A Novel Sensor Fusion Approach for Precise Hand Tracking in Virtual Reality-Based Human—Computer Interaction
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- This paper introduces a multi-modal hand-tracking acquisition system that achieves enhanced tracking accuracy and reliability across diverse scenarios.
- (2)
- The proposed method ensures real-time performance, enabling seamless integration with existing VR applications.
- (3)
- By facilitating more natural and immersive interactions, this approach opens up possibilities for advancements in VR-based HCI across various domains, such as gaming, education, and healthcare.
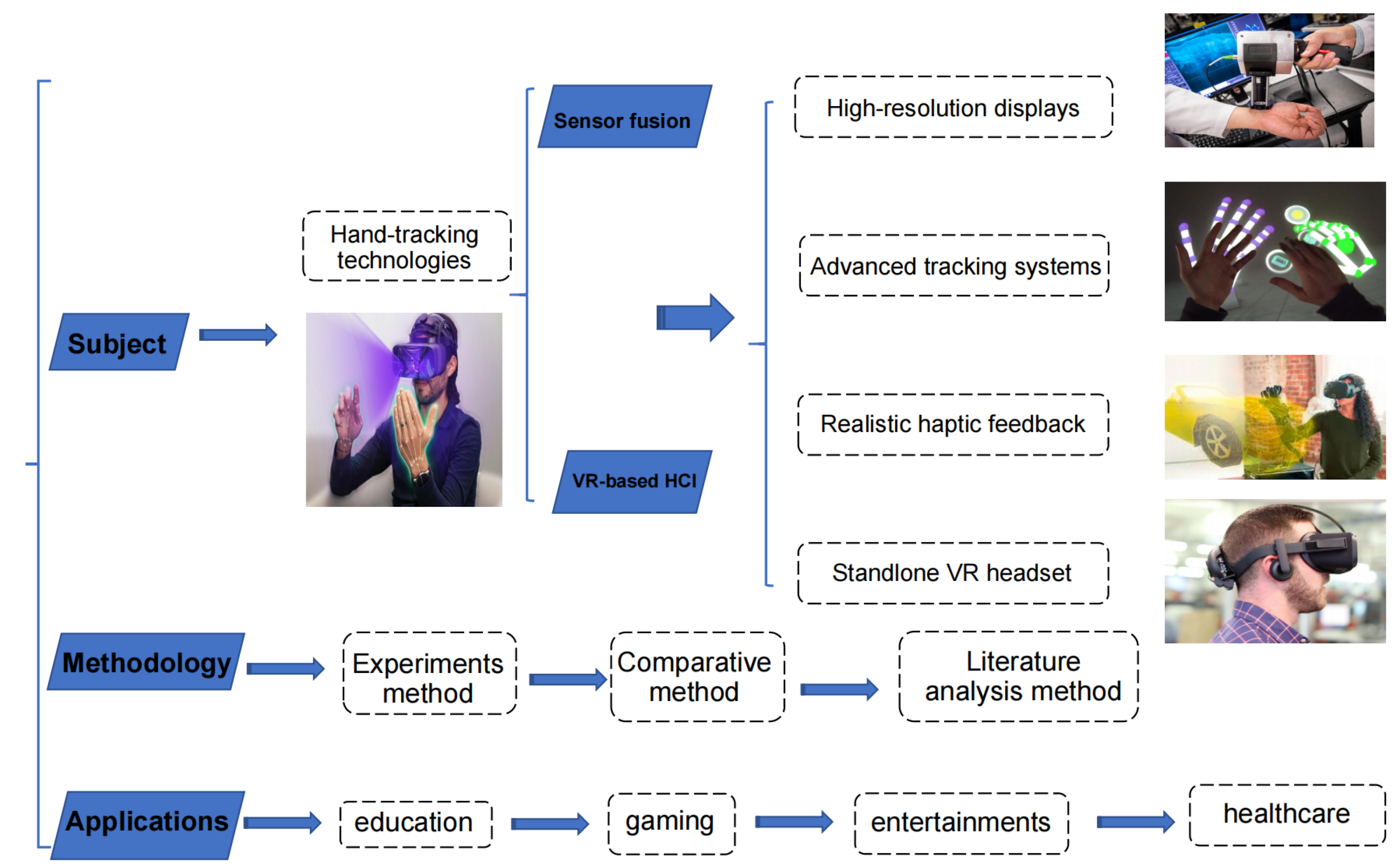
2. Related Work
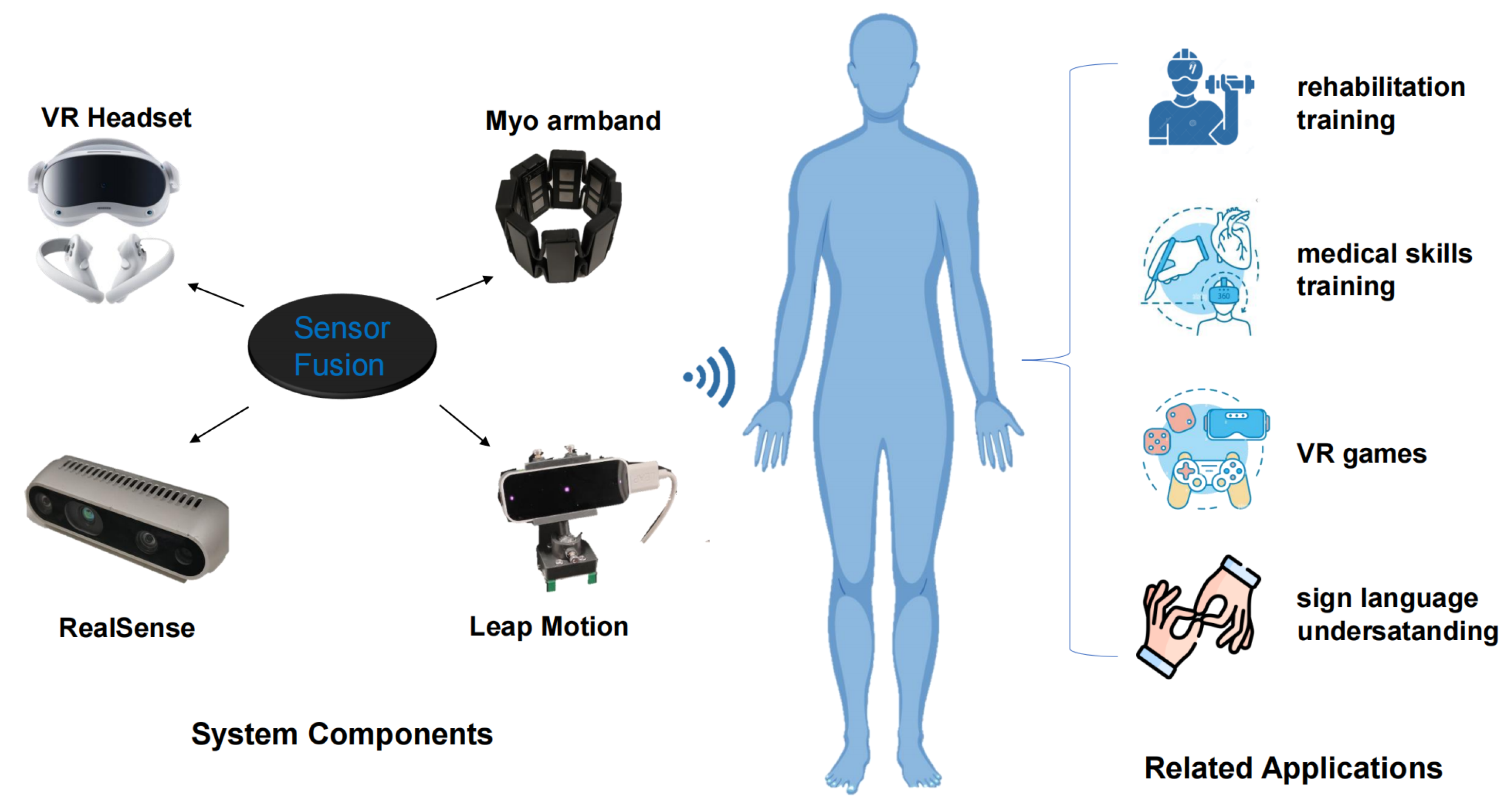
3. Systems Overview
3.1. Leap Motion Controllers
3.2. RealSense Depth Cameras
3.3. EMG Sensors
3.4. VR Headset
3.5. System Framework
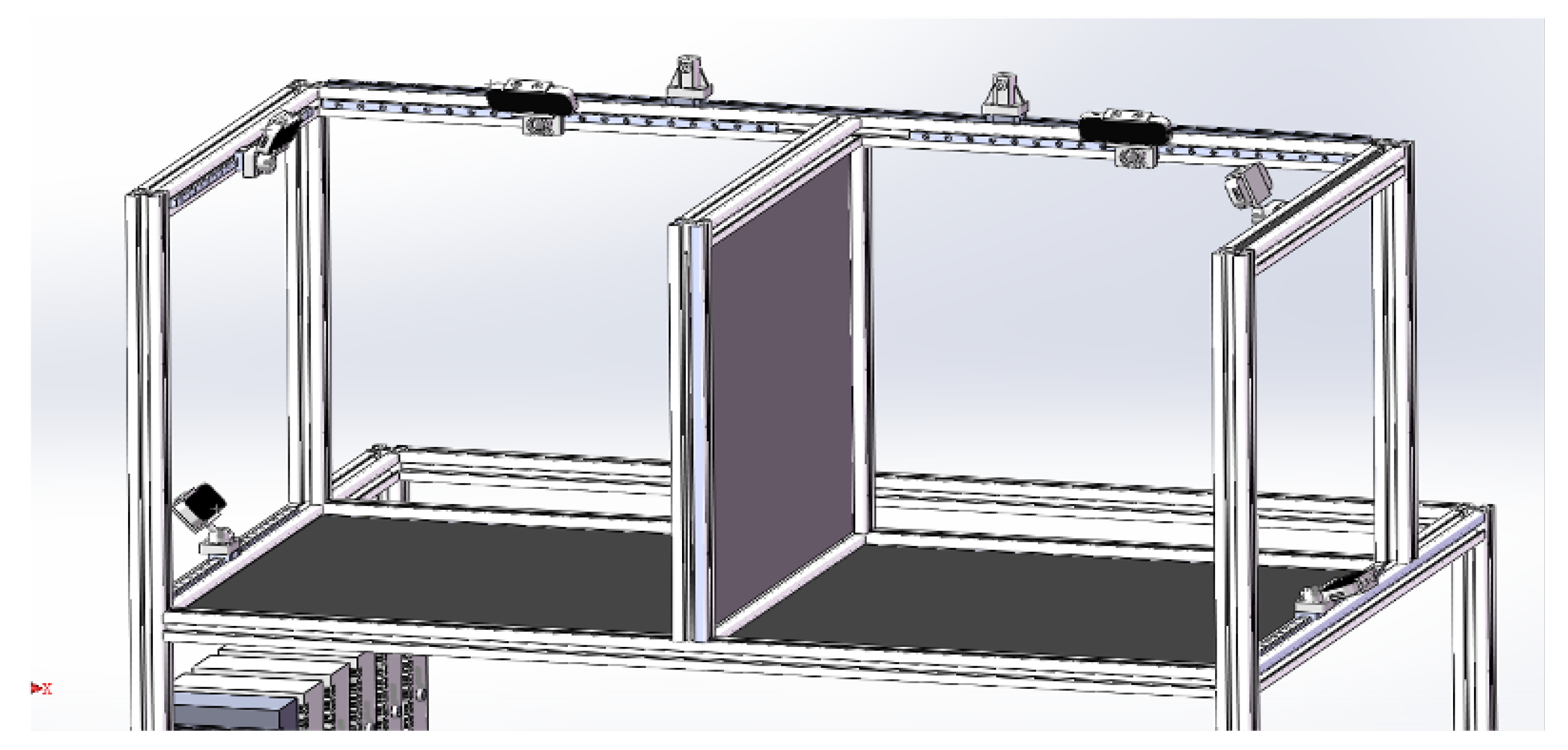
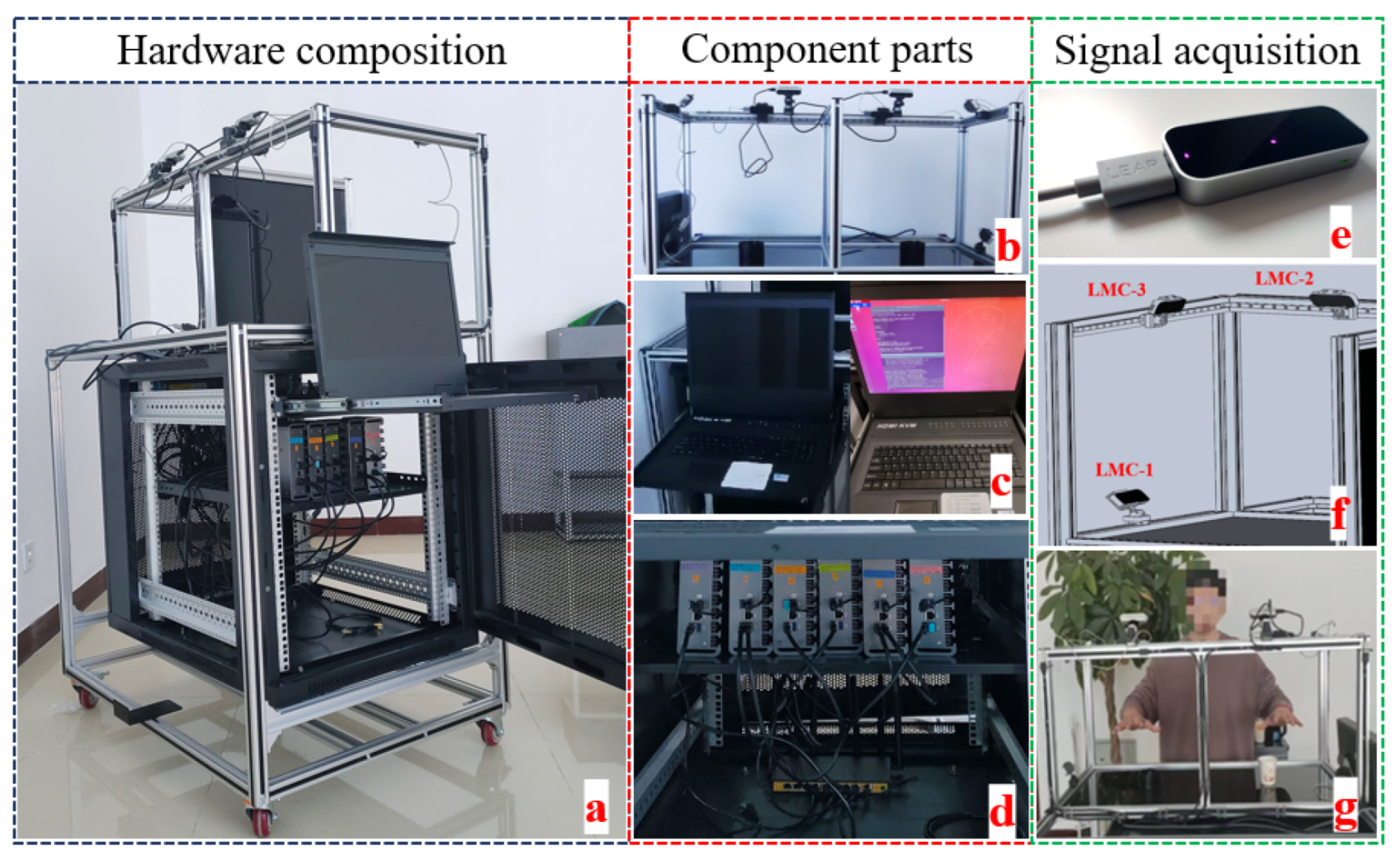
3.6. Construction of Hand Tracking System
4. Sensor Fusion Solution
4.1. Extended Kalman Filter
4.2. LSTM Optimization
5. Performance Validation
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Day, J.A.; Foley, J.D. Evaluating a web lecture intervention in a human—Computer interaction course. IEEE Trans. Educ. 2006, 49, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, P.; Noble, J.; Biddle, R. Video game values: Human–computer interaction and games. Interact. Comput. 2007, 19, 180–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Qi, W.; Schmirander, Y.; Ovur, S.E.; Cai, S.; Xiong, X. A human activity-aware shared control solution for medical human–robot interaction. Assem. Autom. 2022, 42, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Su, Z.; Cheng, C. Virtual reality in human-robot interaction: Challenges and benefits. Electron. Res. Arch. 2023, 31, 2374–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, F.; Chen, H.; Li, M.C.; Lee, S.L.; Wu, S.T. Submillisecond-response liquid crystal for high-resolution virtual reality displays. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 7984–7997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastel, S.; Marlok, J.; Bandow, N.; Witte, K. Application of eye-tracking systems integrated into immersive virtual reality and possible transfer to the sports sector—A systematic review. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 82, 4181–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Meijden, O.A.; Schijven, M.P. The value of haptic feedback in conventional and robot-assisted minimal invasive surgery and virtual reality training: A current review. Surg. Endosc. 2009, 23, 1180–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, P.R.; Phillips, J.R. Ocular effects of virtual reality headset wear in young adults. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiri, U.; Sarkar, M. Adaptive Gaze-Sensitive Virtual Reality Based Human-Computer Interaction for Adolescents with ASD; IASTED, Human-Computer Interaction (HCI, 2012); ACTA Press: Calgary, AB, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.K.; Chan, L.K.; Lau, H.Y. A low-cost lighthouse-based virtual reality head tracking system. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on 3D Immersion (IC3D), Brussels, Belgium, 11–12 December 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Clay, V.; König, P.; Koenig, S. Eye tracking in virtual reality. J. Eye Mov. Res. 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voigt-Antons, J.N.; Kojic, T.; Ali, D.; Möller, S. Influence of hand tracking as a way of interaction in virtual reality on user experience. In Proceedings of the 2020 Twelfth International Conference on Quality of Multimedia Experience (QoMEX), Athlone, Ireland, 26–28 May 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Penelle, B.; Debeir, O. Multi-sensor data fusion for hand tracking using Kinect and Leap Motion. In Proceedings of the 2014 Virtual Reality International Conference, Laval, France, 9–11 April 2014; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Worrallo, A.G.; Hartley, T. Robust optical based hand interaction for virtual reality. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2021, 28, 4186–4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jung, S.; Hoermann, S.; Lindeman, R.W. Towards an articulated avatar in VR: Improving body and hand tracking using only depth cameras. Entertain. Comput. 2019, 31, 100303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, M.A.; Kisa, D.H.; Guren, O.; Onan, A.; Akan, A. Emg based hand gesture recognition using deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 Medical Technologies Congress (TIPTEKNO), Antalya, Turkey, 19–20 November 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Zhang, C.; Han, C.; Bai, B. Gesture recognition based on Kinect v2 and leap motion data fusion. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2019, 33, 1955005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, S.; Vats, S.; Kumar, P. Evaluating and exploring the MYO ARMBAND. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference System Modeling & Advancement in Research Trends (SMART), Moradabad, India, 25–27 November 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, M.; Poupyrev, I.; Harrison, C. Touché: Enhancing touch interaction on humans, screens, liquids, and everyday objects. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Austin, TX, USA, 5–10 May 2012; pp. 483–492. [Google Scholar]
- Premaratne, P.; Premaratne, P. Historical development of hand gesture recognition. In Human Computer Interaction Using Hand Gestures; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 5–29. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Thang, N.D.; Kim, T.S. 3-D hand motion tracking and gesture recognition using a data glove. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 5–8 July 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 1013–1018. [Google Scholar]
- Pamplona, V.F.; Fernandes, L.A.; Prauchner, J.; Nedel, L.P.; Oliveira, M.M. The image-based data glove. In Proceedings of the X Symposium on Virtual Reality (SVR’2008), Porto Alegre, Brazil, 13–16 May 2008; pp. 204–211. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, A.; Hasan, O. Wearable technologies for hand joints monitoring for rehabilitation: A survey. Microelectron. J. 2019, 88, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehg, J.M.; Kanade, T. Digit-Eyes: Vision-based human hand tracking. In Technical Report; Carnegie-Mellon University Pittsburgh Pa Dept of Computer Science: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Rehg, J.M.; Kanade, T. Digiteyes: Vision-based hand tracking for human-computer interaction. In Proceedings of the 1994 IEEE Workshop on Motion of Non-Rigid and Articulated Objects, Austin, TX, USA, 11–12 November 1994; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1994; pp. 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Wachs, J.P.; Kölsch, M.; Stern, H.; Edan, Y. Vision-based hand-gesture applications. Commun. ACM 2011, 54, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, T.N.; Jizhan, L.; Xin, Z.; Shengyi, Z.; Yan, Y.; Mohamed, S.H.A.; Lakhiar, I.A. Seedling-lump integrated non-destructive monitoring for automatic transplanting with Intel RealSense depth camera. Artif. Intell. Agric. 2019, 3, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirac, F.; Kara, Y.E.; Akarun, L. Hierarchically constrained 3D hand pose estimation using regression forests from single frame depth data. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2014, 50, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberweger, M.; Wohlhart, P.; Lepetit, V. Hands deep in deep learning for hand pose estimation. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1502.06807. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, W.; Aliverti, A. A multimodal wearable system for continuous and real-time breathing pattern monitoring during daily activity. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2019, 24, 2199–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Fan, H.; Karimi, H.R.; Su, H. An adaptive reinforcement learning-based multimodal data fusion framework for human–robot confrontation gaming. Neural Netw. 2023, 164, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Qi, W.; Hu, Y.; Karimi, H.R.; Ferrigno, G.; De Momi, E. An incremental learning framework for human-like redundancy optimization of anthropomorphic manipulators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 18, 1864–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; Yan, W. Heterogeneous Network Representation Learning Approach for Ethereum Identity Identification. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2022, 10, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, D.; Wang, Y.; Lu, M.; Li, R. EGNN: Graph structure learning based on evolutionary computation helps more in graph neural networks. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 135, 110040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Su, Z.; He, X.; Cheng, C. Immersive virtual reality application for intelligent manufacturing: Applications and art design. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2023, 20, 4353–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizera, C.; Delrieu, T.; Weistroffer, V.; Andriot, C.; Decatoire, A.; Gazeau, J.P. Evaluation of hand-tracking systems in teleoperation and virtual dexterous manipulation. IEEE Sensors J. 2019, 20, 1642–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, F.; Mehta, D.; Sotnychenko, O.; Sridhar, S.; Casas, D.; Theobalt, C. Real-time hand tracking under occlusion from an egocentric rgb-d sensor. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1154–1163. [Google Scholar]
- Ratchatanantakit, N.; Nonnarit, O.; Sonchan, P.; Adjouadi, M.; Barreto, A. A sensor fusion approach to MARG module orientation estimation for a real-time hand tracking application. Inf. Fusion 2023, 90, 298–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devrio, N.; Harrison, C. DiscoBand: Multiview Depth-Sensing Smartwatch Strap for Hand, Body and Environment Tracking. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, Bend, OR, USA, 29 October–2 November 2022; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, W.; Ovur, S.E.; Li, Z.; Marzullo, A.; Song, R. Multi-sensor guided hand gesture recognition for a teleoperated robot using a recurrent neural network. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 6039–6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdlkarim, D.; Di Luca, M.; Aves, P.; Yeo, S.H.; Miall, R.C.; Holland, P.; Galea, J.M. A methodological framework to assess the accuracy of virtual reality hand-tracking systems: A case study with the oculus quest 2. BioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liliana, L.; Chae, J.H.; Lee, J.J.; Lee, B.G. A robust method for VR-based hand gesture recognition using density-based CNN. TELKOMNIKA (Telecommun. Comput. Electron. Control.) 2020, 18, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emma-Ogbangwo, C.; Cope, N.; Behringer, R.; Fabri, M. Enhancing user immersion and virtual presence in interactive multiuser virtual environments through the development and integration of a gesture-centric natural user interface developed from existing virtual reality technologies. In Proceedings of the HCI International 2014-Posters’ Extended Abstracts: International Conference, HCI International 2014, Heraklion, Crete, Greece, 22–27 June 2014; Proceedings, Part I 16. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 410–414. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Cho, S.; Baek, S.Y.; Lee, K.; Bang, H. GaFinC: Gaze and Finger Control interface for 3D model manipulation in CAD application. Comput.-Aided Des. 2014, 46, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovur, S.E.; Su, H.; Qi, W.; De Momi, E.; Ferrigno, G. Novel adaptive sensor fusion methodology for hand pose estimation with multileap motion. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigas, I.; Raffle, H.; Komogortsev, O.V. Hybrid ps-v technique: A novel sensor fusion approach for fast mobile eye-tracking with sensor-shift aware correction. IEEE Sensors J. 2017, 17, 8356–8366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, L.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Hao, S. Center-based Transfer Feature Learning With Classifier Adaptation for surface defect recognition. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 188, 110001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, H.; Fu, X.; Luan, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, N.; Sun, Z.; Niu, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, C.; et al. Self-powered difunctional sensors based on sliding contact-electrification and tribovoltaic effects for pneumatic monitoring and controlling. Nano Energy 2023, 110, 108339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Xu, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y. Arc fault detection using artificial intelligence: Challenges and benefits. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2023, 20, 12404–12432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, H.T.; Pancholi, M.; Musahl, M.; Murthy, P.; Sanchez, M.A.; Stricker, D. Inertial motion capture using adaptive sensor fusion and joint angle drift correction. In Proceedings of the 2019 22th International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2–5 July 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Colli Alfaro, J.G.; Trejos, A.L. User-independent hand gesture recognition classification models using sensor fusion. Sensors 2022, 22, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, T.D.; Aycard, O.; Tango, F. Object perception for intelligent vehicle applications: A multi-sensor fusion approach. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium Proceedings, Dearborn, MI, USA, 8–11 June 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 774–780. [Google Scholar]
- Bazo, R.; Reis, E.; Seewald, L.A.; Rodrigues, V.F.; da Costa, C.A.; Gonzaga, L., Jr.; Antunes, R.S.; da Rosa Righi, R.; Maier, A.; Eskofier, B.; et al. Baptizo: A sensor fusion based model for tracking the identity of human poses. Inf. Fusion 2020, 62, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Features | This System | Optical Marker-Less Hand-Tracking Systems | NUI | ADAS | HPE | Fast Mobile Eye Tracking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensing Modalities | EMG, Hand tracking | Hand tracking | Motion tracking, Triangulation | Lidar, Camera, Radar | RGB, RF, Radio frequency-tracking | IR, Eye tracking |
| Stereo Vision | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| Capture Depth Information of A Large Area | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No |
| Inside-out Tracking | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| 3D Environment | Yes | No | Yes | No, 2D lidar | Yes | No |
| Research Grade | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Technical Specifications | Details |
|---|---|
| Hand Tracking Method | Multi-sensor fusion incorporating Leap Motion, Realsense depth camera, and Myo Armband |
| Number of Sensors per Hand | 5 (3 Leap Motion controllers, 1 Realsense camera, 1 Myo Armband) |
| Computer System | Ubuntu 20.04 LTS running ROS Noetic Ninjemys |
| Data Processing | MATLAB 2023a |
| Virtual Reality Environment | Unity 2023.1.0, running on PICO 4 |
| Number of Joints Tracked | 22 minor joints per hand |
| Depth Perception | Provided by Realsense depth camera |
| EMG Data Collection | Myo Armband |
| Tracking Accuracy | 0.7 mm (typical for Leap Motion) |
| Depth Image Resolution | 1280 × 720 (typical for Realsense camera) |
| EMG Sampling Rate | 200 Hz (typical for Myo Armband) |
| Latency | 10 ms (average for sensor data fusion systems) |
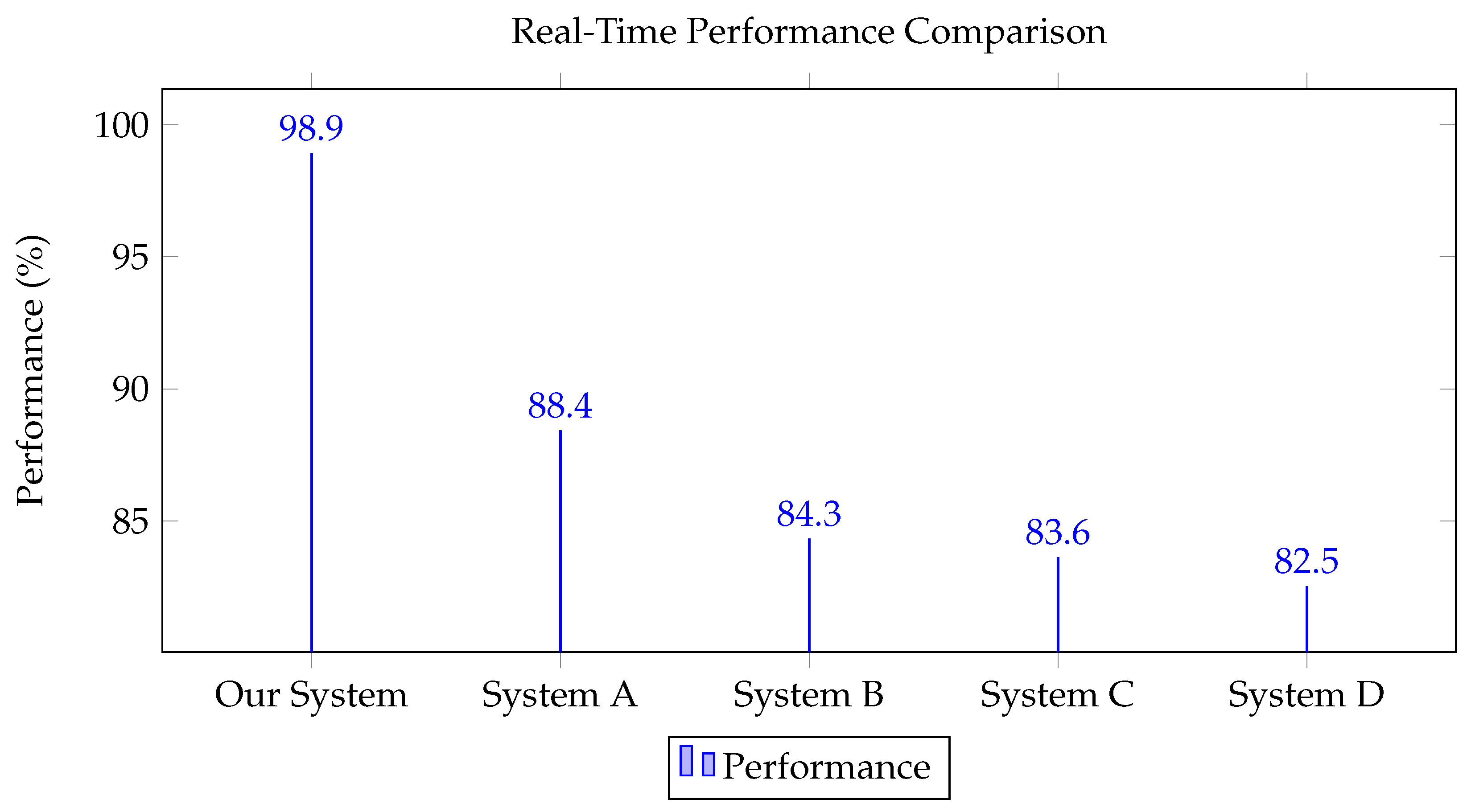
| System/Algorithm | Real-Time Performance (%) | Accuracy (%) | Robustness (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Our System (LSTM based) | 98.9 | 95.6 | 94.3 |
| System A (ANN based) | 88.4 | 85.7 | 80.3 |
| System B (SVM based) | 84.3 | 78.2 | 75.5 |
| System C (Random Forest based) | 83.6 | 77.4 | 70.3 |
| System D (Naive Bayes based) | 82.5 | 75.3 | 65.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, Y.; Deng, Y.; Dong, L.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Su, Z. A Novel Sensor Fusion Approach for Precise Hand Tracking in Virtual Reality-Based Human—Computer Interaction. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8030326
Lei Y, Deng Y, Dong L, Li X, Li X, Su Z. A Novel Sensor Fusion Approach for Precise Hand Tracking in Virtual Reality-Based Human—Computer Interaction. Biomimetics. 2023; 8(3):326. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8030326
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Yu, Yi Deng, Lin Dong, Xiaohui Li, Xiangnan Li, and Zhi Su. 2023. "A Novel Sensor Fusion Approach for Precise Hand Tracking in Virtual Reality-Based Human—Computer Interaction" Biomimetics 8, no. 3: 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8030326
APA StyleLei, Y., Deng, Y., Dong, L., Li, X., Li, X., & Su, Z. (2023). A Novel Sensor Fusion Approach for Precise Hand Tracking in Virtual Reality-Based Human—Computer Interaction. Biomimetics, 8(3), 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8030326









