CF-PEEK vs. Titanium Dental Implants: Stress Distribution and Fatigue Performance in Variable Bone Qualities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
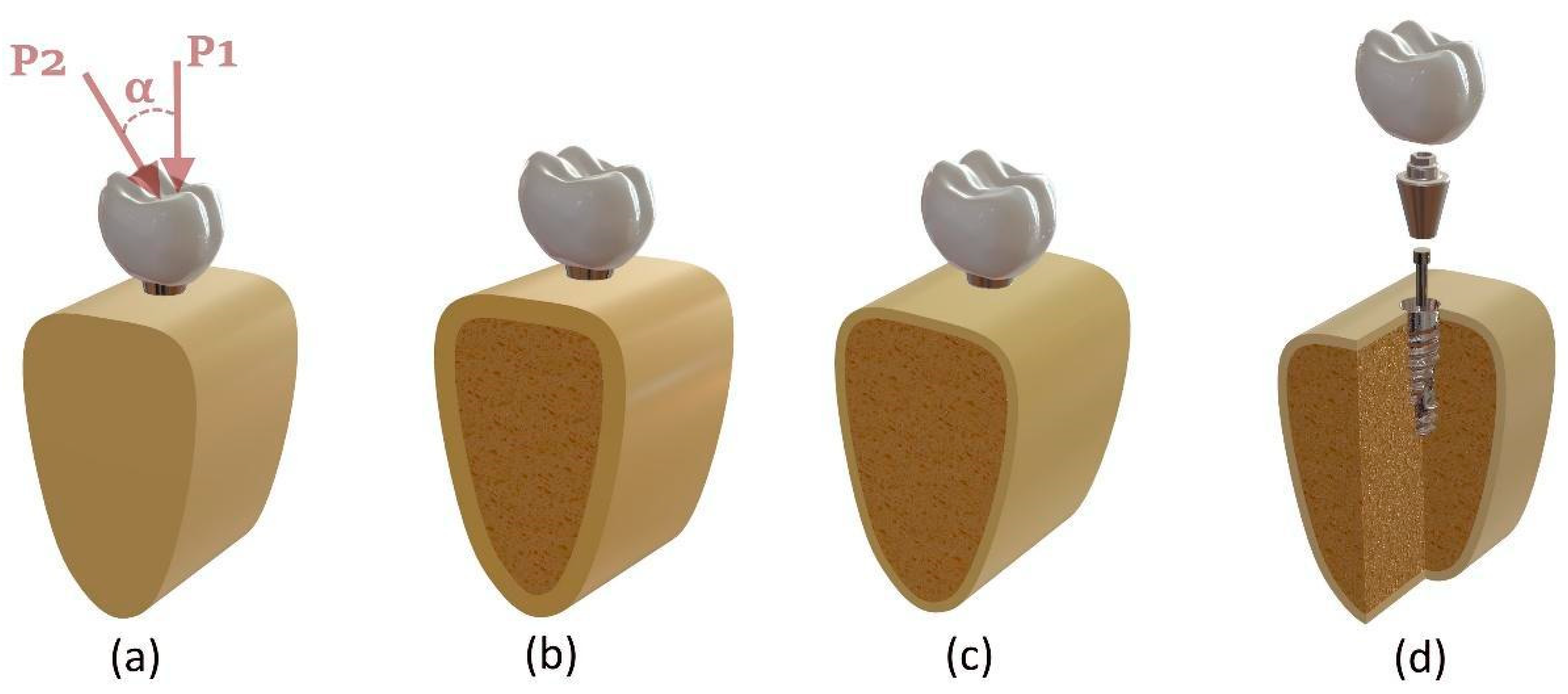
2.1. Three-Dimensional Modeling Procedure
2.2. Boundary and Loading Conditions
2.3. Fatigue Analysis
3. Results
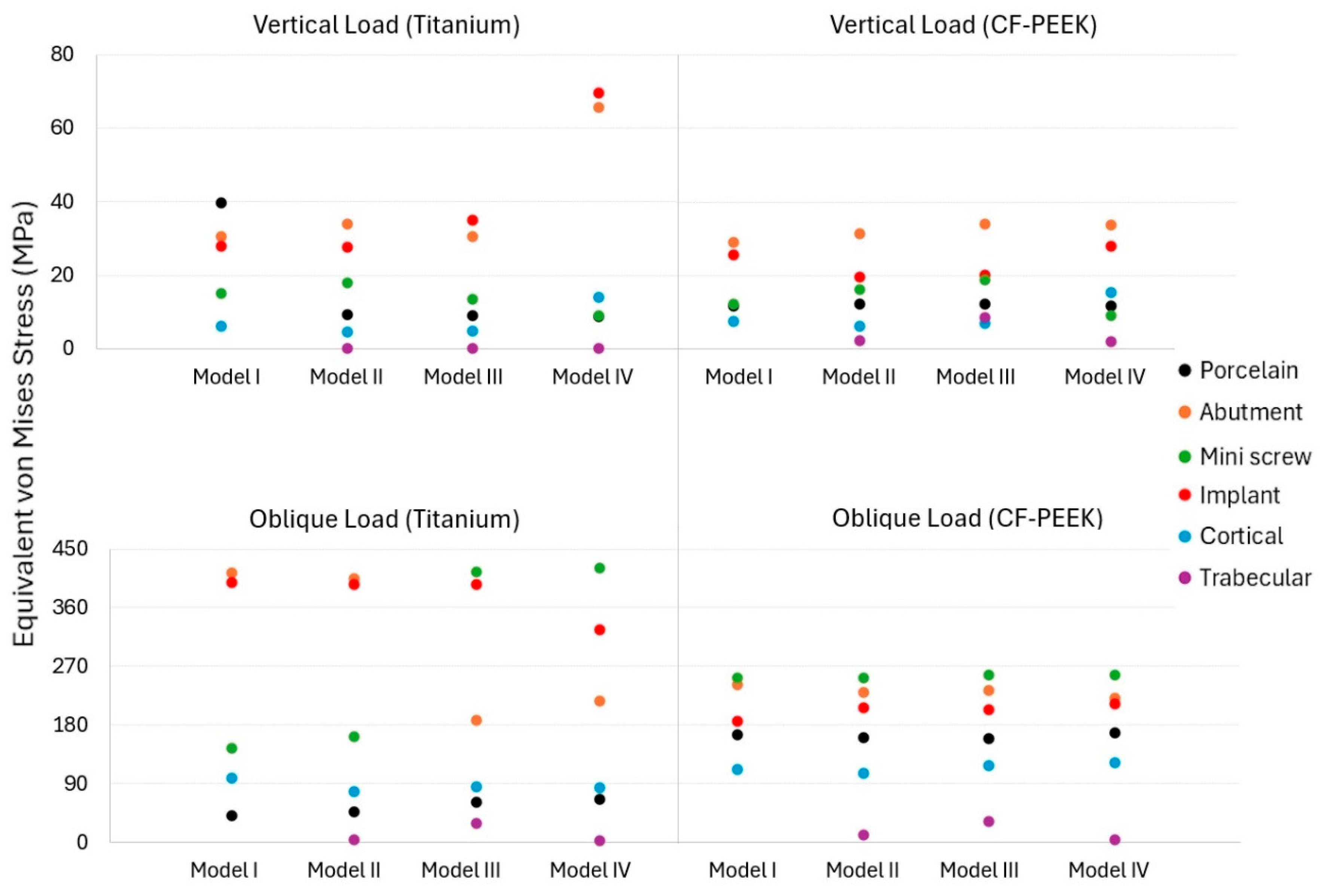
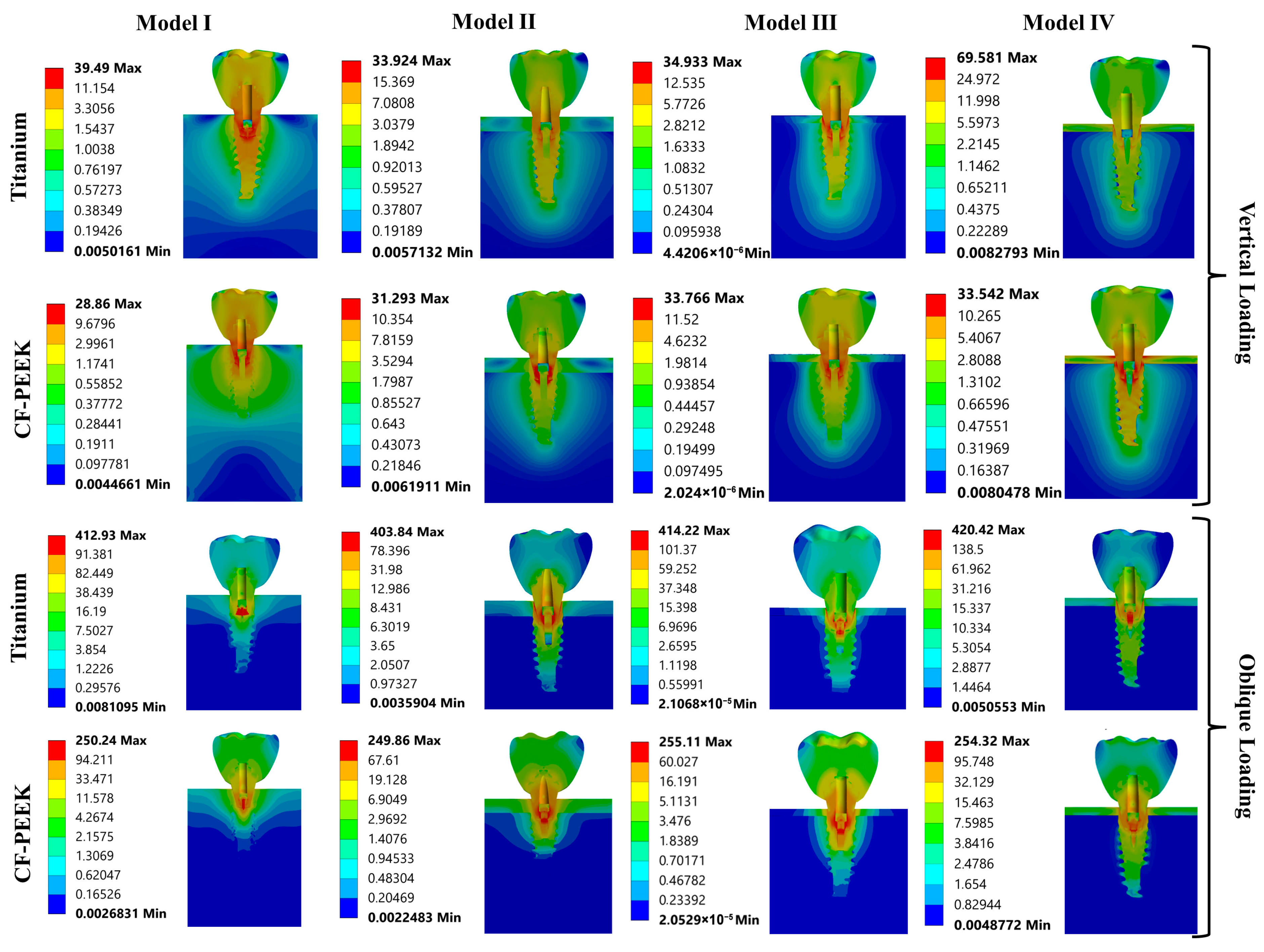
3.1. The Von Mises Stress Analysis Results
3.2. Strain Results
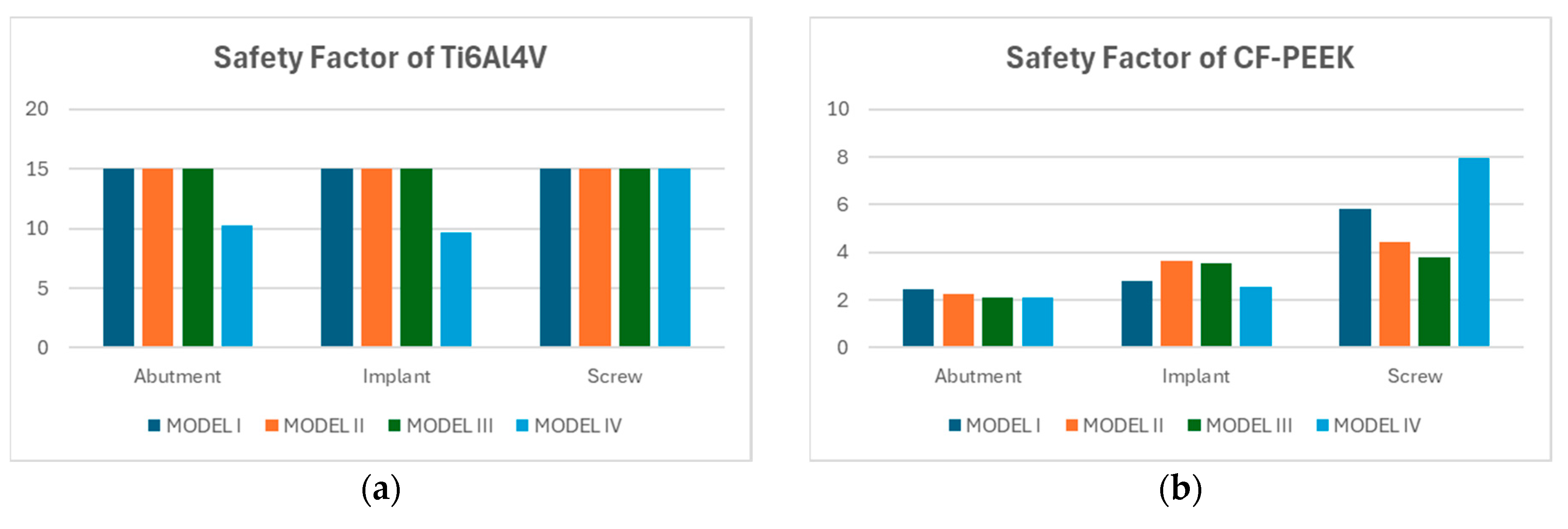
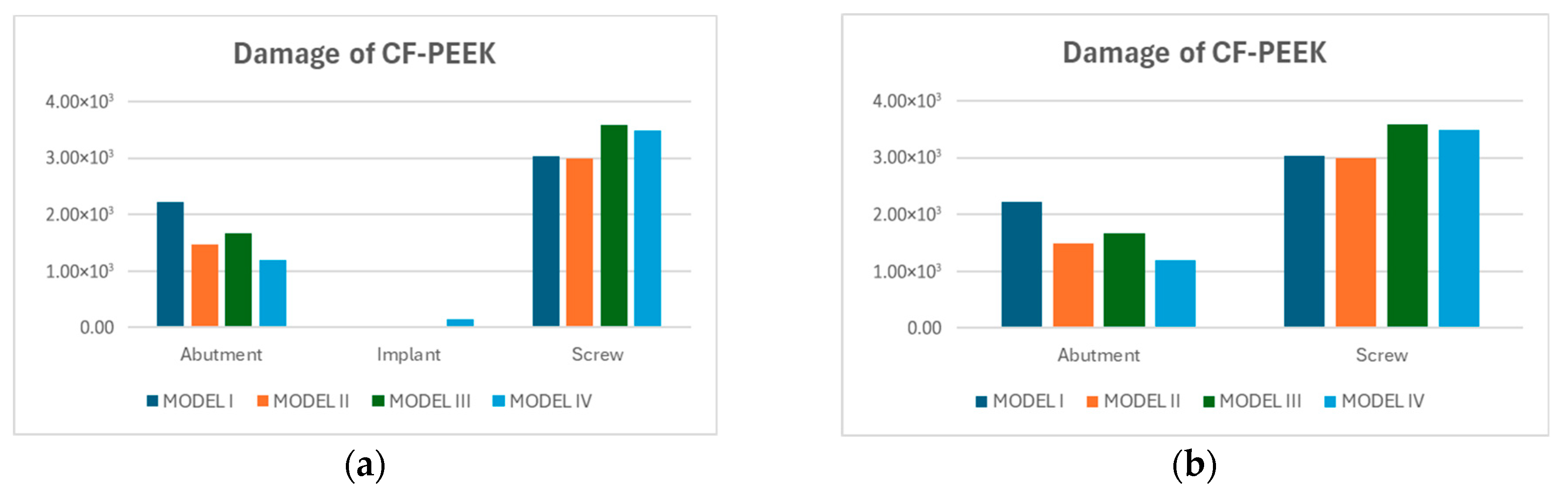
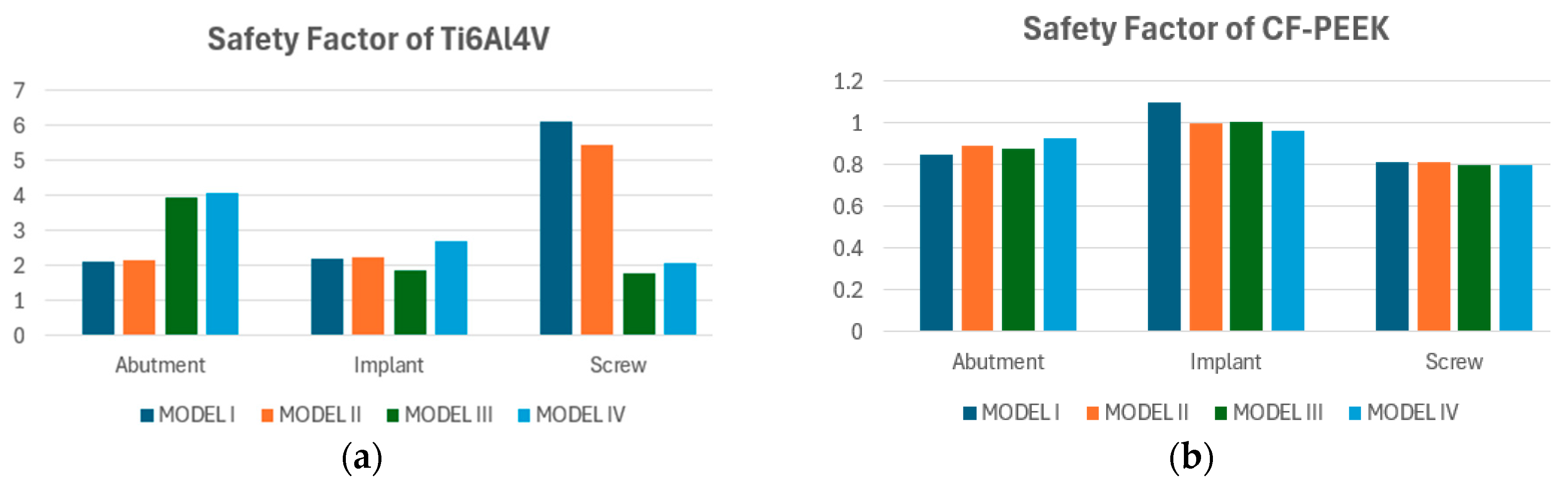
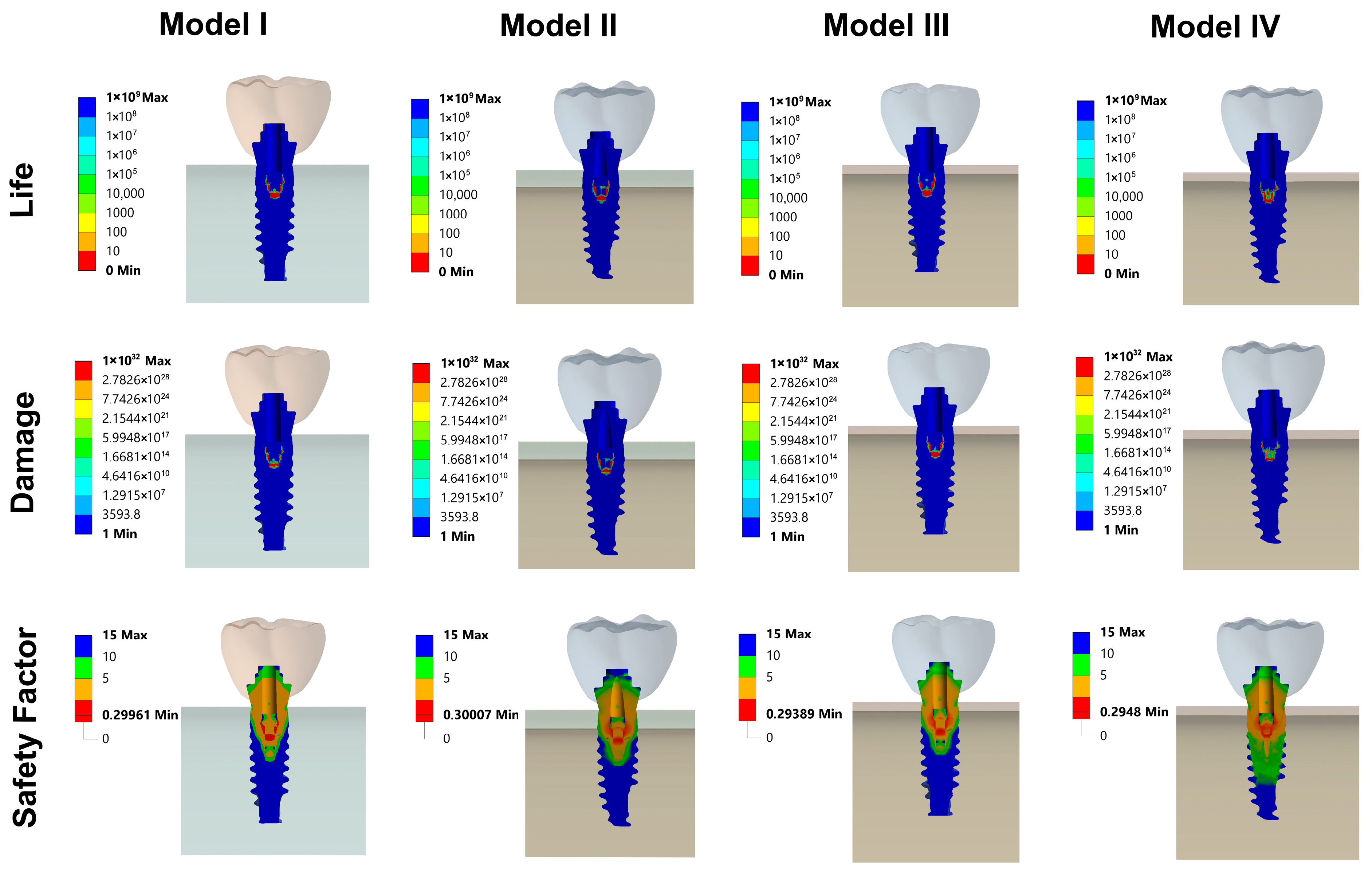
3.3. Fatigue FEA Results
3.3.1. Vertical Loading Conditions
3.3.2. Oblique Loading Conditions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, C.; Xing, Y.; Li, Y.; Lin, Y.; Xu, J.; Wu, D. Bone quality effect on short implants in the edentulous mandible: A finite element study. BMC Oral Health. 2022, 22, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Liu, X.; Yan, Y.; Sun, R.; Li, J.; Geng, W. Effectiveness and Mechanisms of Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound on Osseointegration of Dental Implants and Biological Functions of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2022, 2022, 7397335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimmel, M.; Müller, F.; Suter, V.; Buser, D. Implants for elderly patients. Periodontol 2000 2017, 73, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Gao, J.; Luo, L.; Wang, Y. Does Bruxism Contribute to Dental Implant Failure? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2016, 18, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pjetursson, B.E.; Thoma, D.; Juneg, R.; Zwahlen, M.; Zembic, A. A systematic review of the survival and complication rates of implant-supported fixed dental prostheses (FDPs) after a mean observation period of at least 5 years. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2012, 23 (Suppl. S6), 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premnath, K.; Sridevi, J.; Kalavathy, N.; Nagaranjani, P.; Sharmila, M.R. Evaluation of Stress Distribution in Bone of Different Densities Using Different Implant Designs: A Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2012, 13, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.P.A.; Tan, K.B.C.; Liu, G.R. Application of finite element analysis in implant dentistry: A review of the literature. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2001, 85, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevimay, M.; Turhan, F.; Kiliçarslan, M.A.; Eskitascioglu, G. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the effect of different bone quality on stress distribution in an implant-supported crown. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2005, 93, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misch, C.E. Density of bone: Effect on treatment plans, surgical approach, healing, and progressive bone loading. Int. J. Oral Implantol. 1990, 6, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Misch, C.E. Contemporary implant dentistry. Implant. Dent. 1999, 8, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaviria, L.; Salcido, J.P.; Guda, T.; Ong, J.L. Current trends in dental implants. J. Korean Assoc. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 40, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahlert, M.; Roehling, S.; Sprecher, C.M.; Kniha, H.; Milz, S.; Bormann, K. In vivo performance of zirconia and titanium implants: A histomorphometric study in mini pig maxillae. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2012, 23, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, B.V.; Bose, S.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Low stiffness porous Ti structures for load-bearing implants. Acta Biomater. 2007, 3, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevinç Gül, S.N.; Murat, F.; Şensoy, A.T.A. Evaluation of Biomechanical Effects of Mandible Arch Types in All-on-4 and All-on-5 Dental Implant Design: A 3D Finite Element Analysis. J. Funct. Biomater. 2025, 16, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, G.; Mendonça, D.B.S.; Aragão, F.J.L.; Cooper, L.F. Advancing dental implant surface technology—From micron- to nanotopography. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 3822–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najeeb, S.; Bds, Z.K.; Bds, S.Z.; Bds, M.S.Z. Bioactivity and osseointegration of PEEK are inferior to those of titanium: A systematic review. J. Oral Implantol. 2016, 42, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.M.; Ren, D.N.; Li, S.Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Shen, X.Q.; Yuan, Y.Y. Hydroxyapatite-incorporation improves bone formation on endosseous PEEK implant in canine tibia. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2020, 18, 2280800020975172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankenberger, T.; Graw, C.L.; Engel, N.; Gerber, T.; Frerich, B.; Dau, M. Sustainable Surface Modification of Poly-etheretherketone (PEEK) Implants by Hydroxyapatite/Silica Coating—An In Vivo Animal Study. Materials 2021, 14, 4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; He, X.; Xu, W.; Deng, Y.; Xia, Z.; Chen, J.; He, Y. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the biomechanical properties of different material implants for replacing missing teeth. Odontology 2025, 113, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.; Tang, T. Current strategies to improve the bioactivity of PEEK. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 5426–5445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galteri, G.; Cristofolini, L. In vitro and in silico methods for the biomechanical assessment of osseointegrated transfemoral prostheses: A systematic review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1237919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, M.V.R.; Ribeiro, M.C.O.; dos Reis-Neta, G.R.; Vargas-Moreno, V.F.; Gomes, R.S.; da Silva, W.J.; Del Bel Cury, A.A.; Marcello-Machado, R.M. Dental implant and abutment in PEEK: Stress assessment in single crown retainers on anterior region. Clin. Oral Investig. 2024, 28, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarot, J.R.; Contar, C.M.M.; Cruz ACCDa De Souza Magini, R. Evaluation of the stress distribution in CFR-PEEK dental implants by the three-dimensional finite element method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 2079–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwitalla, A.D.; Abou-Emara, M.; Spintig, T.; Lackmann, J.; Müller, W.D. Finite element analysis of the biomechanical effects of PEEK dental implants on the peri-implant bone. J. Biomech. 2015, 48, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sensoy, A.T.; Çolak, M.; Kaymaz, I.; Findik, F. An application of finite element method in material selection for dental implant crowns. Biomed. Tech. 2021, 66, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiura, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Kawakami, M.; Horita, S.; Murakami, K.; Kirita, T. Influence of bone parameters on peri-implant bone strain distribution in the posterior mandible. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2014, 20, e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armentia, M.; Abasolo, M.; Coria, I.; Albizuri, J. Fatigue design of dental implant assemblies: A nominal stress approach. Metals 2020, 10, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.T.; Wang, K.S.; Woo, J.C. Fatigue life and reliability evaluation for dental implants based on computer simulation and limited test data. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2013, 227, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, N.H.; Ma, C.C.M.; Wu, S.H. Fatigue behaviour of carbon fibre/PEEK laminate composites. Composites 1995, 26, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Huang, J.; Zhang, C. Enabling rapid fatigue life prediction of short carbon fiber reinforced polyether-ether-ketone using a novel energy dissipation–based model. Compos. Struct. 2021, 272, 114227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Mondragon, M.; Urriolagoitia-Sosa, G.; Romero-Angeles, B.; García-Laguna, M.A.; Laguna-Canales, A.S.; Pérez-Partida, J.C.; Mireles-Hernández, J.; Carrasco-Hernández, F.; Urriolagoitia-Calderón, G.M. Biomechanical fatigue behavior of a dental implant due to chewing forces: A finite element analysis. Materials 2024, 17, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, E.G.; Amine, S.; Prasad, B.; Younes, K. Exploring polyetheretherketone in dental implants and abutments: A focus on biomechanics and finite element methods. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2024, 63, 20240031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, W.; Weng, X. Polyetheretherketone development in bone tissue engineering and orthopedic surgery. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1207277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.M.; Devine, J.N. PEEK biomaterials in trauma, orthopedic, and spinal implants. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 4845–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouldyerou, A.; Merdji, A.; Aminallah, L.; Roy, S.; Mehboob, H.; Özcan, M. Biomechanical performance of Ti-PEEK dental implants in bone: An in-silico analysis. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2022, 134, 105422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabris, D.; Moura, J.P.A.; Fredel, M.C.; Souza, J.C.M.; Silva, F.S.; Henriques, B. Biomechanical analyses of one-piece dental implants composed of titanium, zirconia, PEEK, CFR-PEEK, or GFR-PEEK: Stresses, strains, and bone remodeling prediction by the finite element method. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2022, 110, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamrakar, S.; Mishra, S.; Chowdhary, R.; Rao, S. Comparative analysis of stress distribution around CFR-PEEK implants and titanium implants with different prosthetic crowns: A finite element analysis. Dent. Med. Probl. 2021, 58, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Hazari, P.; Verma, P. Do implants made of polyetheretherketone and its composites have reduced stress shielding effects compared to other dental implant materials? A systematic review. Evid. Based Dent. 2023, 24, 193–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, S.; Ahmed, Y.; El-Anwar, M.I.; Elddamony, E.; Ashraf, R. Influence of different polymeric materials of implant and attachment on stress distribution in implant-supported overdentures: A three-dimensional finite element study. BMC Oral Health 2025, 25, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Liu, D.; Yin, W.; Yuan, C.; Hu, Y.; Xu, J.; Yang, Y.; Tang, J.; Chen, J. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the biomechanical behaviour of different dental implants under immediate loading during three masticatory cycles. Heliyon 2024, 10, e32616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondareddy, S.; Avinash, A.C.; Jayyarapu, D.; Devi Kakarlapudi, A. The effect of different abutment designs and materials on stress distribution in implants and peripheral bones: A three-dimensional finite element analysis. Cureus 2024, 16, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naghavi, S.A.; Lin, C.; Sun, C.; Tamaddon, M.; Basiouny, M.; Garcia-Souto, P.; Taylor, S.; Hua, J.; Li, D.; Wang, L.; et al. Stress shielding and bone resorption of press-fit polyether–ether–ketone (PEEK) hip prosthesis: A sawbone model study. Polymers 2022, 14, 4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ediboğlu, E.; Akdeniz, S.S.; Beyler, E. Biomechanical effects of titanium and carbon fiber reinforced PEEK as dental implant material: A finite element analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2024, 40, E33–E39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altıparmak, N.; Polat, S.; Onat, S. Finite element analysis of the biomechanical effects of titanium and CFR-PEEK additively manufactured subperiosteal jaw implant (AMSJI) on maxilla. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 124, 101290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.S.; Lee, M.K.; Hong, M.H. A finite element stress analysis of abutment screw according to the implant abutment material. J. Korean Acedemy Dent. Technol. 2016, 38, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, E.A.F.; Villar, C.C.; França, F.M.G. Fracture resistance of abutment screws made of titanium, polyetheretherketone, and carbon fiber-reinforced polyetheretherketone. Braz. Oral Res. 2014, 28, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuwei, Y.; Wuwei, Y.; Yong, Y.; Zhenzhen, W.; Pei, C.; Zinan, Y.; Zekun, G.; Tengfei, Z.; Mianyan, Z.; Hongxing, C.; et al. Influence of implant cover screw loosening on early peri-implant marginal bone loss: A retrospective evaluation of risk factors. Preprint 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Assoratgoon, I.; Wan, B.; Tenkumo, T.; Sato, T.; Kawata, T.; Putra, R.H.; Wu, C.; Egusa, H.; Li, Q.; Sasaki, K.; et al. Three-dimensional in vivo and finite element analyses of peri-implant bone remodeling after super-structure placement. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2025, 133, 1535–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.U.K.; Seth, A.; Vuppuluri, A.; Verma, P.C.; Narala, S.K.R.; Babu, P.J.; Saravanan, P. Exploring the biomechanical behavior of PEEK and CFR-PEEK materials for dental implant applications using finite element analysis. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2024, 69, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcián, P.; Borák, L.; Valášek, J.; Kaiser, J.; Florian, Z.; Wolff, J. Finite element analysis of dental implant loading on atrophic and non-atrophic cancellous and cortical mandibular bone—A feasibility study. J. Biomech. 2014, 47, 3830–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwitalla, A.; Müller, W.D. PEEK dental implants: A review of the literature. J. Oral Implantol. 2013, 39, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, B.; Yoda, N.; Zheng, K.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, C.; Clark, J.R.; Paradowska, A.; Swain, M.V.; Li, Q. On effect of residual stress on fracture behavior of mandibular reconstruction plates. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2024, 305, 110158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, B.; Entezari, A.; Zhang, Z.; Wilson, T.; Yoda, N.; Zheng, K.; Wu, C.; Sun, G.; Sasaki, K.; Swain, M.; et al. On fatigue failure prediction of prosthetic devices through XFEM analysis. Int. J. Fatigue. 2021, 147, 106160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozakiewicz, M.; Wach, T. Exploring the importance of corticalization occurring in alveolar bone surrounding a dental implant. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Material | Elasticity Modulus [GPa] | Poisson’s Ratios | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| Feldspathic porcelain | 82.8 | 0.35 | [8] |
| Implant | 110 | 0.35 | [8] |
| Abutment | 110 | 0.35 | [8] |
| Cortical Bone | 13.7 | 0.3 | [25] |
| Trabecular Bone (High Density) | 3.507 | 0.3 | [26] |
| Trabecular Bone (Low Density) | 0.259 | 0.3 | [26] |
| %30 CF-PEEK | 18 | 0.39 | [23] |
| Model I | Model II | |||||||
| Vertical | Oblique | Vertical | Oblique | |||||
| Titanium | CF-PEEK | Titanium | CF-PEEK | Titanium | CF-PEEK | Titanium | CF-PEEK | |
| Porcelain | 232.42 | 62.407 | 424.89 | 1596.5 | 111.01 | 65.467 | 378.11 | 1529.2 |
| Abutment | 231.23 | 1320.8 | 2381.5 | 10,019 | 217.9 | 1384.5 | 2405.2 | 9709.8 |
| Implant | 195.05 | 995.79 | 3312.5 | 5380.2 | 217.21 | 823.95 | 3213.6 | 6929.7 |
| Mini screw | 71.237 | 355.39 | 1311.1 | 13,992 | 79.65 | 405.58 | 1477.9 | 13,943 |
| Cortical | 226.01 | 176.23 | 1966.7 | 2854 | 168.74 | 270.99 | 2029 | 3174.2 |
| Trabecular | 383.48 | 372.31 | 711.82 | 1061.5 | ||||
| Model III | Model IV | |||||||
| Vertical | Oblique | Vertical | Oblique | |||||
| Titanium | CF-PEEK | Titanium | CF-PEEK | Titanium | CF-PEEK | Titanium | CF-PEEK | |
| Porcelain | 45.18 | 60.80 | 461.33 | 1521.70 | 44.53 | 59.78 | 507.21 | 1608.90 |
| Abutment | 186.25 | 1587.10 | 1342.80 | 9848.50 | 401.09 | 1067.70 | 2075.90 | 9445.30 |
| Implant | 291.59 | 993.35 | 3207.20 | 5859.90 | 330.62 | 1386.40 | 2723.30 | 6299.10 |
| Mini screw | 49.24 | 439.86 | 3781.50 | 14,228.00 | 27.77 | 263.56 | 3815.70 | 14,187.00 |
| Cortical | 160.51 | 259.83 | 1700.30 | 2523.10 | 776.12 | 889.67 | 2146.00 | 3503.70 |
| Trabecular | 1211.10 | 2556.90 | 8702.20 | 9450.90 | 5329.30 | 4638.80 | 7824.70 | 6562.50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Polat Sağsöz, N.; Murat, F.; Sevinç Gül, S.N.; Şensoy, A.T.; Kaymaz, I. CF-PEEK vs. Titanium Dental Implants: Stress Distribution and Fatigue Performance in Variable Bone Qualities. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10090619
Polat Sağsöz N, Murat F, Sevinç Gül SN, Şensoy AT, Kaymaz I. CF-PEEK vs. Titanium Dental Implants: Stress Distribution and Fatigue Performance in Variable Bone Qualities. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(9):619. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10090619
Chicago/Turabian StylePolat Sağsöz, Nurdan, Fahri Murat, Sema Nur Sevinç Gül, Abdullah Tahir Şensoy, and Irfan Kaymaz. 2025. "CF-PEEK vs. Titanium Dental Implants: Stress Distribution and Fatigue Performance in Variable Bone Qualities" Biomimetics 10, no. 9: 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10090619
APA StylePolat Sağsöz, N., Murat, F., Sevinç Gül, S. N., Şensoy, A. T., & Kaymaz, I. (2025). CF-PEEK vs. Titanium Dental Implants: Stress Distribution and Fatigue Performance in Variable Bone Qualities. Biomimetics, 10(9), 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10090619






