Characterization of Muscle Fatigue Degree in Cyclical Movements Based on the High-Frequency Components of sEMG
Abstract
1. Introduction
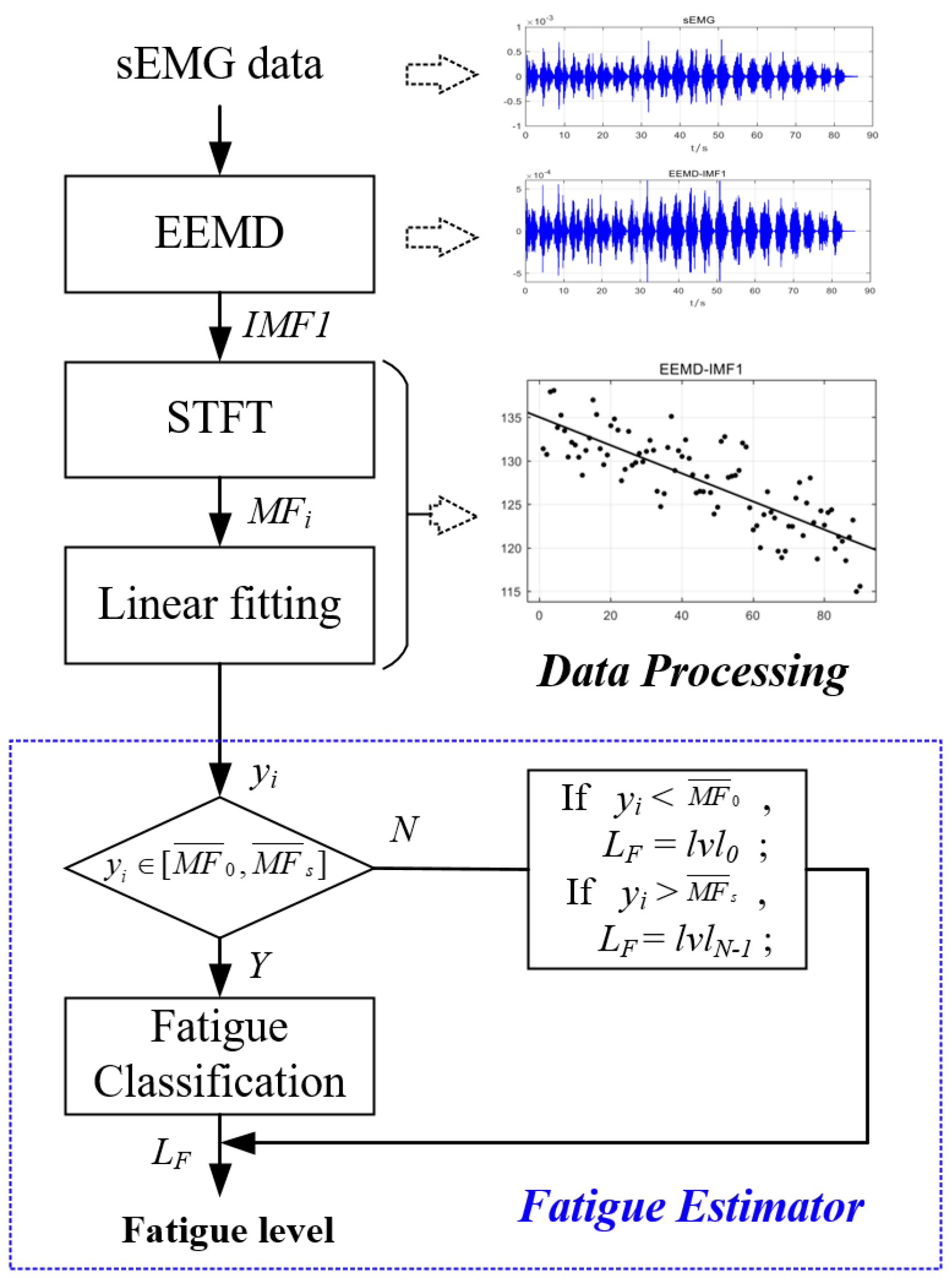
2. Experimental Setup and Signal Preprocessing
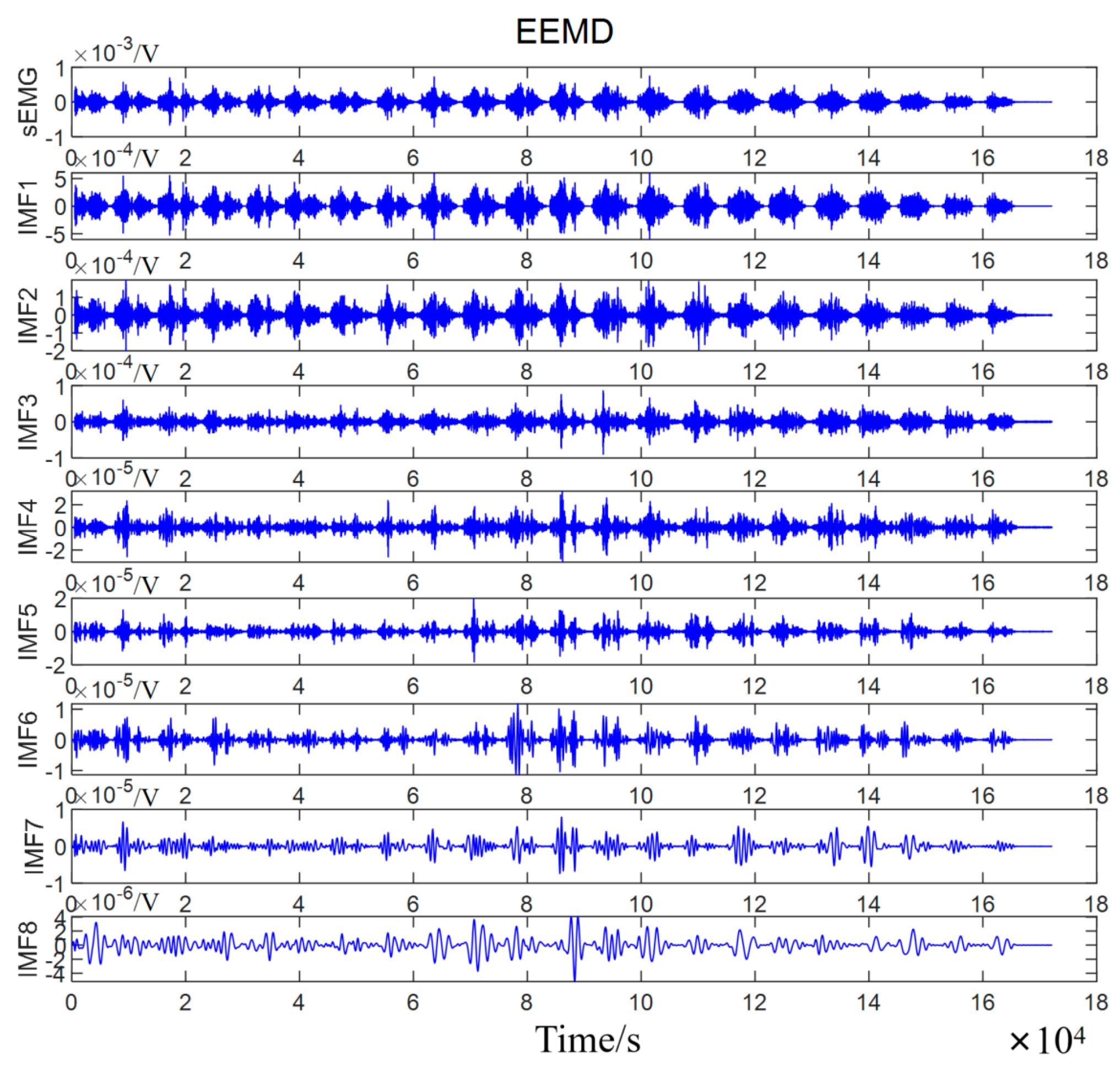
3. sEMG Decomposition by EEMD
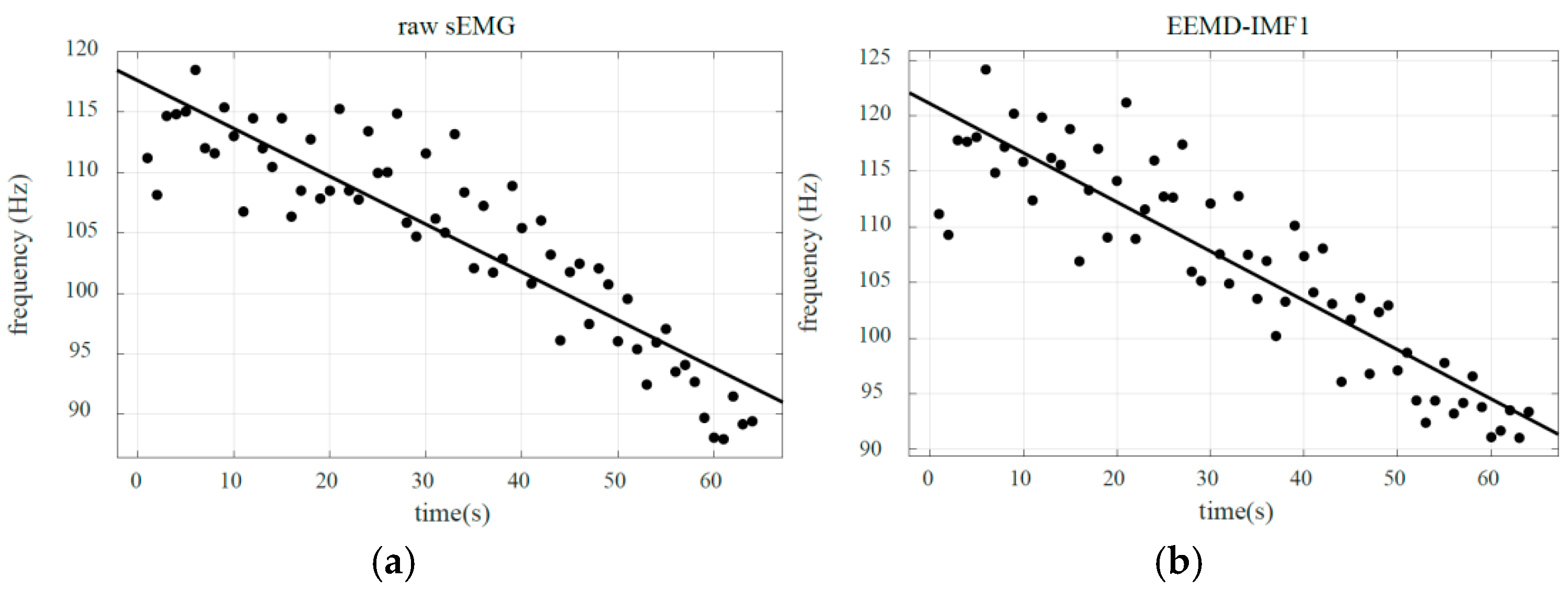
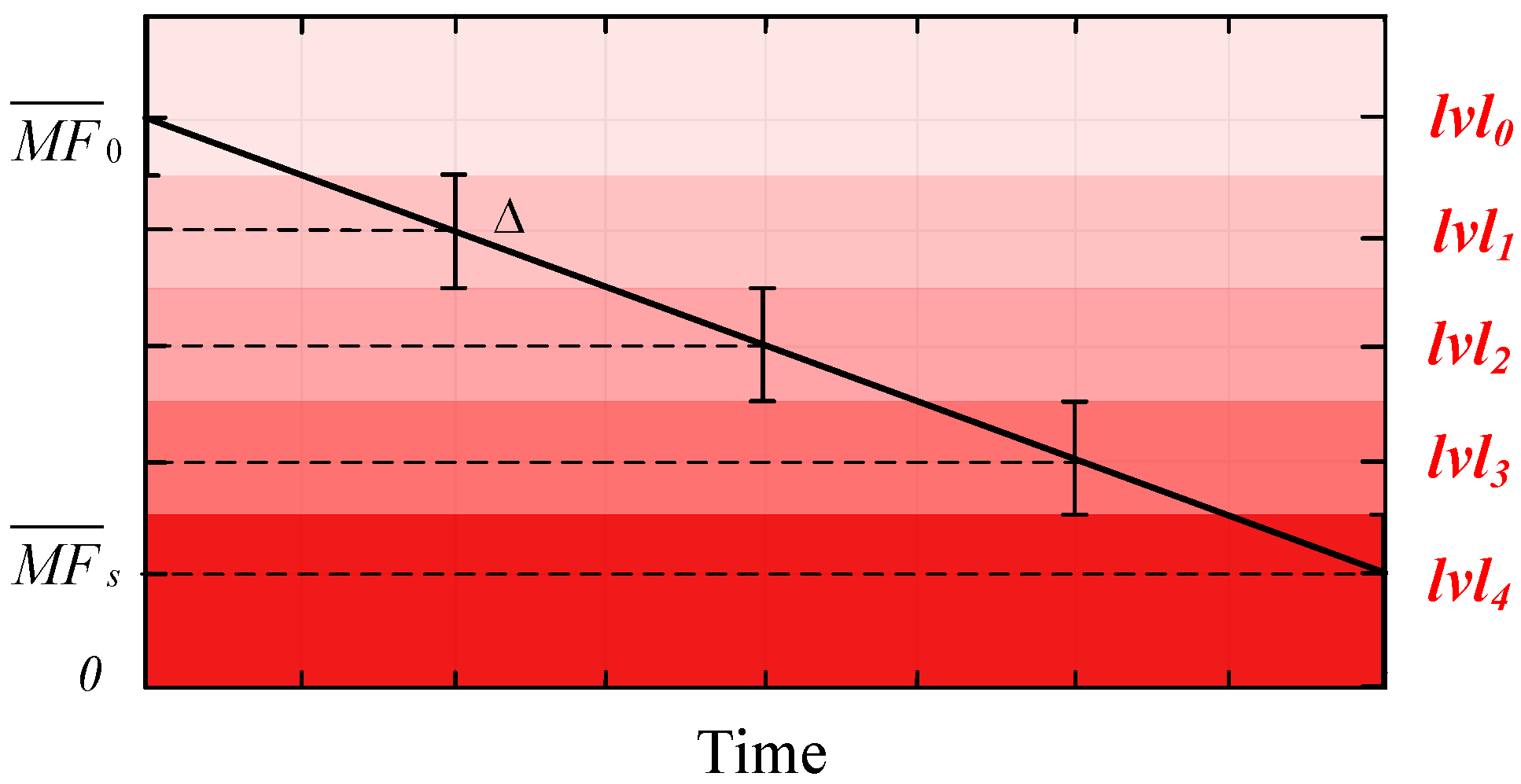
4. High-Frequency Component Linear Fitting
5. Muscle Fatigue Estimator
6. Results
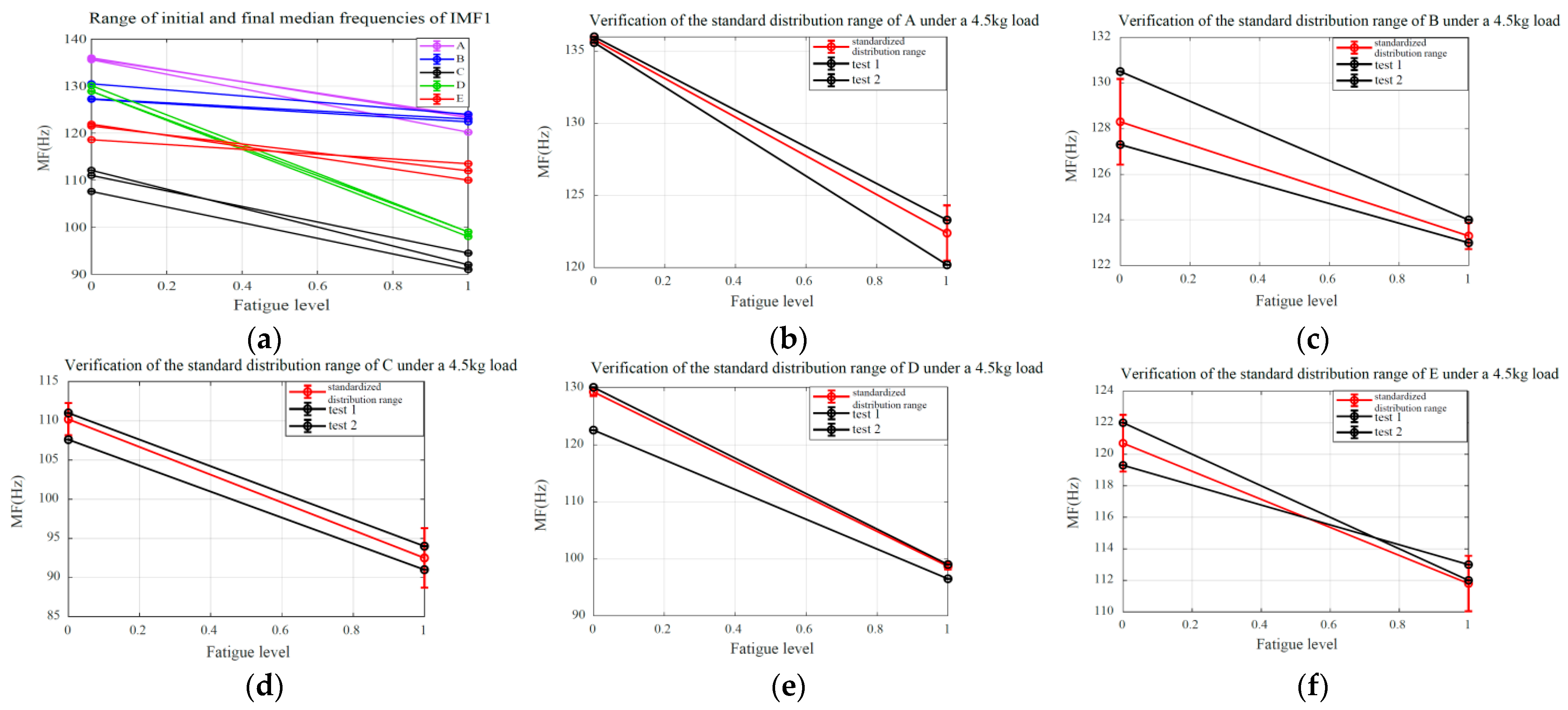
6.1. Validation of SMFDR Consistency
6.2. Fatigue Quantification and Estimation

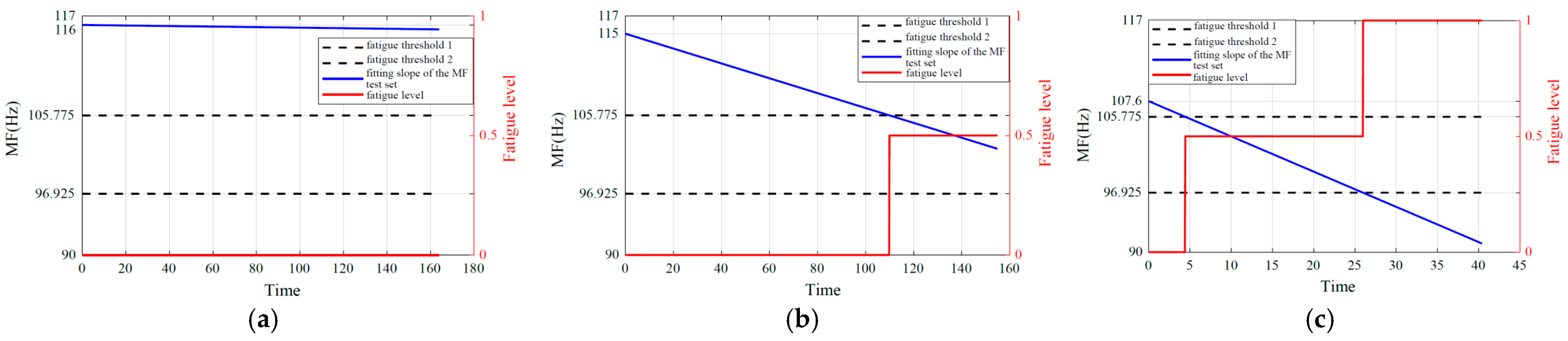

7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
- (1)
- Under identical load conditions, the proposed method exhibits a stable and consistent standardized median frequency distribution range. While variations exist in median frequency ranges under different loads, the overall trends and range differences remain relatively consistent and comparable.
- (2)
- The fatigue estimation methodology presented in this study demonstrates superiority in identifying multiple fatigue level states during periodic motion under consistent load conditions. Furthermore, it proves effective in distinguishing three distinct states (non-fatigue, transition, and fatigue) across varying loads.
- (3)
- The quantitative characterization method of muscle fatigue introduced in this work establishes a foundation for integrating muscle fatigue assessment into the continuous motion analysis of human joints in future studies. This approach provides an effective strategy to compensate for the effects of muscle fatigue during human–robot interaction scenarios.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, N.; Zhou, R.; Krishna, B.; Pradhan, A.; Lee, H.; He, J.; Jiang, N. Non-invasive techniques for muscle fatigue monitoring: A comprehensive survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2024, 56, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Yan, Z.; Guo, S.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Xi, F. Review of sEMG for robot control: Techniques and applications. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrunder, A.D.F.; Huang, Y.-K.; Rodriguez, S.; Rusu, A. A Real-Time Muscle Fatigue Detection System Based on Multi-Frequency EIM and sEMG for Effective NMES. IEEE Sensors J. 2024, 24, 22553–22564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peternel, L.; Fang, C.; Tsagarakis, N.; Ajoudani, A. A selective muscle fatigue management approach to ergonomic human-robot co-manipulation. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2019, 58, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Lu, J.; Wu, Y.; Hu, X.; Yang, H. The latest research progress on bionic artificial hands: A systematic review. Micromachines 2024, 15, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.X.; Zhang, J.H.; Wang, L.F.; Zhang, M.L.; Li, J.Y.; Bao, S.C. A review of the key technologies for sEMG-based human-robot interaction systems. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2020, 62, 102074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkawy, A.N.; Koustoumpardis, P.N. Human–robot interaction: A review and analysis on variable admittance control, safety, and perspectives. Machines 2022, 10, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karheily, S.; Moukadem, A.; Courbot, J.B.; Abdeslam, D.O. sEMG time–frequency features for hand movements classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 210, 118282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghchehli, E.; Kyranou, I.; Dyson, M.; Nazarpour, K. Digital Sensing Systems for Electromyography. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2024, 32, 2826–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yan, J.; Liu, H. Fatigue-Sensitivity Comparison of sEMG and A-Mode Ultrasound based Hand Gesture Recognition. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022, 26, 1718–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behm, D.G.; Alizadeh, S.; Hadjizedah Anvar, S.; Hanlon, C.; Ramsay, E.; Mahmoud, M.M.; Whitten, J.; Fisher, J.P.; Prieske, O.; Chaabene, H.; et al. Non-local muscle fatigue effects on muscle strength, power, and endurance in healthy individuals: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2021, 51, 1893–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Place, N.; Millet, G.Y. Quantification of neuromuscular fatigue: What do we do wrong and why? Sports Med. 2020, 50, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatain, C.; Gruet, M.; Vallier, J.-M.; Ramdani, S. Effects of Nonstationarity on Muscle Force Signals Regularity During a Fatiguing Motor Task. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2020, 28, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Yan, L.; Treebak, J.T.; Li, M.D. Circadian nutrition: Is meal timing an elixir for fatigue? Sci. Bull. 2025, 70, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, M.; Gube, M.; Chaabene, H.; Prieske, O.; Zenon, A.; Broscheid, K.C.; Schega, L.; Husmann, F.; Weippert, M. Fatigue and human performance: An updated framework. Sports Med. 2023, 53, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Singh, A.K. Decoding The Mechanism Behind Exercise-Induced Fatigue. Neuroquantology 2022, 20, 5187–5214. [Google Scholar]
- Debold, E.P.; Westerblad, H. New insights into the cellular and molecular mechanisms of skeletal muscle fatigue: The Marion J. Siegman Award Lectureships. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2024, 327, C946–C958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitts, R.H. Cellular mechanisms of muscle fatigue. Physiol. Rev. 1994, 74, 49–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampichini, S.; Vieira, T.M.; Castiglioni, P.; Merati, G. Complexity analysis of surface electromyography for assessing the myoelectric manifestation of muscle fatigue: A review. Entropy 2020, 22, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousif, H.A.; Zakaria, A.; Rahim, N.A.; Salleh, A.F.; Mahmood, M.; Alfarhan, K.A.; Kamarudin, L.M.; Mamduh, S.M.; Hasan, A.M.; Hussain, M.K. Assessment of muscles fatigue based on surface EMG signals using machine learning and statistical approaches: A review. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 705, 012010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scano, A.; Pirovano, I.; Manunza, M.E.; Spinelli, L.; Contini, D.; Torricelli, A.; Re, R. Sustained fatigue assessment during isometric exercises with time-domain near infrared spectroscopy and surface electromyography signals. Biomed. Opt. Express 2020, 11, 7357–7375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Xi, C.; Ding, L.; Wei, C.; Ren, H.; Law, R.; Dong, H.; Li, X.L. Classification of EMG signals by BFA-optimized GSVCM for diagnosis of fatigue status. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2016, 14, 915–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.R.; Lam, C.K.; Sundaraj, K.; Rahiman, M.H. Fatigue effect on cross-talk in mechanomyography signals of extensor and flexor forearm muscles during maximal voluntary isometric contractions. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2021, 21, 481. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Gao, M.; Guo, M.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jin, X. Vibration comfort assessment of tractor drivers based on sEMG and vibration signals. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2024, 27, 1875–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, S.; McDaid, A.; Lu, Y. Dynamic muscle fatigue assessment using s-EMG technology towards human-centric human-robot collaboration. J. Manuf. Syst. 2023, 68, 508–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Hong, L.; Liu, X.; Dong, B.; Wang, H.; Liu, X. Directed information flow analysis reveals muscle fatigue-related changes in muscle networks and corticomuscular coupling. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 750936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Gong, J.; Chen, B.; Zhang, B.; Luo, F.; Yerabakan, M.O.; Pan, Y.; Hu, B. Use of advanced materials and artificial intelligence in electromyography signal detection and interpretation. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2022, 4, 2200063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariatzadeh, M.; Hafshejani, E.H.; Mitchell, C.J.; Chiao, M.; Grecov, D. Predicting muscle fatigue during dynamic contractions using wavelet analysis of surface electromyography signal. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 43, 428–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, G.; Sun, Y.; Lin, K.; Zhou, Z.; Cai, J. Application of surface electromyography in exercise fatigue: A review. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 893275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yin, K.; Fei, F.; Zhang, K. Surface electromyography–based hand movement recognition using the Gaussian mixture model, multilayer perceptron, and AdaBoost method. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2019, 15, 1550147719846060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Guillou, R.; Schmoll, M.; Sijobert, B.; Lobato Borges, D.; Fachin-Martins, E.; Resende, H.; Pissard-Gibollet, R.; Fattal, C.; Azevedo Coste, C. A novel framework for quantifying accuracy and precision of event detection algorithms in FES-cycling. Sensors 2021, 21, 4571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, B.; Wong, S.F.; Baca, A. Comparison of different time-frequency analyses techniques based on sEMG-signals in table tennis: A case study. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Sport 2018, 17, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pinto-Bernal, M.J.; Cifuentes, C.A.; Perdomo, O.; Rincón-Roncancio, M.; Múnera, M. A data-driven approach to physical fatigue management using wearable sensors to classify four diagnostic fatigue states. Sensors 2021, 21, 6401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmud, M.; Kaiser, M.S.; McGinnity, T.M.; Hussain, A. Deep learning in mining biological data. Cogn. Comput. 2021, 13, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouast, P.V.; Adam, M.T.P.; Chiong, R. Deep learning for human affect recognition: Insights and new developments. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2019, 12, 524–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Guo, Z.; Xia, S.; Zhu, L. Intention recognition of aerial target based on deep learning. Evol. Intell. 2024, 17, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Fu, Y. Human action recognition and prediction: A survey. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2022, 130, 1366–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, S.; Sun, Y. A muscle fatigue classification model based on LSTM and improved wavelet packet threshold. Sensors 2021, 21, 6369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tao, Q.; Wu, B. Dynamic muscle fatigue state recognition based on deep learning fusion model. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 95079–95091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, M.; Bouyer, L.; Roy, J.S.; Campeau-Lecours, A. Reducing noise, artifacts and interference in single-channel EMG signals: A review. Sensors 2023, 23, 2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise-assisted data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2009, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.S.; Lin, Y.T.; Huang, C.C.; Chen, Y.C. Fatigue-related modulation of low-frequency common drive to motor units. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 120, 1305–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, D.C. Precision spectral peak frequency measurement using a window leakage ratio function. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2015, 54, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yi, W.; Kirubarajan, T.; Kong, L. An efficient recursive multiframe track-before-detect algorithm. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2017, 54, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.H.; Chang, K.M.; Cheng, D.C. The progression of muscle fatigue during exercise estimation with the aid of high-frequency component parameters derived from ensemble empirical mode decomposition. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2014, 18, 1647–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoukos, A.; Brown, L.E.; Terzis, G.; Wilk, M.; Zajac, A.; Bogdanis, G.C. Changes in EMG and movement velocity during a set to failure against different loads in the bench press exercise. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2021, 31, 2071–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Cai, S.; Li, G.; Chen, Y.; Ma, K.; Xie, L. sEMG-based detection of compensation caused by fatigue during rehabilitation therapy: A pilot study. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 127055–127065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.I.; Lim, K.W.; Lai, Y.H.; Chen, C.S.; Chou, L.W. Effects of muscle fatigue and recovery on the neuromuscular network after an intermittent handgrip fatigue task: Spectral analysis of electroencephalography and electromyography signals. Sensors 2023, 23, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Sheng, X.; Zhu, X. Assessment of muscle fatigue based on motor unit firing, muscular vibration and oxygenation via hybrid mini-grid sEMG, MMG, and NIRS sensing. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raizen, D.M.; Mullington, J.; Anaclet, C.; Clarke, G.; Critchley, H.; Dantzer, R.; Davis, R.; Drew, K.L.; Fessel, J.; Fuller, P.M.; et al. Beyond the symptom: The biology of fatigue. Sleep 2023, 46, zsad069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cáceres-Diego, B.; Alcaraz, P.E.; Marín-Pagán, C. Neuromuscular Responses to 5 K Time Trial Load Carried by Spanish Army Marines. Sports 2025, 13, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, P.; Cureton, K.; Collins, M. Sex difference in muscular strength in equally-trained men and women. Ergonomics 1987, 30, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, L.; Degens, H.; Li, M.; Salviati, L.; Lee, Y.I.; Thompson, W.; Kirkland, J.L.; Sandri, M. Sarcopenia: Aging-related loss of muscle mass and function. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 427–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, M.I.; Jones, A.M.; Blackwell, J.R.; Bailey, S.J.; Wylie, L.J.; McDonagh, S.T.; Thompson, C.; Kelly, J.; Sumners, P.; Mileva, K.N.; et al. Muscle metabolic and neuromuscular determinants of fatigue during cycling in different exercise intensity domains. J. Appl. Physiol. 2017, 122, 446–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Age (year) | Height (cm) | Weight (kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 24 | 170 | 55 |
| B | 26 | 175 | 65 |
| C | 24 | 180 | 60 |
| D | 23 | 180 | 56 |
| E | 25 | 173 | 57 |
| A (Hz/s) | mf0 (Hz) | mfS (Hz) | R | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| sEMG | −0.111 (0.0137) | 132.2 (0.231) | 121.7 (1.537) | 0.777 (0.065) |
| IMF1 | −0.141 (0.0184) | 135.8 (0.200) | 122.4 (1.916) | 0.760 (0.077) |
| IMF2 | −0.077 (0.0147) | 84.3 (0.753) | 76.9 (0.666) | 0.608 (0.088) |
| IMF3 | −0.078 (0.0198) | 47.8 (0.811) | 40.4 (1.100) | 0.564 (0.061) |
| IMF4 | −0.031 (0.0118) | 24.5 (0.622) | 21.6 (0.611) | 0.356 (0.124) |
| Subjects | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw | IMF1 | Raw | IMF1 | |
| A | 132.2 (0.231) | 135.8 (0.200) | 121.7 (1.537) | 122.4 (1.916) |
| B | 124.1 (1.270) | 128.3 (1.877) | 120.8 (0.289) | 123.3 (0.577) |
| C | 108.5 (2.566) | 110.2 (2.348) | 89.7 (0.577) | 92.5 (1.803) |
| D | 127 (0.520) | 129.3 (0.6928) | 102 (7.000) | 98.7 (0.5774) |
| E | 117.6 (1.365) | 120.7 (1.801) | 109.3 (1.528) | 111.8 (1.756) |
| Subjects | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw | IMF1 | Raw | IMF1 | |
| A | 127.3 (0.850) | 129.9 (1.102) | 126.9 (0.520) | 129.2 (0.173) |
| B | 127.4 (0.850) | 130.5 (0.625) | 127.7 (0.265) | 130.6 (0.321) |
| C | 118 (2.261) | 120 (3.639) | 118 (2.454) | 119.5 (3.897) |
| D | 125.2 (1.137) | 128.2 (1.179) | 125.5 (0.755) | 128.2 (0.608) |
| E | 123.3 (0.458) | 125.5 (0.839) | 124.1 (0.723) | 126.4 (1.365) |
| Subjects | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw | IMF1 | Raw | IMF1 | |
| A | 125.4 (0.907) | 128.5 (0.625) | 125.2 (0.709) | 127.1 (0.902) |
| B | 117.7 (2.818) | 120.6 (3.219) | 118.8 (5.052) | 120.6 (6.577) |
| C | 115.2 (2.558) | 115.9 (2.060) | 101.8 (3.928) | 102.3 (3.799) |
| D | 127.6 (1.069) | 130.6 (1.106) | 128.1 (0.400) | 130.9 (0.208) |
| E | 115.5 (2.250) | 117.3 (3.119) | 118.4 (2.138) | 121.4 (2.601) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, K.; Sun, Y.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L. Characterization of Muscle Fatigue Degree in Cyclical Movements Based on the High-Frequency Components of sEMG. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10050291
Li K, Sun Y, Li J, Li H, Zhang J, Wang L. Characterization of Muscle Fatigue Degree in Cyclical Movements Based on the High-Frequency Components of sEMG. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(5):291. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10050291
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Kexiang, Ye Sun, Jiayi Li, Hui Li, Jianhua Zhang, and Li Wang. 2025. "Characterization of Muscle Fatigue Degree in Cyclical Movements Based on the High-Frequency Components of sEMG" Biomimetics 10, no. 5: 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10050291
APA StyleLi, K., Sun, Y., Li, J., Li, H., Zhang, J., & Wang, L. (2025). Characterization of Muscle Fatigue Degree in Cyclical Movements Based on the High-Frequency Components of sEMG. Biomimetics, 10(5), 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10050291





