clinical presentation of compound heterozygotes. Ann. Neurol. 1999, 45, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, F.; Amantini, A.; de Scisciolo, G.; Scaioli, V.; Guidi, L.; Frosini, R. Visual involvement in Friedreich’s ataxia: pERG and VEP study. Eur. Neurol. 1998, 28, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stricker, S.; Oberwahrenbrock, T.; Zimmermann, H.; Schroeter, J.; Endres, M.; Brandt, A.U.; Paul, F. Temporal retinal nerve fiber loss in patients with spinocerebellar ataxia type 1. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, G.; Rey, A.; Sanchez-Dalmau, F.B.; Muñoz, E.; Ríos, J.; Adán, A. Optical coherence tomography findings in spinocerebellar ataxia-3. Eye 2013, 27, 1376–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monte, T.L.; Reckziegel, E.D.R.; Augustin, M.C.; Locks-Coelho, L.D.; Santos, A.S.P.; Furtado, G.V.; De Mattos, E.P.; Pedroso, J.L.; Barsottini, O.P.; Vargas, F.R.; et al. The progression rate of spinocerebellar ataxia type 2 changes with stage of disease. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2018, 13, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, A.P.; Trip, S.A.; Schlottmann, P.G.; Altmann, D.R.; Garway-Heath, D.F.; Plant, G.T.; Miller, D.H. A preliminary longitudinal study of the retinal nerve fiber layer in progressive multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. 2010, 257, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forte, R.; Cennamo, G.L.; Finelli, M.L.; de Crecchio, G. Comparison of time domain Stratus OCT and spectral domain SLO/OCT for assessment of macular thickness and volume. Eye 2009, 23, 2071–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, A.P.; Sadjadi, R.; Saeedi, J.; Lindley, J.; Costello, F.; Traboulsee, A. Time-Domain and Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer in MS Patients and Healthy Controls. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 2012, 564627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, I.A.; Farmer, J.; Hersch, S.; Larkindale, J.; Lynch, D.R.; Napierala, J.; Napierala, M.; Payne, R.M.; Subramony, S.H. The current state of biomarker research for Friedreich’s ataxia: A report from the 2018. FARA biomarker meeting. Futur. Sci. OA 2019, 5, FSO398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Pt | Fam Hx | Sex | Age at Onset (yrs) | Age at Exam (yrs) | Disease Duration (yrs) | SARA | Ataxia | NP | WC Bound | Hearing Loss | LVH | Diabetes mellitus | Scoliosis/Surgery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | No | M | 5 | 31 | 26 | 37 | + | + | + | + | + | + | +/no surgery |
| 2 | No | F | 16 | 19 | 3 | 8.5 | + | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| 3 | No | M | 37 | 42 | 5 | 4.5 | + | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| 4 | Yes | F | 11 | 26 | 15 | 23 | + | + | + | - | + | - | +/surgery |
| 5 | Yes | M | 11 | 25 | 14 | 27.5 | + | + | + | - | + | - | - |
| 6 | Yes | M | 19 | 40 | 21 | 19 | + | + | + | - | - | - | +/no surgery |
| 7 | Yes | F | 19 | 30 | 11 | 11 | + | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| 8 | Yes | F | 16 | 30 | 14 | 13 | + | + | - | - | - | - | +/no surgery |
| 9 | No | F | 16 | 52 | 36 | 36 | + | + | + | - | - | + | +/surgery |
| 10 | No | M | 35 | 47 | 12 | 16 | + | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 11 | No | M | 11 | 33 | 22 | 38 | + | + | + | + | + | - | +/no surgery |
| 12 | Yes | M | 11 | 41 | 30 | 34 | + | + | + | - | + | + | +/no surgery |
| 13 | No | F | 11 | 18 | 7 | 18 | + | + | + | - | - | - | +/+ |
| 14 | No | F | 9 | 35 | 26 | 37 | + | + | + | - | + | - | - |
| 15 | No | M | 5 | 21 | 16 | 16.5 | + | + | + | - | - | + | +/+ |
| 16 | Yes | M | 30 | 63 | 33 | 15 | + | + | + | + | - | + | - |
| 17 | No | M | 3 | 27 | 24 | 25 | + | + | + | - | + | - | +/+ |
| 18 | Yes | F | 18 | 54 | 36 | 15.5 | + | + | + | - | - | - | - |
| 19 | Yes | M | 5 | 18 | 13 | 28.5 | + | + | + | - | - | - | +/- |
| 20 | Yes | F | 13 | 19 | 6 | 11.5 | + | + | - | - | + | - | +/- |
| 21 | Yes | F | 10 | 24 | 14 | 20.5 | + | + | + | - | - | - | +/+ |
| 22 | Yes | F | 11 | 27 | 16 | 19.5 | + | + | + | - | - | - | +/+ |
| 23 | No | M | 16 | 35 | 19 | 21 | + | + | + | - | - | - | +/- |
| 24 | No | F | 40 | 60 | 20 | 29 | + | + | + | - | - | - | - |
| 25 | No | F | 5 | 18 | 13 | 24.5 | + | + | + | - | + | + | - |
| 26 | Yes | M | 14 | 54 | 40 | 27.5 | + | + | + | + | - | + | - |
| 27 | Yes | M | 23 | 45 | 22 | 28 | + | - | + | - | - | - | +/- |
| 28 | No | F | 4 | 31 | 27 | 26 | + | + | + | - | + | + | +/+ |
| 29 | Yes | F | 12 | 36 | 24 | 30 | + | + | + | + | + | - | - |
| 30 | No | M | 12 | 51 | 39 | 37.5 | + | + | + | - | + | - | +/+ |
| 31 | No | M | 10 | 20 | 10 | 23 | + | + | + | - | + | - | +/- |
| 32 | Yes | M | 17 | 47 | 30 | 31.5 | + | + | + | - | - | + | +/- |
| 33 | Yes | M | 21 | 45 | 24 | 18 | + | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| 34 | No | M | 13 | 18 | 5 | 11.5 | + | + | - | - | + | - | +/- |
| 35 | No | F | 7 | 21 | 14 | 27 | + | + | + | - | - | + | +/- |
| 36 | Yes | M | 6 | 22 | 16 | 20.5 | + | + | + | - | + | - | +/- |
| 37 | Yes | F | 8 | 26 | 18 | 26 | + | + | + | - | + | - | - |
| 38 | No | M | 8 | 18 | 10 | 29.5 | + | + | + | - | + | - | +/- |
| 39 | Yes | F | 16 | 51 | 35 | 16 | + | + | + | - | - | - | - |
| 40 | No | F | 10 | 23 | 13 | 19 | + | + | + | - | + | - | +/- |
| 41 | No | M | 15 | 36 | 21 | 14 | + | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| 42 | No | M | 10 | 19 | 9 | 18 | + | + | + | - | + | - | +/+ |
| 43 | Yes | F | 9 | 34 | 25 | 23.5 | + | + | + | - | - | - | +/+ |
| 44 | No | F | 11 | 29 | 18 | 22 | + | + | + | - | + | - | +/- |
| 45 | Yes | M | 10 | 53 | 43 | 24 | + | + | + | - | - | - | - |
| 46 | No | F | 10 | 21 | 11 | 10.5 | + | + | - | - | - | - | +/- |
| 47 | No | M | 6 | 22 | 16 | 10.5 | + | + | - | + | + | - | +/- |
| 48 | Yes | M | 29 | 44 | 15 | 9.5 | + | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| Retinal Nerve Fibre Layer | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt | SWJ | Ny | BCVA | Optic Disc Pallor | Average Macula (µm) | Foveal (µm) | Average (µm) | Superior (µm) | Nasal (µm) | Inferior (µm) | Temporal (µm) | |
| R | L | |||||||||||
| 1 | + | + | HM | HM | + | 234.6 | 225 | |||||
| 2 | + | - | 20/20 | 20/20 | + | 276.45 | 249.5 | 94 | 110.5 | 81.5 | 115 | 68.5 |
| 3 | + | + | 20/20 | 20/25 | - | 286.9 | 277 | 114 | 122 | 111 | 136 | 87 |
| 4 | + | + | 20/40 | 20/40 | + | 267 | 246 | 80 | 101.5 | 63.5 | 93.5 | 63 |
| 5 | + | + | 20/40 | 20/30 | - | 259.1 | 277.5 | 74 | 93 | 55 | 93 | 57 |
| 6 | - | - | 20/20 | 20/20 | - | 275.55 | 274 | 94 | 101.5 | 80 | 127.5 | 67 |
| 7 | + | - | 20/20 | 20/20 | - | 272.35 | 243.5 | 108 | 138 | 86.5 | 135 | 74 |
| 8 | + | - | 20/20 | 20/20 | - | 276.85 | 230 | 98 | 106 | 83 | 121.5 | 81.5 |
| 9 | - | - | NLP | 20/50 | + | 252.8 | 234 | |||||
| 10 | + | - | 20/40 | 20/25 | - | 290.15 | 283 | 104 | 112 | 110 | 109 | 85 |
| 11 | + | + | 20/70 | 20/70 | - | 271.6 | 238 | |||||
| 12 | + | + | 20/50 | 20/50 | - | 265.8 | 269 | |||||
| 13 | - | - | 20/20 | 20/20 | + | 264.55 | 243.5 | 86.5 | 99 | 66 | 117 | 76 |
| 14 | + | + | 20/200 | 20/200 | + | 254.15 | 225.5 | 66 | 75 | 95 | 48 | 48 |
| 15 | - | + | 20/70 | 20/30 | - | 234.3 | 279 | 55 | 62 | 52 | 56 | 50 |
| 16 | - | - | 20/20 | 20/25 | - | 260.7 | 223.5 | 104 | 132 | 78 | 128 | 79 |
| 17 | + | - | 20/70 | 20/40 | + | 266 | 274.5 | 69 | 70 | 47 | 67 | 54 |
| 18 | - | - | 20/20 | 20/25 | - | 272.95 | 220 | 107 | 120 | 99 | 120.5 | 84 |
| 19 | + | + | 20/40 | 20/40 | + | 290.8 | 274 | |||||
| 20 | - | + | 20/20 | 20/20 | - | 279.45 | 268 | 99.5 | 119 | 101.5 | 107.5 | 70.5 |
| 21 | + | + | 20/30 | 20/30 | + | 254.75 | 233 | 81 | 87.5 | 58 | 107 | 71 |
| 22 | - | - | 20/25 | 20/20 | - | 256 | 243 | 82.5 | 80.5 | 71.5 | 100 | 73 |
| 23 | + | - | 20/20 | 20/20 | - | 288.7 | 74 | 75 | 69 | 85 | 66 | |
| 24 | + | + | 20/30 | 20/40 | - | 283.75 | 210 | 93 | 110 | 68.5 | 103.5 | 80.5 |
| 25 | - | - | 20/20 | 20/25 | + | 263.1 | 283 | 97 | 116 | 78.5 | 113.5 | 79 |
| 26 | - | + | 20/40 | 20/40 | - | 261.1 | ||||||
| 27 | + | - | 20/20 | 20/20 | - | 288.85 | 254 | 94.5 | 108.5 | 86.5 | 119.5 | 64 |
| 28 | + | - | 20/20 | 20/20 | + | 246.95 | 207 | 85 | 97 | 67 | 100 | 74 |
| 29 | + | + | 20/25 | 20/30 | + | 265.3 | 265.5 | |||||
| 30 | + | + | CF | CF | - | 267.6 | 290.5 | 75 | 85.5 | 70 | 97 | 60.5 |
| 31 | + | - | 20/25 | 20/20 | - | 261.65 | 277 | |||||
| 32 | + | - | 20/20 | 20/20 | - | 255.15 | 230 | 79 | 95 | 63 | 98 | 62 |
| 33 | - | + | 20/20 | 20/20 | - | 272.7 | 233.5 | 90.5 | 103.5 | 75.5 | 107.5 | 74.5 |
| 34 | + | - | 20/30 | 20/30 | - | 272.8 | 210 | 96 | 108 | 54 | 103 | 55 |
| 35 | - | - | 20/20 | 20/20 | + | 274.1 | 266.5 | 98.5 | 110.5 | 82 | 116 | 87 |
| 36 | + | - | 20/70 | 20/70 | + | 258.8 | 271 | 87 | 102.5 | 80 | 96 | 45.5 |
| 37 | + | + | 20/30 | 20/25 | + | 273.4 | 275 | 76 | 82.5 | 70.5 | 93.5 | 58 |
| 38 | + | - | 20/50 | 20/30 | - | 268.35 | 267 | |||||
| 39 | - | - | 20/40 | 20/40 | - | 291.35 | 196.5 | 105.5 | 132 | 82 | 110.5 | 97 |
| 40 | + | + | 20/20 | 20/20 | + | 265 | 251 | 86 | 88.5 | 75 | 107 | 74.5 |
| 41 | + | - | 20/20 | 20/20 | + | 278.9 | 242.5 | 99 | 112.5 | 81 | 129.5 | 74.5 |
| 42 | - | + | 20/20 | 20/20 | + | 277.45 | 267.5 | 83 | 89.5 | 71 | 110.5 | 61.5 |
| 43 | - | - | 20/20 | 20/20 | + | 266.45 | 261.5 | 84.5 | 75 | 68.5 | 118.5 | 76 |
| 44 | + | - | 20/20 | 20/20 | + | 270.15 | 235 | 88 | 95 | 60 | 117.5 | 80.5 |
| 45 | - | - | 20/20 | 20/20 | - | 259.05 | 268.5 | 80.5 | 104.5 | 83 | 82.5 | 50.5 |
| 46 | - | - | 20/20 | 20/20 | - | 255.45 | 220 | 94.5 | 101 | 77.5 | 107.5 | 93 |
| 47 | + | - | 20/40 | 20/30 | + | 272.45 | 253.5 | 82.5 | 73 | 71 | 117.5 | 69 |
| 48 | + | + | 20/20 | 20/25 | - | 273.5 | 239 | 95.5 | 108 | 87.5 | 109.5 | 76 |
| 3D Macula | 3D Disc | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M/F Ratio | Age (Years) | BCVA (LogMAR) | Average (µm) | Foveal (µm) | Average RNFL (µm) | Superior (µm) | Nasal (µm) | Inferior (µm) | Temporal (µm) | ||
| FRDA | mean ± SD | 26/22 | 33.4 ± 13 | 0.26 ± 0.5 | 268.1 ± 13.2 | 250.4 ± 24.2 | 88.4 ± 12.9 | 97.9 ± 20.1 | 75.4 ± 15.1 | 105.7 ± 19.4 | 70.3 ± 12.7 |
| range | (18–63) | (0–2.3) | (233.9–294.3) | (194–300) | (55–114) | (58–134) | (54–111) | (56–138) | (51–96) | ||
| Controls | mean ± SD | 23/25 | 34.2 ± 10.2 | 0.03 ± 0.07 | 273.8 ± 10.9 | 238.3 ± 22.8 | 103.9 ± 8.4 | 122.3 ± 12.9 | 88.5 ± 10.1 | 130.6 ± 11.3 | 74.5 ± 7.8 |
| range | (16–63) | (-0.1–+0.3) | (252–300) | (214–293) | (92–124) | (90–155) | (72–124) | (110–156) | (60–96) | ||
| p value | 0.6 | 0.5 | <0.001 | 0.003 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.102 | |
| 3D Macula | 3D Disc | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average (µm) | Foveal (µm) | Average RNFL (µm) | Superior (µm) | Nasal (µm) | Inferior (µm) | Temporal (µm) | |
| Baseline | 270.3 ± 12.4 | 257.9 ± 22.3 | 88.8 ± 14.3 | 97.6 ± 20.6 | 75.8 ± 17.1 | 105.4 ± 18.9 | 68.9 ± 12.5 |
| Follow up | 267.4 ± 12.4 | 246.9 ± 24.1 | 85.2 ± 15.5 | 92.6 ± 24.4 | 72.5 ± 14.9 | 105.1 ± 21.4 | 67.1 ± 12.2 |
| p value | 0.01 | 0.007 | 0.001 | 0.016 | 0.036 | 0.046 | 0.17 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bogdanova-Mihaylova, P.; Plapp, H.M.; Chen, H.; Early, A.; Cassidy, L.; Walsh, R.A.; Murphy, S.M. Longitudinal Assessment Using Optical Coherence Tomography in Patients with Friedreich’s Ataxia. Tomography 2021, 7, 915-931. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography7040076
Bogdanova-Mihaylova P, Plapp HM, Chen H, Early A, Cassidy L, Walsh RA, Murphy SM. Longitudinal Assessment Using Optical Coherence Tomography in Patients with Friedreich’s Ataxia. Tomography. 2021; 7(4):915-931. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography7040076
Chicago/Turabian StyleBogdanova-Mihaylova, Petya, Helena Maria Plapp, Hongying Chen, Anne Early, Lorraine Cassidy, Richard A. Walsh, and Sinéad M. Murphy. 2021. "Longitudinal Assessment Using Optical Coherence Tomography in Patients with Friedreich’s Ataxia" Tomography 7, no. 4: 915-931. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography7040076
APA StyleBogdanova-Mihaylova, P., Plapp, H. M., Chen, H., Early, A., Cassidy, L., Walsh, R. A., & Murphy, S. M. (2021). Longitudinal Assessment Using Optical Coherence Tomography in Patients with Friedreich’s Ataxia. Tomography, 7(4), 915-931. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography7040076






