Bionic Energy-Efficient Inverse Kinematics Method Based on Neural Networks for the Legs of Hydraulic Legged Robots
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- A novel EIKNN method is proposed. Based on the multi-solution characteristics of the inverse kinematics of the leg of the hydraulic legged robot with RDOFs, an NN is used to learn the inverse kinematics model under the minimum energy loss by referring to the autonomous energy-efficient consciousness of mammals.
- (2)
- An energy loss model for the leg motion of the hydraulic legged robot with RDOFs is proposed. An energy loss function for evaluating the leg motion is designed based on the along-travel loss of the oil and the friction loss of the HDU motion.
- (3)
- This method not only ensures effective motion accuracy but also has an excellent energy-saving effect, which can effectively improve the endurance of the hydraulic legged robot in the field and reduce the application cost of the hydraulic legged robot.
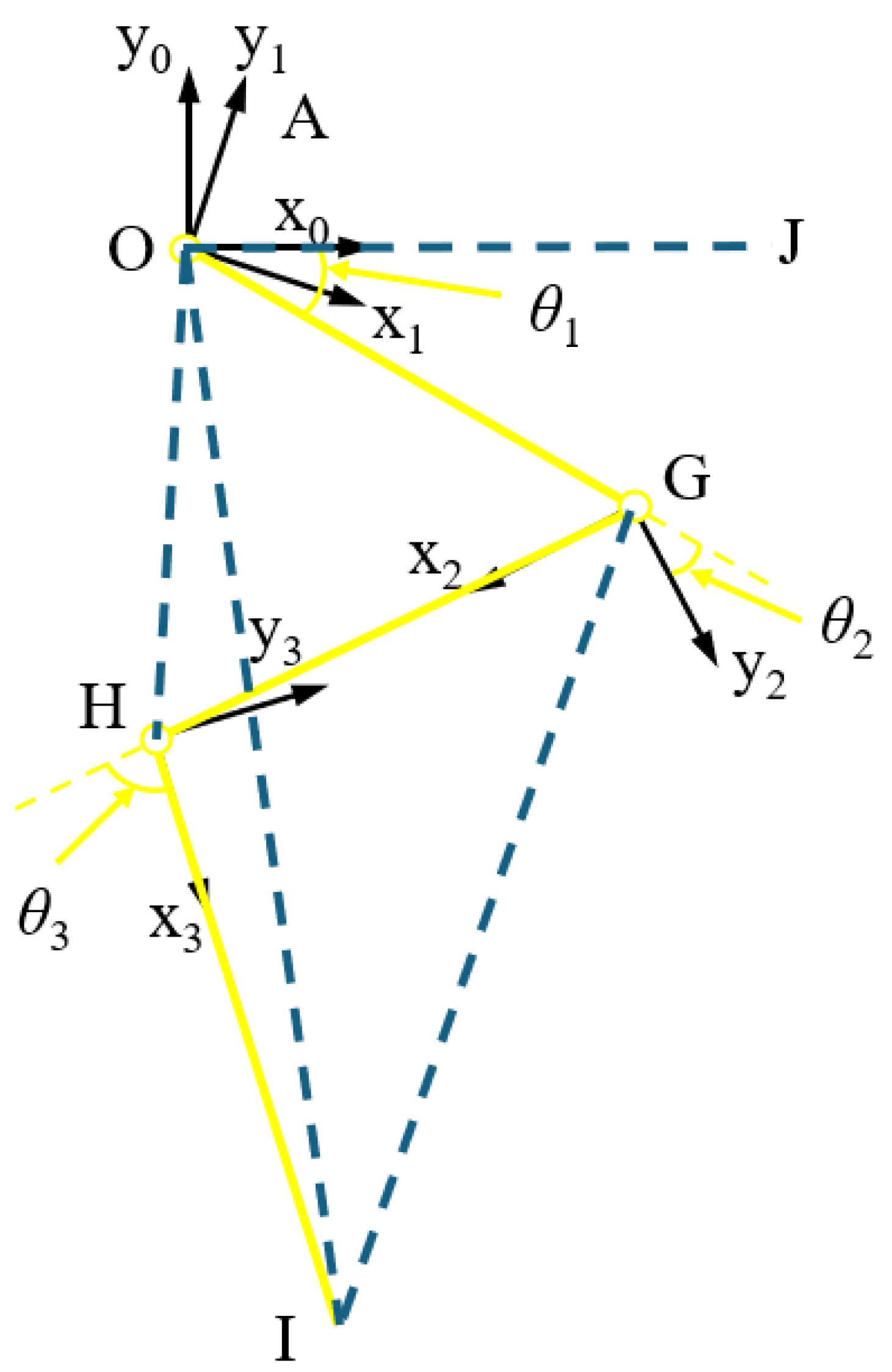
2. Mathematical Modeling of the Leg of Hydraulic Legged Robot with RDOFs
2.1. Mapping of the Drive Space
2.2. Analysis of the Foot-End Movement Space
2.3. Inverse Kinematics Modeling
- (1)
- When the hip joint angle is taken as a fixed value, is a known quantity.
- (2)
- When the knee joint angle is used as a fixed value, is a known quantity.
- (3)
- When the ankle joint angle is used as a fixed value, is a known quantity.
3. Energy-Saving Analysis of the Leg of Hydraulic Legged Robot with RDOFs
3.1. Energy Loss Model of Valve Components and Pipeline Along the Way
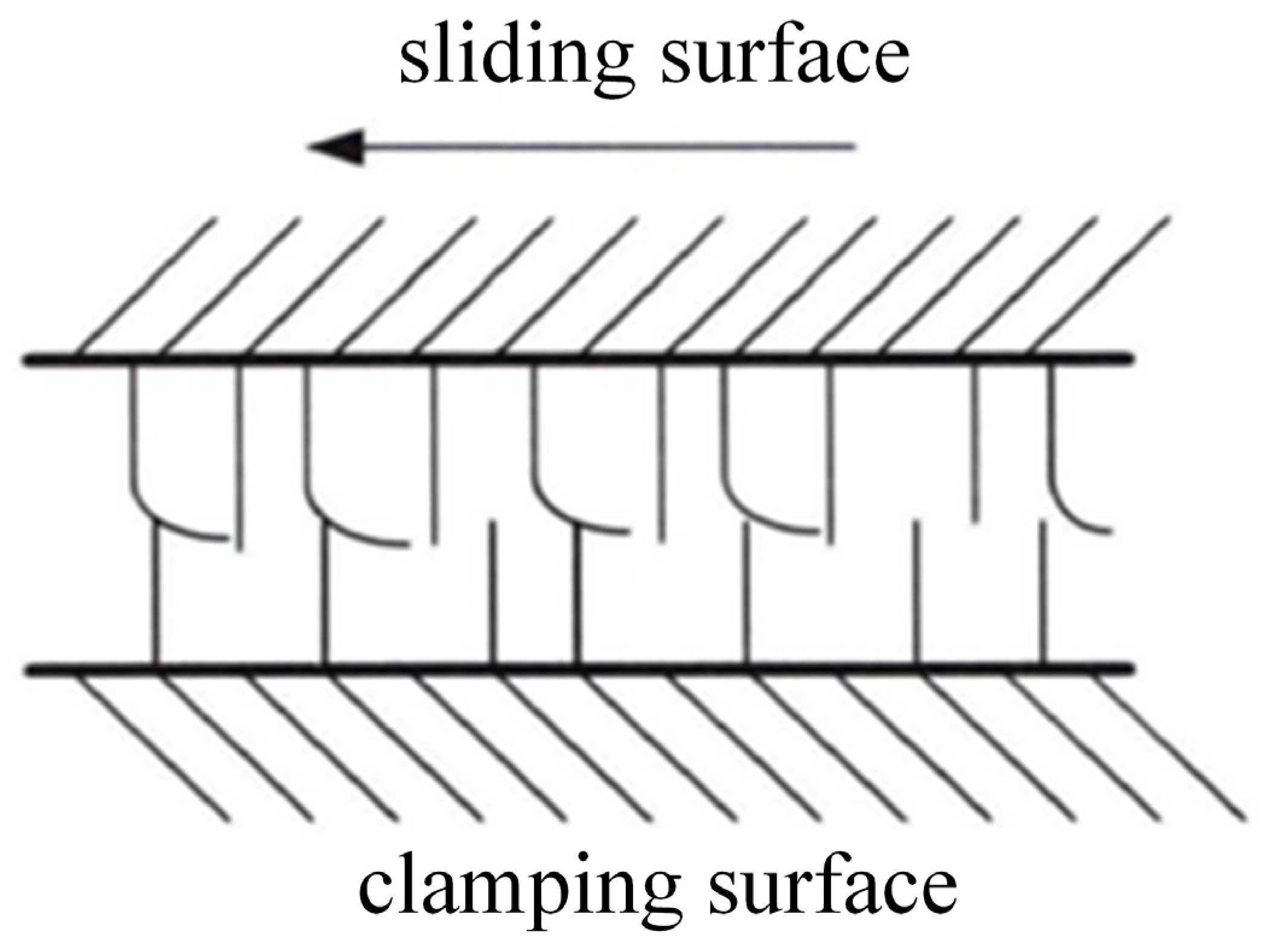
3.2. Energy Loss Model of Friction Based on HDU Motion
3.3. The Planning of the Foot End and Joint
3.4. Optimal Joint Configuration Based on DP Algorithm
| Algorithm 1: Dynamic programming algorithm |
| Part 1: Solution in reverse order Initialize , and Calculate energy loss for k = N − 1 to 0 for all do for all ∈ do Using parametric inverse kinematics to compute , , at time k. Using the joint mapping relationship to calculate , , at time k. Calculate energy loss end for end for end for Part 2: Forward solution Read for k = 0 to N − 1 do Take out end for Using parametric inverse kinematics to compute , , at time k. |
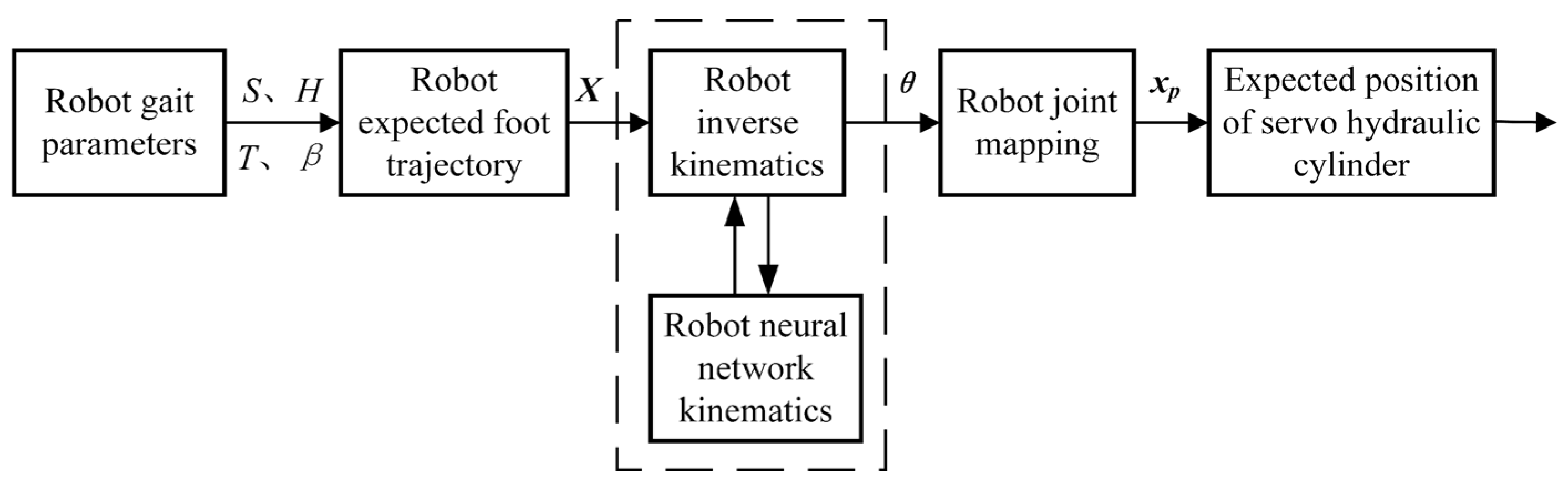
4. Neural Network Learning
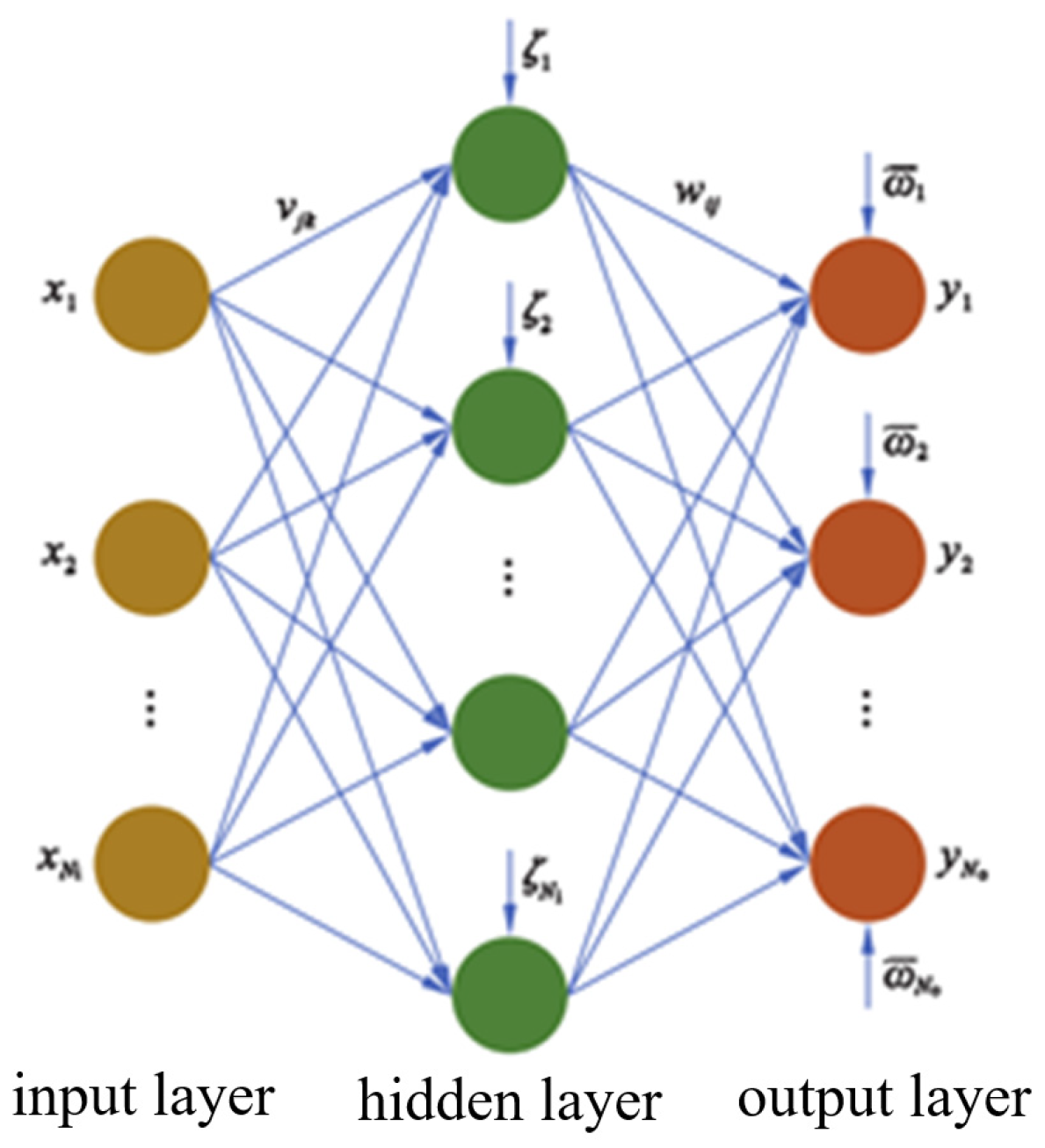
4.1. Structure of Neural Networks
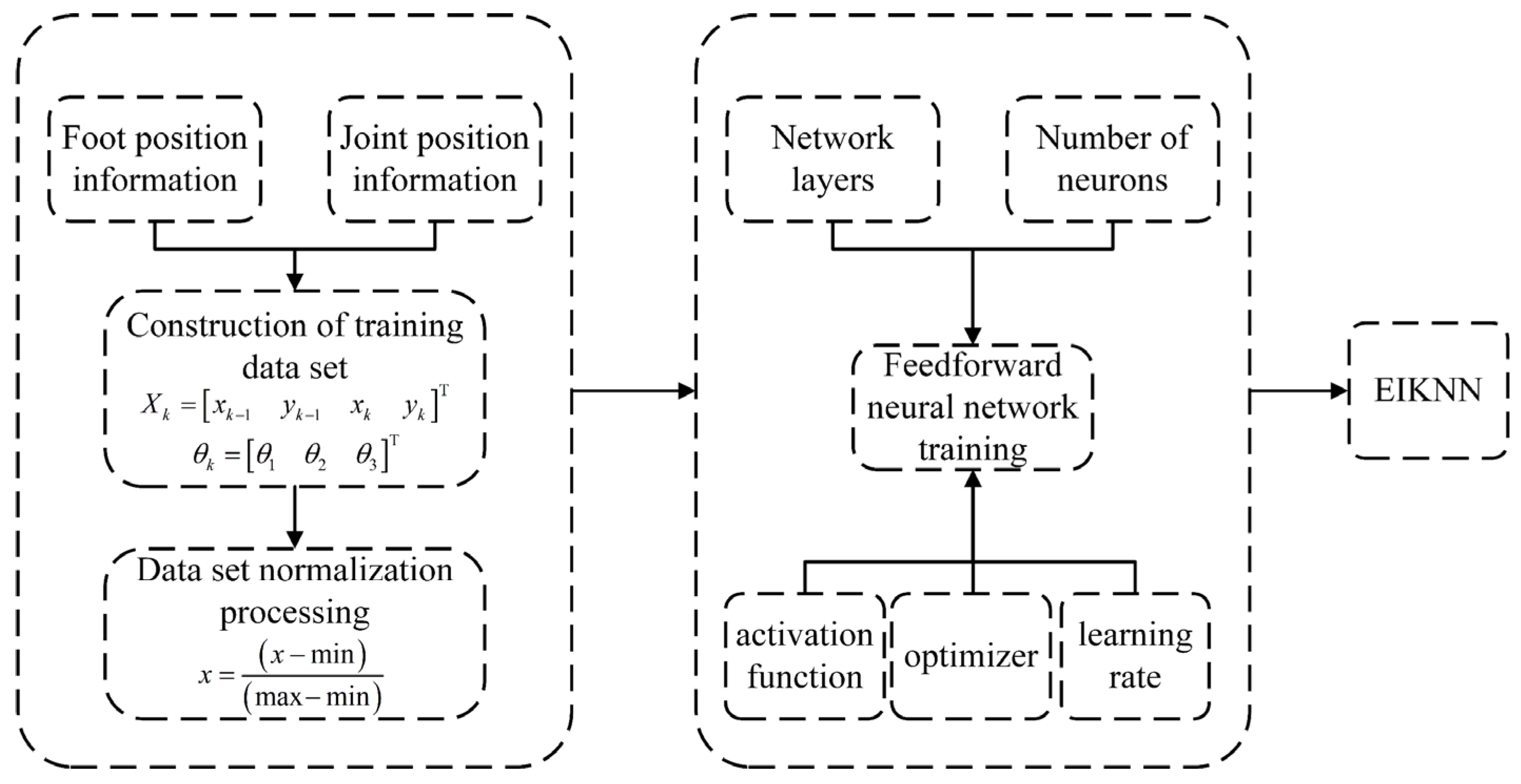
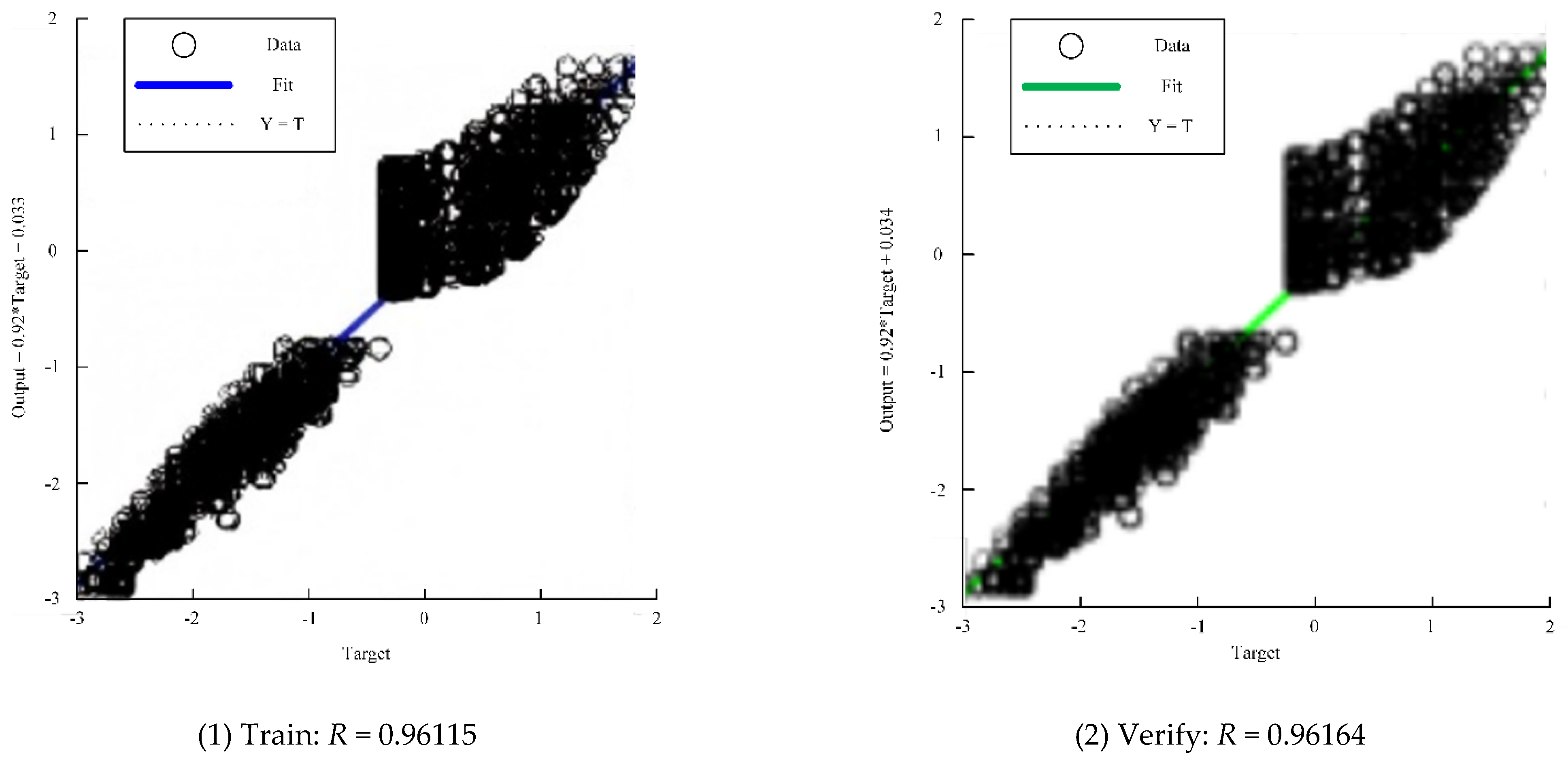
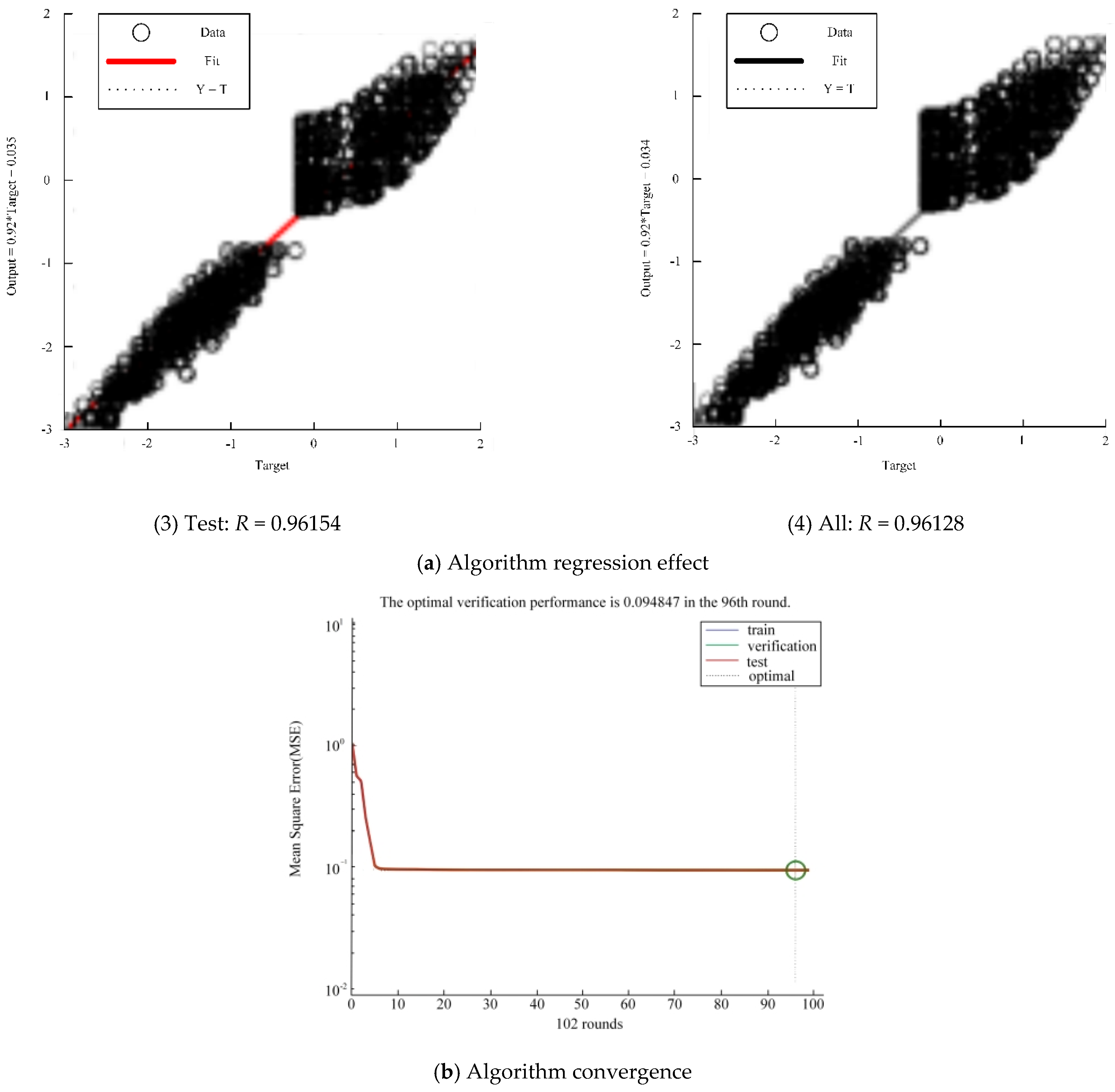
4.2. Training Process of Neural Network
5. Experimental Verification
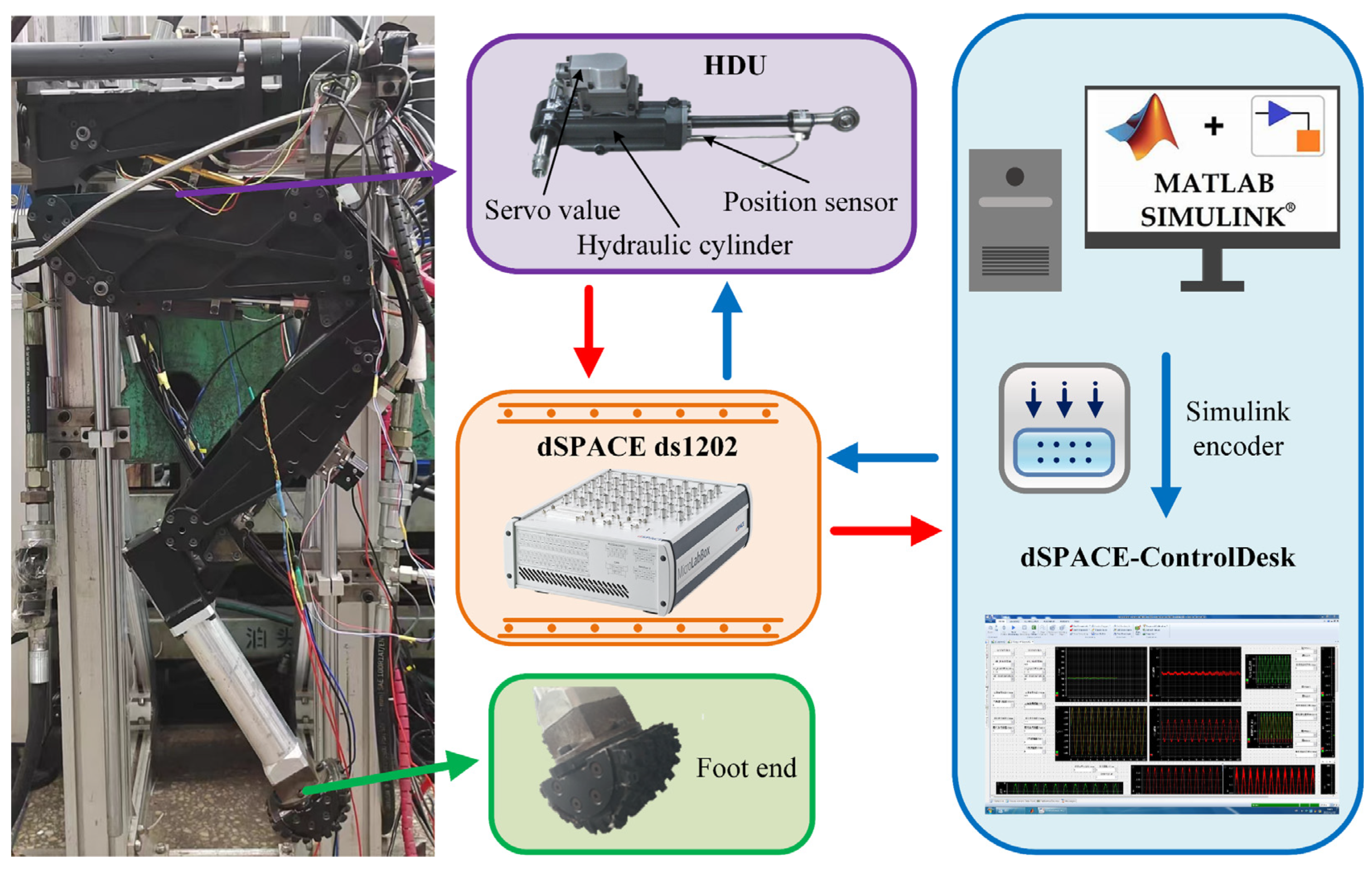
5.1. Experimental Platform and Scheme Comparison
- (1)
- This is the EIKNN method proposed in this paper.
- (2)
- Pseudo-inverse matrix method. This method utilizes the pseudo-inverse of the Jacobian matrix to update joint positions. By computing joint velocities (, where is the pseudo-inverse of the Jacobian matrix), it enables rapid joint movements to achieve the desired foot-end velocity. The joint positions are then obtained through time integration until the foot-end position error is minimized. It is worth noting that the pseudo-inverse matrix of the Jacobi matrix does not always exist and may lead to numerical instability when the robot is in a singular configuration. In the comparative approach of this paper, this problem is solved by introducing a regularization term, specifically .
- (3)
- Gradient projection method. This method searches for joint positions by iterative optimization using gradient information to minimize the error between the actual position of the foot end and the desired position (, where is the desired position of the foot end, and is the actual position of the foot end with the joint angle as the variable). The iteration step size is set to 0.001. The boundary constraint is set to Trajectory amplitude/100.
- (4)
- Geometric constraint method. This method performs an inverse kinematics solution by adding geometric constraints. In this paper, the 3-DOF hydraulic single leg is added with the motion constraints as shown in Figure 13 to ensure that the three points of the hip joint O, the ankle joint H, and the foot end I are kept in a straight line, thereby obtaining an accurate resolution of the inverse kinematics. However, this method reduces the motion space of the foot end. In addition, the inverse kinematics model of this method is not the focus of this paper; we omit the detailed derivation process and directly give the inverse kinematics expression as
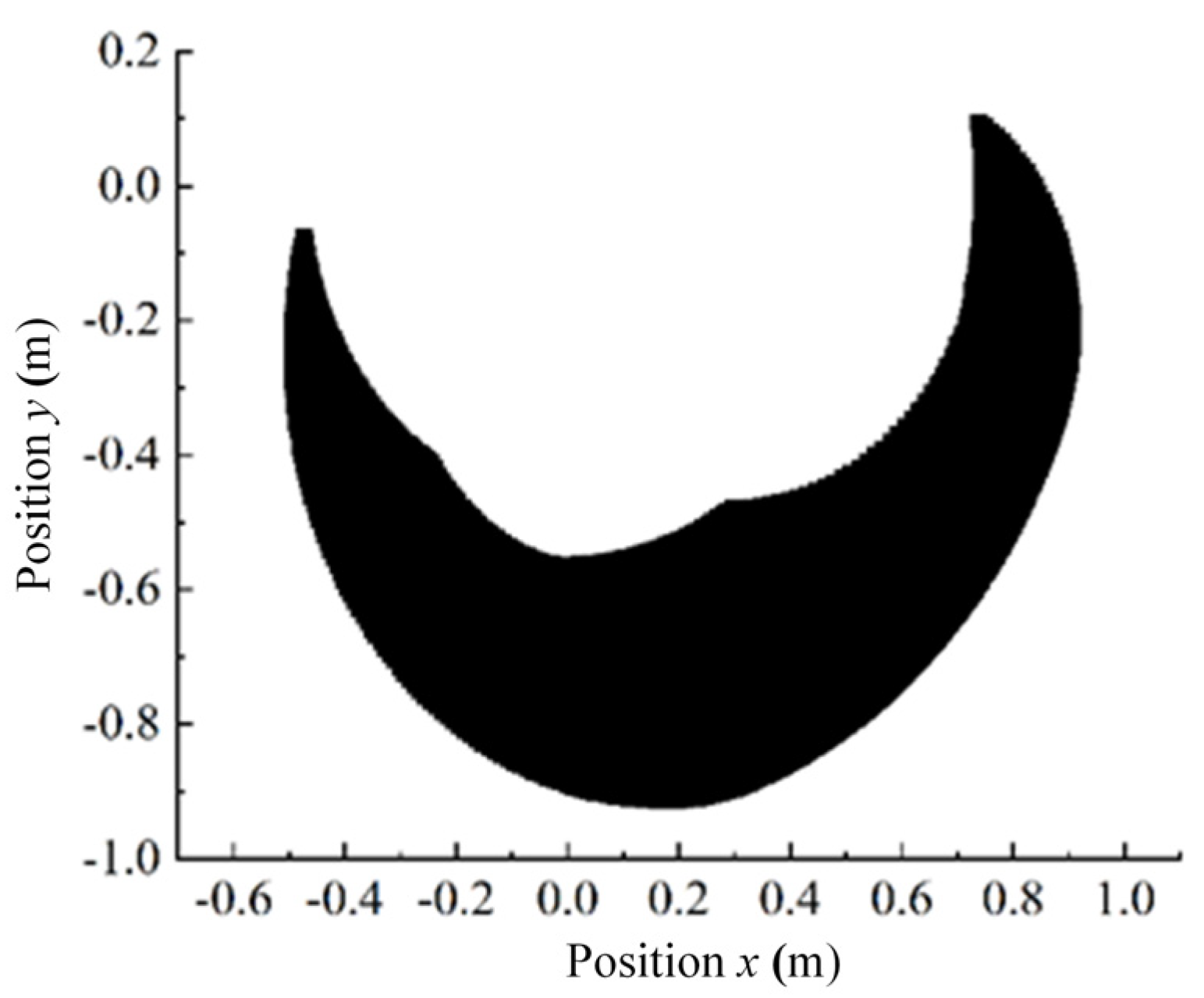
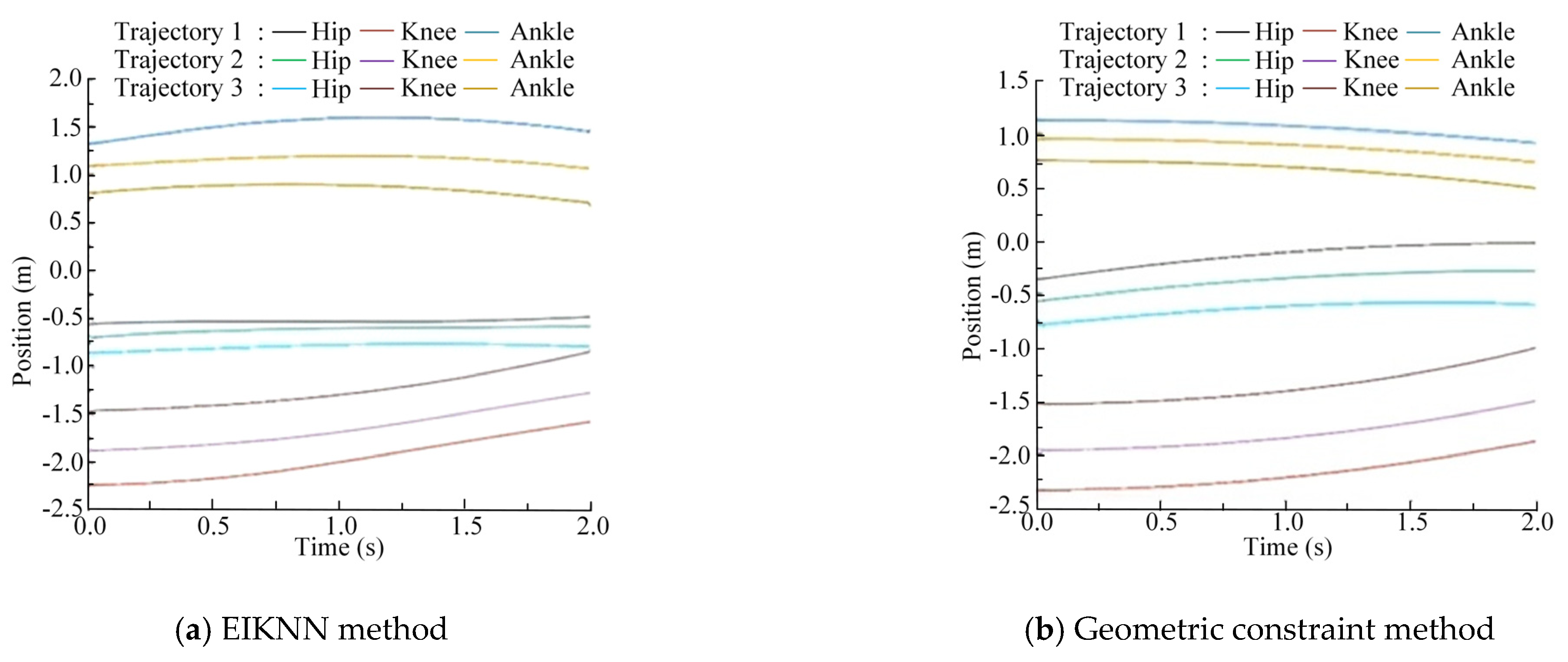
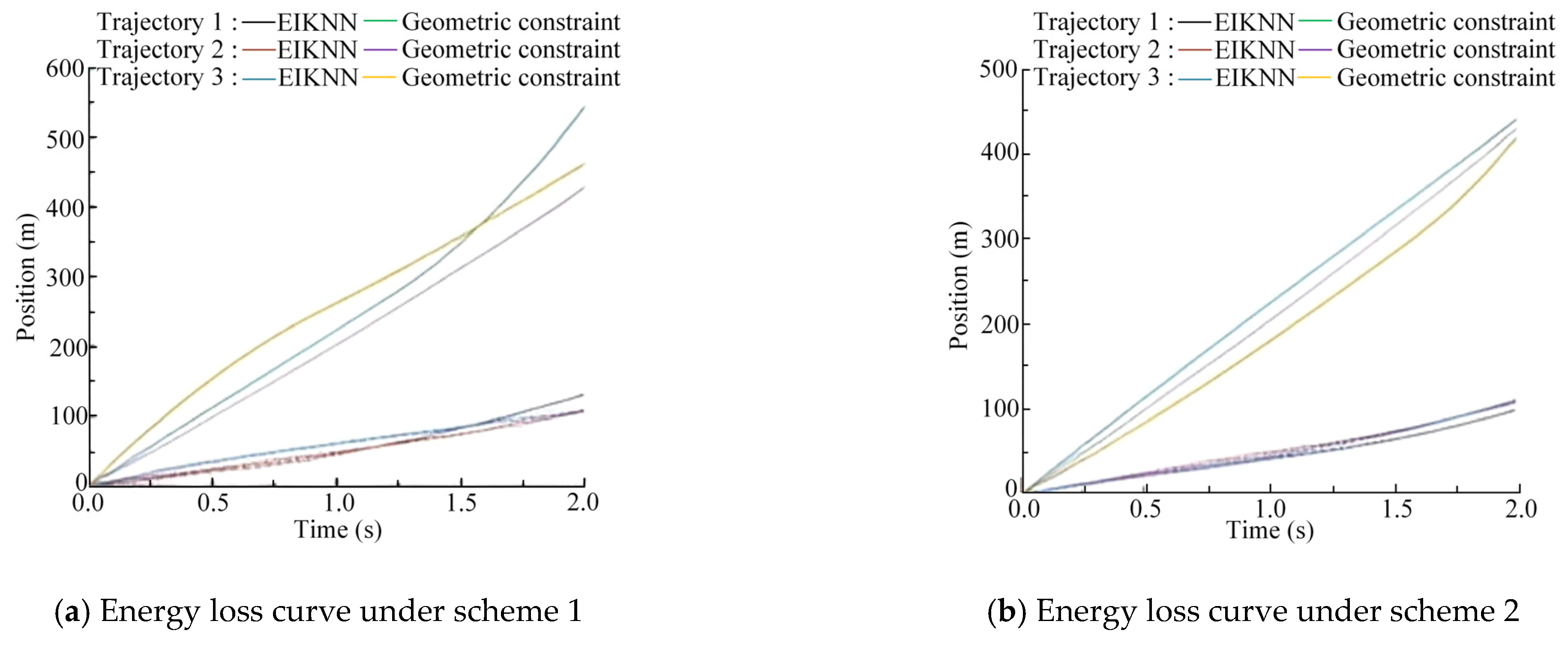
5.2. Experimental Results and Analysis
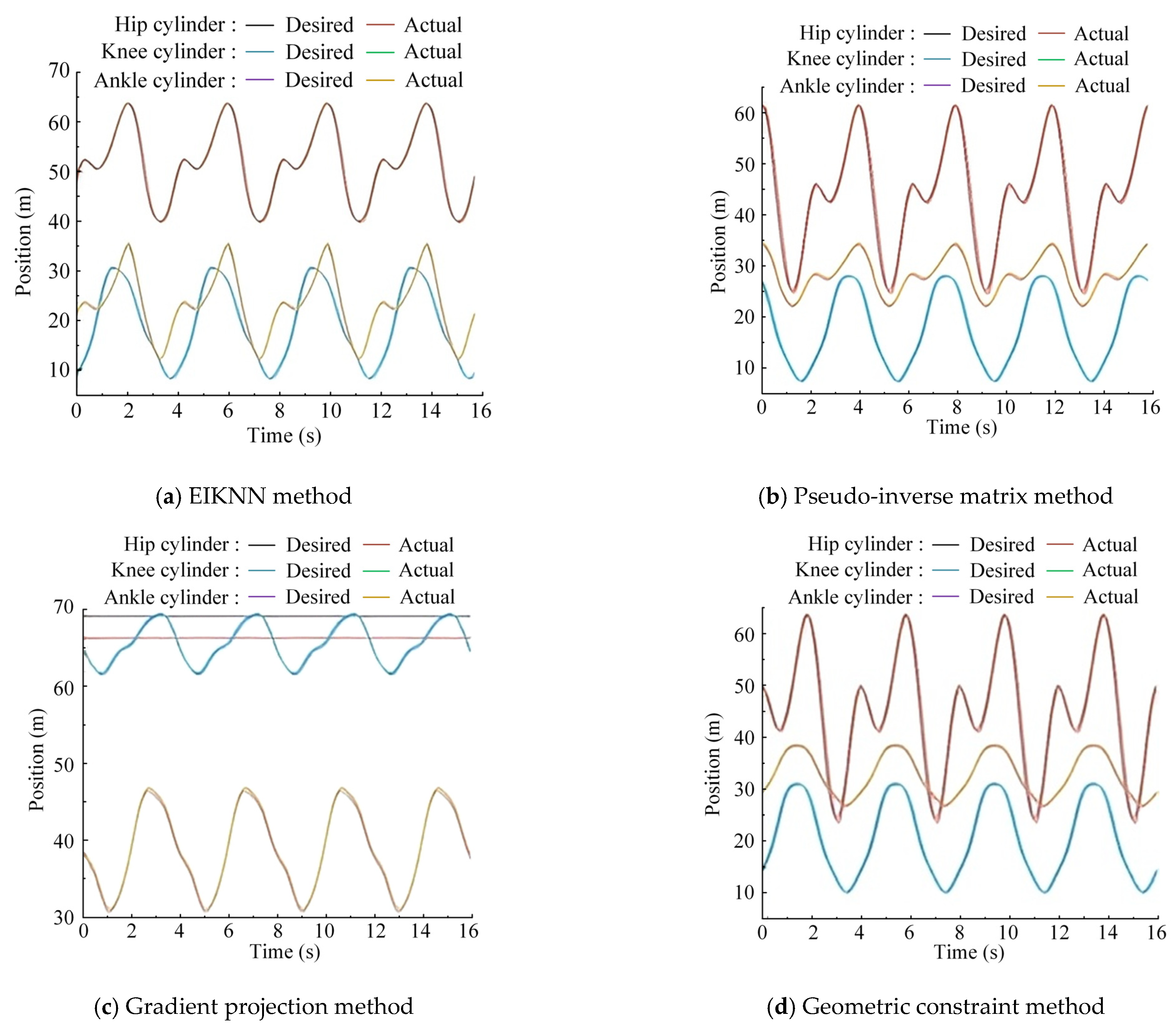

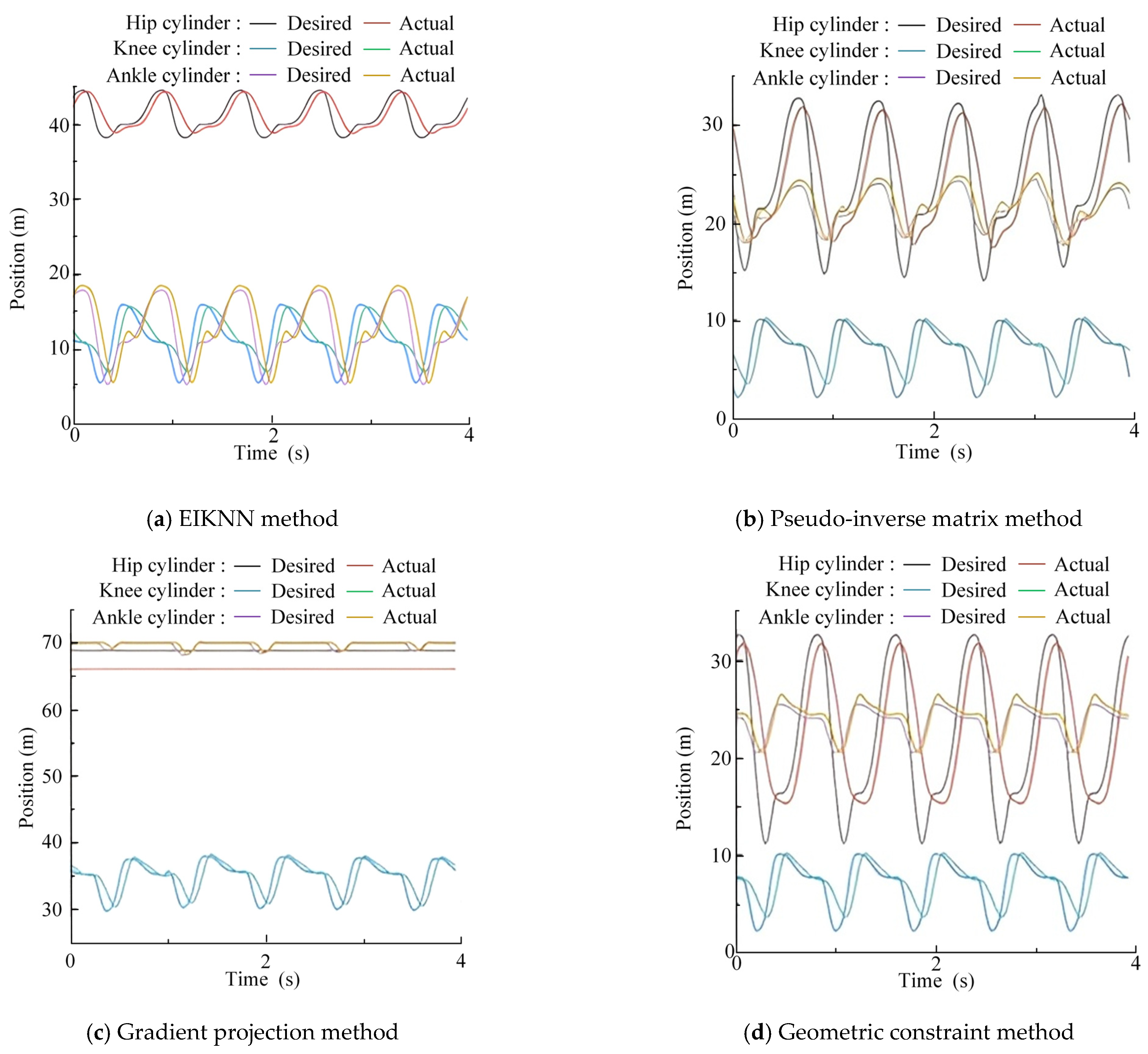
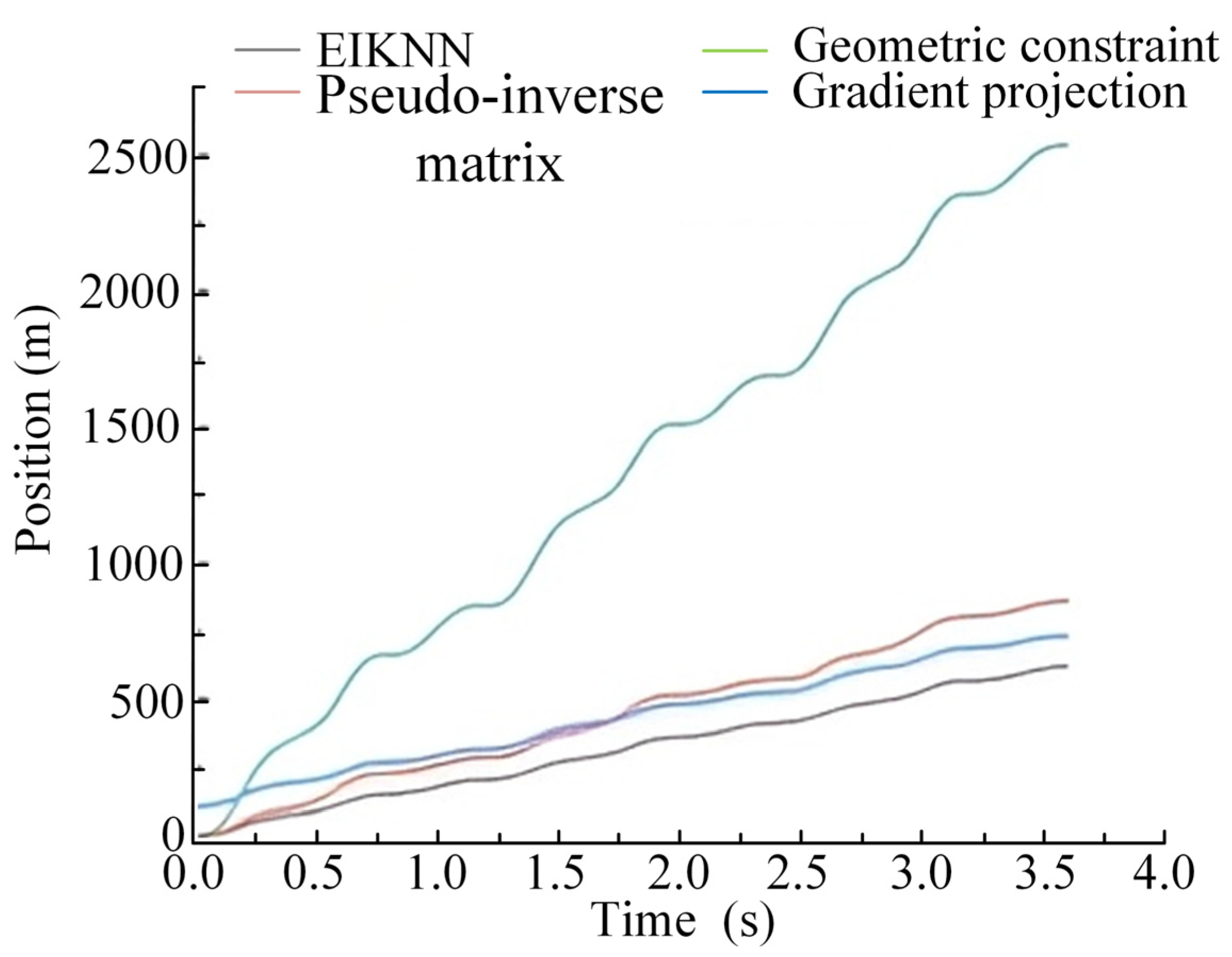
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, J.; Jin, H.; Gao, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Cai, H. Jump Control Based on Nonlinear Wheel-Spring-Loaded Inverted Pendulum Model: Validation of a Wheeled-Bipedal Robot with Single-Degree-of-Freedom Legs. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Yu, Z.; Han, L.; Chen, X.; Qiu, X.; Huang, Q. Compliant motion control of wheel-legged humanoid robot on rough terrains. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2023, 29, 1949–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Yoon, S.; Jeong, Y.; Seo, J.; Park, S.; Han, S.; Kim, J.T.; Kim, J.; Choi, H.R.; Cho, J. Design and implementation of a two-wheeled inverted pendulum robot with a sliding mechanism for off-road transportation. IEEE Rob. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 4004–4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamegawa, T.; Akiyama, T.; Sakai, S.; Fujii, K.; Une, K.; Wang, Y.; Matsumura, Y.; Kishutani, T.; Nose, E.; Yoshizaki, Y.; et al. Development of a separable search-and-rescue robot composed of a mobile robot and a snake robot. Adv. Rob. 2020, 34, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, T.; Yan, L. Real-time control strategy of exoskeleton locomotion trajectory based on multi-modal fusion. J. Bionic Eng. 2023, 20, 2670–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, K.; Li, M.; Qin, J.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q. Differential game-based control for nonlinear human–robot interaction system with unknown desired trajectory. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2024, 54, 6832–6842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Deng, Y.; Ng, W.W.; Li, D. An intelligent interaction framework for teleoperation based on human-machine cooperation. IEEE Trans. Human-Machine Syst. 2022, 52, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Yang, S.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, D.; Chi, W.; Chen, K.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, R.; et al. Max: A wheeled-legged quadruped robot for multimodal agile locomotion. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2023, 21, 7562–7582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zong, H.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, J.; Fang, L.; Ai, J.; Xu, B. Design and parameter identification of model-based control integrating hydraulic cylinders in robotic leg dynamics. Control Eng. Pract. 2025, 162, 106367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.; Kim, S.W.; Shin, S.; Oh, J.H.; Park, H.S.; Park, H.W. Energy-efficient hydraulic pump control for legged robots using model predictive control. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2022, 2, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, H.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, K.; Shen, J.; Lu, Z.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Xu, B. Bionic lightweight design of limb leg units for hydraulic quadruped robots by additive manufacturing and topology optimization. Bio-Des. Manuf. 2024, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, H.; Yue, Y.; Meng, K.; Yang, Z. Active Disturbance Rejection Control With Backstepping for Decoupling Control of Hydraulic Driven Lower Limb Exoskeleton Robot. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 31, 1324–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, H.; Kang, H.; Lee, J.H.; Phan, L.T.; Jin, S.; Kim, Y.B.; Seok, D.-Y.; Lee, S.Y.; et al. Development of a quadruped robot system with torque-controllable modular actuator unit. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 68, 7263–7273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; An, H.; Yang, Y.; Wu, C.; Wei, Q.; Ma, H. Model predictive trajectory tracking control of electro-hydraulic actuator in legged robot with multi-scale online estimator. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 95918–95933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Jin, L.; Luo, X.; Sun, Z.; Liu, M. RNN for repetitive motion generation of redundant robot manipulators: An orthogonal projection-based scheme. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 2020, 33, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Li, S.; Luo, X.; Li, Y.; Qin, B. Neural dynamics for cooperative control of redundant robot manipulators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2018, 14, 3812–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, G.; Scoccia, C. Motion planning and control of redundant manipulators for dynamical obstacle avoidance. Machines 2021, 9, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, K.; Gosselin, C. Exploiting redundancies for workspace enlargement and joint trajectory optimization of a kinematically redundant hybrid parallel robot. J. Mech. Rob. 2021, 13, 040905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.; Shang, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Xue, Y.; Wu, W. An Energy Efficient Two-Stage Supply Pressure Hydraulic System for the Downhole Traction Robot. Math. Probl. Eng. 2018, 2018, 2161937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Bian, Y.; Yang, M.; Liu, G. Characteristic analysis and motion control of a novel ball double-screw hydraulic robot joint. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2022, 16, 1305–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Luo, L.; Zhao, H.; Ge, D.; Ding, H. Inverse Kinematics Solution Based on Redundancy Modeling and Desired Behaviors Optimization for Dual Mobile Manipulators. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2023, 108, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, K.X.; Yu, B.; Kong, X.D.; Li, C.H.; Zhu, Q.X.; Zhao, H.L.; Kong, L.J. Parameters sensitivity characteristics of highly integrated valve-controlled cylinder force control system. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2018, 31, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, S.; Sudheer, A.P.; Magid, E. Torque control of a wheeled humanoid robot with dual redundant arms. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part I J. Syst. Control. Eng. 2024, 238, 252–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flight, J.; Gosselin, C. Kinematically redundant (6+ 2)-dof HEXA robot for singularity avoidance and workspace augmentation. Mech. Mach. Theory 2024, 195, 105615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, J.; Yao, J. Neural network-based adaptive asymptotic prescribed performance tracking control of hydraulic manipulators. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2022, 53, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Deng, W.; Yao, J. Neural adaptive dynamic surface asymptotic tracking control of hydraulic manipulators with guaranteed transient performance. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 2022, 34, 7339–7349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramar, V.; Kramar, O.; Kabanov, A. An artificial neural network approach for solving inverse kinematics problem for an anthropomorphic manipulator of robot SAR-401. Machines 2022, 10, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zou, T.; Jiang, X. A neural network based approach to inverse kinematics problem for general six-axis robots. Sensors 2022, 22, 8909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X. Kinematics model identification and motion control of robot based on fast learning neural network. J. Ambient Intell. Hum. Comput. 2020, 11, 6145–6154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, Y. Robust zeroing neural-dynamics and its time-varying disturbances suppression model applied to mobile robot manipulators. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 2017, 29, 4385–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, L. Kinematic control of redundant manipulators using neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 2016, 28, 2243–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Li, S.; La, H.M.; Luo, X. Manipulability optimization of redundant manipulators using dynamic neural networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 4710–4720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Xu, F.; Yan, L. New pseudoinverse-based path-planning scheme with PID characteristic for redundant robot manipulators in the presence of noise. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2017, 26, 2008–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudreau, R.; Léger, J.; Tinaou, H.; Gallant, A. Dynamic analysis and optimization of a kinematically redundant planar parallel manipulator. Trans. Can. Soc. Mech. Eng. 2018, 42, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyt, D.F.; Taylor, C.R. Gait and the energetics of locomotion in horses. Nature 1981, 292, 239–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyt, D.F.; Wickler, S.J.; Dutto, D.J.; Catterfeld, G.E.; Johnsen, D. What are the relations between mechanics, gait parameters, and energetics in terrestrial locomotion ? J. Exp. Zool. A Comp. Exp. Biol. 2006, 305, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Li, Y.; Zhou, L.; Rong, X. Energy efficient foot trajectory of trot motion for hydraulic quadruped robot. Energies 2019, 12, 2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Rong, X.; Li, Y. Design and control method of a hydraulic power unit for a wheel-legged robot. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2022, 36, 2043–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Parameter | OA | OB | OG | GC | GD | GH | HE | HF | HI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value (mm) | 85 | 245 | 300 | 249 | 44 | 310 | 248 | 46 | 359 |
| Parameter | - | - | - | ||||||
| Value (°) | 1 | 12 | 13.5 | 13 | 37.35 | 65 |
| Parameter | Minimum Value | Maximum Value |
|---|---|---|
| Position of HDU (m) | −0.07 | 0.07 |
| Velocity of HDU (m/s) | −0.1 | 0.1 |
| Acceleration of HDU (m/s2) | −0.5 | 0.5 |
| Rotation angle of hip joint (°) | −54.439 | −4.618 |
| Rotation angle of knee joint (°) | −137.587 | −32.156 |
| Rotation angle of ankle joint (°) | −4.5412 | 94.5897 |
| Fluid Flow Type | Different Kinds of Pipes | Value of |
|---|---|---|
| Laminar flow | Circular pipe | |
| Curved pipe | ||
| Hose with small bending radius | ||
| Straight pipe with standard pipe joint |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| (m/s) | 0.0103 |
| (N) | 2.4440 |
| (N) | 0.5991 |
| (Ns/m) | 0.4766 |
| (Ns/m) | 0.2701 |
| (Ns/m) | 0.0049 |
| Unit | Initial Value | Stop Value | Target Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Round | 0 | 102 | 1000 |
| Duration | - | 00:00:17 | - |
| Performance | 1.05 | 0.0955 | 0 |
| Gradient | 1.39 | 0.000169 | 1 × 10−7 |
| Mu | 0.001 | 1 × 10−6 | 1 × 1010 |
| Verification Check | 0 | 6 | 6 |
| Parameter | Value | Unit | Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.5 × 10−4 | m/V | 0.5 × 107 | Pa | ||
| 0 | m3/(s * Pa) | 2.38 × 10−13 | m3/(s * Pa) | ||
| 5.97 × 10−4 | m2 | 1.1315 | kg | ||
| 3.97 × 10−4 | m2 | 8.0 × 108 | Pa | ||
| 6.2 × 10−7 | m3 | 0 | N/m | ||
| 8.6 × 10−7 | m3 | 2000 | N/(m/s) | ||
| 0.07 | m | 1.0 × 107 | Pa |
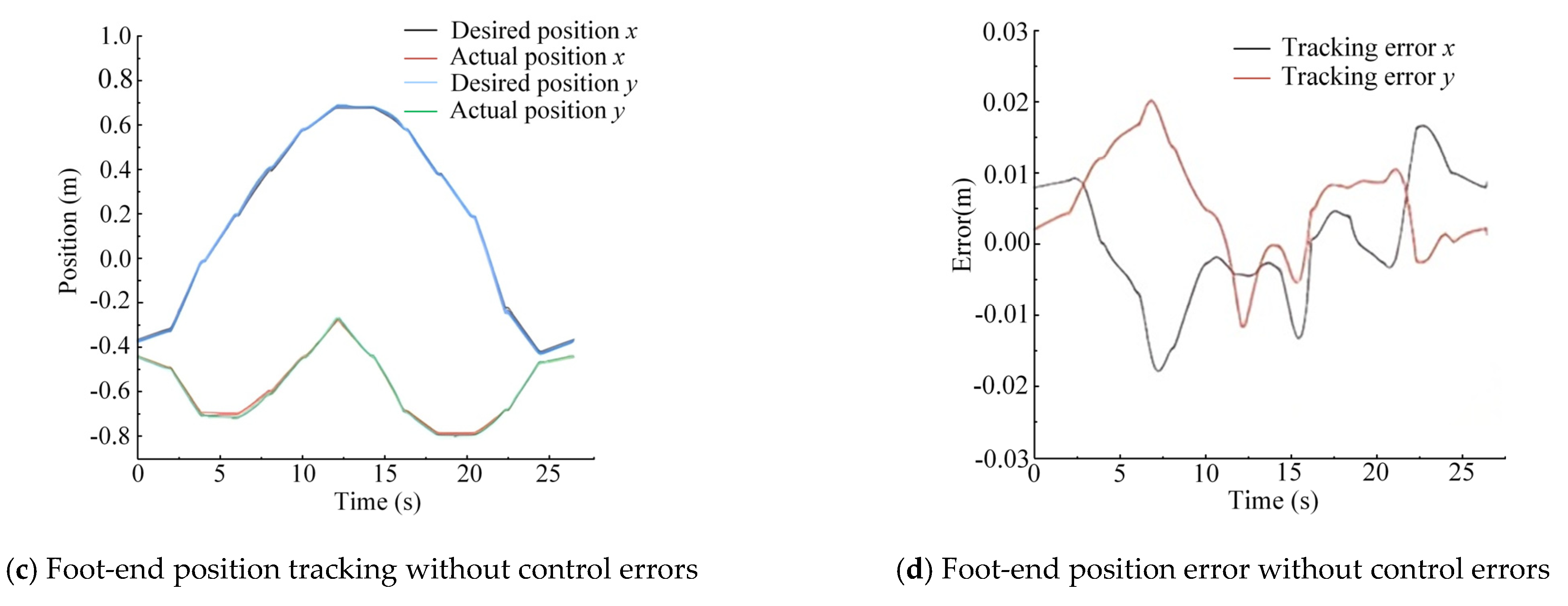
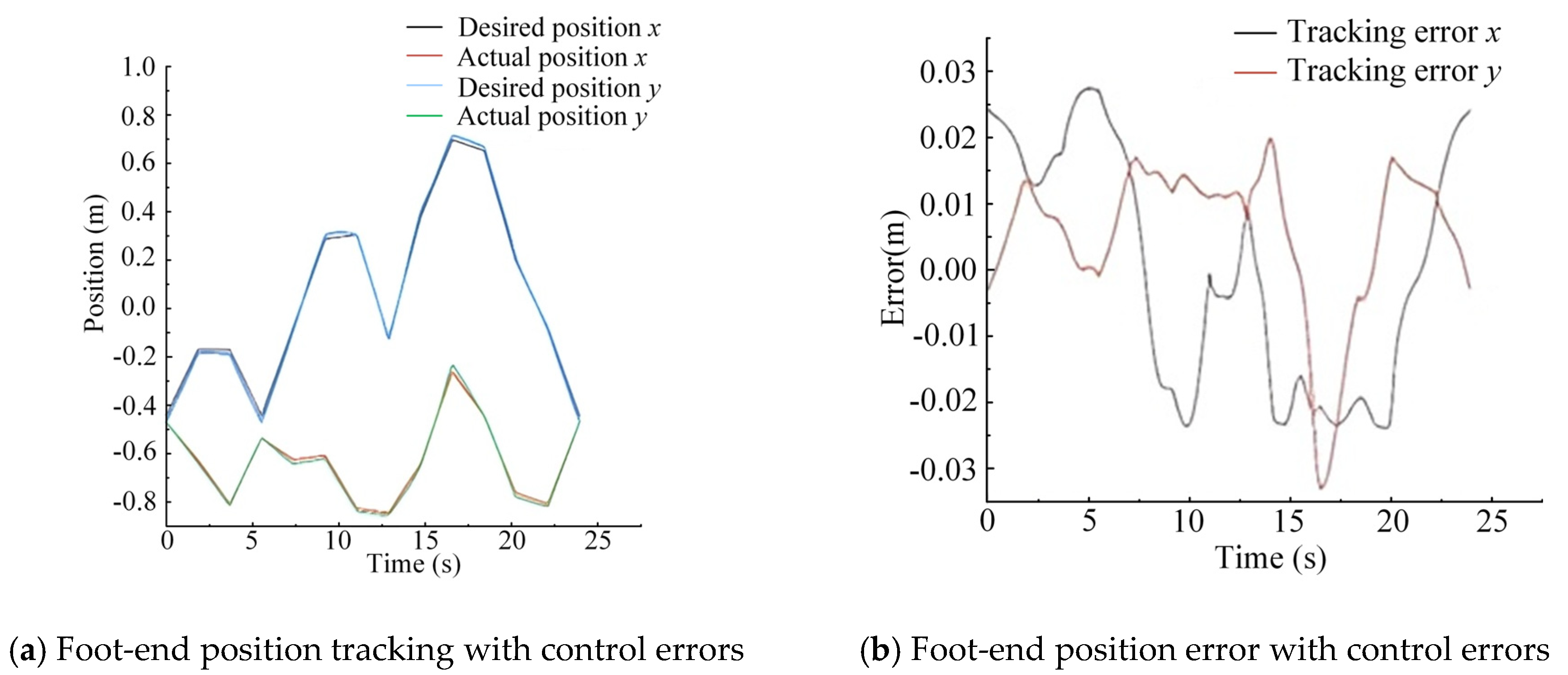
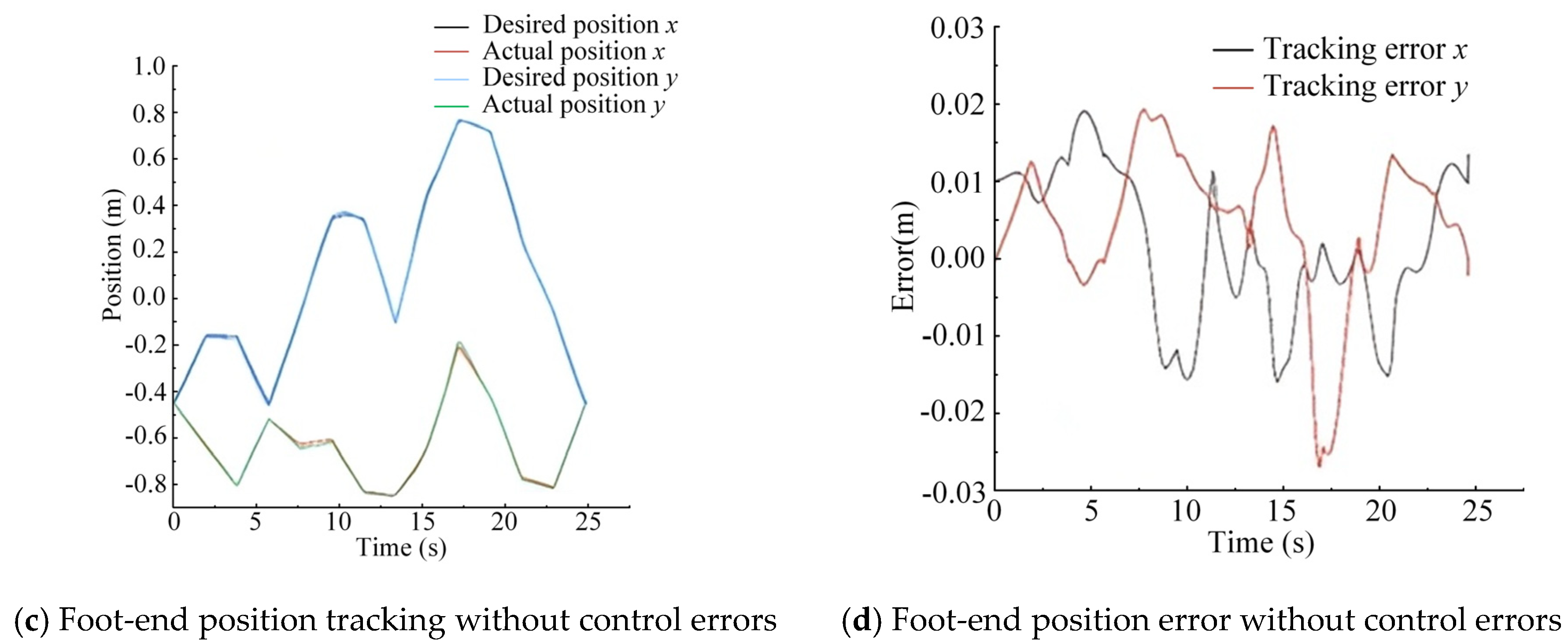
| Foot-End Trajectory Tracking | Trajectory Amplitude x (m) | Error Amplitude x (m) | Error Rate | Trajectory Amplitude y (m) | Error Amplitude y (m) | Error Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Random trajectory 1 | Testing method 1 | 1.1 | 0.0295 | 2.68% | 0.5 | 0.022 | 4.40% |
| Testing method 2 | 1.1 | 0.018 | 1.63% | 0.5 | 0.02 | 4.00% | |
| Random trajectory 2 | Testing method 1 | 1.27 | 0.0305 | 2.40% | 0.64 | 0.032 | 5.00% |
| Testing method 2 | 1.27 | 0.019 | 1.50% | 0.64 | 0.025 | 3.91% | |
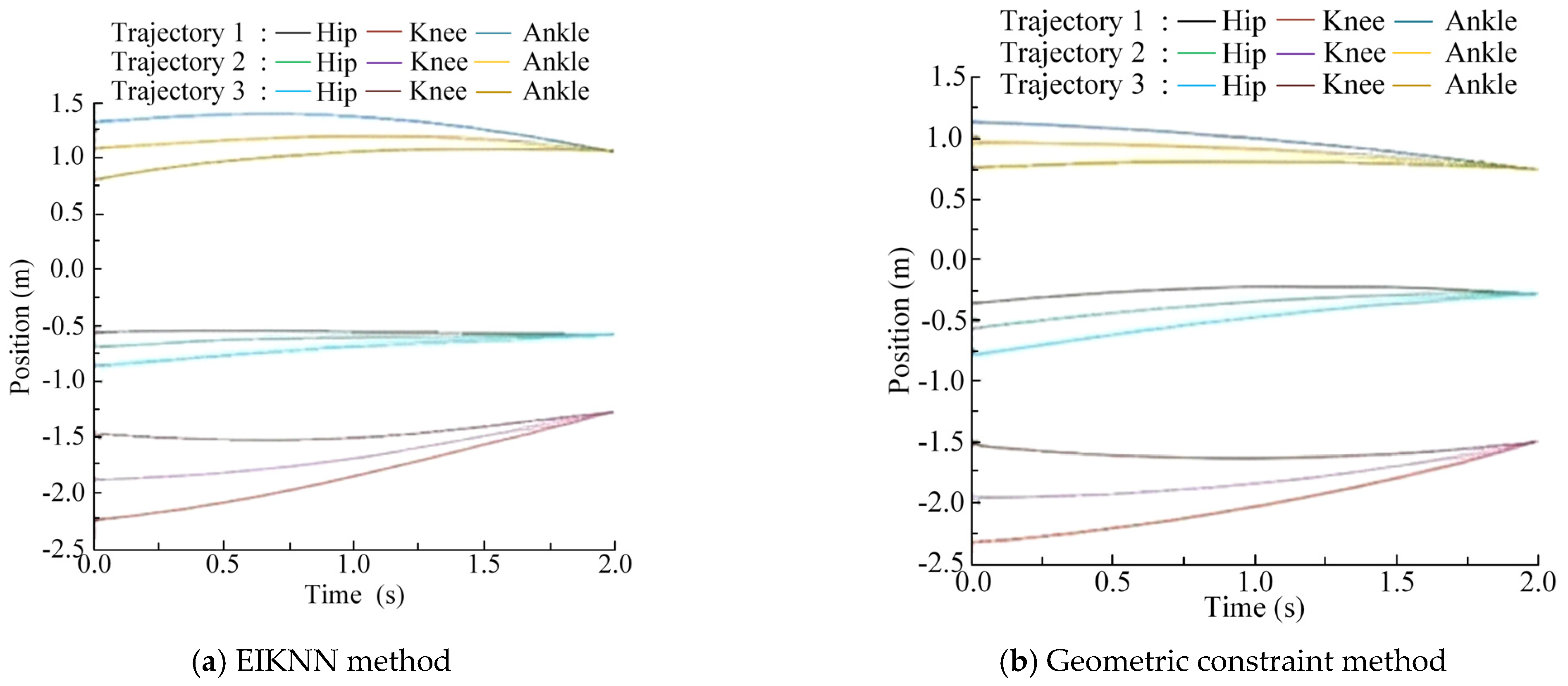
| Trajectory Scheme | Starting Point | Ending Point | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scheme 1 (Different starting points with the same ending point) | Trajectory 1 | ((0, −0.6) | (0.4, −0.7) |
| Trajectory 2 | (0, −0.7) | (0.4, −0.7) | |
| Trajectory 3 | (0, −0.8) | (0.4, −0.7) | |
| Scheme 2 (Different starting points with different ending points) | Trajectory 1 | (0, −0.6) | (0.4, −0.6) |
| Trajectory 2 | (0, −0.7) | (0.4, −0.7) | |
| Trajectory 3 | (0, −0.8) | (0.4, −0.8) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
She, J.; Feng, X.; Xu, B.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, N.; Zou, W.; Ma, G.; Yu, B.; Ba, K. Bionic Energy-Efficient Inverse Kinematics Method Based on Neural Networks for the Legs of Hydraulic Legged Robots. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10060403
She J, Feng X, Xu B, Chen L, Wang Y, Liu N, Zou W, Ma G, Yu B, Ba K. Bionic Energy-Efficient Inverse Kinematics Method Based on Neural Networks for the Legs of Hydraulic Legged Robots. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(6):403. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10060403
Chicago/Turabian StyleShe, Jinbo, Xiang Feng, Bao Xu, Linyang Chen, Yuan Wang, Ning Liu, Wenpeng Zou, Guoliang Ma, Bin Yu, and Kaixian Ba. 2025. "Bionic Energy-Efficient Inverse Kinematics Method Based on Neural Networks for the Legs of Hydraulic Legged Robots" Biomimetics 10, no. 6: 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10060403
APA StyleShe, J., Feng, X., Xu, B., Chen, L., Wang, Y., Liu, N., Zou, W., Ma, G., Yu, B., & Ba, K. (2025). Bionic Energy-Efficient Inverse Kinematics Method Based on Neural Networks for the Legs of Hydraulic Legged Robots. Biomimetics, 10(6), 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10060403






