A Mantis-Inspired Multi-Quadrupole Adaptive Landing Gear Design and Performance Study
Abstract
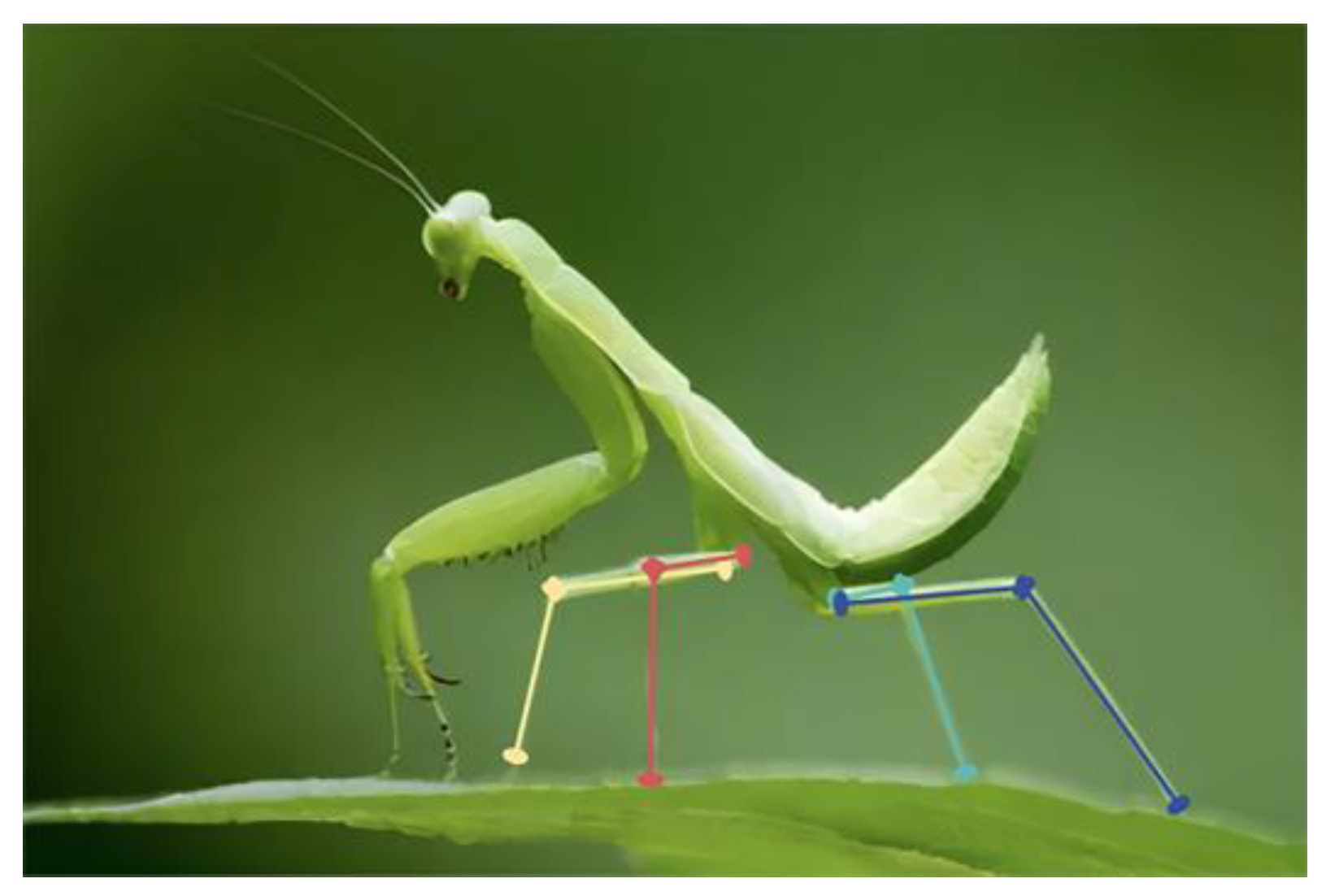
1. Introduction
2. Design and Analysis
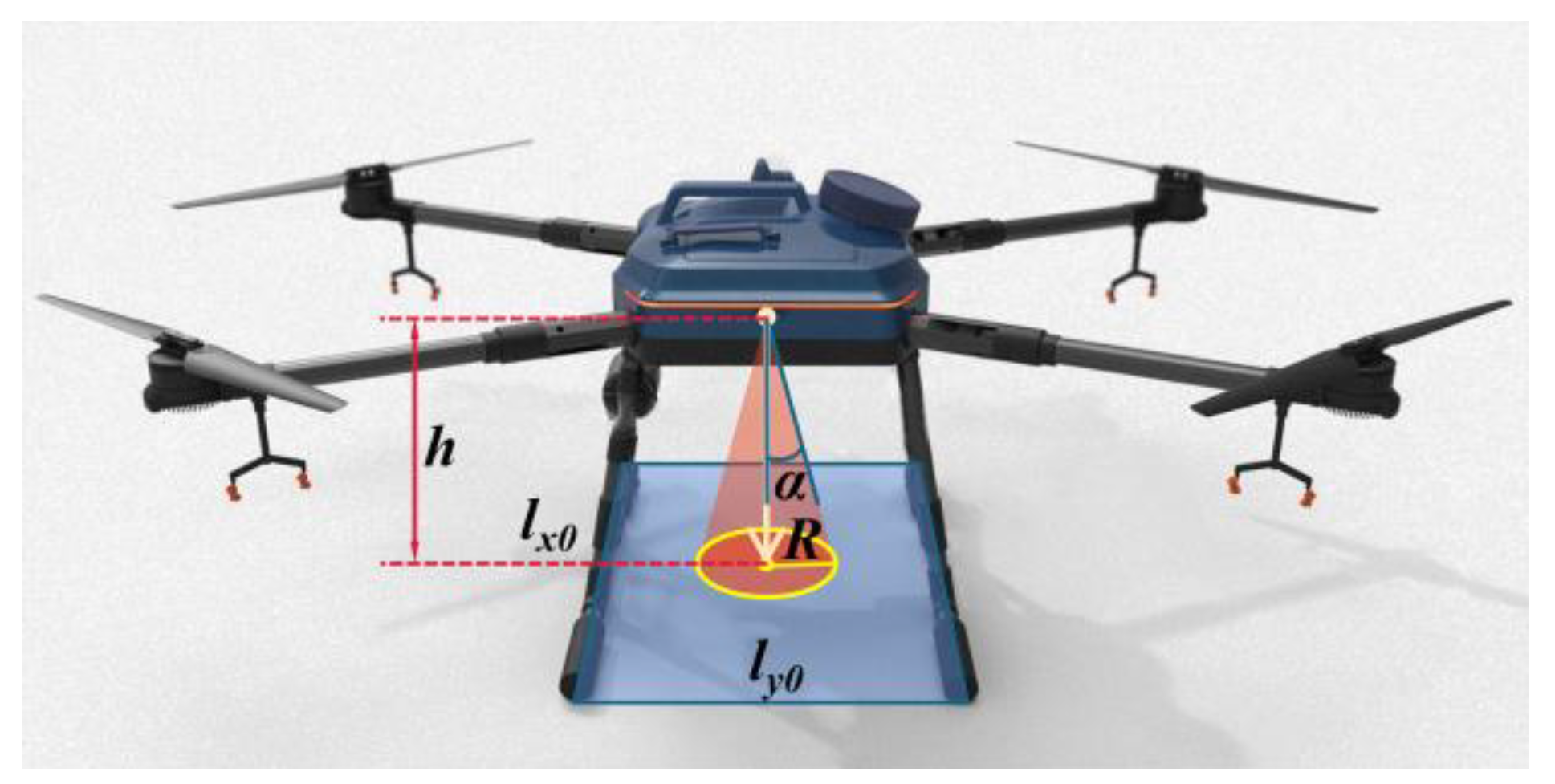
2.1. Landing Gear Mechanism Design
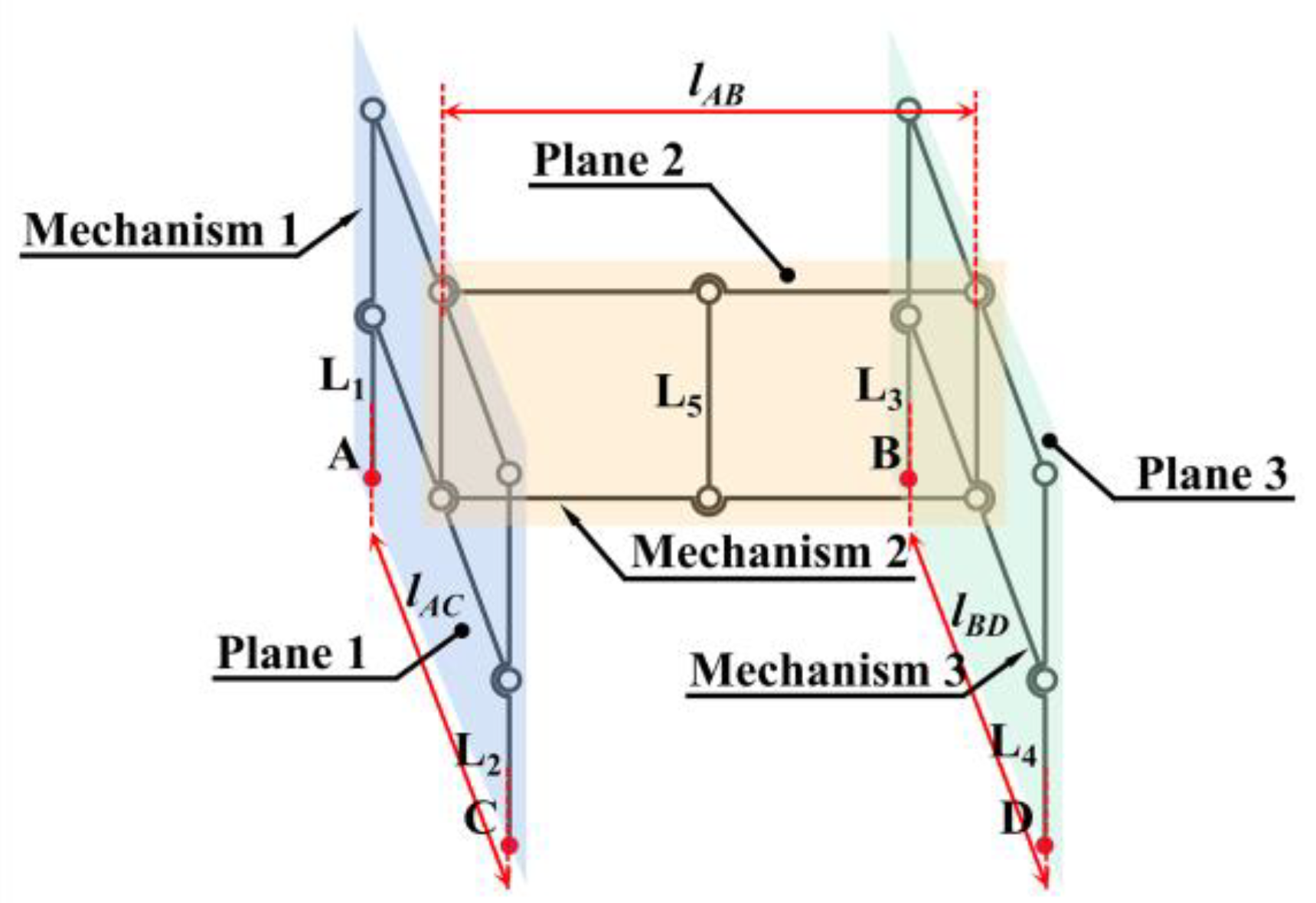
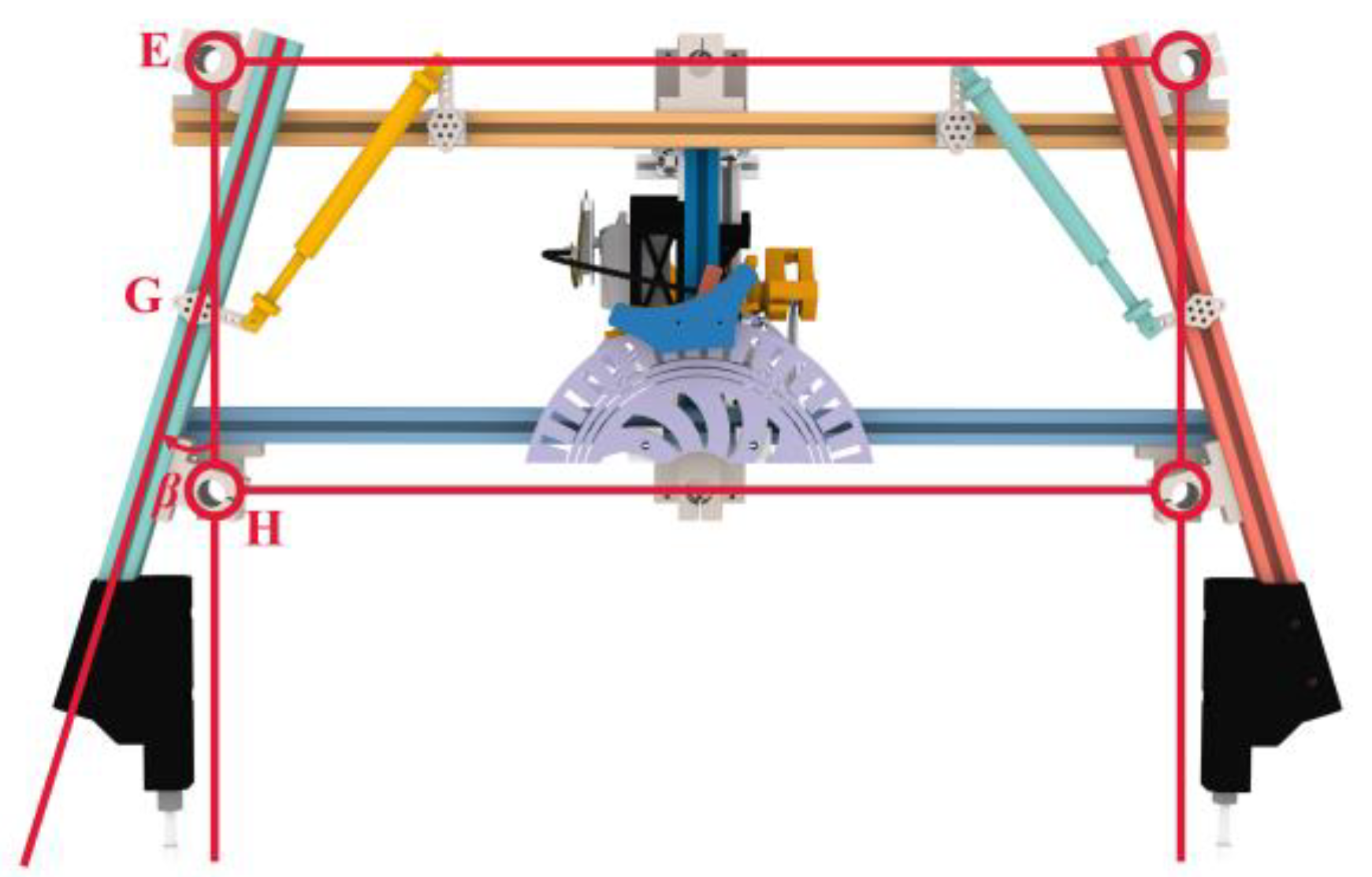
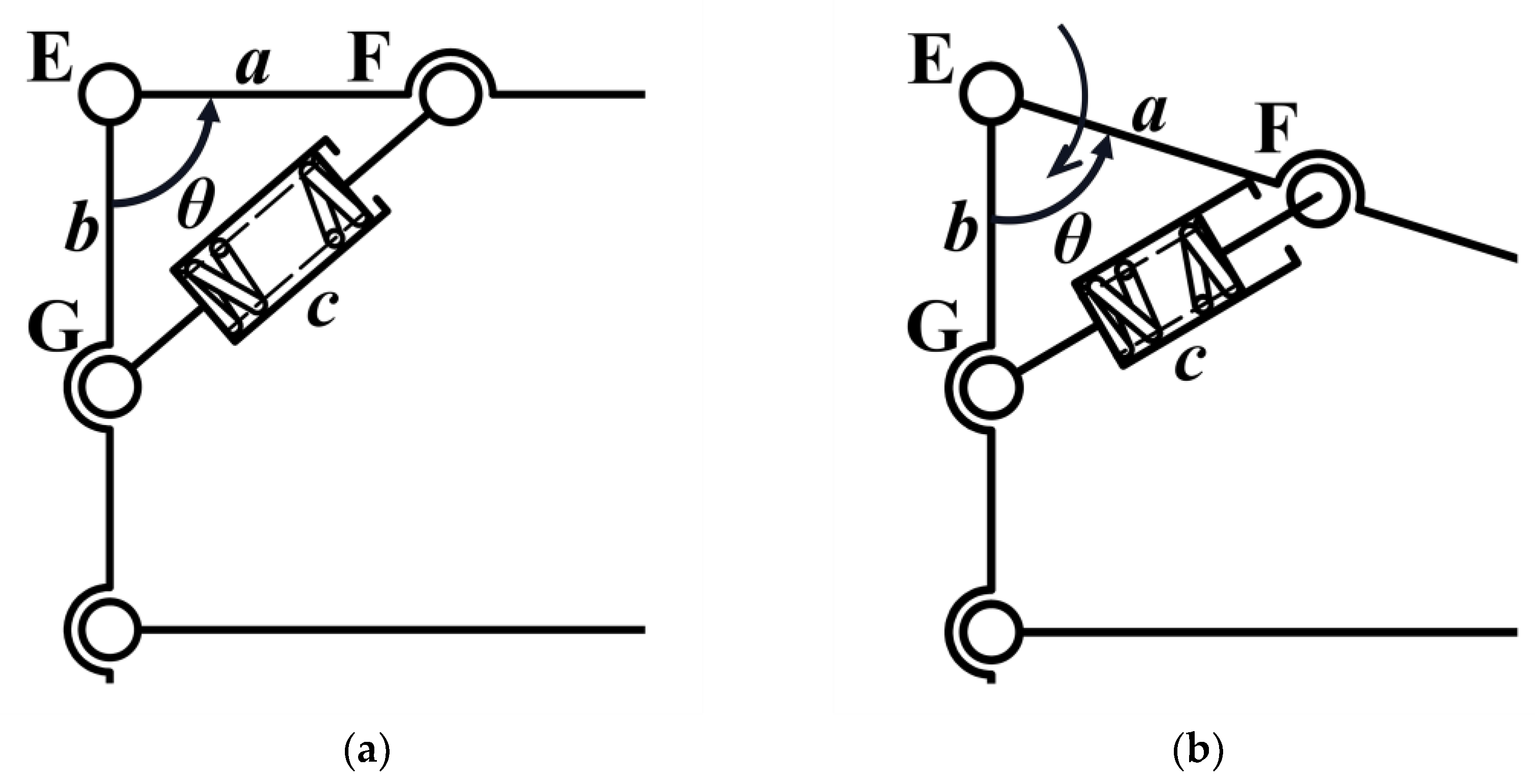
2.1.1. Mechanism Design
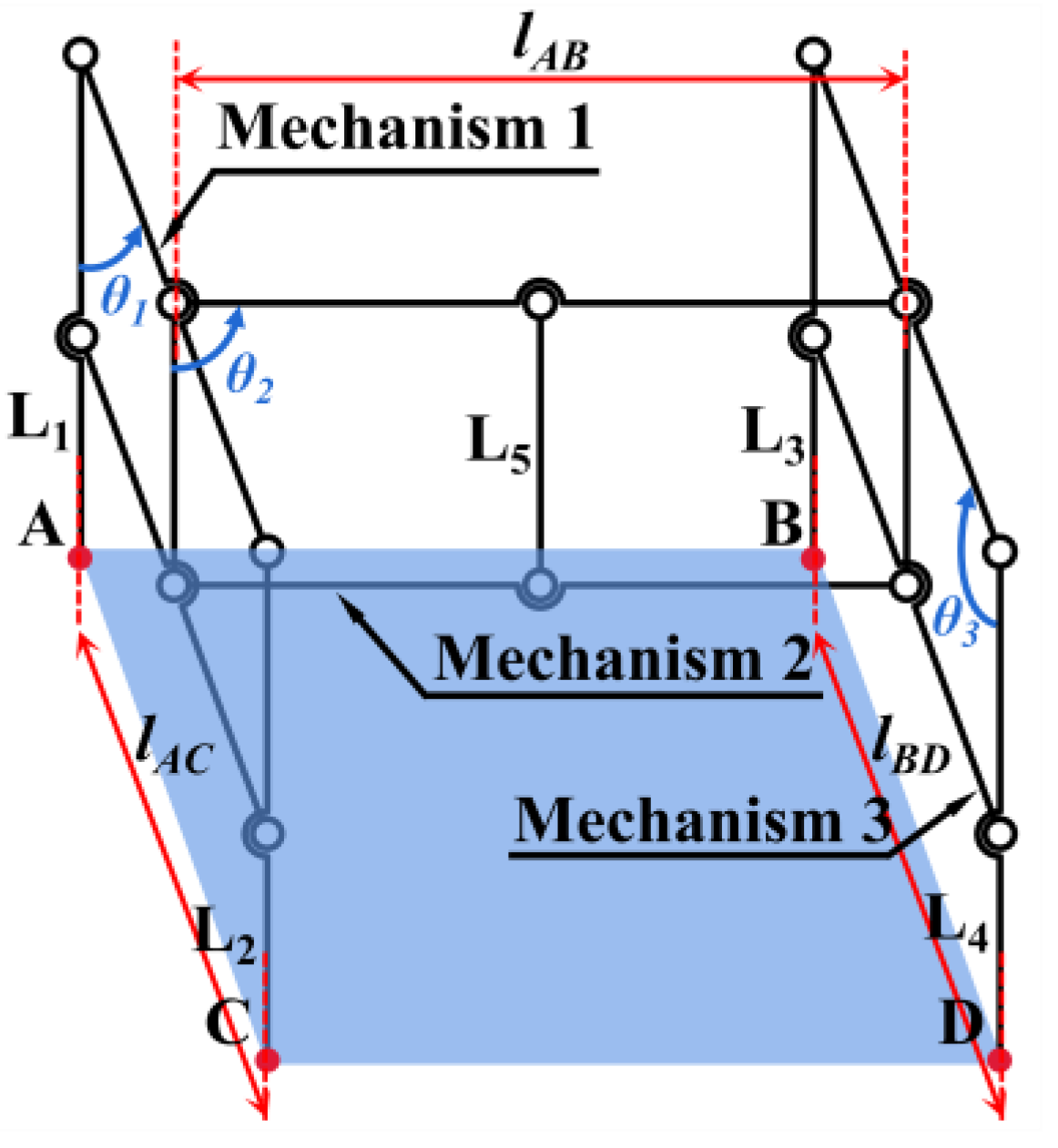
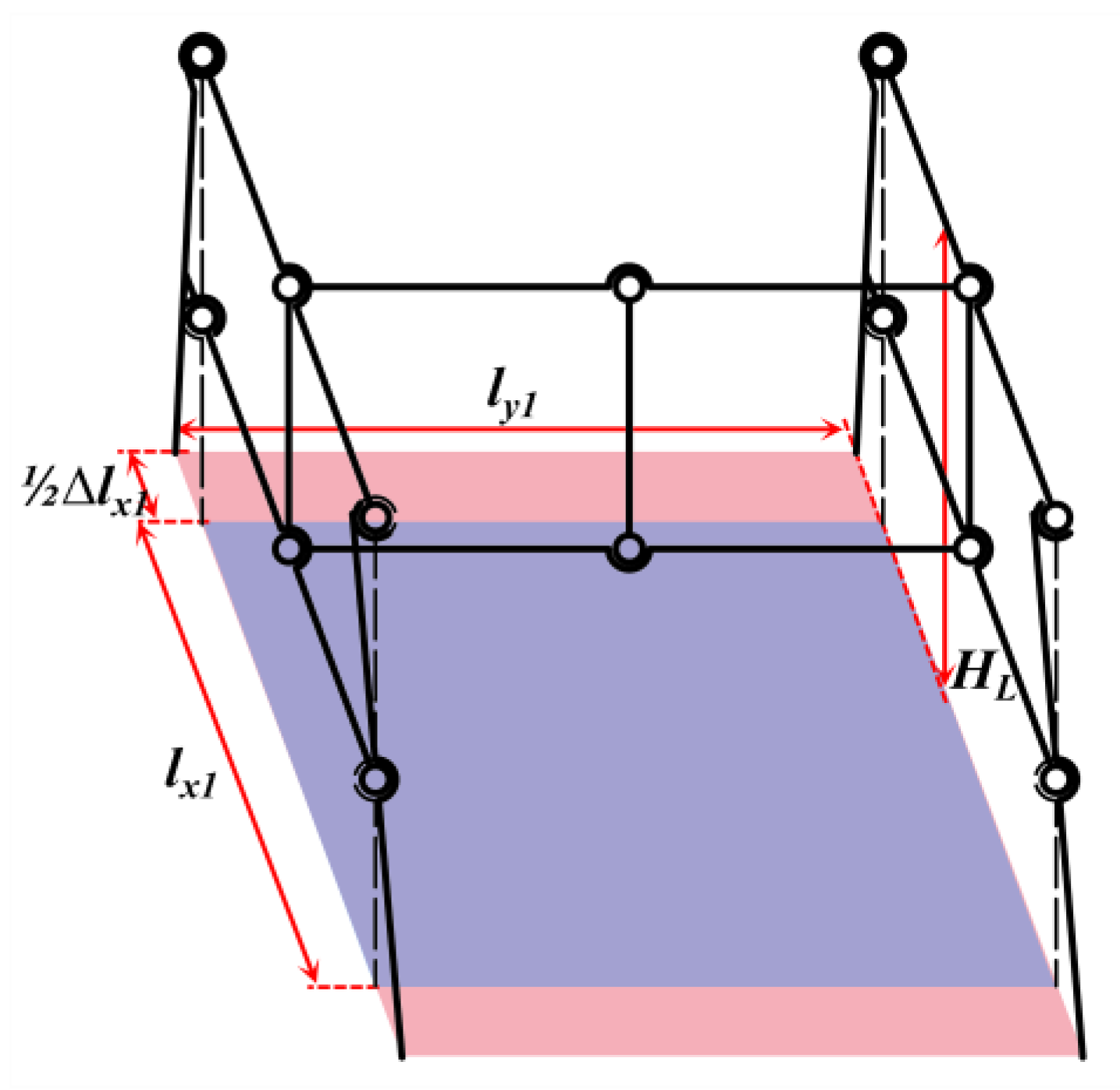
- Mechanism 1 is used to adapt the height difference between two places, A and C, in plane 1.
- Mechanism 3 is used to adapt the height difference between places B and D in plane 3.
- Mechanism 2 is used to adapt the height difference between the median height values of mechanisms 1 and 3.
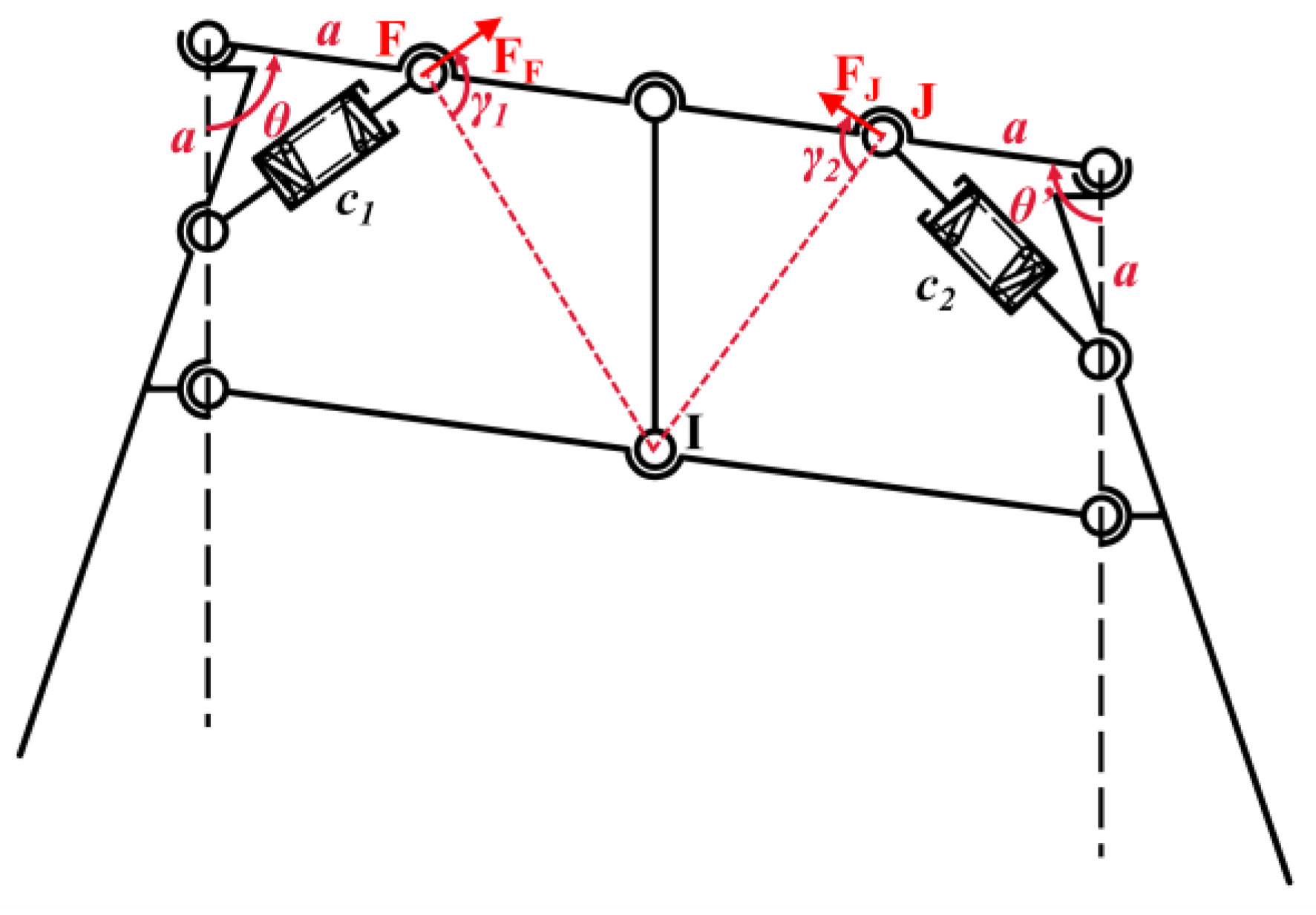
2.1.2. Adaptation Range Calculation
- When 0 ≤ x ≤ lAH, there exists a shear stress FS(x) and a bending moment Ms(x), respectively:
- When lAH ≤ x ≤ lAE, there exists a shear stress FS(x) and a bending moment Ms(x), respectively:
2.2. Cushion Damping Mechanism Design
2.2.1. Design Proposal
2.2.2. Mounting Position Design
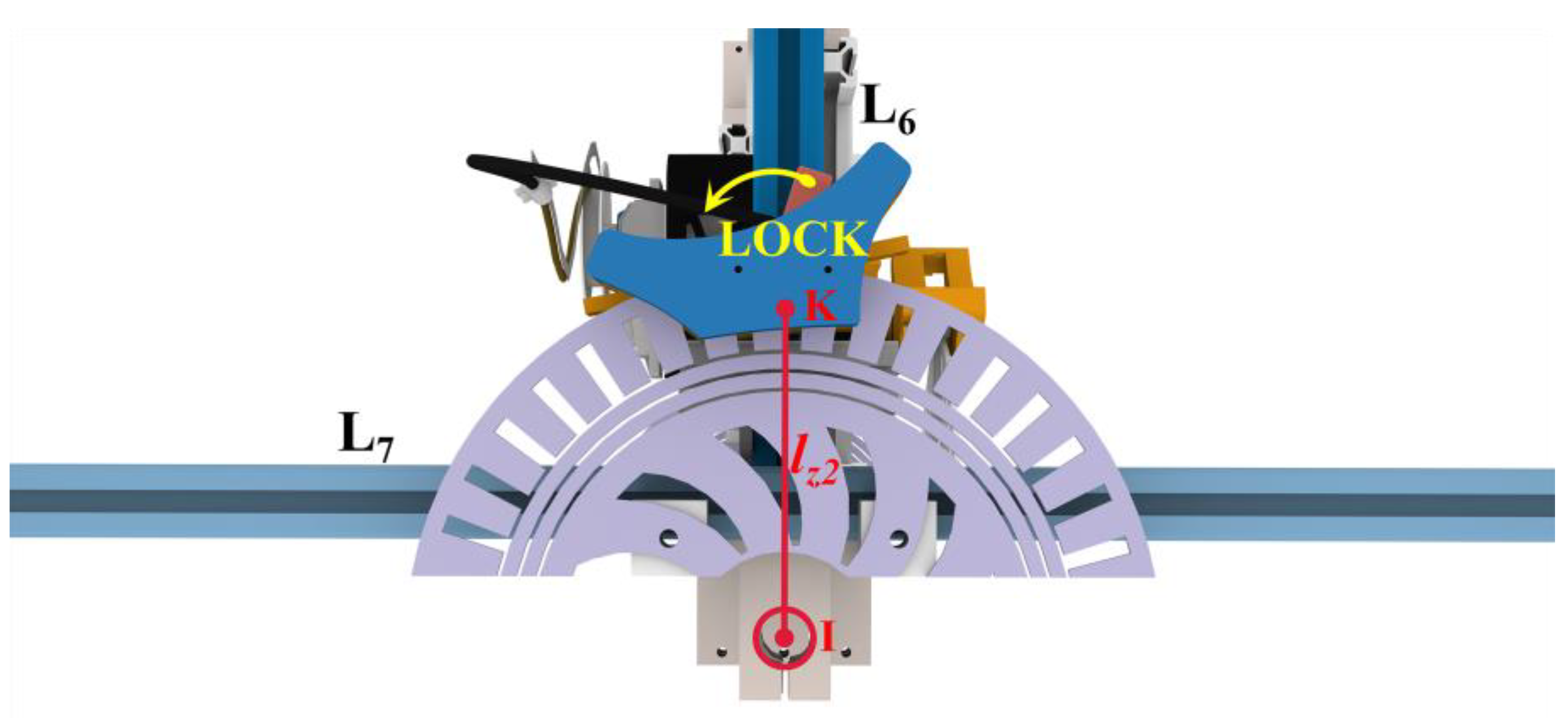
2.3. Locking Mechanism Design
2.4. Energy Recovery System Design
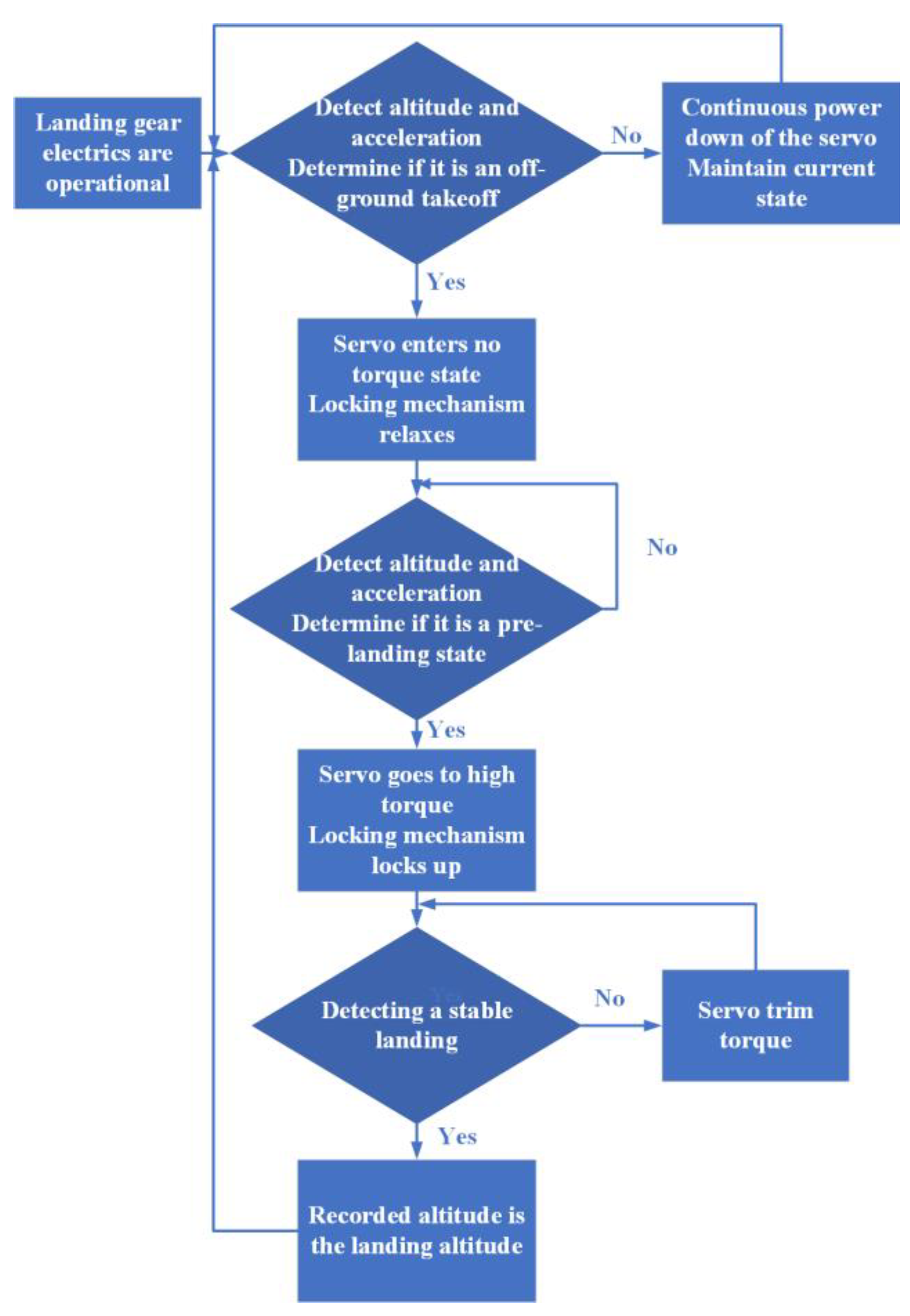
3. Electronic Controls and Circuit Design
3.1. Hardware Design
3.2. Software Design
4. Experimentation and Testing
4.1. Energy Recovery Experiment
- Parallel same quadrilateral bilateral barriers, i.e., only mechanism 1 or only mechanism 3 deformations;
- Unilateral barriers, i.e., only mechanism 2 deformations;
- Different quadrilateral bilateral barriers, i.e., only mechanisms 1 and 3 deform and have the same value of the deformation variable angle sin.
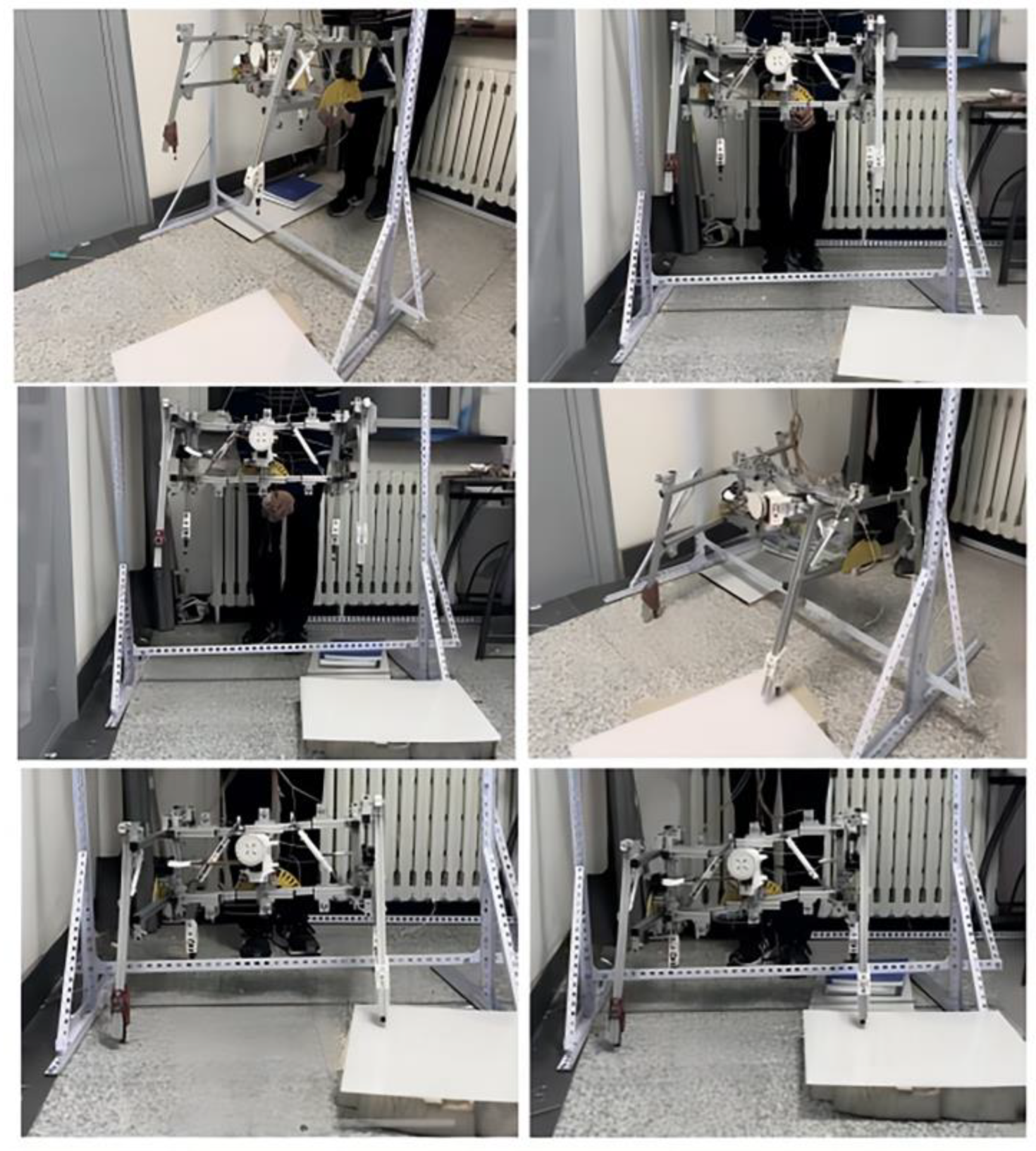
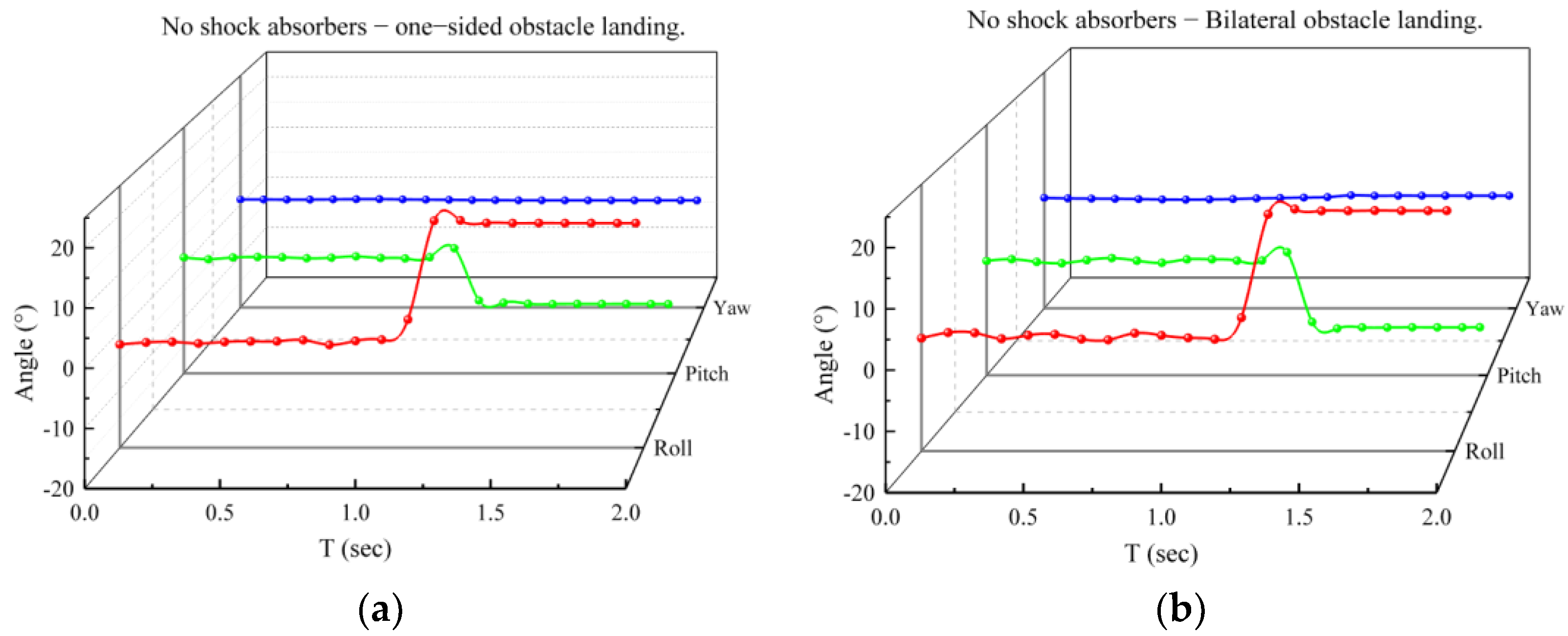
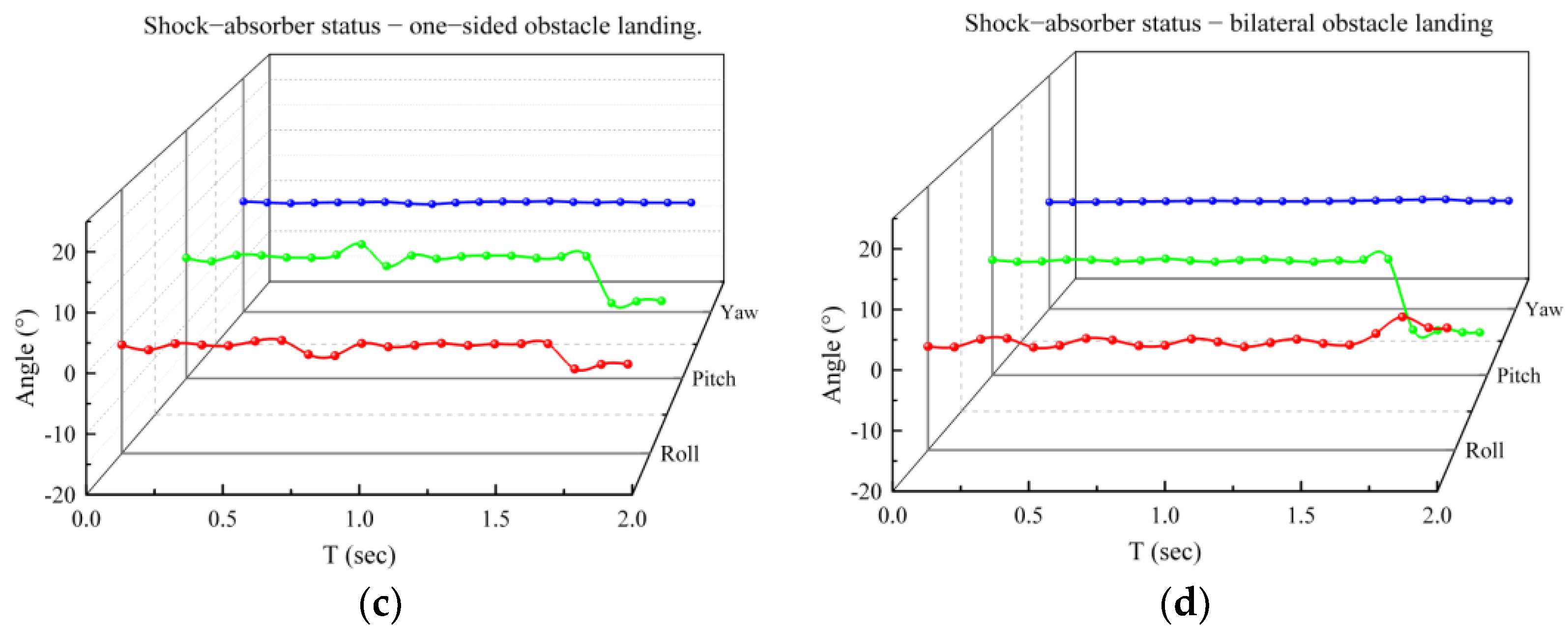
4.2. Actual Landing Test
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Viegas, C.; Chehreh, B.; Andrade, J.; Lourenço, J. Tethered UAV with Combined Multi-Rotor and Water Jet Propulsion for Forest Fire Fighting. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2022, 104, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsan, S.A.H.; Khan, M.A.; Noor, F.; Ullah, I.; Alsharif, M.H. Towards the Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs): A Comprehensive Review. Drones 2022, 6, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmeseiry, N.; Alshaer, N.; Ismail, T. A Detailed Survey and Future Directions of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) with Potential Applications. Aerospace 2021, 8, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, C.; Huang, H. Unmanned Aerial Vehicles for Search and Rescue: A Survey. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Yin, Q.; Wei, X.; Zhong, P.; Nie, H. Research on Landing Stability of Four-Legged Adaptive Landing Gear for Multirotor UAVs. Aerospace 2022, 9, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Montoya, J.; Carvajal-Castrillón, A.; Sierra-Pérez, J. In-Flight and Wireless Damage Detection in a UAV Composite Wing Using Fiber Optic Sensors and Strain Field Pattern Recognition. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 136, 106526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, H.B. Design and Analysis of Retractable Structure of New Quadrotor Landing Gear. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1750, 012022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mir, H.; King, S.; Skote, M.; Alam, M.; Place, S. Landing Gear Health Assessment: Synergising Flight Data Analysis with Theoretical Prognostics in a Hybrid Assessment Approach. PHM Soc. Eur. Conf. 2024, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raouf, I.; Kumar, P.; Cheon, Y.; Tanveer, M.; Jo, S.-H.; Kim, H.S. Advances in Prognostics and Health Management for Aircraft Landing Gear—Progress, Challenges, and Future Possibilities. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Technol. 2025, 12, 301–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivannan, V.; Langley, J.P.; Costello, M.; Ruzzene, M. Rotorcraft Slope Landings with Articulated Landing Gear. In Proceedings of the AIAA Atmospheric Flight Mechanics (AFM) Conference, Boston, MA, USA, 19–22 August 2013; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, D.; Tian, C.; Ma, W.; Xia, Z. A Virtual Parallel Model for the Buffer Landing of Multi-Legged Landing Gear. Mech. Mach. Theory 2024, 200, 105724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Zhang, D.; Tian, C. A Method for Comprehensive Performance Optimization of Four-Leg Landing Gear Based on the Virtual Equivalent Parallel Mechanism. Mech. Mach. Theory 2022, 174, 104924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Zhang, J.M.; Zhang, D. A New Comprehensive Performance Optimization Approach for Earth-Contact Mechanism Based on Terrain-Adaptability Task. Robotica 2023, 41, 193–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkisov, Y.S.; Yashin, G.A.; Tsykunov, E.V.; Tsetserukou, D. DroneGear: A Novel Robotic Landing Gear with Embedded Optical Torque Sensors for Safe Multicopter Landing on an Uneven Surface. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 1912–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolz, B.; Brodermann, T.; Castiello, E.; Englberger, G.; Erne, D.; Gasser, J.; Hayoz, E.; Muller, S.; Muhlebach, L.; Low, T.; et al. An Adaptive Landing Gear for Extending the Operational Range of Helicopters. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1757–1763. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Gao, F.; Yin, K. Helicopter Bionic Landing Gear Design and Verification Technology Based on Multi-Link Structure. In Proceedings of the 6th China Aeronautical Science and Technology Conference, Wuzhen, China, 25–27 September 2023; pp. 455–468. [Google Scholar]
- Nadan, P.M.; Lee, C.L. Computational Design of a Bird-Inspired Perching Landing Gear Mechanism. In Proceedings of the ASME 2018 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Volume 4A: Dynamics, Vibration, and Control, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 9–15 November 2018; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, B.; Gao, H.; Yu, H.; Shan, H.; Hou, J.; Yu, H.; Deng, Z. Cable-Driven Legged Landing Gear for Unmanned Helicopter: Prototype Design, Optimization and Performance Assessment. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2024, 67, 1196–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arık, A.E.; Bilgiç, B. Fuzzy Control of a Landing Gear System with Oleo-Pneumatic Shock Absorber to Reduce Aircraft Vibrations by Landing Impacts. Aircr. Eng. Aerosp. Technol. 2023, 95, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, Q.-N.; Park, H.-M.; Kim, Y.; Pham, H.-H.; Hwang, J.-H.; Luong, Q.-V. An Intelligent Control and a Model Predictive Control for a Single Landing Gear Equipped with a Magnetorheological Damper. Aerospace 2023, 10, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, Q.-V.; Jo, B.-H.; Hwang, J.-H.; Jang, D.-S. A Supervised Neural Network Control for Magnetorheological Damper in an Aircraft Landing Gear. Appl. Sci. 2021, 12, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.-C.; Chin, P.-C.; Sun, Y.-P.; Wang, M.-R. Design and Manufacture of Composite Landing Gear for a Light Unmanned Aerial Vehicle. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancea, C.; Chicos, L.-A.; Zaharia, S.-M.; Pop, M.-A.; Pascariu, I.S.; Buican, G.-R.; Stamate, V.-M. Simulation, Fabrication and Testing of UAV Composite Landing Gear. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y. Landing Performance Study for Four Wheels Twin Tandem Landing Gear Based on Drop Test. Aerospace 2022, 9, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikura, M.; Miyashita, L.; Ishikawa, M. Real-Time Landing Gear Control System Based on Adaptive 3D Sensing for Safe Landing of UAV. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII), Honolulu, HI, USA, 12–15 January 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 759–764. [Google Scholar]
- Brindisi, A.; Vendittozzi, C.; Travascio, L.; Di Palma, L.; Ignarra, M.; Fiorillo, V.; Concilio, A. A Preliminary Assessment of an FBG-Based Hard Landing Monitoring System. Photonics 2021, 8, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, D.; Wu, C.; Tang, H.; Tian, C. A Multi-Finger Robot System for Adaptive Landing Gear and Aerial Manipulation. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2021, 146, 103878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagrale, Y.; Mulchandani, N. Design and Analysis of Disc Brake for Honda Shine C125. Int. J. Adv. Res. Sci. Commun. Technol. 2024, 4, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Ding, X. Design and Analysis of a Novel Metamorphic Remote-Centre-of-Motion Mechanism with Parallelogram Joints. Mech. Mach. Theory 2022, 176, 105038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetzke, H.; Burrows, M.; Federle, W. Mantises Jump from Smooth Surfaces by Pushing with “Heel” Pads of Their Hind Legs. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibawa, L.A.N. Effect of Fillet Radius of UAV Main Landing Gear on Static Stress and Fatigue Life Using Finite Element Method. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1811, 012082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 12020-1:2022; Luminium and Aluminium Alloys—Extruded Precision Profiles in Alloys EN AW-6060 and EN AW-6063—Part 1: Technical Conditions for Inspection and Delivery. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2022.
- Swati, R.F.; Khan, A.A. Design and Structural Analysis of Weight Optimized Main Landing Gears for UAV Under Impact Loading. J. Space Technol. 2014, 4, 96–107. [Google Scholar]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chu, Y.; Lv, Z.; Gu, S.; Wang, Y.; Yu, T. A Mantis-Inspired Multi-Quadrupole Adaptive Landing Gear Design and Performance Study. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10050327
Chu Y, Lv Z, Gu S, Wang Y, Yu T. A Mantis-Inspired Multi-Quadrupole Adaptive Landing Gear Design and Performance Study. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(5):327. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10050327
Chicago/Turabian StyleChu, Yichen, Zhifeng Lv, Shuo Gu, Yida Wang, and Tianbiao Yu. 2025. "A Mantis-Inspired Multi-Quadrupole Adaptive Landing Gear Design and Performance Study" Biomimetics 10, no. 5: 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10050327
APA StyleChu, Y., Lv, Z., Gu, S., Wang, Y., & Yu, T. (2025). A Mantis-Inspired Multi-Quadrupole Adaptive Landing Gear Design and Performance Study. Biomimetics, 10(5), 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10050327



