IBKA-MSM: A Novel Multimodal Fake News Detection Model Based on Improved Swarm Intelligence Optimization Algorithm, Loop-Verified Semantic Alignment and Confidence-Aware Fusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- We propose an Improved Black-Winged Kite Algorithm (IBKA) for cross-modal feature generation and optimization. The algorithm introduces an adaptive step-size update strategy, elite memory with opposition-based disturbance, Gaussian-based local refinement, and population diversity monitoring with re-initialization, ensuring a dynamic balance between global exploration and local exploitation.
- (2)
- We design a Modality Generation and Loop Verification mechanism (MGLV) that achieves cyclic cross-modal semantic validation through semantic reconstruction and consistency constraints. By reinforcing semantic coherence during the closed-loop generation–verification process, MGLV ensures the alignability and interpretability of representations within a shared semantic space, effectively mitigating semantic drift caused by cross-modal discrepancies.
- (3)
- We construct a Semantic Confidence Matrix and Modality-Cross Interaction mechanism (SCM-MCI) for adaptive confidence modeling and deep semantic interaction across modalities. The SCM module dynamically evaluates modality reliability during fusion based on semantic confidence distribution and adjusts contribution weights accordingly. On this basis, the MCI module introduces a bidirectional semantic propagation strategy to enhance semantic complementarity and information consistency, enabling highly correlated and stable fused representations in the shared semantic space.
- (4)
- All the proposed enhancement modules are incorporated into the IBKA-MSM framework and comprehensively evaluated on a multimodal fake news detection benchmark. The experimental findings confirm notable improvements across various performance indicators, demonstrating the effectiveness and robustness of the framework in semantic alignment, modality interaction, and cross-modal feature representation.
2. Related Work
2.1. Single-Modal Fake News Detection
2.2. Multimodal Fake News Detection
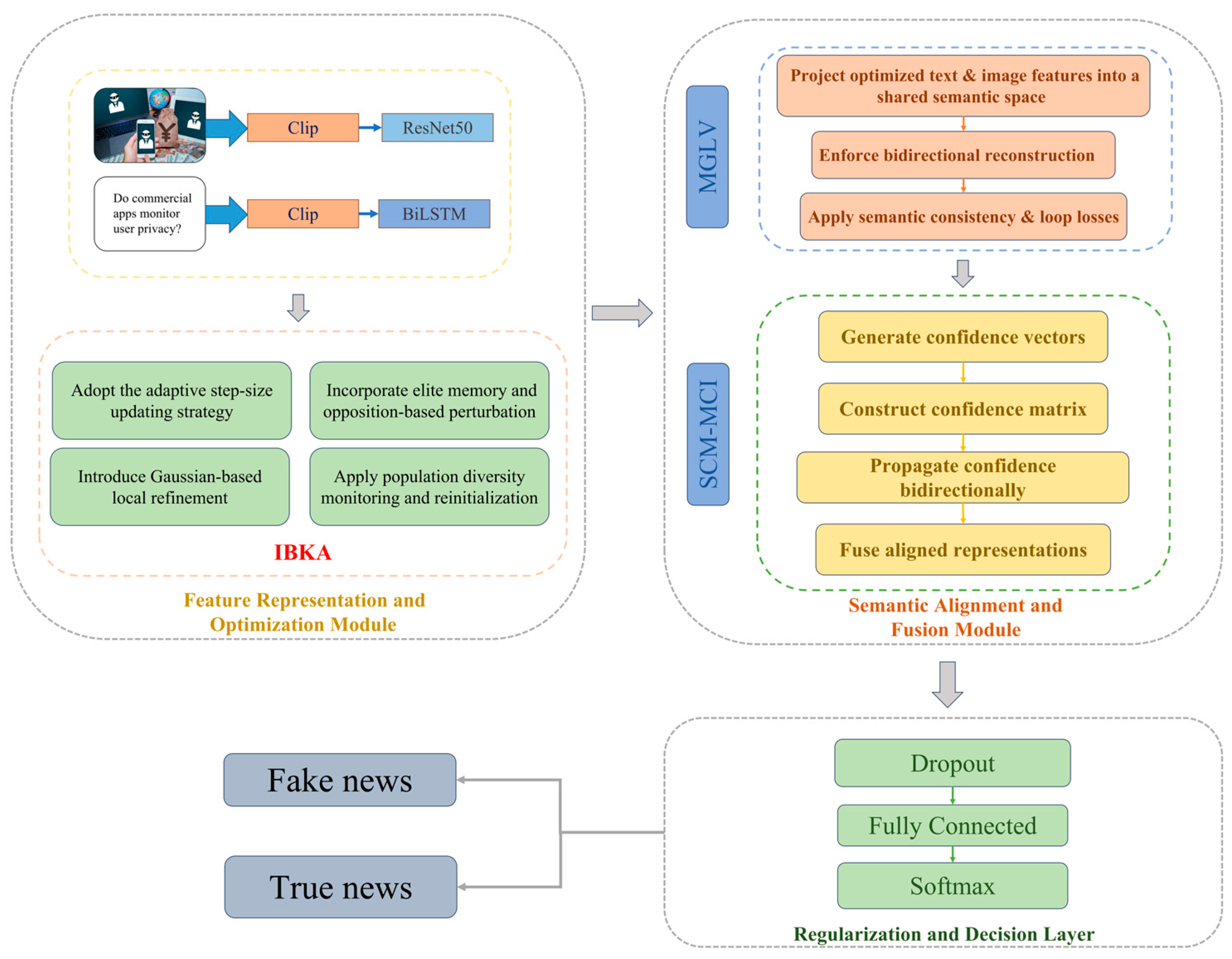
3. Method
3.1. Feature Extraction
3.1.1. Text Feature Extraction
3.1.2. Image Feature Extraction
3.2. Black-Winged Kite Algorithm (BKA)
3.2.1. Encircling the Prey
3.2.2. Tracking the Prey
3.2.3. Attacking the Prey
3.3. Improved Black-Winged Kite Algorithm (IBKA)
3.3.1. Introduce Dynamic Step-Length Regulation Mechanism
| Algorithm 1: Adaptive Step-Size Update Strategy |
| Input: Maximum/minimum step sizes , ; maximum iteration ; current iteration ; population ; best prey position . |
| Output: Updated population matrix |
| 1 Compute adaptive step size: |
| 2 For each individual in the population do |
| 3 Generate random coefficients . |
| 4 Select a random individual from the population |
| 5 Compute search direction: |
| 6 Update position: |
| 7 (Optional) Apply boundary control to |
| 8 End for |
| End Procedure: Return updated population . |
3.3.2. Integrate Elite Memory and Opposition-Based Perturbation Strategy
Elite Memory Mechanism
Opposition-Based Perturbation Strategy
3.3.3. Apply Local Gaussian Refinement Strategy
3.3.4. Implement Diversity Monitoring and Reinitialization Strategy
| Algorithm 2: Diversity Monitoring and Reinitialization Strategy in IBKA |
| Input: Population size ; individual positions ; bounds , ; scaling factor ; Tent map. |
| Output: Updated population |
| 1 Compute the population mean: |
| 2 Compute the diversity index: |
| 3 Compute minimum diversity threshold: |
| 4 If diversity is too low → Trigger reinitialization. |
| 5 For each individual do |
| 6 Generate . |
| 7 Compute : |
| 8 : |
| 9 : |
| 10 End for |
| 11 Else |
| 12 , for all |
| 13 End if |
| End Procedure: Return updated population . |
3.4. Unified Modality Space and Semantic Alignment
3.4.1. Modality Generation and Loop Verification Mechanism (MGLV)
3.4.2. Semantic Confidence Matrix and Modality-Cross Interaction (SCM-MCI)
4. Experimental Analysis
4.1. Data Collection
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Experimental Settings
4.4. Multimodal Comparison Experiments
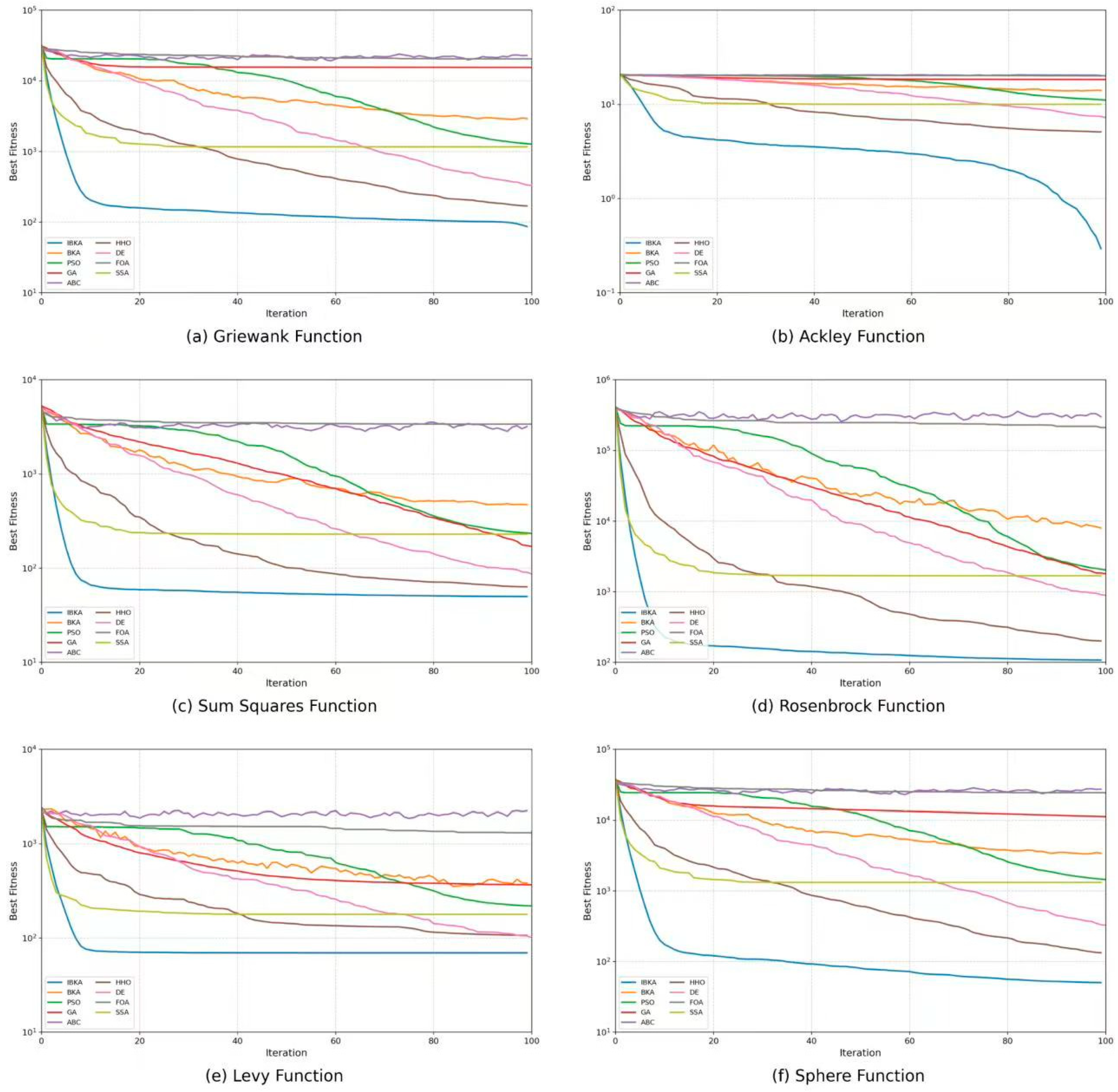
4.5. Comparative Experiments of Meta-Heuristic Algorithms
4.6. Convergence Performance Analysis of the IBKA
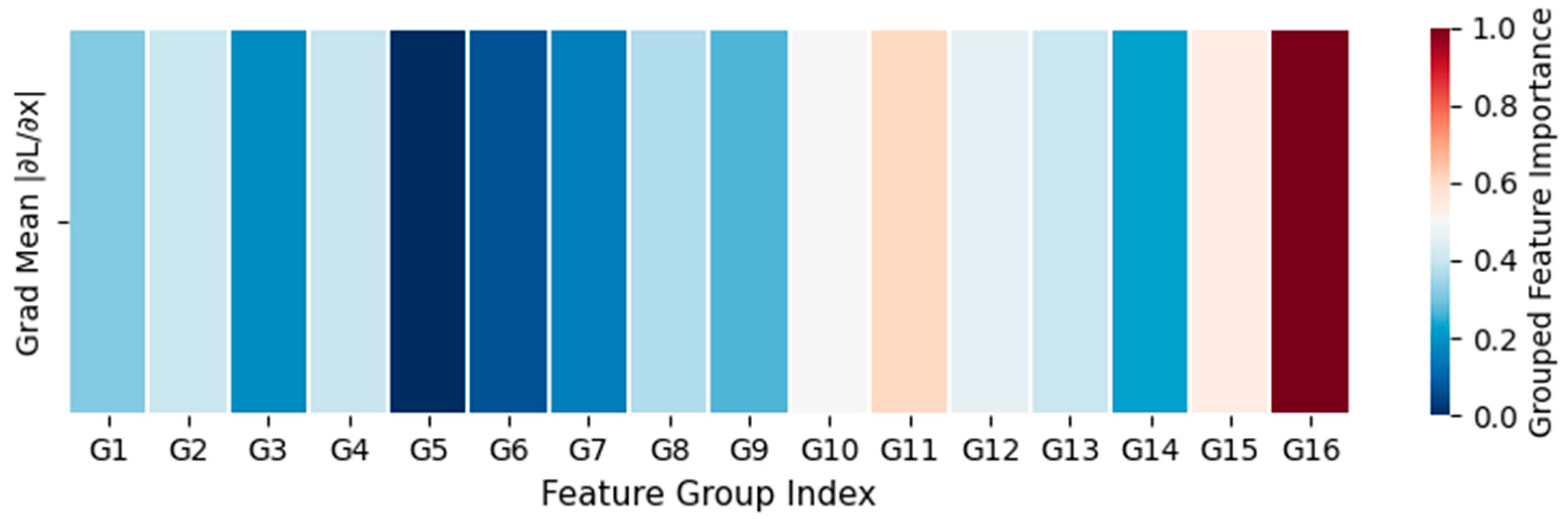
4.7. Model Interpretability and Feature Visualization Analysis
5. Conclusions and Future Work
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, L.; Wei, S.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, B. Deep learning for fake news detection: A comprehensive survey. AI Open 2022, 3, 133–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufchi, S.; Yadav, A.; Ahmed, T. A comprehensive survey of multimodal fake news detection techniques: Advances, challenges, and opportunities. Int. J. Multimed. Inf. Retr. 2023, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdali, S.; Shaham, S.; Krishnamachari, B. Multi-modal misinformation detection: Approaches, challenges and opportunities. arXiv Preprint 2022, arXiv:2203.13883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Ma, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, M. Multi-modal transformer for fake news detection. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2023, 20, 14699–14717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Huang, M.; Hu, Z.; Cai, S.; Zhou, T. Multimodal Fake News Detection with Contrastive Learning and Optimal Transport. Front. Comput. Sci. 2024, 6, 1473457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, G.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Dai, J.; Qu, J.; Li, X. MSBKA: A multi-strategy improved black-winged kite algorithm for feature selection of natural disaster tweets classification. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, W.-C.; Hu, X.-X.; Qiu, L.; Zang, H.-F. Black-winged Kite Algorithm: A nature-inspired meta-heuristic for solving benchmark functions and engineering problems. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Shen, B. A novel swarm intelligence optimization approach: Sparrow search algorithm. Syst. Sci. Control Eng. 2020, 8, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Lewis, A. The whale optimization algorithm. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2016, 95, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Rosas, V.; Kleinberg, B.; Lefevre, A.; Mihalcea, R. Automatic detection of fake news. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Computational Linguistics (COLING 2018), Santa Fe, NM, USA, 20–26 August 2018; pp. 3391–3401. [Google Scholar]
- Rashkin, H.; Choi, E.; Jang, J.Y.; Volkova, S.; Choi, Y. Truth of varying shades: Analyzing language in fake news and political fact-checking. In Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Copenhagen, Denmark, 1 January 2017; pp. 2931–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Lu, Q.; Xiang, R.; Li, M.; Huang, C.-R. Fake news detection through multi-perspective speaker profiles. In Proceedings of the 8th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (IJCNLP 2017), Taipei, Taiwan, 27–30 November 2017; pp. 252–256. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, D.; Dyer, C.; He, X.; Smola, A.; Hovy, E. Hierarchical attention networks for document classification. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, San Diego, CA, USA, 11–13 September 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, A.; Shah, R.; Chakraborty, T.; Kumaraguru, P. SpotFake: A multi-modal framework for fake news detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Fifth International Conference on Multimedia Big Data (BigMM), Singapore, 11–13 September 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jwa, H.; Oh, D.; Park, K.; Kang, J.; Lim, H. exBAKE: Automatic fake news detection model based on BERT architecture. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.12731. [Google Scholar]
- Horne, B.D.; Adalı, S. This just in: Fake news packs a lot in title, uses simpler, repetitive content in text body, more similar to satire than real news. ICWSM 2017, 11, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zafarani, R. A survey of fake news: Fundamental theories, detection methods, and opportunities. ACM Comput. Surv. 2020, 53, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorne, J.; Vlachos, A.; Christodoulopoulos, C.; Mittal, A. FEVER: A large-scale dataset for fact extraction and verification. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, New Orleans, LA, USA, 1–6 June 2018; pp. 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasunaga, M.; Ren, H.; Bosselut, A.; Liang, P.; Leskovec, J. QA-GNN: Reasoning with language models and knowledge graphs for question answering. In Proceedings of the 2021 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Online, 6–11June 2021; 2021; pp. 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayar, B.; Stamm, M.C. Constrained convolutional neural networks: A new approach towards general purpose image manipulation detection. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2018, 13, 2691–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, H.; Jia, C. Unsupervised Cross-Domain Rumor Detection with Contrastive Learning and Cross-Attention. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2023, 37, 13510–13518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J. Detecting fake news by exploring the consistency of multimodal data. Inf. Process. Manag. 2021, 58, 102610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Q.; Wu, H.; Sun, J.; Fang, X.; Zhang, H. Multimodal fake news detection via progressive fusion networks. Inf. Process. Manag. 2023, 60, 103120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Yin, X.; Chung, C.Y.; Rayeem, S.K.; Chen, X.; Yang, H. Managing massive RES integration in hybrid microgrids: A data-driven quad-level approach with adjustable conservativeness. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2025, 21, 7698–7709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, F.; Jin, Z. Event adversarial neural networks for multi-modal fake news detection. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, London, UK, 19–23 August 2018; pp. 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qian, S.; Hu, J. Fake news detection via knowledge-driven multimodal graph convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval, Dublin Ireland, 8–11 June 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ying, Q.; Qian, Z. Multimodal fake news detection via CLIP-guided learning. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.14304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cao, J.; Li, X. Multimodal fake news analysis based on image–text similarity. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2023, 10, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arevalo, J.; Solorio, T.; Montes-y-Gómez, M.; González, F.A. Gated Multimodal Units for Information Fusion. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1702.01992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura-Bedmar, I.; Alonso-Bartolome, S. Multimodal fake news detection: A review. Information 2022, 13, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Levy, S.; Wang, W.Y. r/Fakeddit: A new multimodal benchmark dataset for fine-grained fake news detection. In Proceedings of the 12th Language Resources and Evaluation Conference (LREC 2020), Marseille, France, 11–16 May 2020; pp. 6149–6157. Available online: https://aclanthology.org/2020.lrec-1.755 (accessed on 27 October 2025).
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, P. LLM-enhanced multimodal detection of fake news. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0312240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolova, M.; Lapalme, G. A systematic analysis of performance measures for classification tasks. Inf. Process. Manag. 2009, 45, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, D.M.W. Evaluation: From precision, recall and F-measure to ROC, informedness, markedness and correlation. J. Mach. Learn. Technol. 2011, 2, 37–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.; Goadrich, M. The relationship between precision-recall and ROC curves. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2006); Association for Computing Machinery (ACM): New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Jain, A.; Phoha, V.V.; Zafarani, R. SAFE: Similarity-aware multi-modal fake news detection. In Social, Cultural, and Behavioral Modeling; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattar, D.; Goud, J.S.; Gupta, M.; Varma, V. MVAE: Multimodal variational autoencoder for fake news detection. In Proceedings of the WWW’19: The Web Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 May 2019; pp. 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Jiang, J. Adapting BERT for Target-Oriented Multimodal Sentiment Classification. In Proceedings of the 28th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI 2019), Macao, China, 10–16 August 2019; pp. 5408–5414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, V.; Gupta, P.; Subramanian, R.; Dhall, A. FakeBuster: A DeepFakes detection tool for video conferencing scenarios. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.03321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Q.; Qian, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Chang, S.; Hu, J. MDFEND: Multi-domain fake news detection. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, New York, NY, USA, 1–5 November 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks (ICNN’95), Perth, WA, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995; pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griewank, A.O. Generalized descent for global optimization. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 1981, 34, 11–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackley, D.H. A Connectionist Machine for Genetic Hillclimbing; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Boston, MA, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.; Yang, X.-S. A literature survey of benchmark functions for global optimisation problems. Int. J. Math. Model. Numer. Optim. 2013, 4, 150–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbrock, H.H. An automatic method for finding the greatest or least value of a function. Comput. J. 1960, 3, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, K.A. An Analysis of the Behavior of a Class of Genetic Adaptive Systems. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.H. Adaptation in Natural and Artificial Systems; University of Michigan Press: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Karaboga, D.; Basturk, B. A powerful and efficient algorithm for numerical function optimization: Artificial Bee Colony (ABC) algorithm. J. Glob. Optim. 2007, 39, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, A.A.; Mirjalili, S.; Faris, H.; Aljarah, I.; Mafarja, M.; Chen, H. Harris Hawks Optimization: Algorithm and applications. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 97, 849–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storn, R.; Price, K. Differential evolution: A simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces. J. Glob. Optim. 1997, 11, 341–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.T. A new fruit fly optimization algorithm: Taking the financial distress model as an example. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2012, 26, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Source | Text Samples | Images |
|---|---|---|
| Sina News | 2449 | 1260 |
| Science China | 4186 | 4100 |
| Joint Internet Rumor Refutation Platform | 903 | 902 |
| Hyperparameter | Setting |
|---|---|
| Text embedding dimension | 512 |
| Image embedding dimension | 512 |
| Number of Transformer layers | 2 |
| Number of attention heads | 4 |
| Hidden size | 128 |
| Learning rate | 2 × 10−4 |
| Dropout rate | 0.2 |
| Focal Loss parameters (α = 1.25, γ = 1.5) | A = 1.25, γ = 1.5 |
| Module | Model | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T + I | SAFE | 83.79 | 84.66 | 87.20 | 83.61 |
| T + I | EANN | 85.28 | 86.07 | 81.93 | 83.31 |
| T + I | MDFEND | 91.52 | 90.42 | 92.30 | 91.10 |
| T + I | MVAE | 91.52 | 90.60 | 93.30 | 91.23 |
| T + I | MMFakeBuster | 92.51 | 91.46 | 93.80 | 92.20 |
| T + I | MCAN | 92.76 | 91.70 | 93.71 | 92.41 |
| T + I | IBKA-MSM | 95.80 | 94.02 | 94.27 | 94.14 |
| Model | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WOA-MSM | 66.92 | 34.10 | 71.51 | 46.18 |
| PSO-MSM | 96.48 | 88.83 | 94.09 | 91.38 |
| BKA-MSM | 97.01 | 91.58 | 93.55 | 92.55 |
| IBKA-MSM | 95.80 | 94.02 | 94.27 | 94.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mu, G.; Dai, J.; Li, C.; Li, J. IBKA-MSM: A Novel Multimodal Fake News Detection Model Based on Improved Swarm Intelligence Optimization Algorithm, Loop-Verified Semantic Alignment and Confidence-Aware Fusion. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10110782
Mu G, Dai J, Li C, Li J. IBKA-MSM: A Novel Multimodal Fake News Detection Model Based on Improved Swarm Intelligence Optimization Algorithm, Loop-Verified Semantic Alignment and Confidence-Aware Fusion. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(11):782. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10110782
Chicago/Turabian StyleMu, Guangyu, Jiaxiu Dai, Chengguo Li, and Jiaxue Li. 2025. "IBKA-MSM: A Novel Multimodal Fake News Detection Model Based on Improved Swarm Intelligence Optimization Algorithm, Loop-Verified Semantic Alignment and Confidence-Aware Fusion" Biomimetics 10, no. 11: 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10110782
APA StyleMu, G., Dai, J., Li, C., & Li, J. (2025). IBKA-MSM: A Novel Multimodal Fake News Detection Model Based on Improved Swarm Intelligence Optimization Algorithm, Loop-Verified Semantic Alignment and Confidence-Aware Fusion. Biomimetics, 10(11), 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10110782





