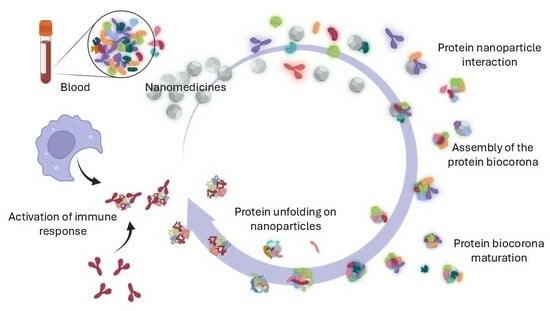
The Protein Corona Paradox: Challenges in Achieving True Biomimetics in Nanomedicines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Challenges in Understanding and Investigating the NP Corona
2.1. Formation and Basic Structure of the Biocorna
2.2. The Dynamic Nature of the NP-Bio Interface
2.3. Challenges in the Study of the Biocorona
2.4. (Bio)Chemical Components of the Biocorona in Nanomedicines
3. The Influence of Nanomaterial Properties on the Protein Corona
3.1. The Shape
3.2. The Size
3.3. The Hydrophobicity
3.4. The Charge
3.5. The Surface Roughness
3.6. The Chirality
| Features | Impact of the Protein Corona | References |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Spherical NPs have the smallest surface. Rod/discoidal shapes have more surface area = stronger interactions. | [15,45] |
| Size | Affect the protein composition. Protein unfolding in small NPs. | [50,53,54,55,56,57] |
| Hydrophobicity | Stabilization of the protein corona but risk aggregation, reducing bioavailability. Causes protein denaturation. | [19,58,59,60,61,62,64,70] |
| Roughness | Surface roughness decreases protein absorption. | [64,66] |
| Charge | Positive charge enhances cellular uptake, and negative charge reduces uptake and prolongs circulation time. | [48] |
| Chirality | Influences protein adsorption, corona dynamics and biological outcomes. | [60,61,62,68,69] |
4. Physicochemical Properties of the Local Milieu on Biocorona Formation
4.1. Ionic Strength
4.2. Local pH
4.3. Temperature
4.4. Time in Protein Biocorona Formation: The Vroman Effect
4.5. Reducing Conditions
4.6. Fluidics, Shear Stress
| Features | Impact of the Protein Corona | References |
|---|---|---|
| Ionic strength | Influences electrostatic interactions and van der Waals forces between NPs and biomolecules | [74,75] |
| pH | Affect NP surface charge and ionize functional groups on proteins, modifying adsorption | [31,50,74] |
| Temperature | Influence protein folding and corona dynamics. Lower temperatures reduce molecular motion, stabilizing the protein corona | [31,34,77] |
| Time | Changes in protein composition due to the Vroman effect | [78,79] |
| Redox state | Structural and stability changes in the protein corona | [82,83] |
| Fluidics | Flow dynamics (e.g., blood flow) create more heterogeneous PC compared to static conditions | [85,86] |
5. The Molecular Changes Occurring in Proteins of the Corona
5.1. Protein Structural Changes Induced by Nanoparticles
5.2. Factors That Trigger Protein Conformational Changes
| Protein Type | Denaturation Evidence | References |
|---|---|---|
| Serum Albumin | Rapid conformational changes at both secondary and tertiary levels. Unfolding reported for SiO2, TiO2 and AuNRs | [53,54,55,57] |
| IgG | PS NP-induced structural and functional changes leading to aggregation. Activation of macrophage responses | [95,98,99,100,101] |
| Fibrinogen | Unfolding induced by negatively charged poly(acrylic acid)-conjugated Au NPs leading to aggregation | [99,102,103,104] |
| Transferrin | NPs surface chirality determines orientation and conformation | [69] |
| Lysozyme | SiO2 NPs trigger secondary structure alterations and reduced activity | [96,98,102,103,104] |
| Trypsin | Silica grades and temperatures impact its structure and function. | [105] |
| Beta-lactoglobulin | SiO2 NPs size and pH-dependent structural changes. Decreased alpha-helical content | [106] |
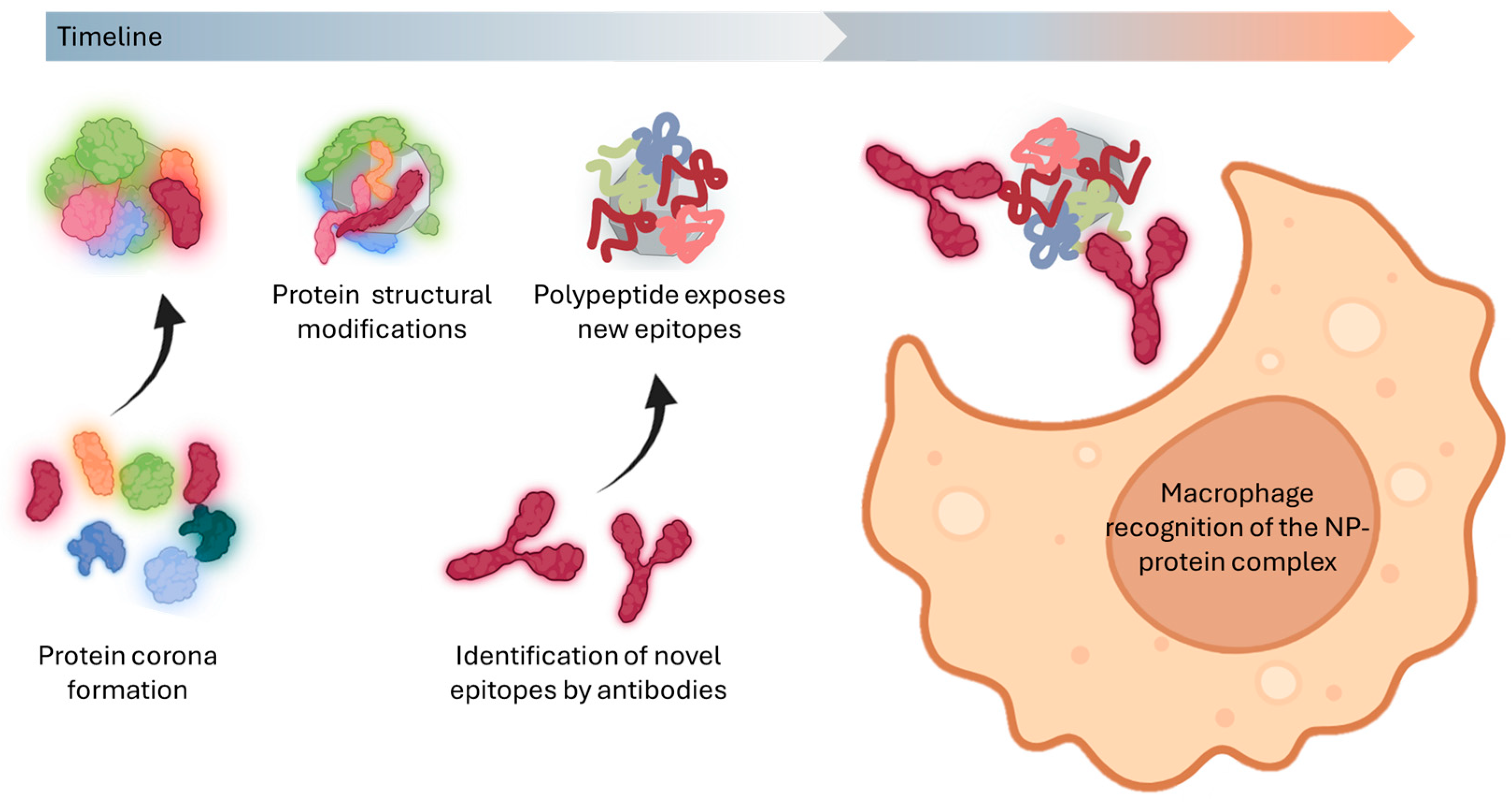
5.3. Consequences of Conformational Changes After Protein Denaturation
6. The Everchanging Nature of Protein Coronas: A Barrier to Effective Nanomedicine
6.1. Beyond the Blood: Diverse Coronas in the Human Body
6.2. The Impact of Individual Variability on Nanoparticle Protein Corona
6.3. The Need for Engineering Predictable Protein Coronas for Improved Nanomedicine Efficacy
7. Discussion and Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Monopoli, M.P.; Åberg, C.; Salvati, A.; Dawson, K.A. Biomolecular Coronas Provide the Biological Identity of Nanosized Materials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, K.A.; Yan, Y. Current Understanding of Biological Identity at the Nanoscale and Future Prospects. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panico, S.; Capolla, S.; Bozzer, S.; Toffoli, G.; Dal Bo, M.; Macor, P. Biological Features of Nanoparticles: Protein Corona Formation and Interaction with the Immune System. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papafilippou, L.; Nicolaou, A.; Kendall, A.C.; Camacho-Muñoz, D.; Hadjidemetriou, M. The Lipidomic Profile of the Nanoparticle-Biomolecule Corona Reflects the Diversity of Plasma Lipids. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 11038–11051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padín-González, E.; Navarro-Palomares, E.; Valdivia, L.; Iturrioz-Rodriguez, N.; Correa-Duarte, M.A.; Valiente, R.; Fanarraga, M.L. A Custom-Made Functionalization Method to Control the Biological Identity of Nanomaterials. Nanomedicine 2020, 102268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caracciolo, G.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Mahmoudi, M. Biological Identity of Nanoparticles In Vivo: Clinical Implications of the Protein Corona. Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenzer, S.; Docter, D.; Kuharev, J.; Musyanovych, A.; Fetz, V.; Hecht, R.; Schlenk, F.; Fischer, D.; Kiouptsi, K.; Reinhardt, C.; et al. Rapid Formation of Plasma Protein Corona Critically Affects Nanoparticle Pathophysiology. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natte, K.; Friedrich, J.F.; Wohlrab, S.; Lutzki, J.; von Klitzing, R.; Österle, W.; Orts-Gil, G. Impact of Polymer Shell on the Formation and Time Evolution of Nanoparticle-Protein Corona. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 104, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjidemetriou, M.; Kostarelos, K. Nanomedicine: Evolution of the Nanoparticle Corona. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 288–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casals, E.; Pfaller, T.; Duschl, A.; Oostingh, G.J.; Puntes, V. Time Evolution of the Nanoparticle Protein Corona. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3623–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Wang, G.; Griffin, J.I.; Brenneman, B.; Banda, N.K.; Holers, V.M.; Backos, D.S.; Wu, L.; Moghimi, S.M.; Simberg, D. Complement Proteins Bind to Nanoparticle Protein Corona and Undergo Dynamic Exchange in Vivo. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Chen, B.; He, M.; Hu, B. Composition of Intracellular Protein Corona around Nanoparticles during Internalization. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisani, C.; Gaillard, J.C.; Dorandeu, C.; Charnay, C.; Guari, Y.; Chopineau, J.; Devoisselle, J.M.; Armengaud, J.; Prat, O. Experimental Separation Steps Influence the Protein Content of Corona around Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 5769–5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vroman, L. Effect of Adsorbed Proteins on the Wettability of Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Solids. Nature 1962, 196, 476–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannahan, J. The Biocorona: A Challenge for the Biomedical Application of Nanoparticles. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2017, 6, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundqvist, M.; Stigler, J.; Elia, G.; Lynch, I.; Cedervall, T.; Dawson, K.A. Nanoparticle Size and Surface Properties Determine the Protein Corona with Possible Implications for Biological Impacts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 14265–14270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, E.; Abolmaali, S.S.; Dehshahri, A.; Mousavi Shaegh, S.A.; Azarpira, N.; Tamaddon, A.M. Navigating the Intricate In-Vivo Journey of Lipid Nanoparticles Tailored for the Targeted Delivery of RNA Therapeutics: A Quality-by-Design Approach. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilaseca, P.; Dawson, K.A.; Franzese, G. Understanding and Modulating the Competitive Surface-Adsorption of Proteins through Coarse-Grained Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 6978–6985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Zhao, L.; Guo, C.; Yan, B.; Su, G. Regulating Protein Corona Formation and Dynamic Protein Exchange by Controlling Nanoparticle Hydrophobicity. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Rehman, M.; Wang, Y.-F.; Guo, S. Protein Corona of Nanoparticles: Isolation and Analysis. Chem. Bio Eng. 2024, 1, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docter, D.; Distler, U.; Storck, W.; Kuharev, J.; Wünsch, D.; Hahlbrock, A.; Knauer, S.K.; Tenzer, S.; Stauber, R.H. Quantitative Profiling of the Protein Coronas That Form around Nanoparticles. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 2030–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhmert, L.; Voß, L.; Stock, V.; Braeuning, A.; Lampen, A.; Sieg, H. Isolation Methods for Particle Protein Corona Complexes from Protein-Rich Matrices. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 563–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strojan, K.; Leonardi, A.; Bregar, V.B.; Križaj, I.; Svete, J.; Pavlin, M. Dispersion of Nanoparticles in Different Media Importantly Determines the Composition of Their Protein Corona. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudi, M. The Need for Improved Methodology in Protein Corona Analysis. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Chetwynd, A.J.; Thorn, J.A.; Lynch, I.; Ramautar, R. Understanding the Significance of Sample Preparation in Studies of the Nanoparticle Metabolite Corona. ACS Meas. Sci. Au 2022, 2, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Cao, M.; Chetwynd, A.J.; Faserl, K.; Abdolahpur Monikh, F.; Zhang, W.; Ramautar, R.; Ellis, L.J.A.; Davoudi, H.H.; Reilly, K.; et al. Analysis of Nanomaterial Biocoronas in Biological and Environmental Surroundings. Nat. Protoc. 2024, 19, 3000–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winzen, S.; Schoettler, S.; Baier, G.; Rosenauer, C.; Mailaender, V.; Landfester, K.; Mohr, K. Complementary Analysis of the Hard and Soft Protein Corona: Sample Preparation Critically Effects Corona Composition. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 2992–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, J.; Prozeller, D.; Ghazaryan, A.; Kokkinopoulou, M.; Mailänder, V.; Morsbach, S.; Landfester, K. Beyond the Protein Corona—Lipids Matter for Biological Response of Nanocarriers. Acta Biomater. 2018, 71, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, T.; Wang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Qiu, L.; Liu, J.; Song, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, J.; et al. Cholesterol Modulates the Physiological Response to Nanoparticles by Changing the Composition of Protein Corona. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2023, 18, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, T.; Bernfur, K.; Vilanova, M.; Cedervall, T. Understanding the Lipid and Protein Corona Formation on Different Sized Polymeric Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarca-Cabrera, L.; Milinovic, O.; Heitler, V.; Rühmann, B.; Kudermann, J.; Kube, M.; Dietz, H.; Sieber, V.; Berensmeier, S.; Fraga-García, P. Biocorona on Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in a Complex Biotechnological Environment: Analysis of Proteins, Lipids, and Carbohydrates. Small Sci. 2023, 3, 2300064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Barbera, G.; Capriotti, A.L.; Caracciolo, G.; Cavaliere, C.; Cerrato, A.; Montone, C.M.; Piovesana, S.; Pozzi, D.; Quagliarini, E.; Laganà, A. A Comprehensive Analysis of Liposomal Biomolecular Corona upon Human Plasma Incubation: The Evolution towards the Lipid Corona. Talanta 2020, 209, 120487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Nilsson, R.; Lázaro-Ibáñez, E.; Duàn, H.; Miliotis, T.; Strimfors, M.; Lerche, M.; Salgado Ribeiro, A.R.; Ulander, J.; Lindén, D.; et al. Multiomics Analysis of Naturally Efficacious Lipid Nanoparticle Coronas Reveals High-Density Lipoprotein Is Necessary for Their Function. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Hevia, L.; Saramiforoshani, M.; Monge, J.; Iturrioz-Rodríguez, N.; Padín-González, E.; González, F.; González-Legarreta, L.; González, J.; Fanarraga, M.L. The Unpredictable Carbon Nanotube Biocorona and a Functionalization Method to Prevent Protein Biofouling. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelescu, D.G. Molecular Modeling of the Carbohydrate Corona Formation on a Polyvinyl Chloride Nanoparticle and Its Impact on the Adhesion to Lipid Bilayers. J. Chem. Phys. 2024, 160, 144901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liu, J. Comprehensive Screen of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles for DNA Adsorption, Fluorescence Quenching, and Anion Discrimination. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 24833–24838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Hossaini Nasr, S.; Chen, D.; Zhang, X.; Sun, L.; Huang, X.; Qian, C. MiRNA Extraction from Cell-Free Biofluid Using Protein Corona Formed around Carboxyl Magnetic Nanoparticles. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, L.; Warrington, J.; Rogan, J.; Rothwell, D.G.; Brady, G.; Dive, C.; Kostarelos, K.; Hadjidemetriou, M. The Biomolecule Corona of Lipid Nanoparticles Contains Circulating Cell-Free DNA. Nanoscale Horiz. 2020, 5, 1476–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahan, P.B. Circulating Nucleic Acids in Plasma and Serum: Diagnosis and Prognosis in Cancer. EPMA J. 2010, 1, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docter, D.; Westmeier, D.; Markiewicz, M.; Stolte, S.; Knauer, S.K.; Stauber, R.H. The Nanoparticle Biomolecule Corona: Lessons Learned—Challenge Accepted? Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 6094–6121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.-H.; Yu, J.; Lee, T.G.; Choi, S.-J. Protein Food Matrix–ZnO Nanoparticle Interactions Affect Protein Conformation, but May Not Be Biological Responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Zhang, L.; Deng, F.; Fang, W.; Wang, R.; Liu, X.; Guo, L.; Rayner, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Comparative Proteomics Reveal Fundamental Structural and Functional Differences between the Two Progeny Phenotypes of a Baculovirus. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connell, D.J.; Bombelli, F.B.; Pitek, A.S.; Monopoli, M.P.; Cahill, D.J.; Dawson, K.A. Characterization of the Bionano Interface and Mapping Extrinsic Interactions of the Corona of Nanomaterials. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 15268–15276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, A.E.; Mädler, L.; Velegol, D.; Xia, T.; Hoek, E.M.; Somasundaran, P.; Klaessig, F.; Castranova, V.; Thompson, M. Understanding Biophysicochemical Interactions at the Nano–Bio Interface. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albanese, A.; Tang, P.S.; Chan, W.C.W. The Effect of Nanoparticle Size, Shape, and Surface Chemistry on Biological Systems. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morbidelli, M.; Papini, E.; Tavano, R. Essential Protocols for Decoding the Composition and the Functional Effects of the Nanoparticle Protein Corona. Front. Nanotechnol. 2024, 6, 1500567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Álvarez, R.; Hadjidemetriou, M.; Sánchez-Iglesias, A.; Liz-Marzán, L.M.; Kostarelos, K. In Vivo Formation of Protein Corona on Gold Nanoparticles. The Effect of Their Size and Shape. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenzer, S.; Docter, D.; Rosfa, S.; Wlodarski, A.; Kuharev, J.; Rekik, A.; Knauer, S.K.; Bantz, C.; Nawroth, T.; Bier, C.; et al. Nanoparticle Size Is a Critical Physicochemical Determinant of the Human Blood Plasma Corona: A Comprehensive Quantitative Proteomic Analysis. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 7155–7167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Kim, H.-J.; Go, M.-R.; Bae, S.-H.; Choi, S.-J. ZnO Interactions with Biomatrices: Effect of Particle Size on ZnO-Protein Corona. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Huang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Shi, J.; Fu, F.; Huang, Y.; Pan, X.; Wu, C. Impact of Particle Size and PH on Protein Corona Formation of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 1030–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portilla, Y.; Mellid, S.; Paradela, A.; Ramos-Fernandez, A.; Daviu, N.; Sanz-Ortega, L.; Pérez-Yagüe, S.; Morales, M.P.; Barber, D.F. Iron Oxide Nanoparticle Coatings Dictate Cell Outcomes despite the Influence of Protein Coronas. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 7924–7944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glancy, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.L.Y.; Ouyang, B.; Ohta, S.; Chan, W.C.W. Characterizing the Protein Corona of Sub-10 nm Nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2019, 304, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satzer, P.; Svec, F.; Sekot, G.; Jungbauer, A. Protein Adsorption onto Nanoparticles Induces Conformational Changes: Particle Size Dependency, Kinetics, and Mechanisms. Eng. Life Sci. 2016, 16, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Qin, M.; Meng, W.; Cao, Y.; Wang, W. How Do Proteins Unfold upon Adsorption on Nanoparticle Surfaces? Langmuir 2012, 28, 12779–12787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudunkotuwa, I.A.; Grassian, V.H. Histidine Adsorption on TiO2 Nanoparticles: An Integrated Spectroscopic, Thermodynamic, and Molecular-Based Approach toward Understanding Nano-Bio Interactions. Langmuir 2014, 30, 8751–8760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walkey, C.D.; Chan, W.C.W. Understanding and Controlling the Interaction of Nanomaterials with Proteins in a Physiological Environment. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2780–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Medina, S.; Kisley, L.; Tauzin, L.J.; Hoggard, A.; Shuang, B.; Indrasekara, A.S.D.S.; Chen, S.; Wang, L.-Y.; Derry, P.J.; Liopo, A.; et al. Adsorption and Unfolding of a Single Protein Triggers Nanoparticle Aggregation. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 2103–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pustulka, S.M.; Ling, K.; Pish, S.L.; Champion, J.A. Protein Nanoparticle Charge and Hydrophobicity Govern Protein Corona and Macrophage Uptake. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 48284–48295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.V.; Mehta, K.K.; Worley, K.; Dordick, J.S.; Kane, R.S.; Wan, L.Q. Carbon Nanotube-Induced Loss of Multicellular Chirality on Micropatterned Substrate Is Mediated by Oxidative Stress. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 2196–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Cacioppo, M.; Megahed, S.; Arcudi, F.; Đorđević, L.; Zhu, D.; Schulz, F.; Prato, M.; Parak, W.J.; Feliu, N. Influence of the Chirality of Carbon Nanodots on Their Interaction with Proteins and Cells. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, F.; Geng, F.; Zhao, X.; Liu, R.; Liu, Q.S.; Zhou, Q.; Jiang, G. Chirality of Gold Nanocluster Affects Its Interaction with Coagulation Factor XII. NanoImpact 2021, 22, 100321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Qiao, Z.; Zhong, W.; Liang, K.; Jiang, X.; Shang, L. Chirality-Dependent Dynamic Evolution of the Protein Corona on the Surface of Quantum Dots. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 44147–44157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saptarshi, S.R.; Duschl, A.; Lopata, A.L.; Duschl, A.; Lopata, A.L. Interaction of Nanoparticles with Proteins: Relation to Bio-Reactivity of the Nanoparticle. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2013, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampado, R.; Crotti, S.; Caliceti, P.; Pucciarelli, S.; Agostini, M. Recent Advances in Understanding the Protein Corona of Nanoparticles and in the Formulation of “Stealthy” Nanomaterials. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 517204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihlasalo, S.; Auranen, L.; Hänninen, P.; Härmä, H. Method for Estimation of Protein Isoelectric Point. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 8253–8258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piloni, A.; Wong, C.K.; Chen, F.; Lord, M.; Walther, A.; Stenzel, M.H. Surface Roughness Influences the Protein Corona Formation of Glycosylated Nanoparticles and Alter Their Cellular Uptake. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 23259–23267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotov, N.A.; Liz-Marzán, L.M.; Weiss, P.S. Chiral Nanostructures: New Twists. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 12457–12460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Zhang, D.; Yang, Q.; Liu, T.; Lei, R.; Zhu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, C. Probing Adsorption Behaviors of BSA onto Chiral Surfaces of Nanoparticles. Small 2018, 14, 1703982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Lei, R.; Zhu, S.F.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, C. Chiral Surface of Nanoparticles Determines the Orientation of Adsorbed Transferrin and Its Interaction with Receptors. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 4606–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H. Hydrodynamics and Aggregation of Nanoparticles with Protein Corona: Effects of Protein Concentration and Ionic Strength. Small 2024, 20, 2403913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, R.; Langhammer, C.; Cedervall, T. Real-Time in Situ Analysis of Biocorona Formation and Evolution on Silica Nanoparticles in Defined and Complex Biological Environments. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 3620–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, N.; Hedberg, J.; Odnevall Wallinder, I.; Blomberg, E. Influence of Biocorona Formation on the Transformation and Dissolution of Cobalt Nanoparticles under Physiological Conditions. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 21778–21791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Marets, C.; Boudon, J.; Millot, N.; Saviot, L.; Maurizi, L. In Vivoprotein Corona on Nanoparticles: Does the Control of All Material Parameters Orient the Biological Behavior? Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 1209–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bychkova, A.V.; Lopukhova, M.V.; Wasserman, L.A.; Degtyarev, Y.N.; Kovarski, A.L.; Chakraborti, S.; Mitkevich, V.A. The Influence of PH and Ionic Strength on the Interactions between Human Serum Albumin and Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 194, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantarutti, C.; Hunashal, Y.; La Rosa, C.; Condorelli, M.; Giorgetti, S.; Bellotti, V.; Fogolari, F.; Esposito, G. The Corona of Protein–Gold Nanoparticle Systems: The Role of Ionic Strength. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2022, 24, 1630–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H. Molecular Modeling of Protein Corona Formation and Its Interactions with Nanoparticles and Cell Membranes for Nanomedicine Applications. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasoli, E. Protein Corona: Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde of Nanomedicine. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2021, 68, 1139–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, H.; Vogler, E.A. Volumetric Interpretation of Protein Adsorption: Competition from Mixtures and the Vroman Effect. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 405–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsh, S.L.; McKenzie, D.R.; Nosworthy, N.J.; Denman, J.A.; Sezerman, O.U.; Bilek, M.M.M. The Vroman Effect: Competitive Protein Exchange with Dynamic Multilayer Protein Aggregates. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 103, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huetz, P.; Ball, V.; Voegel, J.-C.; Schaaf, P. Exchange Kinetics for a Heterogeneous Protein System on a Solid Surface. Langmuir 1995, 11, 3145–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Et Taouil, A.; Brun, E.; Duchambon, P.; Blouquit, Y.; Gilles, M.; Maisonhaute, E.; Sicard-Roselli, C. How Protein Structure Affects Redox Reactivity: Example of Human Centrin 2. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 24493–24498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Xu, P.; Ding, H.-M.; Yu, Y.-S.; Huo, D.; Ma, Y.-Q. Tailoring the Component of Protein Corona via Simple Chemistry. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashiri, G.; Padilla, M.S.; Swingle, K.L.; Shepherd, S.J.; Mitchell, M.J.; Wang, K. Nanoparticle Protein Corona: From Structure and Function to Therapeutic Targeting. Lab Chip 2023, 23, 1432–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Sanden, N.; Paun, R.A.; Yitayew, M.Y.; Boyadjian, O.; Tabrizian, M. An Investigation of the Effect of the Protein Corona on the Cellular Uptake of Nanoliposomes under Flow Conditions Using Quartz Crystal Microgravimetry with Dissipation. Nanoscale Adv. 2025, 7, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Crespy, D.; Landfester, K.; Jiang, S. In Situ Characterization Techniques of Protein Corona around Nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 10827–10851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palchetti, S.; Pozzi, D.; Capriotti, A.L.; Barbera, G.L.; Chiozzi, R.Z.; Digiacomo, L.; Peruzzi, G.; Caracciolo, G.; Laganà, A. Influence of Dynamic Flow Environment on Nanoparticle-Protein Corona: From Protein Patterns to Uptake in Cancer Cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 153, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyano, D.F.; Ray, M.; Rotello, V.M. Nanoparticle-Protein Interactions: Water Is the Key. MRS Bull. 2014, 39, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Yin, D.; Tang, C.; He, E.; Zou, L.; Peng, Q. The Protein Corona and Its Effects on Nanoparticle-Based Drug Delivery Systems. Acta Biomater. 2021, 129, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podila, R.; Vedantam, P.; Ke, P.C.; Brown, J.M.; Rao, A.M. Evidence for Charge-Transfer-Induced Conformational Changes in Carbon Nanostructure-Protein Corona. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 22098–22103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cukalevski, R.; Lundqvist, M.; Oslakovic, C.; Dahlbäck, B.; Linse, S.; Cedervall, T. Structural Changes in Apolipoproteins Bound to Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2011, 27, 14360–14369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavendra, A.J.; Alsaleh, N.; Brown, J.M.; Podila, R. Charge-Transfer Interactions Induce Surface Dependent Conformational Changes in Apolipoprotein Biocorona. Biointerphases 2017, 12, 02D402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbir, R.; Jiménez, R.R.; Martín-Rapún, R.; Strasser, V.; Domazet Jurašin, D.; Dabelić, S.; De La Fuente, J.M.; Vinković Vrček, I. Interaction of Differently Sized, Shaped, and Functionalized Silver and Gold Nanoparticles with Glycosylated versus Nonglycosylated Transferrin. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 27533–27547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagliani, R.; Gatto, F.; Bardi, G. Protein Adsorption: A Feasible Method for Nanoparticle Functionalization? Materials 2019, 12, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemetov, A.A.; Nabiev, I.; Sukhanova, A. Molecular Interaction of Proteins and Peptides with Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 4585–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Seabrook, S.A.; Epa, V.C.; Kurabayashi, K.; Barnard, A.S.; Winkler, D.A.; Kirby, J.K.; Ke, P.C. Contrasting Effects of Nanoparticle Binding on Protein Denaturation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 22069–22078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vertegel, A.A.; Siegel, R.W.; Dordick, J.S. Silica Nanoparticle Size Influences the Structure and Enzymatic Activity of Adsorbed Lysozyme. Langmuir 2004, 20, 6800–6807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadepalli, S.; Wang, Z.; Slocik, J.; Naik, R.R.; Singamaneni, S. Effect of Size and Curvature on the Enzyme Activity of Bionanoconjugates. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 15666–15672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlkönig, A.; Huet, J.; Looze, Y.; Wintjens, R. Structural Relationships in the Lysozyme Superfamily: Significant Evidence for Glycoside Hydrolase Signature Motifs. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cukalevski, R.; Ferreira, S.A.; Dunning, C.J.; Berggård, T.; Cedervall, T. IgG and Fibrinogen Driven Nanoparticle Aggregation. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 2733–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prozeller, D.; Rosenauer, C.; Morsbach, S.; Landfester, K. Immunoglobulins on the Surface of Differently Charged Polymer Nanoparticles. Biointerphases 2020, 15, 031009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemie, M.N.; Bright, R.; Nguyen, N.H.; Truong, V.K.; Palms, D.; Hayball, J.D.; Vasilev, K. Surface Chemistry Induced IgG Unfolding and Modulation of Immune Responses. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 50507–50523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.J.; Liang, M.; Monteiro, M.; Toth, I.; Minchin, R.F. Nanoparticle-Induced Unfolding of Fibrinogen Promotes Mac-1 Receptor Activation and Inflammation. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollman, J.M.; Pandi, L.; Sawaya, M.R.; Riley, M.; Doolittle, R.F. Crystal Structure of Human Fibrinogen. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 3877–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan, A.; Riviere, J.E.; Monteiro-Riviere, N.A. Gold and Silver Nanoparticle Interactions with Human Proteins: Impact and Implications in Biocorona Formation. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 2075–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phue, W.H.; Liu, M.; Xu, K.; Srinivasan, D.; Ismail, A.; George, S. A Comparative Analysis of Different Grades of Silica Particles and Temperature Variants of Food-Grade Silica Nanoparticles for Their Physicochemical Properties and Effect on Trypsin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 12264–12272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrovolskaia, M.A.; Patri, A.K.; Zheng, J.; Clogston, J.D.; Ayub, N.; Aggarwal, P.; Neun, B.W.; Hall, J.B.; McNeil, S.E. Interaction of Colloidal Gold Nanoparticles with Human Blood: Effects on Particle Size and Analysis of Plasma Protein Binding Profiles. Nanomedicine 2009, 5, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawan, C.; Lim, M.; Marquis, C.P.; Amal, R. Nanoparticle-Protein Corona Complexes Govern the Biological Fates and Functions of Nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 2060–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, I.; Dawson, K.A.; Linse, S. Detecting Cryptic Epitopes Created by Nanoparticles. Sci. STKE 2006, 327, pe14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Park, S.J.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Kwon, S.; Jung, Y.J.; Khang, D. Unfolded Protein Corona Surrounding Nanotubes Influence the Innate and Adaptive Immune System. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2004979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talab, M.J.; Valizadeh, A.; Tahershamsi, Z.; Housaindokht, M.R.; Ranjbar, B. Personalized Biocorona as Disease Biomarker: The Challenges and Opportunities. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Gen. Subj. 2024, 1868, 130724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Matteis, V. Exposure to Inorganic Nanoparticles: Routes of Entry, Immune Response, Biodistribution and In Vitro/In Vivo Toxicity Evaluation. Toxics 2017, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konduru, N.V.; Molina, R.M.; Swami, A.; Damiani, F.; Pyrgiotakis, G.; Lin, P.; Andreozzi, P.; Donaghey, T.C.; Demokritou, P.; Krol, S.; et al. Protein Corona: Implications for Nanoparticle Interactions with Pulmonary Cells. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2017, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydn, A.; Sipahi, H.; Charehsaz, M. Nanoparticles Toxicity and Their Routes of Exposures. In Recent Advances in Novel Drug Carrier Systems; InTech: Montreuil, France, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phue, W.H.; Srinivasan, D.; Hameed, A.; Yaylayan, V.; George, S. Food Grade Silica Nanoparticles Cause Non-competitive Type Inhibition of Human Salivary A-amylase Because of Surface Interaction. Nano Sel. 2021, 2, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- António, M.; Lima, T.; Vitorino, R.; Daniel-da-Silva, A.L. Interaction of Colloidal Gold Nanoparticles with Urine and Saliva Biofluids: An Exploratory Study. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhu, G.; Lu, B.; Qian, Z.; Peng, Q. Protein Corona Formed in the Gastrointestinal Tract and Its Impacts on Oral Delivery of Nanoparticles. Med. Res. Rev. 2021, 41, 1835–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarniak, N.; Kamińska, J.; Matowicka-Karna, J.; Koper-Lenkiewicz, O. Cerebrospinal Fluid–Basic Concepts Review. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; He, X.; Xia, X.; Gong, T.; Wang, L.; Gao, H. Unmasking CSF Protein Corona: Effect on Targeting Capacity of Nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2021, 333, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshed, N.; Rennie, C.; Faria, M.; Collins-Praino, L.; Care, A. Protein Coronas Derived from Cerebrospinal Fluid Enhance the Interactions Between Nanoparticles and Brain Cells. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Straten, D.; Sork, H.; van de Schepop, L.; Frunt, R.; Ezzat, K.; Schiffelers, R.M. Biofluid Specific Protein Coronas Affect Lipid Nanoparticle Behavior in Vitro. J. Control. Release 2024, 373, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gossmann, R.; Fahrländer, E.; Hummel, M.; Mulac, D.; Brockmeyer, J.; Langer, K. Comparative Examination of Adsorption of Serum Proteins on HSA- and PLGA-Based Nanoparticles Using SDS–PAGE and LC–MS. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 93, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisneros, E.P.; Morse, B.A.; Savk, A.; Malik, K.; Peppas, N.A.; Lanier, O.L. The Role of Patient-Specific Variables in Protein Corona Formation and Therapeutic Efficacy in Nanomedicine. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczyk, D.; Bombelli, F.B.; Monopoli, M.P.; Lynch, I.; Dawson, K.A. What the Cell “Sees”: In Bionanoscience. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 5761–5768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mayordomo, N.M.; Zatarain-Beraza, A.; Valerio, F.; Álvarez-Méndez, V.; Turegano, P.; Herranz-García, L.; López de Aguileta, A.; Cattani, N.; Álvarez-Alonso, A.; Fanarraga, M.L. The Protein Corona Paradox: Challenges in Achieving True Biomimetics in Nanomedicines. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 276. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10050276
Mayordomo NM, Zatarain-Beraza A, Valerio F, Álvarez-Méndez V, Turegano P, Herranz-García L, López de Aguileta A, Cattani N, Álvarez-Alonso A, Fanarraga ML. The Protein Corona Paradox: Challenges in Achieving True Biomimetics in Nanomedicines. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(5):276. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10050276
Chicago/Turabian StyleMayordomo, Nicole M., Ane Zatarain-Beraza, Fabio Valerio, Victoria Álvarez-Méndez, Paula Turegano, Lucía Herranz-García, Amaia López de Aguileta, Nicolas Cattani, Ana Álvarez-Alonso, and Mónica L. Fanarraga. 2025. "The Protein Corona Paradox: Challenges in Achieving True Biomimetics in Nanomedicines" Biomimetics 10, no. 5: 276. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10050276
APA StyleMayordomo, N. M., Zatarain-Beraza, A., Valerio, F., Álvarez-Méndez, V., Turegano, P., Herranz-García, L., López de Aguileta, A., Cattani, N., Álvarez-Alonso, A., & Fanarraga, M. L. (2025). The Protein Corona Paradox: Challenges in Achieving True Biomimetics in Nanomedicines. Biomimetics, 10(5), 276. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10050276