Towards the First Generation of Biomimetic Fixation for Resurfacing Arthroplasty Endoprostheses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Milestones of Early Materials and Designs of Resurfacing Arthroplasty Endoprostheses
3. Characteristics of Contemporary Hip Resurfacing Arthroplasty Endoprostheses
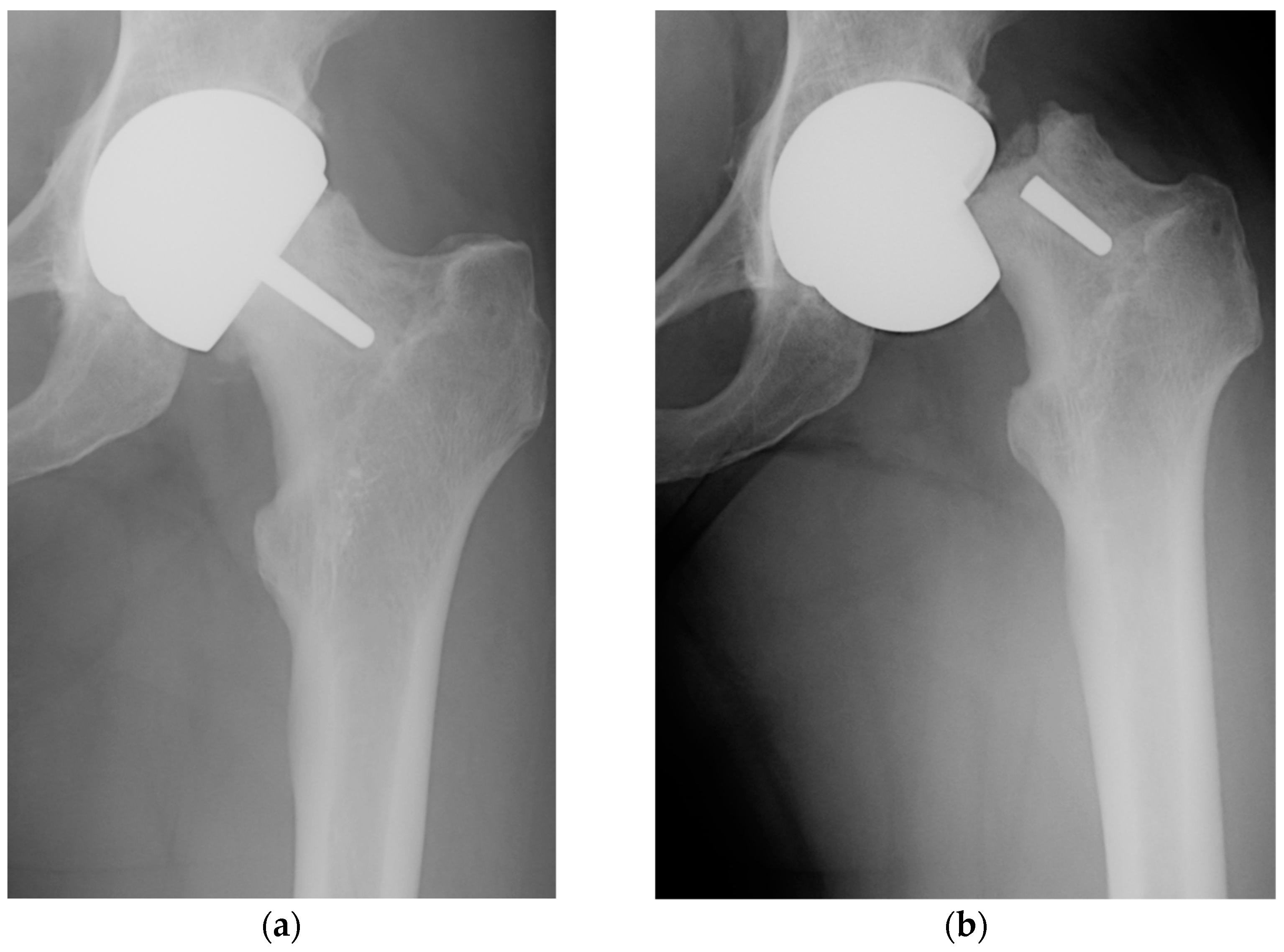
4. First Biomimetic Resurfacing Arthroplasty Endoprosthesis with the Multi-Spiked Connecting Scaffold
5. Summary and Final Remarks
- (1)
- Resemblance to the microstructure of the periarticular subchondral and cancellous bone tissue;
- (2)
- Conservation of the femoral head’s posterolateral and medial epiphyseal arteries (subcapsular arteriae retinaculares: superior and inferior);
- (3)
- Facilitation of a load transfer that mimics natural bone biomechanics, reflecting the mechanical behavior observed in a natural hip joint where the load is transmitted through the trabeculae in the femoral head and neck, continuing along the femoral shaft.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Callaghan, J.J.; Rosenberg, A.G.; Rubash, H.E.; Clohisy, J.C.; Beaulé, P.E.; DellaValle, C.J. The Adult Hip (Two Volume Set): Hip Arthroplasty Surgery, 3rd ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Amstutz, H.C.; Grigoris, P.; Dorey, F.J. Evolution and future of surface replacement of the hip. J. Orthop. Sci. 1998, 3, 169–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amstutz, H.C.; Sparling, E.A.; Grigoris, P.; Campbell, P.A.; Dorey, F.J. Surface Replacement: The Hip Replacement of the Future? HIP Int. 1998, 8, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada, M.J.; Marker, D.R.; Mont, M.A. Metal-on-metal hip resurfacing: Advantages and disadvantages. J. Arthroplast. 2008, 23, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, J.; Pradhan, C.; Ziaee, H.; Pynsent, P.B.; McMinn, D.J. Results of Birmingham hip resurfacing at 12 to 15 years: A single-surgeon series. Bone Jt. J. 2014, 96-B, 1298–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, M.C.; Hellman, M.D.; Kazarian, G.S.; Clohisy, J.C.; Nunley, R.M.; Barrack, R.L. Five to Ten-Year Results of the Birmingham Hip Resurfacing Implant in the US: A Single Institution’s Experience. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2018, 100, 1879–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellman, M.D.; Ford, M.C.; Barrack, R.L. Is there evidence to support an indication for surface replacement arthroplasty?: A systematic review. Bone Jt. J. 2019, 101-B (Suppl. A), 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amstutz, H.C.; Ball, S.T.; Le Duff, M.J.; Dorey, F.J. Resurfacing THA for patients younger than 50 year: Results of 2- to 9-year followup. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2007, 460, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrie, C.M.; Barrack, R.L. Hip resurfacing arthroplasty—What has history taught us? Ann. Jt. 2020, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadossi, M.; Tedesco, G.; Sambri, A.; Mazzotti, A.; Giannini, S. Hip Resurfacing Implants. Orthopedics 2015, 38, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amstutz, H.C.; Le Duff, M.J. Hip resurfacing: History, current status, and future. HIP Int. 2015, 25, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, E.J.; Clough, T.M. Metal on metal hip resurfacing arthroplasty: Where are we now? J. Orthop. 2020, 23, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jabri, T.; Ridha, M.; McCulloch, R.A.; Kayani, B.; Arif, A.; Habad, M.; Kosuge, D.; Jayadev, C.; Donaldson, J.; Skinner, J.A. Hip Resurfacing Arthroplasty: Past, Present and Future. Orthop. Rev. 2023, 15, 77745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith-Petersen, M.N. Evolution of mould arthroplasty of the hip joint. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1948, 30B, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.S.; Chakraborti, P. Development of Biomaterial for Total Hip Joint Replacement. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 377, 012177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, E.W.H. Some contributions to the reconstructive surgery of the hip. Br. J. Surg. 1927, 14, 486–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szostakowski, B.; Jagiello, J.; Skinner, J.A. ArtiFacts: Ivory Hemiarthroplasty: The forgotten concept lives on. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2017, 475, 2850–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gore, D.; Frazer, R.Q.; Kovarik, R.E.; Yepes, J.E. Vitallium. J. Long-Term Eff. Med. Implants 2005, 15, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadat, E.; Tiberi, J.V.; Burke, D.W.; Kwon, Y.-M. Smith-Petersen Vitallium Mold Arthroplasty: Case Report with a Fifty-One-Year Follow-Up and Histopathologic Analysis. JBJS Case Connect. 2013, 3, e112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, J.; Peng, H.; Feng, B.; Weng, X. The Longest Known Follow-Up of Vitallium Mold Arthroplasty in China: A Case Report and Literature Review. Orthop. Surg. 2023, 15, 1915–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, W.A. Post-Operative Study of Vitallium Mould Arthroplasty of the Hip Joint. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1948, 30-B, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, A. Vitallium-cup arthroplasty of the hip joint; review of approximately 100 cases. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1949, 31, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aufranc, O.E. Constructive Hip Surgery With the Vitallium Mold: A Report on 1000 Cases of Arthroplasty of the Hip over a Fifteen-Year Period. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1957, 39, 237–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, S.; Agarwal, A.K.; Rai, K.N. Chronology of Total Hip Joint Replacement and Materials Development. Trends Biomater. Artif. Organs 2005, 19, 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Judet, R.; Judet, J. Technique and results with the acrylic femoral head prosthesis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1952, 34-B, 173–180. [Google Scholar]
- Charnley, J. Surgery of the hip-joint: Present and future developments. Br. Med. J. 1960, 1, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charnley, J. Arthroplasty of the hip. A new operation. Lancet 1961, 1, 1129–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townley, C.O. Hemi and total articular replacement arthroplasty of the hip with the fixed femoral cup. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 1982, 13, 869–894. [Google Scholar]
- Wiles, P. The surgery of the osteoarthritic hip. Br. J. Surg. 1958, 45, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haboush, E.J. A new operation for arthroplasty of the hip based on biomechanics, photoelasticity, fast-setting dental acrylic, and other considerations. Bull. Hosp. Jt. Dis. 1953, 14, 242–277. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, M.E.; Boltzy, X. Artificial hip joints made from Protasul. Bull. Assoc. Study Probl. Intern. Fixat. 1968, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, M.E. Total hip prostheses. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1970, 72, 46–68. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, M.E. The benefits of metal-on-metal total hip replacements. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1995, 311, 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- Gérard, Y.; Ségal, P.; Bedoucha, J.S. Arthroplasty of the hip with coupled cups. Rev. Chir. Orthop. Reparatrice Appar. Mot. 1974, 60 (Suppl. 2), 281–289. [Google Scholar]
- Gérard, Y. Hip arthroplasty by matching cups. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1978, 134, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urist, M.R. The principles of hip-socket arthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1957, 39-A, 786–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, A.; Eguchi, M.; Kaibara, N. Socket and cup surface replacement of the hip. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1978, 134, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, A.; Eguchi, M.; Ogata, K. Socket and cup surface replacement. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 1982, 13, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzer, M.; Knahr, K.; Locke, H.; Stark, N. Cement-free bioceramic double-cup endoprosthesis of the hip joint. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1978, 134, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howie, D.W.; Cornish, B.L.; Vernon-Roberts, B. Resurfacing hip arthroplasty. Classification of loosening and the role of prosthesis wear particles. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1990, 255, 144–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amstutz, H.C.; Campbell, P.; Kossovsky, N.; Clarke, I.C. Mechanism and clinical significance of wear debris-induced osteolysis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1992, 276, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoris, P.; Roberts, P.; Panousis, K.; Jin, Z. Hip resurfacing arthroplasty: The evolution of contemporary designs. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H 2006, 220, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trentani, C.; Vaccarino, F. The Paltrinieri-Trentani hip joint resurface arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1978, 134, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuya, K.; Tsuchiya, M.; Kawachi, S. Socket-cup arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1978, 134, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, M.A. Total surface replacement hip arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1978, 134, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, M.A.R. Conservative total replacement of the hip. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1975, 57, 114. [Google Scholar]
- Capello, W.N.; Ireland, P.H.; Tramell, T.R.; Eicher, P. Conservative total hip arthroplasty: A procedure to conserve bone stock. Part I: Analysis of sixty-six patients. Part II: Analysis of failures. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1978, 134, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, H. Surface replacement arthroplasty of the hip. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1978, 134, 102–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amstutz, H.C.; Clarke, I.C.; Christie, J.; Graff-Radford, A. Total hip articular replacement by internal eccentric shells: The “tharies” approach to total surface replacement arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1977, 128, 261–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amstutz, H.C.; Graff-Radford, A.; Gruen, T.A.; Clarke, I.C. THARIES surface replacements: A review of the first 100 cases. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1978, 134, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S. Surface replacement of the hip joint. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1978, 134, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howie, D.W.; Campbell, D.; McGee, M.; Cornish, B.L. Wagner resurfacing hip arthroplasty. The results of one hundred consecutive arthroplasties after eight to ten years. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1990, 72, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costi, K.; Howie, D.W.; Campbell, D.G.; McGee, M.A.; Cornish, B.L. Long-term survival and reason for revision of Wagner resurfacing hip arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2010, 25, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amstutz, H.C.; Le Duff, M.J. Hip resurfacing: A 40-year perspective. HSS J. 2012, 8, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amstutz, H.C.; Kabo, M.; Hermens, K.; O’Carroll, P.F.; Dorey, F.; Kilgus, D. Porous surface replacement of the hip with chamfer cylinder design. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1987, 222, 140–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amstutz, H.C.; Kabo, M.; Dorey, F.J. Surface replacement arthroplasty: Evolution of today’s ingrowth-fixed design. In Osteoarthritis in the Young Adult Hip; Reynolds, D., Freeman, M., Eds.; Churchill Livingstone: Edinburgh, UK, 1989; pp. 251–275. [Google Scholar]
- Schmalzried, T.P.; Guttmann, D.; Grecula, M.; Amstutz, H.C. The relationship between the design, position, and articular wear of acetabular components inserted without cement and the development of pelvic osteolysis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1994, 76, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, M.J.; Makris, G.; Buechel, F.F. Titanium nitride ceramic film against polyethylene. A 48 million cycle wear test. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1995, 317, 64–70. [Google Scholar]
- Malviya, A.; Lobaz, S.; Holland, J. Mechanism of failure eleven years following a Buechel Pappas hip resurfacing. Acta Orthop. Belg. 2007, 73, 791–794. [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz, S.M.; Gawel, H.A.; Patel, J.D. History and systematic review of wear and osteolysis outcomes for first-generation highly crosslinked polyethylene. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2011, 469, 2262–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amstutz, H.C. (Ed.) Surface replacement arthroplasty. In Hip Arthroplasty; Churchill Livingstone: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 295–333. [Google Scholar]
- Pritchett, J.W. Polyethylene for hip resurfacing—Worth a second look. Ann. Jt. 2020, 5, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoris, P.; Roberts, P.; Panousis, K.; Bosch, H. The evolution of hip resurfacing arthroplasty. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 2005, 36, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howie, D.W.; Cornish, B.L.; Vernon-Roberts, B. The viability of the femoral head after resurfacing hip arthroplasty in humans. Clin. Orthop. 1993, 291, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, P.; Mirra, J.; Amstutz, H.C. Viability of femoral heads treated with resurfacing arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2000, 15, 120–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, M.; Wagner, H. Preliminary results of uncemented metal on metal stemmed and resurfacing hip replacement arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1996, 329, S78–S88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMinn, D.J.W.; Treacy, R.; Lin, K.; Pynsent, P. Metal on metal surface replacement of the hip. Experience of the McMinn prosthesis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1996, 329, S89–S98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaulé, P.; Le Duff, M.; Campbell, P.; Dorey, F.; Park, S.; Amstutz, H.C. Metal-on-metal surface arthroplasty with a cemented femoral component: A 7–10 year follow-up study. J. Arthroplast. 2004, 19 (Suppl. 3), 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southgate, R.D.; Vail, T.P. Resurfacing Hip Arthroplasty: Evolution, Design, Indications, and Results. In Surgery of the Hip, 2nd ed.; Berry, D.J., Lieberman, J.R., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Bohm, R.; Schraml, A.; Schuh, A. Long-term results with the Wagner metal-on-metal hip resurfacing prosthesis. HIP Int. 2006, 16 (Suppl. 4), 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMinn, D.J.W. Modern Hip Resurfacing; Springer: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amstutz, H.C.; Le Duff, M.J. Background of metal-on-metal resurfacing. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H 2006, 220, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treacy, R.B.C.; McBryde, C.W.; Shears, E.; Pynsent, P.B. Birmingham hip resurfacing: A minimum follow-up of ten years. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2011, 93-B, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulter, G.; Young, D.A.; Dalziel, R.E.; Shimmin, A.J. Birmingham hip resurfacing at a mean of ten years: Results from an independent centre. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2012, 94-B, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, D.W.; Grammatopoulos, G.; Pandit, H.; Gundle, R.; Gill, H.S.; McLardy-Smith, P. The ten-year survival of the Birmingham hip resurfacing: An independent series. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2012, 94-B, 1180–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amstutz, H.C.; Le Duff, M.J.; Campbell, P.A.; Gruen, T.A.; Wisk, L.E. Clinical and radiographic results of metal-on-metal hip resurfacing with a minimum ten-year follow-up. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2010, 92, 2663–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Smet, K.; Campbell, P.; Van Der Straeten, C. (Eds.) The Hip Resurfacing Handbook. A Practical Guide to the Use and Management of Modern Hip Resurfacings; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Sawston, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Amstutz, H.C.; Le Duff, M.J. Eleven years of experience with metal-on-metal hybrid hip resurfacing: A review of 1000 conserve plus. J. Arthroplasty 2008, 23 (Suppl. 1), 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMinn, D.J. Development of metal/metal hip resurfacing. HIP Int. 2003, 13, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amstutz, H.C. The Conserve® Plus hip resurfacing prosthesis. In The Hip Resurfacing Handbook. A Practical Guide to the Use and Management of Modern Hip Resurfacings; De Smet, K., Campbell, P., Van Der Straeten, C., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Sawston, UK, 2013; pp. 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, P.; De Smet, K. The Birmingham Hip Resurfacing (BHR) prosthesis. In The Hip Resurfacing Handbook. A Practical Guide to the Use and Management of Modern Hip Resurfacings; De Smet, K., Campbell, P., Van Der Straeten, C., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Sawston, UK, 2013; pp. 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawan, R.; Young, D.A.; Van Eemeren, A.; Shimmin, A. Birmingham Hip Resurfacing at 20 years. Bone Jt. J. 2023, 105-B, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, C.R.; Johnson, A.J.; Naziri, Q.; Mont, M.A. The outcomes of Cormet hip resurfacing compared to standard primary total hip arthroplasty. Bull. NYU Hosp. Jt. Dis. 2011, 69 (Suppl. 1), S12–S15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Norton, M. The Cormet™ hip resurfacing prosthesis. In The Hip Resurfacing Handbook. A Practical Guide to the Use and Management of Modern Hip Resurfacings; De Smet, K., Campbell, P., Van Der Straeten, C., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Sawston, UK, 2013; pp. 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravius, S.; Wirtz, D.; Maus, U.; Andereya, S.; Müller-Rath, R.; Mumme, T. Durom-Hip-Oberflächenersatz am Hüftgelenk: Erste klinische Ergebnisse mit dem lateralen Zugang [Durom hip resurfacing arthroplasty: First clinical experiences with a lateral approach]. Z. Orthop. Unfall. 2007, 145, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, P.; Girard, J. The Durom hip resurfacing prosthesis. In The Hip Resurfacing Handbook. A Practical Guide to the Use and Management of Modern Hip Resurfacings; De Smet, K., Campbell, P., Van Der Straeten, C., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Sawston, UK, 2013; pp. 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebel, T.; Maubach, S.; Morlock, M.M. Lessons learned from early clinical experience and results of 300 ASR hip resurfacing implantations. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H 2006, 220, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Smet, K. The DePuy Articular Surface Replacement (ASR™) hip resurfacing prosthesis. In The Hip Resurfacing Handbook. A Practical Guide to the Use and Management of Modern Hip Resurfacings; De Smet, K., Campbell, P., Van Der Straeten, C., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Sawston, UK, 2013; pp. 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trč, T.; Šťastný, E.; Kopečný, Z.; Kos, P.; Přidal, J.; Havlas, V. Naše zkušenosti s povrchovou náhradou kyčelního kloubu ICON [Our Experience with ICON Hip Resurfacing System]. Acta Chir. Orthop. Traumatol. Cechoslov. 2022, 89, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Straeten, C. The ICON hip resurfacing prosthesis. In The Hip Resurfacing Handbook. A Practical Guide to the Use and Management of Modern Hip Resurfacings; De Smet, K., Campbell, P., Van Der Straeten, C., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Sawston, UK, 2013; pp. 53–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delport, H.P. The BIOMET ReCap hip resurfacing prosthesis. In The Hip Resurfacing Handbook. A Practical Guide to the Use and Management of Modern Hip Resurfacings; De Smet, K., Campbell, P., Van Der Straeten, C., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Sawston, UK, 2013; pp. 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamelynck, K.J.; Woering, R. The advanced ceramic coated implant systems (ACCIS) hip resurfacing prosthesis. In The Hip Resurfacing Handbook. A Practical Guide to the Use and Management of Modern Hip Resurfacings; De Smet, K., Campbell, P., Van Der Straeten, C., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Sawston, UK, 2013; pp. 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancino, F.; Finsterwald, M.A.; Jones, C.W.; Prosser, G.H.; Yates, P.J. Metal-on-Metal Hips: Ten-Year Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes of the ADEPT Metal-on-Metal Hip Resurfacing and Modular Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuke, M. The ADEPT® hip resurfacing prosthesis. In The Hip Resurfacing Handbook. A Practical Guide to the Use and Management of Modern Hip Resurfacings; De Smet, K., Campbell, P., Van Der Straeten, C., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Sawston, UK, 2013; pp. 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, D.; Burke, J. The MITCH hip resurfacing prosthesis. In The Hip Resurfacing Handbook. A Practical Guide to the Use and Management of Modern Hip Resurfacings; De Smet, K., Campbell, P., Van Der Straeten, C., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Sawston, UK, 2013; pp. 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollwitzer, H.; Gerdesmeyer, L.; Horn, C.; Diehl, P.; Töpfer, A.; Gradinger, R. 8-year follow-up after cementless hip arthroplasty with a second generation spongy metal total hip replacement. HIP Int. 2009, 19, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götze, C.; Tschugunow, A.; Wiegelmann, F.; Osada, N.; Götze, H.G.; Böttner, F. Langfristiger Einfluss der anatomisch angepassten spongiösen Endoprothese auf den periprothetischen Knochen [Long-term influence of the spongiosa metal surface prosthesis on the periprosthetic bone. A radiological and osteodensitometric analysis of implantation of the S & G (ESKA) hip prosthesis]. Z. Orthop. Ihre. Grenzgeb. 2006, 144, 192–198. (In German) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Straeten, C. The ESKA hip resurfacing prosthesis. In The Hip Resurfacing Handbook. A Practical Guide to the Use and Management of Modern Hip Resurfacings; De Smet, K., Campbell, P., Van Der Straeten, C., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Sawston, UK, 2013; pp. 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quack, G.; Willmann, G.; Krahl, H.; Grundei, H. Konzeptionelle Uberlegungen zur Verbesserung der Pfanne der ESKA-Hüftendoprothese durch die Gleitpaarung Keramik/Keramik [Design considerations for improving the acetabular cup of the ESKA hip endoprosthesis by using the ceramic/ceramic wear couple]. Biomed. Technol. 1996, 41, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, J.; Grundei, H.; Klingbeil, K. ESKA-Ceram®—Ein neuer Werkstoff in der Endoprothetik des Hüftgelenkes [ESKA-Ceram®—A New Material for Use in Hip Endoprostheses]. Biomed. Technol. 2000, 45, 377–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, T.P.; Liu, F.; Webb, L.A. Clinical outcome of the metal-on-metal hybrid Corin Cormet 2000 hip resurfacing system: An up to 11-year follow-up study. J. Arthroplast. 2012, 27, 533–538.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, S.; Laude, F.; Menge, M.; Sadri, H.; Siccardi, F. The ROMAX® hip resurfacing prosthesis. In The Hip Resurfacing Handbook. A Practical Guide to the Use and Management of Modern Hip Resurfacings; De Smet, K., Campbell, P., Van Der Straeten, C., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Sawston, UK, 2013; pp. 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadossi, M.; Tedesco, G.; Savarino, L.; Baldini, N.; Mazzotti, A.; Greco, M.; Giannini, S. Effect of acetabular cup design on metal ion release in two designs of metal-on-metal hip resurfacing. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2014, 102, 1595–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, J. The Tornier DynaMoM hip resurfacing prosthesis. In The Hip Resurfacing Handbook. A Practical Guide to the Use and Management of Modern Hip Resurfacings; De Smet, K., Campbell, P., Van Der Straeten, C., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Sawston, UK, 2013; pp. 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh Chana, G.; Palmer, S. The MIHR International® hip resurfacing prosthesis. In The Hip Resurfacing Handbook. A Practical Guide to the Use and Management of Modern Hip Resurfacings; De Smet, K., Campbell, P., Van Der Straeten, C., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Sawston, UK, 2013; pp. 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heisel, C.; Kleinhans, J.A.; Menge, M.; Kretzer, J.P. Ten different hip resurfacing systems: Biomechanical analysis of design and material properties. Int. Orthop. 2009, 33, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Replacement Registry. Annu. Rep. 2006, 57–87.
- Hamelynck, K.J.; Woering, R.G. Ceramic Surface Engineered Metal-on-Metal Hips system for Total Hip Arthroplasty and Resurfacing Hip Arthroplasty. The design rationale, pre-clinical testing and interim report on 2–7 years of clinical results. In White Paper; Implantcast: Buxtehude, Germany, 2009; pp. 1–8. Available online: https://silo.tips/download/ceramic-surface-engineered-metal-on-metal-hips-system-for-total-hip-arthroplasty (accessed on 19 December 2023).
- Jemmett, P.; Parfitt, D.; Rice, R. Early clinical failure of the ACCIS® metal on metal hip arthroplasty system—A metal on metal hip with a difference. Acta Orthop. Belg. 2016, 82, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.Y.; Ko, M.S.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, K.S. Short-term Outcomes of Ceramic Coated Metal-on-Metal Large Head in Total Hip Replacement Arthroplasty. HIP Pelvis 2018, 30, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerdesmeyer, L.; Gollwitzer, H.; Al Muderis, M.; Fletcher, S.; Böhling, U. Alternative Bearing Designs for Hip Resurfacing Arthroplasty. Tech. Orthop. 2010, 25, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, R.; Klüss, D.; Gerdesmeyer, L.; Steinhauser, E. Biomechanische Aspekte zur Implantatverankerung und Kinematik von Oberflächenersatzhüftendoprothesen [Biomechanical aspects of the implant fixation and kinematics of hip resurfacing systems]. Orthopade 2008, 37, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimmin, A.J.; Back, D. Femoral neck fractures following Birmingham hip resurfacing: A national review of 50 cases. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2005, 87, 463–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; New, A.M.; Taylor, M. Bone remodelling inside a cemented resurfaced femoral head. Clin. Biomech. 2006, 21, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.P.; Santner, T.J.; Bartel, D.L. Hip resurfacing increases bone strains associated with short-term femoral neck fracture. J. Orthop. Res. 2009, 27, 1319–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, R.T.; Foguet, P.R.; Krikler, S.J.; Gundle, R.; Beard, D.J.; Murray, D.W. Femoral neck fractures after hip resurfacing. J. Arthroplast. 2009, 24, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowble, V.A.; Schuh, A.; Hoke, R.; Bitsch, R.G.; Beaulé, P.E. Clinical correlation of femoral component migration in hip resurfacing arthroplasty analyzed by Einzel-Bild-Röntgen-analyze-femoral component analysis. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 2005, 36, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amstutz, H.C.; Le Duff, M.J.; Campbell, P.A.; Dorey, F.J. The effects of technique changes on aseptic loosening of the femoral component in hip resurfacing. Results of 600 Conserve Plus with a 3 to 9 year follow-up. J. Arthroplast. 2007, 22, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falez, F.; Favetti, F.; Casella, F.; Panegrossi, G. Hip resurfacing: Why does it fail? Early results and critical analysis of our first 60 cases. Int. Orthop. 2008, 32, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zustin, J.; Hahn, M.; Morlock, M.M.; Rüther, W.; Amling, M.; Sauter, G. Femoral component loosening after hip resurfacing arthroplasty. Skelet. Radiol. 2010, 39, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baad-Hansen, T.; Storgaard Jakobsen, S.; Soballe, K. Two-year migration results of the ReCap hip resurfacing system-a radiostereometric follow-up study of 23 hips. Int. Orthop. 2011, 35, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulé, P.; White, C.; Lopez-Castellaro, J.; Kim, P. Acetabular component migration analysis of hip resurfacing using ein bild roentegen analyse (EBRA). Orthop. Procs. 2012, 94-B, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Haan, R.; Buls, N.; Scheerlinck, T. Impact of implant size on cement filling in hip resurfacing arthroplasty. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H 2014, 228, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howald, R.; Kesteris, U.; Klabunde, R.; Krevolin, J. Factors affecting the cement penetration of a hip resurfacing implant: An in vitro study. HIP Int. 2006, 16 (Suppl. 4), 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaulé, P.E.; Lu, Z.; Luck, J.V.; Campbell, P. Bone thermal necrosis and cement penetration in femoral head resurfacing. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2005, 90-B, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulé, P.E.; Campbell, P.; Lu, Z.; Leunig-Ganz, K.; Beck, M.; Leunig, M.; Ganz, R. Vascularity of the arthritic femoral head and hip resurfacing. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2006, 88 (Suppl. 4), 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulé, P.E.; Campbell, P.; Shim, P. Femoral head blood flow during hip resurfacing. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2007, 456, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaulé, P.E.; Matar, W.Y.; Poitras, P.; Smit, K.; May, O. 2008 Otto Aufranc Award: Component design and technique affect cement penetration in hip resurfacing. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2009, 467, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Krause, M.; Breer, S.; Hahn, M.; Rüther, W.; Morlock, M.M.; Amling, M.; Zustin, J. Cementation and interface analysis of early failure cases after hip-resurfacing arthroplasty. Int. Orthop. 2012, 36, 1333–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hug, K.T.; Watters, T.S.; Vail, T.P.; Bolognesi, M.P. The withdrawn ASR™ THA and hip resurfacing systems: How have our patients fared over 1 to 6 years? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2013, 471, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, E.T.; Olsen, M.; Zdero, R.; Smith, G.M.; Waddell, J.P.; Schemitsch, E.H. Predictors of femoral neck fracture following hip resurfacing: A cadaveric study. J. Arthroplast. 2013, 28, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matharu, G.S.; McBryde, C.W.; Revell, M.P.; Pynsent, P.B. Femoral neck fracture after Birmingham Hip Resurfacing Arthroplasty: Prevalence, time to fracture, and outcome after revision. J. Arthroplast. 2013, 28, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haughom, B.D.; Erickson, B.J.; Hellman, M.D.; Jacobs, J.J. Do complication rates differ by gender after metal-on-metal hip resurfacing arthroplasty? A systematic review. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2015, 473, 2521–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amstutz, H.C.; Le Duff, M.J. Aseptic loosening of cobalt chromium monoblock sockets after hip resurfacing. HIP Int. 2015, 25, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, H.S.; Campbell, P.A.; Murray, D.W.; De Smet, K.A. Reduction of the potential for thermal damage during hip resurfacing. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2007, 89, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffen, R.T.; Fern, D.; Norton, M.; Murray, D.W.; Gill, H.S. Femoral oxygenation during hip resurfacing through the trochanteric flip approach. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2009, 467, 934–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheerlinck, T.; Delport, H.; Kiewitt, T. Influence of the cementing technique on the cement mantle in hip resurfacing: An in vitro computed tomography scan-based analysis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2010, 92, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, J. Is it time for cementless hip resurfacing? HSS J. 2012, 8, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.; Whitehouse, M.; Kilshaw, M.; Pabbruwe, M.; Spencer, R.; Blom, A.; Bannister, G. Maximum temperatures of 89 °C recorded during the mechanical preparation of 35 femoral heads for resurfacing. Acta Orthop. 2011, 82, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zustin, J.; Sauter, G.; Morlock, M.M.; Rüther, W.; Amling, M. Association of osteonecrosis and failure of hip resurfacing arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2010, 468, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullmark, G.; Sundgren, K.; Milbrink, J.; Nilsson, O.; Sörensen, J. Osteonecrosis following resurfacing arthroplasty. Acta Orthop. 2009, 80, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Steiger, R.N.; Miller, L.N.; Prosser, G.H.; Graves, S.E.; Davidson, D.C.; Stanford, T.E. Poor outcome of revised resurfacing hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop. 2010, 81, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, T.P.; Liu, F. Metal-on-metal hip resurfacing with an uncemented femoral component. A seven-year follow-up study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2008, 90 (Suppl. 3), 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, R.J.; Gaillard, M.D.; Gross, T.P. Comparison of Cemented and Bone Ingrowth Fixation Methods in Hip Resurfacing for Osteonecrosis. J. Arthroplast. 2017, 32, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gaillard-Campbell, D.M.; Gross, T.P. Femoral Fixation Methods in Hip Resurfacing Arthroplasty: An 11-Year Retrospective Comparison of 4013 Cases. J. Arthroplast. 2019, 34, 2398–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogala, P. Endoprosthesis. EU Patent EP072418 B1, 22 December 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Rogala, P. Acetabulum Endoprosthesis and Head. U.S. Patent US5,911,759 A, 15 June 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Rogala, P. Method and Endoprosthesis to Apply This Implantation. Canadian Patent 2,200,064, 1 April 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Uklejewski, R.; Rogala, P.; Winiecki, M. Prototype of a Biomimetic Multi-Spiked Connecting Scaffold for a New Generation of Resurfacing Endoprostheses, 1st ed.; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruth, J.-P.; Mercelis, P.; Van Vaerenbergh, J.; Froyen, L.; Rombouts, M. Binding mechanisms in selective laser sintering and selective laser melting. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2005, 11, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uklejewski, R.; Winiecki, M.; Rogala, P. Technological issues of additive manufacturing of preprototypes of the multi-spiked connecting scaffold for non-cemented resurfacing arthroplasty endoprostheses. Eng. Biomater. 2014, 17, 81–82. [Google Scholar]
- Uklejewski, R.; Rogala, P.; Winiecki, M.; Mielniczuk, J. Prototype of minimally invasive hip resurfacing endoprosthesis—Bioengineering design and manufacturing. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2009, 11, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Uklejewski, R.; Rogala, P.; Winiecki, M.; Mielniczuk, J. Prototype of innovating bone tissue preserving THRA endoprosthesis with multi-spiked connecting scaffold manufactured in selective laser melting technology. Eng. Biomater. 2009, 12, 2–6. [Google Scholar]
- Uklejewski, R.; Winiecki, M.; Rogala, P.; Mielniczuk, J. Selective laser melted prototype of original minimally invasive hip endoprosthesis. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2011, 17, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uklejewski, R.; Winiecki, M.; Rogala, P.; Patalas, A. Structural-Geometric Functionalization of the Additively Manufactured Prototype of Biomimetic Multispiked Connecting Ti-Alloy Scaffold for Entirely Noncemented Resurfacing Arthroplasty Endoprostheses. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2017, 2017, 5638680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uklejewski, R.; Rogala, P.; Winiecki, M. Structural and Hydroxyapatite-like Functionalization of Bone Contacting Surfaces of Additively Manufactured Multispiked Connecting Scaffold Prototype for Entirely Cementless Resurfacing Arthroplasty Endoprostheses to Enhance its Osteoconduction and Osteointegration. In Advanced Surface Engineering Materials; Tiwari, A., Wang, R., Wei, B., Eds.; WILEY-Scrivener: Beverly, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 175–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uklejewski, R.; Rogala, P.; Winiecki, M.; Kędzia, A.; Ruszkowski, P. Preliminary Results of Implantation in Animal Model and Osteoblast Culture Evaluation of Prototypes of Biomimetic Multispiked Connecting Scaffold for Noncemented Stemless Resurfacing Hip Arthroplasty Endoprostheses. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 689089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uklejewski, R.; Rogala, P.; Winiecki, M.; Tokłowicz, R.; Ruszkowski, P.; Wołuń-Cholewa, M. Biomimetic Multi-spiked Connecting Ti-alloy Scaffold Prototype for Entirely Cementless Resurfacing Arthroplasty Endoprostheses—Exemplary Results of Implantation of the Ca-P Surface Modified Scaffold Prototypes in Animal Model and Osteoblast Culture Evaluation. Materials 2016, 9, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uklejewski, R.; Winiecki, M.; Krawczyk, P.; Tokłowicz, R. Native Osseous CaP Biomineral Coating on a Biomimetic Multi-Spiked Connecting Scaffold Prototype for Cementless Resurfacing Arthroplasty Achieved by Combined Electrochemical Deposition. Materials 2019, 12, 3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uklejewski, R.; Winiecki, M.; Patalas, A.; Rogala, P. Numerical studies of the influence of various geometrical features of a multi-spiked connecting scaffold prototype on mechanical stresses in peri-implant bone. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 21, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uklejewski, R.; Winiecki, M.; Patalas, A.; Rogala, P. Bone Density Micro-CT Assessment during Embedding of the Innovative Multi-Spiked Connecting Scaffold in Periarticular Bone to Elaborate a Validated Numerical Model for Designing Biomimetic Fixation of Resurfacing Endoprostheses. Materials 2021, 14, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogala, P.; Uklejewski, R.; Winiecki, M.; Dąbrowski, M.; Gołańczyk, J.; Patalas, A. First Biomimetic Fixation for Resurfacing Arthroplasty: Investigation in Swine of a Prototype Partial Knee Endoprosthesis. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 6952649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Surgeon/Designer | Introduced | Materials | Fixation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smith-Petersen | 1923 | Glass | [14] | |
| Smith-Petersen | 1925 | Viscaloid | ||
| Groves | 1927 | Ivory | [16] | |
| Smith-Petersen | 1933 | Pyrex | ||
| Smith-Petersen | 1937 | Bakelite | ||
| Smith-Petersen | 1938 | Vitallium® (CoCrMo) | [14,18,19] | |
| Judet and Judet | 1946 | Acrylic | [25] | |
| Charnley | 1951 | Teflon | [26,27] | |
| Townley | 1964 | CoCrMo femoral head/polyurethane acetabular cup CoCrMo femoral head/PE acetabular cup | [28] | |
| Müller and Boltzy | 1968 | CoCrMo femoral head/CoCrMo acetabular cup | [31] | |
| Gérard | 1970 | CoCrMo femoral head/CoCrMo acetabular cup CoCrMo femoral head/PE acetabular cup | [34,35] | |
| Trentani & Paltrinieri | 1971 | stainless steel femoral head/UHMWPE acetabular cup | Cemented | [42] |
| Furuya | 1971 | HDPE femoral head/stainless steel acetabular cup | Cemented | [43] |
| Nishio | 1972 | CoCrMo femoral head/CoCrMo acetabular cup | Cementless | [37] |
| Nishio | 1975 | CoCrMo femoral head/polyethylene acetabular cup | Cementless | [38] |
| Freeman | 1972 1974 | HDPE femoral head/CoCrMo acetabular cup CoCrMo femoral head/UHMWPE acetabular cup | Cemented Cemented | [45,46] |
| Eicher and Capello | 1973 | CoCrMo femoral head/UHMWPE acetabular cup | Cemented | [47] |
| Wagner | 1974 | CoCrMo femoral head/UHMWPE acetabular cup Al2O3 femoral head/UHMWPE acetabular cup | Cemented | [48] |
| Amstutz | 1975 | CoCrMo femoral head/UHMWPE acetabular cup | Cemented | [49,50] |
| Salzer | 1976 | Al2O3 femoral head/Al2O3 acetabular cup | Cementless | [39] |
| Tanaka | 1978 | CoCrMo femoral head/UHMWPE acetabular cup | Cemented | [50] |
| Amstutz | 1982 | CoCrMo femoral head/UHMWPE PS metal-backed acetabular cup | Cementless (Press fit) | [49,50] |
| Amstutz | 1983 | Ti-6Al-4V femoral head with sintered titanium fiber mesh/UHMWPE liner with porous backing of pure titanium mesh | Cementless | [49,50] |
| Amstutz | 1987 | Porous-coated CoCrMo femoral head UHMWPE insert Porous-coated or sintered bead-coated metallic acetabular cup | Cementless | [55] |
| Buechel and Pappas | 1989 | Titanium nitride-coated Ti-6Al-4V femoral head, UHMWPE liner, Ti-6Al-4V acetabular cup | Cementless | [57,59] |
| System | Introduced | Femoral Component Material and Fixation | Acetabular Component Bearing Material/Bone-Contacting Material | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wagner’s | 1991 | CoCrMo cementless, press-fit | CoCrMo/grit-blasted Ti coating, cementless | [66] |
| McMinn’s | 1992 | CoCrMo cementless, initially HA coating, then cemented | CoCrMo/HA coating, cementless | [67] |
| Conserve Plus™ (Wright Medical Technology Inc., Arlington, TN, USA) | 1996 | CoCrMo cemented | CoCrMo/CrCrMo beads + HA coating, cementless | [78,79,80] |
| BHR™ (Smith & Nephew, Memphis, TN, USA) | 1997 | CoCrMo cemented | CoCrMo/CrCrMo beads + HA coating, cementless | [81,82] |
| Cormet™ (Corin Group, Cirencester, UK) | 1997 | CoCrMo cemented (cementless option with PS Ti, HA coating) | CoCrMo/PS Ti + HA coating, cementless | [83,84] |
| Durom™ (Zimmer Inc., Warsaw, IN, USA) | 2001 | CoCrMo cemented | CoCrMo/PS Ti, cementless | [85,86] |
| ASR™ (DePuy Orthopaedics Inc., Warsaw, IN, USA) | 2003 | CoCrMo cemented | CoCrMo/CrCrMo beads + HA coating, cementless | [87,88] |
| Icon™ (IO International Orthopaedics Holding, Geisingen, Germany) | 2004 | CoCrMo cemented | CoCrMo/CrCrMo beads + HA coating | [89,90] |
| ReCap™ (Biomet Inc., Warsaw, IN, USA) | 2004 | CoCrMo cemented (cementless option PS Ti-6Al-4V) | CoCrMo/PS Ti-6Al-4V + HA coating | [91] |
| ACCIS™ (Van Straten Medical, The Netherlands; Implantcast, Buxtehude, Germany) | 2004 | TiNbN-coated CoCrMo cemented fixation, cementless from 2009 | TiNbN-coated CoCrMo/ PS Ti | [92] |
| ADEPT® (Finsbury Orthopaedics Ltd., Leatherhead, UK) | 2005 | CoCrMo cemented | CoCrMo/CrCrMo beads + HA coating | [93,94] |
| MITCH (Stryker, Kalamazoo, MI, USA) | 2006 | CoCrMo cemented | CoCrMo/PS Ti + HA coating | [95] |
| ESKA-BIONIK® (ESKA Implants GmbH & Co., Lübeck, Germany) | 2006 | CoCrMo; Spongiosa Metal® (cemented option) | CoCrMo + CoCrMo insert/Spongiosa Metal® | [96,97,98] |
| ESKA-CERAM® (ESKA Implants GmbH & Co., Lübeck, Germany) | 2007 | CoCrMo; Spongiosa Metal® (CoCrMo with TiNb coating) | polyurethane/Al2O3 + polyurethane/Al2O3 insert/ Spongiosa Metal® (CoCrMo with TiNb coating) | [98,99,100] |
| Cormet 2000 (Corin Medical Ltd., Cirencester, UK) | 2007 | CoCrMo cemented | CoCrMo/PS Ti + HA coating | [84,101] |
| ROMAX® (Medacta, Castel San Pietro, Switzerland) | 2008 | CoCrMo cemented | CoCrMo/PS Ti + HA coating | [102,103] |
| DynaMoM (Tornier, Saint-Ismier, France) | 2008 | CoCrMo cemented | CoCrMo/PS Ti + HA coating | [104] |
| MIHR International® (Comis Orthopaedics Ltd., Birmingham, UK) | 2009 | CoCrMo cemented | CoCrMo/HA coating, cementless | [105] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uklejewski, R.; Winiecki, M.; Dąbrowski, M.; Rogala, P. Towards the First Generation of Biomimetic Fixation for Resurfacing Arthroplasty Endoprostheses. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9020099
Uklejewski R, Winiecki M, Dąbrowski M, Rogala P. Towards the First Generation of Biomimetic Fixation for Resurfacing Arthroplasty Endoprostheses. Biomimetics. 2024; 9(2):99. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9020099
Chicago/Turabian StyleUklejewski, Ryszard, Mariusz Winiecki, Mikołaj Dąbrowski, and Piotr Rogala. 2024. "Towards the First Generation of Biomimetic Fixation for Resurfacing Arthroplasty Endoprostheses" Biomimetics 9, no. 2: 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9020099
APA StyleUklejewski, R., Winiecki, M., Dąbrowski, M., & Rogala, P. (2024). Towards the First Generation of Biomimetic Fixation for Resurfacing Arthroplasty Endoprostheses. Biomimetics, 9(2), 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9020099








