Three-Dimensional Visualization of Shunt Valves with Photon Counting CT and Comparison to Traditional X-ray in a Simple Phantom Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
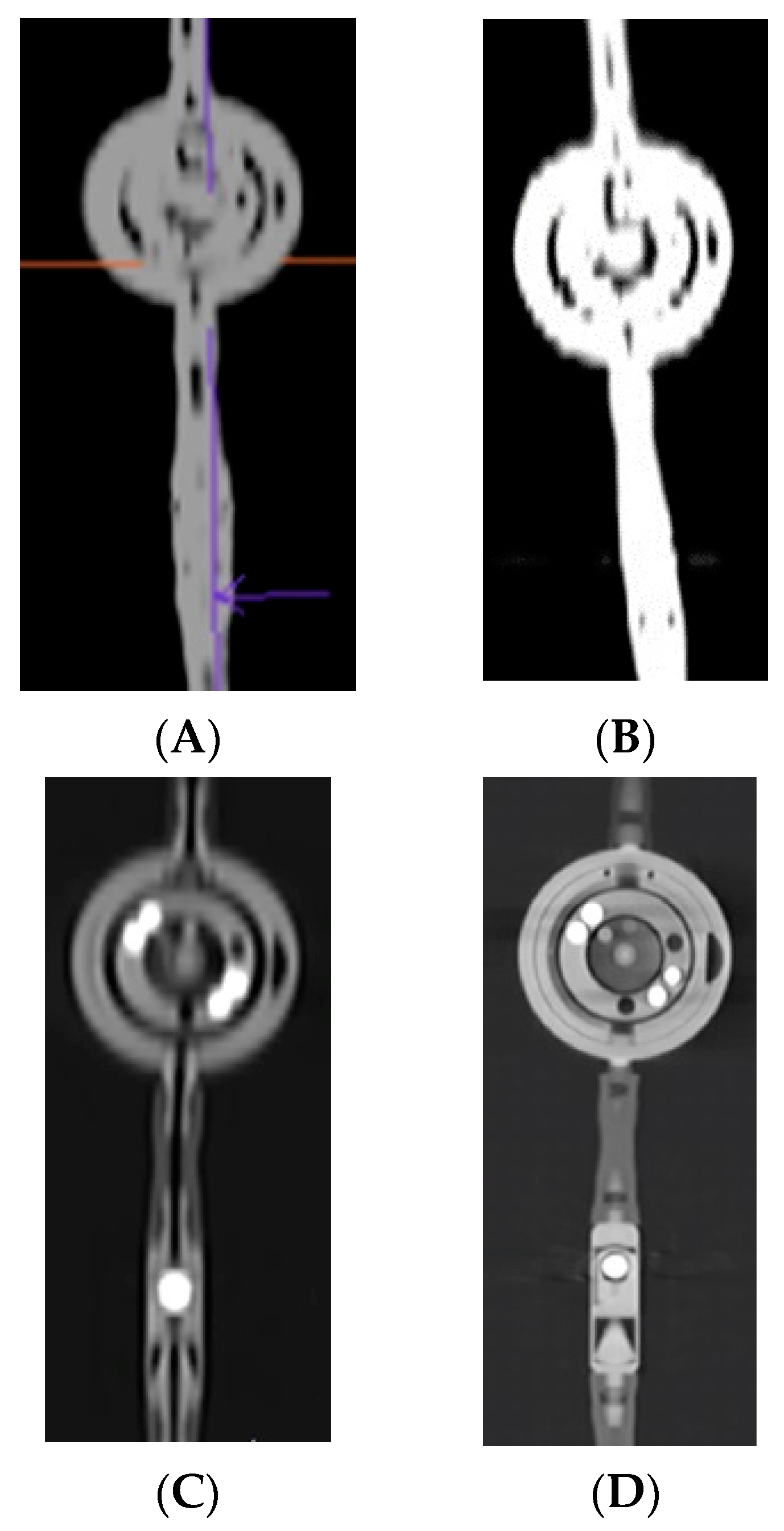
2.1. Three-Dimensional Visualisation
CT Scanners
2.2. Comparative Analysis with X-ray to Scrutinize the Feasibility and Efficacy of PC CT in the Assessment of Shunt Valve Adjustments
2.2.1. X-ray
2.2.2. Photon Counting Computer Tomography
2.2.3. Observer Readings and Levels of Confidence
2.2.4. Statistical Analysis
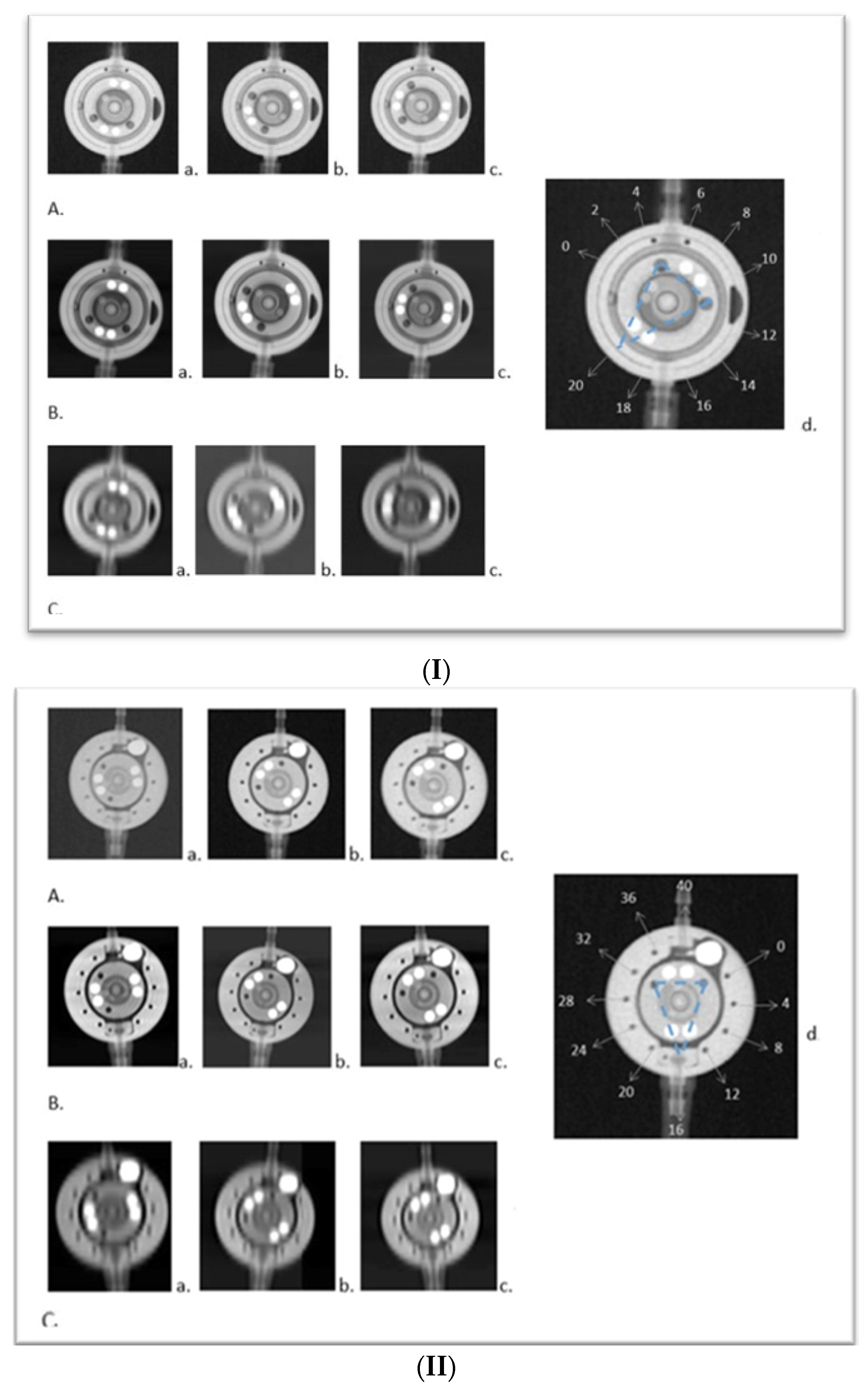
3. Results
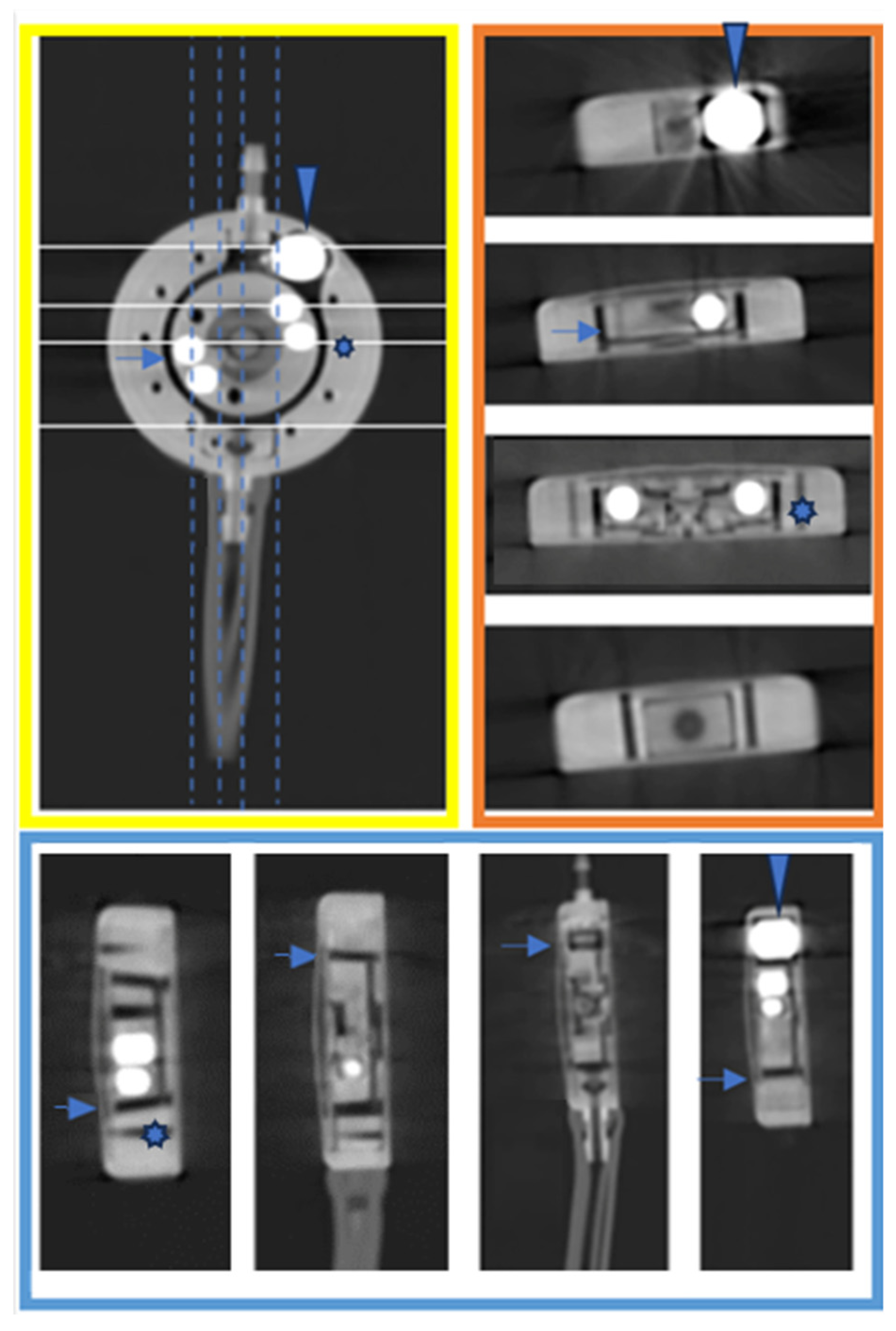
3.1. Three-Dimensional Visualisation
3.2. Comparative Analysis with X-ray to Scrutinize the Feasibility and Efficacy of PC CT in the Assessment of Shunt Valve Adjustments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsermoulas, G.; Thant, K.Z.; Byrne, M.E.; Whiting, J.L.; White, A.M.; Sinclair, A.J.; Mollan, S.P. The Birmingham Standardized Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension Shunt Protocol: Technical Note. World Neurosurg. 2022, 167, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, B.J.; Gillespie, C.S.; Hennigan, D.; Bagga, V.; Mallucci, C.; Pettorini, B. Efficacy and safety of the Miethke programmable differential pressure valve (proGAV®2.0): A single-centre retrospective analysis. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2021, 37, 2605–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donzelli, M. NURS-07. Programmable VP Shunts: Indications, safety and warnings. Neuro Oncol. 2018, 20 (Suppl. S2), i152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lollis, S.S.; Mamourian, A.C.; Vaccaro, T.J.; Duhaime, A.C. Programmable CSF shunt valves: Radiographic identification and interpretation. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2010, 31, 1343–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleipman, A.R.; Bailey, N.O. Programmable shunt radiography. Radiol. Technol. 2001, 73, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Slonimsky, E.; Zacharia, B.; Mamourian, A. Determination of Programmable Shunt Setting Using CT: Feasibility Study. Cureus 2021, 22, e19818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 58. Jahrestagung der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Neuroradiologie e.V. und 30. Jahrestagung der Österreichischen Gesellschaft für Neuroradiologie e.V. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2023, 33 (Suppl. S1), 1–140. [CrossRef]
- Byl, A.; Klein, L.; Sawall, S.; Heinze, S.; Schlemmer, H.P.; Kachelrieß, M. Photon-counting normalized metal artifact reduction (NMAR) in diagnostic CT. Med. Phys. 2021, 48, 3572–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esquivel, A.; Ferrero, A.; Mileto, A.; Baffour, F.; Horst, K.; Rajiah, P.S.; Inoue, A.; Leng, S.; McCollough, C.; Fletcher, J.G. Photon-Counting Detector CT: Key Points Radiologists Should Know. Korean J. Radiol. 2022, 23, 854–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, F.; Schubert, T.; Winklhofer, S. Advanced Neuroimaging with Photon-Counting Detector CT. Investig. Radiol. 2023, 58, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkadhi, H.; Runge, V. The Future Arrived: Photon-Counting Detector CT. Investig. Radiol. 2023, 58, 439–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lell, M.; Kachelrieß, M. Computed Tomography 2.0: New Detector Technology, AI, and Other Developments. Investig. Radiol. 2023, 58, 587–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortora, M.; Gemini, L.; D‘Iglio, I.; Ugga, L.; Spadarella, G.; Cuocolo, R. Spectral Photon-Counting Computed Tomography: A Review on Technical Principles and Clinical Applications. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chari, A.; Czosnyka, M.; Richards, H.K.; Pickard, J.D.; Czosnyka, Z.H. Hydrocephalus shunt technology: 20 years of experience from the Cambridge Shunt Evaluation Laboratory. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 120, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toma, A.K.; Tarnaris, A.; Kitchen, N.D.; Watkins, L.D. Use of the proGAV shunt valve in normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 2011, 68 (Suppl. S2), 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourmorteza, A.; Symons, R.; Reich, D.; Bagheri, M.; Cork, T.; Kappler, S.; Ulzheimer, S.; Bluemke, D. Photon-Counting CT of the Brain: In Vivo Human Results and Image-Quality Assessment. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 2257–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decramer, T.; Smeijers, S.; Vanhoyland, M.; Coudyzer, W.; Van Calenbergh, F.; van Loon, J.; De Vloo, P.; Theys, T. Computed tomography based assessment of programmable shunt valve settings. Brain Spine 2021, 6, 100003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, G.M.; Dalton, A.K.; Nicholson, C.L.; Jenkins, A.J.; Mitchell, P.B.; Cowie, C.J.A. CT scan exposure in children with ventriculo-peritoneal shunts: Single centre experience and review of the literature. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2020, 36, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehrse, E.; Klein, L.; Rotkopf, L.T.; Wagner, W.L.; Uhrig, M.; Heußel, C.P.; Ziener, C.H.; Delorme, S.; Heinze, S.; Kachelrieß, M.; et al. Photon-counting detectors in computed tomography: From quantum physics to clinical practice. Radiologe 2021, 61 (Suppl. S1), 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreisler, B. Photon counting Detectors: Concept, technical Challenges, and clinical outlook. Eur. J. Radiol. 2022, 149, 110229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettag, C.; von der Brelie, C.; Freimann, F.B.; Thomale, U.W.; Rohde, V.; Fiss, I. In vitro testing of explanted shunt valves in hydrocephalic patients with suspected valve malfunction. Neurosurg. Rev. 2022, 45, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, E.; Schaumann, A.; Pennacchietti, V.; Schulz, M.; Thomale, U.W. Retrospective single-center historical comparative study between proGAV and proGAV2.0 for surgical revision and implant duration. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2022, 38, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayer, D.R.; Kim, N.Y.; Otto, B.J.; Grayev, A.M.; Kuner, A.D. Unintended Consequences: Review of New Artifacts Introduced by Iterative Reconstruction CT Metal Artifact Reduction in Spine Imaging. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 1973–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, T.G.; Sammut, B.A.; Barber, R.F.; Pan, X.; Sidky, E.Y. Addressing CT metal artifacts using photon-counting detectors and one-step spectral CT image reconstruction. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 3021–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Layer, Y.C.; Mesropyan, N.; Kupczyk, P.A.; Luetkens, J.A.; Isaak, A.; Dell, T.; Attenberger, U.I.; Kuetting, D. Combining iterative metal artifact reduction and virtual monoenergetic images severely reduces hip prosthesis-associated artifacts in photon-counting detector CT. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldeck, S.; Overhoff, D.; Alizadeh, L.; Becker, B.V.; Port, M.; Froelich, M.F.; Brockmann, M.A.; Schumann, S.; Vogl, T.J.; Schoenberg, S.O.; et al. Photon-Counting Detector CT Virtual Monoengergetic Images for Cochlear Implant Visualization-A Head to Head Comparison to Energy-Integrating Detector CT. Tomography 2022, 8, 1642–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| EID 1 | EID 1 | PC CT 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Computed Tomography Scanner | Sensation 64 | Somatom Definition Flash | Neaotom Alfa |
| KV | 120 | 120 | 120 |
| mAs (quality ref.) | 355 | 292 | 71/25 * |
| Pitch Factor | 1.01 | 0.55 | 0.35/0.85 * |
| Collimation | 14.2 | 12 | 57.6 |
| Exposure time per rotation | 1 | 1 | 0.5 |
| CTDI | 54.99 | 54.6 | 39.5 |
| Acquisition | sequential | spiral | spiral |
| SNR | 4 | 5.9 | 7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klempka, A.; Clausen, S.; Soltane, M.I.; Ackermann, E.; Groden, C. Three-Dimensional Visualization of Shunt Valves with Photon Counting CT and Comparison to Traditional X-ray in a Simple Phantom Model. Tomography 2024, 10, 543-553. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10040043
Klempka A, Clausen S, Soltane MI, Ackermann E, Groden C. Three-Dimensional Visualization of Shunt Valves with Photon Counting CT and Comparison to Traditional X-ray in a Simple Phantom Model. Tomography. 2024; 10(4):543-553. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10040043
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlempka, Anna, Sven Clausen, Mohamed Ilyes Soltane, Eduardo Ackermann, and Christoph Groden. 2024. "Three-Dimensional Visualization of Shunt Valves with Photon Counting CT and Comparison to Traditional X-ray in a Simple Phantom Model" Tomography 10, no. 4: 543-553. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10040043
APA StyleKlempka, A., Clausen, S., Soltane, M. I., Ackermann, E., & Groden, C. (2024). Three-Dimensional Visualization of Shunt Valves with Photon Counting CT and Comparison to Traditional X-ray in a Simple Phantom Model. Tomography, 10(4), 543-553. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10040043






