Joint k-ω Space Image Reconstruction and Data Fitting for Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Model for Joint Reconstruction and Data Fitting
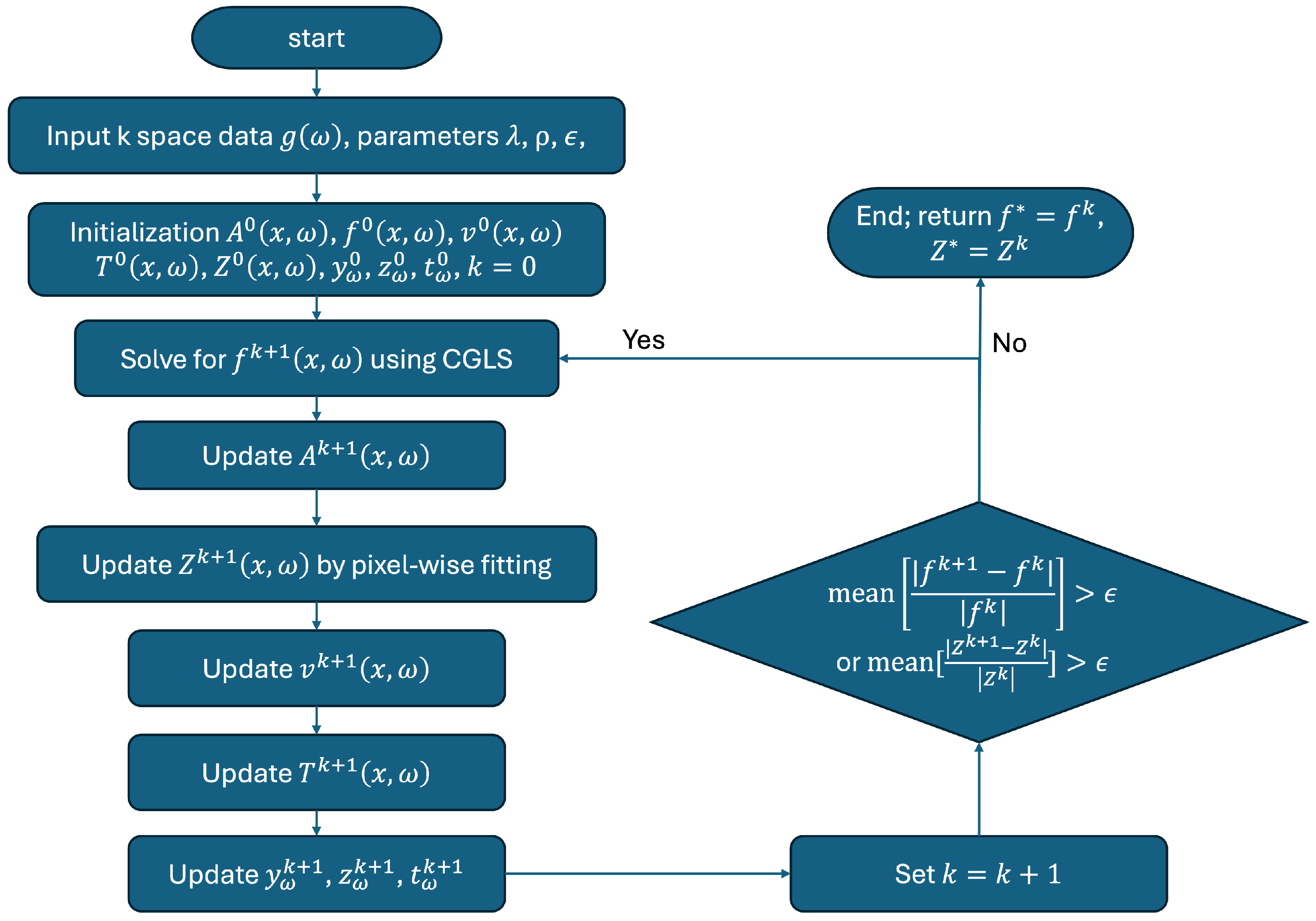
2.2. Numerical Algorithm and Implementation
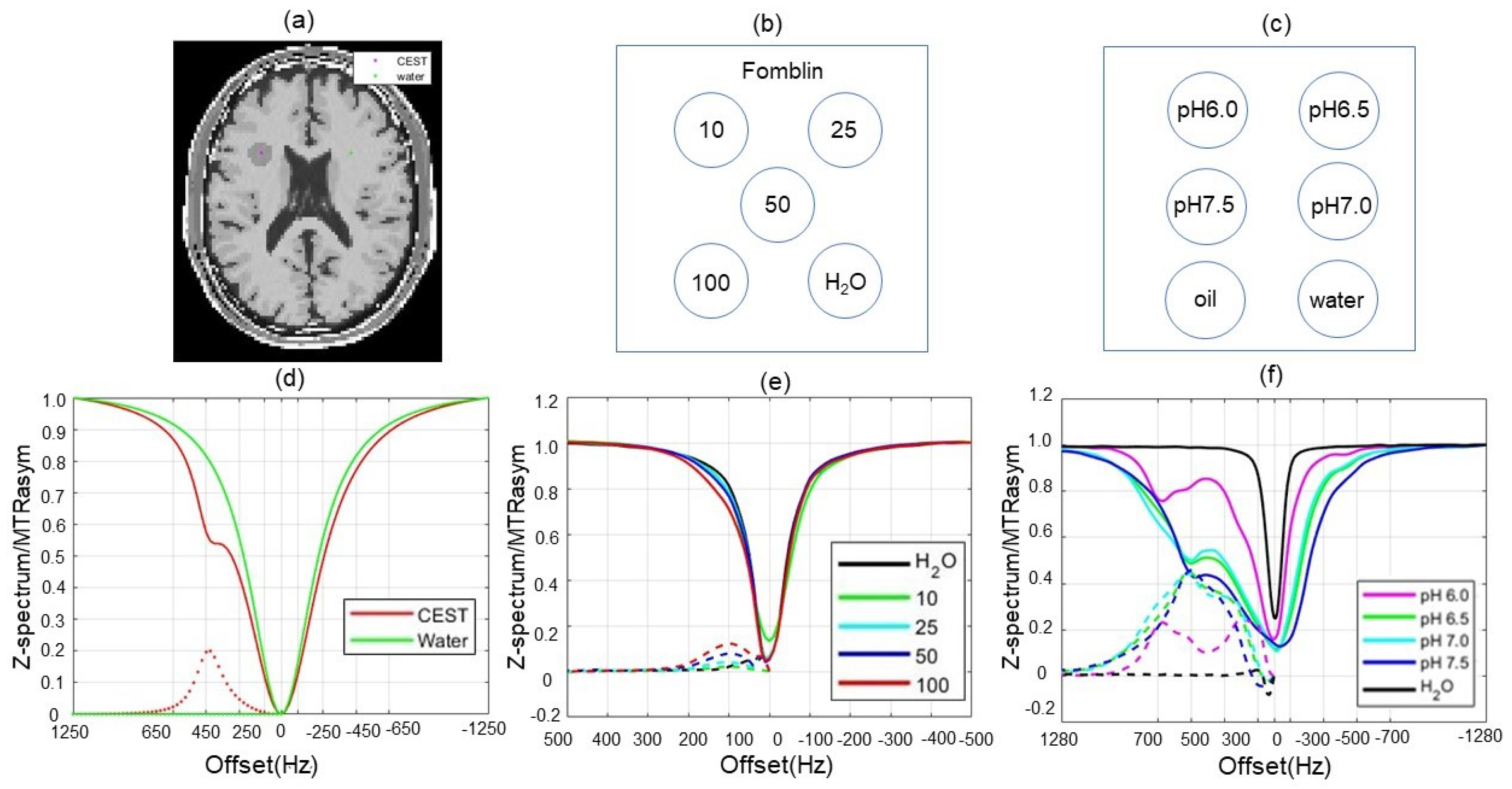
2.3. Evaluations
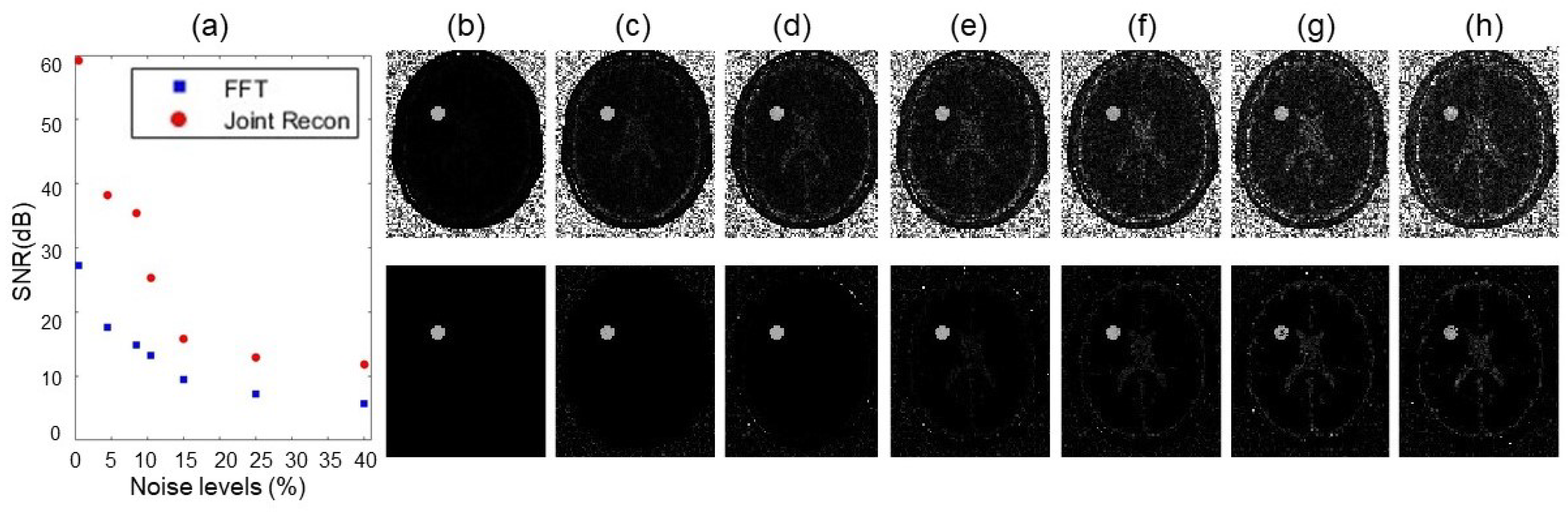
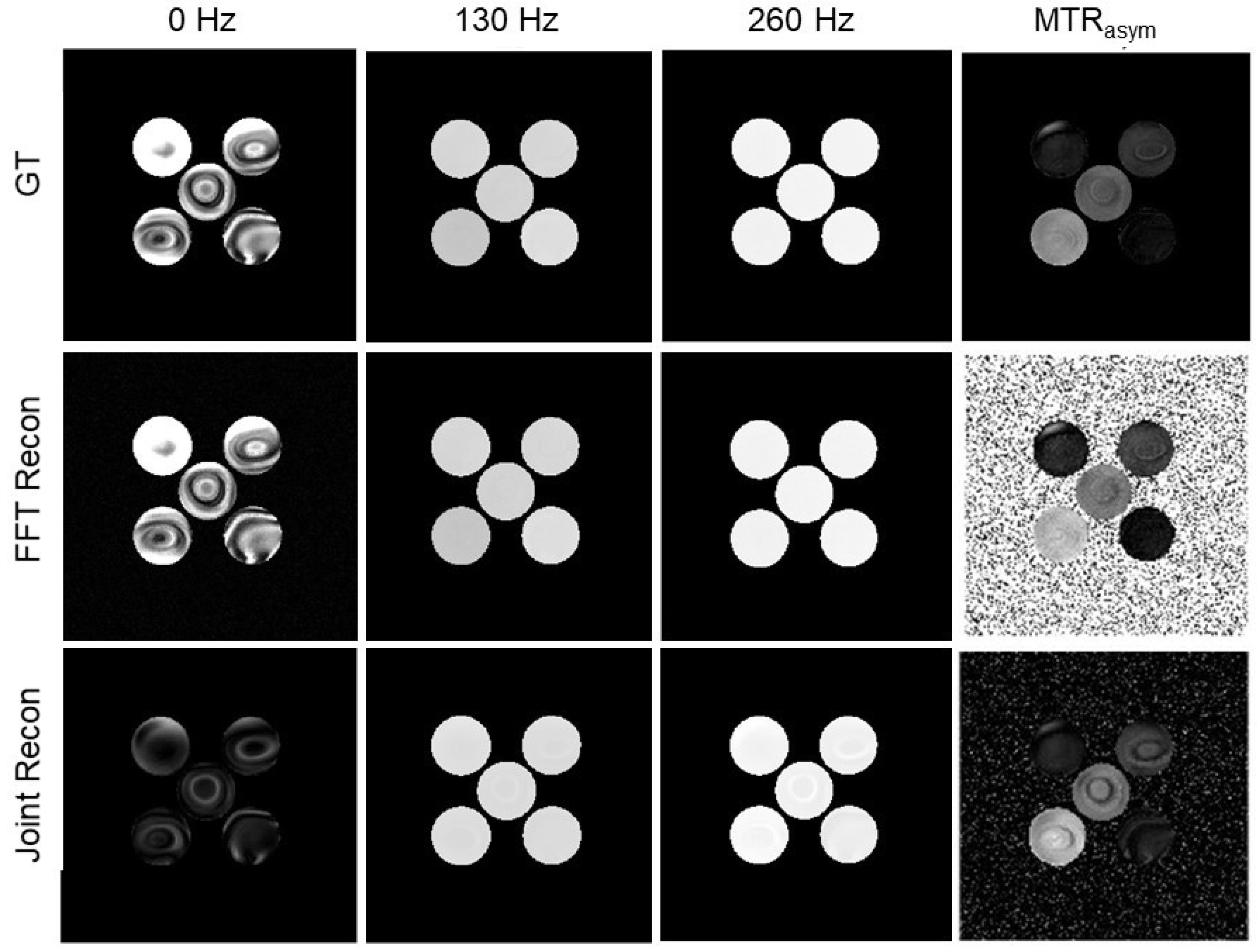
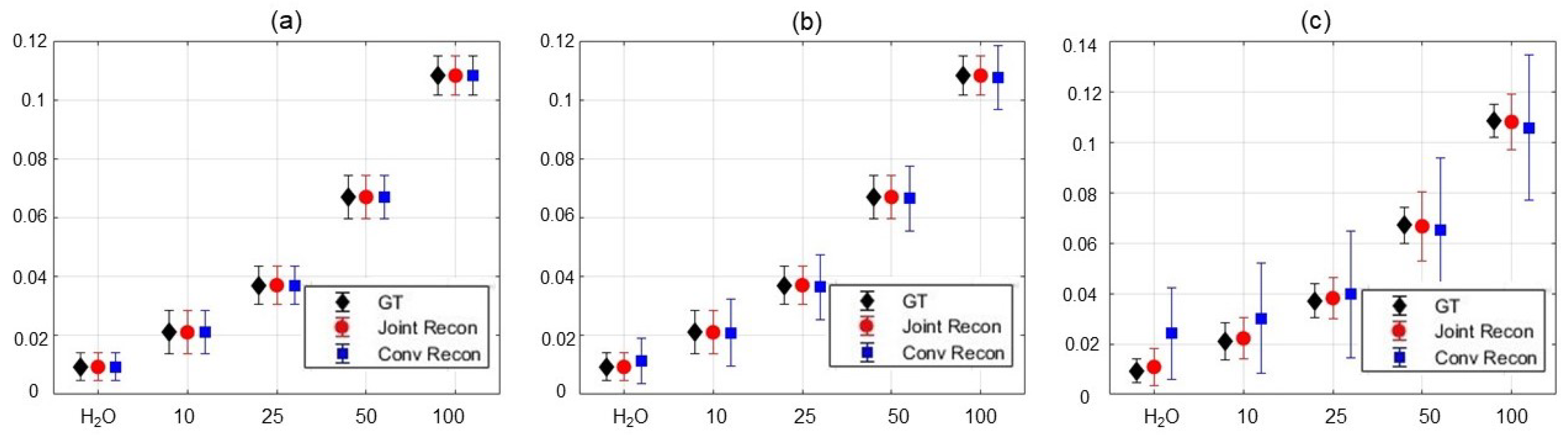
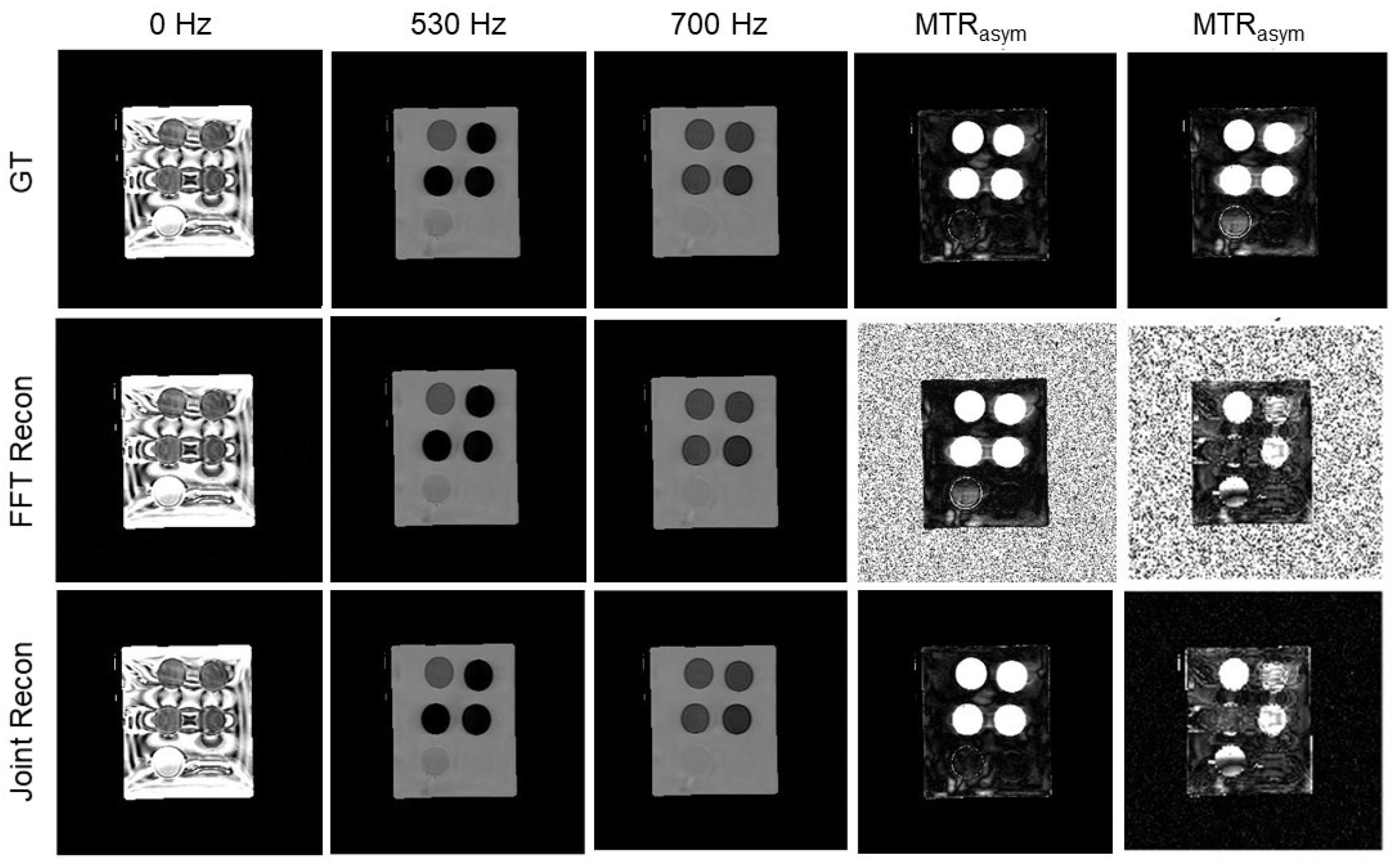
3. Results
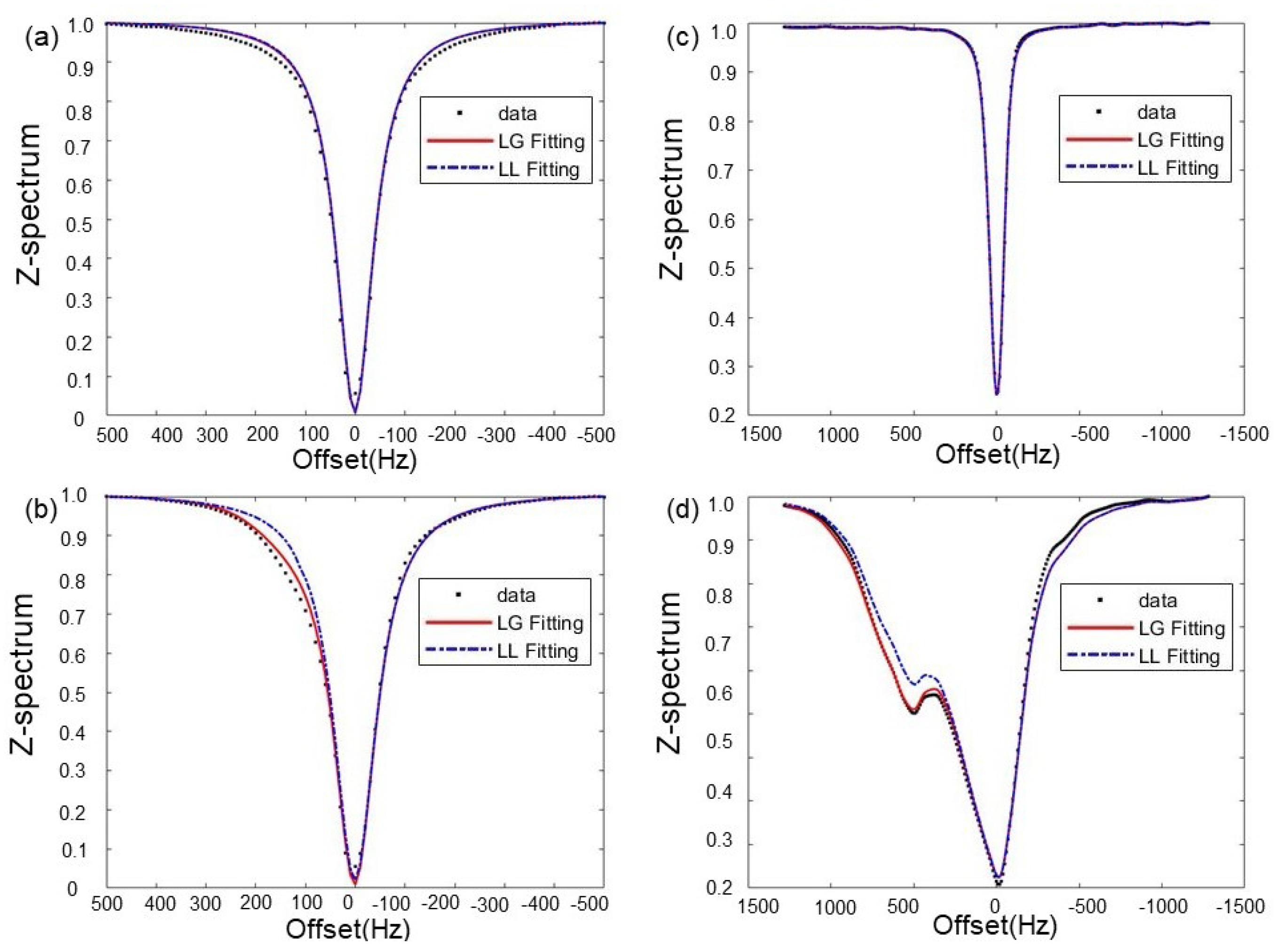
3.1. Choice of Fitting Functions
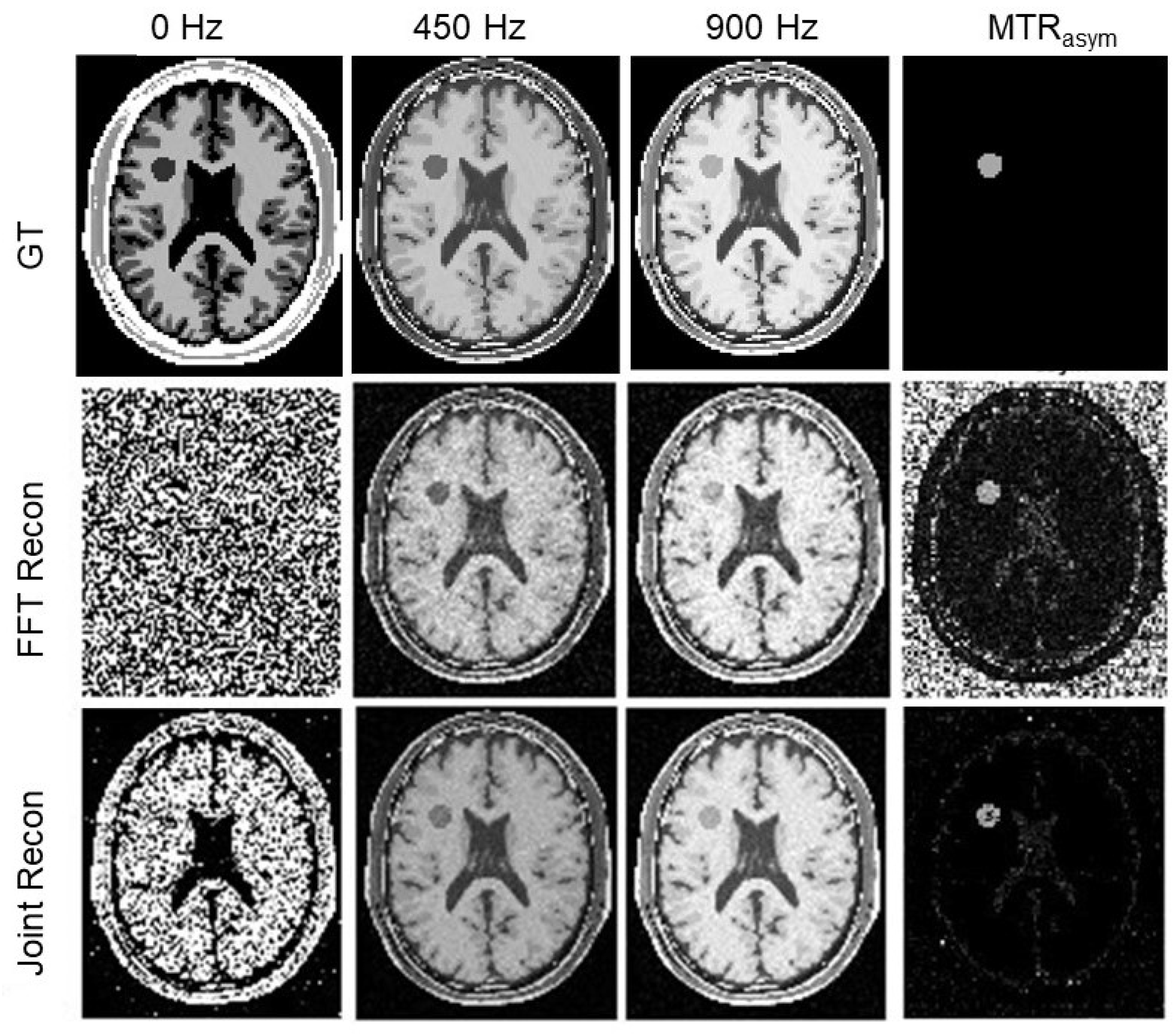
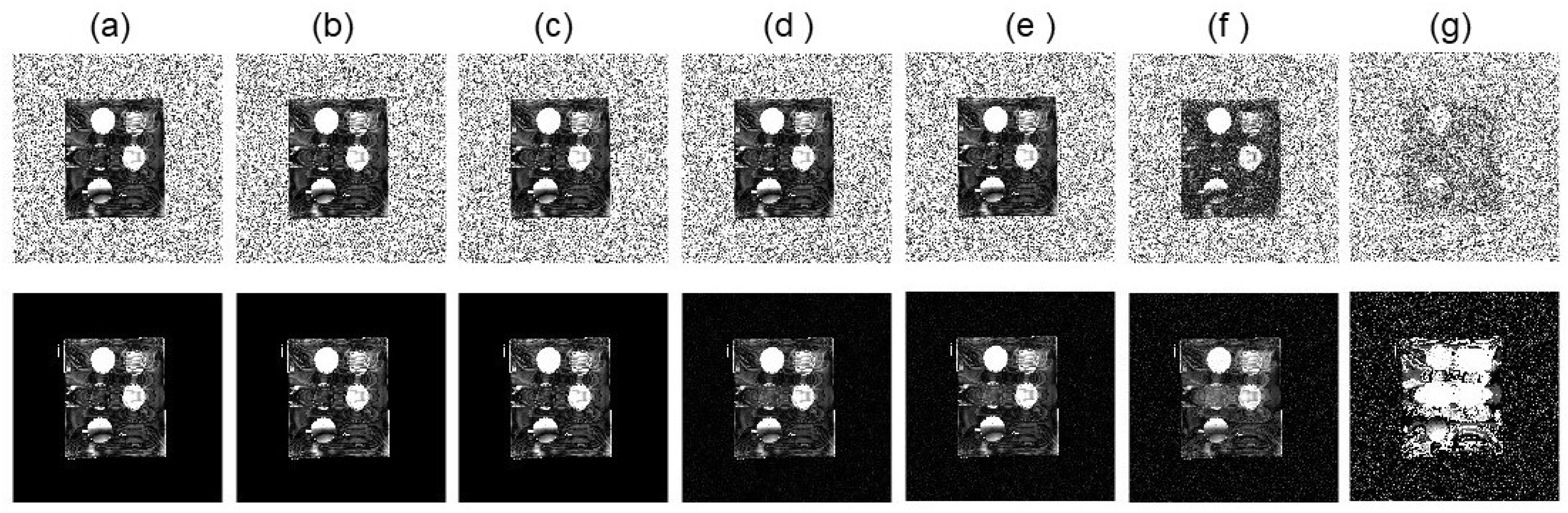
3.2. Numerical Simulations
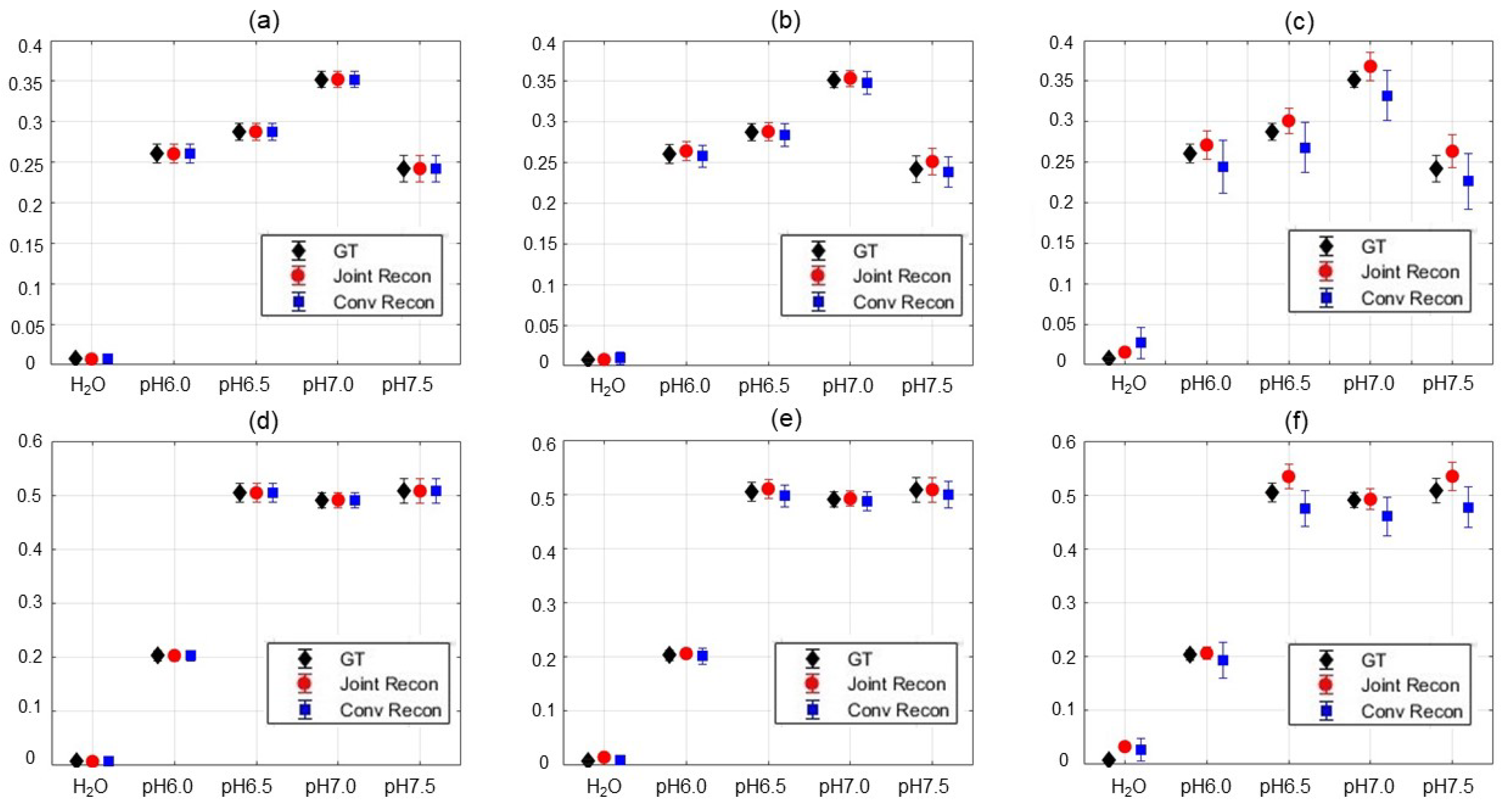
3.3. Results of Choline Phantom Case
3.4. Results of Iopamidol Phantom Case
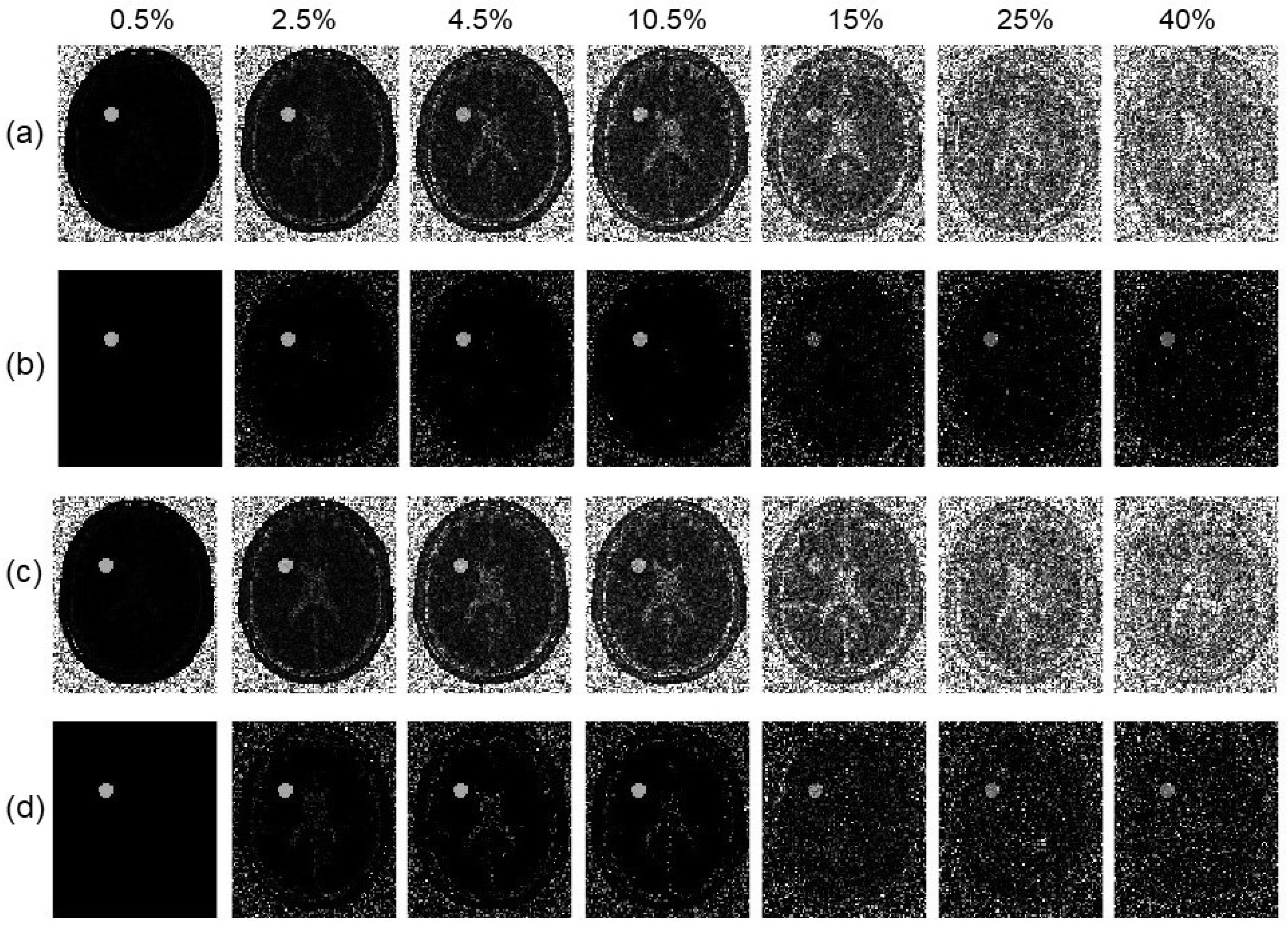
3.5. Reduction in Number of Offset Frequencies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ward, K.; Aletras, A.; Balaban, R.S. A new class of contrast agents for MRI based on proton chemical exchange dependent saturation transfer (CEST). J. Magn. Reson. 2000, 143, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Lal, B.; Wilson, D.A.; Laterra, J.; Van Zijl, P.C. Amide proton transfer (APT) contrast for imaging of brain tumors. Magn. Reson. Med. Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2003, 50, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagher, A.P.; Aletras, A.; Choyke, P.; Balaban, R.S. Imaging of urea using chemical exchange-dependent saturation transfer at 1.5 T. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2000, 12, 745–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, K.M.; Pollard, A.C.; Pagel, M.D. Clinical applications of chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 47, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Z.; Hu, S.; Huang, F.; Wang, X.; Guo, L.; Quan, X.; Wang, S.; Zhou, J. MR imaging of high-grade brain tumors using endogenous protein and peptide-based contrast. Neuroimage 2010, 51, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.K.; Schlosser, M.J.; Van Zijl, P.C.; Pomper, M.G.; Golay, X.; Zhou, J. Amide proton transfer imaging of human brain tumors at 3 T. Magn. Reson. Med. Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2006, 56, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.Z.; Benner, T.; Kumar, A.; Sorensen, A.G. Investigation of optimizing and translating pH-sensitive pulsed-chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) imaging to a 3T clinical scanner. Magn. Reson. Med. Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2008, 60, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Hong, X.; Chang, C.F.; Li, Q.; Ma, B.; Zhang, H.; Xiang, S.; Heo, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lee, D.H.; et al. Simultaneous detection and separation of hyperacute intracerebral hemorrhage and cerebral ischemia using amide proton transfer MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 74, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dula, A.N.; Asche, E.M.; Landman, B.A.; Welch, E.B.; Pawate, S.; Sriram, S.; Gore, J.C.; Smith, S.A. Development of chemical exchange saturation transfer at 7 T. Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 66, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dula, A.N.; Pawate, S.; Dethrage, L.M.; Conrad, B.N.; Dewey, B.E.; Barry, R.L.; Smith, S.A. Chemical exchange saturation transfer of the cervical spinal cord at 7 T. NMR Biomed. 2016, 29, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donahue, M.J.; Donahue, P.C.; Rane, S.; Thompson, C.R.; Strother, M.K.; Scott, A.O.; Smith, S.A. Assessment of lymphatic impairment and interstitial protein accumulation in patients with breast cancer treatment-related lymphedema using CEST MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016, 75, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, W.; Regatte, R.R.; Navon, G.; Jerschow, A. Assessment of glycosaminoglycan concentration in vivo by chemical exchange-dependent saturation transfer (gagCEST). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2266–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, B.; Zbỳň, Š.; Stelzeneder, D.; Jellus, V.; Paul, D.; Lauer, L.; Bachert, P.; Trattnig, S. Cartilage quality assessment by using glycosaminoglycan chemical exchange saturation transfer and 23Na MR imaging at 7 T. Radiology 2011, 260, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.Z.; Zhou, J.; Huang, J.; Van Zijl, P. Simplified quantitative description of amide proton transfer (APT) imaging during acute ischemia. Magn. Reson. Med. Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2007, 57, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.Z.; Sorensen, A.G. Imaging pH using the chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI: Correction of concomitant RF irradiation effects to quantify CEST MRI for chemical exchange rate and pH. Magn. Reson. Med. Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2008, 60, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, K.A.; Nanga, R.P.R.; Das, S.; Chen, S.H.; Hadar, P.N.; Pollard, J.R.; Lucas, T.H.; Shinohara, R.T.; Litt, B.; Hariharan, H.; et al. Glutamate imaging (GluCEST) lateralizes epileptic foci in nonlesional temporal lobe epilepsy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 309ra161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, R.G. The dynamics of water-protein interactions. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 1996, 25, 29–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zijl, P.C.; Yadav, N.N. Chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST): What is in a name and what isn’t? Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 65, 927–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; van Zijl, P.C. Chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging and spectroscopy. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2006, 48, 109–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmond, K.L.; Moosvi, F.; Stanisz, G.J. Mapping of amide, amine, and aliphatic peaks in the CEST spectra of murine xenografts at 7 T. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 71, 1841–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, K.; Singh, A.; Poptani, H.; Li, W.; Yang, S.; Lu, Y.; Hariharan, H.; Zhou, X.J.; Reddy, R. CEST signal at 2 ppm (CEST@ 2ppm) from Z-spectral fitting correlates with creatine distribution in brain tumor. NMR Biomed. 2015, 28, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Lee, D.H.; Zhou, J. Quantitative assessment of amide proton transfer (APT) and nuclear overhauser enhancement (NOE) imaging with extrapolated semisolid magnetization transfer reference (EMR) signals: II. Comparison of three EMR models and application to human brain glioma at 3 Tesla. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016, 75, 1630–1639. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zaiß, M.; Schmitt, B.; Bachert, P. Quantitative separation of CEST effect from magnetization transfer and spillover effects by Lorentzian-line-fit analysis of z-spectra. J. Magn. Reson. 2011, 211, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Chung, J.J.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.G.; Han, J.H.; Park, J. Model-based chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI for robust z-spectrum analysis. IEEE Trans. Med Imaging 2019, 39, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, H.; Greer, J.S.; Zhang, S.; Li, B.; Keupp, J.; Madhuranthakam, A.J.; Dimitrov, I.E.; Lenkinski, R.E.; Vinogradov, E. Accelerating chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI with parallel blind compressed sensing. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 81, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lee, D.H.; Jiang, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, J. Accelerating chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI by combining compressed sensing and sensitivity encoding techniques. Magn. Reson. Med. 2017, 77, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, D.; Wu, G.; Suk, H.I. Deep learning in medical image analysis. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 19, 221–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Nguyen, D.; Zhou, Z.; Jiang, S.B.; Dong, B.; Jia, X. An introduction to deep learning in medical physics: Advantages, potential, and challenges. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 05TR01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, C.M.; Kim, H.P.; Lee, S.M.; Lee, S.; Seo, J.K. Deep learning for undersampled MRI reconstruction. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 135007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glang, F.; Deshmane, A.; Prokudin, S.; Martin, F.; Herz, K.; Lindig, T.; Bender, B.; Scheffler, K.; Zaiss, M. DeepCEST 3T: Robust MRI parameter determination and uncertainty quantification with neural networks—Application to CEST imaging of the human brain at 3T. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 84, 450–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Wu, J.; Rosenberg, J.T.; Roussel, T.; Cai, S.; Cai, C. Fast chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging based on PROPELLER acquisition and deep neural network reconstruction. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 84, 3192–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zu, T.; Hsu, Y.C.; Wang, X.; Chan, K.W.; Zhang, Y. Accelerating CEST imaging using a model-based deep neural network with synthetic training data. Magn. Reson. Med. 2024, 91, 583–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Zhang, X.; Tang, H.; Huang, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhuang, C.; Chen, B.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Yan, G.; et al. Deep learning for dense Z-spectra reconstruction from CEST images at sparse frequency offsets. Front. Neurosci. 2024, 17, 1323131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamilov, U.S.; Bouman, C.A.; Buzzard, G.T.; Wohlberg, B. Plug-and-play methods for integrating physical and learned models in computational imaging: Theory, algorithms, and applications. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2023, 40, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabov, K.; Foi, A.; Katkovnik, V.; Egiazarian, K. Image denoising by sparse 3-D transform-domain collaborative filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2007, 16, 2080–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, S.; Parikh, N.; Chu, E.; Peleato, B.; Eckstein, J. Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers. Found. Trends Mach. Learn. 2011, 3, 1–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Velikina, J.V.; Block, W.F.; Kijowski, R.; Samsonov, A.A. Fast Realistic MRI Simulations Based on Generalized Multi-Pool Exchange Tissue Model. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandinetti, J.; Gao, Y.; Gonzalez, Y.; Deng, J.; Shen, C.; Jia, X. MR image reconstruction from undersampled data for image-guided radiation therapy using a patient-specific deep manifold image prior. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1013783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Ren, L.; Cai, J. Clinical implementation of AI technologies will require interpretable AI models. Med. Phys. 2020, 47, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, Y.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, S.; Deng, J.; Jia, X. Joint k-ω Space Image Reconstruction and Data Fitting for Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Tomography 2024, 10, 1123-1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10070085
Peng Y, Dai Y, Zhang S, Deng J, Jia X. Joint k-ω Space Image Reconstruction and Data Fitting for Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Tomography. 2024; 10(7):1123-1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10070085
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Yuting, Yan Dai, Shu Zhang, Jie Deng, and Xun Jia. 2024. "Joint k-ω Space Image Reconstruction and Data Fitting for Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer Magnetic Resonance Imaging" Tomography 10, no. 7: 1123-1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10070085
APA StylePeng, Y., Dai, Y., Zhang, S., Deng, J., & Jia, X. (2024). Joint k-ω Space Image Reconstruction and Data Fitting for Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Tomography, 10(7), 1123-1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10070085






