Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias and COVID-19 Pneumonia: Review of the Main Radiological Features and Differential Diagnosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. COVID-19 Pneumonia
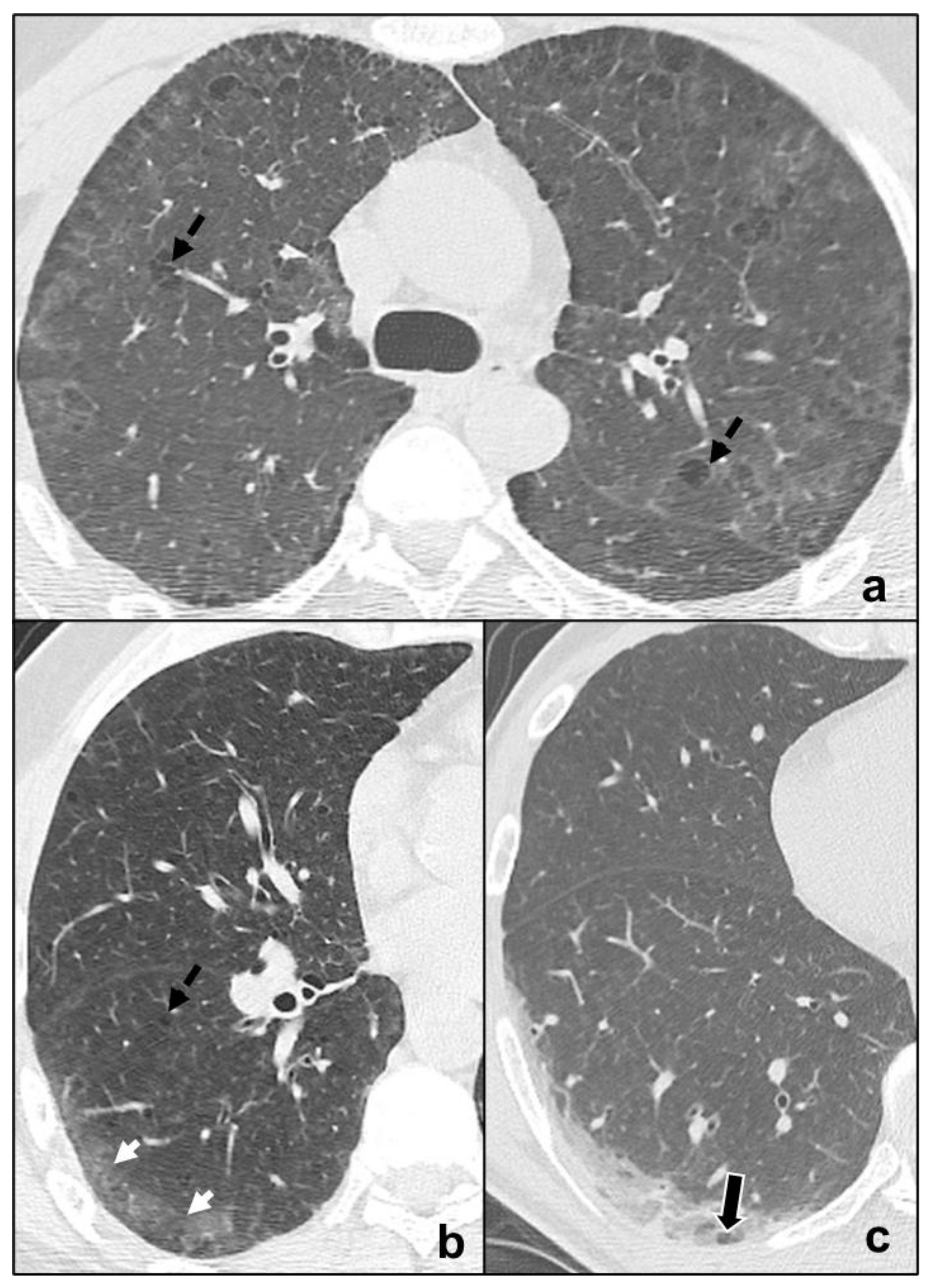
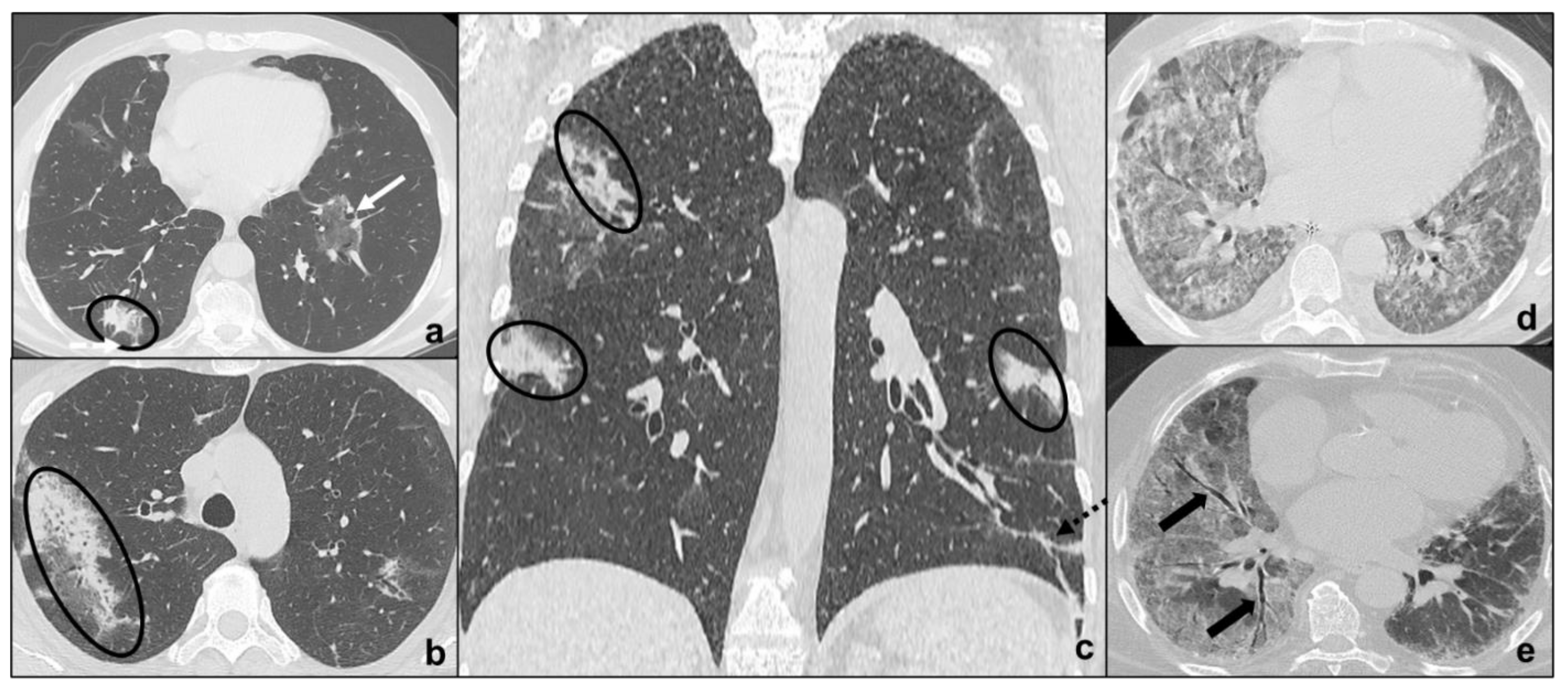
- Early phase/Stage 1 refers to days 0–4, and ground glass opacities represent the main radiological findings (Figure 1a);
- Progressive phase/Stage 2 refers to days 5–8, and the hallmark is represented by crazy paving pattern (Figure 1b) coexisting with extensive ground glass opacities and initial consolidative foci;
- Peak phase/Stage 3 is typical of days 9 to 13, and CT shows consolidations (Figure 1c), sometimes surrounded by a ground glass halo (halo sign);
- Absorption phase/Stage 4 starts around day 14, and ground-glass areas together with linear consolidations are appreciable (Figure 1d).
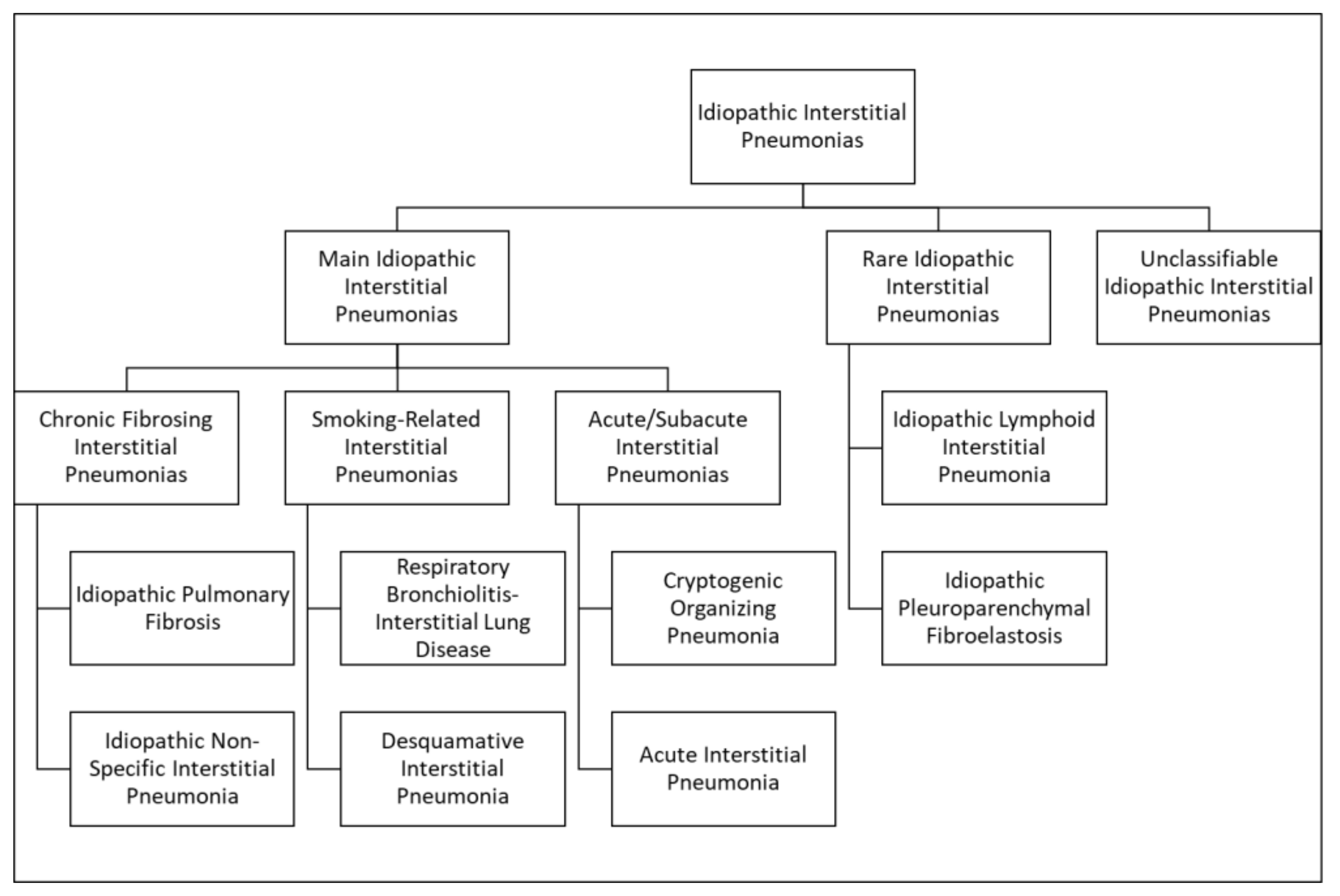
3. Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias
3.1. Major Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias
3.1.1. Chronic Fibrosing IIPs
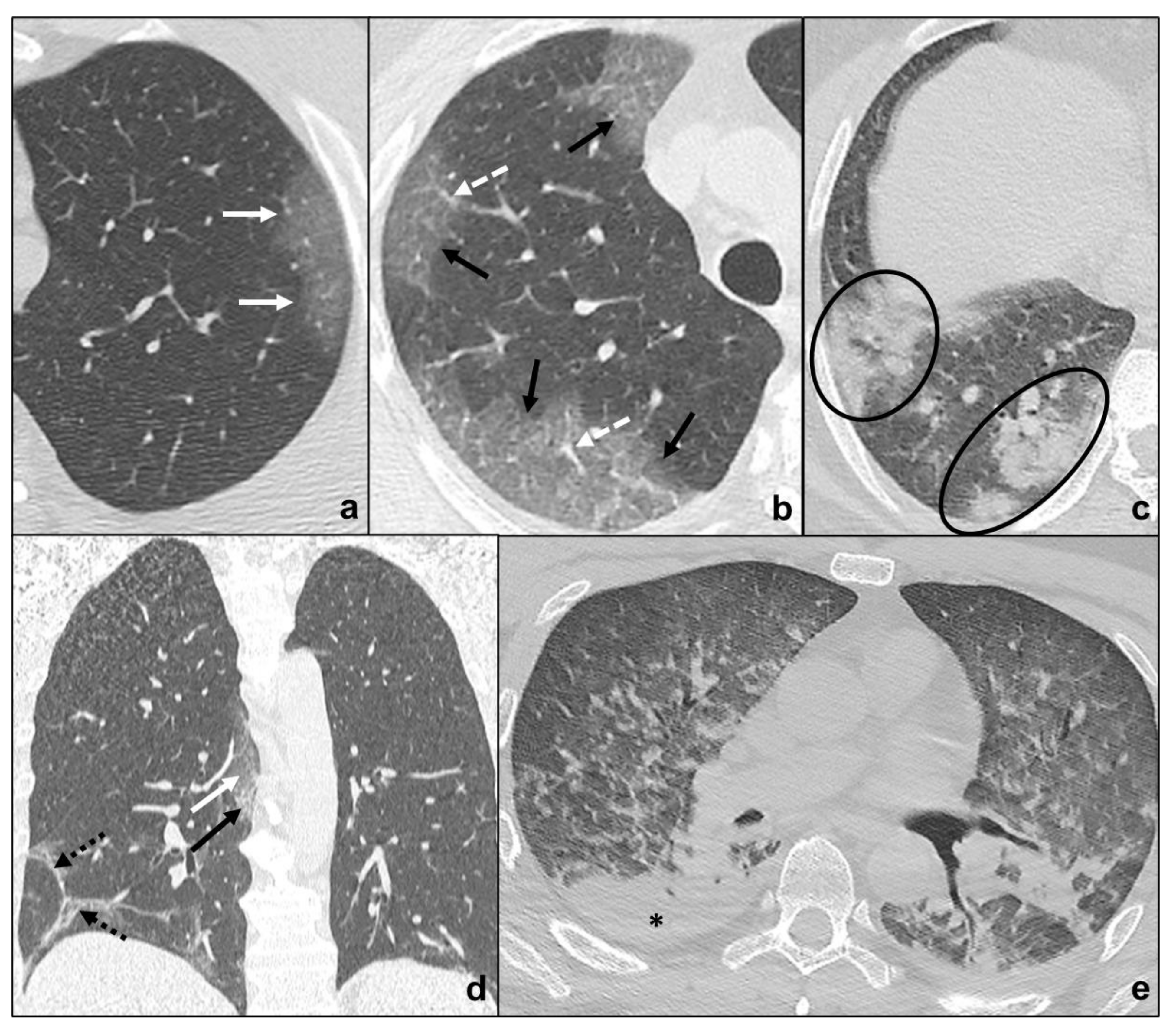
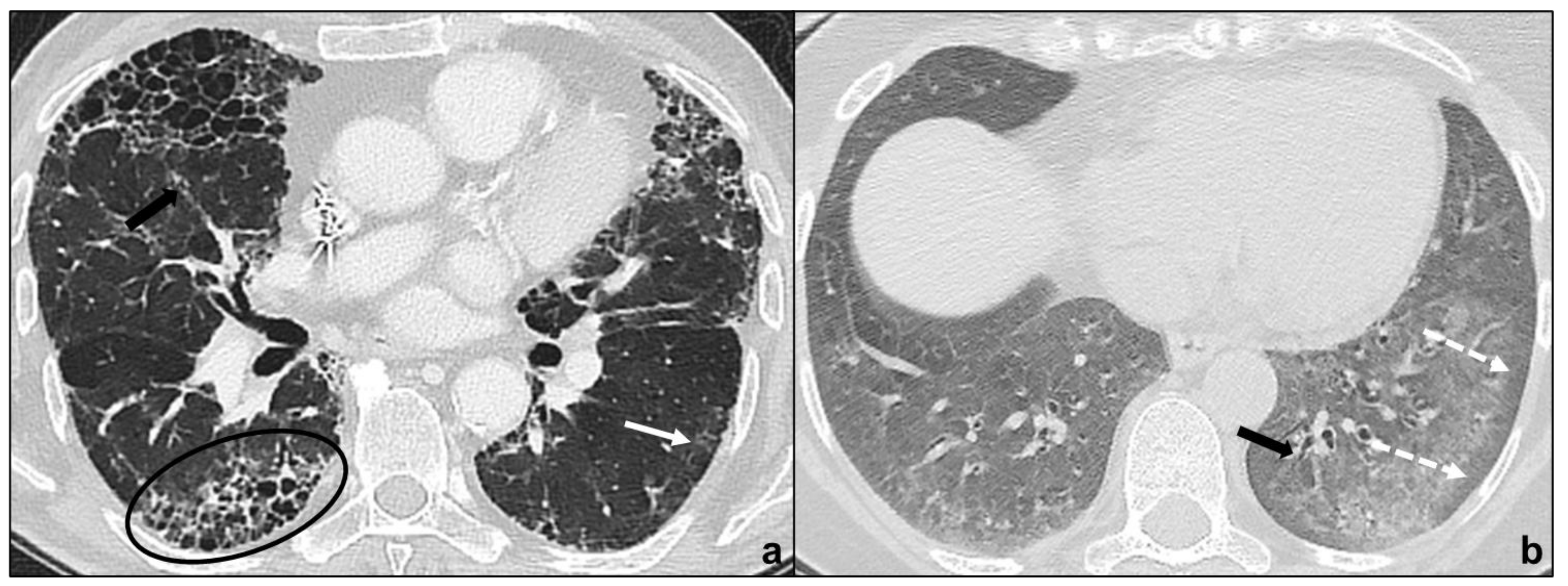
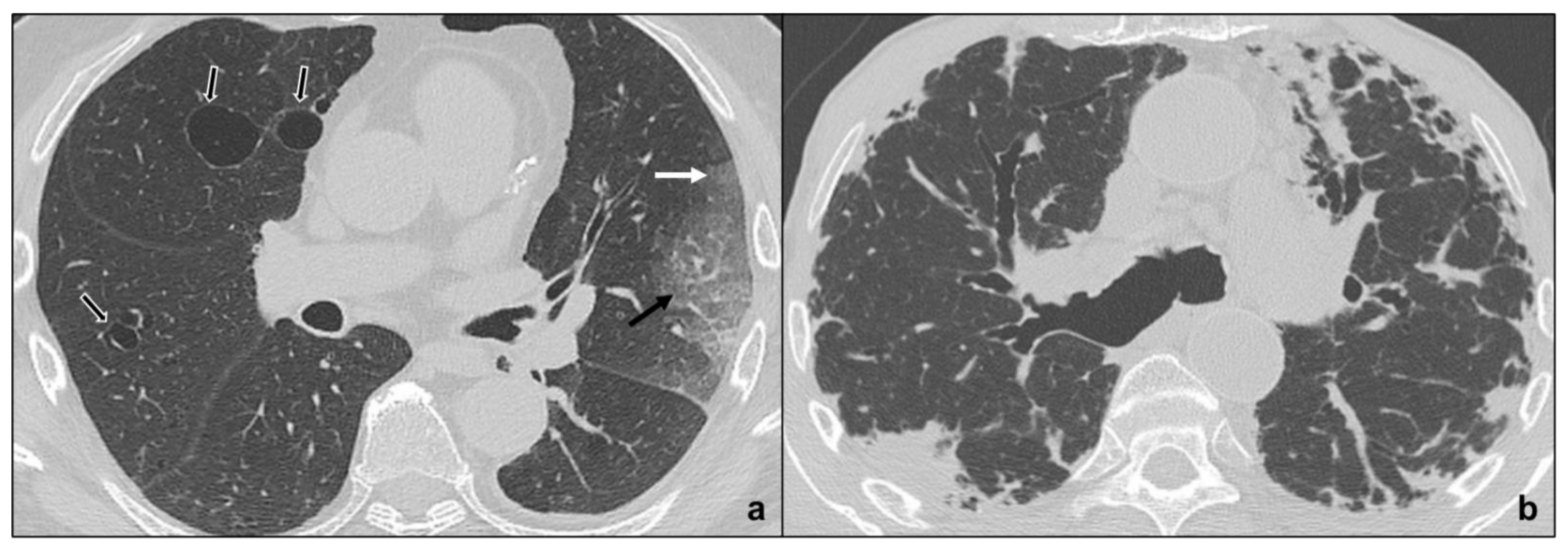
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Non-Specific Interstitial Pneumonia
3.1.2. Smoking-Related IIPs
Respiratory Bronchiolitis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease
Desquamative Interstitial Pneumonia
3.1.3. Acute/Subacute IIPs
Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia
Acute Interstitial Pneumonia
3.2. Rare Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias
3.2.1. Lymphoid Interstitial Pneumonia
3.2.2. Idiopathic Pleuroparenchymal Fibroelastosis
3.3. Unclassifiable Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias
4. Differential Diagnosis between COVID-19 Pneumonia and Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Rogers, H.L.; Barros, P.P.; Maeseneer, J.D.; Lehtonen, L.; Lionis, C.; McKee, M.; Siciliani, L.; Stahl, D.; Zaletel, J.; Kringos, D.L. Resilience Testing of Health Systems: How Can It Be Done? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hani, C.; Trieu, N.H.; Saab, I.; Dangeard, S.; Bennani, S.; Chassagnon, G.; Revel, M.-P. COVID-19 pneumonia: A review of typical CT findings and differential diagnosis. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2020, 101, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarnera, A.; Podda, P.; Santini, E.; Paolantonio, P.; Laghi, A. Differential diagnoses of COVID-19 pneumonia: The current challenge for the radiologist-a pictorial essay. Insights Imaging 2021, 12, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.-C.; Zhang, H.-W.; Yu, J.; Xu, H.-J.; Chen, H.; Luo, S.-P.; Zhang, H.; Liang, L.-H.; Wu, X.-L.; Lei, Y.; et al. CT Imaging and Differential Diagnosis of COVID-19. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 2020, 71, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Travis, W.D.; Costabel, U.; Hansell, D.M.; King, T.E., Jr.; Lynch, D.A.; Nicholson, A.G.; Ryerson, C.J.; Ryu, J.H.; Selman, M.; Wells, A.U.; et al. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: Update of the international multidisciplinary classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 733–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.F.-W.; Yuan, S.; Kok, K.-H.; To, K.K.-W.; Chu, H.; Yang, J.; Xing, F.; Liu, J.; Yip, C.C.-Y.; Poon, R.W.-S.; et al. A Familial Cluster of Pneumonia Associated with the 2019 Novel Coronavirus Indicating Person-to-Person Transmission: A Study of a Family Cluster. Lancet 2020, 395, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guan, W.-J.; Ni, Z.-Y.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.-H.; Ou, C.-Q.; He, J.-X.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.-L.; Hui, D.S.C.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pormohammad, A.; Ghorbani, S.; Baradaran, B.; Khatami, A.; Turner, R.; Mansournia, M.A.; Kyriacou, D.N.; Idrovo, J.-P.; Bahr, N.C. Clinical characteristics, laboratory findings, radiographic signs and outcomes of 61,742 patients with confirmed COVID-19 infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 147, 104390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böger, B.; Fachi, M.M.; Vilhena, R.O.; Cobre, A.F.; Tonin, F.S.; Pontarolo, R. Systematic review with meta-analysis of the accuracy of diagnostic tests for COVID-19. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2021, 49, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, G.D.; Ryerson, C.J.; Haramati, L.B.; Sverzellati, N.; Kanne, J.P.; Raoof, S.; Schluger, N.W.; Volpi, A.; Yim, J.-J.; Martin, I.B.K.; et al. The Role of Chest Imaging in Patient Management during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Multinational Consensus Statement from the Fleischner Society. Radiology 2020, 296, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, H.Y.F.; Lam, H.Y.S.; Fong, A.H.-T.; Leung, S.T.; Chin, T.W.-Y.; Lo, C.S.Y.; Lui, M.M.-S.; Lee, J.C.Y.; Chiu, K.W.-H.; Chung, T.W.-H.; et al. Frequency and Distribution of Chest Radiographic Findings in Patients Positive for COVID-19. Radiology 2020, 296, E72–E78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacobi, A.; Chung, M.; Bernheim, A.; Eber, C. Portable chest X-ray in coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19): A pictorial review. Clin. Imaging 2020, 64, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, F.; Ye, T.; Sun, P.; Gui, S.; Liang, B.; Li, L.; Zheng, D.; Wang, J.; Hesketh, R.L.; Yang, L.; et al. Time Course of Lung Changes on Chest CT During Recovery from 2019 Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) Pneumonia. Radiology 2020, 295, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernheim, A.; Mei, X.; Huang, M.; Yang, Y.; Fayad, Z.A.; Zhang, N.; Diao, K.; Lin, B.; Zhu, X.; Li, K.; et al. Chest CT Findings in Coronavirus Disease-19 (COVID-19): Relationship to Duration of Infection. Radiology 2020, 295, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, M.; Bernheim, A.; Mei, X.; Zhang, N.; Huang, M.; Zeng, X.; Cui, J.; Xu, W.; Yang, Y.; Fayad, Z.A.; et al. CT Imaging Features of 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Radiology 2020, 295, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kanne, J.P.; Little, B.P.; Chung, J.H.; Elicker, B.M.; Ketai, L.H. Essentials for Radiologists on COVID-19: An Update—Radiology Scientific Expert Panel. Radiology 2020, 296, E113–E114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheard, S.; Rao, P.; Devaraj, A. Imaging of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Respir. Care 2012, 57, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Myers, J.; Richeldi, L.; Wilson, K.C. The 2018 Diagnosis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Guidelines: Surgical Lung Biopsy for Radiological Pattern of Probable Usual Interstitial Pneumonia Is Not Mandatory. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 1089–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller-Mang, C.; Grosse, C.; Schmid, K.; Stiebellehner, L.; Bankier, A.A. What every radiologist should know about idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Radiographics 2007, 27, 595–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dodd, J.D.; de Jong, P.A.; Levy, R.D.; Coxson, H.O.; Mayo, J.R. Conventional high-resolution CT versus contiguous multidetector CT in the detection of bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome in lung transplant recipients. J. Thorac. Imaging 2008, 23, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansell, D.M. Thin-section CT of the lungs: The Hinterland of normal. Radiology 2010, 256, 695–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, T.; Ohno, Y.; Kauczor, H.U.; Hatabu, H. Radiation dose reduction in chest CT—Review of available options. Eur. J. Radiol. 2014, 83, 1953–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, F.M.; Johnson, T.R.C.; Sommer, W.H.; Thierfelder, K.M.; Meinel, F.G. Chest CT using spectral filtration: Radiation dose, image quality, and spectrum of clinical utility. Eur. Radiol. 2015, 25, 1598–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontana, F.; Billard, A.-S.; Duhamel, A.; Schmidt, B.; Faivre, J.-B.; Hachulla, E.; Matran, R.; Remy, J.; Remy-Jardin, M. Effect of Iterative Reconstruction on the Detection of Systemic Sclerosis–related Interstitial Lung Disease: Clinical Experience in 55 Patients. Radiology 2016, 279, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Margerie-Mellon, C.; de Bazelaire, C.; Montlahuc, C.; Lambert, J.; Martineau, A.; Coulon, P.; de Kerviler, E.; Beigelman, C. Reducing Radiation Dose at Chest CT: Comparison Among Model-based Type Iterative Reconstruction, Hybrid Iterative Reconstruction, and Filtered Back Projection. Acad. Radiol. 2016, 23, 1246–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo, J.R. CT evaluation of diffuse infiltrative lung disease: Dose considerations and optimal technique. J. Thorac. Imaging 2009, 24, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokura, S.; Okuma, T.; Akira, M.; Arai, T.; Inoue, Y.; Kitaichi, M. Utility of expiratory thin-section CT for fibrotic interstitial pneumonia. Acta Radiol. 2014, 55, 1050–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.T., Jr.; Chatzkel, J.; Hewitt, M.G. Expiratory air trapping on thoracic computed tomography. A diagnostic subclassification. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2014, 11, 874–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Lee, S.M.; Song, J.-W.; Do, K.-H.; Lee, H.J.; Lim, S.; Choe, J.; Park, K.J.; Park, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; et al. Added value of prone CT in the assessment of honeycombing and classification of usual interstitial pneumonia pattern. Eur. J. Radiol. 2017, 91, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sverzellati, N.; Lynch, D.A.; Hansell, D.M.; Johkoh, T.; King, T.E., Jr.; Travis, W.D. American Thoracic Society-European Respiratory Society Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias: Advances in Knowledge since 2002. Radiographics 2015, 35, 1849–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunninghake, G.W.; Lynch, D.A.; Galvin, J.R.; Gross, B.H.; Mu¨ller, N.; Schwartz, D.A.; King, T.E.; Lynch, J.P.; Hegele, R.; Waldron, J.; et al. Radiologic Findings Are Strongly Associated with a Pathologic Diagnosis of Usual Interstitial Pneumonia. Chest 2003, 124, 1215–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, D.S.; de Araújo Filho, J.A.; Paiva, A.F.L.; Ikari, E.S.; Chate, R.C.; Nomura, C.H. Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: Review of the latest American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society classification. Radiol. Bras. 2018, 51, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akira, M.; Inoue, Y.; Kitaichi, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Arai, T.; Toyokawa, K. Usual interstitial pneumonia and nonspecific interstitial pneumonia with and without concurrent emphysema: Thin-section CT findings. Radiology 2009, 251, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Souza, H.A.P.H.M.; Nogueira, K.S.; Matos, A.P.; Vieira, R.P.; Riedi, C.A.; Rosário, N.A.; Telles, F.Q.; Costa, L.M.D. Early microbial colonization of cystic fibrosis patients identified by neonatal screening, with emphasis on Staphylococcus aureus. J. Pediatr. 2006, 82, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johkoh, T.; Müller, N.L.; Colby, T.V.; Ichikado, K.; Taniguchi, H.; Kondoh, Y.; Fujimoto, K.; Kinoshita, M.; Arakawa, H.; Yamada, H.; et al. Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia: Correlation between thin-section CT findings and pathologic subgroups in 55 patients. Radiology 2002, 225, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suda, T.; Kono, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Enomoto, N.; Kaida, Y.; Fujisawa, T.; Imokawa, S.; Yasuda, K.; Hashizume, H.; Yokomura, K.; et al. Distinct prognosis of idiopathic nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP) fulfilling criteria for undifferentiated connective tissue disease (UCTD). Respir. Med. 2010, 104, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silva, C.I.S.; Müller, N.L.; Lynch, D.A.; Curran-Everett, D.; Brown, K.K.; Lee, K.S.; Chung, M.P.; Churg, A. Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis: Differentiation from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and nonspecific interstitial pneumonia by using thin-section CT. Radiology 2008, 246, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieminska, A.; Kuziemski, K. Respiratory bronchiolitis-interstitial lung disease. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2014, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.S.; Brown, K.K.; Tuder, R.M.; Hale, V.A.E.; King, T.E., Jr.; Lynch, D.A. Respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease: Radiologic features with clinical and pathologic correlation. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2002, 26, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akira, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Hara, H.; Sakatani, M.; Ueda, E. Serial computed tomographic evaluation in desquamative interstitial pneumonia. Thorax 1997, 52, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawabata, Y.; Hoshi, E.; Murai, K.; Ikeya, T.; Takahashi, N.; Saitou, Y.; Kurashima, K.; Ubukata, M.; Takayanagi, N.; Sugita, H.; et al. Smoking-related changes in the background lung of specimens resected for lung cancer: A semiquantitative study with correlation to postoperative course. Histopathology 2008, 53, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzenstein, A.-L.A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Zanardi, C.; Dexter, E. Clinically occult interstitial fibrosis in smokers: Classification and significance of a surprisingly common finding in lobectomy specimens. Hum. Pathol. 2010, 41, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snider, G.L.; Kleinerman, J.; Thurlbeck, W.M.; Bengali, Z.H. The definition of emphysema. Report of a National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Division of Lung Diseases workshop. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1985, 132, 182–185. [Google Scholar]
- Cordier, J.F. Organising pneumonia. Thorax 2000, 55, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.J.; Lee, K.S.; Ryu, Y.H.; Yoon, Y.C.; Choe, K.O.; Kim, T.S.; Sung, K.J. Reversed halo sign on high-resolution CT of cryptogenic organizing pneumonia: Diagnostic implications. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2003, 180, 1251–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordier, J.-F. Cryptogenic organising pneumonia. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 28, 422–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Izumi, T.; Kitaichi, M.; Nishimura, K.; Nagai, S. Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia. Clinical features and differential diagnosis. Chest 1992, 102, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cordier, J.-F.; Loire, R.; Brune, J. Idiopathic Bronchiolitis Obliterans Organizing Pneumonia. Chest 1989, 96, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akira, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Sakatani, M. Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia manifesting as multiple large nodules or masses. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1998, 170, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haro, M.; Vizcaya, M.; Texidó, A.; Aguilar, X.; Arevalo, M. Idiopathic bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia with multiple cavitary lung nodules. Eur. Respir. J. 1995, 8, 1975–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-R.; Peng, S.-C.; Wei, L.-Q. Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia overlaps organizing pneumonia in lung-dominant connective tissue disease. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 11230–11235. [Google Scholar]
- Johkoh, T.; Müller, N.L.; Taniguchi, H.; Kondoh, Y.; Akira, M.; Ichikado, K.; Ando, M.; Honda, O.; Tomiyama, N.; Nakamura, H. Acute interstitial pneumonia: Thin-section CT findings in 36 patients. Radiology 1999, 211, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikado, K.; Suga, M.; Muranaka, H.; Gushima, Y.; Miyakawa, H.; Tsubamoto, M.; Johkoh, T.; Hirata, N.; Yoshinaga, T.; Kinoshita, Y.; et al. Prediction of prognosis for acute respiratory distress syndrome with thin-section CT: Validation in 44 cases. Radiology 2006, 238, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikado, K.; Johkoh, T.; Ikezoe, J.; Takeuchi, N.; Kohno, N.; Arisawa, J.; Nakamura, H.; Nagareda, T.; Itoh, H.; Ando, M. Acute interstitial pneumonia: High-resolution CT findings correlated with pathology. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol 1997, 168, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ichikado, K.; Suga, M.; Müller, N.L.; Taniguchi, H.; Kondoh, Y.; Akira, M.; Johkoh, T.; Mihara, N.; Nakamura, H.; Takahashi, M.; et al. Acute interstitial pneumonia: Comparison of high-resolution computed tomography findings between survivors and nonsurvivors. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 1551–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, A.J.; Wells, A.U.; Bouros, D.; du Bois, R.M.; Hansell, D.M.; Polychronopoulos, V.; Vassilakis, D.; Kerr, J.R.; Evans, T.W.; Nicholson, A.G. Terminal diffuse alveolar damage in relation to interstitial pneumonias. An autopsy study. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2003, 119, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzenstein, A.L.; Fiorelli, R.F. Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia/fibrosis. Histologic features and clinical significance. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1994, 18, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collard, H.R.; Moore, B.B.; Flaherty, K.R.; Brown, K.K.; Kaner, R.J.; King, T.E., Jr.; Lasky, J.A.; Loyd, J.E.; Noth, I.; Olman, M.A.; et al. Acute exacerbations of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 176, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akira, M.; Kozuka, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Sakatani, M. Computed Tomography Findings in Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 178, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, O.; Johkoh, T.; Ichikado, K.; Tomiyama, N.; Maeda, M.; Mihara, N.; Higashi, M.; Hamada, S.; Naito, H.; Yamamoto, S.; et al. Differential diagnosis of lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia and malignant lymphoma on high-resolution CT. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1999, 173, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, S.K.; Cool, C.D.; Lynch, D.A.; Brown, K.K. Idiopathic pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis: Description of a novel clinicopathologic entity. Chest 2004, 126, 2007–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler, P.W.; Shin, M.S.; Friedman, S.E.; Myers, J.L.; Katzenstein, A.L. Radiographic manifestations of bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia vs usual interstitial pneumonia. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1986, 147, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Stage | Phase | Timing (Days) | Predominant Radiological Findings | Additional Findings | Spatial Distribution of Radiological Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Early | 0–4 | ground glass opacities |
|
|
| 2 | Progressive | 5–8 | crazy paving pattern, ground glass opacities and small consolidations | ||
| 3 | Peak | 9–13 | consolidative foci | ||
| 4 | Absorption | ≥14 | ground-glass opacities and linear consolidation |
| Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias | Typical CT Features | Pattern of Distribution | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias | Chronic Fibrosing Interstitial Pneumonias | Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis | macrocystic honeycombing, architectural distortion, traction bronchiectases, irregular reticular opacities, decreased lung volumes, non-predominant ground glass opacities | apicobasal gradient, heterogeneous involvement, subpleural location |
| Non Specific Interstitial Pneumonia | no apicobasal gradient, basal predominance, homogeneous involvement, symmetric, peripheral, subpleural sparing | ground glass, irregular reticular opacities, traction bronchiectases | ||
| Smoking-Related Interstitial Pneumonias | Respiratory Bronchiolitis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease | centrilobular nodules, bronchial wall thickening, ground glass opacities, centrilobular emphysema | diffuse or upper lobes predominance, centrilobular | |
| Desquamative Interstitial Pneumonia | ground glass, linear or reticular opacities, rare perivascular cysts | apicobasal gradient, peripheral | ||
| Acute/Subacute Interstitial Pneumonias | Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia | ground glass, consolidations, rare centrilobular nodules and reticular opacities | apicobasal gradient, unilateral or bilateral, patchy distribution, peribronchial or peripheral, migration tendency, possible subpleural sparing | |
| Acute Interstitial Pneumonia | exudative: patchy ground glass, consolidation; organizing: architectural distortions, traction bronchiectases, honeycombing | bilateral, symmetric, dependent lung segments, basal | ||
| Rare Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias | Lymphoid Interstitial Pneumonia | perivascular thin-walled cysts, ground glass, centrilobular nodules, septal thickening | bilateral, basal, or diffuse | |
| Idiopathic Pleuroparenchymal Fibroelastosis | fibrotic changes, pleural thickening, consolidations, architectural distortions, traction bronchiectasis, hilar elevation, progressive upper lobe volume loss | bilateral, upper field predominance, subpleural | ||
| Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias | Ground Glass | Crazy Paving | Consolidations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias | Chronic Fibrosing Interstitial Pneumonias | Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis | C (non predominant pattern, exacerbation) | R | R |
| Non-Specific Interstitial Pneumonia | C | OD/A | R | ||
| Smoking-Related Interstitial Pneumonias | Respiratory Bronchiolitis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease | C | R | OD/A | |
| Desquamative Interstitial Pneumonia | C | OD/A | OD/A | ||
| Acute/Subacute Interstitial Pneumonias | Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia | C (initial exacerbation) | OD/A | C (late) | |
| Acute Interstitial Pneumonia | C (early) | C | C (early) | ||
| Rare Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias | Lymphoid Interstitial Pneumonia | C | C/R | R | |
| Idiopathic Pleuroparenchymal Fibroelastosis | OD/A | OD/A | C | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guarnera, A.; Santini, E.; Podda, P. Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias and COVID-19 Pneumonia: Review of the Main Radiological Features and Differential Diagnosis. Tomography 2021, 7, 397-411. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography7030035
Guarnera A, Santini E, Podda P. Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias and COVID-19 Pneumonia: Review of the Main Radiological Features and Differential Diagnosis. Tomography. 2021; 7(3):397-411. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography7030035
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuarnera, Alessia, Elena Santini, and Pierfrancesco Podda. 2021. "Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias and COVID-19 Pneumonia: Review of the Main Radiological Features and Differential Diagnosis" Tomography 7, no. 3: 397-411. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography7030035
APA StyleGuarnera, A., Santini, E., & Podda, P. (2021). Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias and COVID-19 Pneumonia: Review of the Main Radiological Features and Differential Diagnosis. Tomography, 7(3), 397-411. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography7030035






