Application of Artificial Intelligence in the Management of Pancreatic Cystic Lesions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Artificial Intelligence:
1.2. The Application of AI to Manage Pancreatic Cystic Lesions: EUS
2. AI and EUS in PCL Risk Stratification
3. AI and EUS-Guided Advanced Diagnostics
4. The Future of AI and EUS
4.1. Radiomics
4.1.1. Radiomics and PDAC
4.1.2. Radiomics and PCLs
4.2. Genomics
4.2.1. Current Use of Genomics in PCL Management
4.2.2. AI Genomics in Early Detection of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
5. Risk Stratification Using AI + Genomics in PCL
6. The Future: Integrative Computational Models
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zerboni, G.; Signoretti, M.; Crippa, S.; Falconi, M.; Arcidiacono, P.G.; Capurso, G. Systematic review and meta-analysis: Prevalence of incidentally detected pancreatic cystic lesions in asymptomatic individuals. Pancreatology 2019, 19, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, A.; Donahue, T.R.; Reber, H.A.; Hines, O.J. Pancreatic Cyst Disease. JAMA 2016, 315, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Fernández-del Castillo, C.; Kamisawa, T.; Jang, J.Y.; Levy, P.; Ohtsuka, T.; Salvia, R.; Shimizu, Y.; Tada, M.; Wolfgang, C.L. Revisions of international consensus Fukuoka guidelines for the management of IPMN of the pancreas. Pancreatology 2017, 17, 738–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elta, G.H.; Enestvedt, B.K.; Sauer, B.G.; Lennon, A.M. ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Pancreatic Cysts. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 464–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babiker, H.M.; Hoilat, G.J.; Recio-Boiles, A. Mucinous Cystic Pancreatic Neoplasms; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.W.; Jang, J.Y.; Kang, M.J.; Kwon, W.; Chang, Y.R.; Kim, S.W. Mucinous cystic neoplasm of the pancreas: Is surgical resection recommended for all surgically fit patients? Pancreatology 2014, 14, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dababneh, Y.; Mousa, O.Y. Pancreatic Serous Cystadenoma; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Law, J.K.; Ahmed, A.; Singh, V.K.; Akshintala, V.S.; Olson, M.T.; Raman, S.P.; Ali, S.Z.; Fishman, E.; Kamel, I.; Canto, M.I.; et al. A Systematic Review of Solid-Pseudopapillary Neoplasms. Pancreas 2014, 43, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jais, B.; Rebours, V.; Malleo, G.; Salvia, R.; Fontana, M.; Maggino, L.; Bassi, C.; Manfredi, R.; Moran, R.; Lennon, A.M.; et al. Serous cystic neoplasm of the pancreas: A multinational study of 2622 patients under the auspices of the International Association of Pancreatology and European Pancreatic Club (European Study Group on Cystic Tumors of the Pancreas). Gut 2016, 65, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morales-Oyarvide, V.; Fong, Z.V.; Fernández-del Castillo, C.; Warshaw, A.L. Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms of the Pancreas: Strategic Considerations. Visc. Med. 2017, 33, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyama, H.; Tada, M.; Takagi, K.; Tateishi, K.; Hamada, T.; Nakai, Y.; Hakuta, R.; Ijichi, H.; Ishigaki, K.; Kanai, S.; et al. Long-term Risk of Malignancy in Branch-Duct Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 226–237.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shuja, A.; Alkimawi, K.A. Solid pseudopapillary tumor: A rare neoplasm of the pancreas. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2014, 2, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, S.; Johnson, P.T.; Shi, C.; Singhi, A.D.; Hruban, R.H.; Wolfgang, C.L.; Edil, B.H.; Fishman, E.K. Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor with Cystlike Changes: Evaluation with MDCT. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2013, 200, W283–W290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ro, C.; Chai, W.; Yu, V.E.; Yu, R. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: Biology, diagnosis, and treatment. Chin. J. Cancer 2013, 32, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vege, S.S.; Ziring, B.; Jain, R.; Moayyedi, P.; Adams, M.A.; Dorn, S.D.; Dudley-Brown, S.L.; Flamm, S.L.; Gellad, Z.F.; Gruss, C.B.; et al. American Gastroenterological Association Institute Guideline on the Diagnosis and Management of Asymptomatic Neoplastic Pancreatic Cysts. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, M.; Fernández-del Castillo, C.; Adsay, V.; Chari, S.; Falconi, M.; Jang, J.-Y.; Kimura, W.; Levy, P.; Pitman, M.B.; Schmidt, C.M.; et al. International consensus guidelines 2012 for the management of IPMN and MCN of the pancreas. Pancreatology 2012, 12, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, S.; Masica, D.L.; Dal Molin, M.; Douville, C.; Thoburn, C.J.; Afsari, B.; Li, L.; Cohen, J.D.; Thompson, E.; Allen, P.J.; et al. A multimodality test to guide the management of patients with a pancreatic cyst. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaav4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perri, G.; Marchegiani, G.; Frigerio, I.; Dervenis, C.G.; Conlon, K.C.; Bassi, C.; Salvia, R. Management of Pancreatic Cystic Lesions. Dig. Surg. 2020, 37, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litchinko, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Halkic, N. A retrospective study of histological outcome for IPMN after surgery in Lausanne, Switzerland: A case series. Ann. Med. Surg. 2020, 60, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Berre, C.; Sandborn, W.J.; Aridhi, S.; Devignes, M.-D.; Fournier, L.; Smaïl-Tabbone, M.; Danese, S.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Application of Artificial Intelligence to Gastroenterology and Hepatology. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 76–94.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sahora, K.; Ferrone, C.R.; Brugge, W.R.; Morales-Oyarvide, V.; Warshaw, A.L.; Lillemoe, K.D.; Castillo, C.F.-D. Effects of Comorbidities on Outcomes of Patients with Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 1816–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaujoux, S.; Brennan, M.F.; Gonen, M.; D’Angelica, M.I.; DeMatteo, R.; Fong, Y.; Schattner, M.; DiMaio, C.; Janakos, M.; Jarnagin, W.R.; et al. Cystic Lesions of the Pancreas: Changes in the Presentation and Management of 1424 Patients at a Single Institution over a 15-Year Time Period. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2011, 212, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valsangkar, N.P.; Morales-Oyarvide, V.; Thayer, S.P.; Ferrone, C.R.; Wargo, J.A.; Warshaw, A.L.; Fernandez-del Castillo, C. 851 resected cystic tumors of the pancreas: A 33-year experience at the Massachusetts General Hospital. Surgery 2012, 152, S4–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marchegiani, G.; Pollini, T.; Andrianello, S.; Tomasoni, G.; Biancotto, M.; Javed, A.A.; Kinny-Köster, B.; Amini, N.; Han, Y.; Kim, H.; et al. Progression vs Cyst Stability of Branch-Duct Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms After Observation and Surgery. JAMA Surg. 2021, 156, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahora, K.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Brugge, W.; Thayer, S.P.; Ferrone, C.R.; Sahani, D.; Pitman, M.B.; Warshaw, A.L.; Lillemoe, K.D.; Fernandez-del Castillo, C.F. Branch Duct Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms. Ann. Surg. 2013, 258, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.J.; Bang, C.S. Application of artificial intelligence in gastroenterology. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 1666–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Jiang, Y.; Zhi, H.; Dong, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, S.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Q.; Shen, H.; Wang, Y. Artificial intelligence in healthcare: Past, present and future. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2017, 2, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalal, V.; Carmicheal, J.; Dhaliwal, A.; Jain, M.; Kaur, S.; Batra, S.K. Radiomics in stratification of pancreatic cystic lesions: Machine learning in action. Cancer Lett. 2020, 469, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkomar, A.; Dean, J.; Kohane, I. Machine Learning in Medicine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1347–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.K.; Kwak, M.S.; Cha, J.M. Overview of Deep Learning in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Gut Liver 2019, 13, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hekler, A.; Utikal, J.S.; Enk, A.H.; Solass, W.; Schmitt, M.; Klode, J.; Schadendorf, D.; Sondermann, W.; Franklin, C.; Bestvater, F.; et al. Deep learning outperformed 11 pathologists in the classification of histopathological melanoma images. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 118, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brinker, T.J.; Hekler, A.; Enk, A.H.; Klode, J.; Hauschild, A.; Berking, C.; Schilling, B.; Haferkamp, S.; Schadendorf, D.; Holland-Letz, T.; et al. Deep learning outperformed 136 of 157 dermatologists in a head-to-head dermoscopic melanoma image classification task. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 113, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Okusaka, T.; Shimizu, K.; Furuse, J.; Ito, Y.; Hanada, K.; Shimosegawa, T.; Okazaki, K. Clinical Practice Guidelines for Pancreatic Cancer 2016 from the Japan Pancreas Society. Pancreas 2017, 46, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, Y.T.; Kim, K.G. Automatic Pancreatic Cyst Lesion Segmentation on EUS Images Using a Deep-Learning Approach. Sensors 2021, 22, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitano, M.; Yoshida, T.; Itonaga, M.; Tamura, T.; Hatamaru, K.; Yamashita, Y. Impact of endoscopic ultrasonography on diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 54, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Norton, I.D.; Zheng, Y.; Wiersema, M.S.; Greenleaf, J.; Clain, J.E.; DiMagno, E.P. Neural network analysis of EUS images to differentiate between pancreatic malignancy and pancreatitis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2001, 54, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marya, N.B.; Powers, P.D.; Chari, S.T.; Gleeson, F.C.; Leggett, C.L.; Abu Dayyeh, B.K.; Chandrasekhara, V.; Iyer, P.G.; Majumder, S.; Pearson, R.K.; et al. Utilisation of artificial intelligence for the development of an EUS-convolutional neural network model trained to enhance the diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut 2021, 70, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, L.; Chu, Y.; Hou, X.; Xing, L.; Kong, F.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jin, Z.; Li, Z. A new descriptor for computer-aided diagnosis of EUS imaging to distinguish autoimmune pancreatitis from chronic pancreatitis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 82, 831–836.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Săftoiu, A.; Vilmann, P.; Gorunescu, F.; Janssen, J.; Hocke, M.; Larsen, M.; Iglesias–Garcia, J.; Arcidiacono, P.G.; Will, U.; Giovannini, M.; et al. Efficacy of an Artificial Neural Network–Based Approach to Endoscopic Ultrasound Elastography in Diagnosis of Focal Pancreatic Masses. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonozuka, R.; Itoi, T.; Nagata, N.; Kojima, H.; Sofuni, A.; Tsuchiya, T.; Ishii, K.; Tanaka, R.; Nagakawa, Y.; Mukai, S. Deep learning analysis for the detection of pancreatic cancer on endosonographic images: A pilot study. J. Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat. Sci. 2021, 28, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwahara, T.; Hara, K.; Mizuno, N.; Okuno, N.; Matsumoto, S.; Obata, M.; Kurita, Y.; Koda, H.; Toriyama, K.; Onishi, S.; et al. Usefulness of Deep Learning Analysis for the Diagnosis of Malignancy in Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms of the Pancreas. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2019, 10, e00045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguon, L.; Seo, K.; Lim, J.-H.; Song, T.-J.; Cho, S.-H.; Park, J.-S.; Park, S. Deep Learning-Based Differentiation between Mucinous Cystic Neoplasm and Serous Cystic Neoplasm in the Pancreas Using Endoscopic Ultrasonography. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, Y.; Iwashita, T.; Park, D.H.; Samarasena, J.B.; Lee, J.G.; Chang, K.J. Diagnosis of pancreatic cysts: EUS-guided, through-the-needle confocal laser-induced endomicroscopy and cystoscopy trial: DETECT study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 81, 1204–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konda, V.J.A.; Meining, A.; Jamil, L.H.; Giovannini, M.; Hwang, J.H.; Wallace, M.B.; Chang, K.J.; Siddiqui, U.D.; Hart, J.; Lo, S.K.; et al. A pilot study of in vivo identification of pancreatic cystic neoplasms with needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy under endosonographic guidance. Endoscopy 2013, 45, 1006–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, S.G.; Hart, P.A.; Malli, A.; Kruger, A.J.; McCarthy, S.T.; Eldika, S.; Walker, J.P.; Dillhoff, M.E.; Manilchuk, A.; Schmidt, C.R.; et al. Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy Increases Accuracy of Differentiation of Pancreatic Cystic Lesions. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machicado, J.D.; Chao, W.-L.; Carlyn, D.E.; Pan, T.-Y.; Poland, S.; Alexander, V.L.; Maloof, T.G.; Dubay, K.; Ueltschi, O.; Middendorf, D.M.; et al. High performance in risk stratification of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms by confocal laser endomicroscopy image analysis with convolutional neural networks (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 94, 78–87.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, S.G.; Chao, W.-L.; Strobel, S.G.; Stanich, P.P.; Patel, A.; Luthra, A.; Chan, M.Q.; Blaszczak, A.; Lee, D.; Porter, K.; et al. Mo2052—Application of Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence in the Detection of Dyplasia in Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms Using Eus-Guided Needle-Based Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, S-938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Jiang, F.; Zhu, J.; Du, Y.; Jin, Z.; Li, Z. Assessment of morbidity and mortality associated with endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration for pancreatic cystic lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig. Endosc. 2017, 29, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertani, H.; Pezzilli, R.; Pigò, F.; Bruno, M.; De Angelis, C.; Manfredi, G.; Delconte, G.; Conigliaro, R.; Buscarini, E. Needle-based confocal endomicroscopy in the discrimination of mucinous from non-mucinous pancreatic cystic lesions. World J. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 13, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacevic, B.; Antonelli, G.; Klausen, P.; Hassan, C.; Larghi, A.; Vilmann, P.; Karstensen, J. EUS-guided biopsy versus confocal laser endomicroscopy in patients with pancreatic cystic lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Endosc. Ultrasound 2021, 10, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán-Calderón, E.; Martinez-Moreno, B.; Casellas, J.A.; de Madaria, E.; Aparicio, J.R. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided, through-the-needle forceps biopsy for diagnosis of pancreatic cystic lesions: A systematic review. Endosc. Int. Open 2020, 8, E1123–E1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayerhoefer, M.E.; Materka, A.; Langs, G.; Häggström, I.; Szczypiński, P.; Gibbs, P.; Cook, G. Introduction to Radiomics. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, B.A.; Cen, S.Y.; Hwang, D.H.; Duddalwar, V.A. Texture Analysis of Imaging: What Radiologists Need to Know. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 212, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, W.; Seetha, S.T.; Refaee, T.A.G.; Lieverse, R.I.Y.; Granzier, R.W.Y.; Ibrahim, A.; Keek, S.A.; Sanduleanu, S.; Primakov, S.P.; Beuque, M.P.L.; et al. Radiomics: From qualitative to quantitative imaging. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20190948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dmitriev, K.; Kaufman, A.E.; Javed, A.A.; Hruban, R.H.; Fishman, E.K.; Lennon, A.M.; Saltz, J.H. Classification of Pancreatic Cysts in Computed Tomography Images Using a Random Forest and Convolutional Neural Network Ensemble. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2017, 10435, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Yang, F.; Yang, P.; Yang, M.; Xu, L.; Zhuo, J.; Wang, J.; Lu, D.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, S.-S.; et al. A Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography Based Radiomics Approach for Preoperative Differentiation of Pancreatic Cystic Neoplasm Subtypes: A Feasibility Study. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, H.; Ma, S.; Guo, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Preoperative differentiation of pancreatic mucinous cystic neoplasm from macrocystic serous cystic adenoma using radiomics: Preliminary findings and comparison with radiological model. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 122, 108747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, R.; Lin, K.; Yan, W.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, J. Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Pancreas Serous Cystic Neoplasms: A Radiomics Method on Preoperative MDCT Images. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Granata, V.; Grassi, R.; Fusco, R.; Galdiero, R.; Setola, S.V.; Palaia, R.; Belli, A.; Silvestro, L.; Cozzi, D.; Brunese, L.; et al. Pancreatic cancer detection and characterization: State of the art and radiomics. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 3684–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udare, A.; Agarwal, M.; Alabousi, M.; McInnes, M.; Rubino, J.G.; Marcaccio, M.; van der Pol, C.B. Diagnostic Accuracy of MRI for Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Pancreatic Cystic Lesions Compared to CT and Endoscopic Ultrasound: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2021, 54, 1126–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, T.; Preczewski, L.; Stocker, S.J.; Rao, S.M.; Parsons, W.G.; Wayne, J.D.; Bell, R.H.; Talamonti, M.S. Incidence of benign inflammatory disease in patients undergoing Whipple procedure for clinically suspected carcinoma: A single-institution experience. Am. J. Surg. 2006, 191, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Ming, B.; Zhou, T.; Wu, J.-L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Chen, T.-W.; Zhang, X.-M. Radiomics Model Based on MR Images to Discriminate Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma and Mass-Forming Chronic Pancreatitis Lesions. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hu, L.; Zhou, B.; Wu, C.; Cheng, Y. Development and validation of a novel model incorporating MRI-based radiomics signature with clinical biomarkers for distinguishing pancreatic carcinoma from mass-forming chronic pancreatitis. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 18, 101357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.K.; Jang, J.-Y.; Kwon, W.; Kim, H.; Han, Y.; Kim, D.; Park, D.; Kim, J.H. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Prediction of next-generation sequencing-based tumor cellularity and prognosis after surgical resection. Abdom. Radiol. 2021, 46, 4787–4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Ding, Y.; Yu, Y.; Liu, K.; Rao, S.; Ge, Y.; Zeng, M. Whole-tumour evaluation with MRI and radiomics features to predict the efficacy of S-1 for adjuvant chemotherapy in postoperative pancreatic cancer patients: A pilot study. BMC Med. Imaging 2021, 21, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.; Shi, H.; Lu, M.; Wang, C.; Duan, S.; Xu, Q.; Shi, H. Radiomics Analysis for Predicting Malignant Potential of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms of the Pancreas: Comparison of CT and MRI. Acad. Radiol. 2022, 29, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, D.H.; Ream, J.M.; Hajdu, C.H.; Rosenkrantz, A.B. Utility of whole-lesion ADC histogram metrics for assessing the malignant potential of pancreatic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs). Abdom. Radiol. 2017, 42, 1222–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Tang, T.; Su, Q.; Wang, Y.; Shu, Z.; Yang, W.; Gong, X. Radiomic nomogram based on MRI to predict grade of branching type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: A multicenter study. Cancer Imaging 2021, 21, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Liang, H.; Zhong, J.; Wei, Y.; Ma, Y. How does the pancreatic solid pseudopapillary neoplasm confuse us: Analyzing from the point view of MRI-based radiomics? Magn. Reson. Imaging 2022, 85, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobaly, D.; Santinha, J.; Sartoris, R.; Burgio, M.D.; Matos, C.; Cros, J.; Couvelard, A.; Rebours, V.; Sauvanet, A.; Ronot, M.; et al. CT-Based Radiomics Analysis to Predict Malignancy in Patients with Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm (IPMN) of the Pancreas. Cancers 2020, 12, 3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buerlein, R.C.D.; Shami, V.M. Management of pancreatic cysts and guidelines: What the gastroenterologist needs to know. Ther. Adv. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 14, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardeshna, D.R.; Cao, T.; Rodgers, B.; Onongaya, C.; Jones, D.; Chen, W.; Koay, E.J.; Krishna, S.G. Recent advances in the diagnostic evaluation of pancreatic cystic lesions. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, R.; Krishna, S.G.; Chen, W.; Frankel, W.L.; Shen, R.; Zhao, W.; Avenarius, M.R.; Garee, J.; Caruthers, S.; Jones, D. Activation of the RAS pathway through uncommon BRAF mutations in mucinous pancreatic cysts without KRAS mutation. Mod. Pathol. 2021, 34, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhi, A.D.; McGrath, K.; Brand, R.E.; Khalid, A.; Zeh, H.J.; Chennat, J.S.; Fasanella, K.E.; Papachristou, G.I.; Slivka, A.; Bartlett, D.L.; et al. Preoperative next-generation sequencing of pancreatic cyst fluid is highly accurate in cyst classification and detection of advanced neoplasia. Gut 2018, 67, 2131–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goonetilleke, K.S.; Siriwardena, A.K. Systematic review of carbohydrate antigen (CA 19-9) as a biochemical marker in the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2007, 33, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.M.; Wang, J.S.; Zulfiqar, H.; Lv, H.; Dao, F.Y.; Lin, H. Early Diagnosis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma by Combining Relative Expression Orderings with Machine-Learning Method. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 582864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blyuss, O.; Zaikin, A.; Cherepanova, V.; Munblit, D.; Kiseleva, E.M.; Prytomanova, O.M.; Duffy, S.W.; Crnogorac-Jurcevic, T. Development of PancRISK, a urine biomarker-based risk score for stratified screening of pancreatic cancer patients. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinkala, M.; Mulder, N.; Martin, D. Machine Learning and Network Analyses Reveal Disease Subtypes of Pancreatic Cancer and their Molecular Characteristics. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Savareh, B.A.; Aghdaie, H.A.; Behmanesh, A.; Bashiri, A.; Sadeghi, A.; Zali, M.; Shams, R. A machine learning approach identified a diagnostic model for pancreatic cancer through using circulating microRNA signatures. Pancreatology 2020, 20, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, B.; Lee, H. Prediction of survival and recurrence in patients with pancreatic cancer by integrating multi-omics data. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maker, A.V.; Hu, V.; Kadkol, S.S.; Hong, L.; Brugge, W.; Winter, J.; Yeo, C.J.; Hackert, T.; Büchler, M.; Lawlor, R.T.; et al. Cyst Fluid Biosignature to Predict Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms of the Pancreas with High Malignant Potential. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2019, 228, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheiman, J.M.; Hwang, J.H.; Moayyedi, P. American Gastroenterological Association Technical Review on the Diagnosis and Management of Asymptomatic Neoplastic Pancreatic Cysts. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 824–848.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dbouk, M.; Gutierrez, O.I.B.; Lennon, A.M.; Chuidian, M.; Shin, E.J.; Kamel, I.R.; Fishman, E.K.; He, J.; Burkhart, R.A.; Wolfgang, C.L.; et al. Guidelines on management of pancreatic cysts detected in high-risk individuals: An evaluation of the 2017 Fukuoka guidelines and the 2020 International Cancer of the Pancreas Screening (CAPS) consortium statements. Pancreatology 2021, 21, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaimakliotis, P.; Riff, B.; Pourmand, K.; Chandrasekhara, V.; Furth, E.E.; Siegelman, E.S.; Drebin, J.; Vollmer, C.M.; Kochman, M.L.; Ginsberg, G.G.; et al. Sendai and Fukuoka Consensus Guidelines Identify Advanced Neoplasia in Patients with Suspected Mucinous Cystic Neoplasms of the Pancreas. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 1808–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heckler, M.; Michalski, C.W.; Schaefle, S.; Kaiser, J.; Büchler, M.W.; Hackert, T. The Sendai and Fukuoka consensus criteria for the management of branch duct IPMN—A meta-analysis on their accuracy. Pancreatology 2017, 17, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
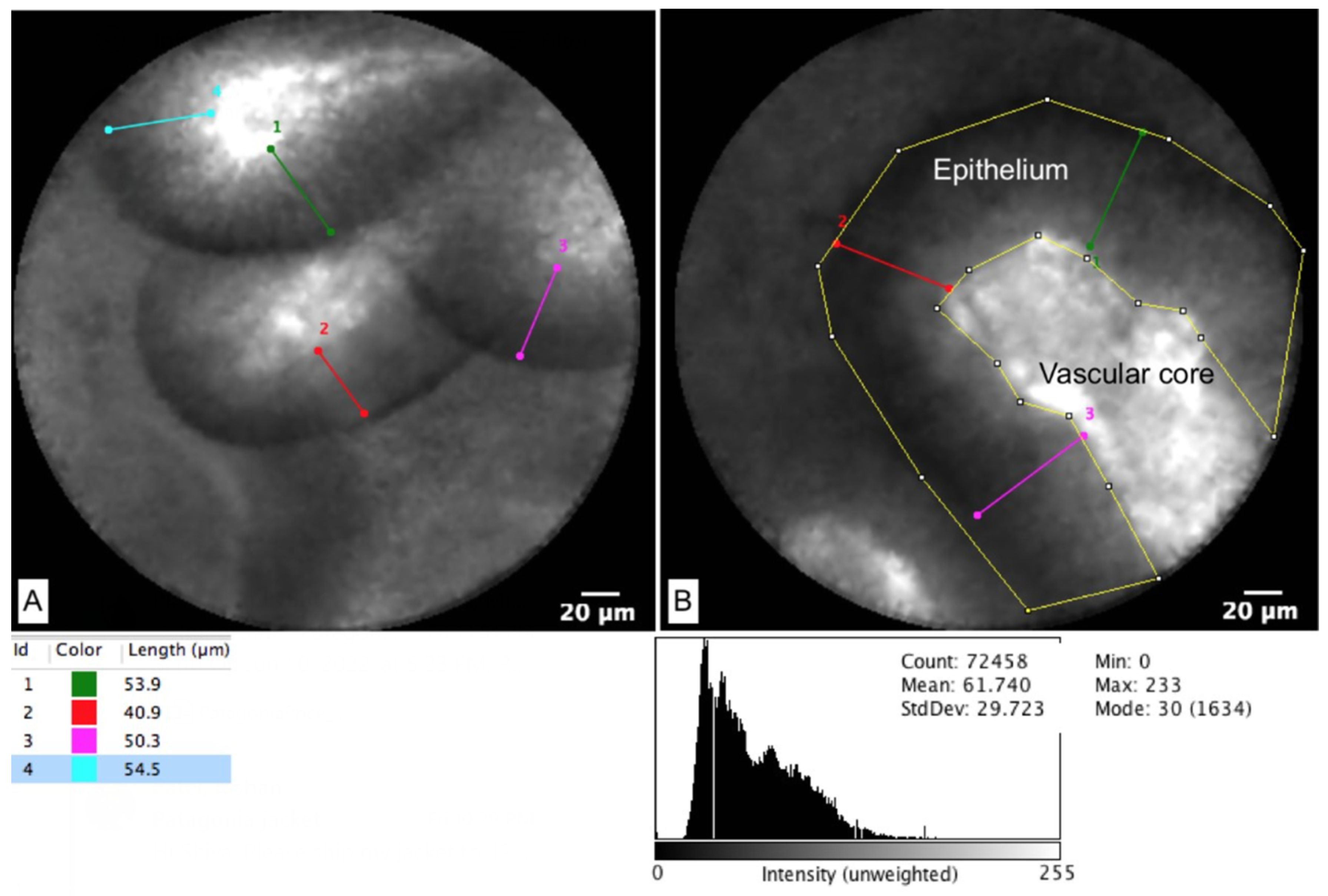
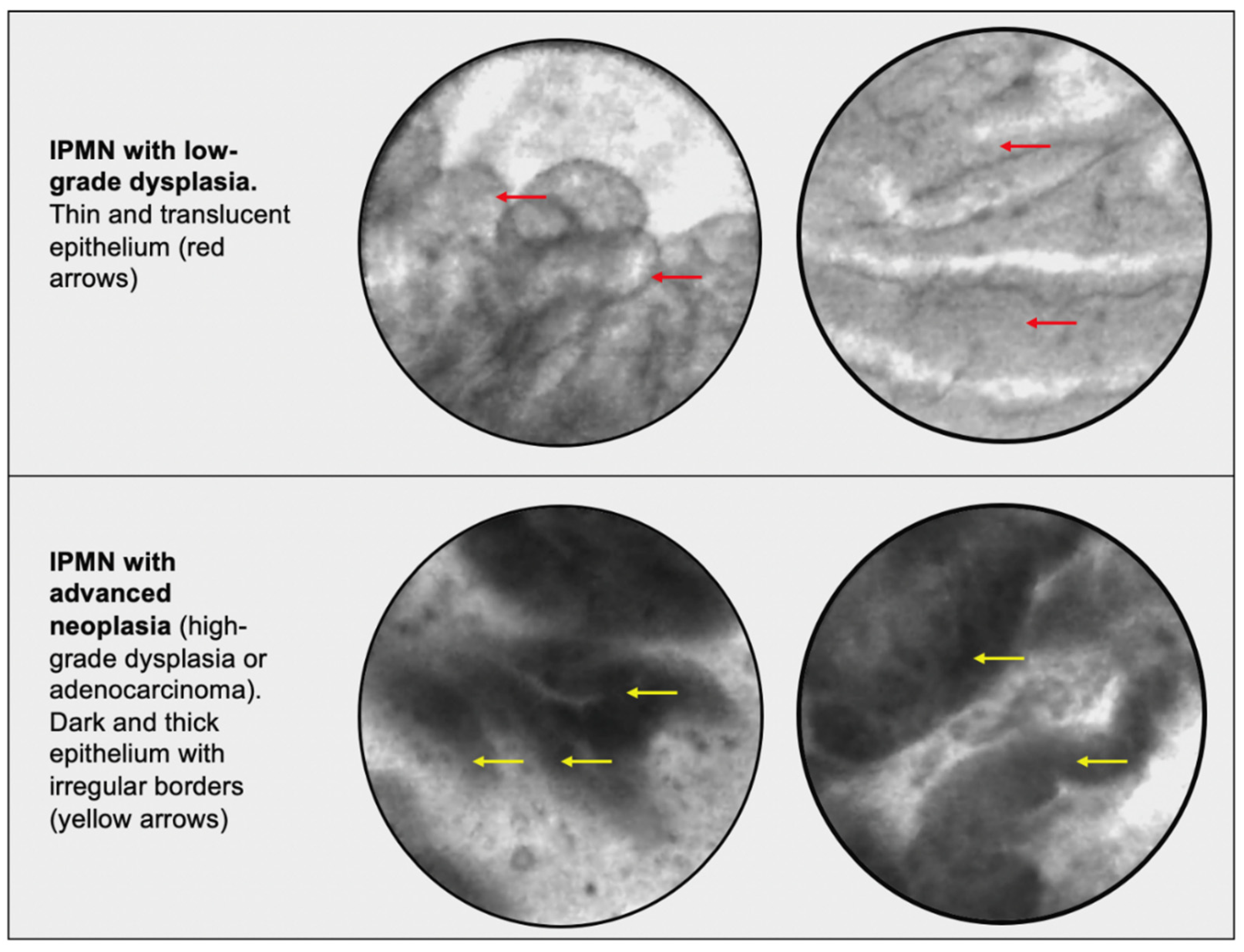
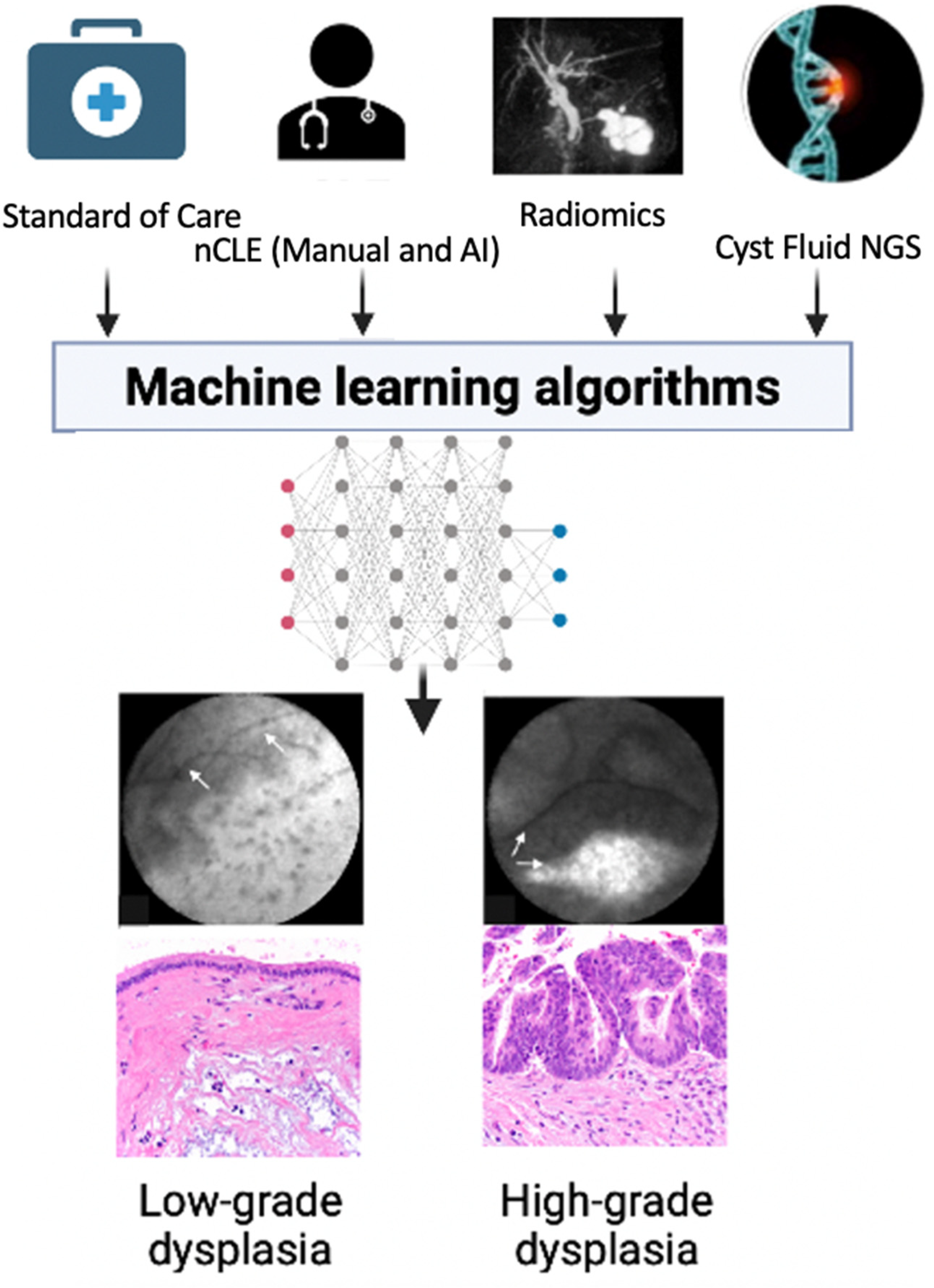
| Cyst Type | Characteristics | Rate of Malignancy (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Main duct IPMN | Mucinous cyst with variable malignant potential, characterized by main pancreatic duct dilation > 5 mm in the absence of other causes of obstruction [3] | 38–68% [2] |
| Branch duct IPMN | Mucinous cyst with variable malignant potential, characterized as a cyst > 5 mm in diameter that is in communication with the main pancreatic duct. Most common IPMN type [3]. | 15–17% [3,11] |
| Mixed IPMN | Displays features of both MD-IPMN and BD-IPMN [3] | 28-31% [10] |
| Mucinous cystic neoplasm | Found almost exclusively in middle-aged women. Mucinous cyst most commonly found in the body or tail of the pancreas. Usually no communication with the pancreatic duct. Columnar epithelium with ovarian stroma differentiates from IPMN [5]. | 10% [6] |
| Cystic pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor | Can be solid, cystic, or mixed composition. Can mimic other cyst types on imaging. Can be associated with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) [13]. | 6–31% [14] |
| Serous cystadenoma | More common in women. Benign, usually found in the tail of the pancreas. Imaging shows microcystic or macrocystic appearance. Central stellate scar is characteristic but not always present. Associated with von Hippel-Lindau disease [7]. | 0.01% [9] |
| Solid pseudopapillary neoplasm | More common in younger women, commonly third decade of life. Can occur anywhere in the pancreas. Small tumors are usually solid. Large tumors usually have mixed solid and cystic components. Generally well encapsulated and carry a good prognosis [12]. | 10% [8] |
| Pseudocyst | Benign cyst in patients with history of pancreatitis. Typically high lipase and amylase in cyst fluid. | 0% [4] |
| Term | Definition | Subset of AI |
|---|---|---|
| Machine learning (ML) | Models that use historical data (inputs) to categorize and predict outcomes (outputs). Requires human intervention via algorithm training. | ML |
| Deep learning (DL) | A subfield of ML that uses layered neural networks to automatically record and categorize data outputs without human intervention. | DL |
| Linear discriminants | A method used to create a linear combination of characteristics that separates/characterizes data into two subsets | ML |
| Bayesian networks | A probabilistic model that relies on independent/dependent input variables to identify causal probabilities of scenarios | ML |
| Random forest | A model made up of a large number of decision trees, each producing their own prediction. Predictions are combined to formulate a more accurate prediction of an event occurrence. | ML |
| Support vector machines (SVM) | Supervised ML algorithm that is capable of performing regression, classification, and outlier prediction | ML |
| Artificial neural networks (ANN) | Computing algorithms that mimic the human neuron. Each ANN has an input layer and an output layer. Between these layers are hidden layers in which variables are weighted, similar to action potentials. | ML/DL |
| Convoluted neural networks (CNN) | Type of ANN that allows for unsupervised evaluation of input data, usually in the form of image, speech, or text | DL |
| Method | Logistic Regression | Neural Network | Random Forest | Support Vector Machines | Neuro-Fuzzy Technology |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.86 | 0.82 | 0.87 |
| Specificity | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.82 | 0.89 | 0.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rangwani, S.; Ardeshna, D.R.; Rodgers, B.; Melnychuk, J.; Turner, R.; Culp, S.; Chao, W.-L.; Krishna, S.G. Application of Artificial Intelligence in the Management of Pancreatic Cystic Lesions. Biomimetics 2022, 7, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7020079
Rangwani S, Ardeshna DR, Rodgers B, Melnychuk J, Turner R, Culp S, Chao W-L, Krishna SG. Application of Artificial Intelligence in the Management of Pancreatic Cystic Lesions. Biomimetics. 2022; 7(2):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7020079
Chicago/Turabian StyleRangwani, Shiva, Devarshi R. Ardeshna, Brandon Rodgers, Jared Melnychuk, Ronald Turner, Stacey Culp, Wei-Lun Chao, and Somashekar G. Krishna. 2022. "Application of Artificial Intelligence in the Management of Pancreatic Cystic Lesions" Biomimetics 7, no. 2: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7020079
APA StyleRangwani, S., Ardeshna, D. R., Rodgers, B., Melnychuk, J., Turner, R., Culp, S., Chao, W.-L., & Krishna, S. G. (2022). Application of Artificial Intelligence in the Management of Pancreatic Cystic Lesions. Biomimetics, 7(2), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7020079







