A Boron-Based Topical Strategy for Enhancing Flap Survival: Mechanistic Insights Through Proteomic Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of the Gel
2.2. Animals and Experimental Design
2.3. Tissue Collection and Histological Analysis
2.4. Preparation of Pooled Protein Extracts
2.5. Tryptic Digestion and Mass Spectrometry-Based Protein Identification
2.6. In Silico Analysis of Proteomic Data
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
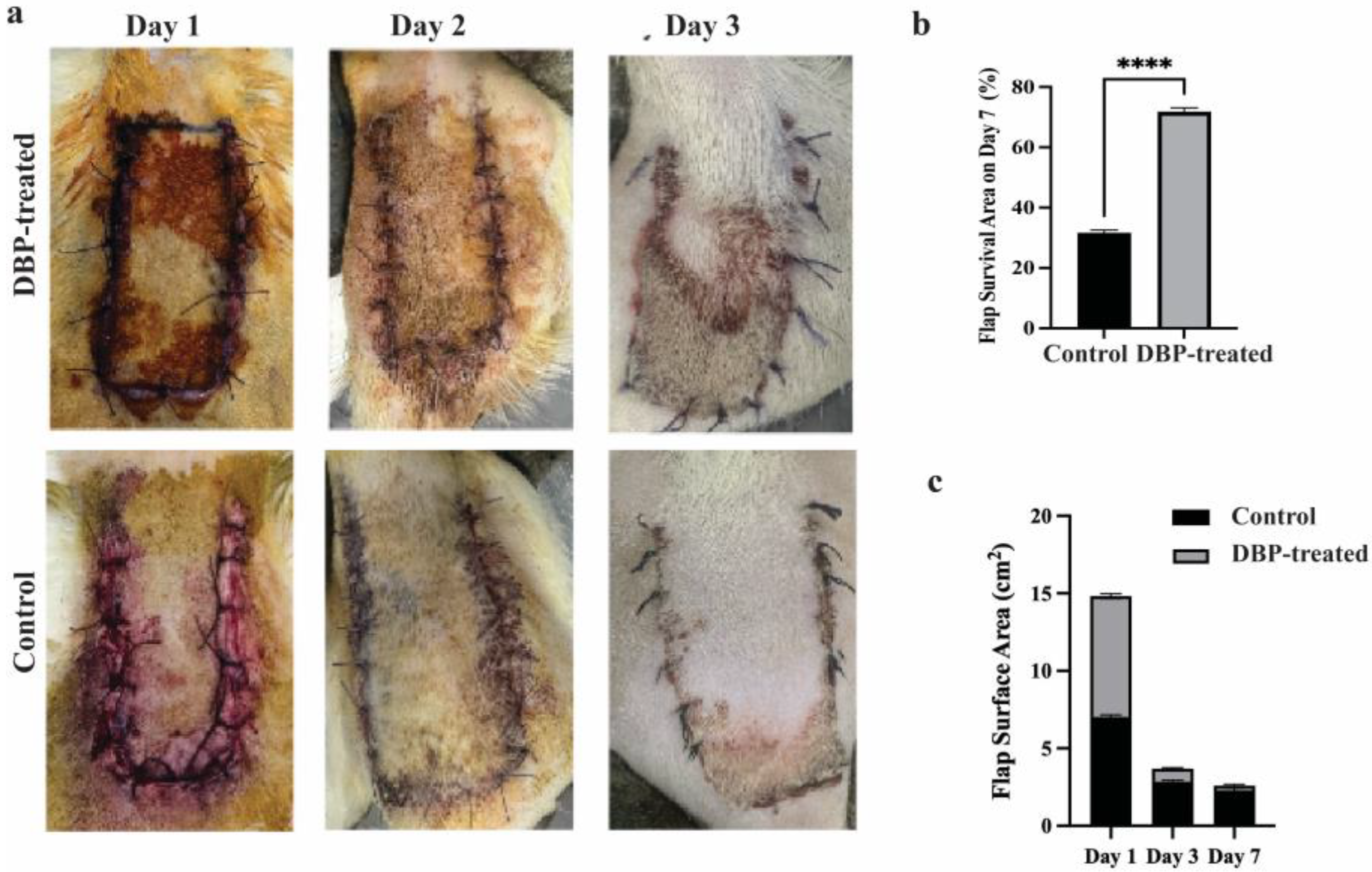
3.1. Photo Area Calculation Results
3.2. Histopathological Evaluation
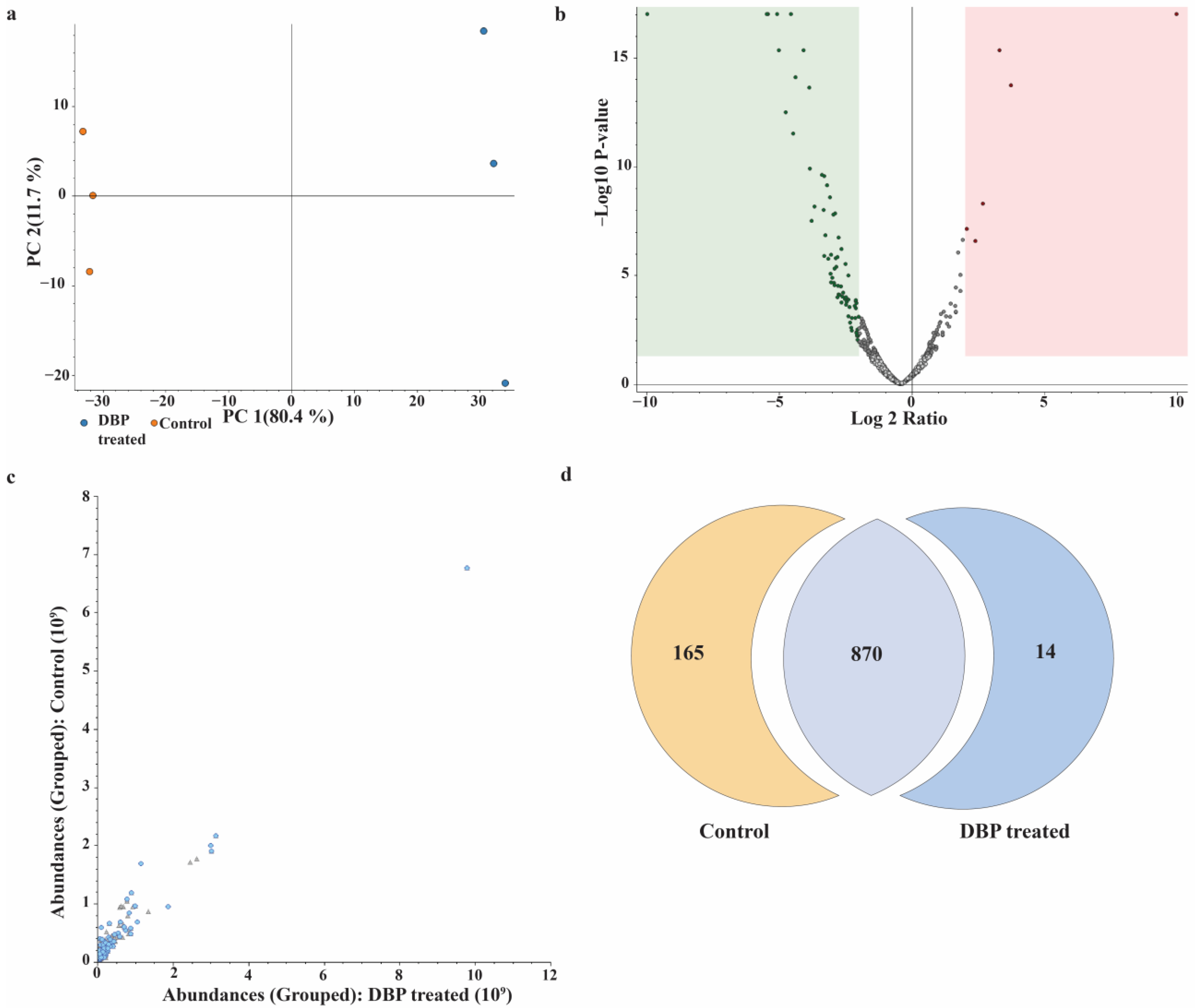
3.3. Label-Free Quantification and Comparative Proteome Analysis
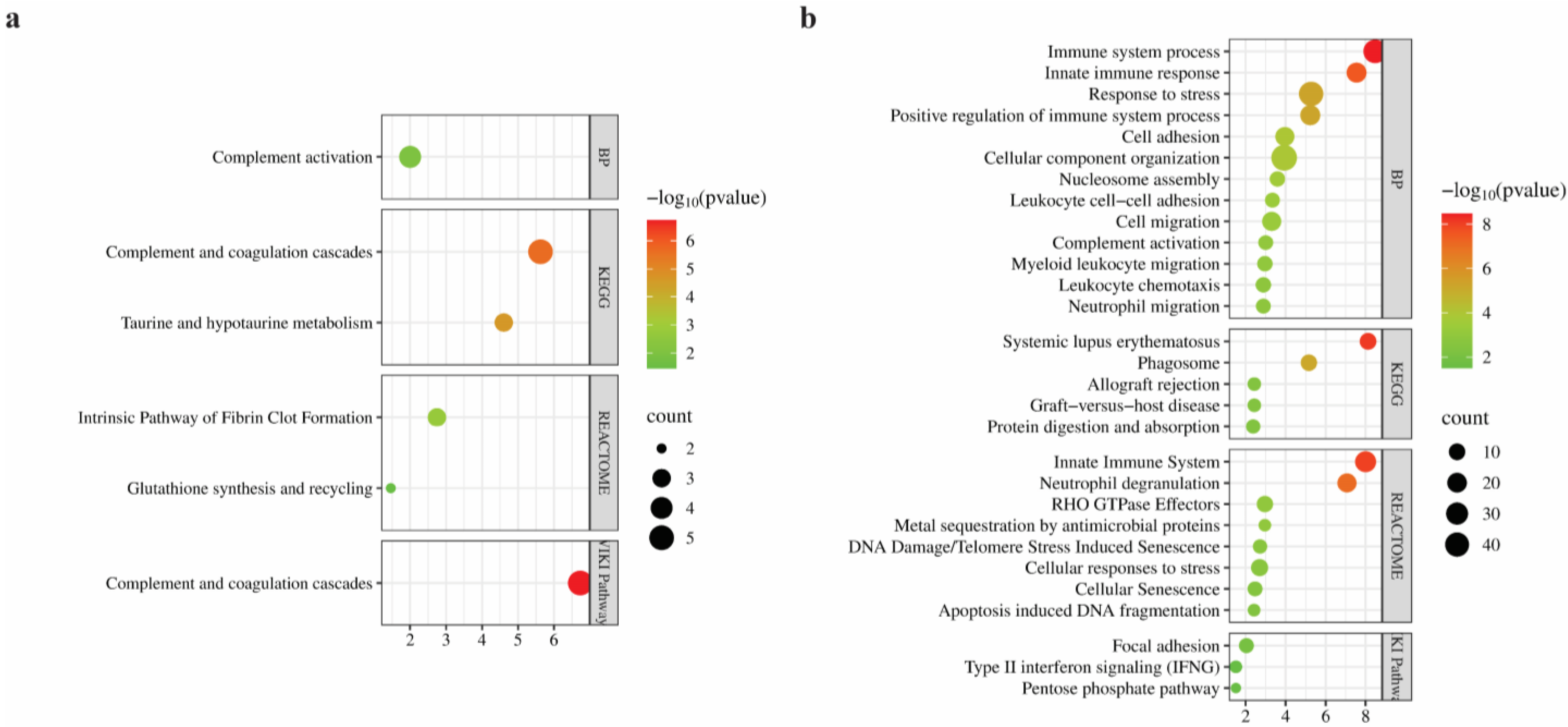
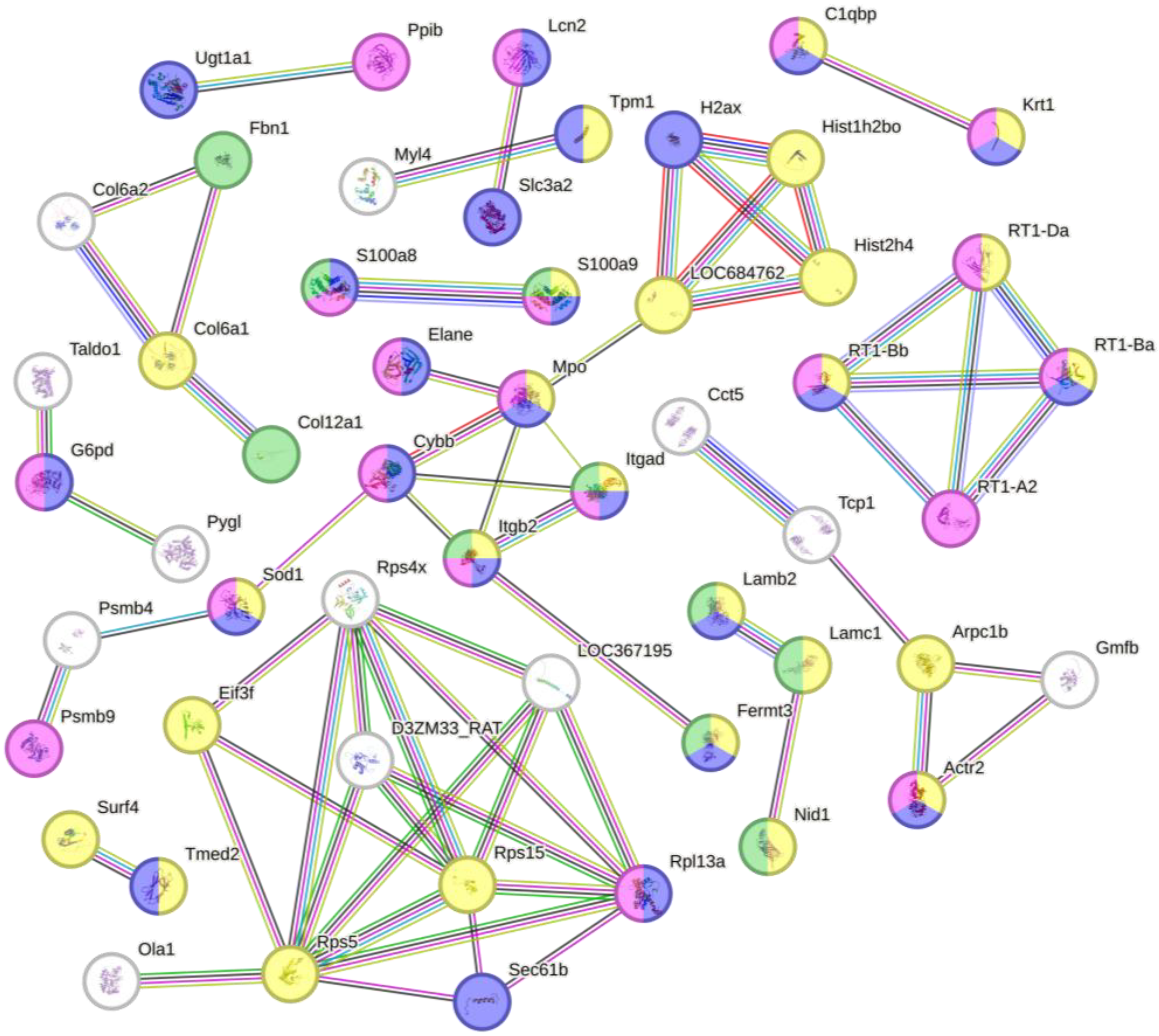
3.4. Bioinformatics Analysis of Differentially Regulated Proteins
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DBP | Dermobor Plus |
| SPP | Sodium pentaborate pentahydrate |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| MT | Masson’s Trichrome-stained |
| HE | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| FDR | False discovery rate |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| DFO | Deferoxamine |
| nLC-MS/MS | nanoLC-MS/MS |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| WP | WikiPathways |
References
- Liu, H.; Zhang, M.; Dong, X.; Liu, Y.; Hao, Y.; Wang, Y. Necrostatin-1 Protects against Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Inhibiting Receptor-Interacting Protein 1 in a Rat Flap Model. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2019, 72, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, K.; Lin, Y.; Meng, Z.; Lan, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, J.; Lin, Y.; Liu, X.; et al. Activation of Aldehyde Dehydrogenase-2 Improves Ischemic Random Skin Flap Survival in Rats. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1127610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Chen, H.; Fu, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, H.; Li, Z.; Li, S. The eNOS-Induced Leonurine’s New Role in Improving the Survival of Random Skin Flap. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 124, 111037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, H.; Lei, L.; Yang, P.; Ju, Y.; Fan, X.; Fang, B. Exosomes-Carried Curcumin Based on Polysaccharide Hydrogel Promote Flap Survival. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 270, 132367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballestín, A.; Casado, J.G.; Abellán, E.; Vela, F.J.; Álvarez, V.; Usón, A.; López, E.; Marinaro, F.; Blázquez, R.; Sánchez-Margallo, F.M. Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in a Rat Microvascular Skin Free Flap Model: A Histological, Genetic, and Blood Flow Study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0209624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Li, G.; Cui, L. Local Injection of Deferoxamine Improves Neovascularization in Ischemic Diabetic Random Flap by Increasing HIF-1α and VEGF Expression. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Hu, X.; Wang, Z.-H.; Zhu, Y.-Z.; Wang, J.-W.; Nie, J.-Y.; Yang, J.-M.; Yi, Y.-Y. Extracellular Vesicles Isolated From Hypoxia-Preconditioned Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Promote Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α–Mediated Neovascularization of Random Skin Flap in Rats. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2022, 89, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Yi, C.; Xia, W.; Ding, T.; Zhou, Z.; Han, Y.; Guo, S. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Transduced by Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Gene for Ischemic Random Skin Flaps. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2008, 121, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Xie, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, D.; Xian, S.; Sun, H.; Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Lu, J.; et al. Current Application of Tissue-Engineered Dermal Scaffolds Mimicking the Extracellular Matrix Microenvironment in Wound Healing. Regen. Ther. 2025, 28, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.H.; Kim, M.; Kim, T.Y.; Choi, H.; Hahn, S.K. Biomimetic Supramolecular Drug Delivery Hydrogels for Accelerated Skin Tissue Regeneration. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 4581–4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakarla, A.B.; Kong, I.; Nguyen, T.H.; Kong, C.; Irving, H. Boron Nitride Nanotubes Reinforced Gelatin Hydrogel-Based Ink for Bioprinting and Tissue Engineering Applications. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 141, 213103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedighi-Pirsaraei, N.; Tamimi, A.; Khamaneh, F.S.; Dadras-Jeddi, S.; Javaheri, N. Boron in Wound Healing: A Comprehensive Investigation of Its Diverse Mechanisms. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1475584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, S.; Doğan, A.; Karakuş, E.; Halıcı, Z.; Topçu, A.; Demirci, E.; Sahin, F. Boron and Poloxamer (F68 and F127) Containing Hydrogel Formulation for Burn Wound Healing. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2015, 168, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, S.; Doğan, A.; Aydın, S.; Dülger, E.Ç.; Şahin, F. Boron Promotes Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Wound Healing: Roles in Cell Proliferation and Migration, Growth Factor Expression, and Inflammation. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 417, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikzad, S.; Same, S.; Safiri, S.; Dolati, S.; Zineh, B.R.; Meshgi, S.; Roshangar, L.; Şahin, F. The Effect of Wharton’s Jelly-Derived Stem Cells Seeded/Boron-Loaded Acellular Scaffolds on the Healing of Full-Thickness Burn Wounds in the Rat Model. Biomed. Mater. 2024, 19, 025042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boran, R.; Baygar, T.; Saraç, N.; Ayrıkçil, S.; Yılmaz, D.; Uğur, A. Antimicrobial, Antifibrinolytic, Enzyme Inhibitory and Wound Healing Properties of Zinc Borate. J. Boron 2023, 8, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkez, H.; Yıldırım, Ö.Ç.; Öner, S.; Kadı, A.; Mete, A.; Arslan, M.E.; Şahin, İ.O.; Yapça, Ö.E.; Mardinoğlu, A. Lipoic Acid Conjugated Boron Hybrids Enhance Wound Healing and Antimicrobial Processes. Pharmaceutics 2022, 15, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, H.M.U.; Hanif, M.; Mahmood, K.; Aziz, M.; Abbas, G.; Latif, H. Wound-Healing and Antibacterial Activity of the Quercetin–4-Formyl Phenyl Boronic Acid Complex against Bacterial Pathogens of Diabetic Foot Ulcer. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 24415–24422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, S.N.; Arslan, T.S.; Arslan, Y.E. Organic-Inorganic Biohybrid Films from Wool-Keratin/Jellyfish-Collagen/Silica/Boron via Sol-Gel Reactions for Soft Tissue Engineering Applications. Biomed. Mater. 2024, 19, 025032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gioffredi, E.; Boffito, M.; Calzone, S.; Giannitelli, S.M.; Rainer, A.; Trombetta, M.; Mozetic, P.; Chiono, V. Pluronic F127 Hydrogel Characterization and Biofabrication in Cellularized Constructs for Tissue Engineering Applications. Procedia CIRP 2016, 49, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangabhatla, A.S.L.; Tantishaiyakul, V.; Boonrat, O.; Hirun, N.; Ouiyangkul, P. Novel in Situ Mucoadhesive Gels Based on Pluronic F127 and Xyloglucan Containing Metronidazole for Treatment of Periodontal Disease. Iran. Polym. J. 2017, 26, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.-R.; Kim, E.-J.; Choi, T.H.; Han, J.; Kang, D. Enhancing Human Cutaneous Wound Healing through Targeted Suppression of Large Conductance Ca2+-Activated K+ Channels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doğan, A.; Demirci, S.; Çağlayan, A.B.; Kılıç, E.; Günal, M.Y.; Uslu, Ü.; Cumbul, A.; Şahin, F. Sodium Pentaborate Pentahydrate and Pluronic Containing Hydrogel Increases Cutaneous Wound Healing In Vitro and In Vivo. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2014, 162, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, F.; Pirouzpanah, M.B.; Farshbaf-Khalili, A.; Ayşan, E.; Doğan, A.; Demirci, S.; Ostadrahimi, A.; Mobasseri, M. The Effect of the Boron-Based Gel on the Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Prospective, Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2023, 79, 127261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, J.; Molla, M.R.; Kamal, M.; Shahidullah, M.; Begum, F.; Bashar, M.A. Histological Differences in Wound Healing in Maxillofacial Region in Patients with or without Risk Factors. Bangladesh, J. Pathol. 2009, 24, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, T.S.; Santos, I.D.D.; Pereira-Filho, R.N.; Gomes, S.V.F.; Lima-Verde, I.B.; Marques, M.N.; Cardoso, J.C.; Severino, P.; Souto, E.B.; Albuquerque-Júnior, R.L.D. Histological Evidence of Wound Healing Improvement in Rats Treated with Oral Administration of Hydroalcoholic Extract of Vitis Labrusca. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2021, 43, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simsek, T.; Albayrak, M.G.B.; Akpinar, G.; Canturk, N.Z.; Kasap, M. Downregulated GPD1 and MAGL Protein Levels as Potential Biomarkers for the Metastasis of Triple-negative Breast Tumors to Axillary Lymph Nodes. Oncol. Lett. 2023, 27, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korak, T.; Baloğlu, İ.H.; Kasap, M.; Arisan, E.D.; Akpinar, G.; Arisan, S. Proteomic and In Silico Analyses Highlight Complement System’s Role in Bladder Cancer Immune Regulation. Medicina 2025, 61, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanar, S.; Sarihan, M.; Kasap, M.; Akpinar, G.; Teke, K.; Bayrak, B.Y. GFP Transfection Alters Protein Expression Patterns in Prostate Cancer Cells: A Proteomic Study. J. Fluoresc. 2025, 35, 2121–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; You, H.-J.; Lee, T.-Y.; Kang, H.J. Current Status of Experimental Animal Skin Flap Models: Ischemic Preconditioning and Molecular Factors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Büyük, B.; Aydeğer, C.; Adalı, Y.; Eroğlu, H.A. The Effect of Topically Applied Boric Acid on Ephrin-Eph Pathway in Wound Treatment: An Experimental Study. Int. J. Low. Extrem. Wounds 2024, 23, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebassier, N.; Houssein, O.E.; Viegas, I.; Dréno, B. In Vitro Induction of Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 and Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Expression in Keratinocytes by Boron and Manganese. Exp. Dermatol. 2004, 13, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakki, S.S.; Bozkurt, B.S.; Hakki, E.E. Boron Regulates Mineralized Tissue-Associated Proteins in Osteoblasts (MC3T3-E1). J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2010, 24, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Yin, T.; Jiang, J.; He, Y.; Xiang, T.; Zhou, S. Wound Microenvironment Self-Adaptive Hydrogel with Efficient Angiogenesis for Promoting Diabetic Wound Healing. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 20, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ning, F.; Du, C.; Chen, M.; Feng, C.; Dong, C.-M. Dynamic Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels for Comprehensively Regulating Inflammation, Angiogenesis, and Metabolism to Effectively Proheal Diabetic Wounds. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 70256–70273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Yi, C.; He, L.; Wang, Y.; Feng, S.; Liu, D.; Guo, S. Effects of Mouse NIH3T3 Cells Transfected with VEGF Gene on Neovascularization of Ischemic Flaps. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi Chin. J. Surg. 2007, 45, 203–206. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.; Ashrafpour, H.; Huang, N.; Neligan, P.C.; Kontos, C.; Zhong, A.; Forrest, C.R.; Pang, C.Y. Acute Local Subcutaneous VEGF165 Injection for Augmentation of Skin Flap Viability: Efficacy and Mechanism. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2004, 287, R1219–R1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasmaie, F.M.; Roshan, M.M.; Nasiry, D.; Abdollahifar, M.A.; Ashtiani, M.K.; Erfanian, S.; Zarkesh, I.; Meybodi, A.M.; Piryaei, A. Fabrication of Curcumin-Incorporated Human Amniotic Membrane Extracellular Matrix-Derived Scaffold to Enhance Full-Thickness Wound Healing in Diabetic Rats. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2025, 163, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Fang, Y.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, X. ROS-Scavenging Lipid-Based Liquid Crystalline as a Favorable Stem Cell Extracellular Vesicles Delivery Vector to Promote Wound Healing. J. Control. Release 2024, 371, 298–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Johnson, J.A.; Dunne, L.W.; Chen, Y.; Iyyanki, T.; Wu, Y.; Chang, E.I.; Branch-Brooks, C.D.; Robb, G.L.; Butler, C.E. Decellularized Skin/Adipose Tissue Flap Matrix for Engineering Vascularized Composite Soft Tissue Flaps. Acta Biomater. 2016, 35, 166–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafail, S.; Kourtzelis, I.; Foukas, P.G.; Markiewski, M.M.; DeAngelis, R.A.; Guariento, M.; Ricklin, D.; Grice, E.A.; Lambris, J.D. Complement Deficiency Promotes Cutaneous Wound Healing in Mice. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 1285–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, E. 25 The Interface of Complement and Coagulation Pathways. Lupus Sci. Med. 2021, 8, A15–A16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, D.; Qiu, P.; Wang, Y.; Hong, F.; Ren, P.; Cheng, X.; Wang, L.; Dou, X.; Liu, T.; Liu, J.; et al. Multifunctional Chitosan-Based Hydrogel Wound Dressing Loaded with Acanthopanax senticosus and Osmundastrum cinnamomeum: Preparation, Characterization and Coagulation Mechanism. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2024, 151, 106384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockman, K.S.; Kizhakkedathu, J.N.; Santerre, J.P. Hemocompatibility Studies on a Degradable Polar Hydrophobic Ionic Polyurethane (D-PHI). Acta Biomater. 2017, 48, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Hu, J.; Zhao, X.; Wei, Q.; Zhao, R.; Li, M.; Li, Q. Taurine Attenuates the Hypotaurine-Induced Progression of CRC via ERK/RSK Signaling. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 631163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkiewicz, J.; Nagl, M.; Kyriakopoulos, A.; Walczewska, M.; Skóra, M.; Skalska, P. Current Opinion on the Therapeutic Capacity of Taurine-Containing Halogen Derivatives in Infectious and Inflammatory Diseases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2022, 1370, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, A.B.; Barbosa, J.N. The Role of Neutrophils in Biomaterial-Based Tissue Repair—Shifting Paradigms. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korndörfer, I.P.; Brueckner, F.; Skerra, A. The Crystal Structure of the Human (S100A8/S100A9)2 Heterotetramer, Calprotectin, Illustrates How Conformational Changes of Interacting α-Helices Can Determine Specific Association of Two EF-Hand Proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 370, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, S.; Torregrossa, M.; Anderegg, U.; Ertel, A.; Saalbach, A. Dysregulated S100A9 Expression Impairs Matrix Deposition in Chronic Wounds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Bie, F.; Chen, S.; Xu, Y.; Chen, L.; Shu, B.; Yang, F.; Lu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, J. Targeting S100A12 to Improve Angiogenesis and Accelerate Diabetic Wound Healing. Inflammation 2025, 48, 633–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zou, M.; Chen, H.; Zhu, F.; Wang, T.; Huang, X. Forkhead Box A1 Induces Angiogenesis through Activation of the S100A8/P38 MAPK Axis in Cutaneous Wound Healing. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2023, 45, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Cho, W.J.; Pulimamidi, V.K.; Mittal, S.K.; Chauhan, S.K. Interleukin-11 Suppresses Ocular Surface Inflammation and Accelerates Wound Healing. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2023, 64, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahhab, A.; Danner, R.; Rouse, J.; Timmler, S.; Lochhead, R.B. Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes Shape Inflammation and Wound Healing in Lyme Arthritis. J. Immunol. 2021, 206, 11.04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastre, J.; Pérez, S.; Sabater, L.; Rius-Pérez, S. Redox Signaling in the Pancreas in Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2025, 105, 593–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweikl, H.; Petzel, C.; Bolay, C.; Hiller, K.-A.; Buchalla, W.; Krifka, S. 2-Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate-Induced Apoptosis through the ATM- and P53-Dependent Intrinsic Mitochondrial Pathway. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 2890–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosef, R.; Krizhanovsky, V. mTOR Signaling Orchestrates the Expression of Cytoprotective Factors during Cellular Senescence. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 48859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matera, D.L.; Lee, A.T.; Hiraki, H.L.; Baker, B.M. The Role of Rho GTPases During Fibroblast Spreading, Migration, and Myofibroblast Differentiation in 3D Synthetic Fibrous Matrices. Cell. Mol. Bioeng. 2021, 14, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydasch, M.; Hinderling, L.; van Unen, J.; Dobrzynski, M.; Pertz, O. GTPase Activating Protein DLC1 Spatio-Temporally Regulates Rho Signaling. bioRxiv 2023. bioRxiv:2023.06.19.545304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, Y.; Kondo, T.; Takayasu, T.; Iwakura, Y.; Mukaida, N. The Essential Involvement of Cross-Talk between IFN-γ and TGF-β in the Skin Wound-Healing Process. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 1848–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, H.; Fan, Z.; Dai, J.; Sun, Y.; Yan, L.; Wang, R.; Li, X.; Wang, J. IFN-α-2b Inhibits the Proliferation and Migration of Fibroblasts via the TGFβ/Smad Signaling Pathway to Reduce Postoperative Epidural Fibrosis. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2021, 41, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Fan, Z.; Wang, R.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, J. IFN-α-2b Reduces Postoperative Arthrofibrosis in Rats by Inhibiting Fibroblast Proliferation and Migration through STAT1/P21 Signaling Pathway. Mediat. Inflamm. 2023, 2023, 1699946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
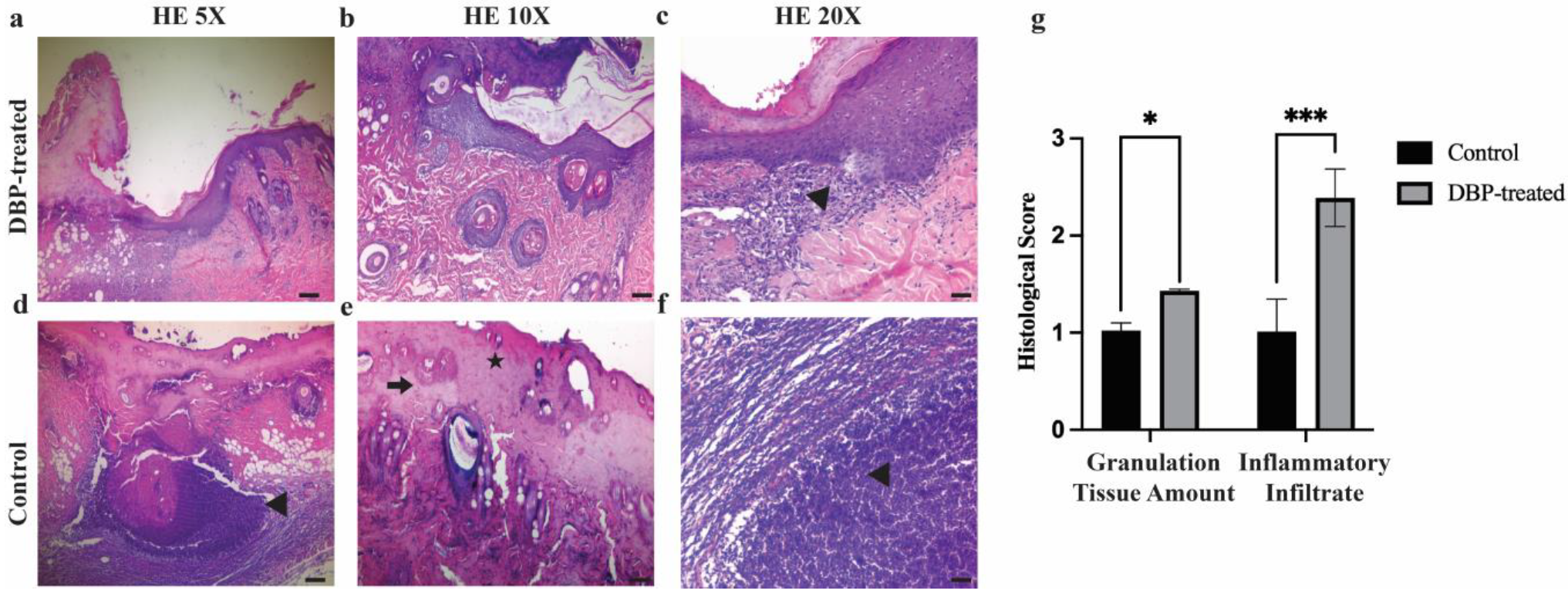
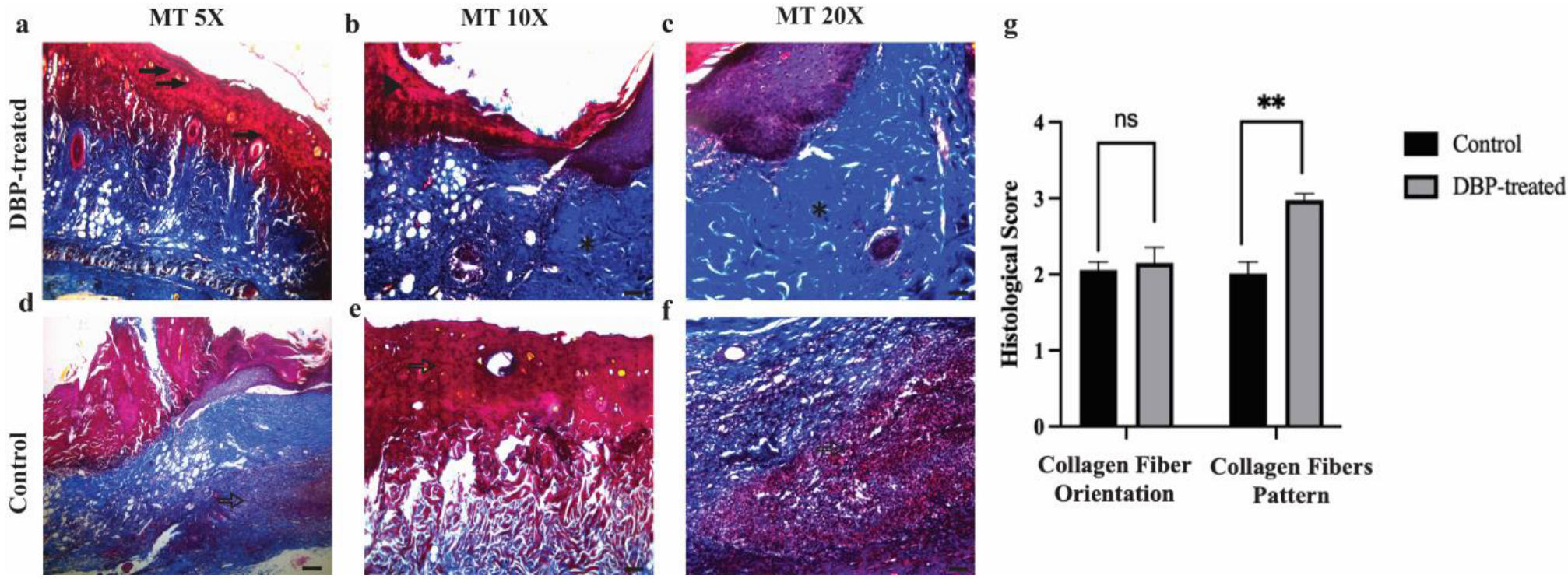
| Histological Parameters | Scoring System | Histological Grading |
|---|---|---|
| Amount of granulation tissue | Profound | 1 |
| Moderate | 2 | |
| Scanty | 3 | |
| Absent | 4 | |
| Inflammatory infiltrate | Plenty | 1 |
| Moderate | 2 | |
| A few | 4 | |
| Collagen fiber orientation | Vertical | 1 |
| Mixed | 2 | |
| Horizontal | 4 | |
| Pattern of collagen | Reticular | 1 |
| Mixed | 2 | |
| Fascicle | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yildirim, C.; Bal Albayrak, M.G.; Yanar, S.; Kayir, N.; Yozgat, A.H.; Aydin, S.; Şahin, F. A Boron-Based Topical Strategy for Enhancing Flap Survival: Mechanistic Insights Through Proteomic Analysis. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10110741
Yildirim C, Bal Albayrak MG, Yanar S, Kayir N, Yozgat AH, Aydin S, Şahin F. A Boron-Based Topical Strategy for Enhancing Flap Survival: Mechanistic Insights Through Proteomic Analysis. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(11):741. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10110741
Chicago/Turabian StyleYildirim, Cafer, Merve Gulsen Bal Albayrak, Sevinc Yanar, Nihal Kayir, Ayse Hande Yozgat, Sevim Aydin, and Fikrettin Şahin. 2025. "A Boron-Based Topical Strategy for Enhancing Flap Survival: Mechanistic Insights Through Proteomic Analysis" Biomimetics 10, no. 11: 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10110741
APA StyleYildirim, C., Bal Albayrak, M. G., Yanar, S., Kayir, N., Yozgat, A. H., Aydin, S., & Şahin, F. (2025). A Boron-Based Topical Strategy for Enhancing Flap Survival: Mechanistic Insights Through Proteomic Analysis. Biomimetics, 10(11), 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10110741







