Robotic Removal and Collection of Screws in Collaborative Disassembly of End-of-Life Electric Vehicle Batteries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Human–Robot Collaborative Disassembly of EV Batteries
2.2. Automated Disassembly of Screws
3. A Robotic Unfastening and Collecting System of Screws
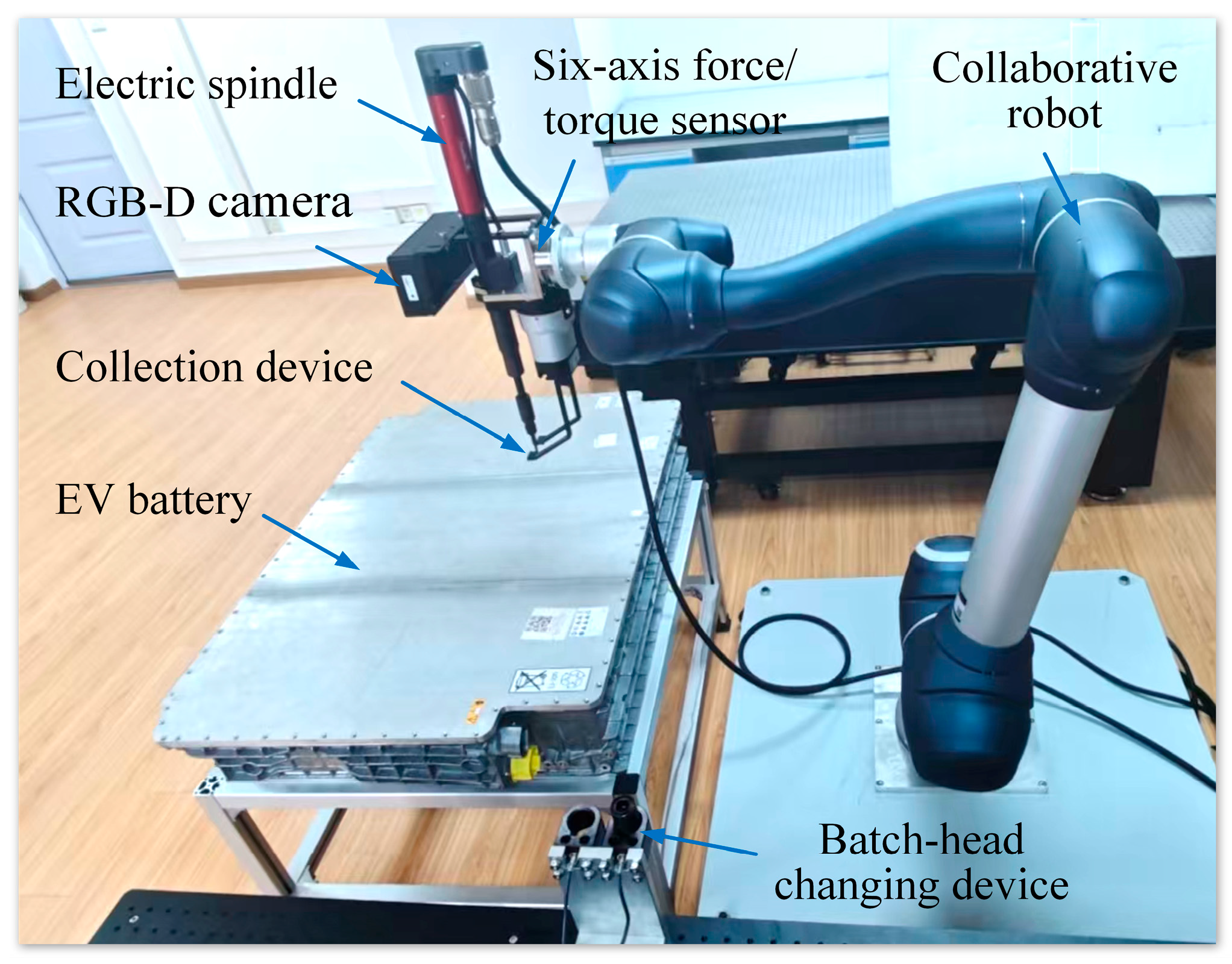
3.1. A Human–Robot Collaborative Disassembly Cell
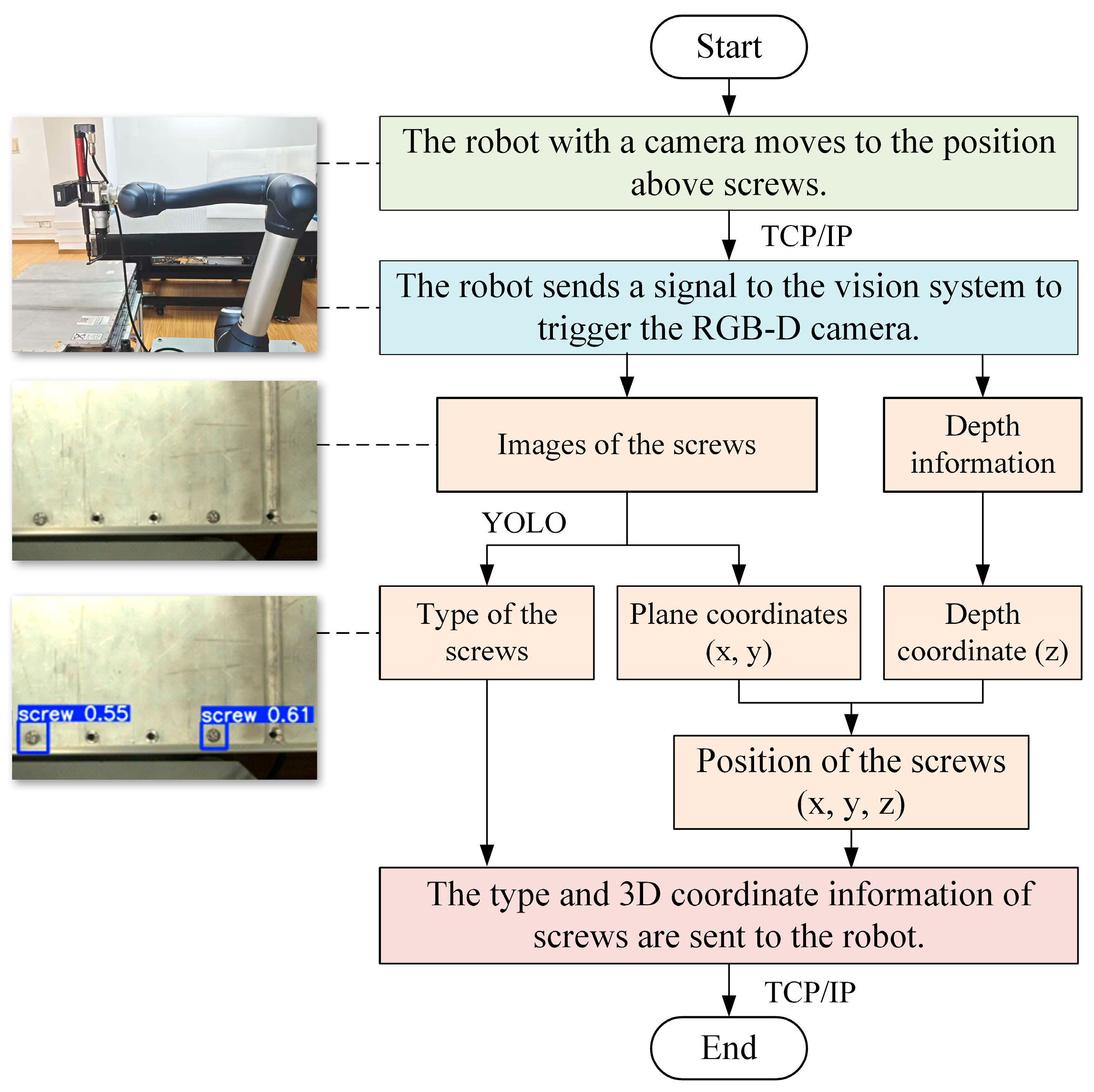
3.2. Vision System for Recognition and Location of Screws
3.3. Screw Unfastening and Collecting System
4. The Process of Robotic Unfastening and Collecting a Screw
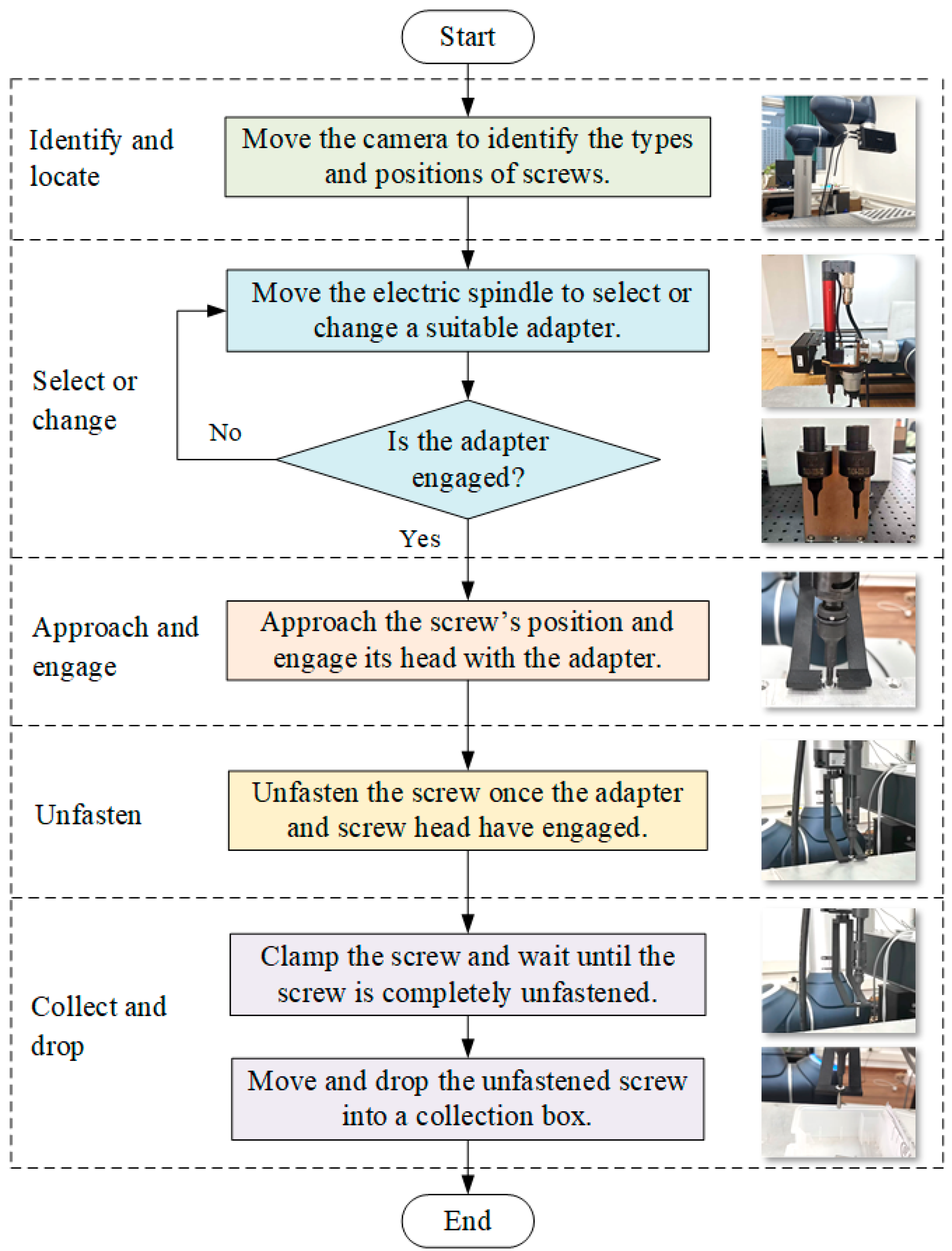
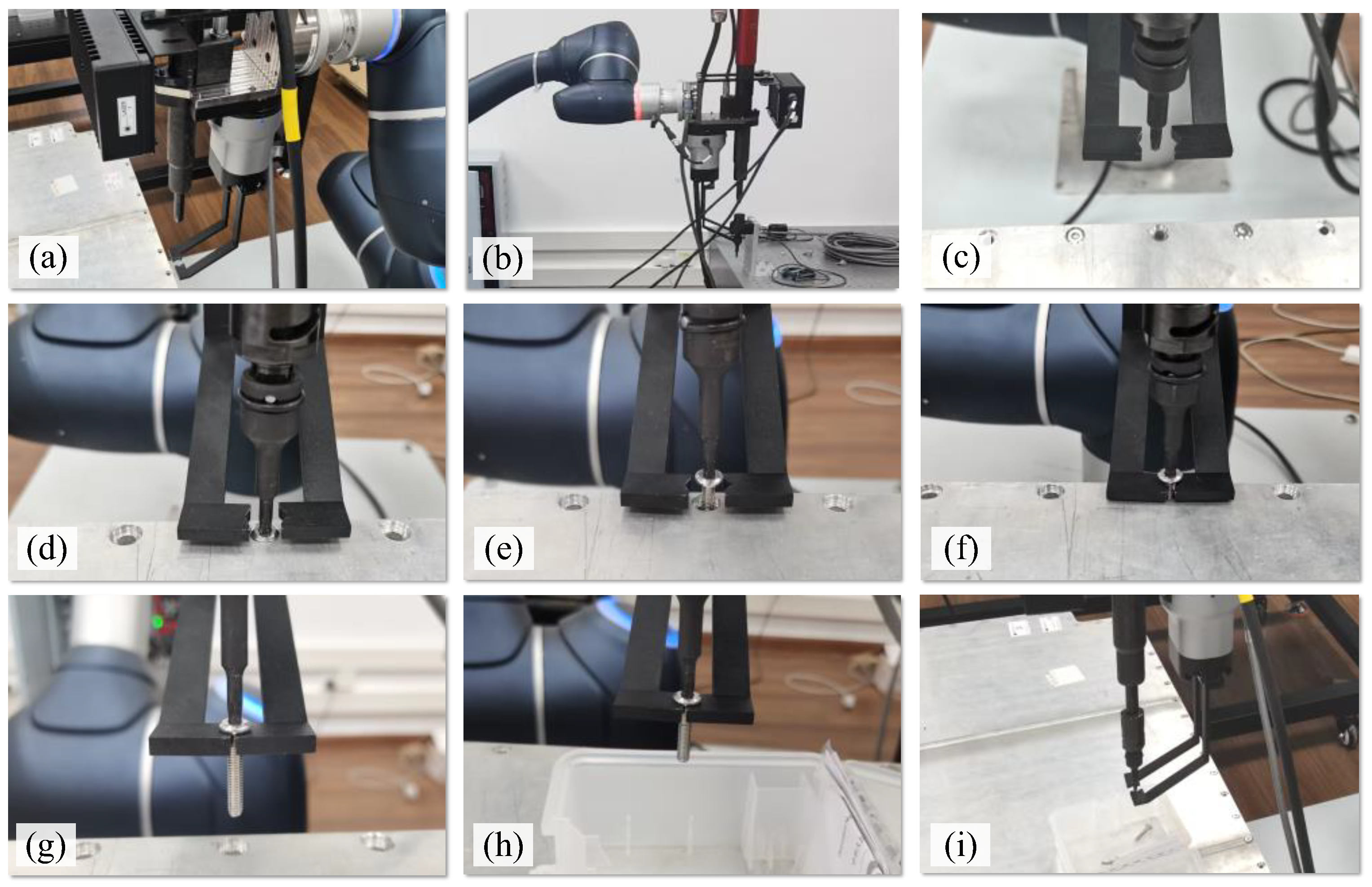
4.1. Disassembly Process
- Identify and locate. The first step is to identify the type and find the positions of the screws in the EV battery using the vision system. The robot, equipped with a 3D camera, moves to the positions above the screws to capture images and depth information. The type and position information of screws can be obtained using machine learning (ML) algorithms, which will then be sent to the robot.
- Select or change. Based on the type of screws, the robot with an electric spindle moves to select or change a suitable adapter by using a batch-head changing device. Therefore, the robotic cell could disassemble various types of screws, improving its flexibility.
- Approach and engage. The robot, equipped with an electric spindle and adapter, moves and approaches the position above a screw to be disassembled. The electric spindle rotates in the direction of the screw fastening and searches for, then engages, the screw head. The fastening torque information regarding the electric spindle is employed to assess whether the adapter engages the screw head successfully.
- Unfasten. Once the adapter and screw head have engaged, the electric spindle rotates in the direction of unfastening. The screw will move out of the screw hole.
- Collect and drop. As the screw runs out enough distance from the screw hole, the two fingers of the collection device clamp the screw and follow its movement until the screw is free from the threaded hole. Then, the unfastened screw will be moved away and dropped into a collection box. The process is now complete.
4.2. Recognising and Locating Screws Based on Machine Vision
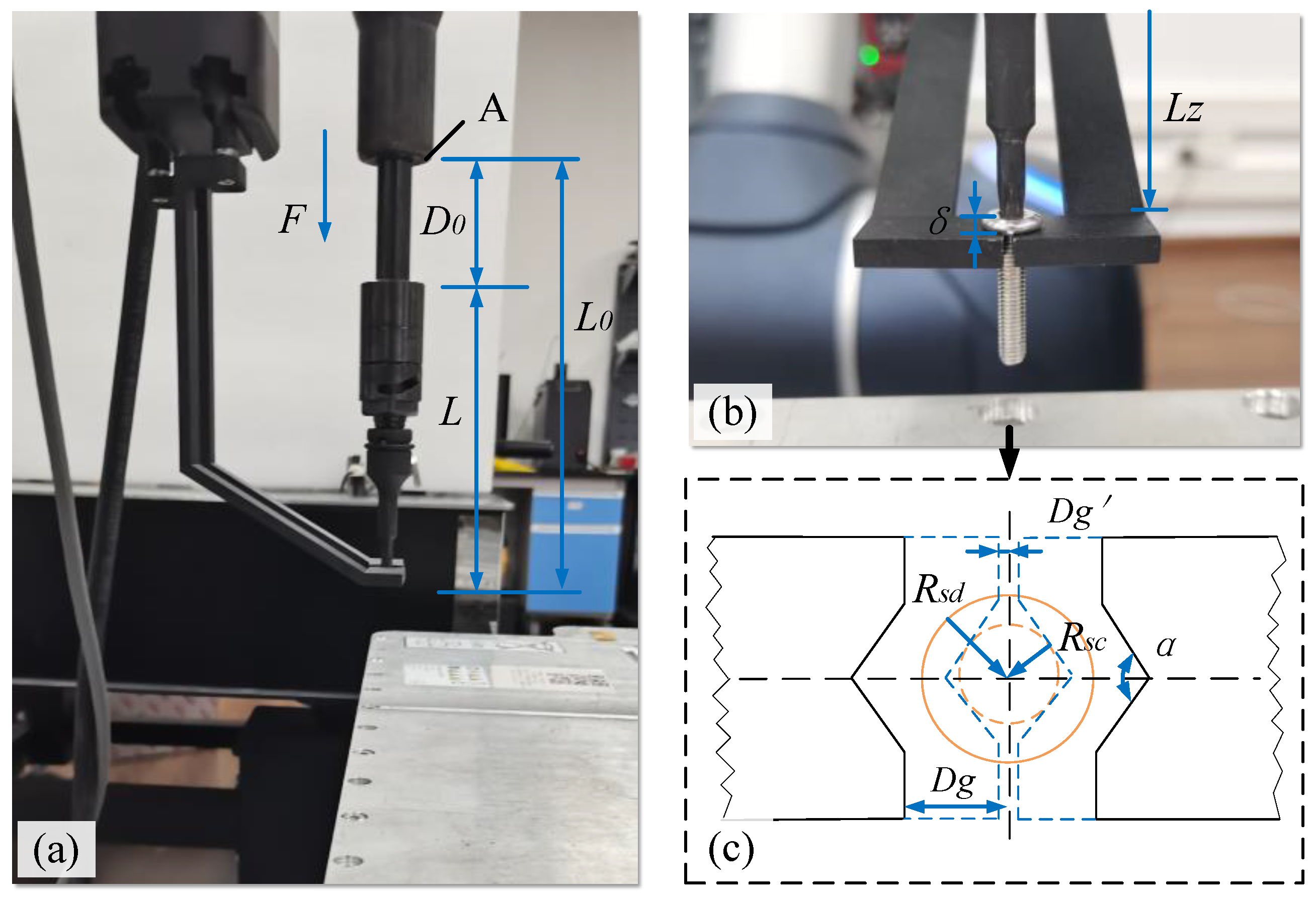
4.3. Clamping and Dropping Screws Using a Self-Developed Collection Device
5. Experimental Results and Discussion
5.1. End-of-Life EV Battery
5.2. Experimental Parameter Settings
5.3. Experimental Results
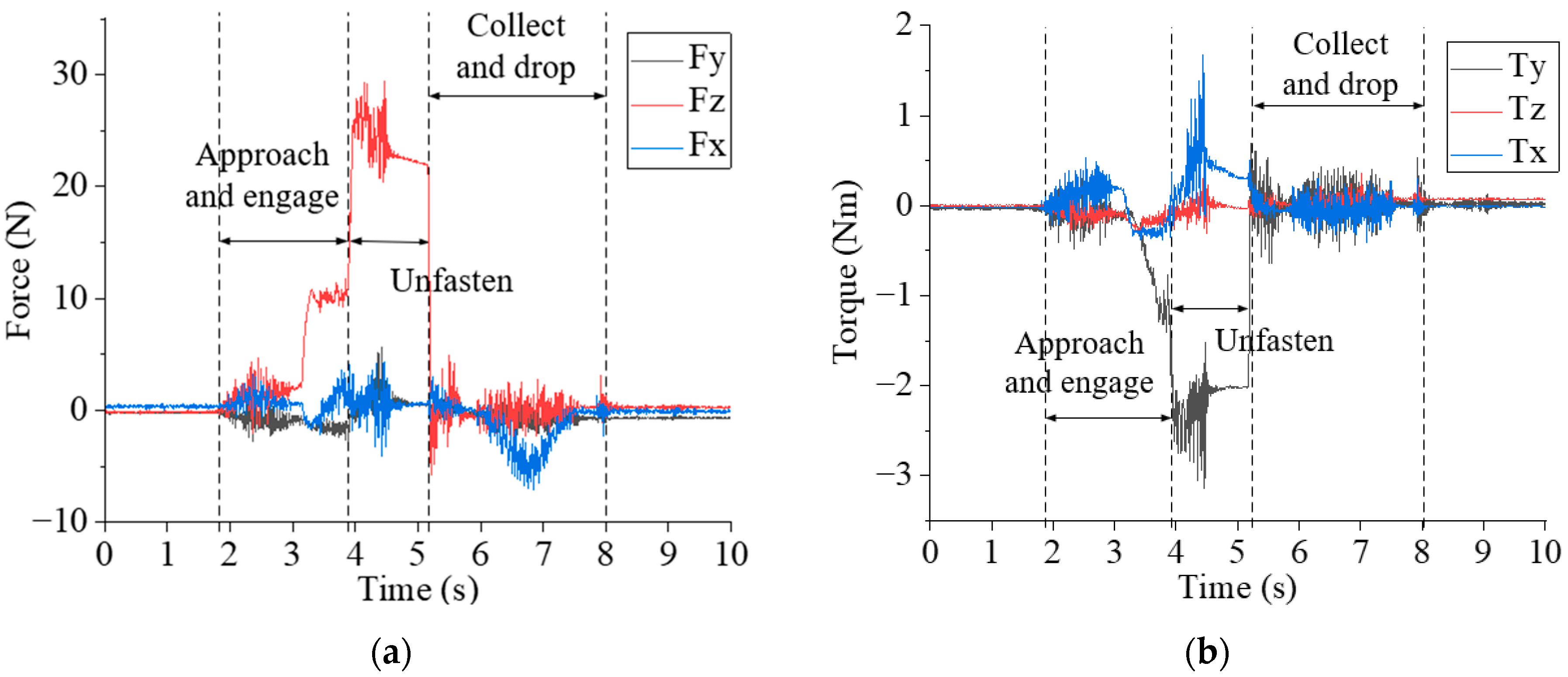
5.4. Analysis of Force and Torque in Unfastening and Collecting Screws
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EoL | End of life |
| EV | Electric vehicle |
| HRC | Human–robot collaboration |
| HRCD | Human–robot collaboration disassembly |
| PHEV | Plug-in hybrid electric vehicle |
| ML | Machine learning |
| DOF | Degree of freedom |
References
- Asif, M.E.; Rastegarpanah, A.; Stolkin, R. Robotic disassembly for end-of-life products focusing on task and motion planning: A comprehensive survey. J. Manuf. Syst. 2024, 77, 483–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Huang, K.; Terzi, S.; Bandinelli, R. Towards uncertainty of End-of-Use product recycling: A general screw connection-oriented disassembly analysis. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2025, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vongbunyong, S.; Kara, S.; Pagnucco, M. A framework for using cognitive robotics in disassembly automation. In Leveraging Technology for a Sustainable World, Proceedings of the 19th CIRP Conference on Life Cycle Engineering, Berkeley, CA, USA, 23–25 May 2012; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; Yang, C.; Chu, H.; Cheng, Q. A novel disassembly strategy of hexagonal screws based on robot vision and robot-tool cooperated motion. Appl. Sci. 2022, 13, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.J.; Chin, C.M.M.; Garg, A.; Gao, L. A hybrid disassembly framework for disassembly of electric vehicle batteries. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 8073–8082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Chen, M. A novel knowledge-driven flexible human–robot hybrid disassembly line and its key technologies for electric vehicle batteries. J. Manuf. Syst. 2023, 68, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangold, S.; Steiner, C.; Friedmann, M.; Fleischer, J. Vision-based screw head detection for automated disassembly for remanufacturing. Procedia CIRP 2022, 105, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, S.; Wakamatsu, S.; Abe, T.; Tennomi, M.; Morita, K.; Ubata, H.; Okamura, A.; Hirai, Y.; Morino, K.; Suzuki, Y. Robust bin-picking system using tactile sensor. Adv. Robot. 2020, 34, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Li, W.; Liang, Y.; Pham, D.T. Robotic disassembly of screws for end-of-life product remanufacturing enabled by deep reinforcement learning. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 439, 140863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Pham, D.T.; Huang, J.; Tan, Y.; Qu, M.; Wang, Y.; Kerin, M.; Jiang, K.; Su, S.; Ji, C. Unfastening of hexagonal headed screws by a collaborative robot. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2020, 17, 1455–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjorth, S.; Chrysostomou, D. Human–robot collaboration in industrial environments: A literature review on non-destructive disassembly. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2022, 73, 102208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Pham, D.T.; Li, R.; Qu, M.; Wang, Y.; Kerin, M.; Su, S.; Ji, C.; Mahomed, O.; Khalil, R. An experimental human-robot collaborative disassembly cell. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 155, 107189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Yang, P.; Jiang, H.; Shi, T. A Multi-Robot Task Allocation Method Based on the Synergy of the K-Means++ Algorithm and the Particle Swarm Algorithm. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwert, T.; Römer, F.; Schneider, K.; Hua, Q.; Buchert, M. Recycling of batteries from electric vehicles. In Behaviour of Lithium-Ion Batteries in Electric Vehicles: Battery Health, Performance, Safety and Cost; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 289–321. [Google Scholar]
- Morato, C.; Kaipa, K.N.; Zhao, B.; Gupta, S.K. Toward safe human robot collaboration by using multiple kinects based real-time human tracking. J. Comput. Inf. Sci. Eng. 2014, 14, 011006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, I.; Farhad, S.; Mahajan, A.; Esmaeeli, R.; Hashemi, S.R. Robotic disassembly of electric vehicles’ battery modules for recycling. Energies 2022, 15, 4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogenyi, U.E.; Liu, J.; Yang, C.; Ju, Z.; Liu, H. Physical human–robot collaboration: Robotic systems, learning methods, collaborative strategies, sensors, and actuators. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 51, 1888–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Yin, S.; Tan, M.; Liu, Q.; Li, R.; Pham, D. Task Allocation and Sequence Planning for Human–Robot Collaborative Disassembly of End-of-Life Products Using the Bees Algorithm. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerbers, R.; Wegener, K.; Dietrich, F.; Dröder, K. Safe, flexible and productive human-robot-collaboration for disassembly of lithium-ion batteries. In Recycling of Lithium-Ion Batteries: The Lithorec Way; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 99–126. [Google Scholar]
- Hellmuth, J.F.; DiFilippo, N.M.; Jouaneh, M.K. Assessment of the automation potential of electric vehicle battery disassembly. J. Manuf. Syst. 2021, 59, 398–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Xiao, J.; Wang, G. Human-robot collaboration re-manufacturing for uncertain disassembly in retired battery recycling. In Proceedings of the 2022 5th World Conference on Mechanical Engineering and Intelligent Manufacturing (WCMEIM), Ma’anshan, China, 18–20 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Wang, G.; Xiao, J.; Zheng, P.; Pei, E. Partially observable deep reinforcement learning for multi-agent strategy optimization of human-robot collaborative disassembly: A case of retired electric vehicle battery. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2024, 89, 102775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Hu, Y.; Pang, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C. Leveraging Large Language Models to Empower Bayesian Networks for Reliable Human-Robot Collaborative Disassembly Sequence Planning in Remanufacturing. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2025, 21, 3117–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegener, K.; Andrew, S.; Raatz, A.; Dröder, K.; Herrmann, C. Disassembly of electric vehicle batteries using the example of the Audi Q5 hybrid system. Procedia CIRP 2014, 23, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vongbunyong, S.; Kara, S.; Pagnucco, M. Application of cognitive robotics in disassembly of products. CIRP Ann.-Manuf. Technol. 2013, 62, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apley, D.W.; Seliger, G.; Voit, L.; Shi, J. Diagnostics in disassembly unscrewing operations. Int. J. Flex. Manuf. Syst. 1998, 10, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seliger, G.; Keil, T.; Rebafka, U.; Stenzel, A. Flexible disassembly tools. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE International Symposium on Electronics and the Environment (Cat. No. 01CH37190), Denver, CO, USA, 9 May 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Al Assadi, A.; Götza, T.; Gebhardta, A.; Mannußa, O.; Meesea, B.; Wannera, J.; Singhaa, S.; Halta, L.; Birkea, P.; Sauera, A. Automated Disassembly of Battery Systems to Battery Modules. Procedia CIRP 2024, 122, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiFilippo, N.M.J.; Musa, K. A system combining force and vision sensing for automated screw removal on laptops. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2017, 15, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Eltouny, K.; Liang, X.; Behdad, S. Automatic Screw Detection and Tool Recommendation System for Robotic Disassembly. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2023, 145, 031008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.H.; Foo, G.; Kara, S.; Pagnucco, M. Application of a multi-head tool for robotic disassembly. Procedia CIRP 2020, 90, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Fan, J.; Jing, F.; Jun, H.; Xing, S.; Ma, Y.; Tan, M. A robotic end-effector for screwing and unscrewing bolts from the side. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 9786–9793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Assadi, A.; Holtz, D.; Nägele, F.; Nitsche, C.; Kraus, W.; Huber, M.F. Machine learning based screw drive state detection for unfastening screw connections. J. Manuf. Syst. 2022, 65, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Gu, K.; Peng, Y.; Chen, M. Design and implementation of a multifunctional screw disassembly workstation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Applications, Hangzhou, China, 5–7 July 2023. [Google Scholar]



| Parameters | Direction | Stages | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identify and Locate | Select or Change | Approach and Engage | Unfasten | Collect and Drop | ||
| Translational stiffness (N/m) | X | 2000 | 3000 | 3000 | 100 | 2000 |
| Y | 2000 | 3000 | 3000 | 100 | 2000 | |
| Z | 2000 | 2000 | 2000 | 50 | 2000 | |
| Rotational stiffness (Nm/rad) | X | 200 | 100 | 100 | 10 | 200 |
| Y | 200 | 100 | 100 | 10 | 200 | |
| Z | 200 | 100 | 100 | 10 | 200 | |
| Parameters | Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Select or Change | Approach and Engage | Unfasten | |
| FZ (N) | 10 | 5 | 15 |
| Rotation speed (rpm) | 87.2 | 43.6 | 163.8 |
| Min torque (Nm) | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| Target torque (Nm) | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| Max torque (Nm) | 4 | 3 | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, M.; Huang, J.; Jiang, X.; Fang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Pham, D. Robotic Removal and Collection of Screws in Collaborative Disassembly of End-of-Life Electric Vehicle Batteries. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10080553
Tan M, Huang J, Jiang X, Fang Y, Liu Q, Pham D. Robotic Removal and Collection of Screws in Collaborative Disassembly of End-of-Life Electric Vehicle Batteries. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(8):553. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10080553
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Muyao, Jun Huang, Xingqiang Jiang, Yilin Fang, Quan Liu, and Duc Pham. 2025. "Robotic Removal and Collection of Screws in Collaborative Disassembly of End-of-Life Electric Vehicle Batteries" Biomimetics 10, no. 8: 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10080553
APA StyleTan, M., Huang, J., Jiang, X., Fang, Y., Liu, Q., & Pham, D. (2025). Robotic Removal and Collection of Screws in Collaborative Disassembly of End-of-Life Electric Vehicle Batteries. Biomimetics, 10(8), 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10080553









