Design and Optimization of an Adaptive Knee Joint Orthosis for Biomimetic Motion Rehabilitation Assistance
Abstract
1. Introduction
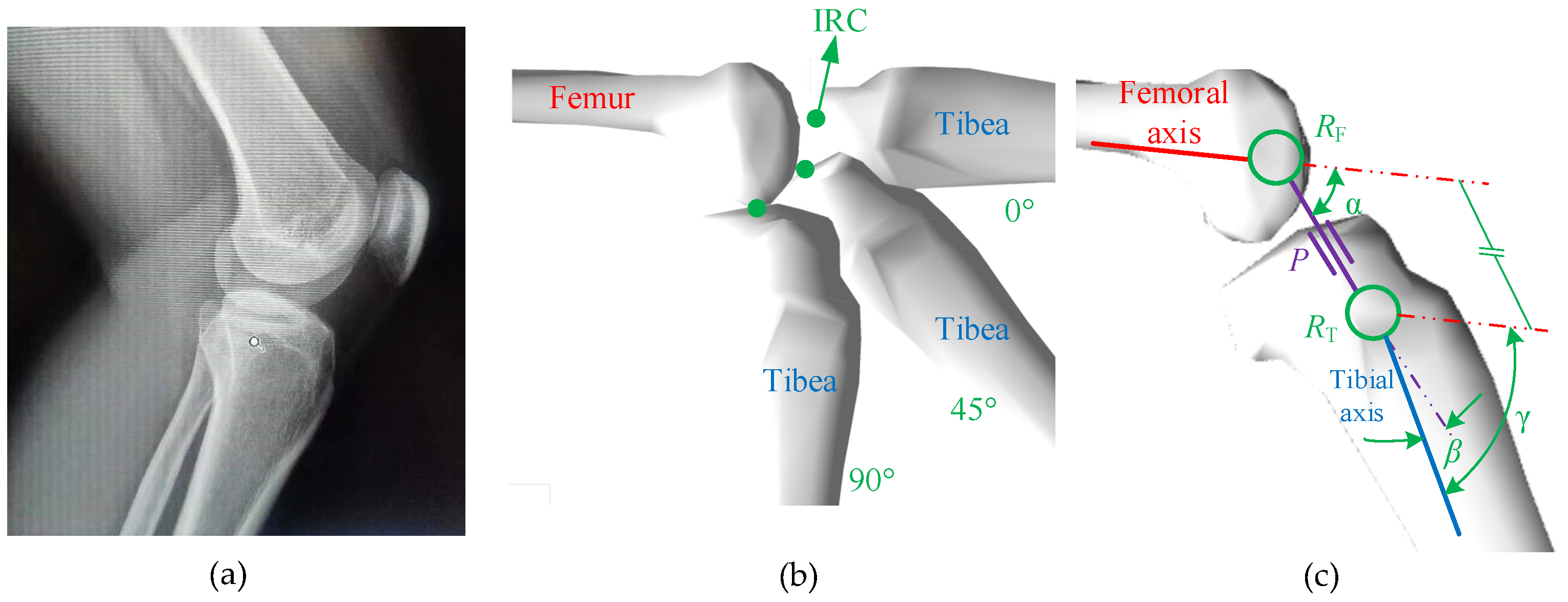
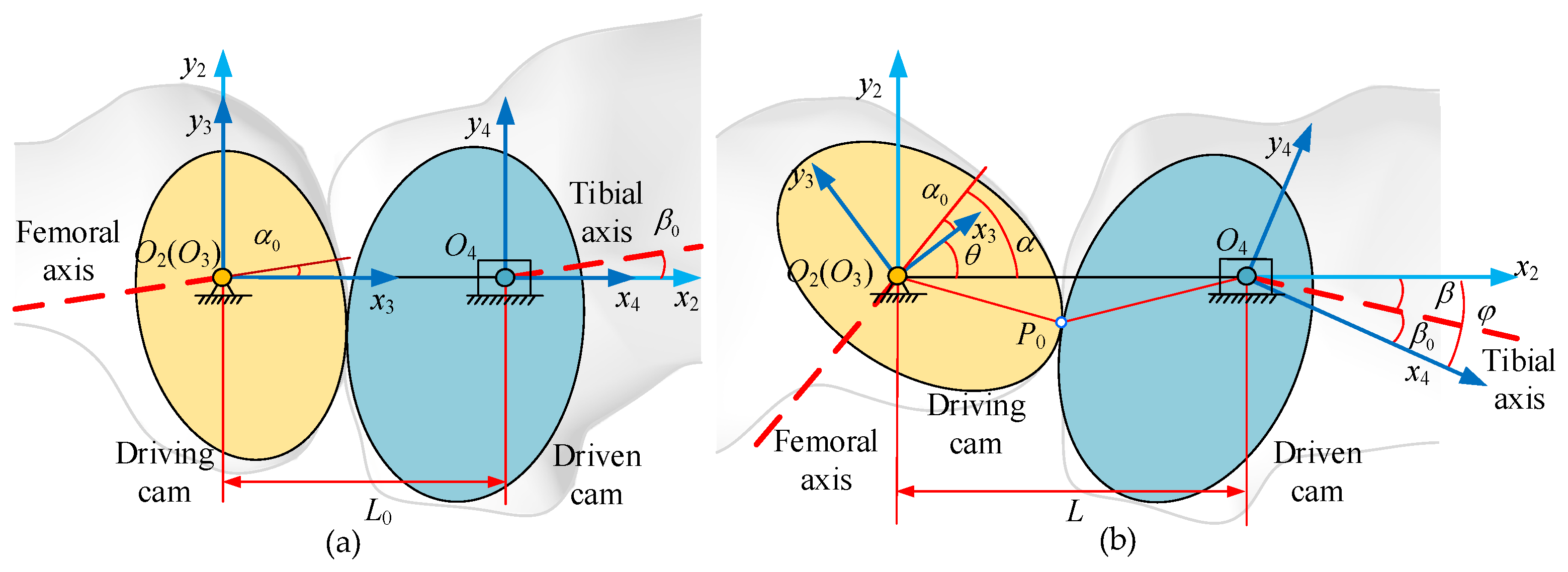
2. Analysis of Knee Joint Motion Characteristics
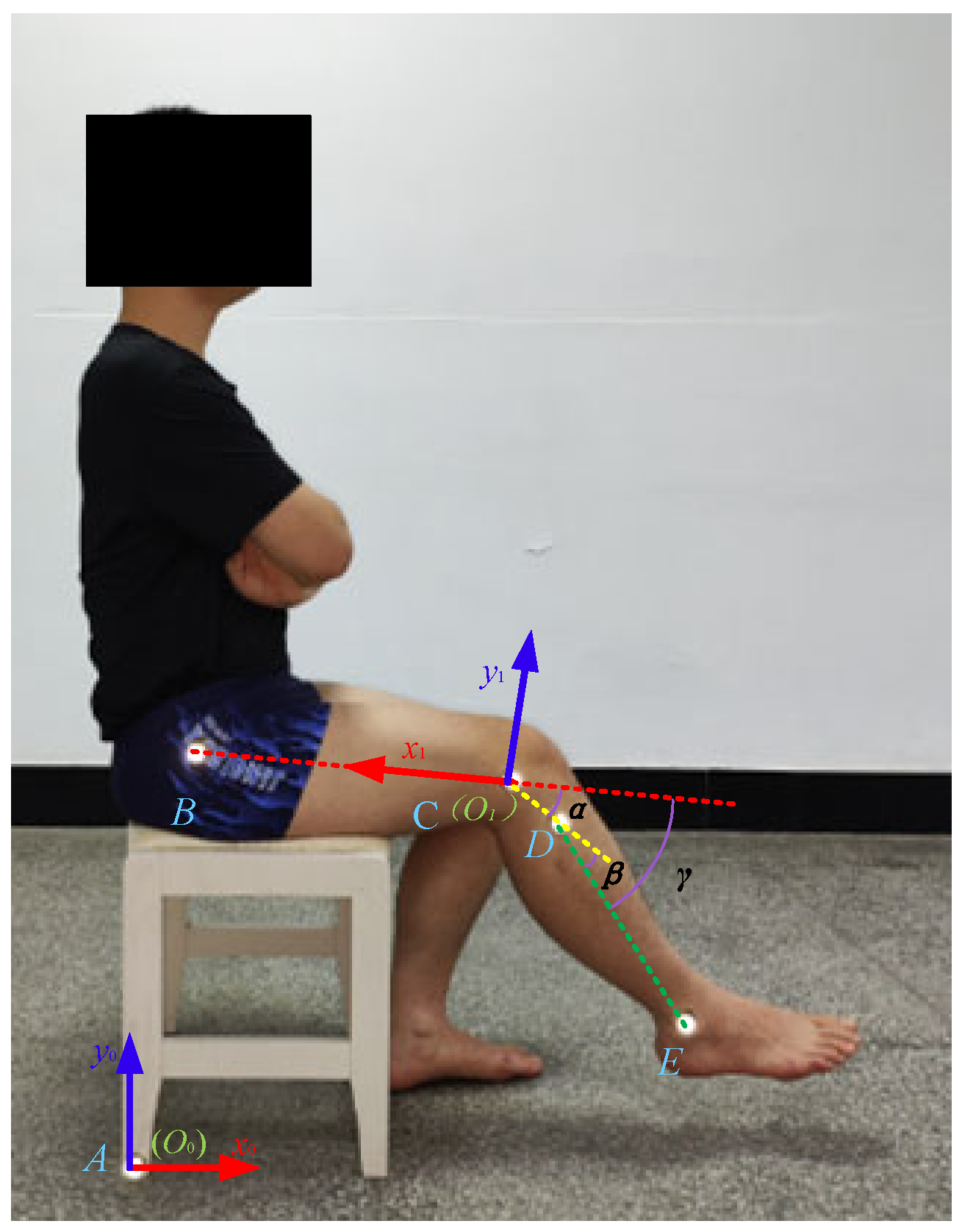
3. Knee Joint Movement Experiment
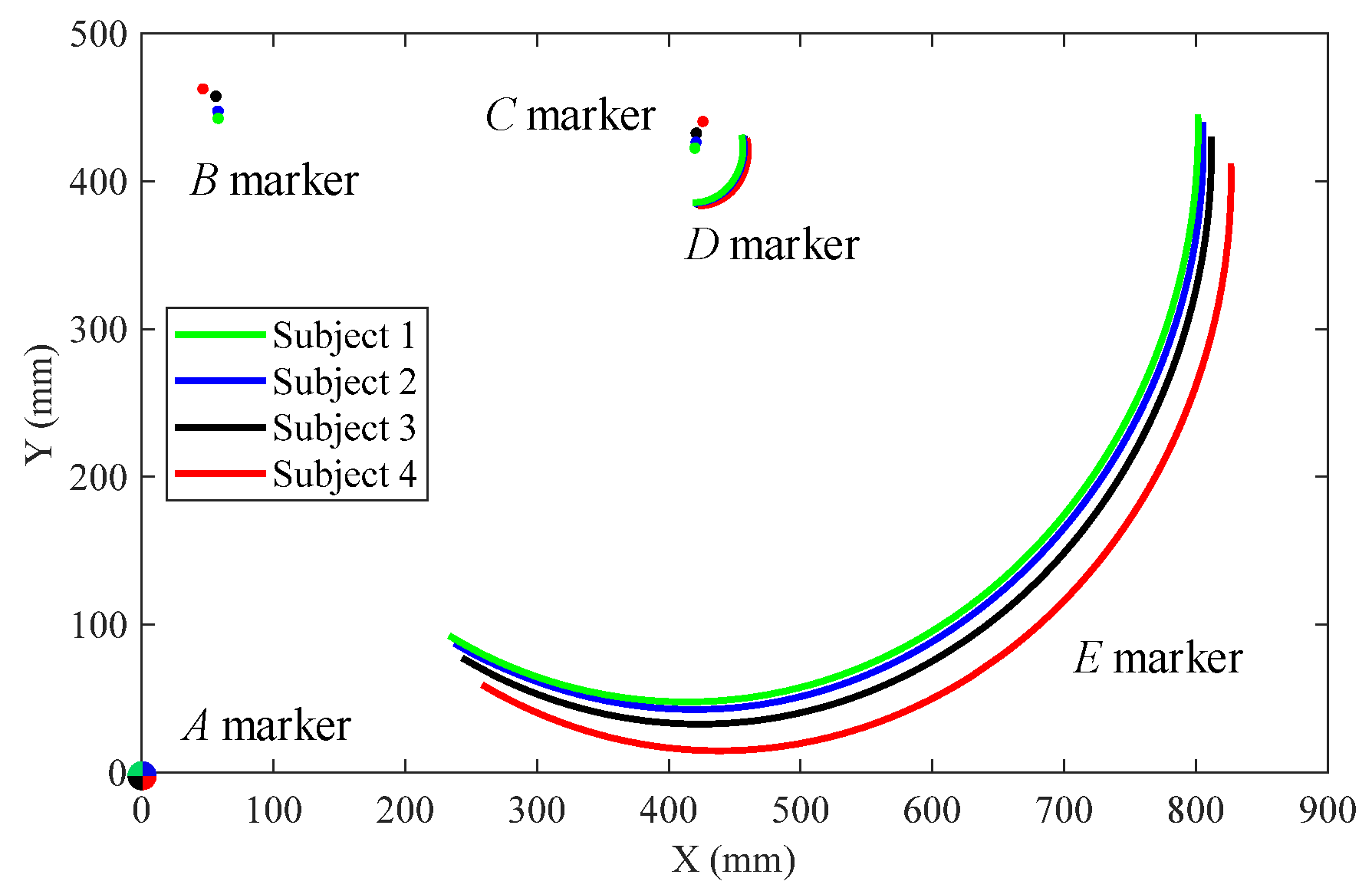
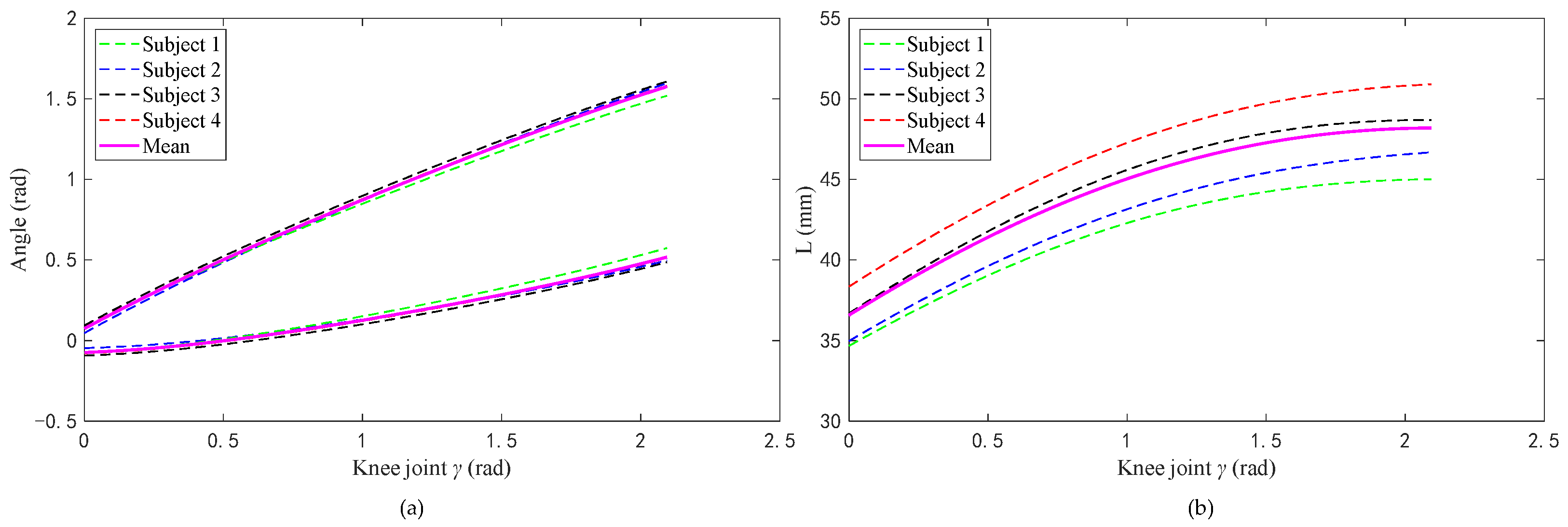
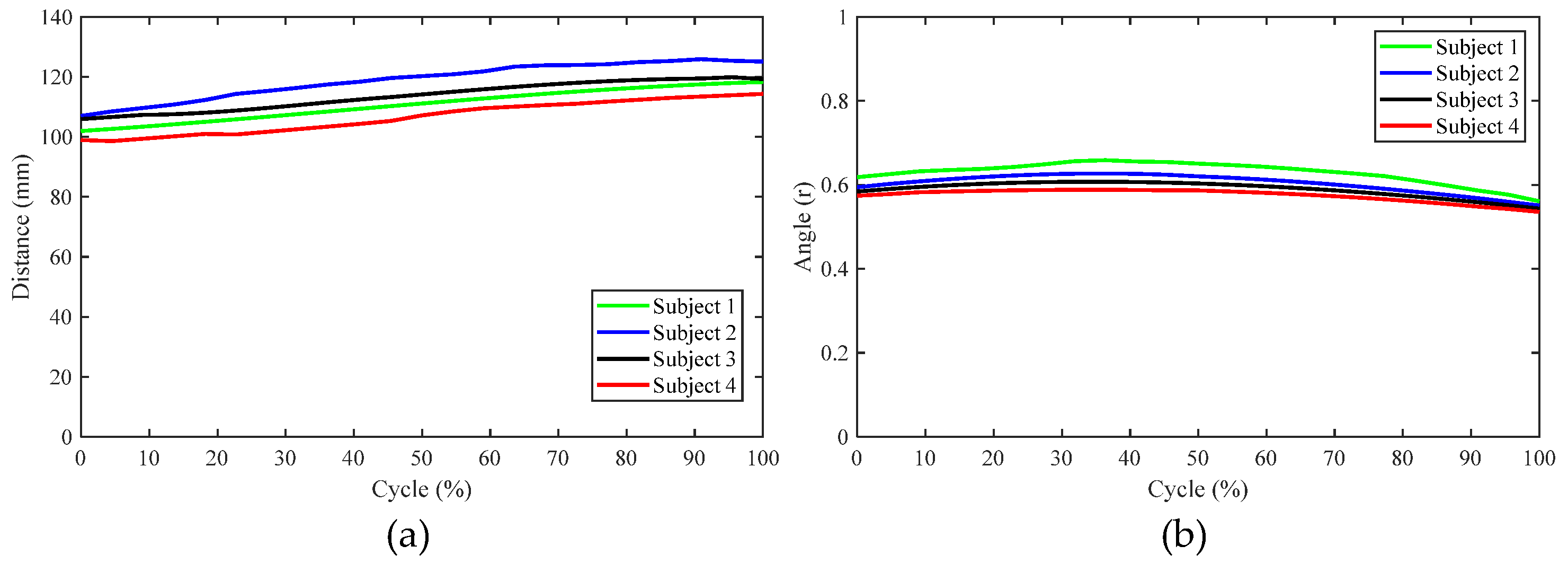
4. Experimental Results
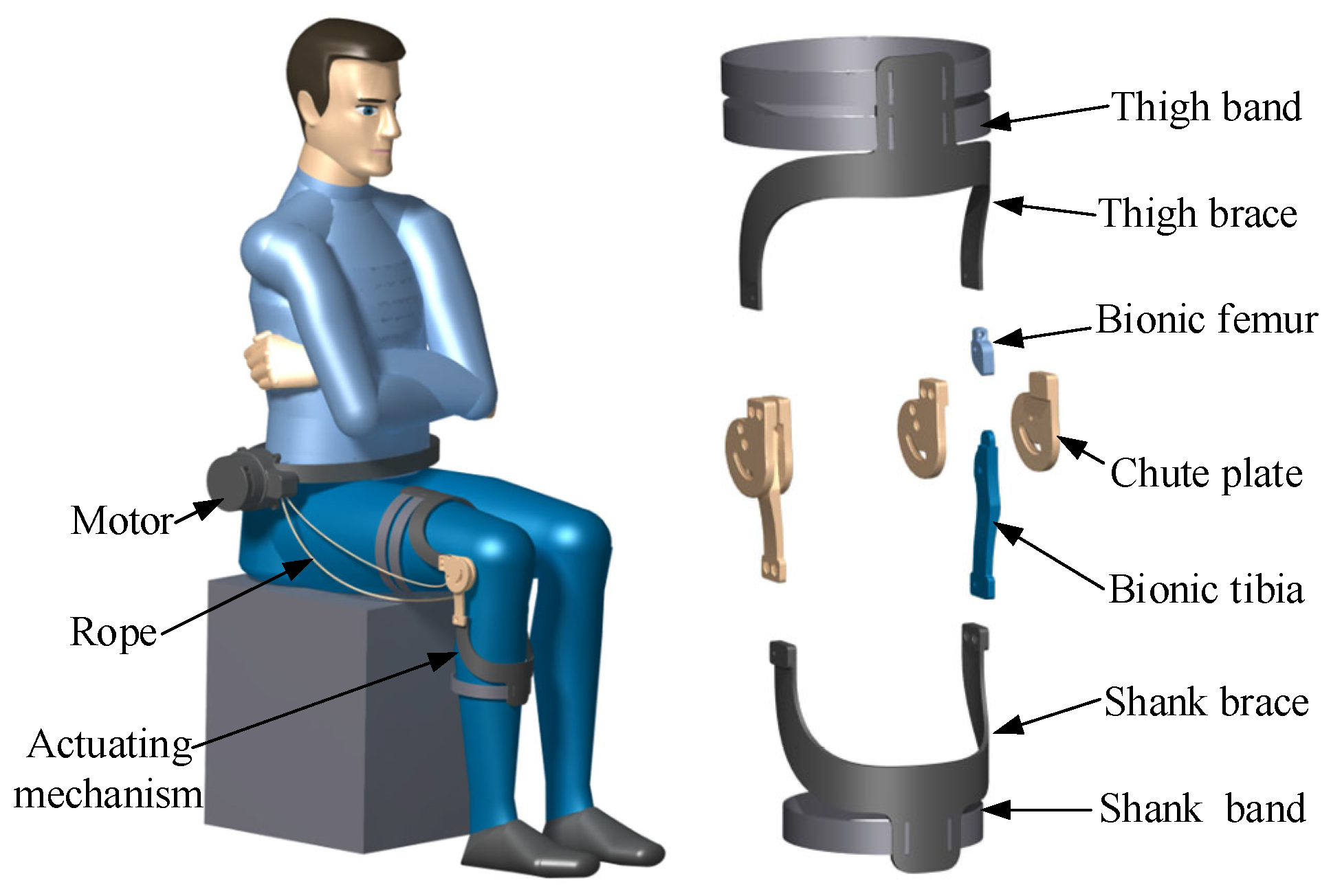
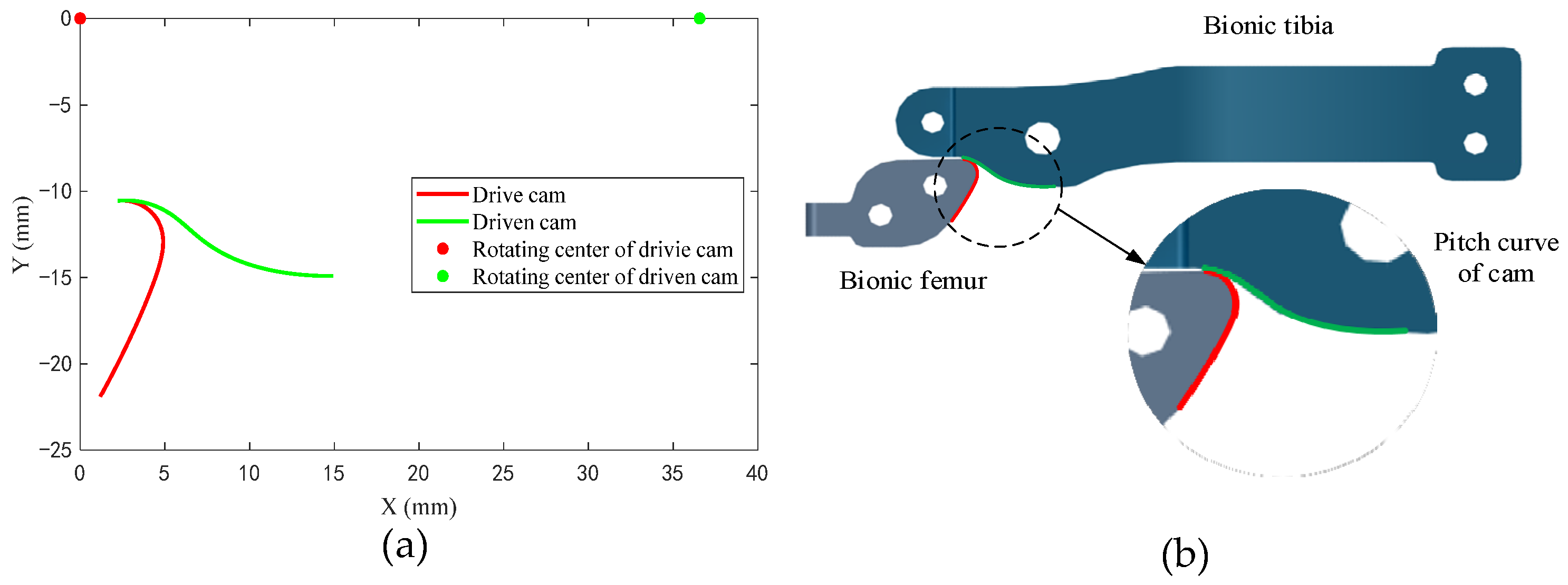
5. Characteristic Structural Design of the Knee Orthosis
6. Light Weight of the Orthosis
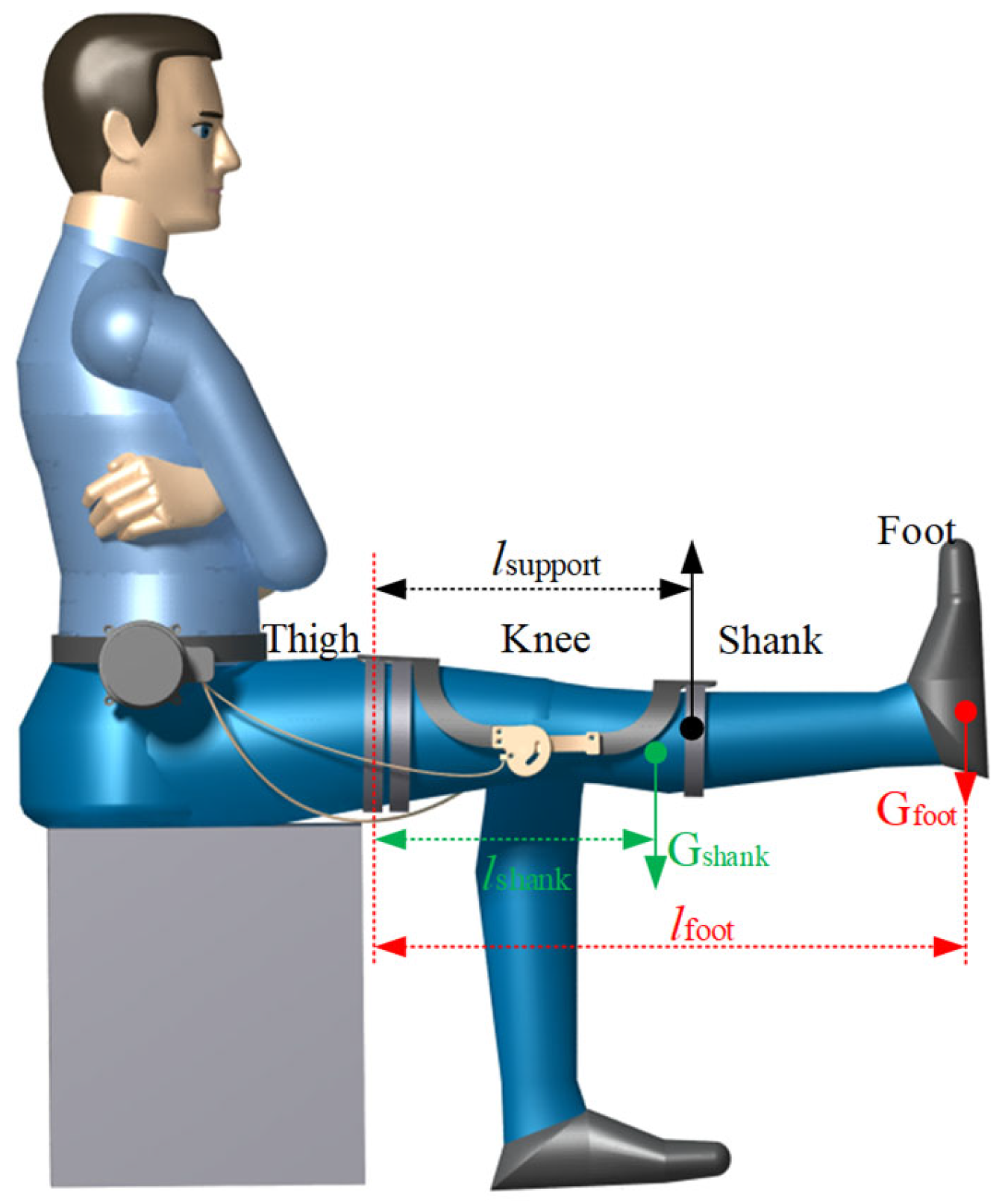
6.1. Loading in the Extreme Condition
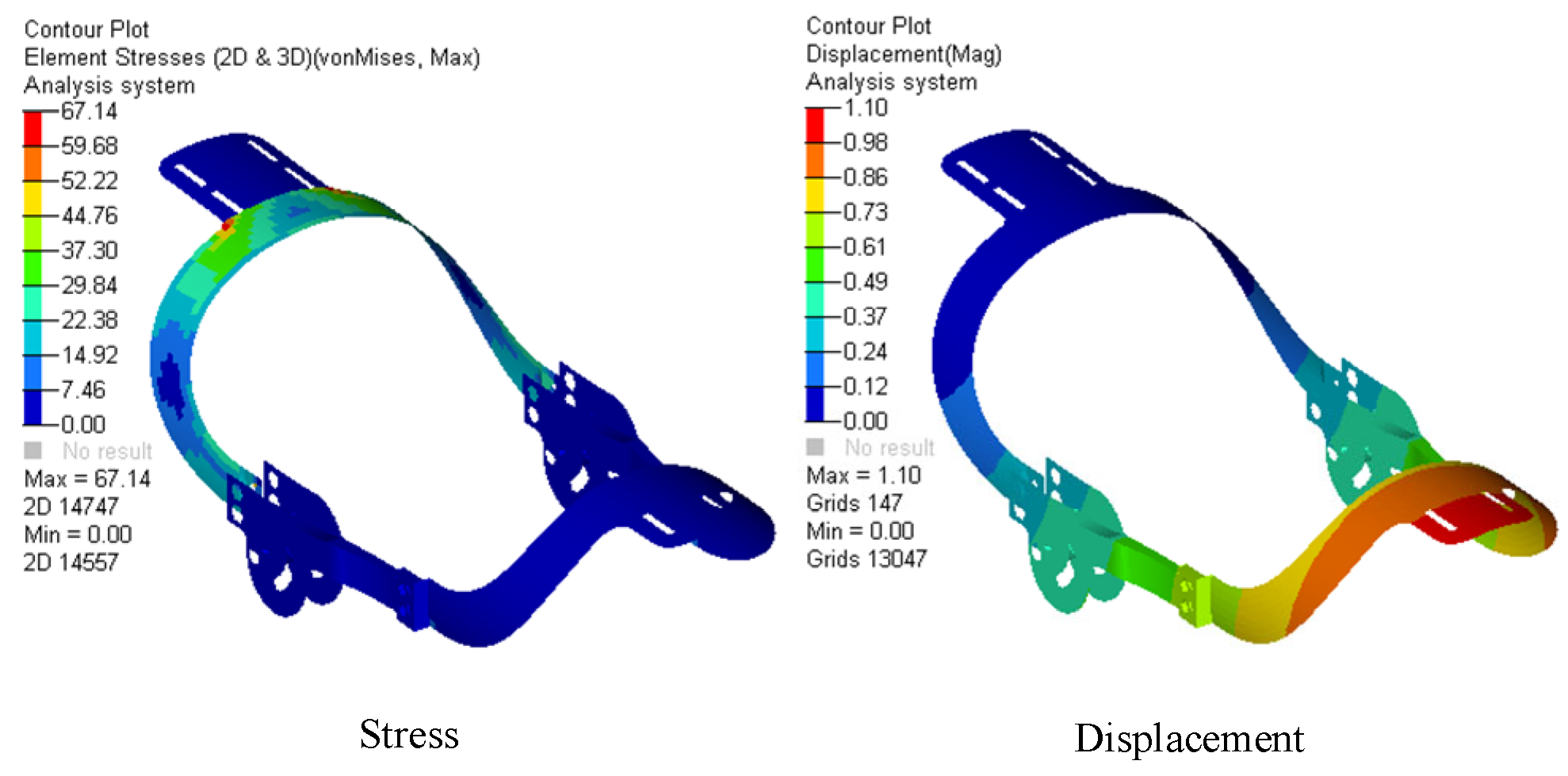
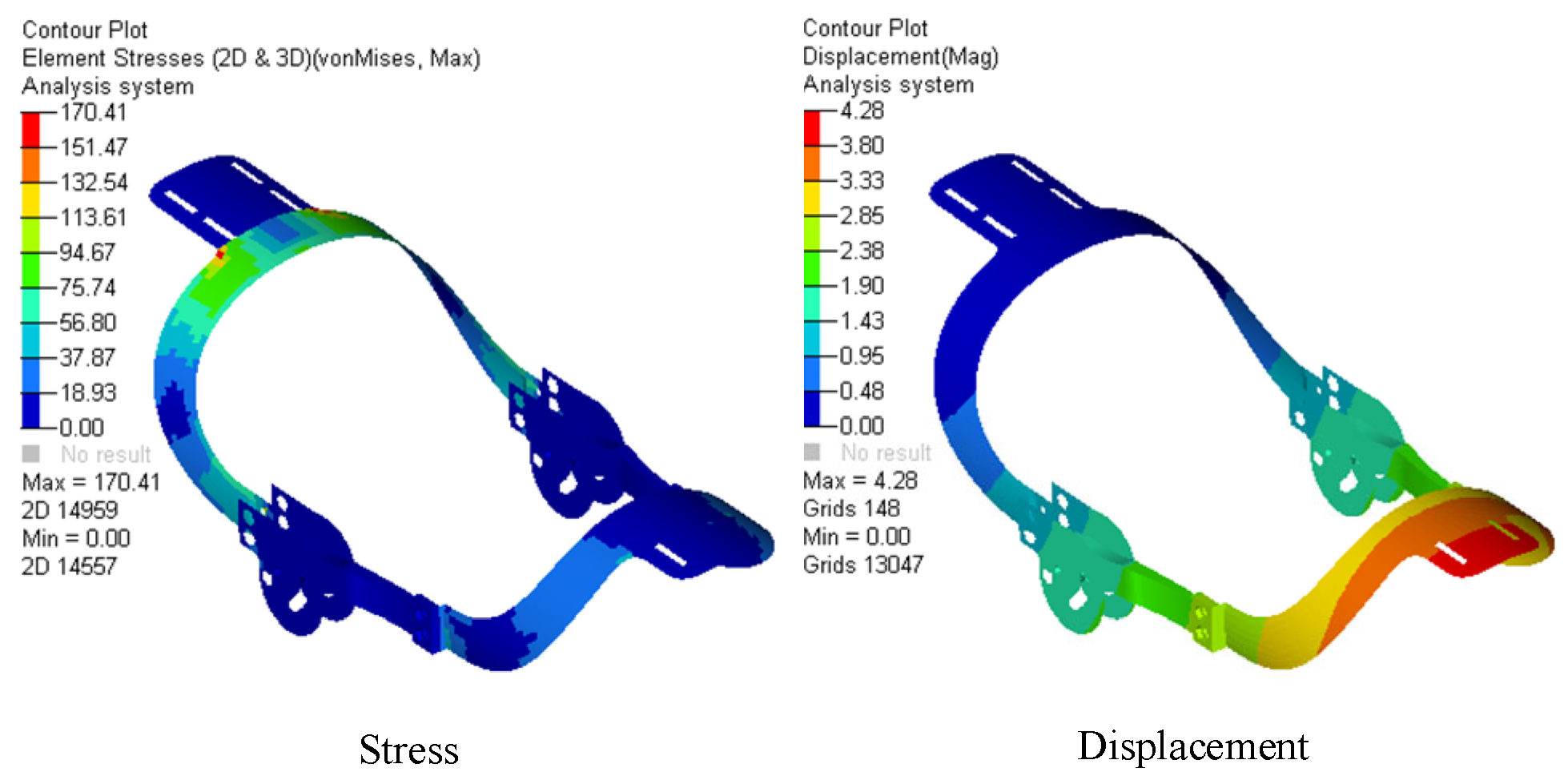
6.2. Finite Element Analysis of the Mechanical Structure
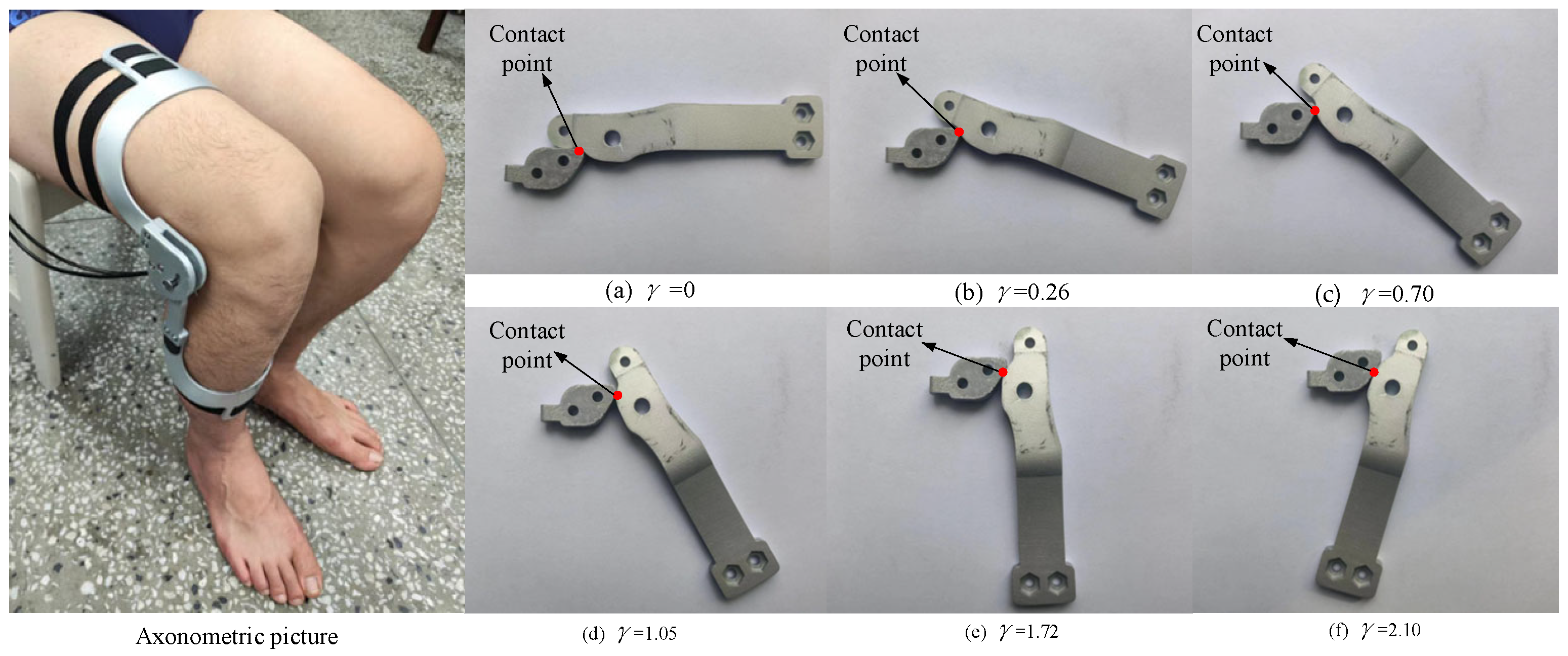
7. Verification of the Prototype
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, T.; Chen, S.; Wu, K.; Sun, M.; Zhang, X.; You, C. Trends in Incidence and Mortality of Stroke in China From 1990 to 2019. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 759221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defebvre, L.; Krystkowiak, P. Movement disorders and stroke. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 172, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canonica, A.C.; Alonso, A.C.; Silva, V.C.; Bombana, H.S.; Muzaurieta, A.A.; Leyton, V.; Greve, J.M.D. Factors Contributing to Traffic Accidents in Hospitalized Patients in Terms of Severity and Functionality. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Ji, S.; Liu, Y.; Gao, C.; Zhang, S.Z.; Fu, J.; Dai, L. Analysis of Ankle Muscle Dynamics during the STS Process Based on Wearable Sensors. Sensors 2023, 23, 6607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, D.E.; Yu, Y.; McNamara, P.J.; Mayer, B.K. Biomimetics in the design of a robotic exoskeleton for upper limb therapy. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 1933, 04006. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Chen, P.; Peng, J.; Qiao, X.; Zhu, F.; Zhong, J. Design and Optimization of Lower Limb Rehabilitation Exoskeleton with a Multiaxial Knee Joint. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Lee, K.; Guo, J.; Yang, C. Adaptive knee joint exoskeleton based on biological geometries. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2014, 19, 1268–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, S.; Kumar, N.A.; Hur, P. Evaluating Knee Mechanisms for Assistive Devices. Front. Neurorobotics 2022, 16, 790070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Ding, X. A Review on Lower Limb Rehabilitation Exoskeleton Robots. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2019, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Peng, J.; Lu, Z.; Huang, K. The Wearable Lower Limb Rehabilitation Exoskeleton Kinematic Analysis and Simulation. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 5029663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Liu, K.; Li, C.; Sun, Z.; Liu, S.; Gu, J. Development and Evaluation of a Wearable Lower Limb Rehabilitation Robot. J. Bionic Eng. 2022, 19, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, W.; Bai, S.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, X.; Yu, X. Lower limb exoskeleton parasitic force modeling and minimizing with an adaptive trajectory controller. Mech. Mach. Theory 2022, 170, 104731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shi, D.; Geng, Y. Design and Control of an Adaptive Knee Joint Exoskeleton Mechanism with Buffering Function. Sensors 2021, 21, 8390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, D.J.; Park, H.; Ha, T.; Park, S.; Jung, K. Biomechanical design of an agile, electricity-powered lower-limb exoskeleton for weight-bearing assistance. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2017, 95, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuan, J.Y.; Pasch, K.A.; Herr, H.M. Design of a knee joint mechanism that adapts to individual physiology. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. Conf. Proc. 2014, 2014, 2061–2064. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Jia, F.; Gao, P.; Gao, Y. Lightweight Design of Shell Based on Finite Element Method. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2023, 2501, 012014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.J. Light-weight design and fatigue characteristics of automotive knuckle by using finite element analysis. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2021, 35, 2989–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, D.E.; Sharifi, M. Design and Fabrication of a Lightweight and Wearable Semirigid Robotic Knee Chain Exoskeleton. J. Eng. Sci. Med. Diagn. Ther. 2024, 7, 021007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Ji, S.; Liu, Y.; Gao, C.; Fu, J.; Dai, L.; Zhang, S. Design and Optimization of Multifunctional Human Motion Rehabilitation Training Robot EEGO. Actuators. 2023, 12, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwani, K.; Deepak, C. Multidisciplinary topology and material optimization approach for developing patient-specific limb orthosis using 3D printing. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2023, 29, 1757–1771. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhao, G.; Richard, K.; Liu, F. Deep convolutional neural network for segmentation of knee joint anatomy. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 80, 2759–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, F.; Hua, L.; Han, X. The mathematical model and mechanical properties of variable center distance gears based on screw theory. Mech. Mach. Theory 2016, 101, 116–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, L.; Diao, K.; Guo, W. Lightweight design of an automotive battery-pack enclosure via advanced high-strength steels and size optimization. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2021, 22, 1279–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 10000-1988; Human Dimensions of Chinese Adults. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1988.
- GB/T 17245-2004; Inertial Parameters of Adult Human Body. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2004.

| Subjects | Ages | Sex | Height (m) | Heathy | Range of Motion of Knee Joint (r) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 23 | Male | 1.69 | Yes | 0–2.09 |
| 2 | 25 | Male | 1.76 | Yes | 0–2.09 |
| 3 | 21 | Female | 1.65 | Yes | 0–2.09 |
| 4 | 24 | Female | 1.70 | Yes | 0–2.09 |
| Body Segments | Weight (kg) | Size (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| Thigh | 10.5 | 470 |
| Shank | 2.72 | 373 |
| Part | Original Thicknesses (mm) | Range of Thicknesses (mm) | Optimized Thicknesses (mm) | Final integer Thicknesses (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thigh brace | 5 | 1–10 | 2.54 | 3 |
| Shank brace | 5 | 1–10 | 1.05 | 2 |
| Chute plate | 5 | 1–10 | 1 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, K.; Ji, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Dai, L. Design and Optimization of an Adaptive Knee Joint Orthosis for Biomimetic Motion Rehabilitation Assistance. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9020098
Liu K, Ji S, Liu Y, Zhang S, Dai L. Design and Optimization of an Adaptive Knee Joint Orthosis for Biomimetic Motion Rehabilitation Assistance. Biomimetics. 2024; 9(2):98. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9020098
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Kun, Shuo Ji, Yong Liu, Shizhong Zhang, and Lei Dai. 2024. "Design and Optimization of an Adaptive Knee Joint Orthosis for Biomimetic Motion Rehabilitation Assistance" Biomimetics 9, no. 2: 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9020098
APA StyleLiu, K., Ji, S., Liu, Y., Zhang, S., & Dai, L. (2024). Design and Optimization of an Adaptive Knee Joint Orthosis for Biomimetic Motion Rehabilitation Assistance. Biomimetics, 9(2), 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9020098







