UWB Indoor Localization Based on Artificial Rabbit Optimization Algorithm and BP Neural Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- The development of an innovative hybrid localization algorithm model, ARO-BP.
- (2)
- The integration of the BP neural network with the ARO algorithm to create a new method for optimizing the neural network structure, which enhances the accuracy and anti-jamming capability of the UWB indoor positioning system.
- (3)
- The substantial reduction in the original positioning error in the UWB positioning system, as demonstrated through the application and validation of the algorithm model in practical scenarios.
2. Model Fundamentals of Positioning
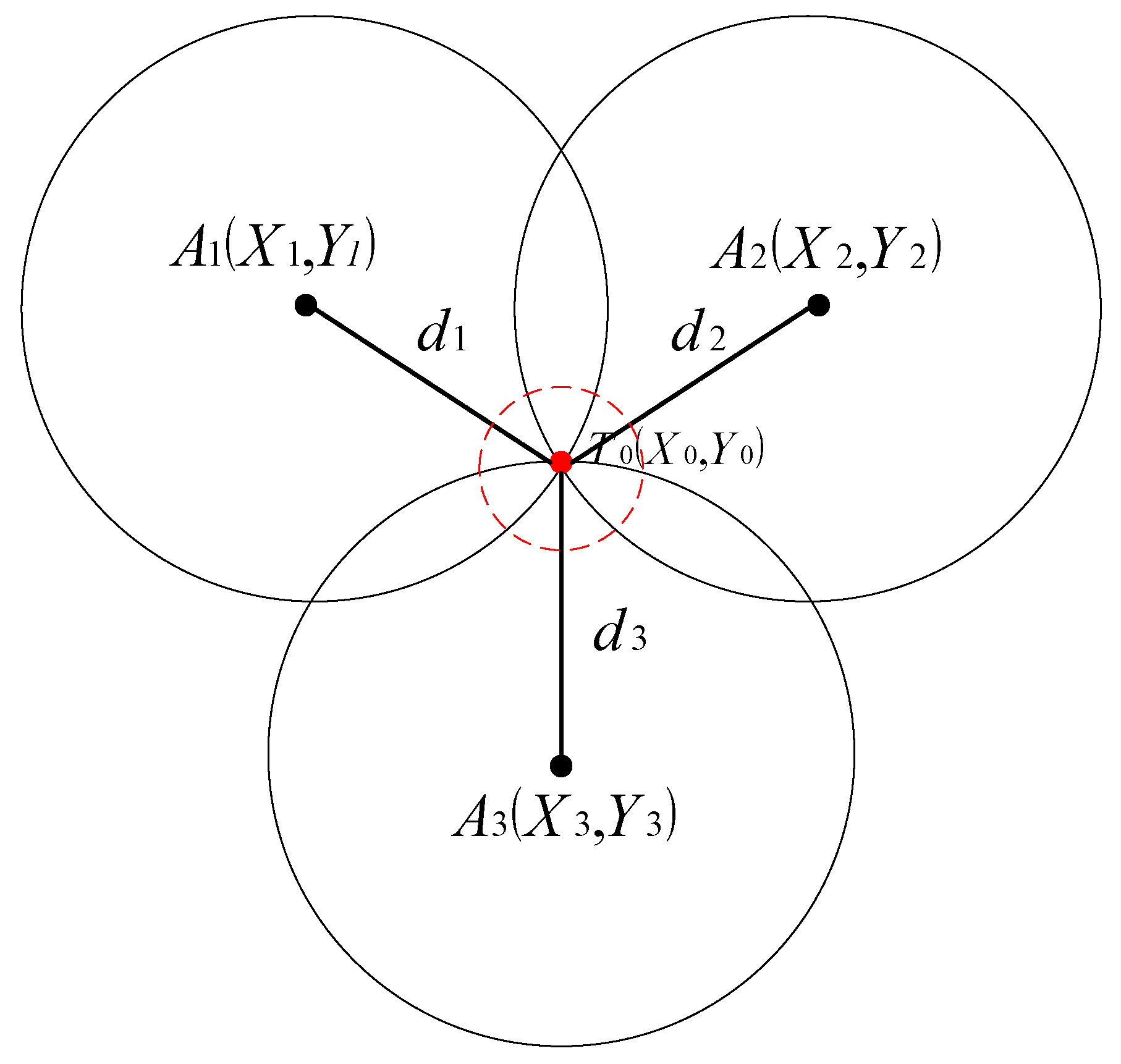
2.1. The UWB Localization Principle
2.2. BP Neural Network
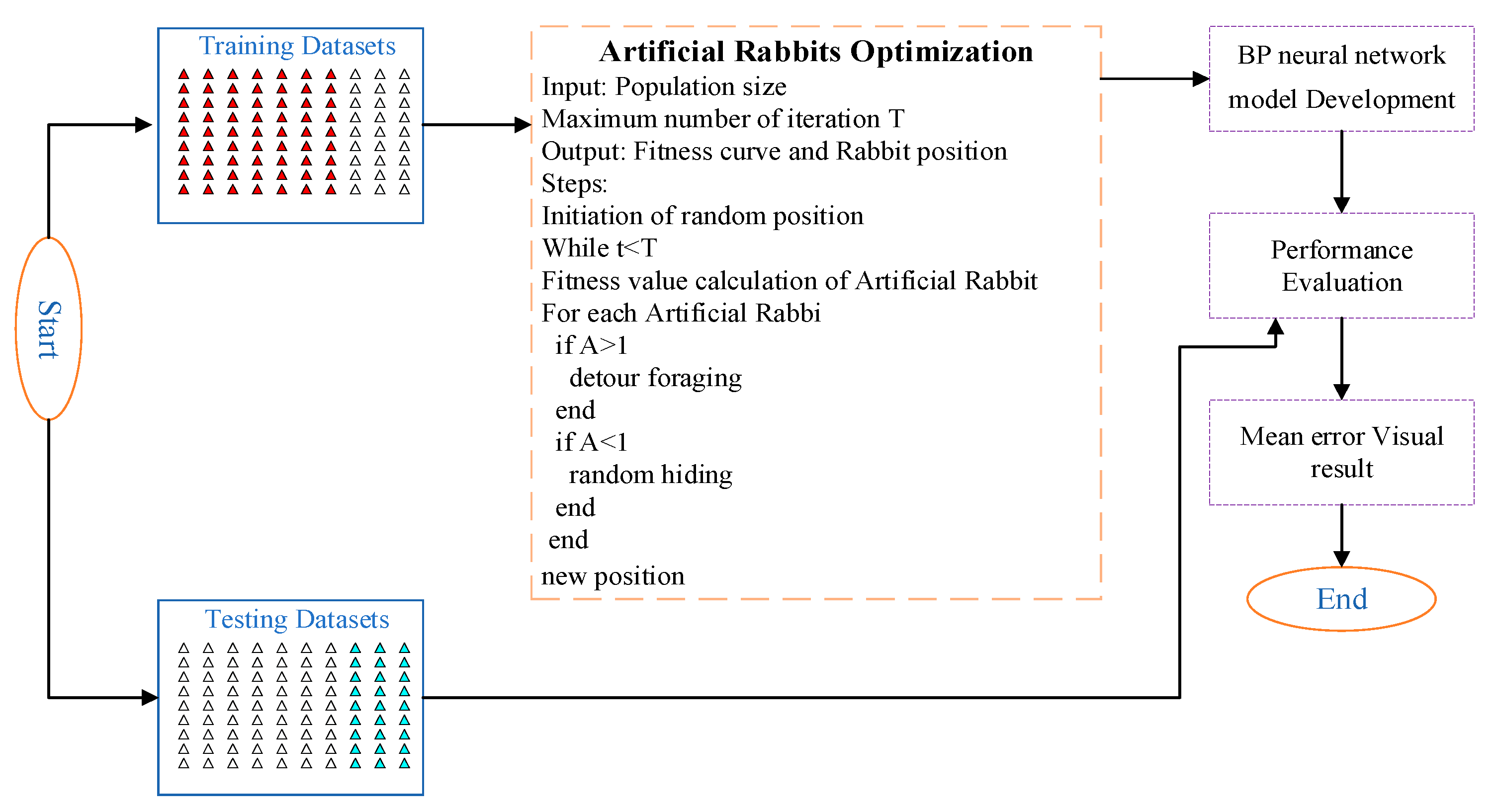
2.3. Model Building
- Rabbit Position and Energy Factor Initialization: the initial position of the rabbit is determined using the ARO algorithm’s initialization method, while the energy factor is set based on the specific characteristics of the problem.
- Input Data Determination: the rabbit’s position serves as the input data for training and prediction within the BP neural network.
- BP Neural Network Training: The input, derived from the rabbit’s position, is processed by the network. The difference between the predicted and actual output is used as the loss function, guiding the adjustment of network weights and biases through backpropagation to minimize errors.
- Rabbit Position and Energy Factor Update: the position and energy factors of the rabbits are updated according to the ARO algorithm’s strategy, incorporating the outcomes of the BP network’s training.
- Iterative Execution: steps 2 through 4 are repeated until the termination condition is met, either when the maximum number of iterations is reached or when the error falls below a predefined threshold.
3. Performance Evaluation and Analysis
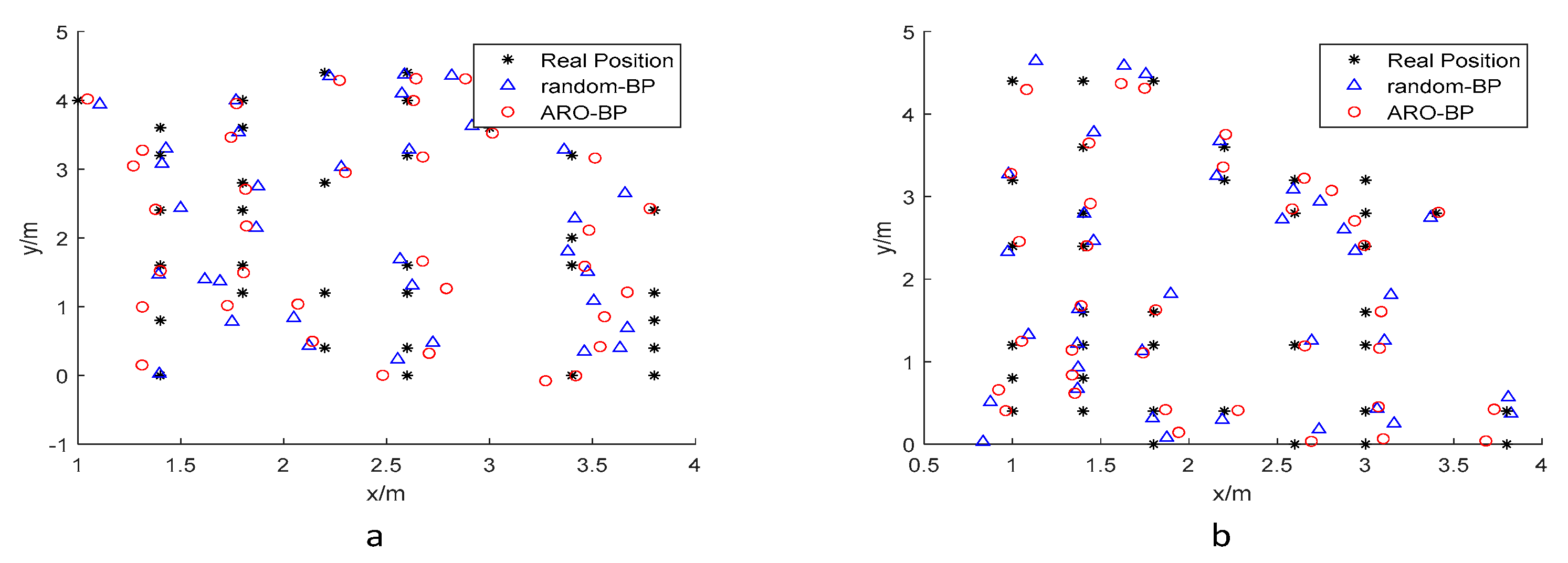
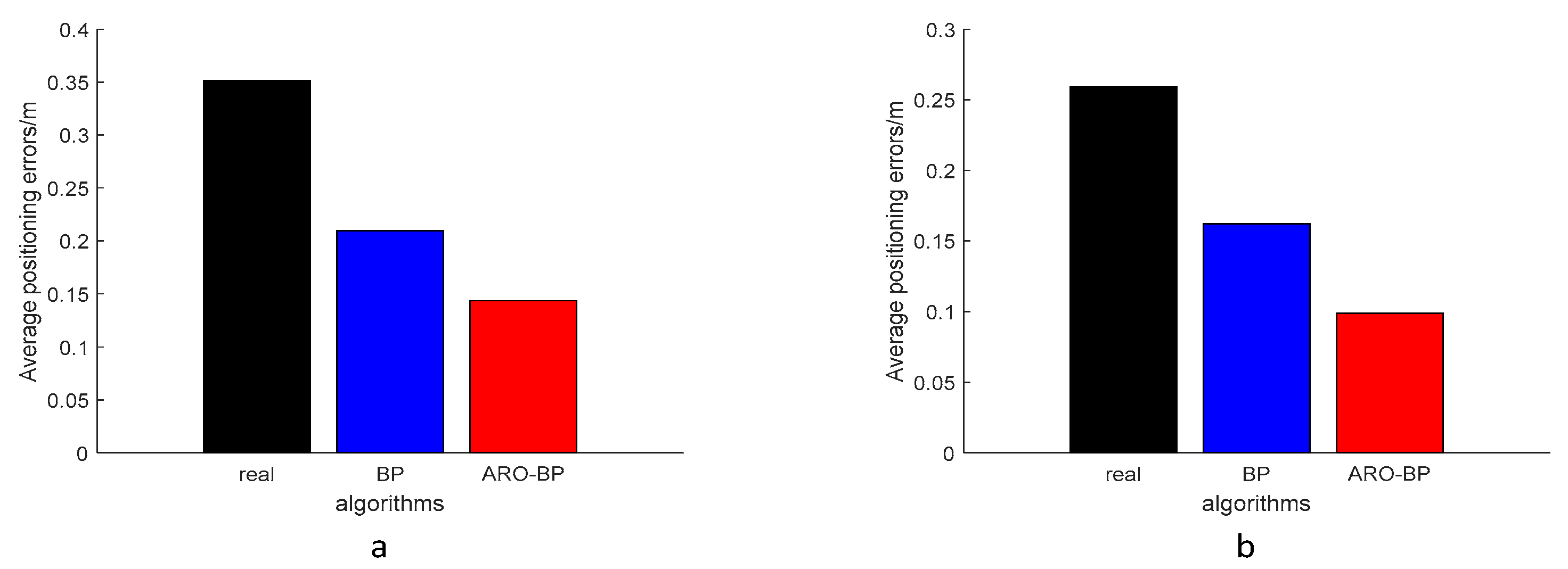
3.1. LOS Environment Experiment
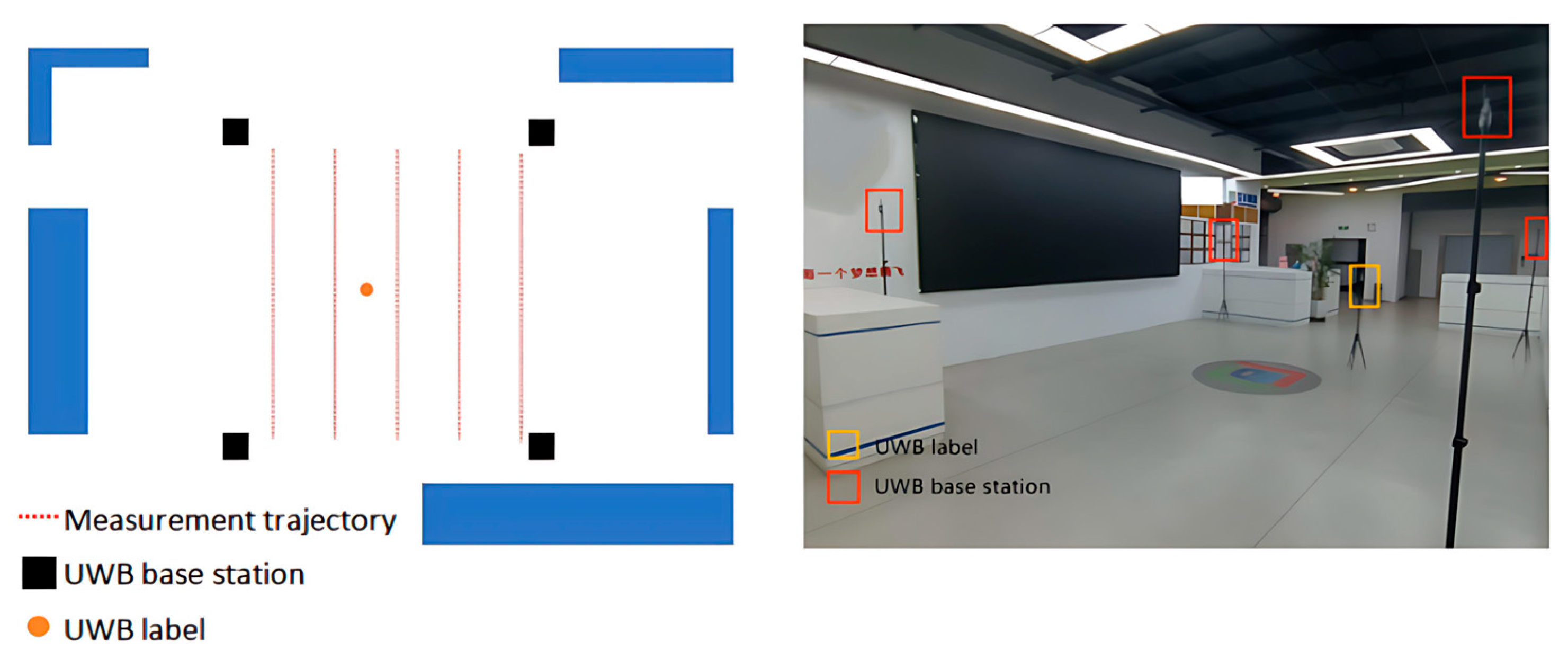
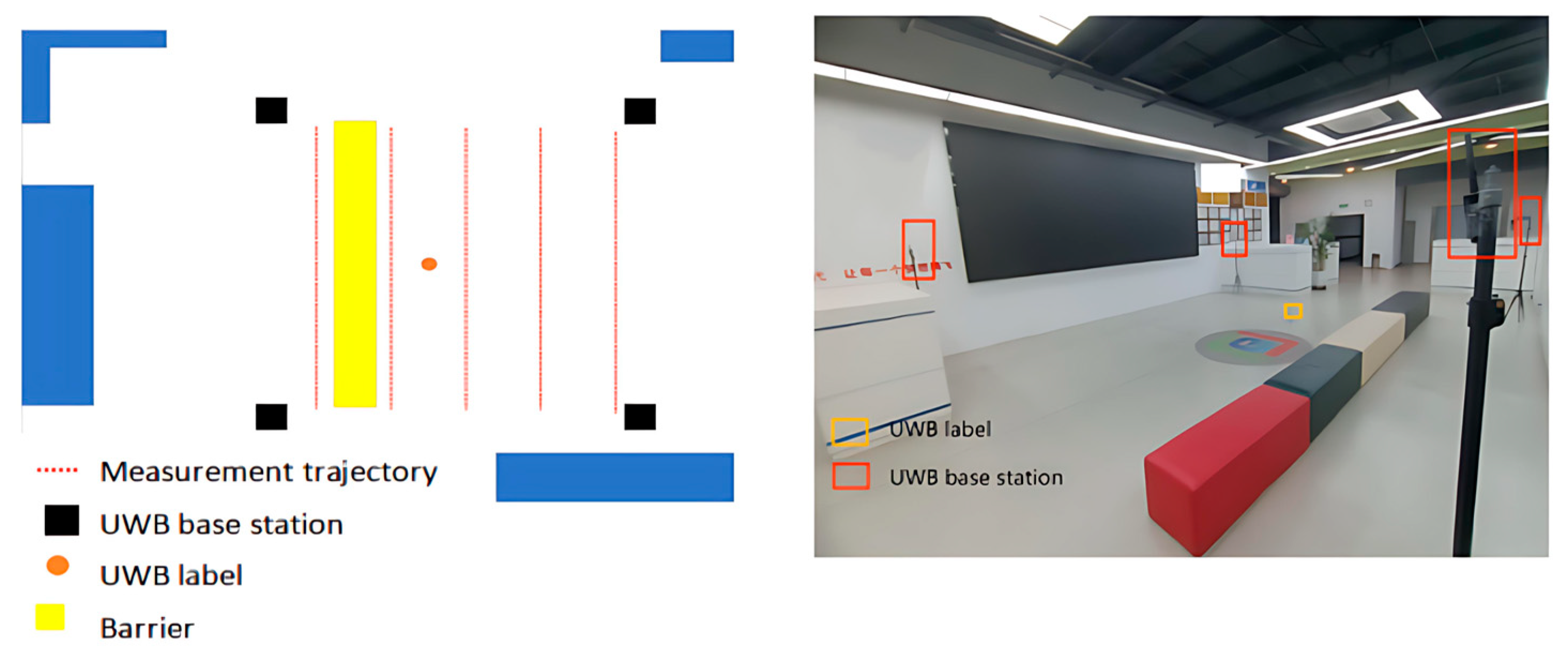
3.1.1. Scene Configuration
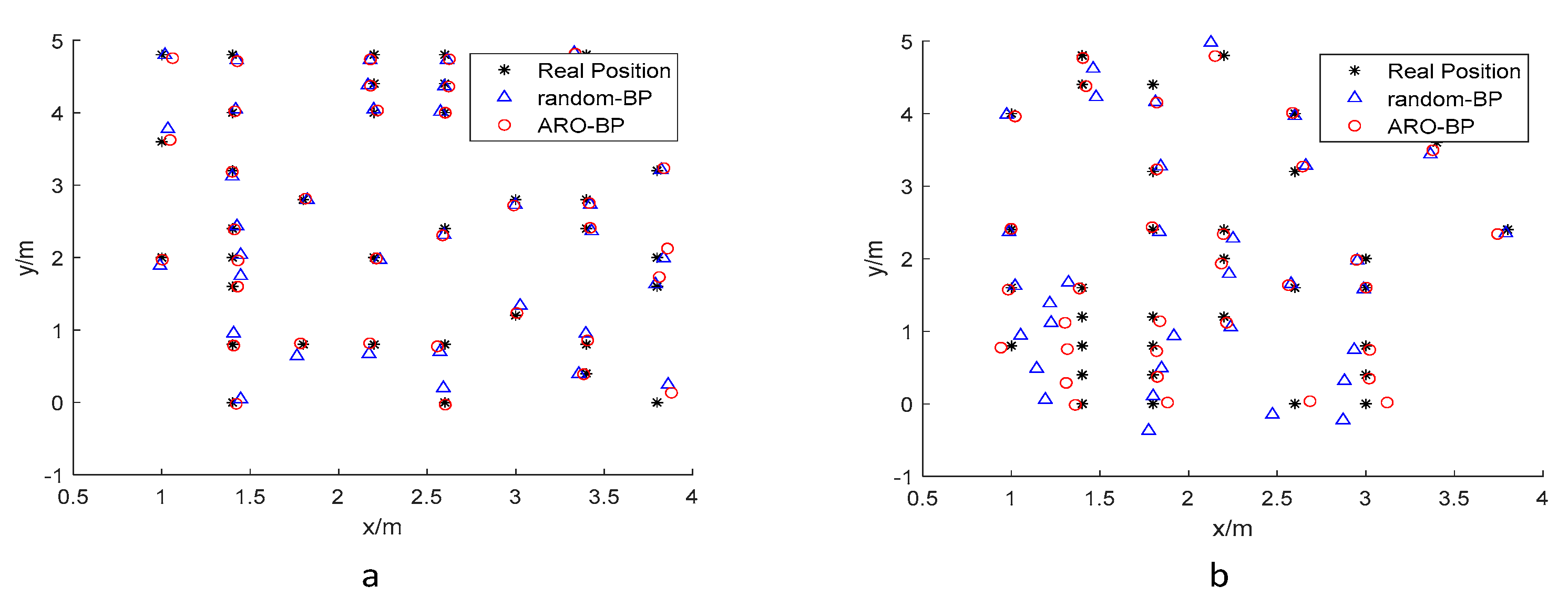
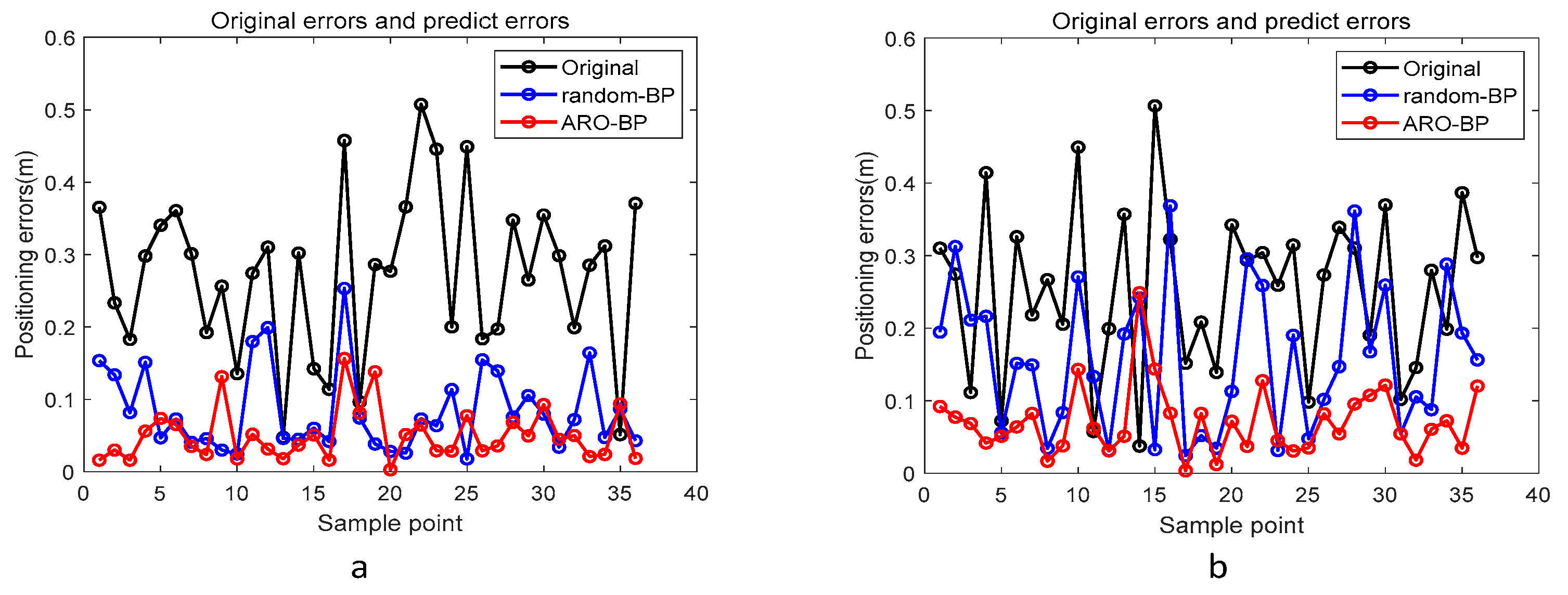
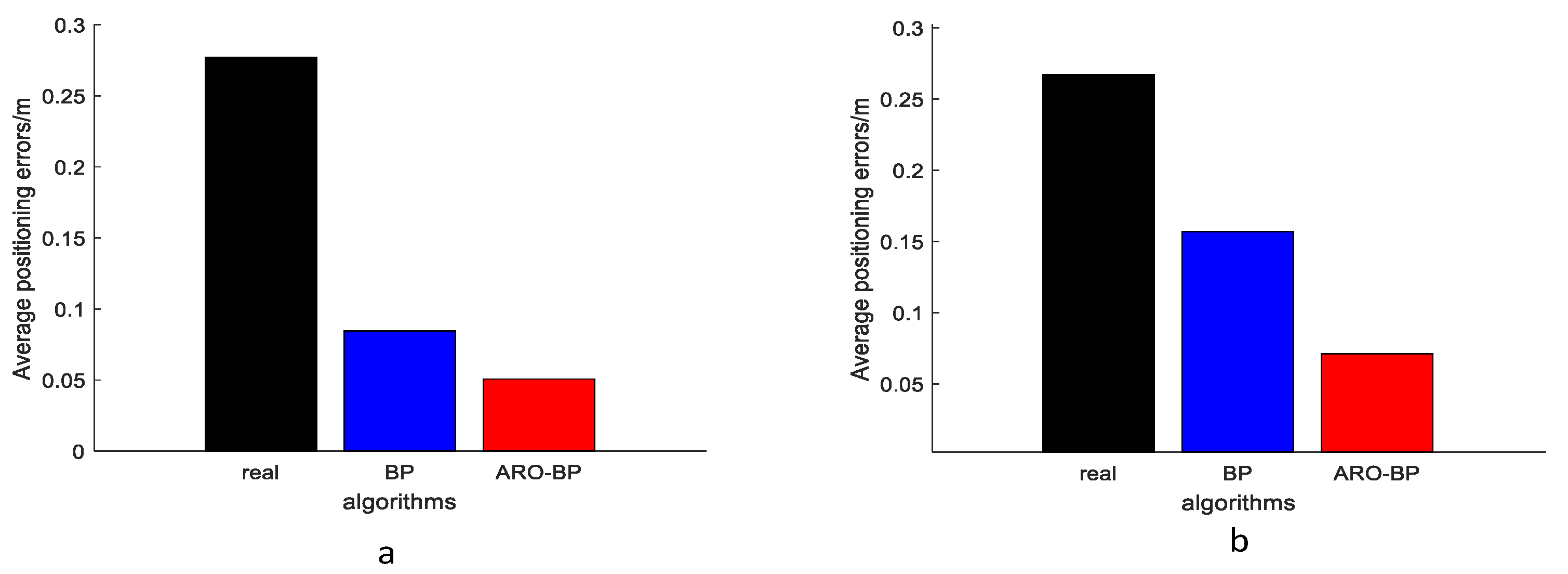
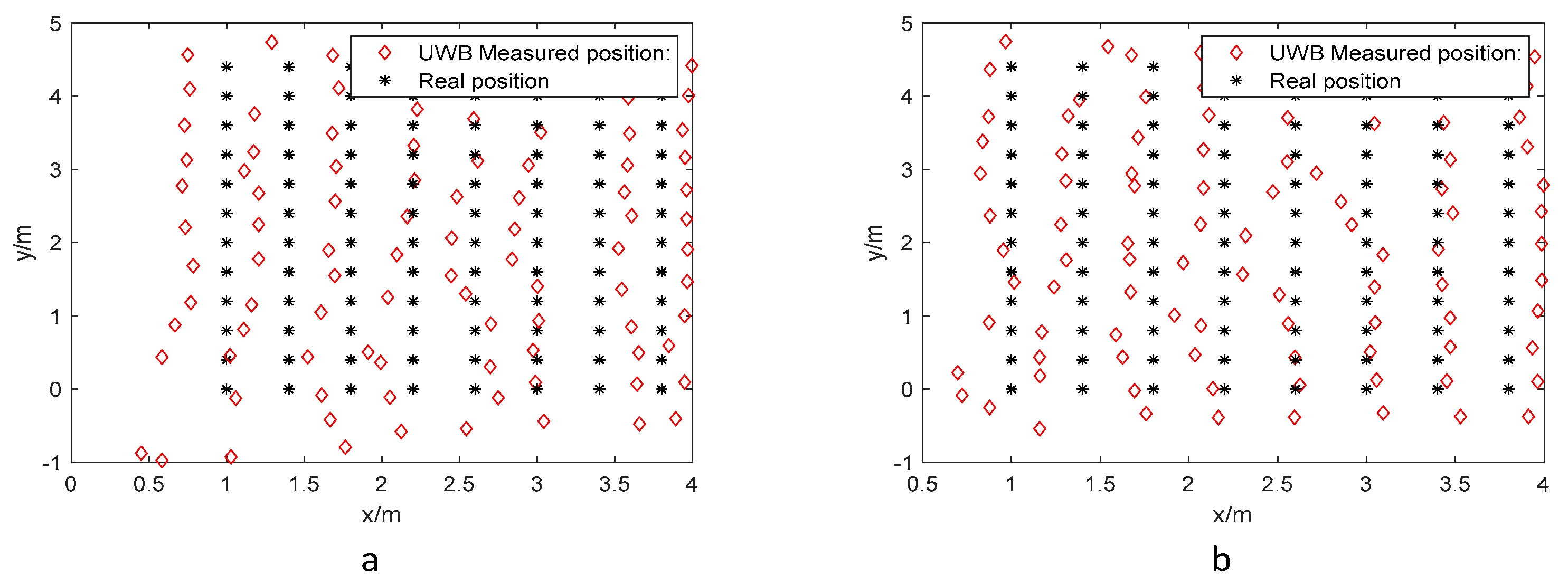
3.1.2. Analysis of Results
3.2. NLOS Environment Experiment
3.2.1. Scene Configuration
3.2.2. Analysis of Results
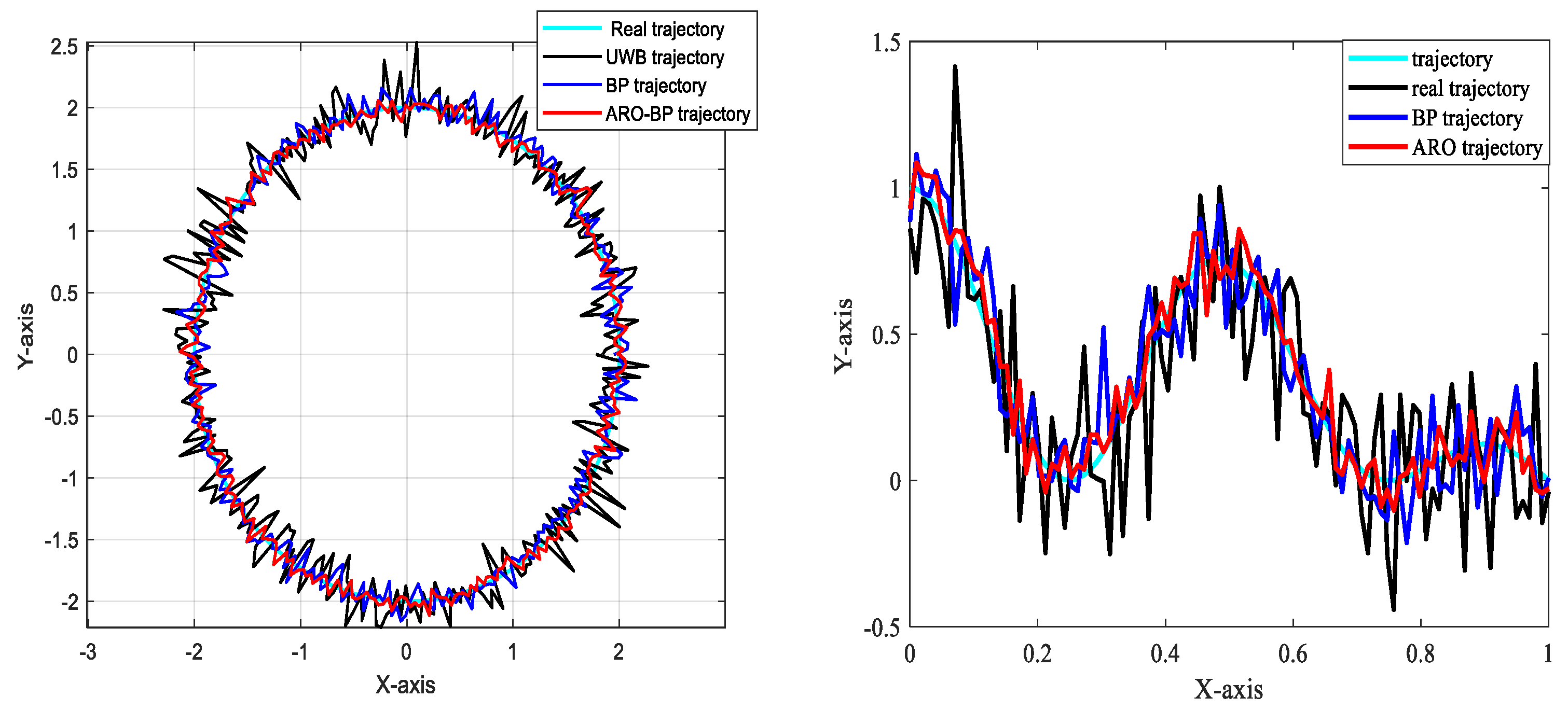
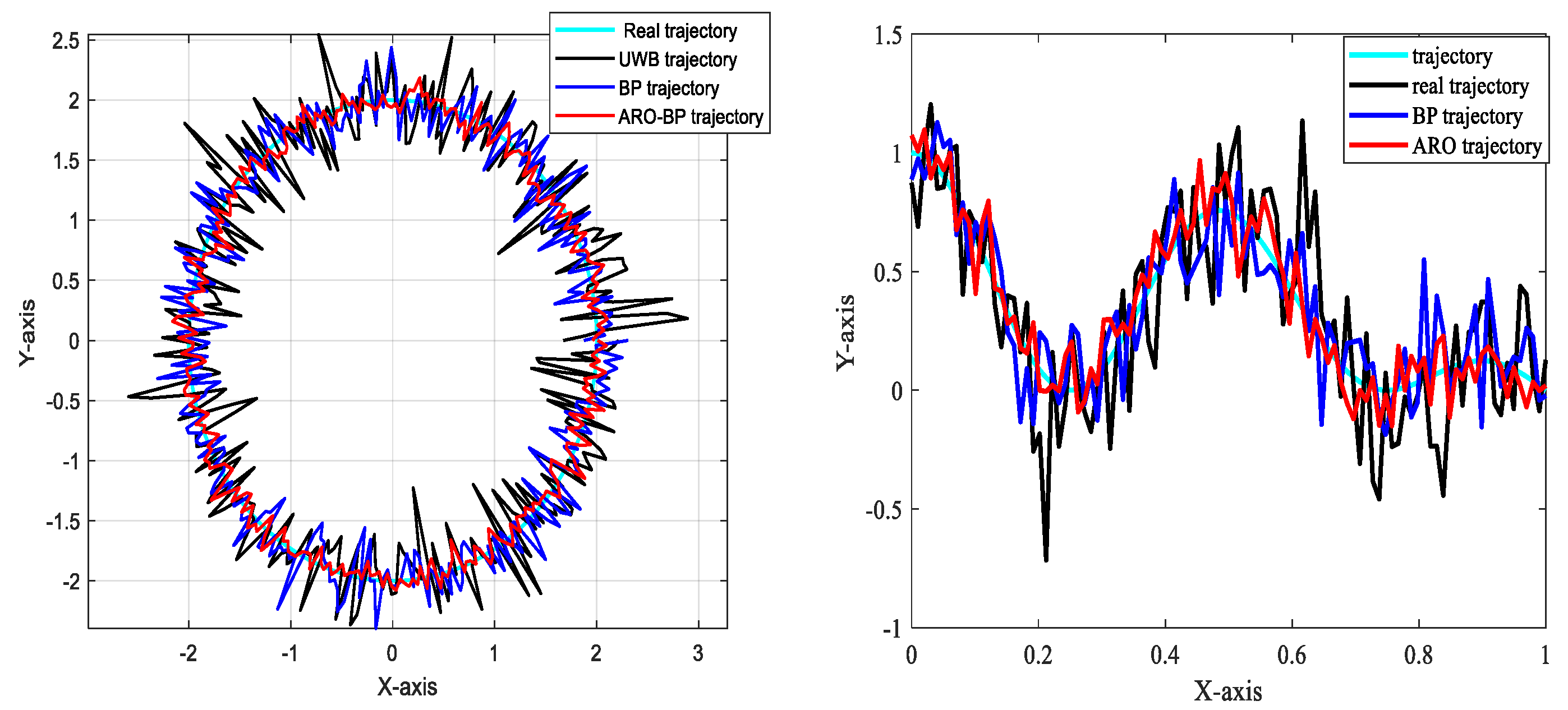
3.3. Actual Motion Scene Experiment
3.3.1. Scene Configuration
3.3.2. Analysis of Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ARO | Artificial Rabbit Optimization |
| BP | Backpropagation Neural Network |
| LOS | Line-of-Sight |
| NLOS | Non-Line-of-Sight |
| UWB | Ultra-Wideband |
References
- Ashraf, I.; Hur, S.; Park, Y. Recent Advancements in Indoor Positioning and Localization. Electronics 2022, 11, 2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, C.; Dou, H.; Liu, B. Robust Depth-Aided RGBD-Inertial Odometry for Indoor Localization. Measurement 2023, 209, 112487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, G.; Abed-Meraim, K.; Ouyang, Z. Magnetic-Field-Based Indoor Positioning Using Temporal Convolutional Networks. Sensors 2023, 23, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perković, T.; Dujić Rodić, L.; Šabić, J.; Solic, P. Machine Learning Approach towards LoRaWAN Indoor Localization. Electronics 2023, 12, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Niu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Hou, C. Improved CNN-Based Indoor Localization by Using RGB Images and DBSCAN Algorithm. Sensors 2022, 22, 9531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesyuk, A.; Ioannou, S.; Raspopoulos, M. A Survey of 3D Indoor Localization Systems and Technologies. Sensors 2022, 22, 9380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, U.; Yesilirmak, Y.E.; Bayman, I.O.; Arsan, T.; Panayirci, E.; Stevens, N. 3D indoor positioning with spatial modulation for visible light communications. Opt. Commun. 2023, 529, 129091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Nguyen, K.A.; Luo, Z. WiFi Access Points Line-of-Sight Detection for Indoor Positioning Using the Signal Round Trip Time. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Kim, S. Practical and Accurate Indoor Localization System Using Deep Learning. Sensors 2022, 22, 6764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, B.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, J.W. Survey of Landmark-based Indoor Positioning Technologies. Inf. Fusion 2023, 89, 166–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidey, H.T.; Guo, X.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y. Heterogeneous Transfer Learning for Wi-Fi Indoor Positioning Based Hybrid Feature Selection. Sensors 2022, 22, 5840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Yao, S.; Wu, X.; Chen, L. Research on a Wi-Fi RSSI Calibration Algorithm Based on WOA-BPNN for Indoor Positioning. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyeon, J.J.; Kim, S. Indoor Smartphone Localization Based on LOS and NLOS Identification. Sensors 2018, 18, 3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Wang, Y.; Bi, J.; Xu, S.; Si, M.; Qi, H. Indoor Positioning Method Using WiFi RTT Based on LOS Identification and Range Calibration. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Bi, D.; Peng, L.; Xie, Y. Kernel-based online prediction algorithms for indoor localization in Internet of Things. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 217, 119547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Cheng, Z.; Jia, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Zhao, Q. A Novel Deep Learning Approach to 5G CSI/Geomagnetism/VIO Fused Indoor Localization. Sensors 2023, 23, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suns, Q.; He, L.; Meng, F.; Tong, H.; Xiao, N.; Zheng, Y. Wireless communication indoor positioning method in 5G sub-station using deep neural network and location fingerprint algorithm. Optik 2022, 271, 170159. [Google Scholar]
- Si, M.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Sun, M.; Cao, H. A Wi-Fi FTM-Based Indoor Positioning Method with LOS/NLOS Identification. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abudalfa, S.; Bouchard, K. Two-stage RFID approach for localizing objects in smart homes based on gradient boosted decision trees with under- and over-sampling. J. Reliab. Intell. Environ. 2023, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Cara, M.; Talla-Chumpitaz, R.; Orozco-Barbosa, L.; García-Castro, R. A novel deep learning approach using blurring image techniques for Bluetooth-based indoor localisation. Inf. Fusion 2023, 91, 173–186. [Google Scholar]
- Zhen, J.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. An improved method for indoor positioning based on ZigBee technique. Int. J. Embed. Syst. 2020, 13, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, K.; Huang, H.; El-Rabbany, A. Geomagnetic Field-Based Indoor Positioning Using Back-Propagation Neural Networks. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, 13, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Niu, S.; Chen, S.; Su, B.; Cheng, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y. A smart city used low-latency seamless positioning system based on inverse global navigation satellite system technology. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2019, 15, 155014771987381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morar, A.; Modoveanu, A.; Mocanu, I.G.; Moldoveanu, F.; Radoi, I.E.; Asavei, V.; Gradinaru, A.; Butean, A. A Comprehensive Survey of Indoor Localization Methods Based on Computer Vision. Sensors 2020, 20, 2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Abdalmajeed, M.; Mahmoud, M.; Abd El-Rahman, A.; El-Fikky, A.; Heba, A.; Fayed, A.; Moustafa, H.A. Improved indoor visible light positioning system using machine learning. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2023, 55, 209. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Navarro, A.; Montoliu, R.; Torres-Sospedra, J. Advances in Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation. Sensors 2022, 22, 7375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Tong, Z.; Kang, Z. A novel indoor positioning algorithm based on UWB. Int. J. Sens. Netw. 2022, 40, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Li, Z.; Song, Y. UWB Positioning Analysis and Algorithm Research. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 198, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yan, M. Implementation of UWB indoor location and distance measurement based on TOF algorithm. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 173, 03018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Yang, S.-H.; Li, H. Design and Implementation of Real-Time Localization System (RTLS) Based on UWB and TDoA Algorithm. Sensors 2022, 22, 4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margiani, T.; Silvano Cortesi, M.R.K.; Vogt, C.; Polonelli, T.; Magno, M. Angle of Arrival and Centimeter Distance Estimation on a Smart UWB Sensor Node. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibnatta, Y.; Khaldoun, M.; Sadik, M. The Indoor Localization System Based on Federated Learning and RSS Using UWB-OFDM. In International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Systems for Sustainable Development; Lecture notes in networks and systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; Volume 14, pp. 152–167. [Google Scholar]
- Sandra, M.D.I.; Stojanovic, Z.; Jovanovic, M.; Goran, T. Djordjevic. Multi-algorithm UWB-based localization method for mixed LOS/NLOS environments. Comput. Commun. 2022, 181, 365–373. [Google Scholar]
- Retscher, G.; Kiss, D.; Gabela, J. Fusion of GNSS Pseudoranges with UWB Ranges Based on Clustering and Weighted Least Squares. Sensors 2023, 23, 3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Hao, Z.; Dang, X. An indoor location algorithm based on Kalman filter fusion of ultra-wide band and inertial measurement unit. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 085210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Li, J.; Zhang, H. Resilient Indoor Localization System Based on UWB and Visual–Inertial Sensors for Complex Environments. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Hu, D.Y.; Hu, P. Research on UWB fusion location algorithm. J. Phys. 2022, 2303, 012017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, W.Y.; Chen, Y. A Group Learning based Optimization Algorithm Applied to UWB Positioning. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2294, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.H.; Wang, Q.; Yan, C.; Xu, J.; Zhang, B. Research on UWB Indoor Positioning Algorithm under the Influence of Human Occlusion and Spatial NLOS. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gao, T.; Wang, X.; Guo, W.; Bai, D. Study on the UWB location algorithm in the NLOS environment. J. Phys. 2022, 2400, 012043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Liu, M.; Sun, Y. Cell Recognition Using BP Neural Network Edge Computing. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2022, 2022, 7355233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jiang, S. Study on the application of BP neural network optimized based on various optimization algorithms in storm surge prediction. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part M J. Eng. Marit. Environ. 2022, 236, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Wang, Y. Short-term Power Load Forecasting Based on Improved BP Neural Network from Genetic Algorithm and Simulated Annealing Algorithm. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2401, 012087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Y. Research on Indoor Positioning Algorithm Based on SAGA-BP Neural Network. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 3736–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, M.; Abdushkour, A.H.; Maghrabi, L.; Alsalman, D.; Ayman, G.F.; AL-Ghamdi, A.A.-M. Improved Artificial Rabbits Optimization with Ensemble Learning-Based Traffic Flow Monitoring on Intelligent Transportation System. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cao, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Mirjalili, S.; Zhao, W. Artificial rabbits optimization: A new bio-inspired meta-heuristic algorithm for solving engineering optimization problems. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 114, 105082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennet, G.; Deepa, S.N. Solar PV system with modified artificial rabbit optimizati on algorithm for MPPT. Electr. Eng. 2024, 106, 4543–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wu, R.; Huang, H.; Wei, J.; Han, Z.; Wen, L.; Yuan, Y. Multi-strategy improved artificial rabbit optimization algorithm based on fusion centroid and elite guidance mechanisms. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2024, 425, 116915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Algorithm | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| BP Neural Network | Simple implementation; Fast training. | Prone to local optima; Low robustness in NLOS. |
| ARO-BP | Global optimization; High NLOS accuracy. | Higher computational cost; Complex parameter tuning. |
| Environment | Height (m) | BP Error (cm) | ARO-BP Error (cm) | Improvement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOS | 1.8 | 9.98 | 5.11 | 48.80% |
| LOS | 1 | 14.91 | 7.48 | 49.80% |
| NLOS | 0.45 | 20.81 | 12.78 | 38.60% |
| NLOS | 0.15 | 16.38 | 9.01 | 45.00% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, C.; Tao, C.; Yang, T.; Fu, M.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Z. UWB Indoor Localization Based on Artificial Rabbit Optimization Algorithm and BP Neural Network. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10060367
Jia C, Tao C, Yang T, Fu M, Zhou X, Huang Z. UWB Indoor Localization Based on Artificial Rabbit Optimization Algorithm and BP Neural Network. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(6):367. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10060367
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Chaochuan, Can Tao, Ting Yang, Maosheng Fu, Xiancun Zhou, and Zhendong Huang. 2025. "UWB Indoor Localization Based on Artificial Rabbit Optimization Algorithm and BP Neural Network" Biomimetics 10, no. 6: 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10060367
APA StyleJia, C., Tao, C., Yang, T., Fu, M., Zhou, X., & Huang, Z. (2025). UWB Indoor Localization Based on Artificial Rabbit Optimization Algorithm and BP Neural Network. Biomimetics, 10(6), 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10060367






