Development of an Oblique Cone Dielectric Elastomer Actuator Module-Connected Vertebrate Fish Robot
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Structure of White Muscle in Fish and Oblique Cone DEA Module
2.1. Structure of White Muscle in Fish
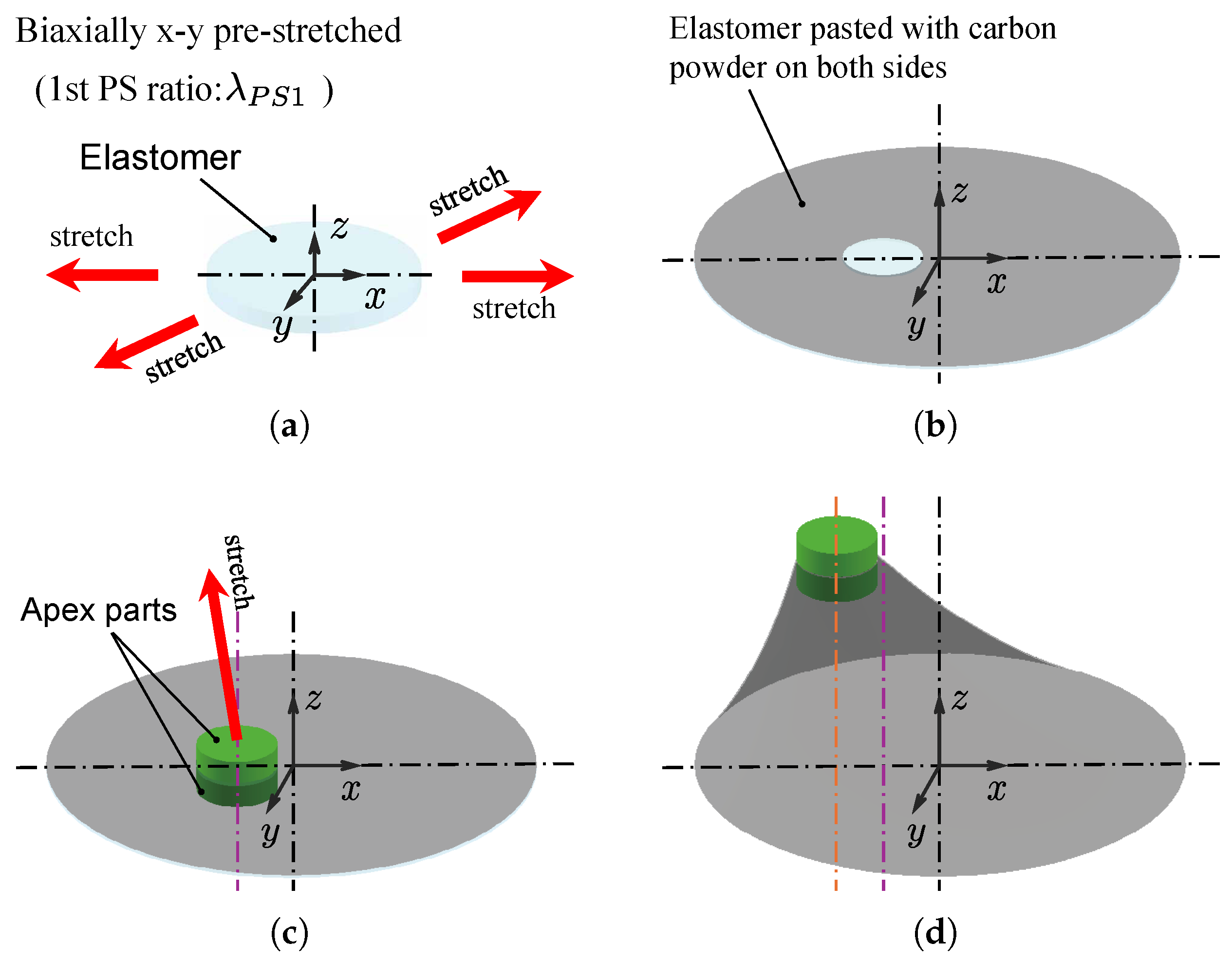
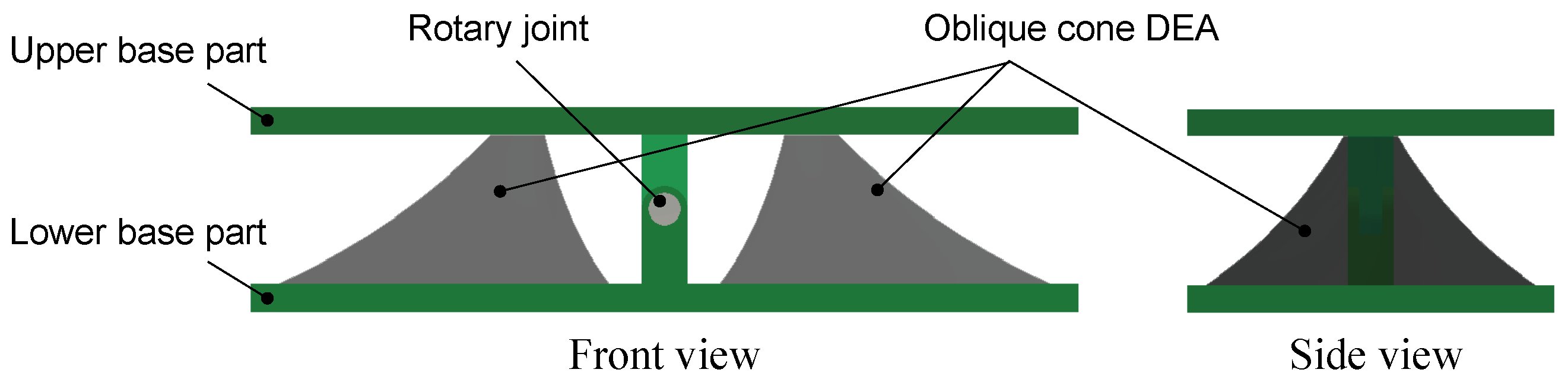
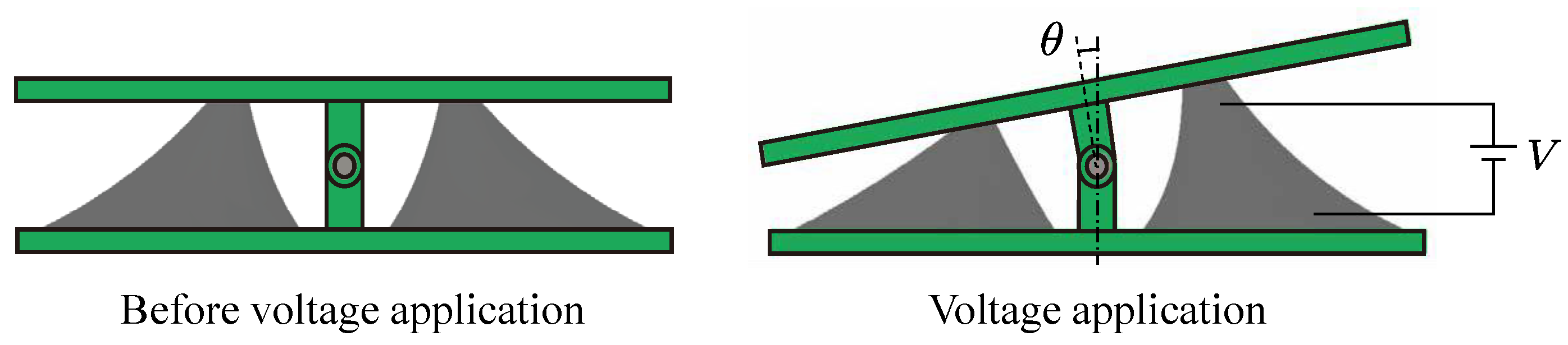
2.2. Oblique Cone DEA and Module
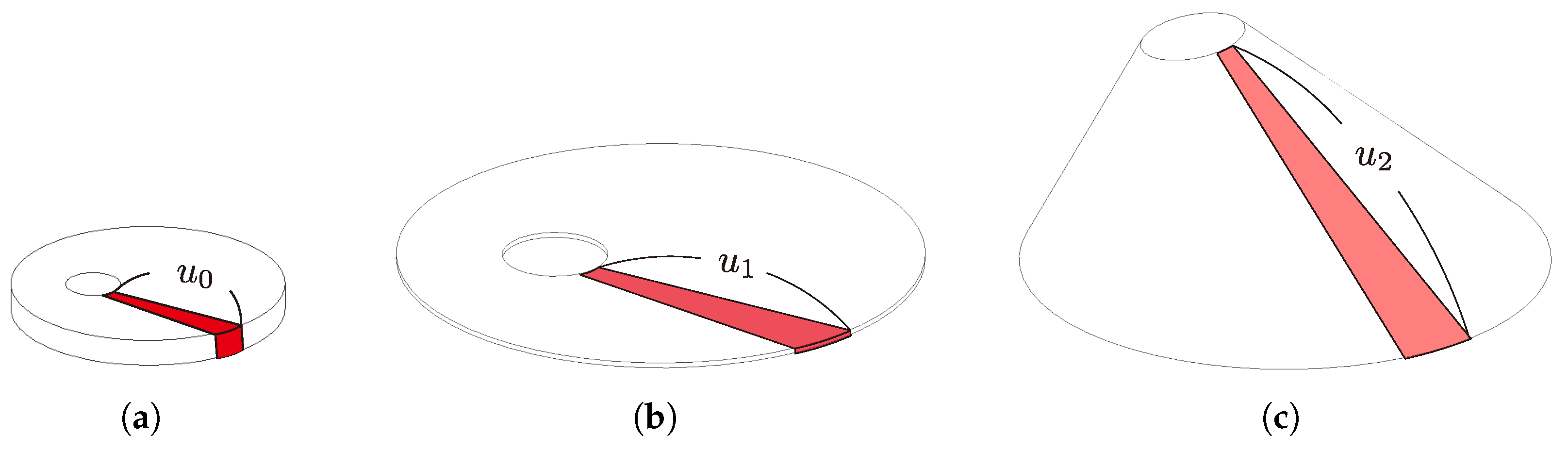
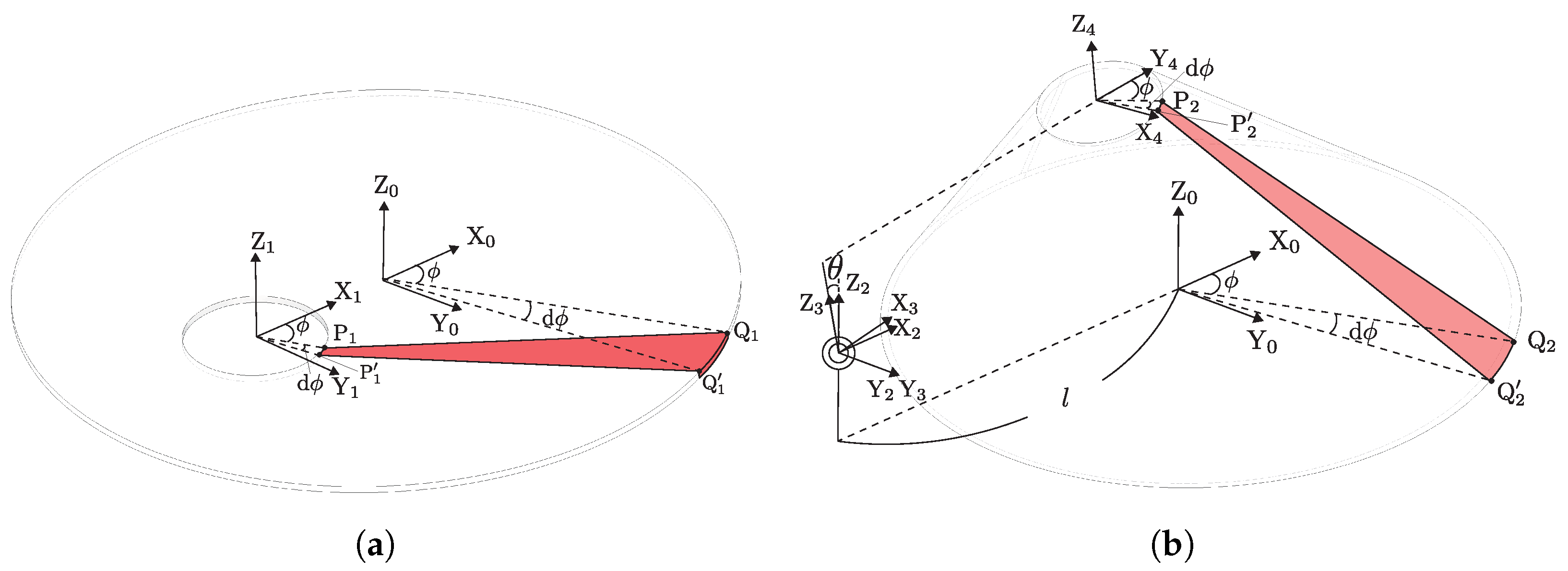
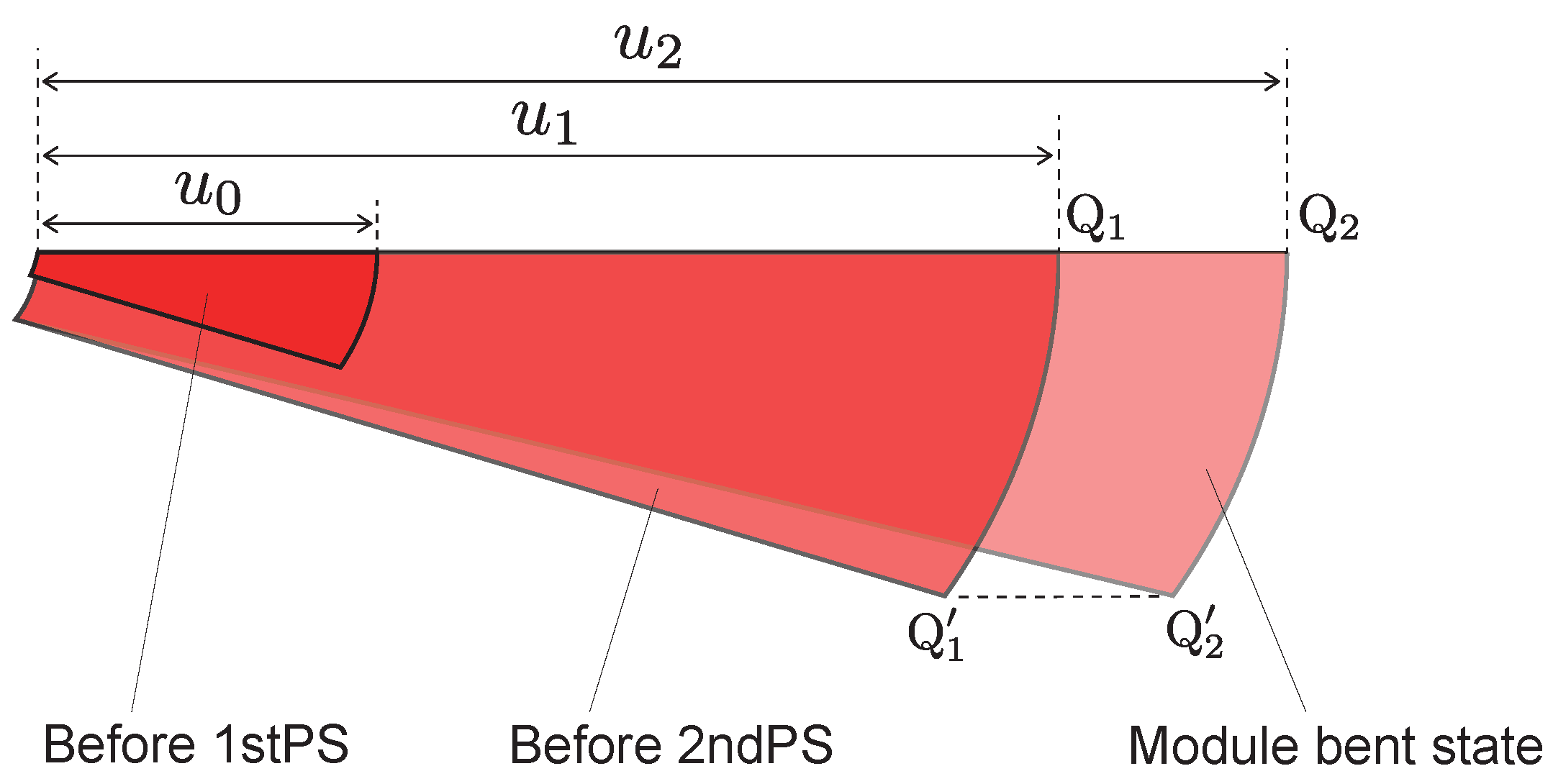
3. Modeling of Oblique Cone DEA Modules for Design
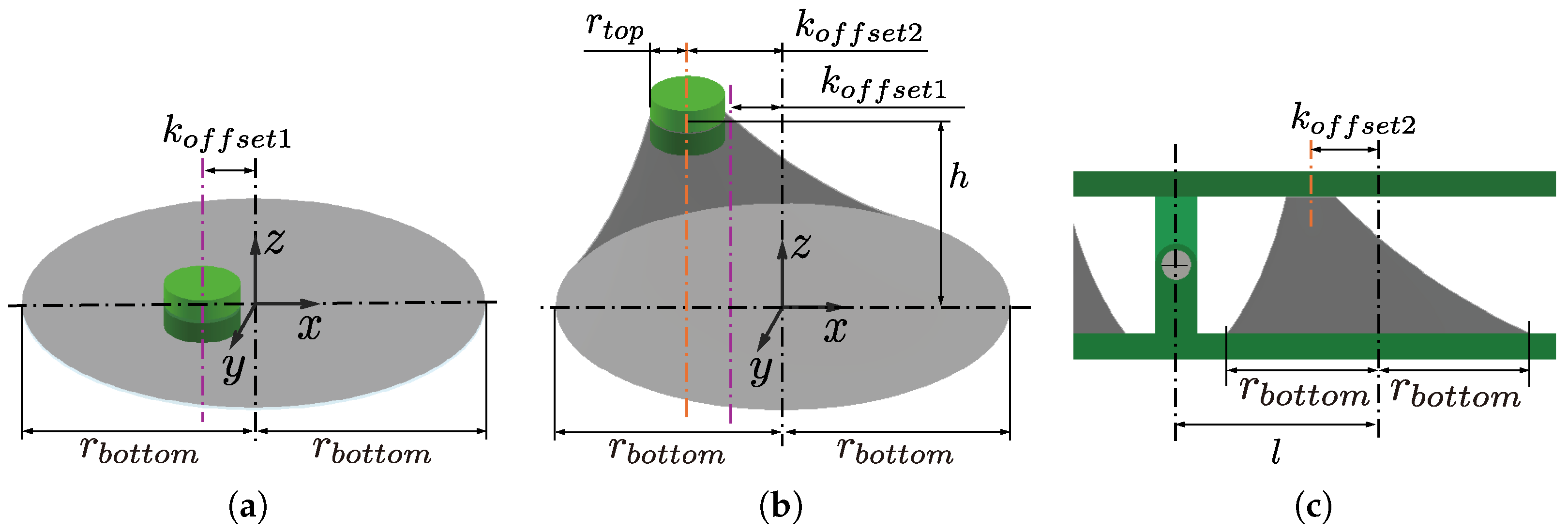
3.1. Model and Design Parameters
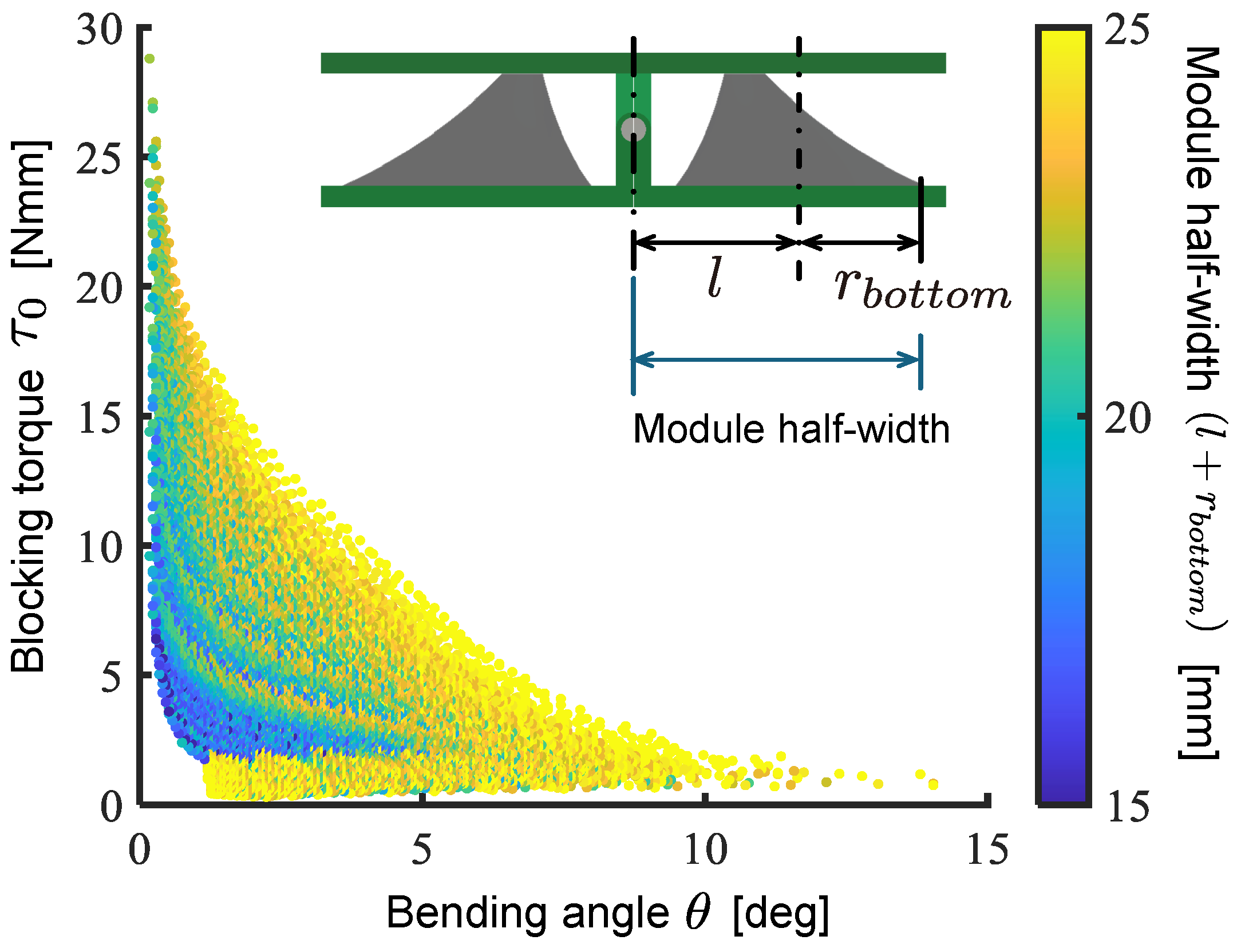
3.2. Calculation of Output Bending Angle and Blocking Torque
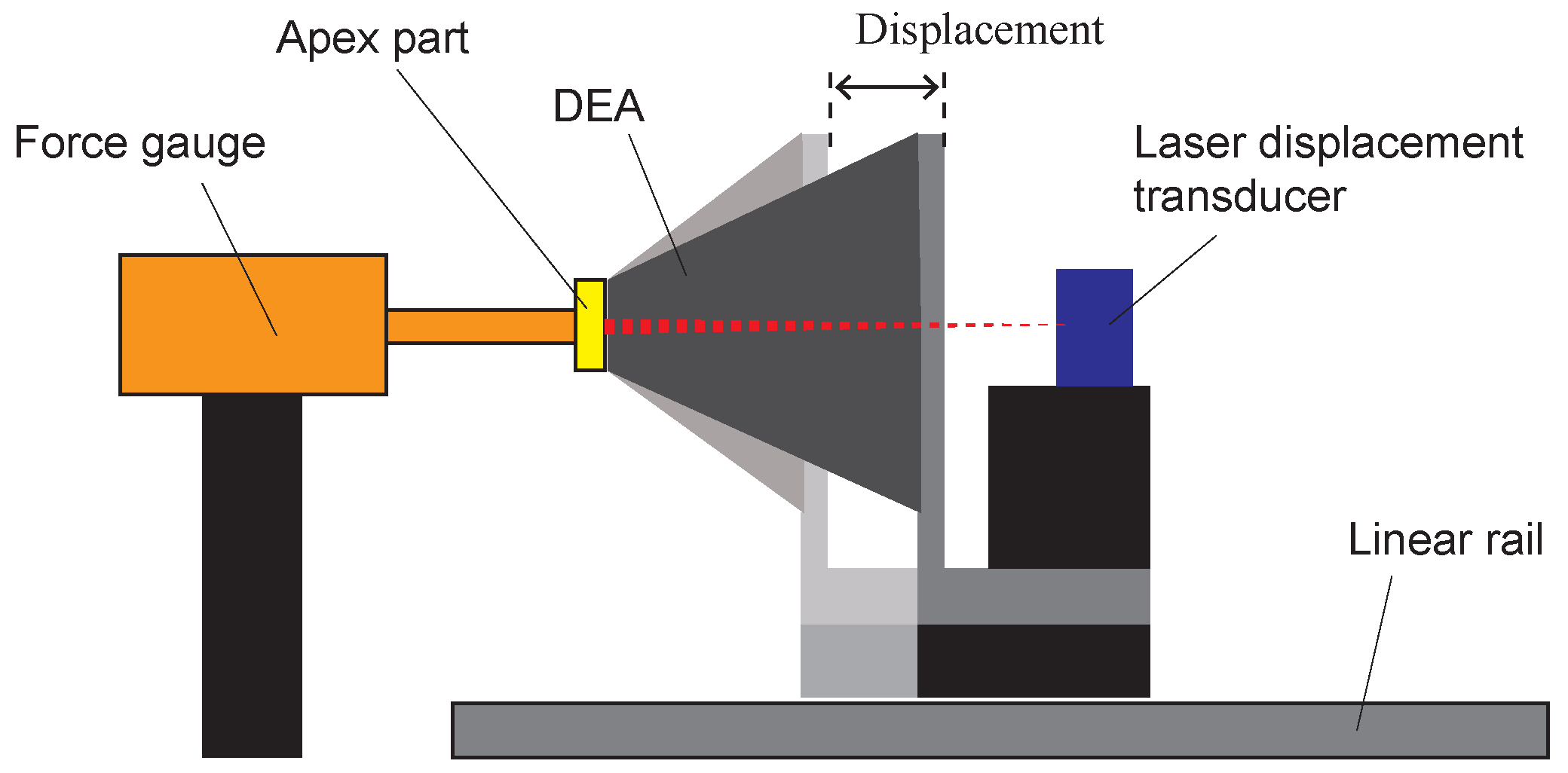
3.3. Identification of Material Parameters
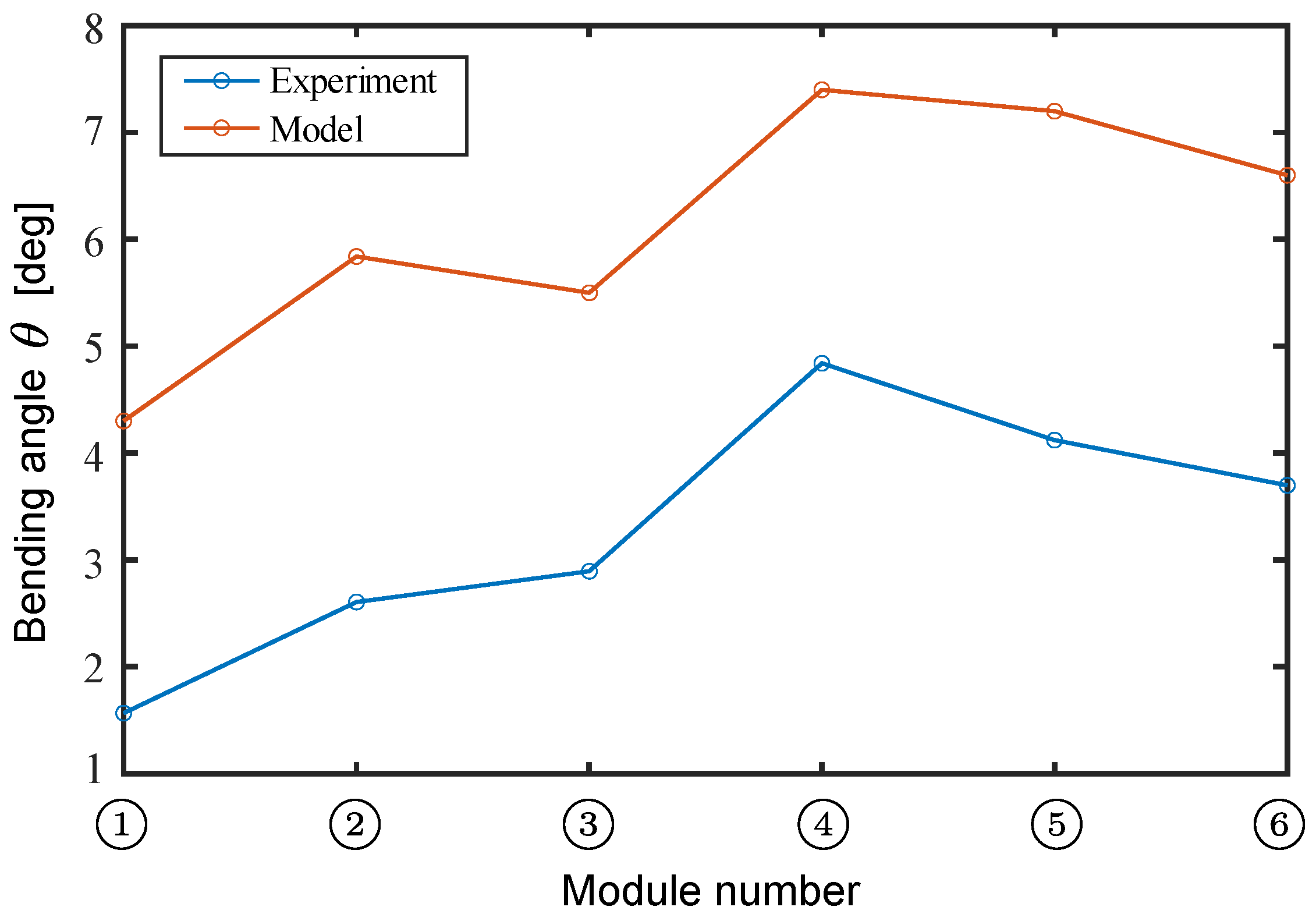
3.4. Output Comparison Between Calculated Results and Experimental Results
4. Design of a Fish Robot Using Multiple Oblique Cone DEA Modules
4.1. Basic Policy for Design
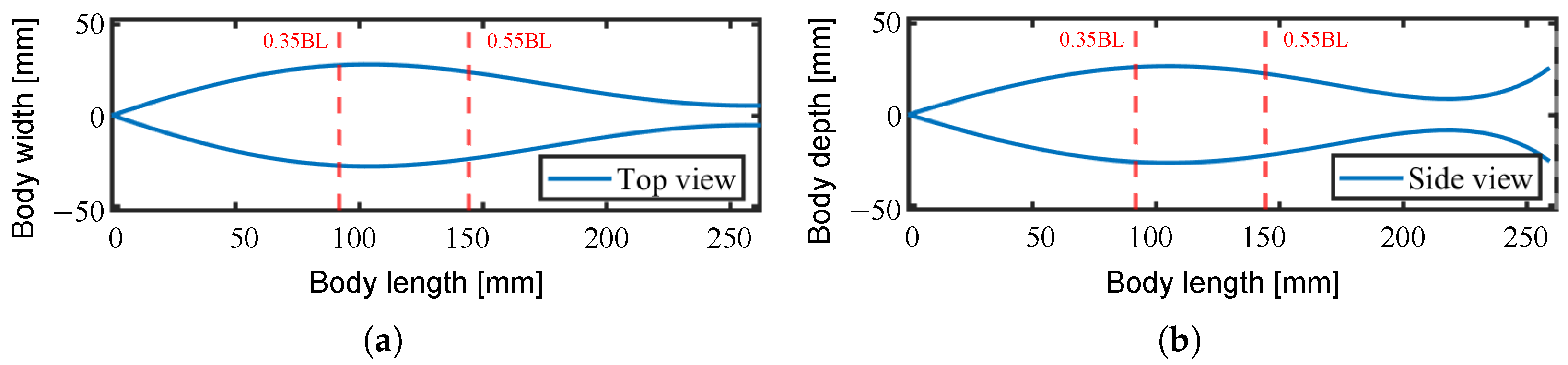
4.2. Details of Design
5. Fabrication and Experimental Results
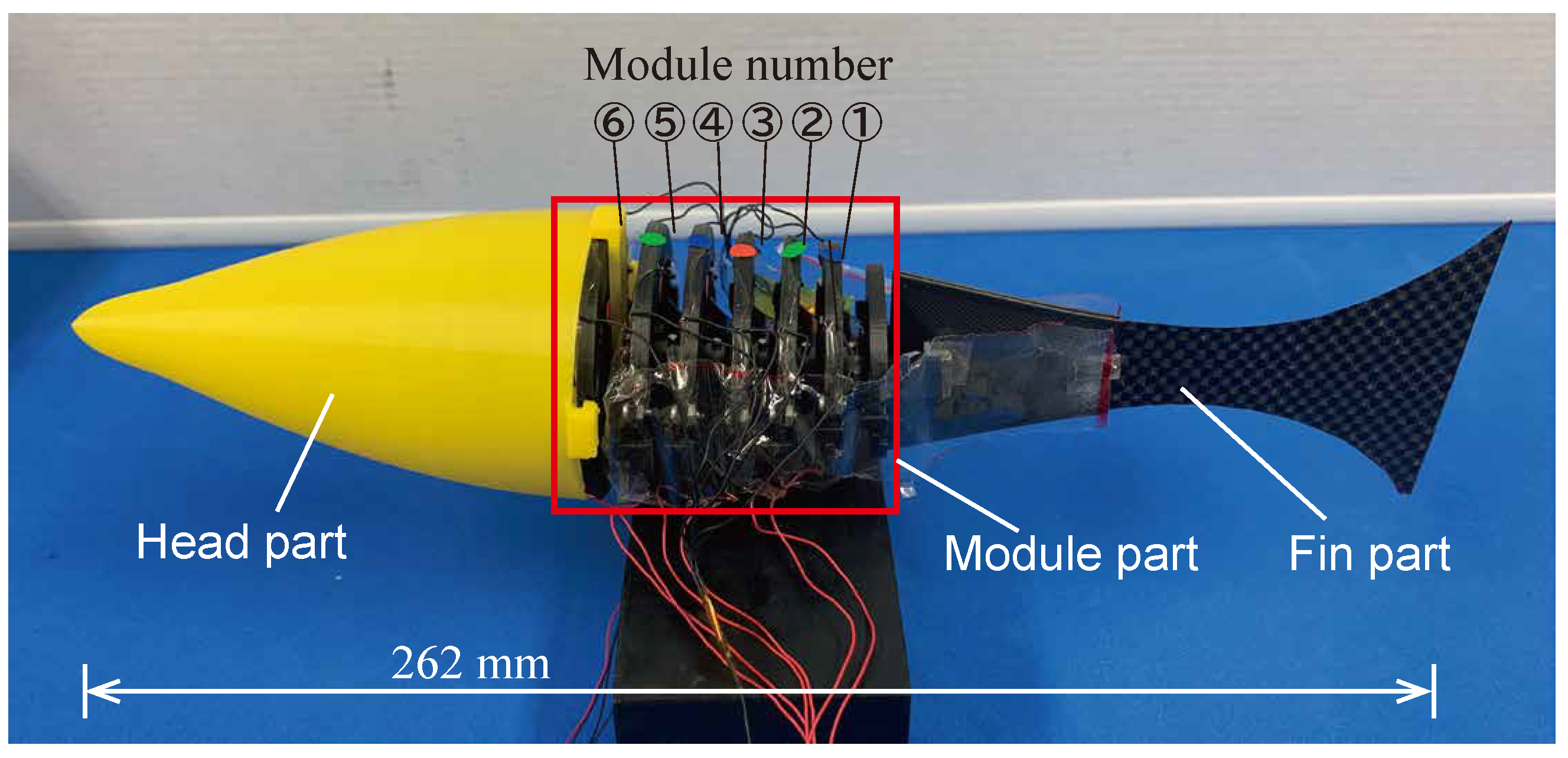
5.1. Fabrication
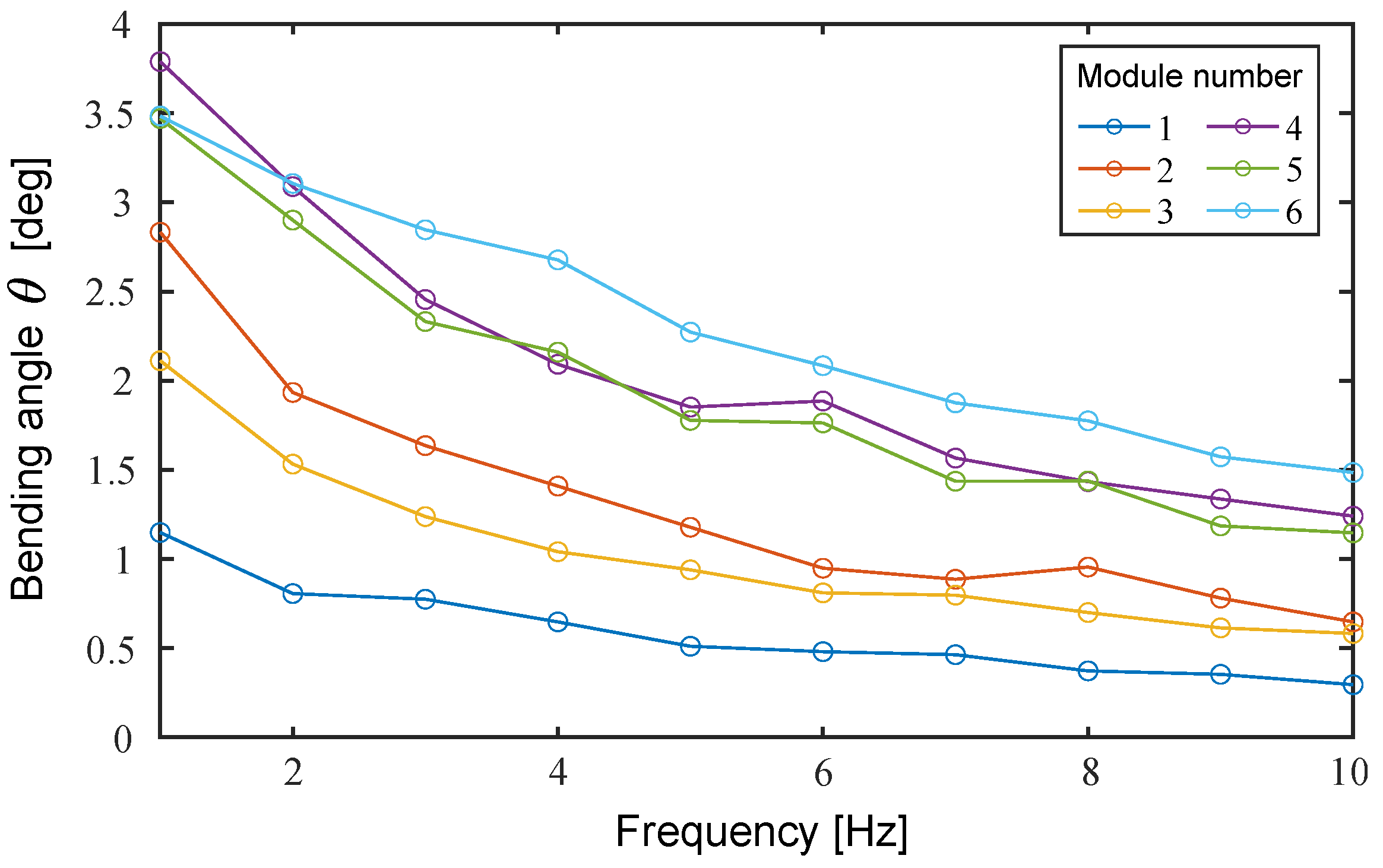
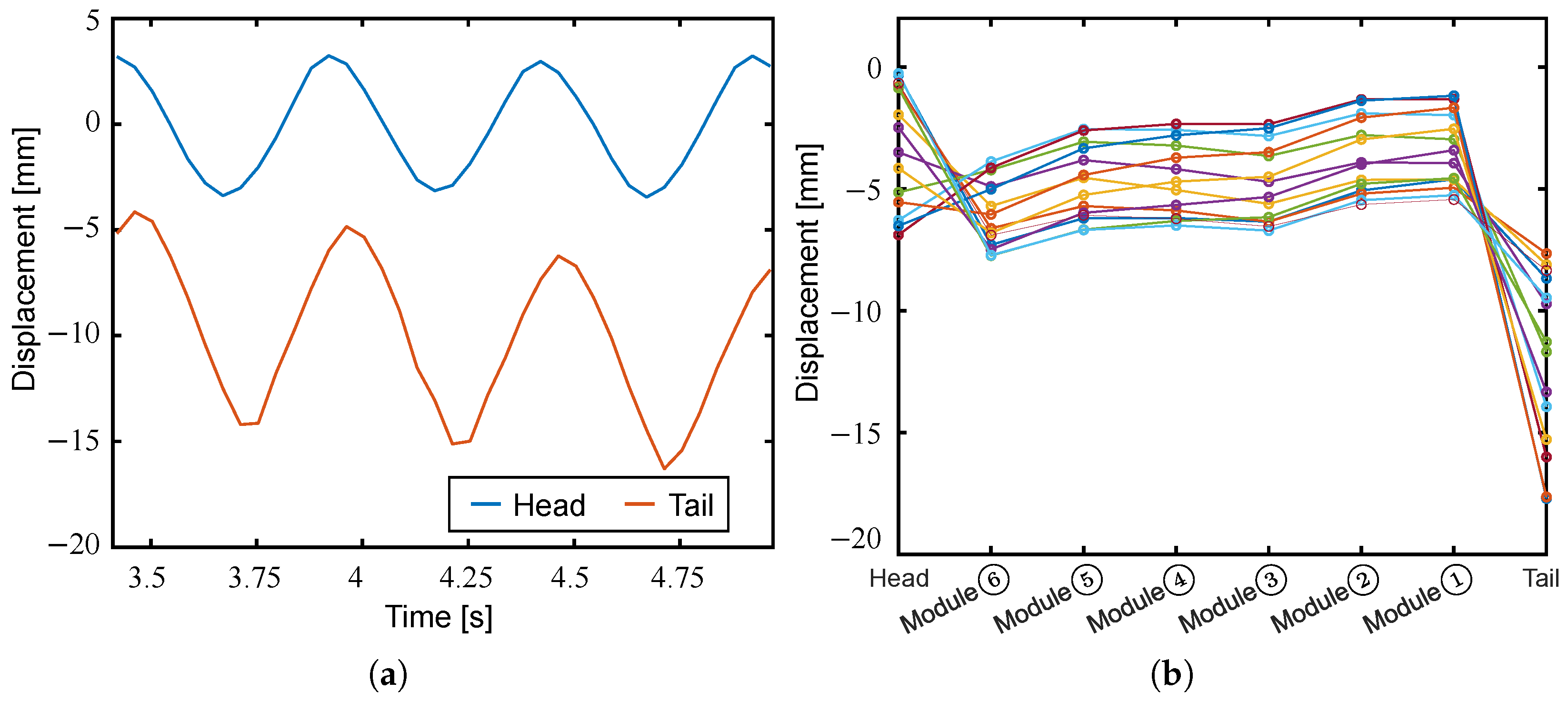
5.2. Experiments in Air
5.3. Experiments in Insulating Fluid
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morgansen, K.A.; Triplett, B.I.; Klein, D.J. Geometric Methods for Modeling and Control of Free-Swimming Fin-Actuated Underwater Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2007, 23, 1184–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, K.H.; Chong, C.W. Parametric study of the swimming performance of a fish robot propelled by a flexible caudal fin. Bioinspiration Biomimetics 2010, 5, 046002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.H.; Choi, W.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, H.S.; Ryuh, Y.S. Control and design of a 3 DOF fish robot ‘ICHTUS’. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, Karon Beach, Thailand, 7–11 December 2011; pp. 2108–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, P.S.; Pinto, M.F.; Pereira, G.D.; Batista, J.L.; De O. Carneiro, M.M.; Dias, J.T.; Almeida, L.F. Low-Cost Fish-Based Soft Robot Development for Underwater Environment. In Proceedings of the 2023 15th IEEE International Conference on Industry Applications (INDUSCON), São Bernardo do Campo, Brazil, 22–24 November 2023; pp. 1672–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koiri, M.K.; Dubey, V.; Sharma, A.K.; Chuchala, D. Design of a Shape-Memory-Alloy-Based Carangiform Robotic Fishtail with Improved Forward Thrust. Sensors 2024, 24, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, I.; Musgrave, P. A Continuum Soft Robotic Trout with Embedded HASEL Actuators: Design, Fabrication, and Swimming Kinematics. Smart Mater. Struct. 2024, 33, 105043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Xu, C. Pitch Motion Control of a Soft Bionic Robot Fish Based on Centroid Adjustment. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), Tianjin, China, 4–7 August 2019; pp. 1883–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, A.; Hashimoto, K.; Zhao, W.; Shimojo, M. Fundamental analysis for design and control of soft fish robots using piezoelectric fiber composite. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, Takamatsu, Japan, 4–7 August 2013; pp. 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaszadeh, S.; Leidhold, R.; Hoerner, S. A Design Concept and Kinematic Model for a Soft Aquatic Robot with Complex Bio-mimicking Motion. J. Bionic Eng. 2022, 19, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, T.; Shintake, J. Rolled Dielectric Elastomer Antagonistic Actuators for Biomimetic Underwater Robots. Polymers 2022, 14, 4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, C.; Tan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, W.; Wang, F.; Tian, J.; Liu, L. Soft Robotic Fish Actuated by Bionic Muscle with Embedded Sensing for Self-Adaptive Multiple Modes Swimming. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2025, 41, 1329–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Hitomi, T.; Nishimura, T.; Sato, R.; Ming, A. Development of DEA Underwater Robot Mimicking Fish White Muscle Structure. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Bangkok, Thailand, 10–14 December 2024; pp. 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeuwen, J.L.V. A mechanical analysis of myomere shape in fish. J. Exp. Biol. 1999, 202, 3405–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Pei, X.; Wang, X.; Hou, T. Bionic Robot Manta Ray Based on Dielectric Elastomer Actuator. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Frontiers of Robotics and Software Engineering (FRSE), Changsha, China, 16–18 June 2023; pp. 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godaba, H.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J. A Soft Jellyfish Robot Driven by a Dielectric Elastomer Actuator. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2016, 1, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berselli, G.; Vertechy, R.; Vassura, G.; Parenti-Castelli, V. Optimal Synthesis of Conically Shaped Dielectric Elastomer Linear Actuators: Design Methodology and Experimental Validation. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2011, 16, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Chen, L.; Duan, W.; Hill, T.L.; Li, B.; Chen, G.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Gao, X. On the Mechanical Power Output Comparisons of Cone Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2021, 26, 3151–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altringham, J.D.; Ellerby, D.J. Fish swimming: Patterns in muscle function. J. Exp. Biol. 1999, 202, 3397–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdivia y Alvarado, P. Design of Biomimetic Compliant Devices for Locomotion in Liquid Environments. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]






| [MPa] | [MPa] | [MPa] |
|---|---|---|
| () | l | h | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ([mm], [mm]) | [mm] | [mm] | [mm] | [mm] | [mm] | [-] |
| 3 | 18 | 24 | 16 | 1 | 3 | |
| Parameter | Range | Increment | |
|---|---|---|---|
| [mm] | 0.5 | ||
| [mm] | 1 | ||
| h | [mm] | 1 | |
| [mm] | 1 | ||
| l | [mm] | 1 | |
| [-] | 0.5 | ||
| ← Head | Tail → | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location | 0.38 BL | 0.41 BL | 0.45 BL | 0.48 BL | 0.52 BL | 0.55 BL | ||
| Module Number | ➅ | ➄ | ➃ | ➂ | ➁ | ➀ | ||
| Parameters | ||||||||
| [mm] | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | ||
| [mm] | 9 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 8 | 7 | ||
| h | [mm] | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | |
| [mm] | 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 2 | ||
| l | [mm] | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 13 | 12 | |
| [-] | 4 | 4 | 3.5 | 3 | 3 | 2.5 | ||
| Performance | ||||||||
| [Nmm] | 9.0 | 8.2 | 6.3 | 5.5 | 5.3 | 4.3 | ||
| [deg] | 6.6 | 7.2 | 7.4 | 5.5 | 5.8 | 4.3 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hitomi, T.; Sato, R.; Ming, A. Development of an Oblique Cone Dielectric Elastomer Actuator Module-Connected Vertebrate Fish Robot. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10060365
Hitomi T, Sato R, Ming A. Development of an Oblique Cone Dielectric Elastomer Actuator Module-Connected Vertebrate Fish Robot. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(6):365. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10060365
Chicago/Turabian StyleHitomi, Taro, Ryuki Sato, and Aiguo Ming. 2025. "Development of an Oblique Cone Dielectric Elastomer Actuator Module-Connected Vertebrate Fish Robot" Biomimetics 10, no. 6: 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10060365
APA StyleHitomi, T., Sato, R., & Ming, A. (2025). Development of an Oblique Cone Dielectric Elastomer Actuator Module-Connected Vertebrate Fish Robot. Biomimetics, 10(6), 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10060365






