Design and Simulation of a Bio-Inspired Deployable Mechanism Achieved by Mimicking the Folding Pattern of Beetles’ Hind Wings
Abstract
1. Introduction
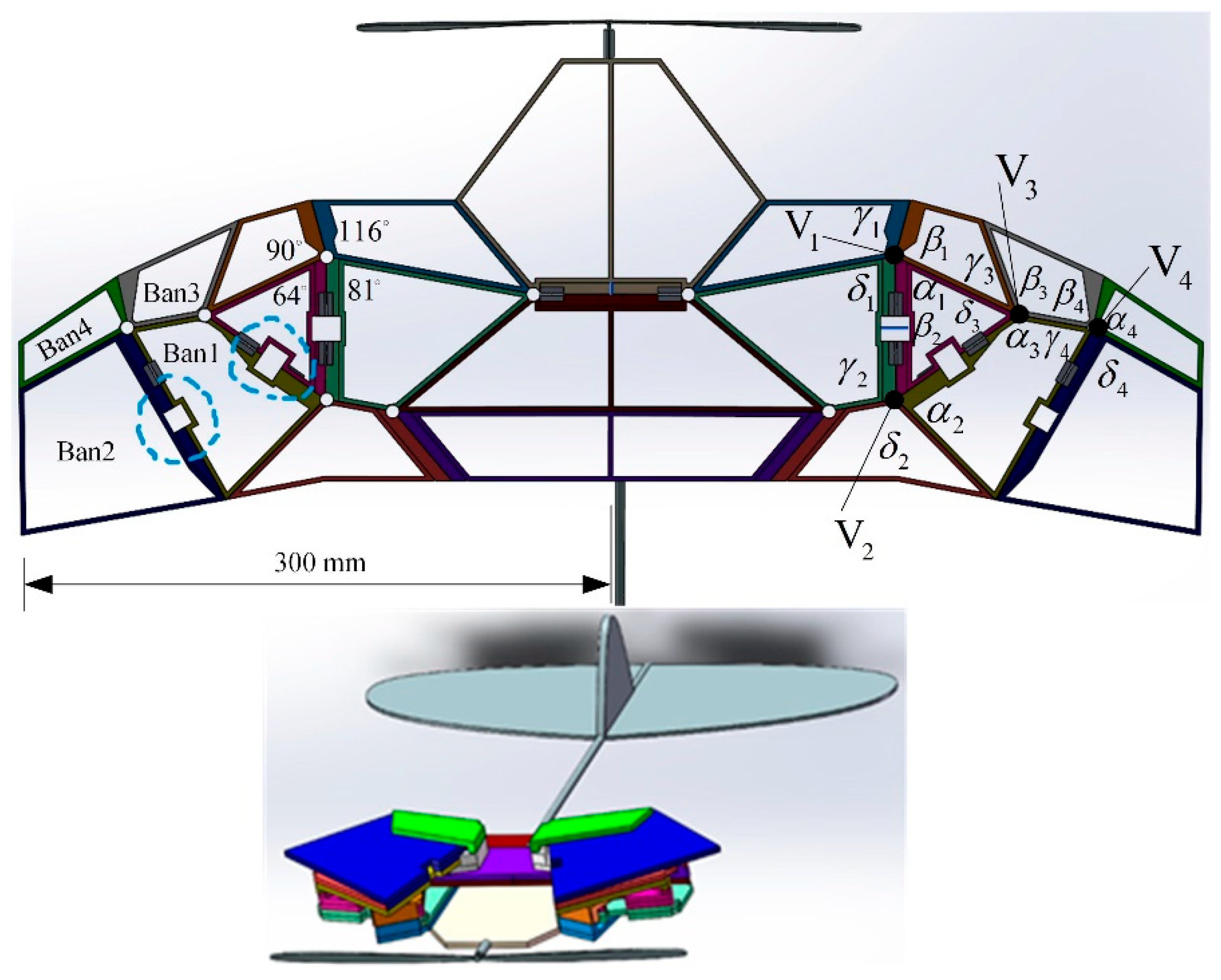
2. Design and Analysis of Biomimetic Space Deployable Mechanism
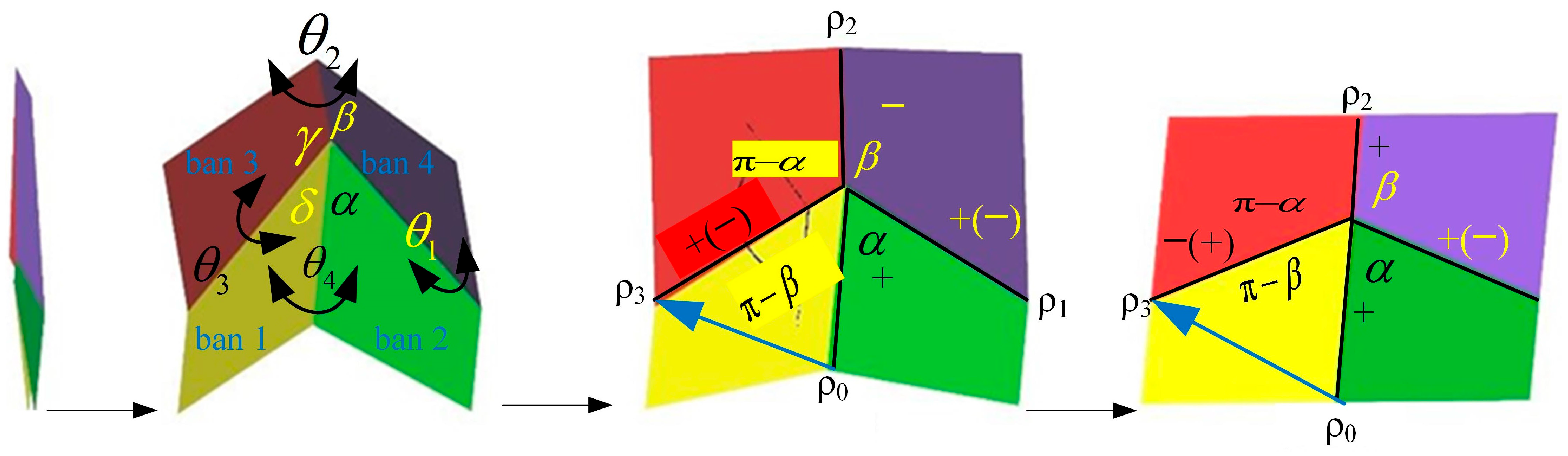
2.1. Folding Pattern of Hind Wings
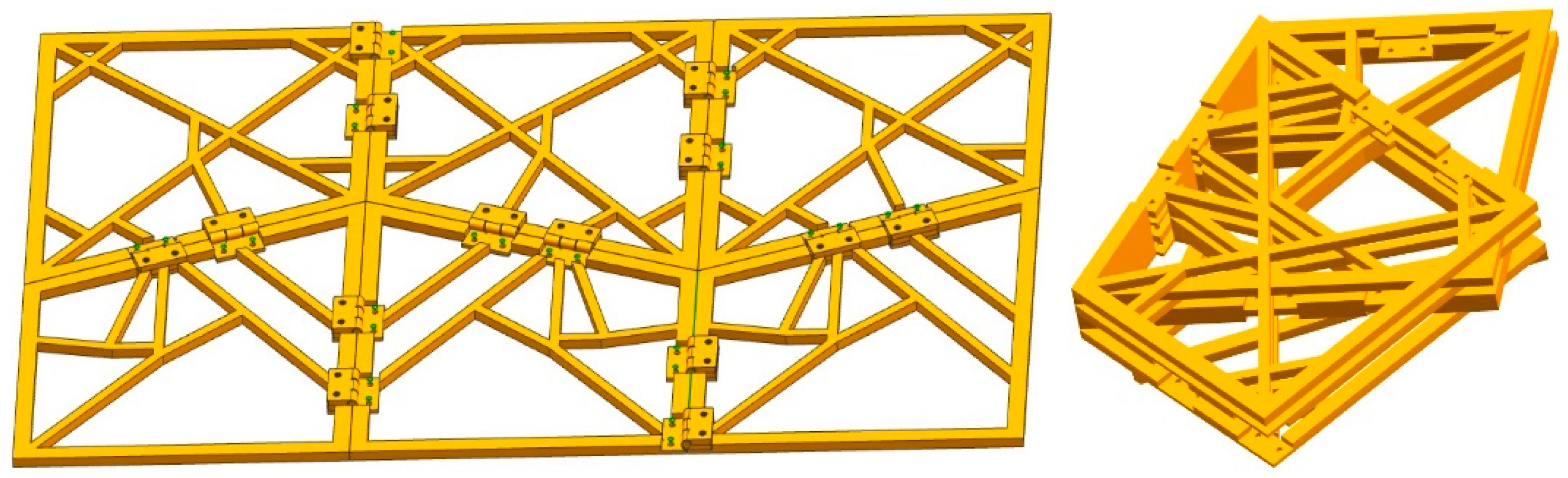
2.2. Design of Biomimetic Space Deployable Mechanism
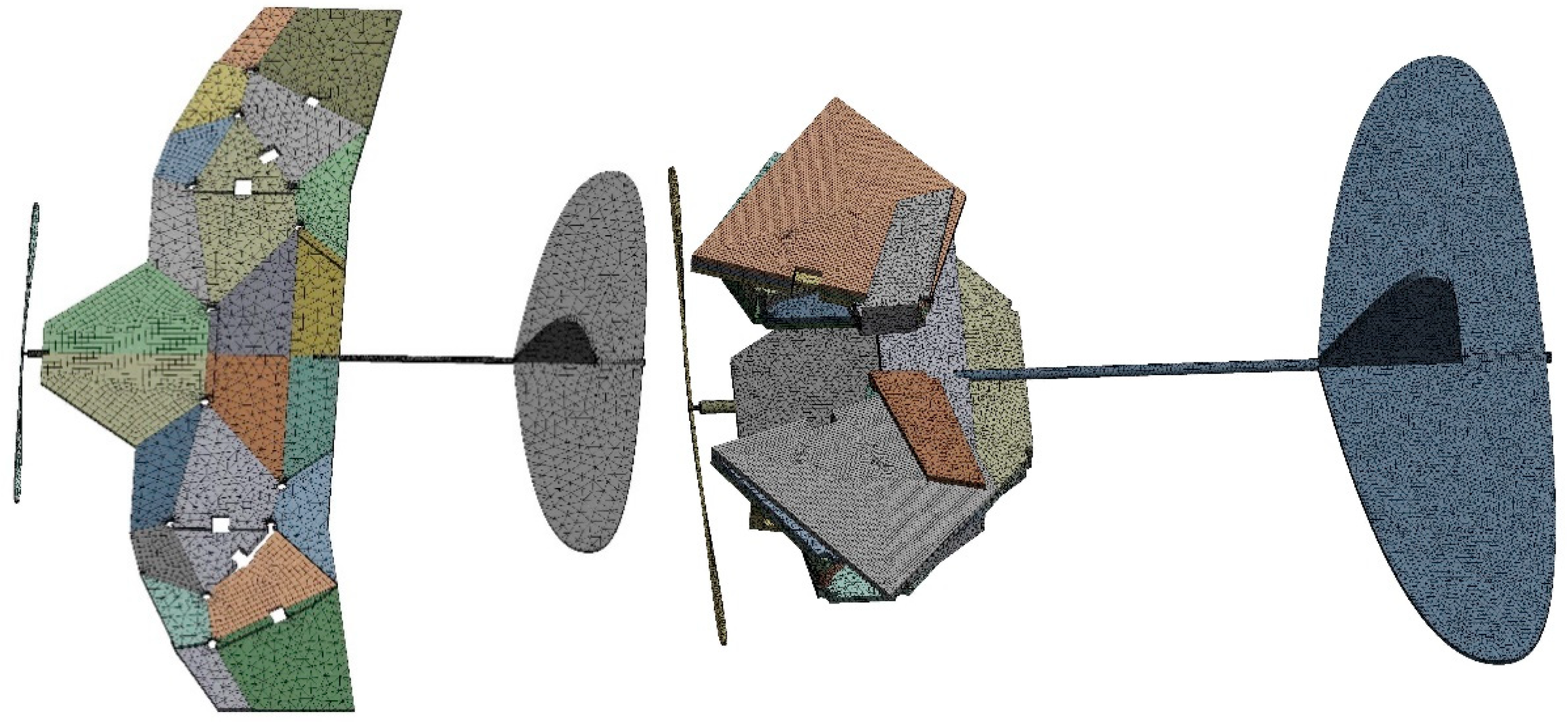
2.3. ADAMS Simulation of Biomimetic Space-Deformable Wing MAV
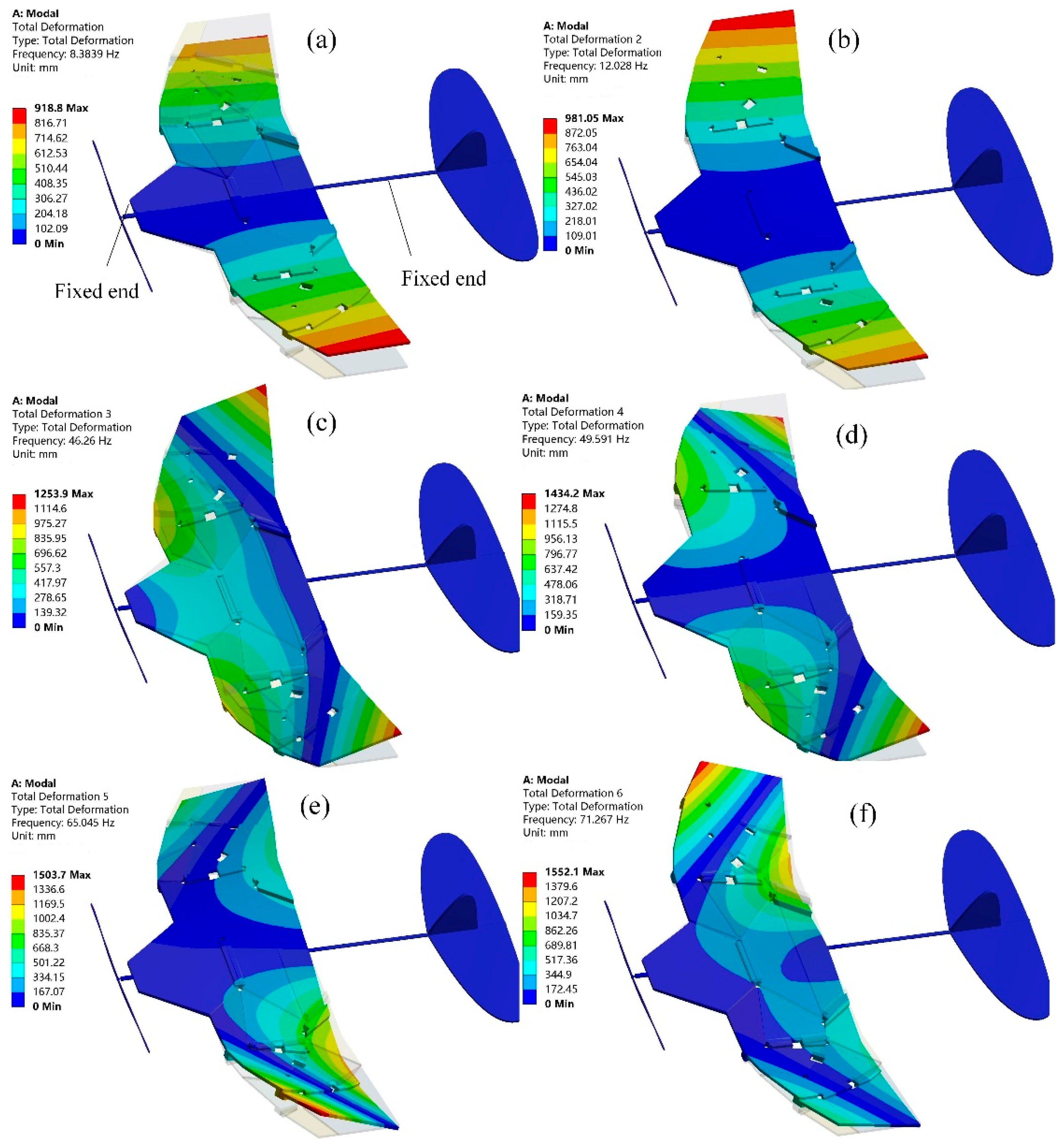
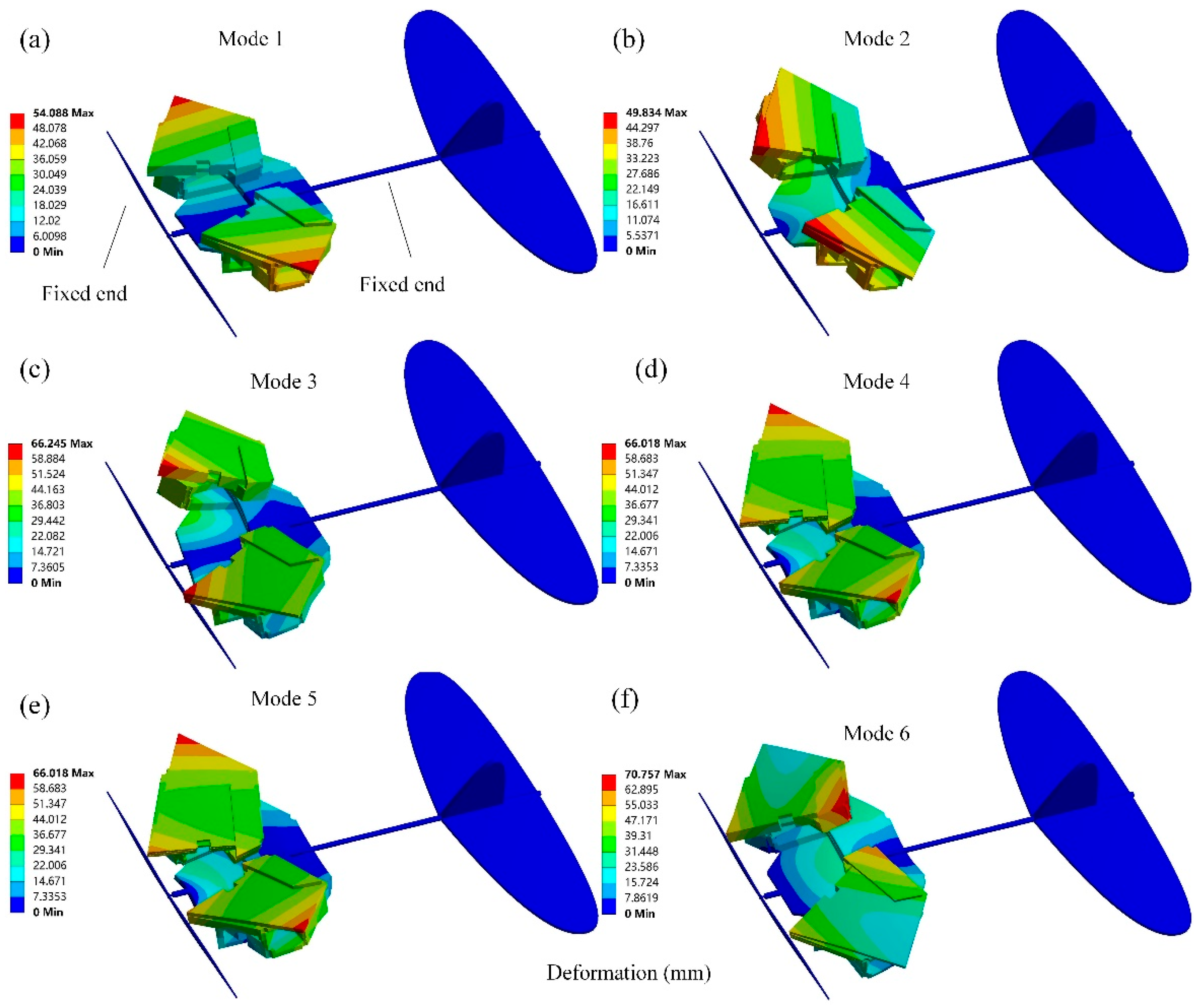
2.4. Modal Characteristics of Biomimetic Space-Deformable Wing MAV
3. Results and Discussion
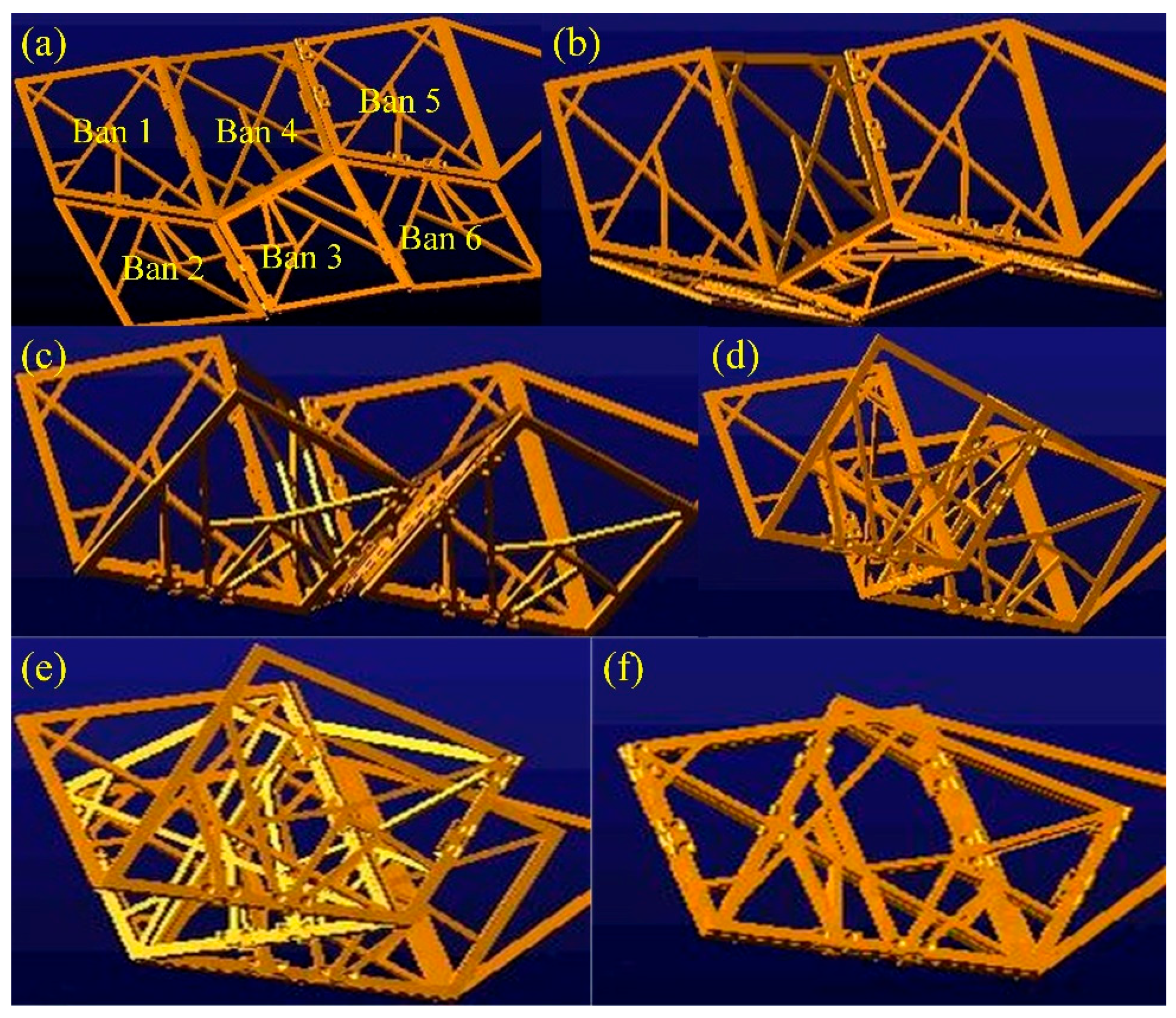
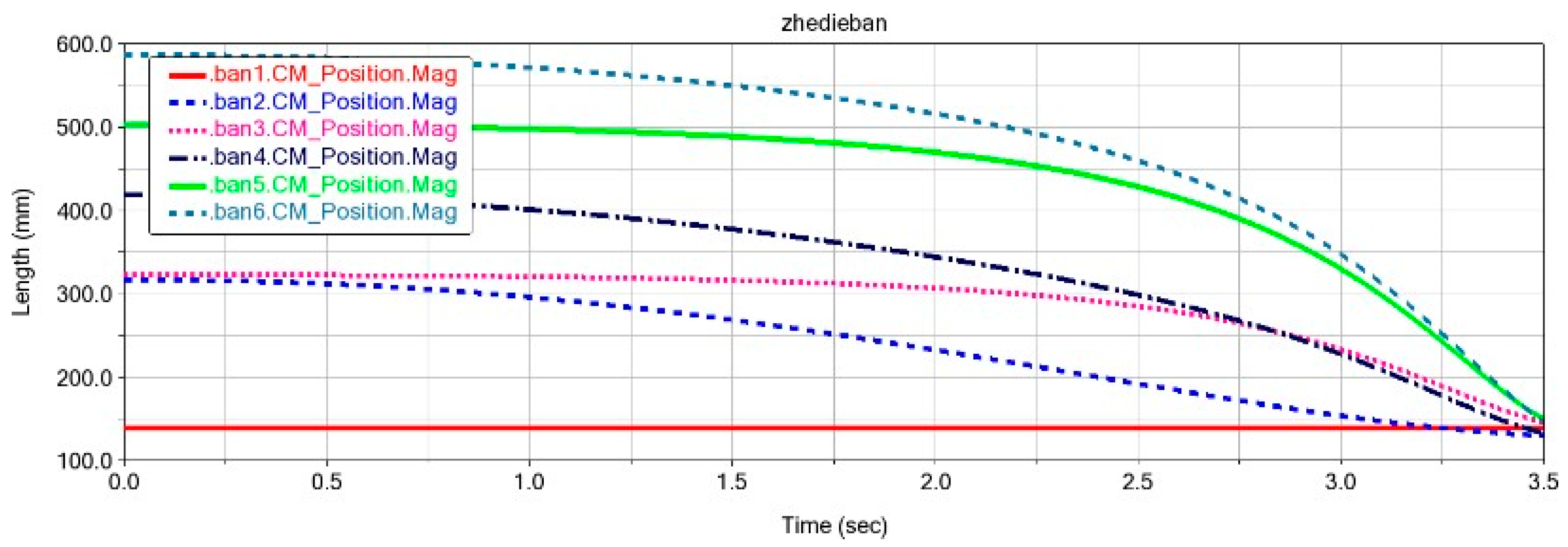
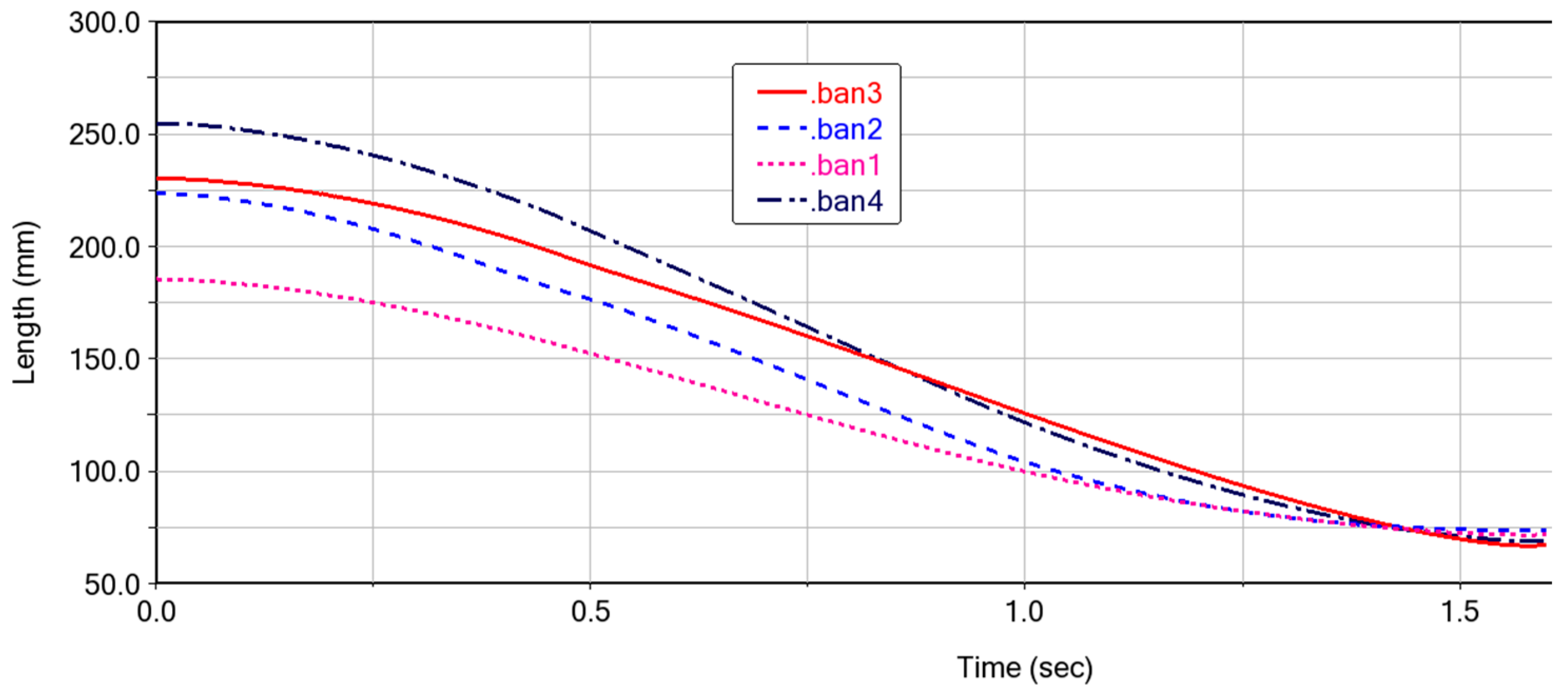
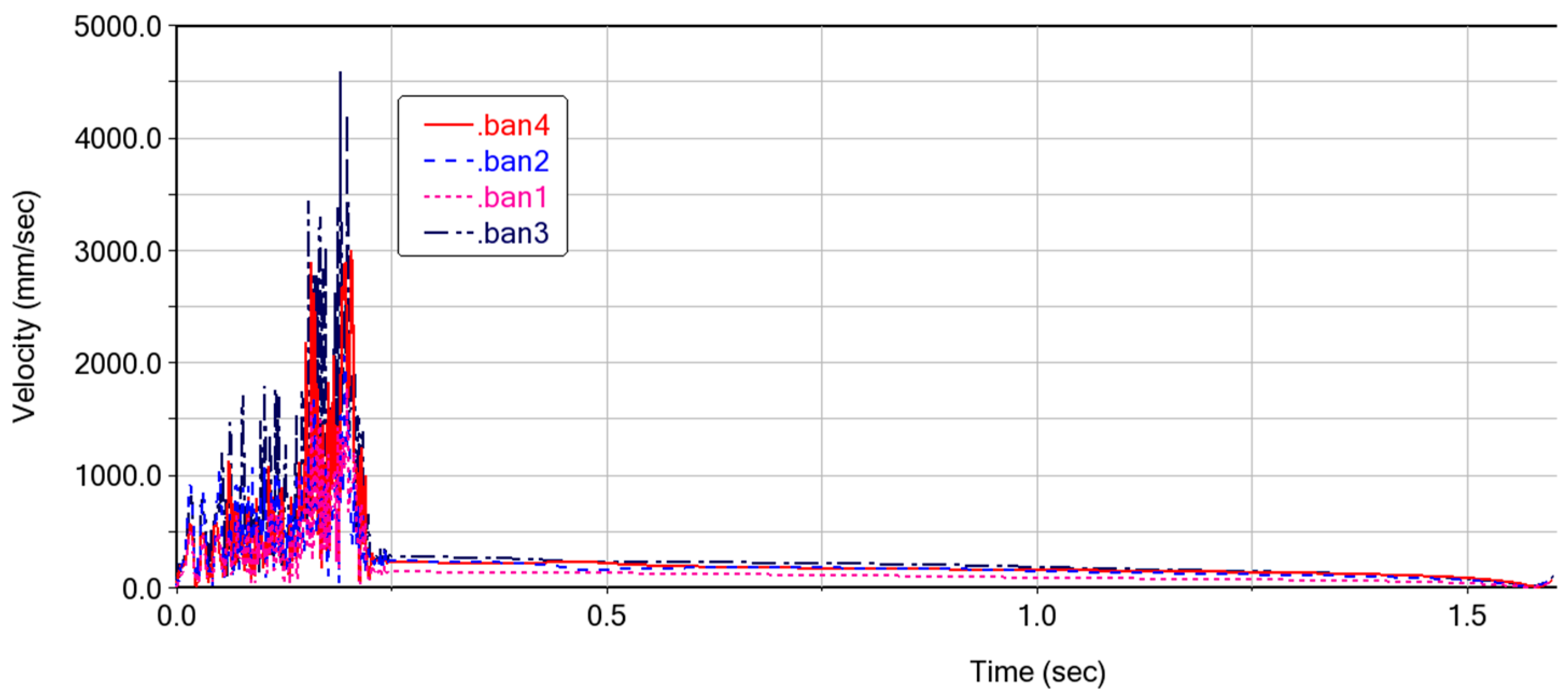
3.1. Kinematics of the Deformable Wing MAV
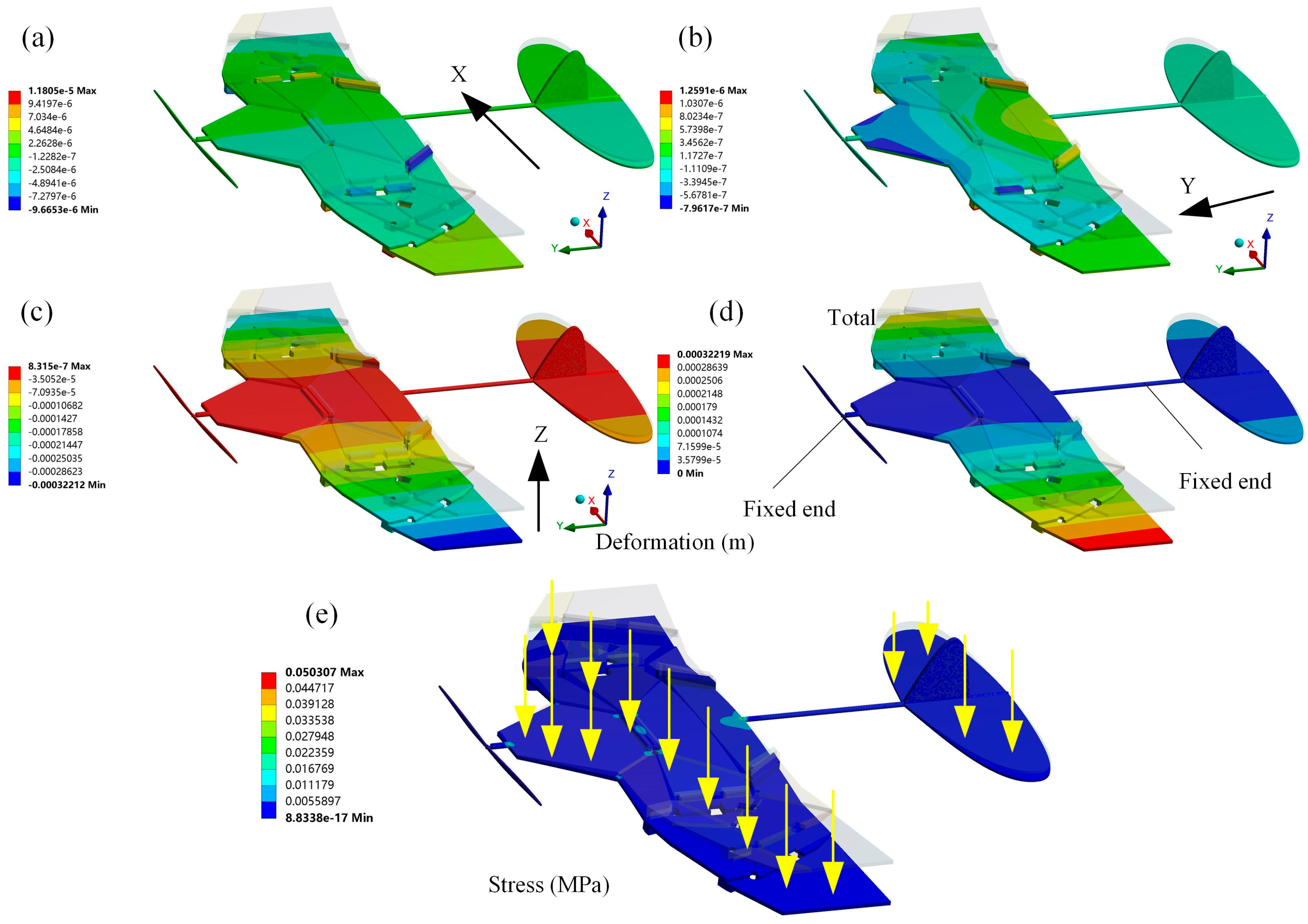
3.2. Structural Response of the Deformable Wing MAV
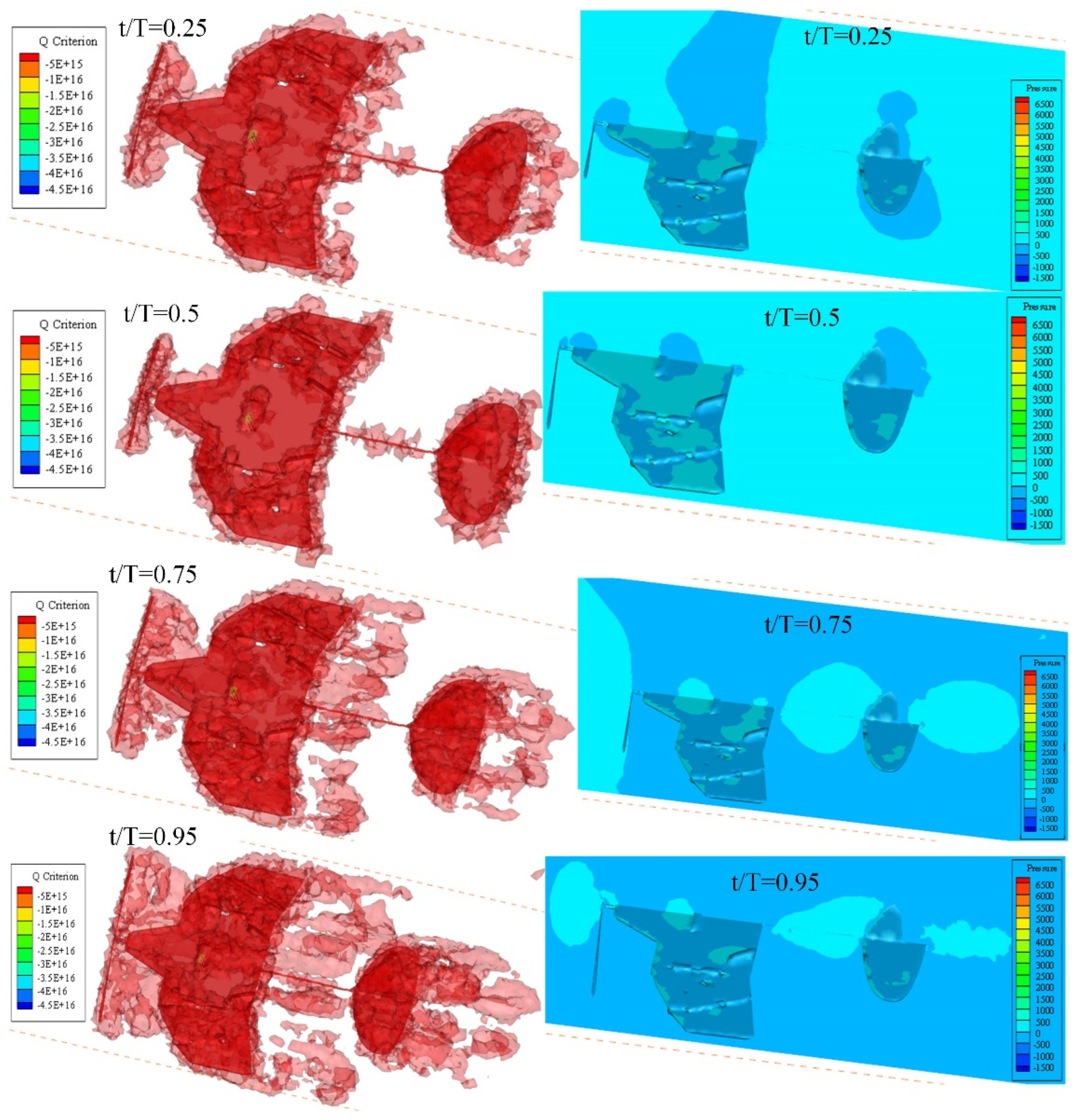
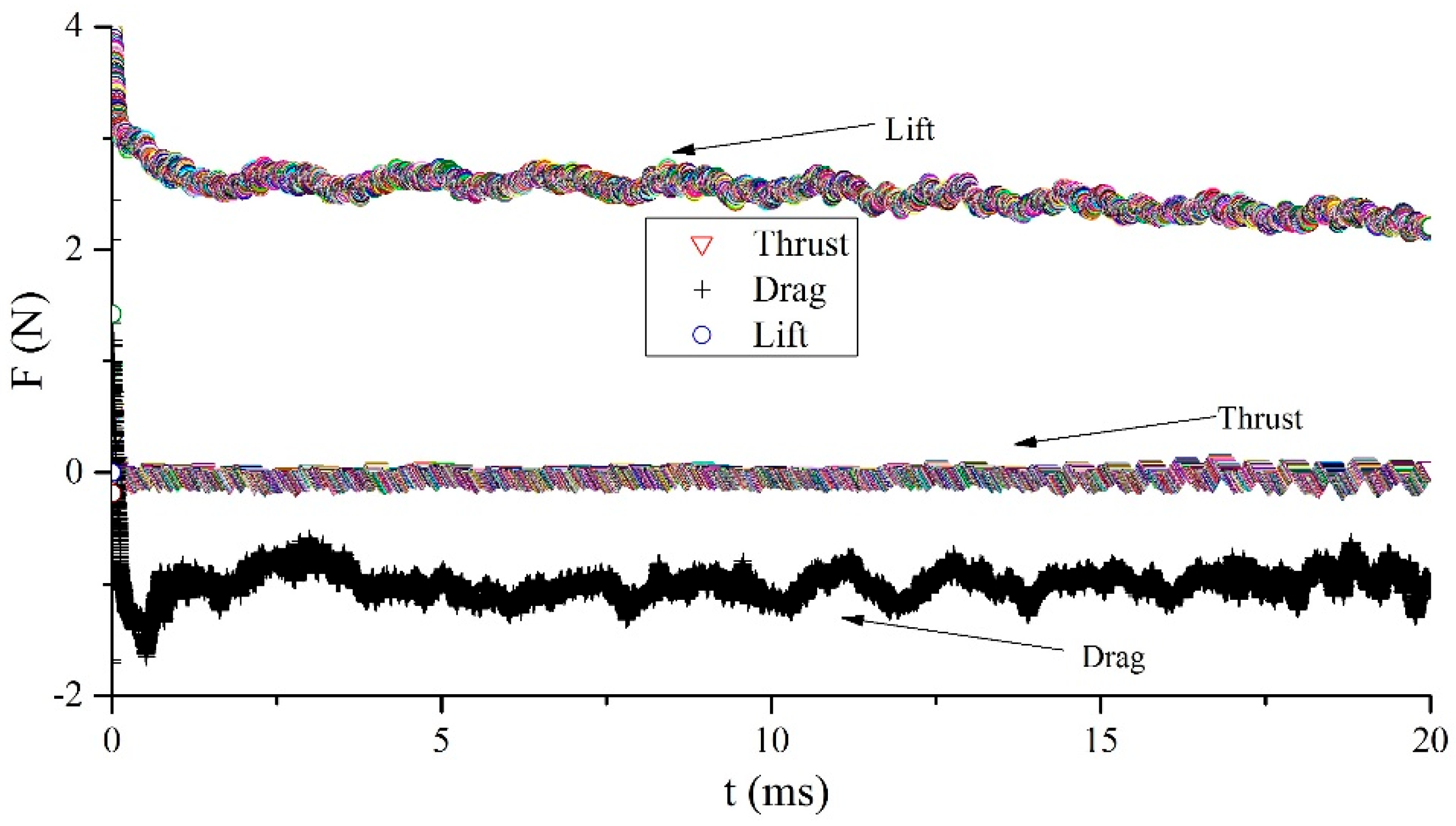
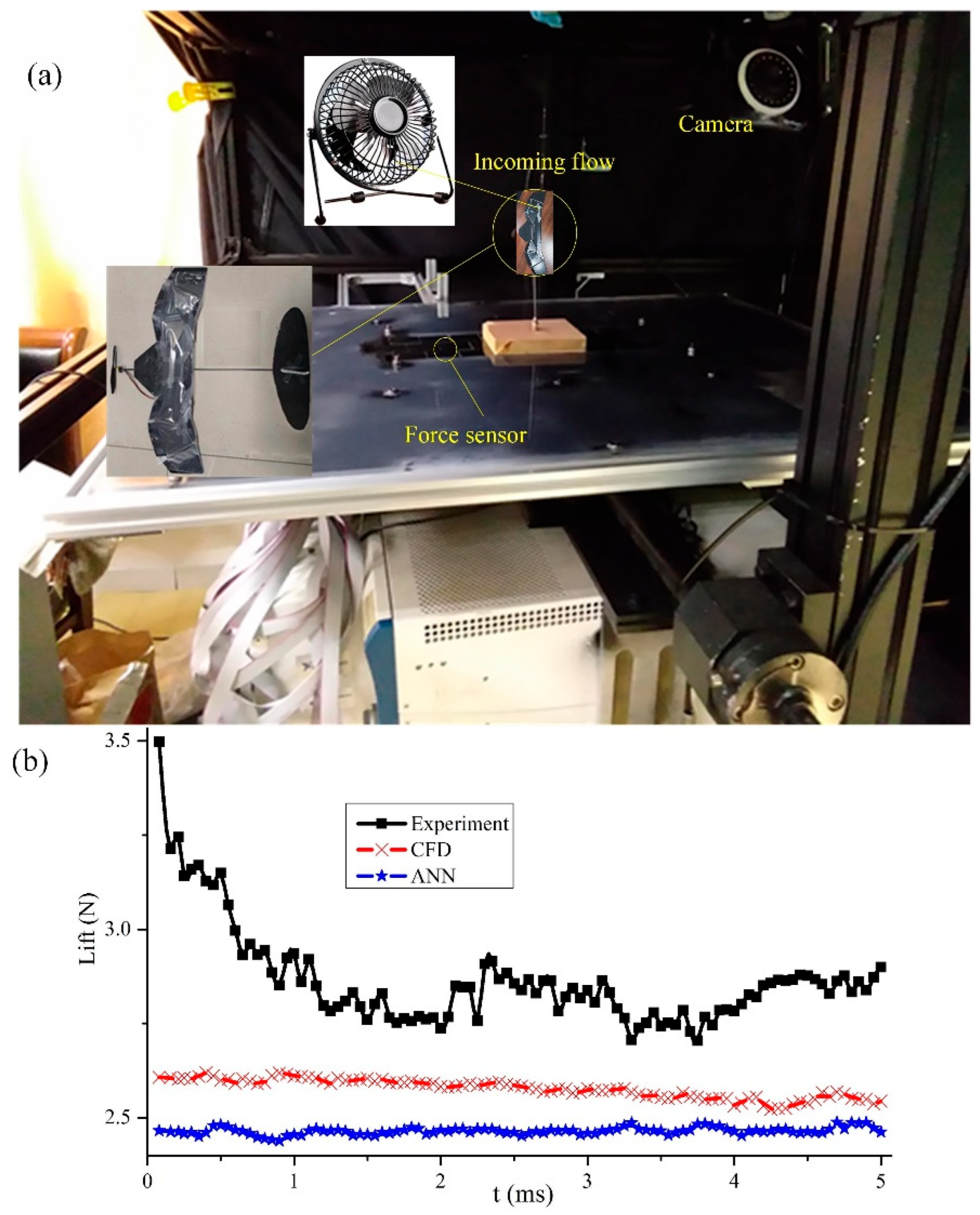
3.3. Aerodynamic Performance of the Deformable Wing MAV
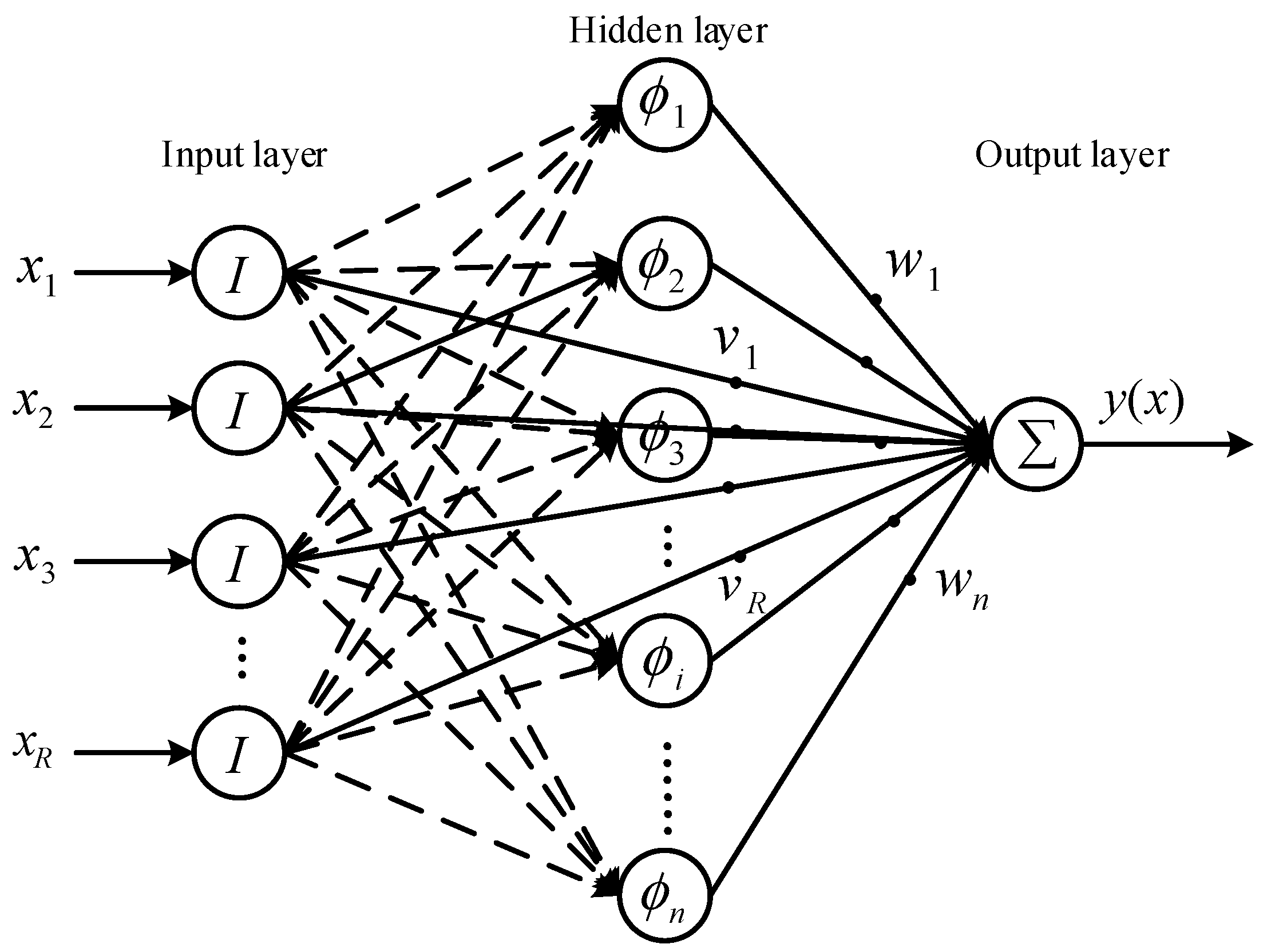
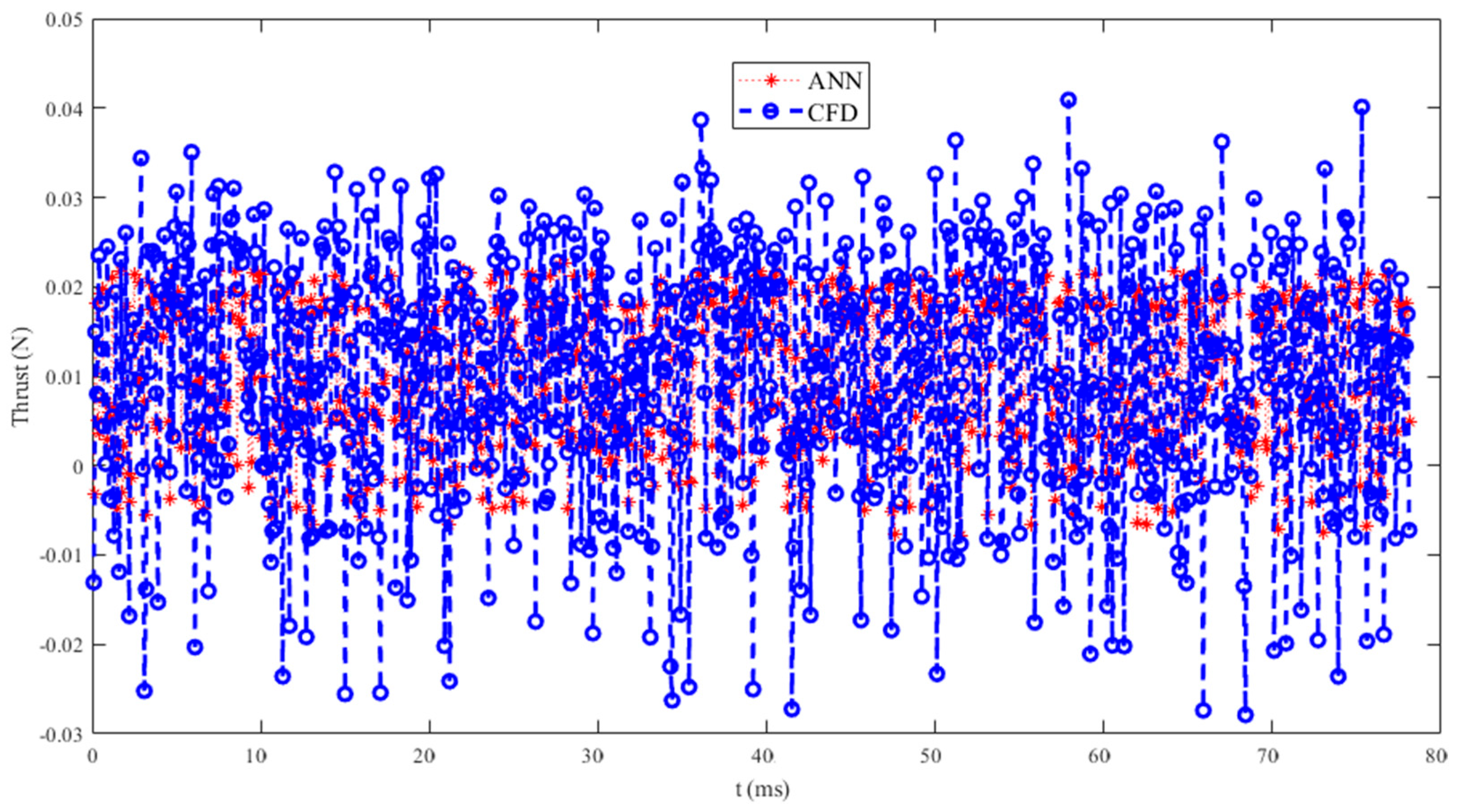
3.4. Aerodynamic Prediction of Biomimetic Deformable Wing MAV
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mintchev, S.; Shintake, J.; Floreano, D. Bioinspired dual-stiffness origami. Sci. Robot. 2018, 3, eaau0275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mintchev, S.; Rivaz, S.D.; Floreano, D. Insect-Inspired Mechanical Resilience for Multicopters. IEEE Robot. Autom. Let. 2017, 2, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumkam, N.; Suratemeekul, N.; Sleesongsom, S. A New Conceptual Design of Twisting Morphing Wing. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornatowski, P.M.; Feroskhan, M.; Stewart, W.J.; Floreano, D. A morphing cargo drone for safe flight in proximity of humans. IEEE Robot. Autom. Let. 2020, 5, 4233–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflüger, J.; Von Langsdorff, M.; Breitsamter, C. Efficacy of an elasto-flexible morphing wing at high lift using fluid-structure-interaction simulations. Front. Aerospace Eng. 2022, 1, 975600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.V.; Floreano, D. A twist of the tail in turning maneuvers of bird-inspired drones. Sci. Robot. 2024, 9, eado3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiters, J.; Kowalczyk, W.; Seidl, T. Simultaneous optimisation of earwig hindwings for flight and folding. Biol. Open 2016, 5, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, F.; Gorb, S.; Wootton, R.J. Elastic joints in dermapteran hind wings: Materials and wing folding. Arthropod Struct. Dev. 2000, 29, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, F.; Chek, J.T.; Tang, H.B. New evidence on the mechanics of wing unfolding in Dermaptera (Insecta). Arthropod Struct. Dev. 2012, 70, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Pérez-de la Fuente, R.; Arimoto, K.; Seong, Y.A.; Aonuma, H.; Niiyama, R.; You, Z. Earwig fan designing: Biomimetic and evolutionary biology applications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 17622–17626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, J.A.; Arrieta, A.F.; Studart, A.R. Bioinspired spring origami. Science 2018, 359, 1386–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heleodoro, R.A.; Rafael, J.A. Dermaptera (Insecta): A guide for hind wing stretching and hind wing preservation. Zootaxa 2020, 4732, zootaxa.4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stowers, A.K.; Lentink, D. Folding in and out: Passive morphing in flapping wings. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2015, 10, 025001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.; Matloff, L.Y.; Stowers, A.K.; Lentink, D. Soft biohybrid morphing wings with feathers underactuated by wrist and finger motion. Sci. Robot. 2020, 5, eaay1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, A.; Chung, S.J.; Hutchinson, S. A biomimetic robotic platform to study flight specializations of bats. Sci. Robot. 2017, 2, eaal2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiguro, R.; Kawasetsu, T.; Motoori, Y.; Paik, J.; Hosoda, K. Earwig-inspired foldable origami wing for micro air vehicle gliding. Front. Robot. AI 2023, 10, 1255666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.; Park, H.C.; Hwang, D.Y.; Byun, D.; Goo, N.S. Mimicking unfolding motion of a beetle hind wing. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2009, 54, 2416–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.; Nguyen, Q.V.; Park, H.C.; Hwang, D.Y.; Buun, D.; Goo, N.S. Improvement of artificial foldable wing models by mimicking the unfolding/folding mechanism of a beetle hind wing. J. Bionic Eng. 2010, 7, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, Q.T.; Argyoganendro, B.W.; Park, H.C. Design and demonstration of insect mimicking foldable artificial wing using four-bar linkage systems. J. Bionic Eng. 2014, 11, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Sun, X.; Du, P.; Sun, J.; Wu, J. Design of a hydraulically-driven bionic folding wing. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. 2018, 82, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zheng, Y.; Shen, H. A wing-flapping robot with a bio-inspired folding mechanism derived from the beetle’s hind wing. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2025, 20, 026016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.V.; Aurecianus, S.; Kang, T.; Park, H.C. KUBeetle-S: An insect-like, tailless, hover-capable robot that can fly with a low-torque control mechanism. Int. J. Micro Air Veh. 2019, 11, 1756829319861371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.V.; Park, H.C. Mechanisms of collision recovery in flying beetles and flapping-wing robots. Science 2020, 370, 1214–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.V.; Park, H.C.; Floreano, D. Passive wing deployment and retraction in beetles and flapping microrobots. Nature 2024, 632, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Li, P.; Song, F.; Stamhuis, E.J.; Sun, J. Design optimization and wind tunnel investigation of a flapping system based on the flapping wing trajectories of a beetle’s hindwings. Comput. Boil. Med. 2022, 140, 105085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zheng, Y. Structural response and mechanical properties of the hind wing of the beetle Protaetia brevitarsis. Microsc. Res. Techniq. 2024, 87, 2013–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Wang, W.; Li, P.; Zhang, Z. Research on Deployable Wings for MAVs Bioinspired by the Hind Wings of the Beetle Protaetia brevitarsis. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, F.; Gorb, S.; Blickhan, R. The function of resilin in beetle wings. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2000, 267, 1375–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, P.; Yan, Y.; Song, F.; Xu, N.; Zhang, Z. Micro-structures, nanomechanical properties and flight performance of three beetles with different folding ratios. Beilstein J. Nanotech. 2022, 13, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Tachi, T.; Niiyama, R.; Kawahara, Y. Design of a beetle inspired deployable wing. In Proceedings of the International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, St. Louis, MI, USA, 6 August 2017; Volume 58189, p. V05BT08A045. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Guo, C.; Ma, Y.; Zheng, Y. Design of bionic foldable wing mimicking the hind wings of the C. buqueti bamboo weevil. J. Mech. Des. 2021, 143, 083303. [Google Scholar]
- Dufour, L.; Owen, K.; Mintchev, S.; Floreano, D. A Drone with Insect-Inspired Folding Wings. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 9–14 October 2016; pp. 1576–1581. [Google Scholar]
- Bras, M.; Warwick, S.; Suleman, A. Aeroelastic evaluation of a flexible high aspect ratio wing UAV: Numerical simulation and experimental flight validation. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2022, 122, 107400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milewski, M.; Wróbel, J.; Kierzkowski, A.; Vališ, D. Experimental and numerical modal analysis of an unmanned aerial vehicle’s composite wing. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2025, 142, 103106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seewoogolam, V.; Prasad, B.; Manral, A.R.; Alarifi, I.M.; Asmatulu, R. Modal analysis and improvement of lightweight wings for micro air vehicle (MAV) applications. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2022, 36, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, N.V.; Le, V.T.; Park, H.C.; Goo, N.S. Modal analysis using a virtual speckle pattern based digital image correlation method: An application for an artificial flapping wing. Exp. Mech. 2022, 1, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasankaran, P.N.; Ward, T.A.; Viyapuri, R.; Johan, M.R. Static strength analysis of dragonfly inspired wings for biomimetic micro aerial vehicles. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2016, 29, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, C. Structural characteristics analysis of the hind wings in a bamboo weevil (Cyrtotrachelus buqueti). IET Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 13, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.; Au, L.T.K.; Phan, H.V.; Park, S.H.; Park, H.C. Effects of wing kinematics, corrugation, and clap-and-fling on aerodynamic efficiency of a hovering insect-inspired flapping-wing micro air vehicle. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2021, 118, 106990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, A.; Jabbari, H.; Zehtabzadeh, H.; Zamiri, M. Investigating Mechanical Response and Structural Integrity of Tubercle Leading Edge under Static Loads. Modelling 2024, 5, 569–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cheng, G.; Chen, G. A New Type Bionic Foldable Wing Design for High Maneuverable Unmanned Aerial Vehicle. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Du, R.; Liu, X.; Bechkoum, K.; Tong, J.; Chen, D. A simulation of the flight characteristics of the deployable hindwings of beetle. J. Bionic Eng. 2017, 14, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.Q.; Byun, D.; Ko, J.H.; Park, H.C.; Kim, M. Numerical investigation of the aerodynamic characteristics of a hovering Coleopteran insect. J. Theor. Biol. 2010, 266, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreelakshmi, K.; Jagadeeswar, K.K. Aerodynamic analysis over unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) using CFD. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Telangana, India, 1 December 2018; Volume 455, No. 1. p. 012044. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X. Numerical Simulations of the Effect of the Asymmetrical Bending of the Hindwings of a Hovering C. buqueti Bamboo Weevil with Respect to the Aerodynamic Characteristics. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Dong, H.; Gai, K. Computational investigation of cicada aerodynamics in forward flight. J. R. Soc. Interface 2015, 102, 20141116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, J.; Wu, H.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Z. Study of aerodynamic noise from UAV rotor in hover and forward flight. Phys. Scripta 2025, 3, 035025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtulus, D.F. Ability to forecast unsteady aerodynamic forces of flapping airfoils by artificial neural network. Neural Comput. Appl. 2009, 18, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, B.; Lin, Y.J.; Lai, Y.H.; Tang, C.H.; Yang, J.T. A Neural Network Approach to Estimate Transient Aerodynamic Properties of a Flapping Wing System. Drones 2022, 6, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Zang, J.; Yan, M.; Zhu, B.; Liu, J. Research on Adaptive Prescribed Performance Control Method Based on Online Aerodynamics Identification. Drones 2023, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitsaz, H.; Amjady, N.; Zareipour, H. Wind power forecast using wavelet neural network trained by improved Clonal selection algorithm. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 89, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, W.; Wang, Z.; Xing, Q.; Zhu, J.; Wang, L.; Qin, K.; Bai, H.; Yu, M.; Dai, Z. The method of multi-camera layout in motion capture system for diverse small animals. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, C. Wing-kinematics measurement and flight modelling of the bamboo weevil C. buqueti. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 14, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Order | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency (HZ) | 8.3839 | 12.0280 | 46.2600 | 49.5910 | 65.0450 | 71.2670 |
| Order | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency (HZ) | 237.24 | 559.89 | 959.84 | 1384.10 | 1832.60 | 2038.40 |
| NN | R2 | MAE | MBE | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thrust | Training set | 0.6025 | 0.0055885 | −2.2751 × 10−5 | 0.0067924 |
| Test set | 0.58188 | 0.005785 | 8.2895 × 10−5 | 0.0069812 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, Y. Design and Simulation of a Bio-Inspired Deployable Mechanism Achieved by Mimicking the Folding Pattern of Beetles’ Hind Wings. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10050320
Chen H, Li X, Wang S, Zhao Y, Zheng Y. Design and Simulation of a Bio-Inspired Deployable Mechanism Achieved by Mimicking the Folding Pattern of Beetles’ Hind Wings. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(5):320. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10050320
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Hongyun, Xin Li, Shujing Wang, Yan Zhao, and Yu Zheng. 2025. "Design and Simulation of a Bio-Inspired Deployable Mechanism Achieved by Mimicking the Folding Pattern of Beetles’ Hind Wings" Biomimetics 10, no. 5: 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10050320
APA StyleChen, H., Li, X., Wang, S., Zhao, Y., & Zheng, Y. (2025). Design and Simulation of a Bio-Inspired Deployable Mechanism Achieved by Mimicking the Folding Pattern of Beetles’ Hind Wings. Biomimetics, 10(5), 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10050320






